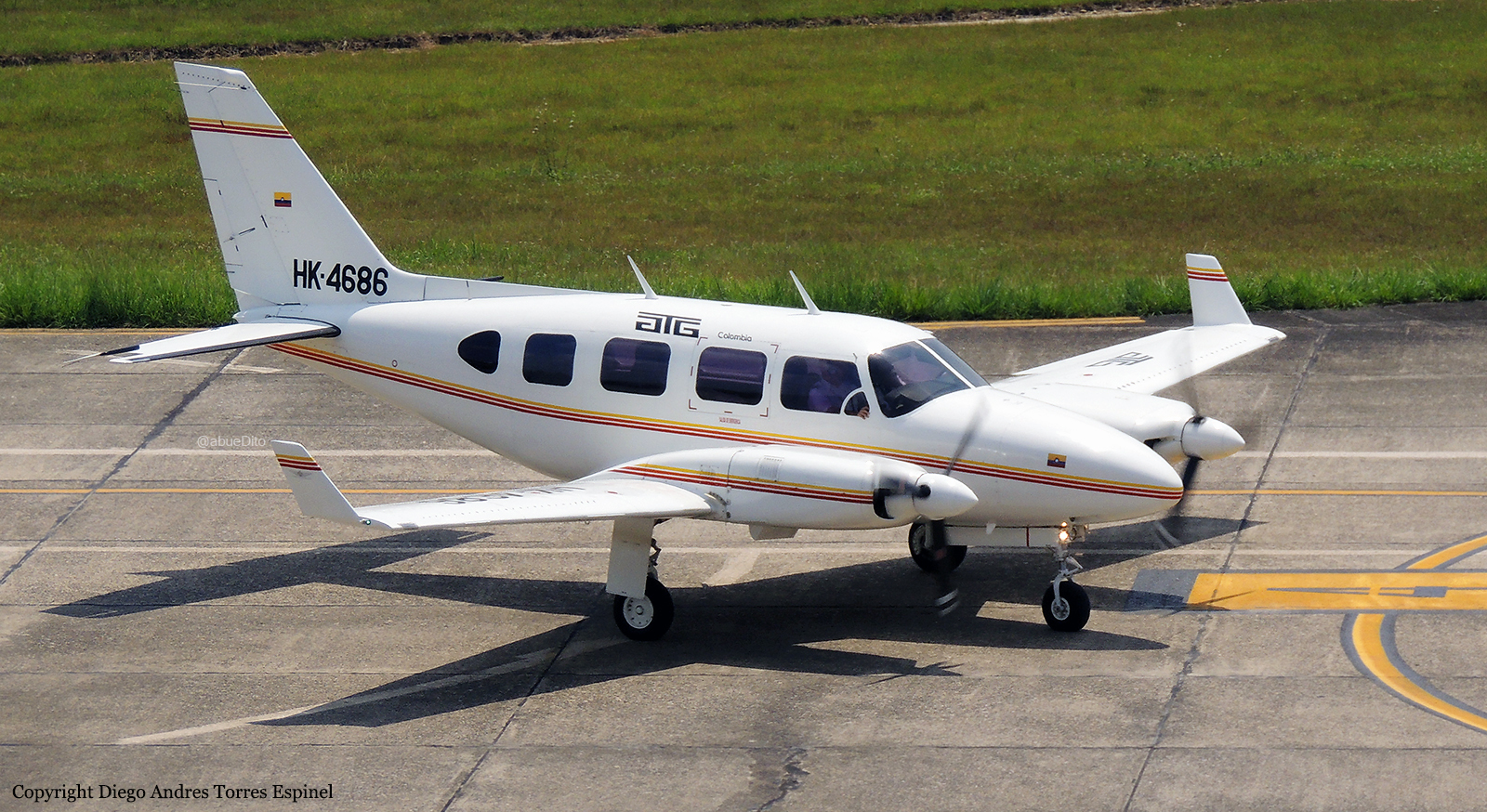
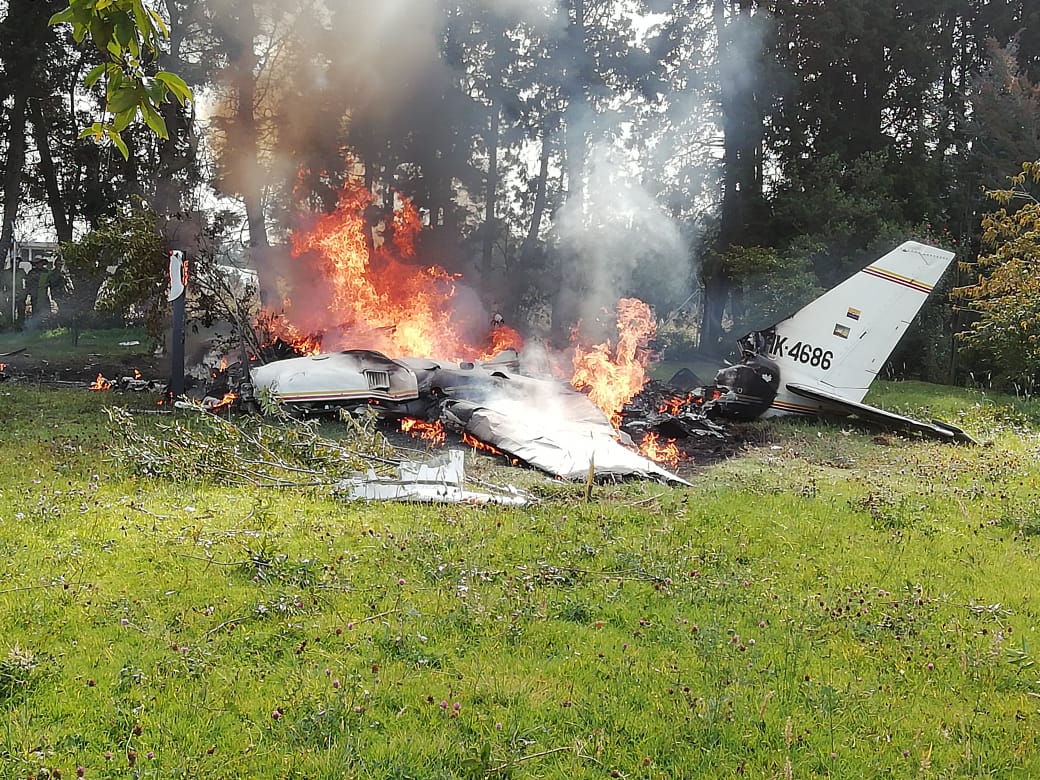
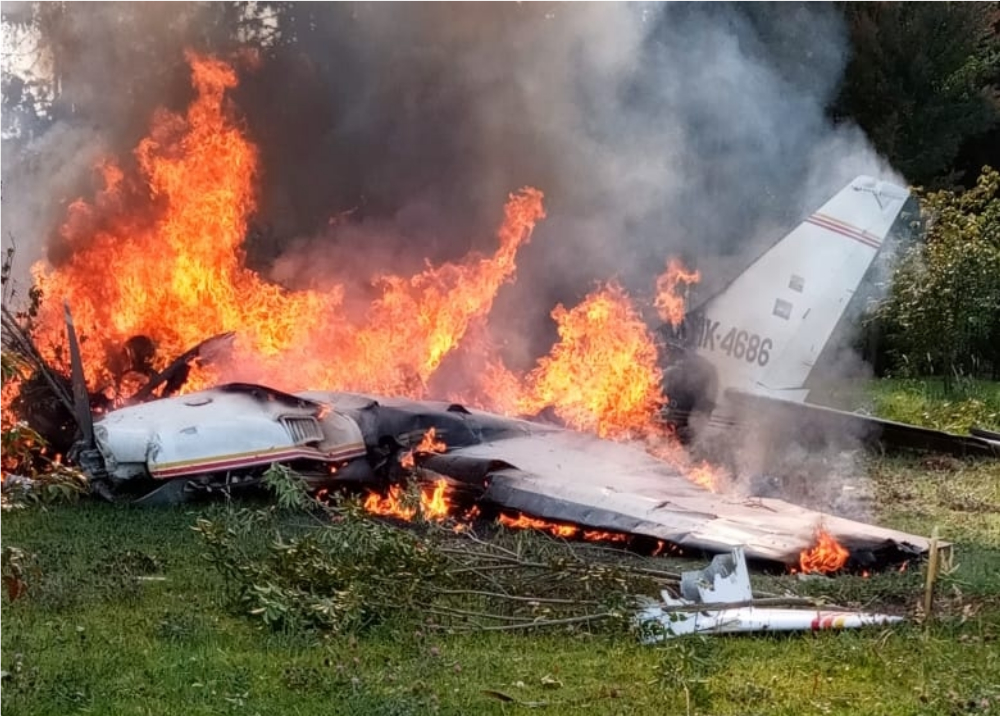
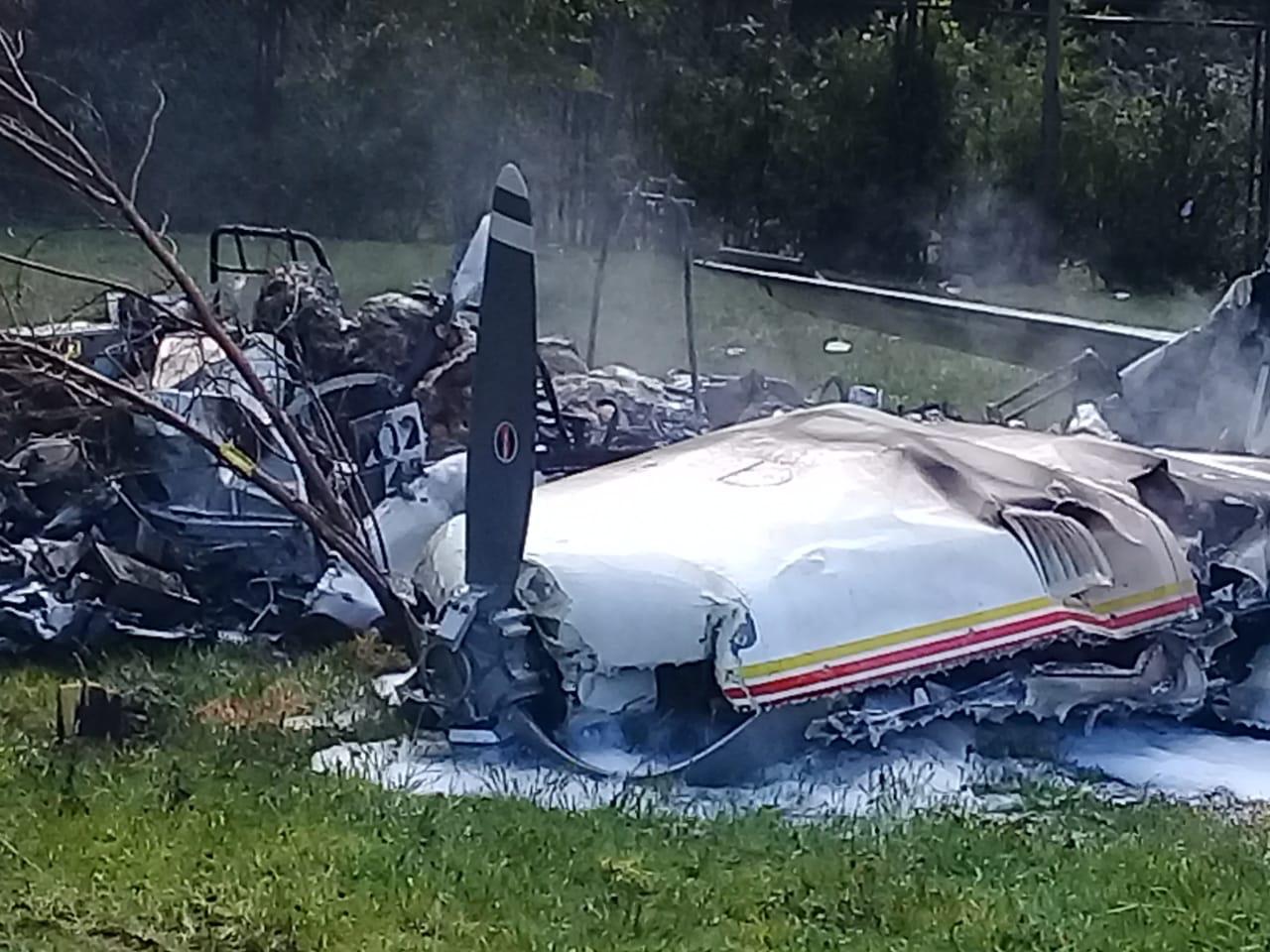
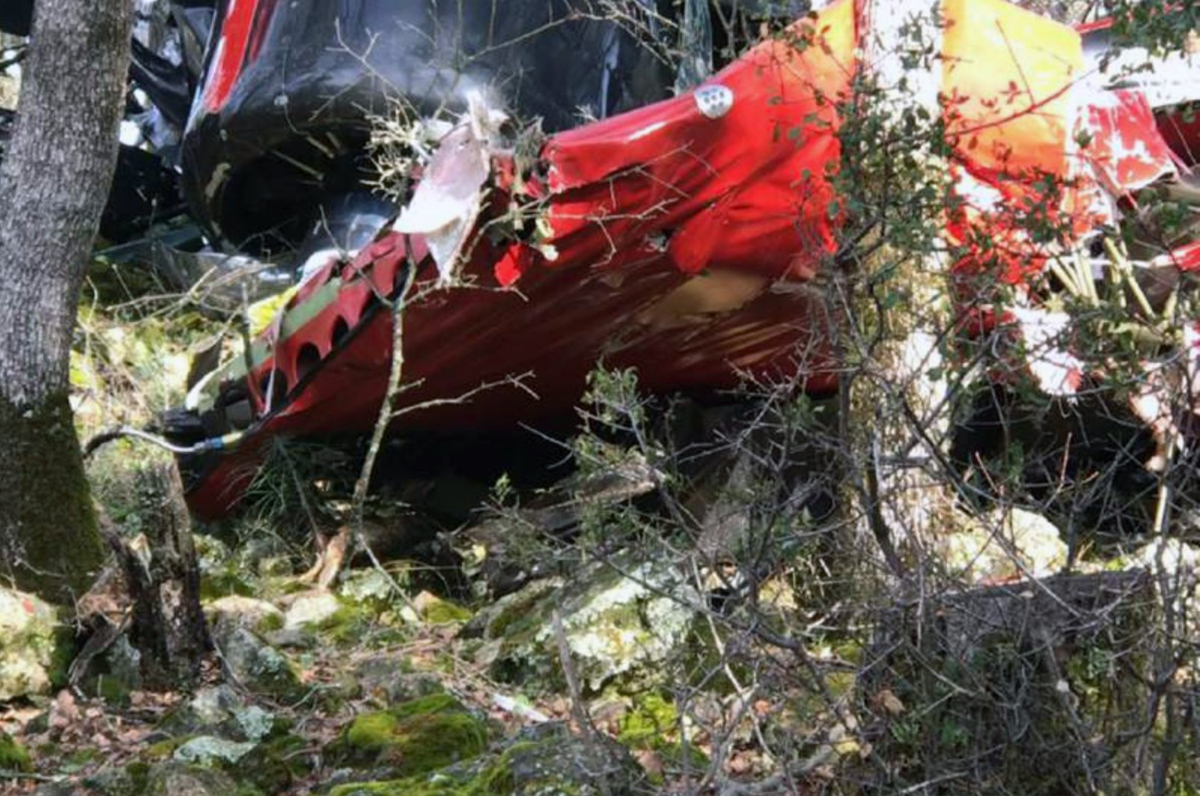
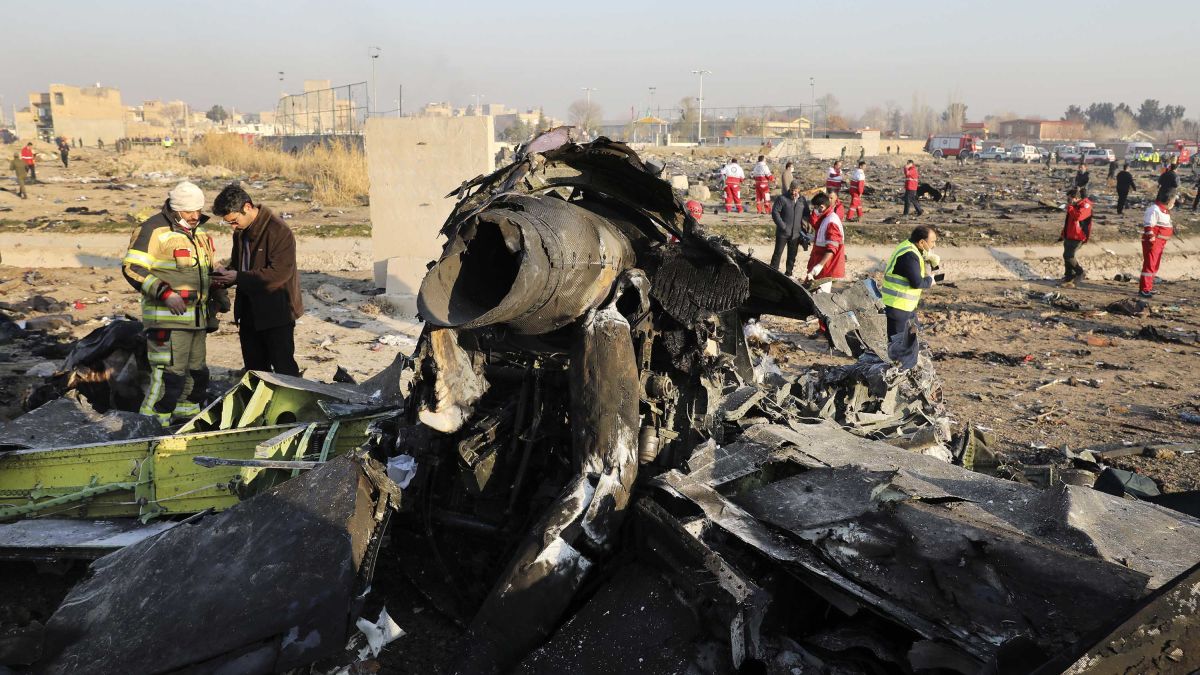
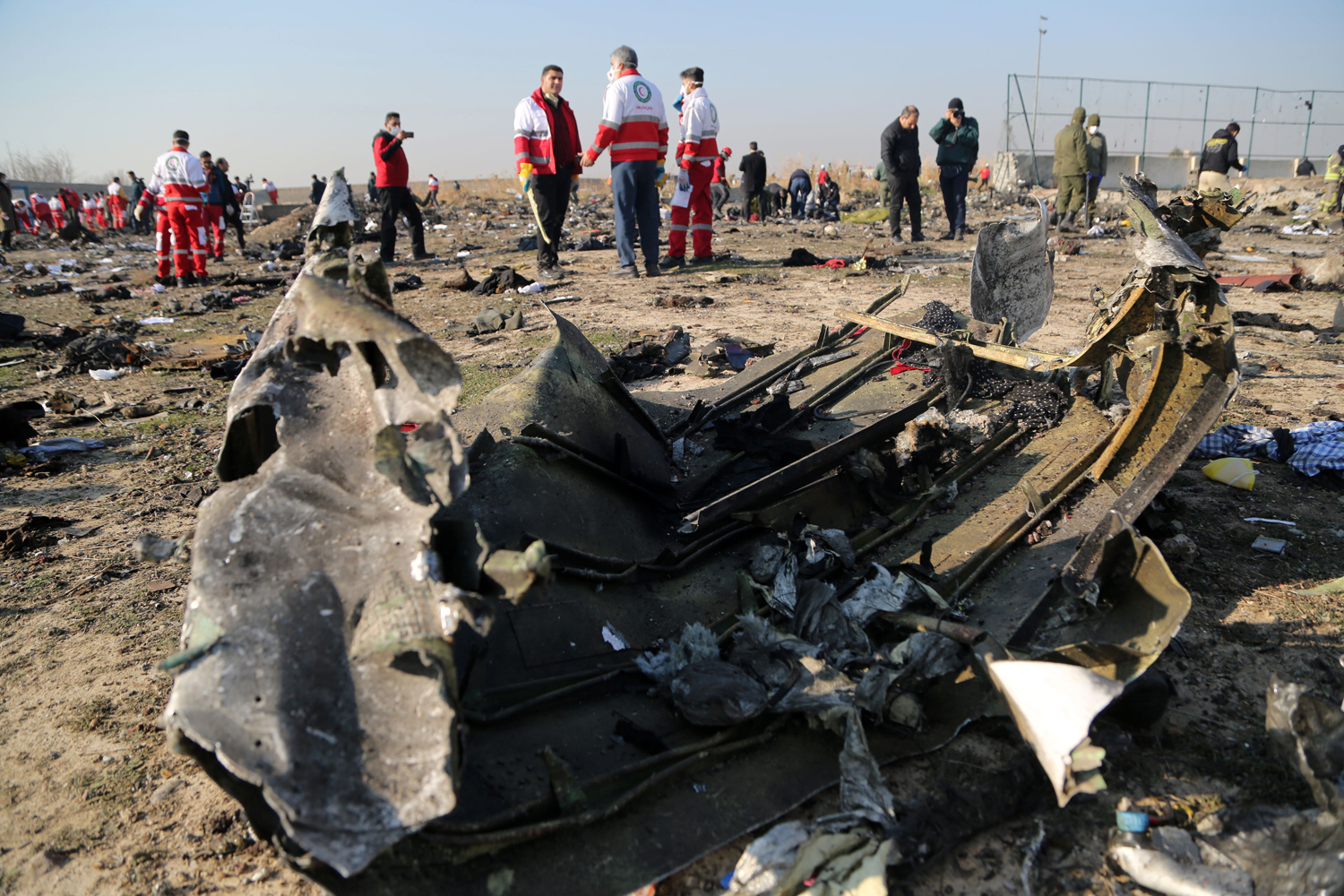
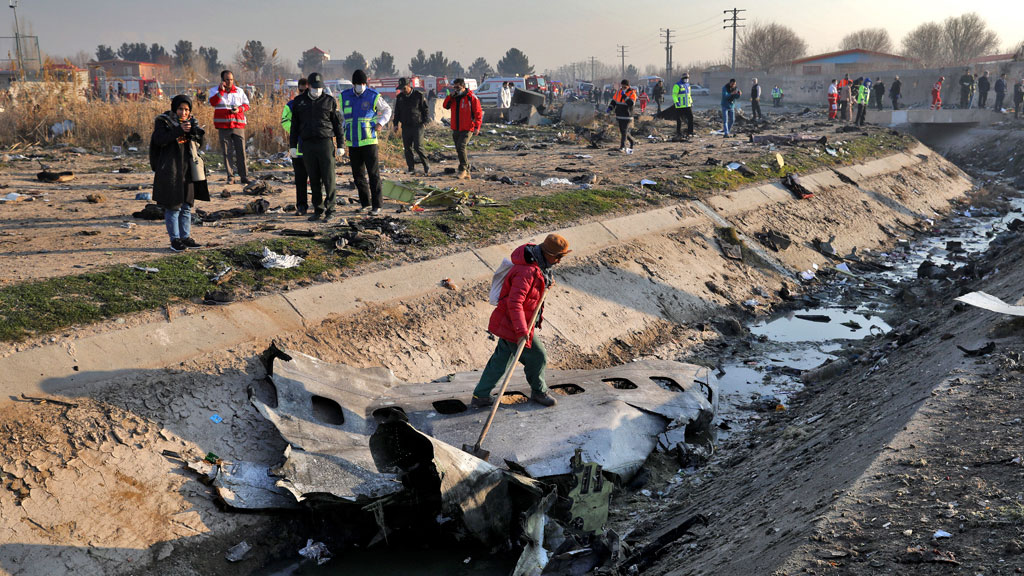
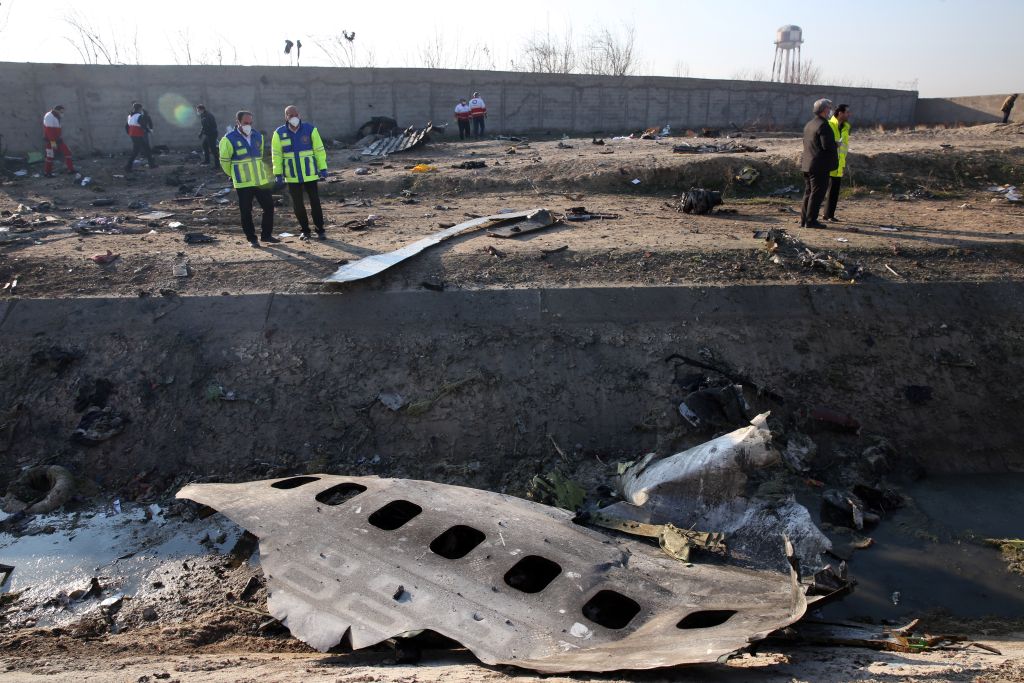
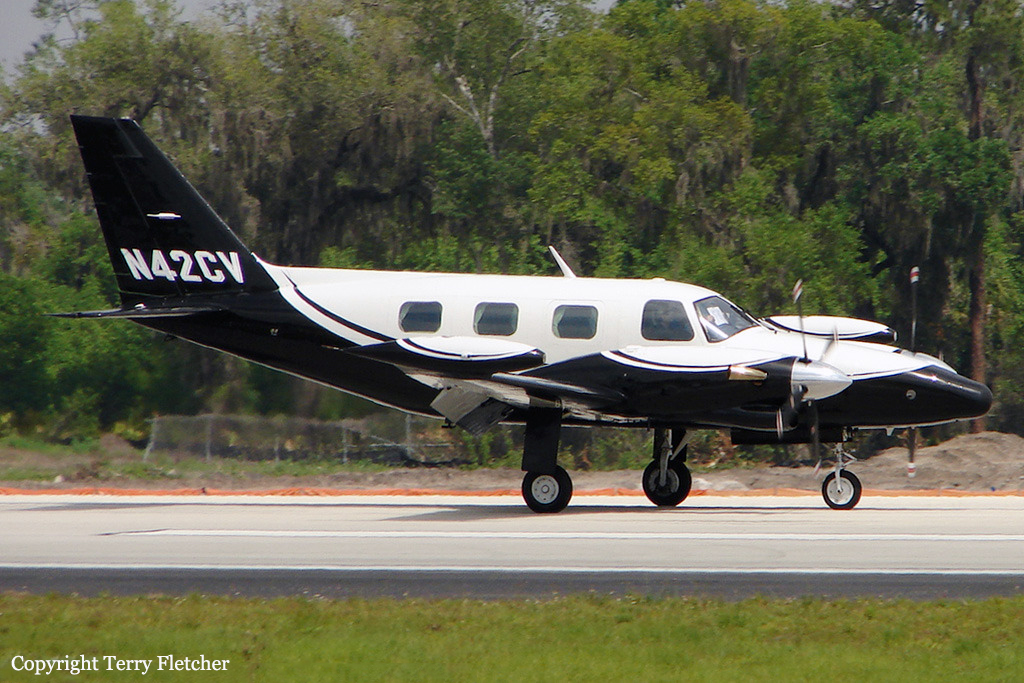
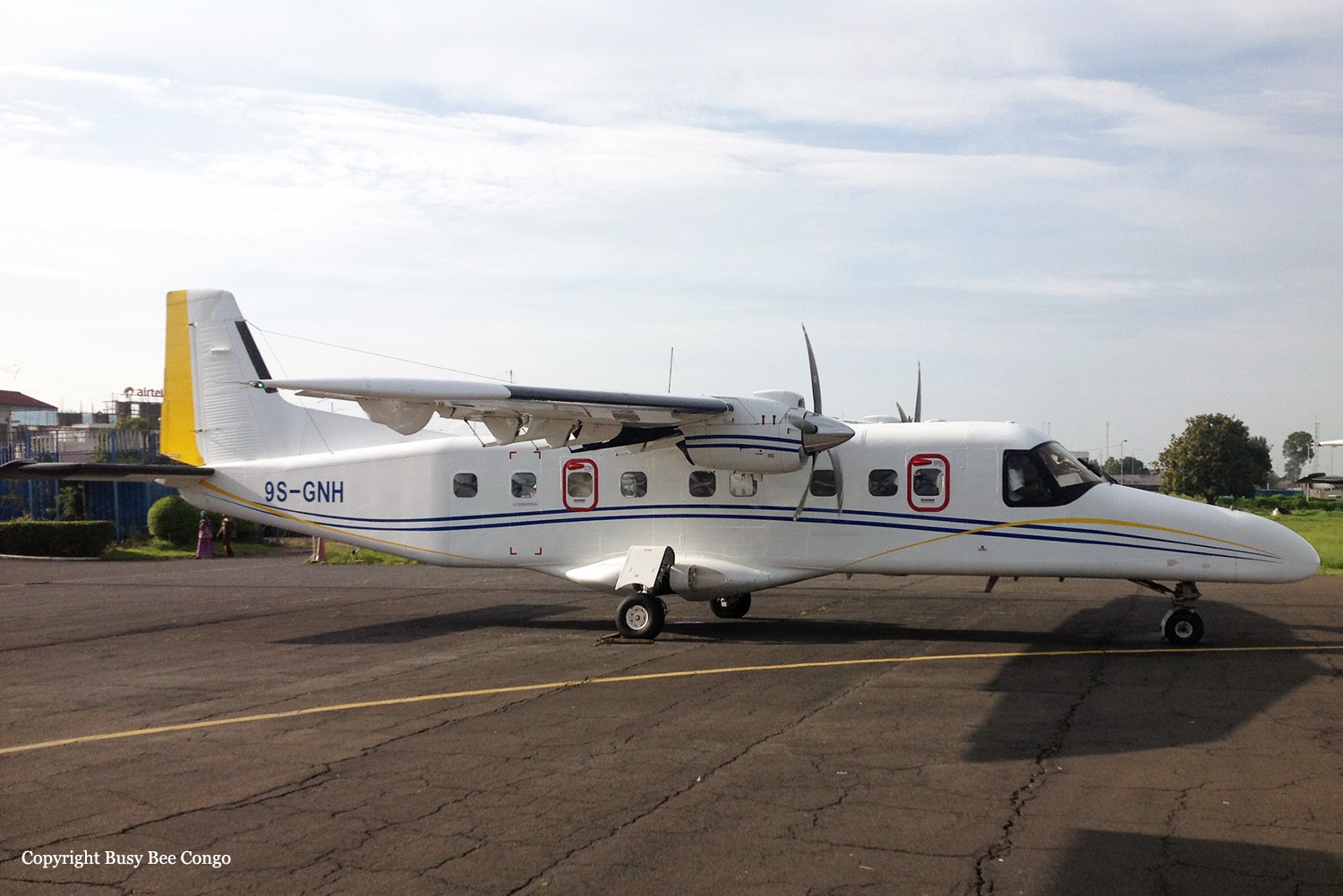
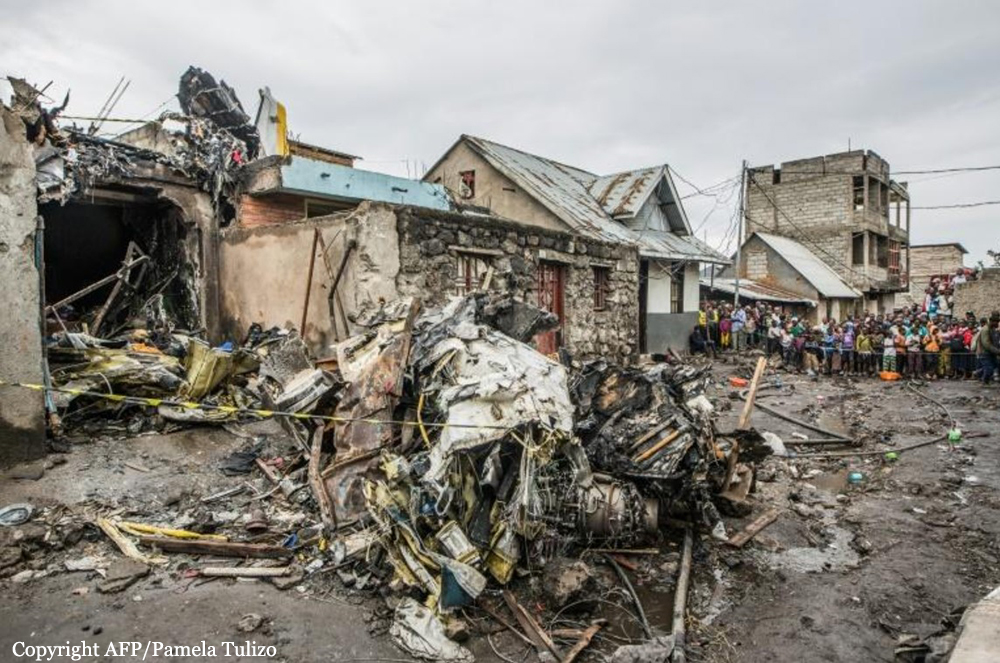Crash of a Piper PA-31-310 Navajo in Bogotá: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 12, 2020 at 1544 LT
Registration:
HK-4686
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bogotá – Villagarzón
MSN:
31-344
YOM:
1968
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Captain / Total hours on type:
250.00
Aircraft flight hours:
10251
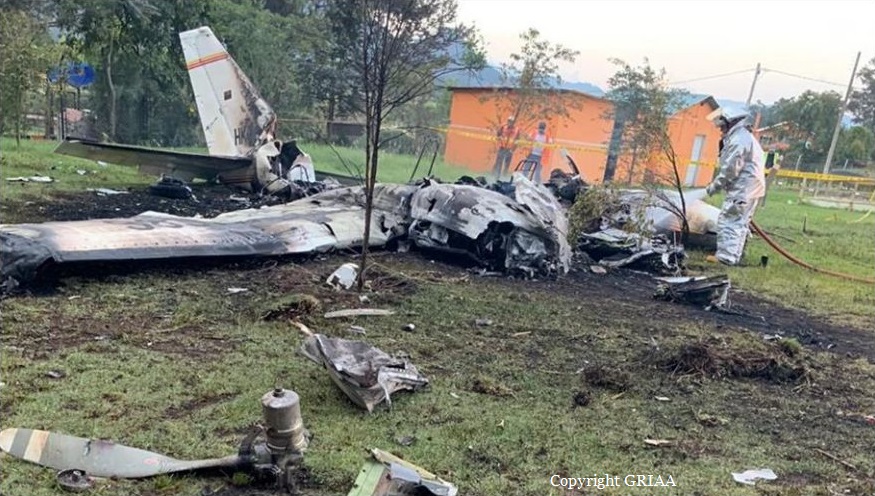
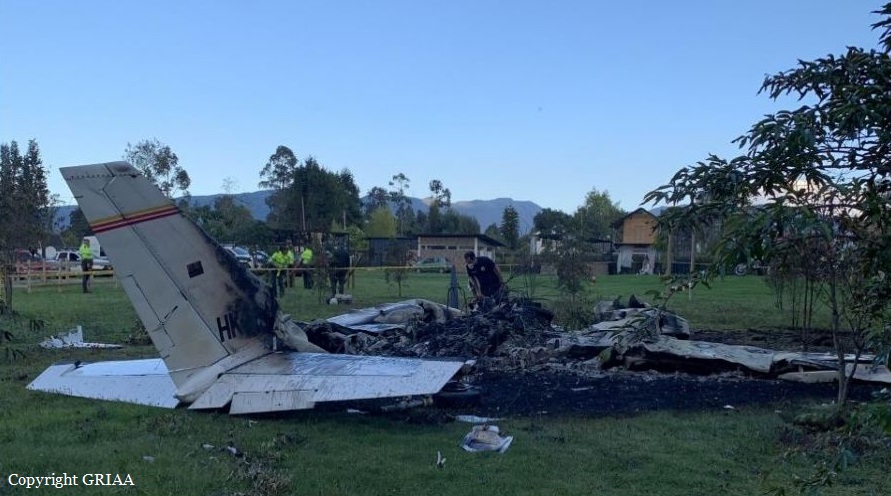
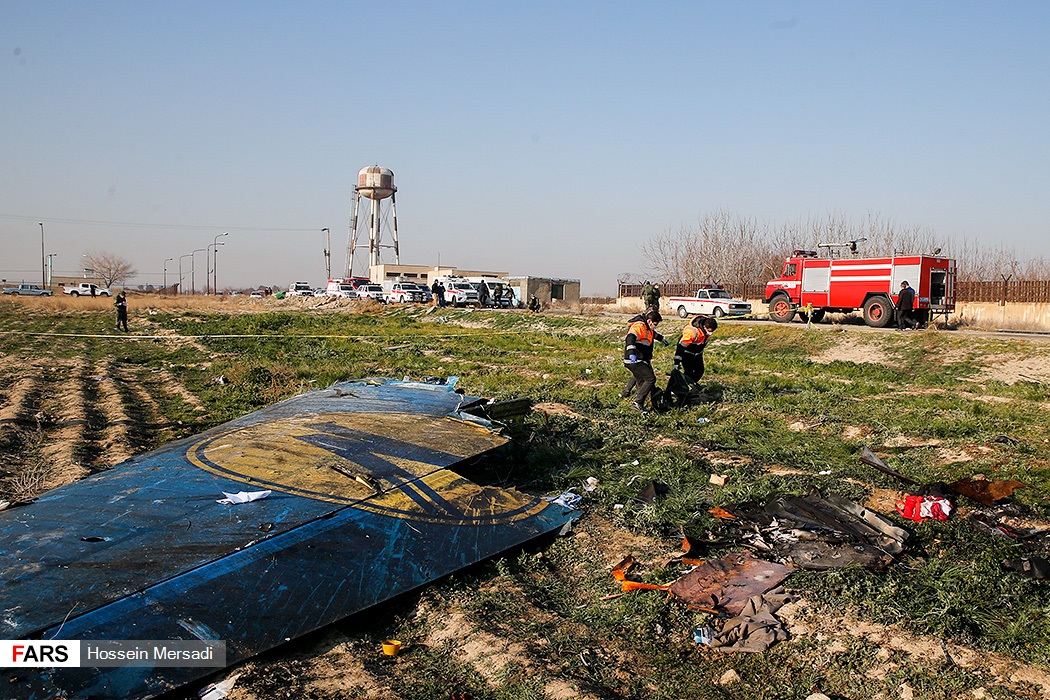
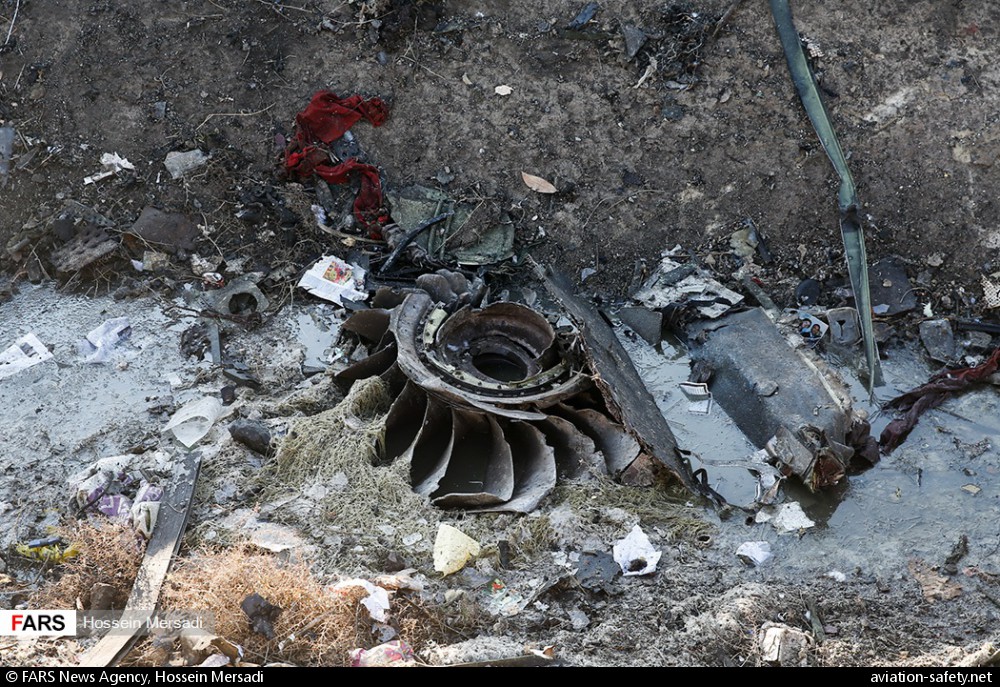
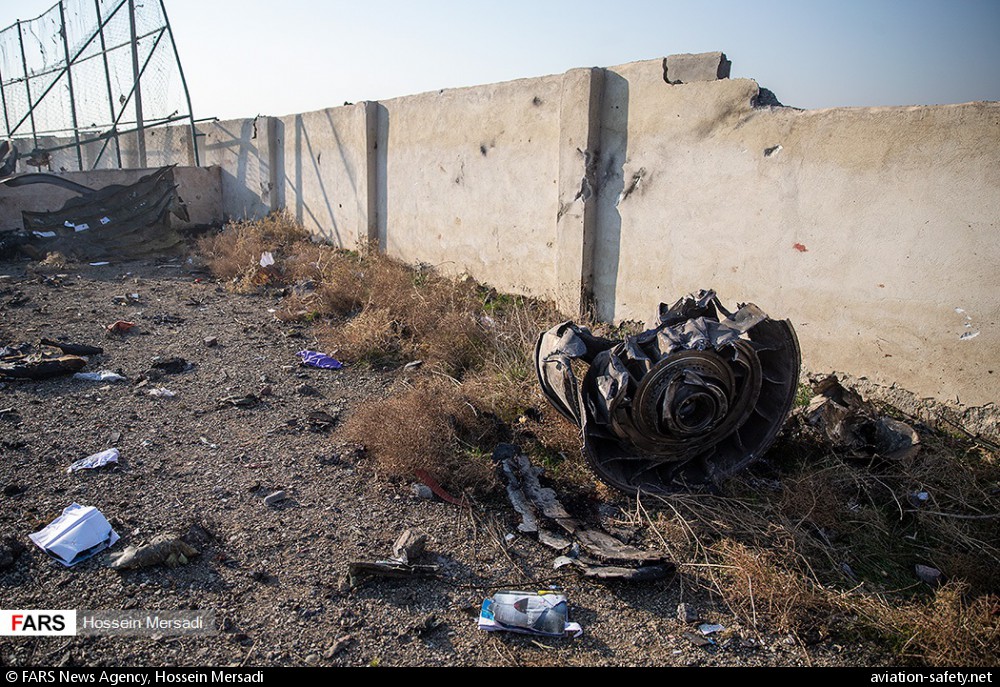
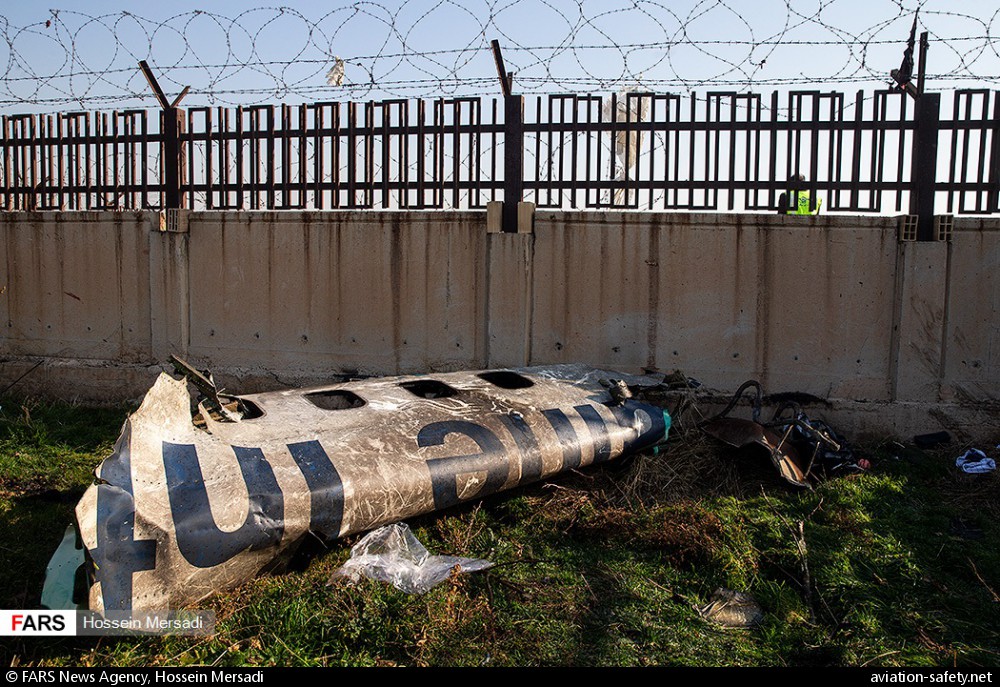
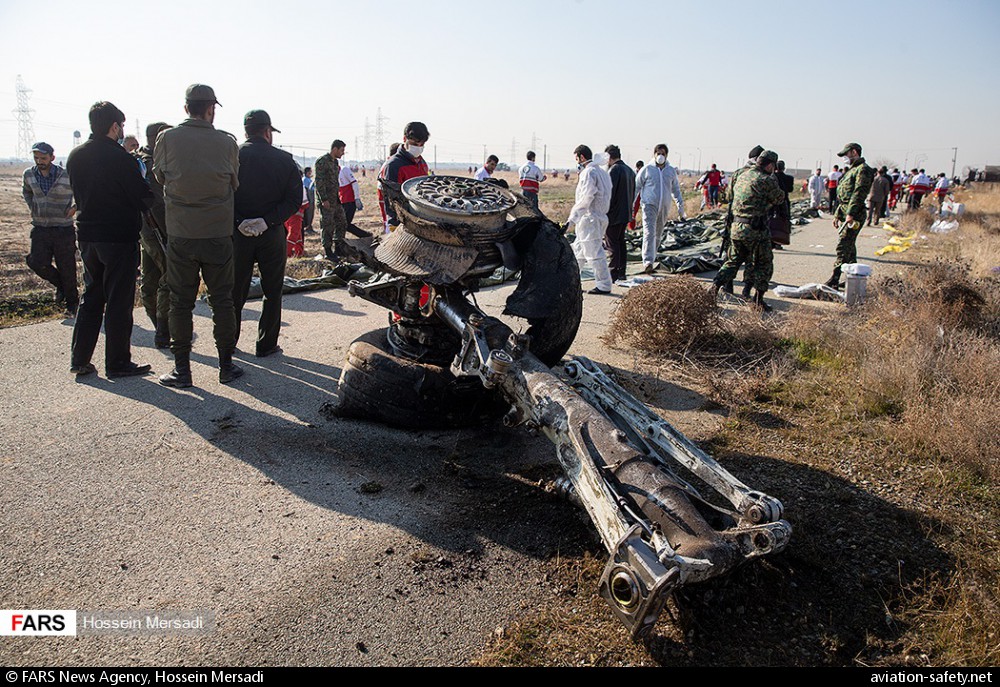
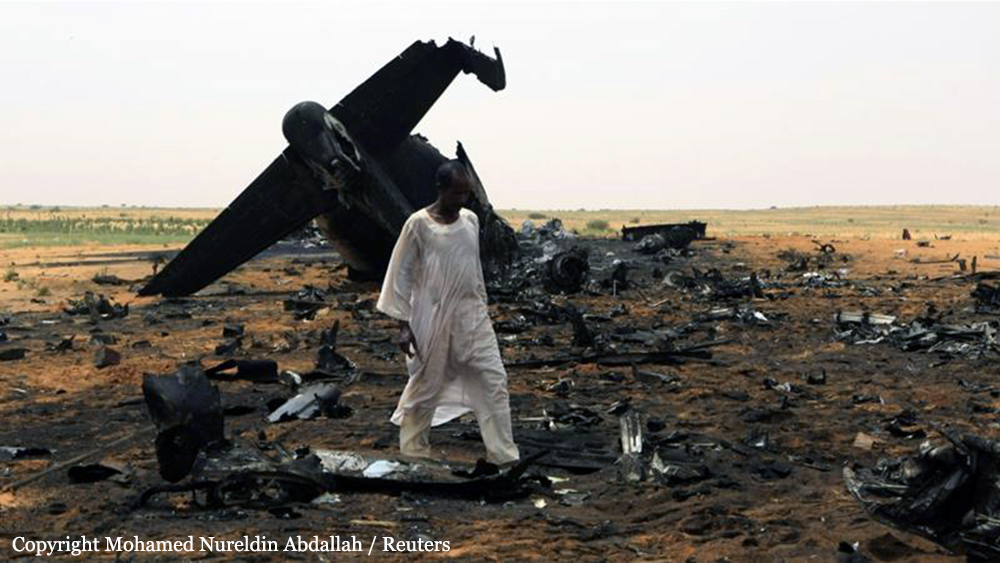
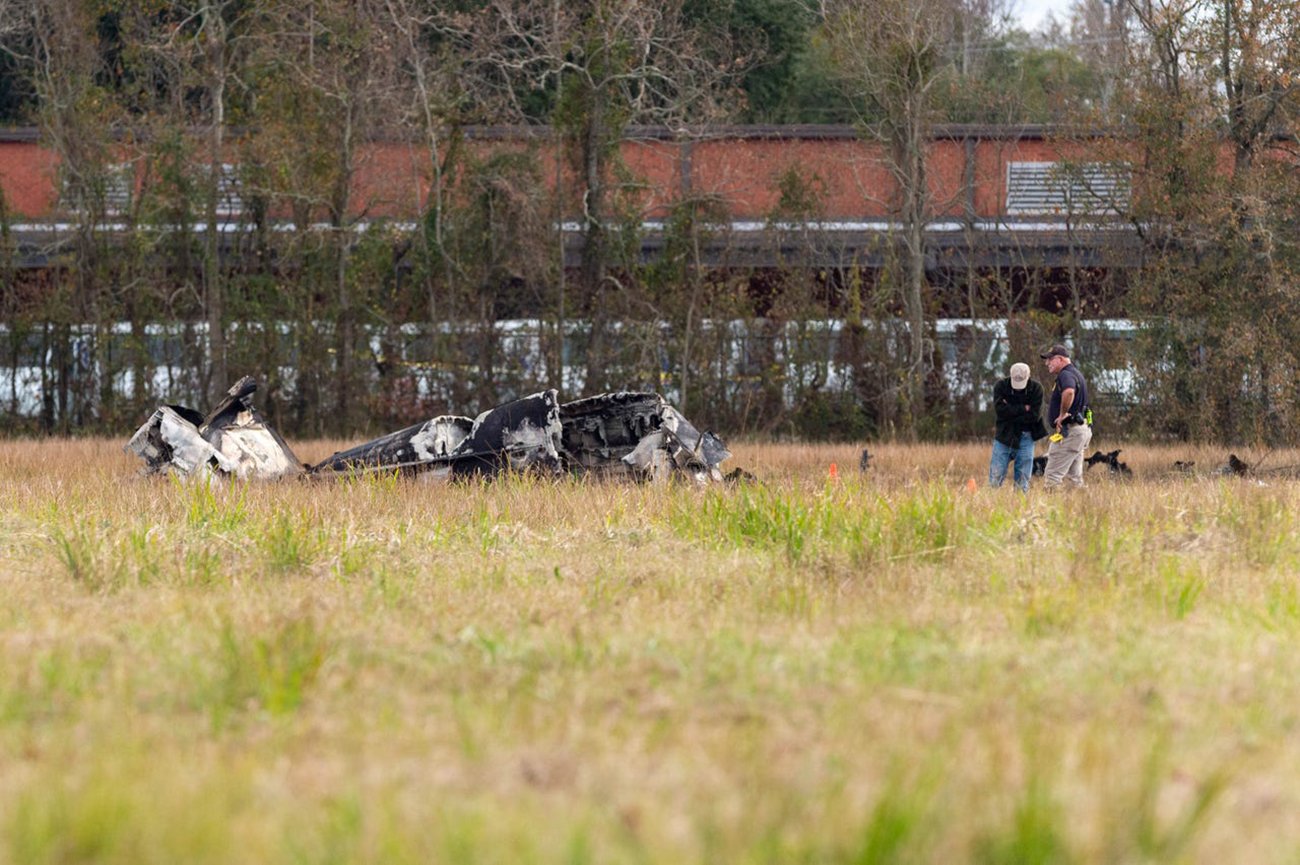
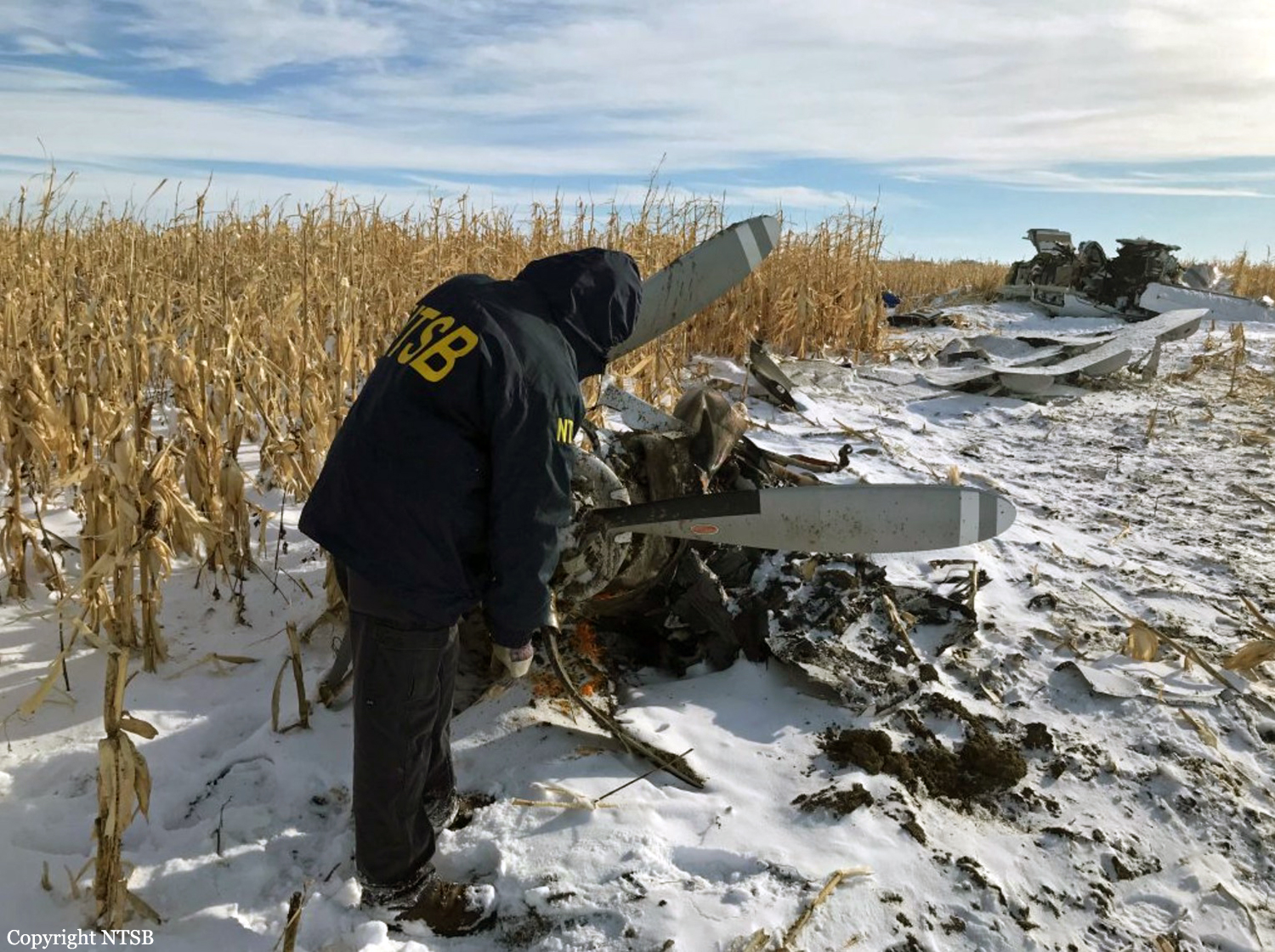
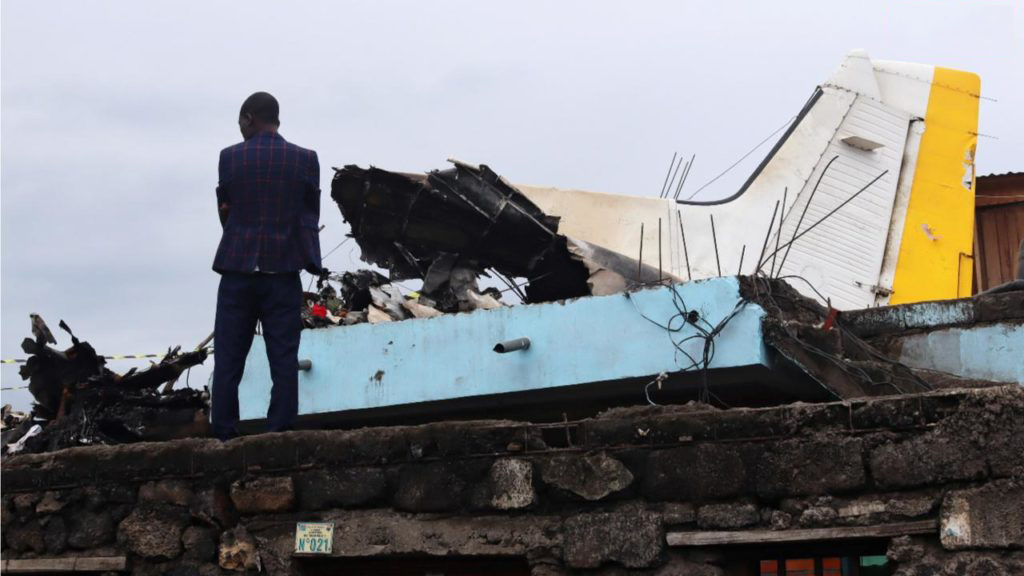
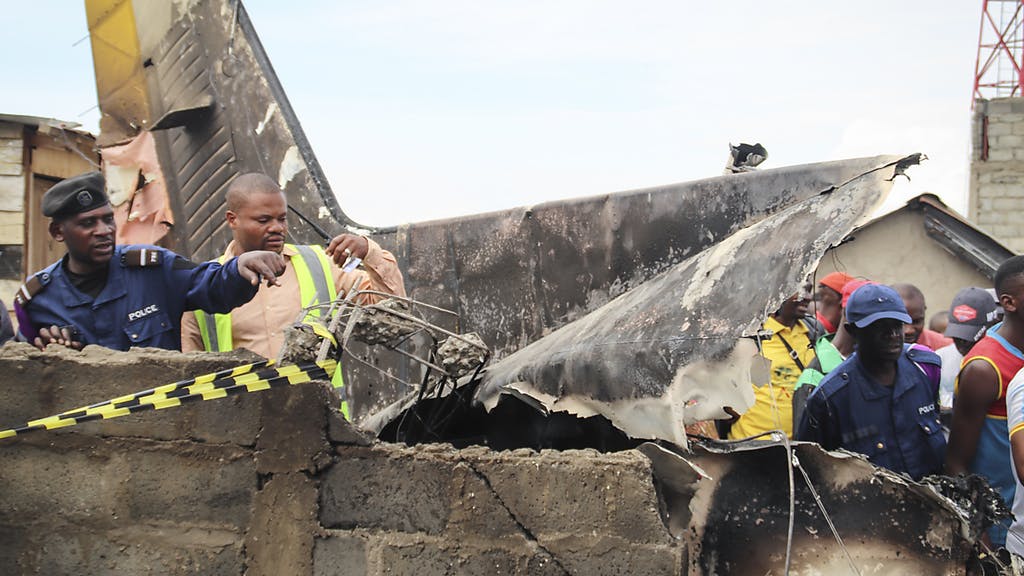
Circumstances:
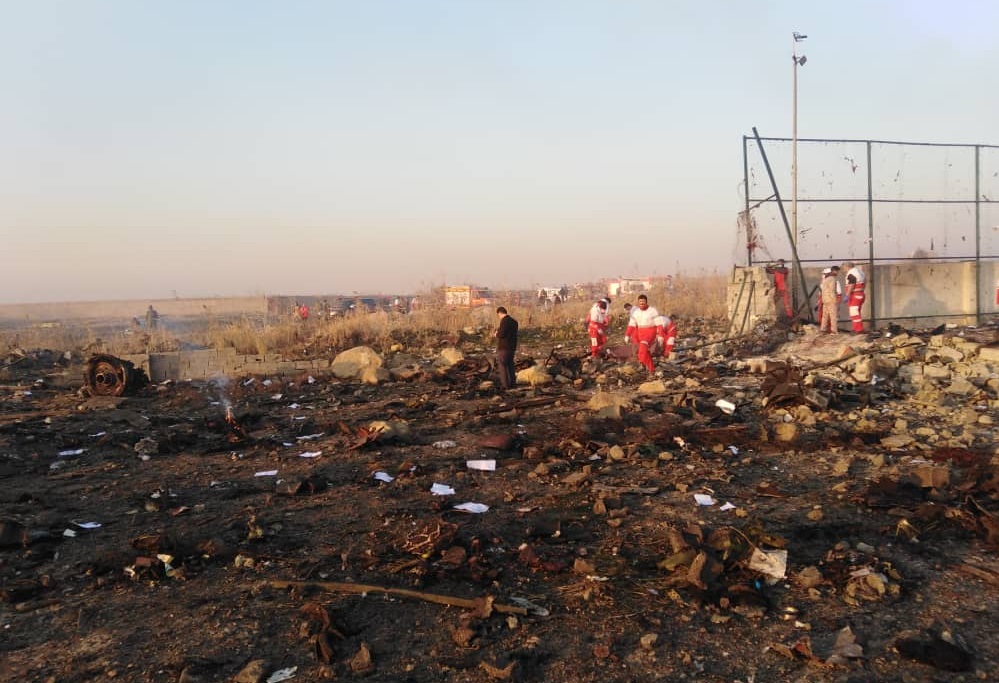
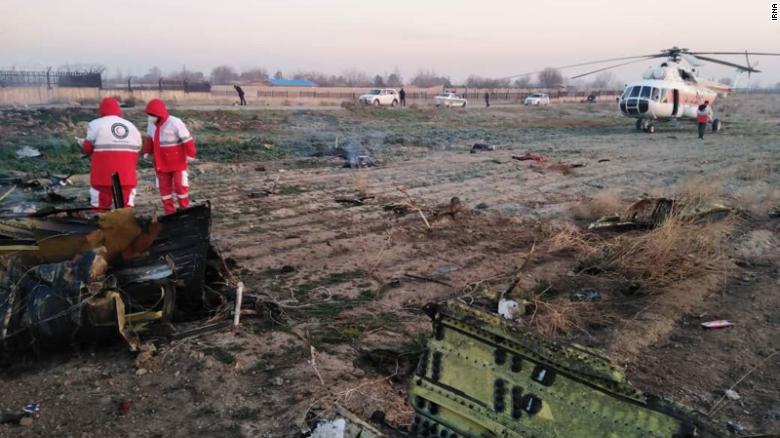
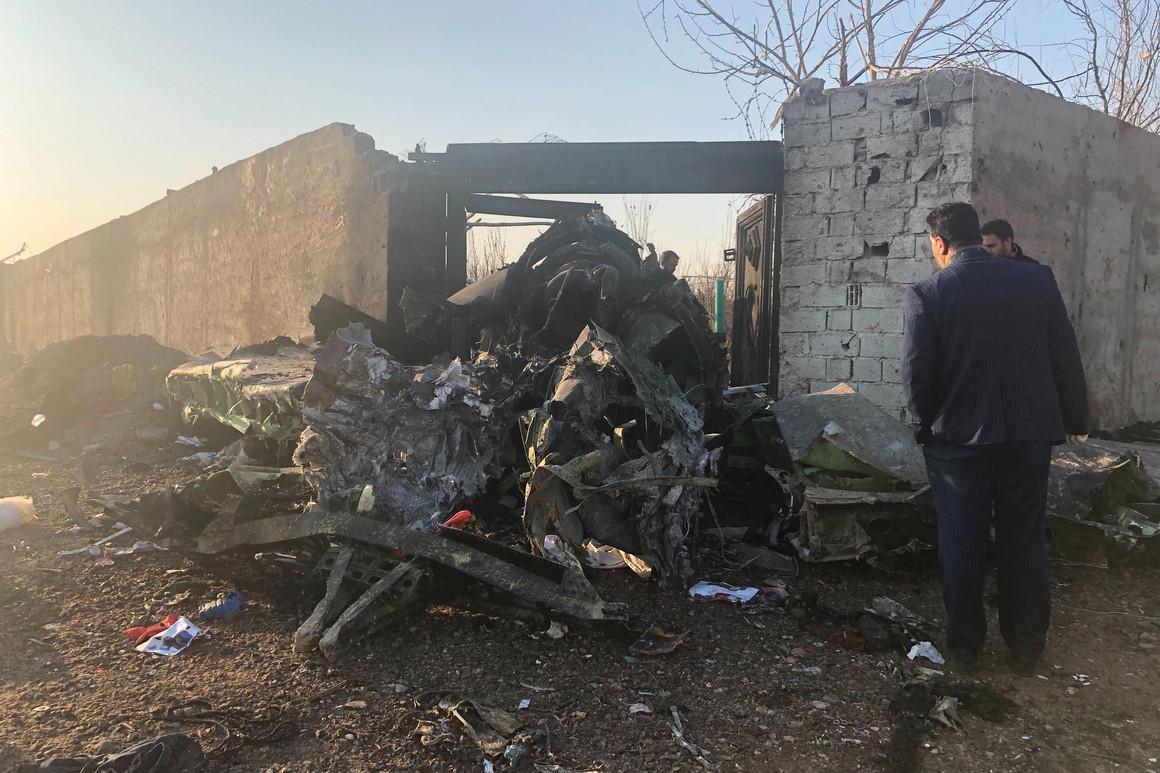
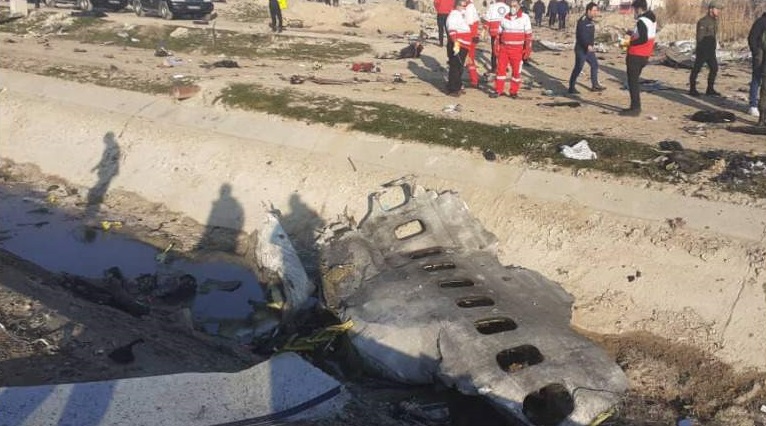
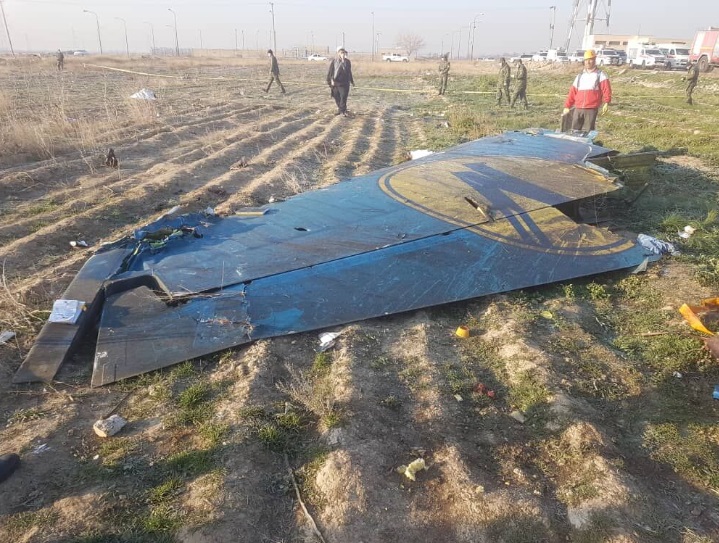
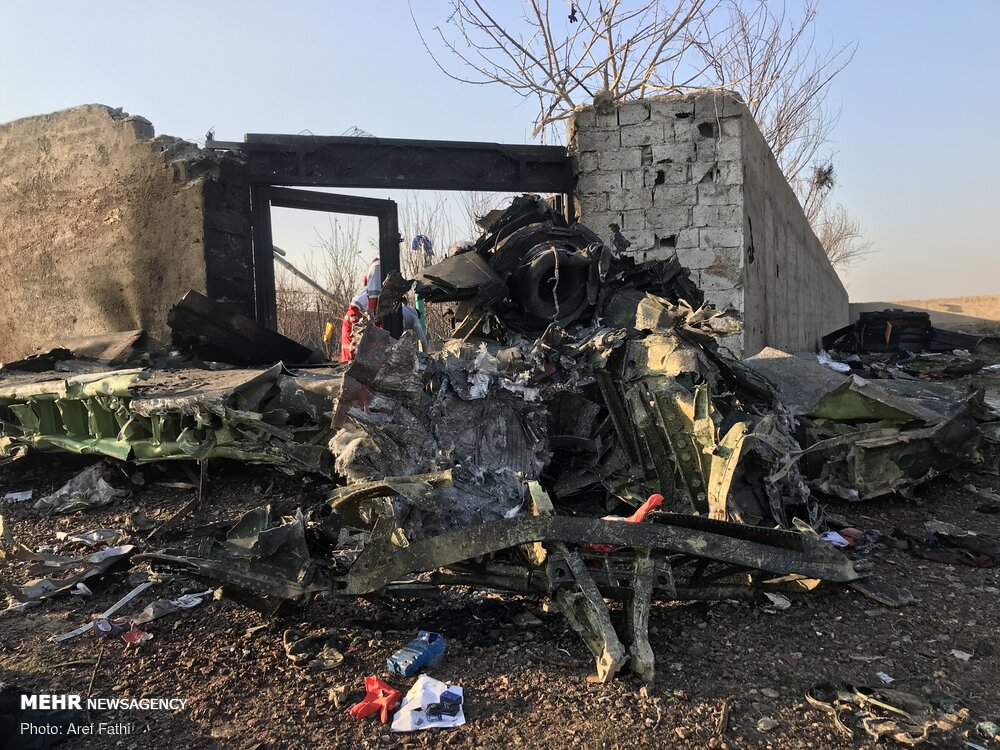
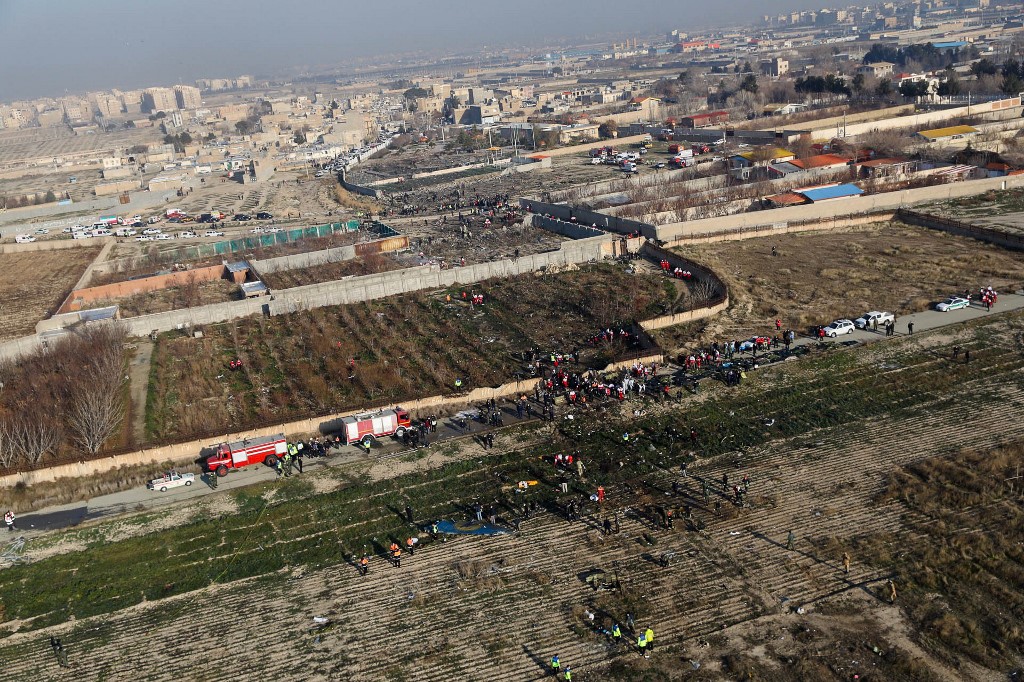
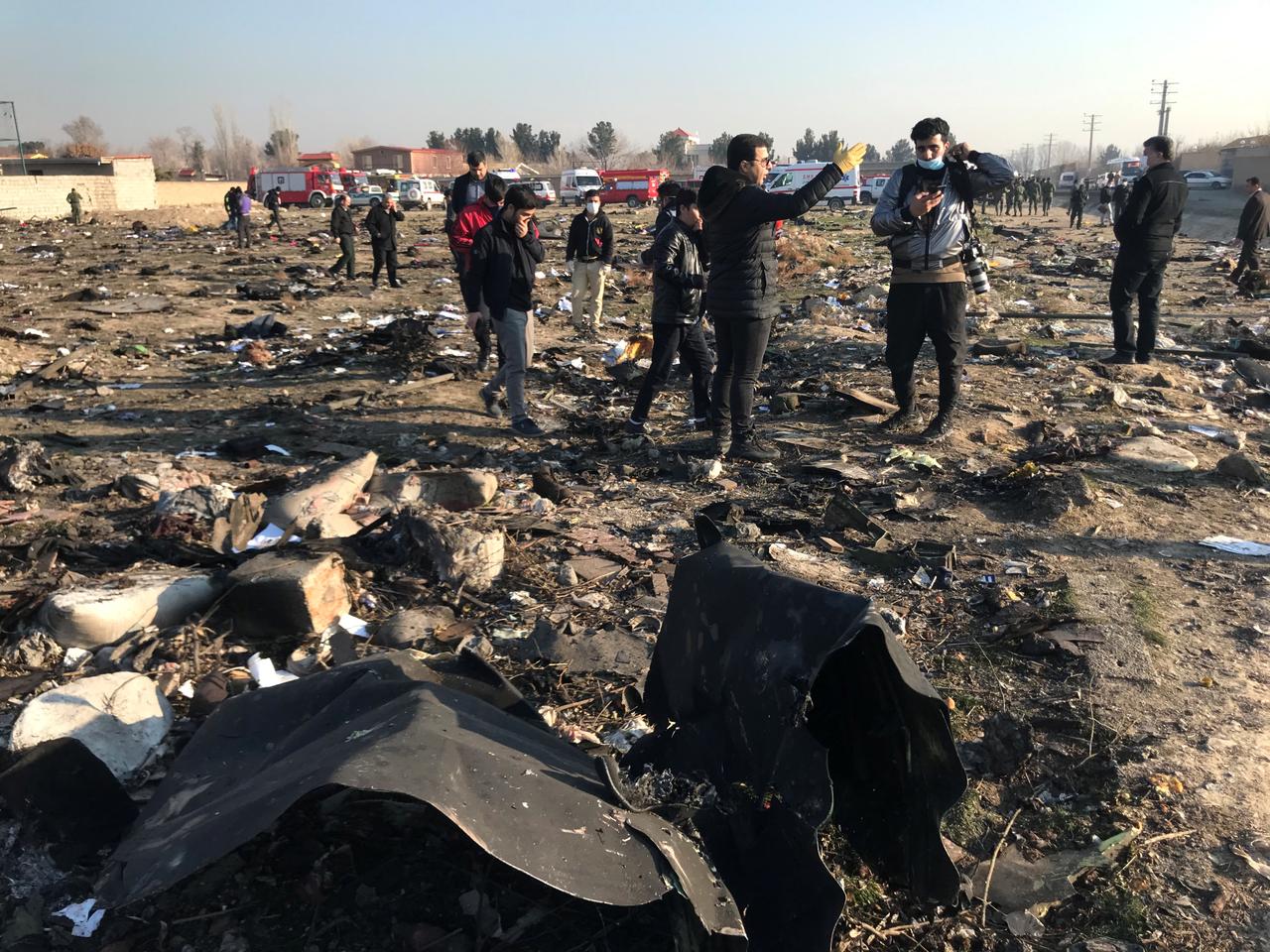
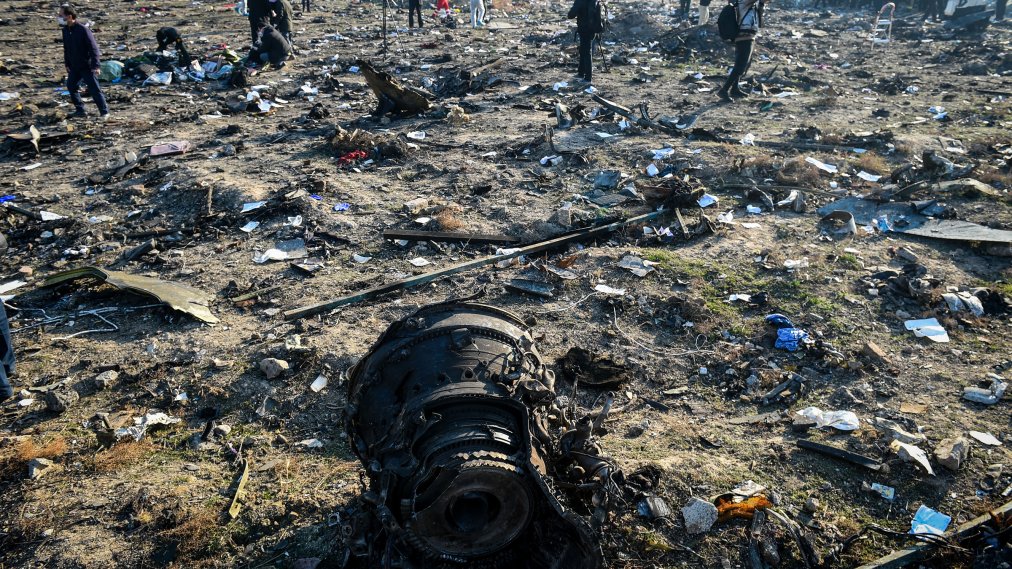
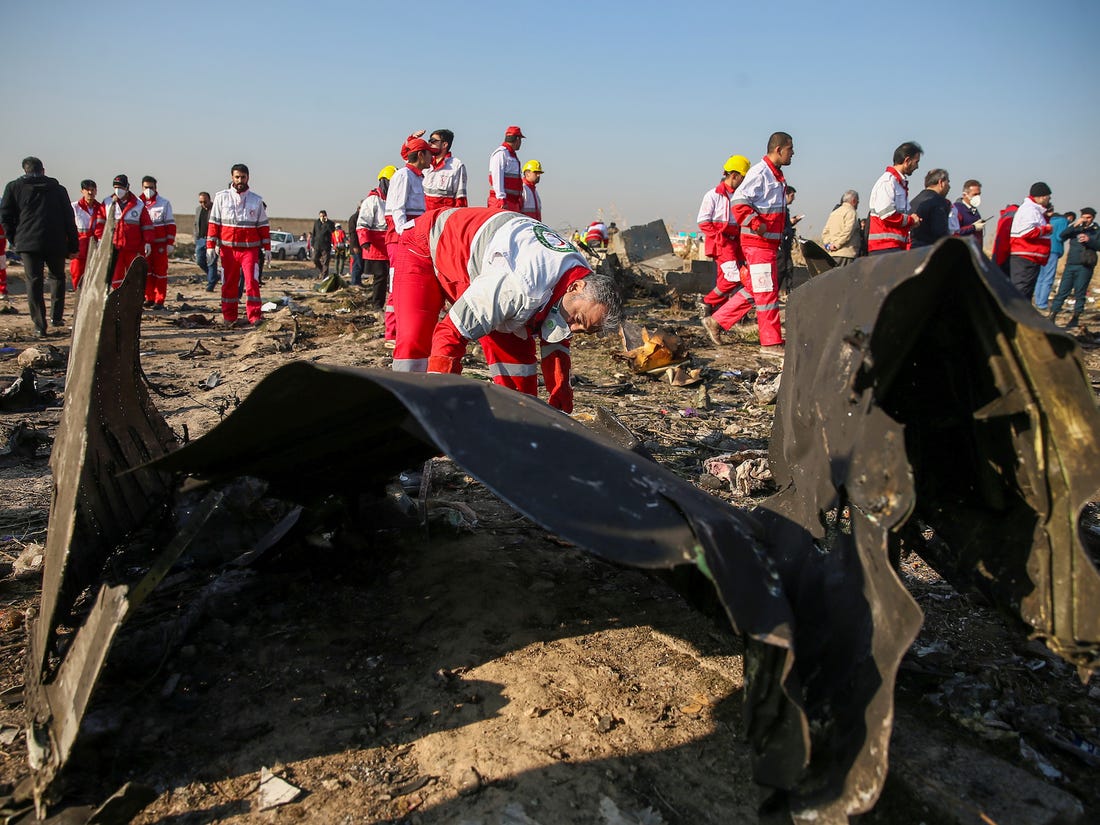
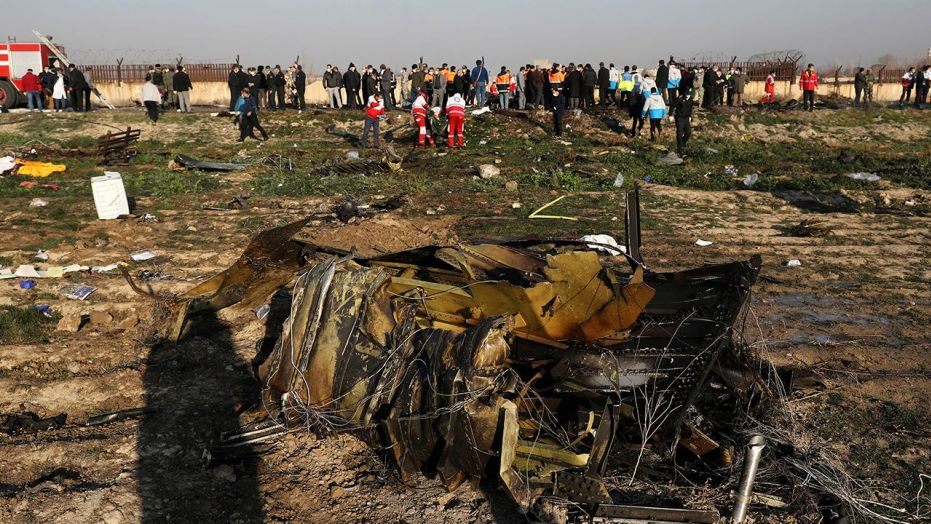
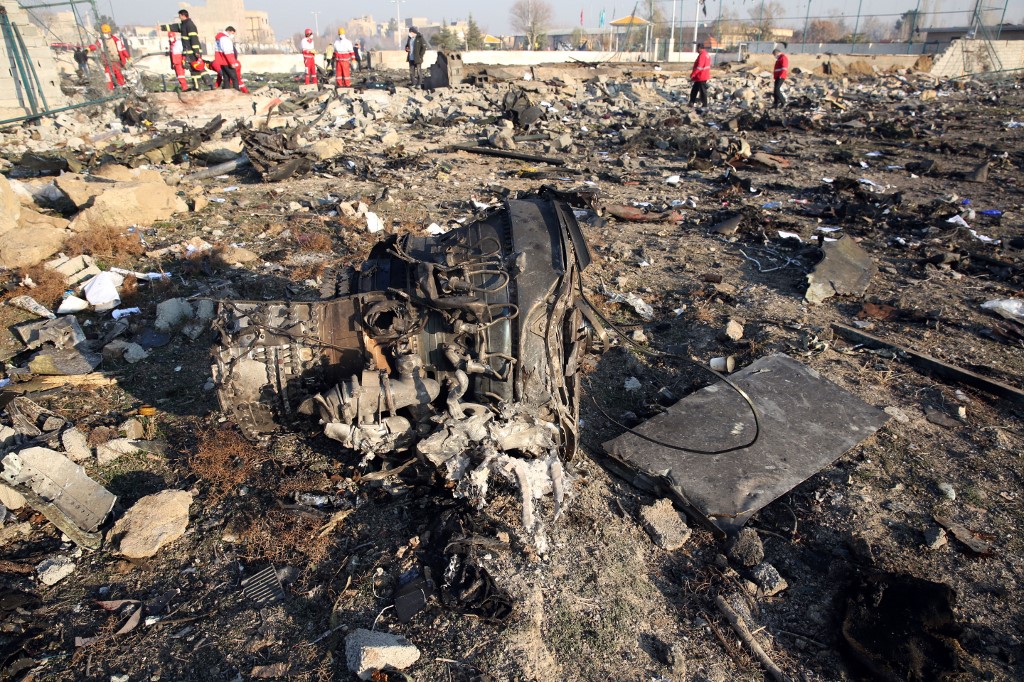
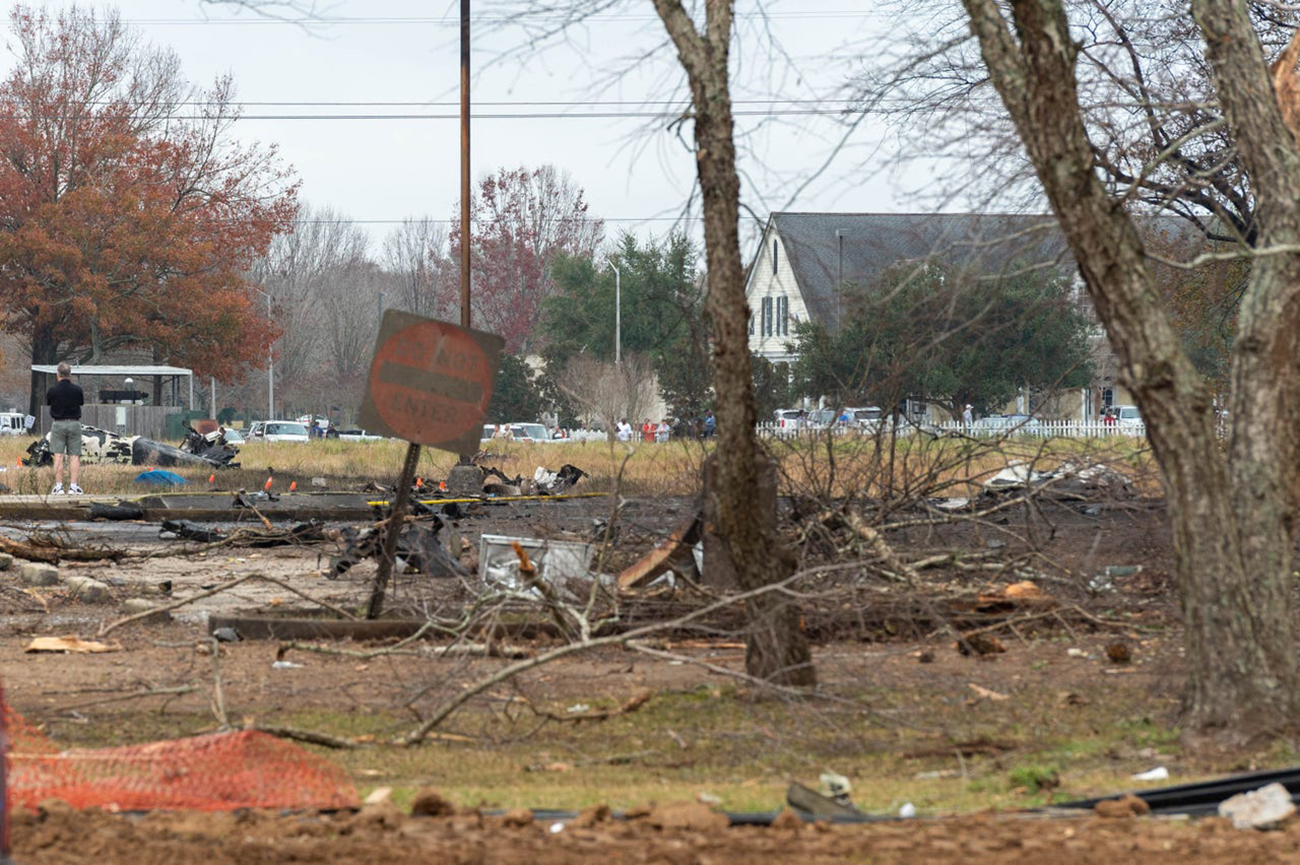
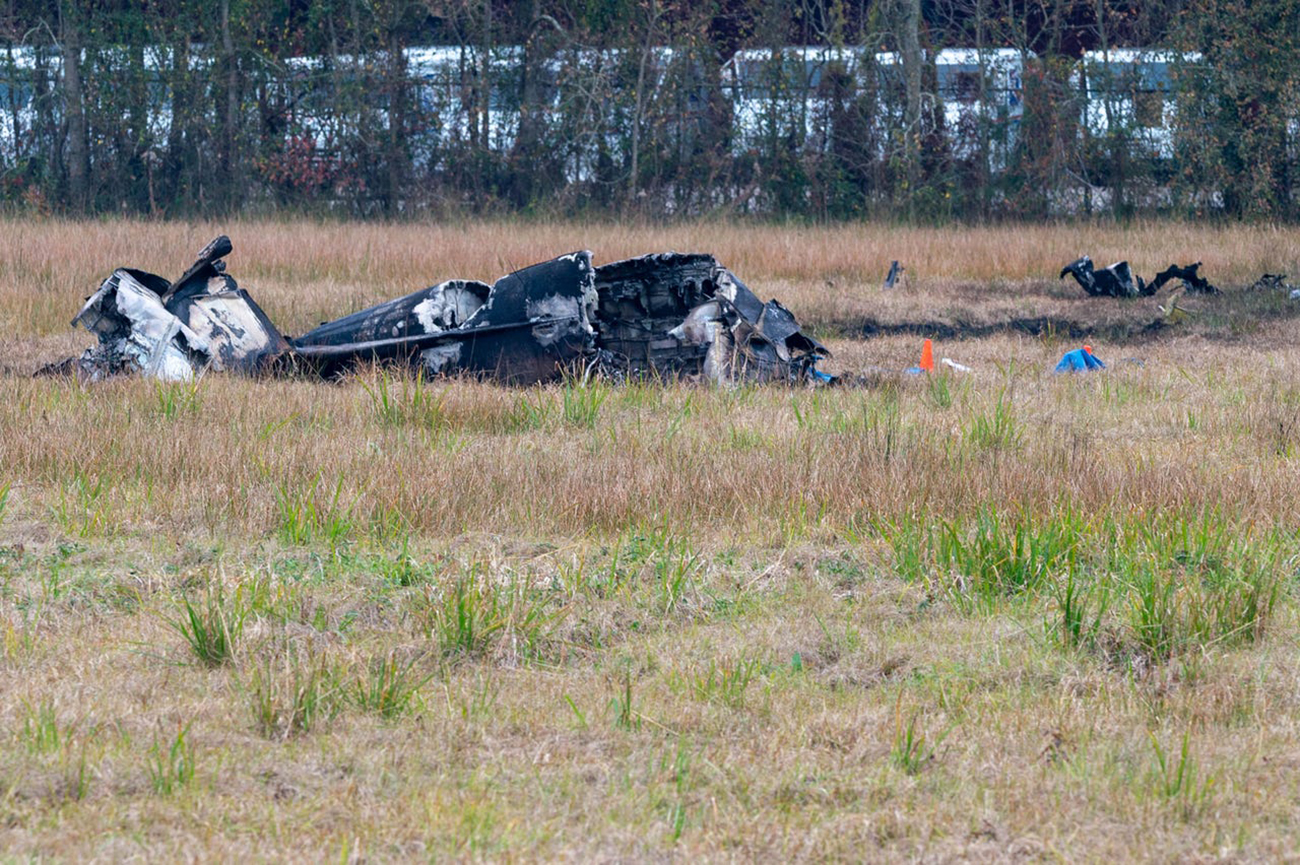
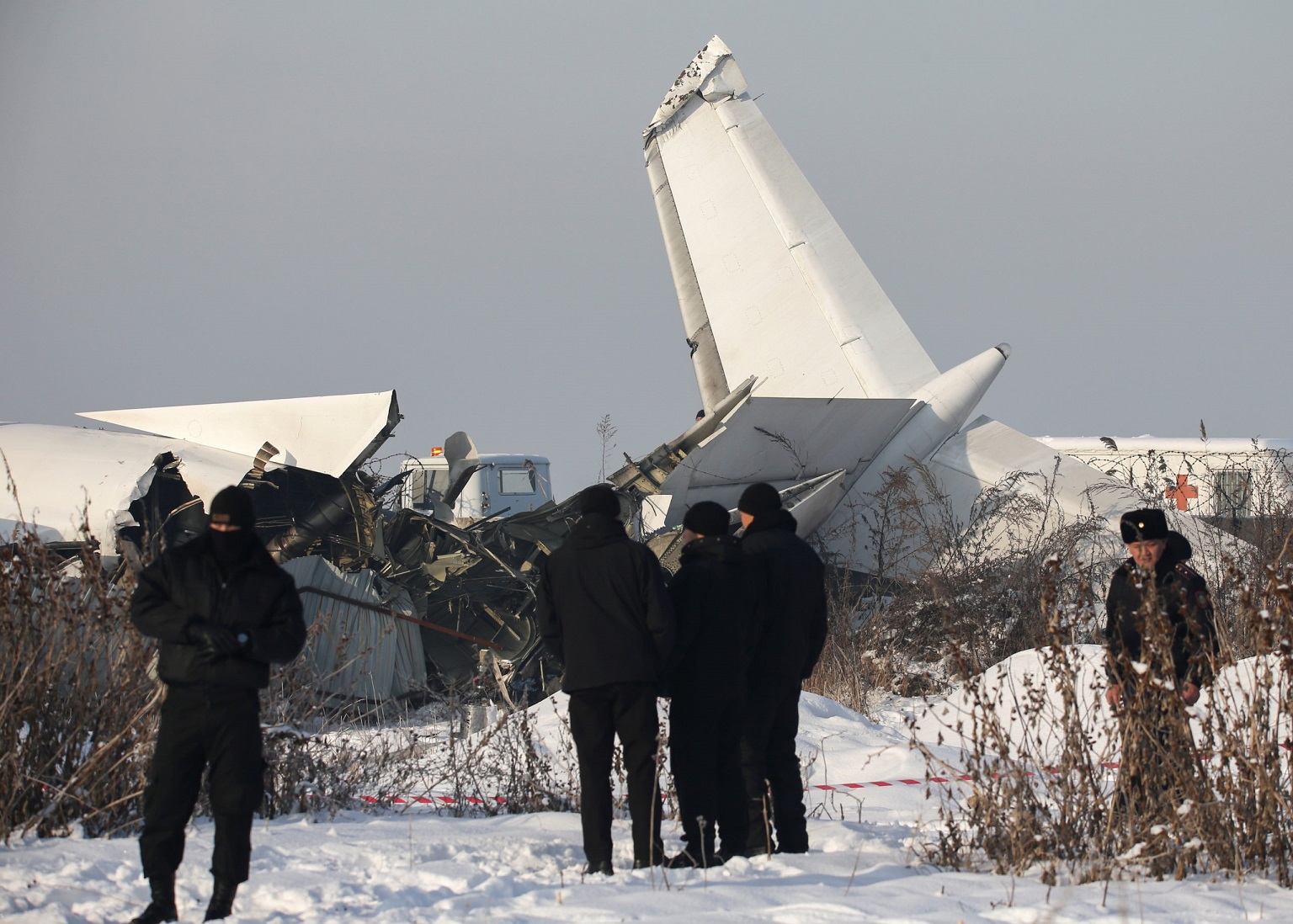
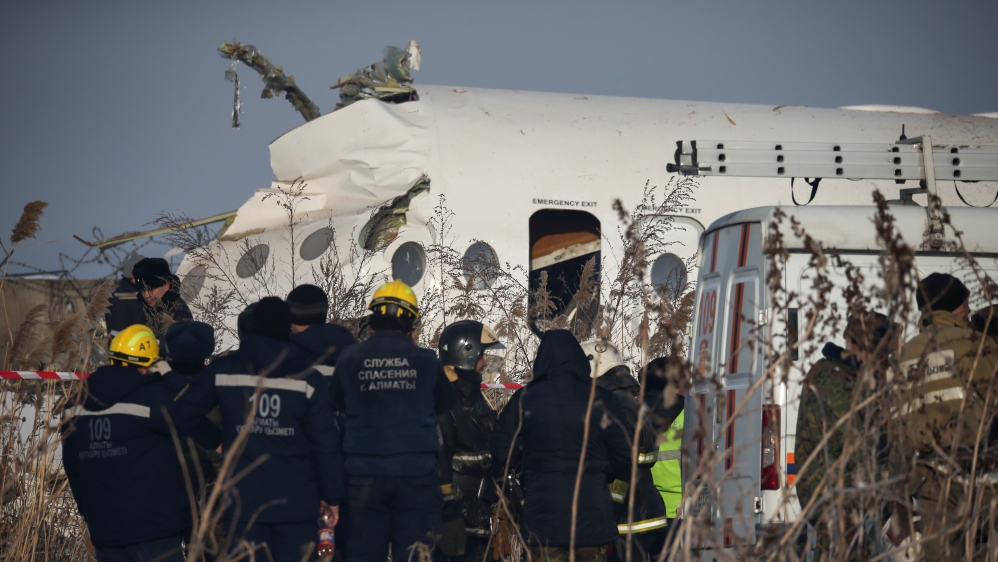
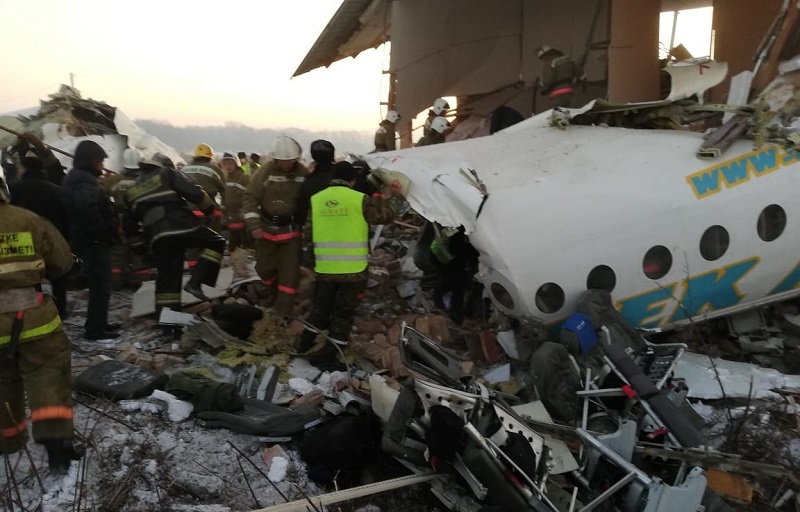
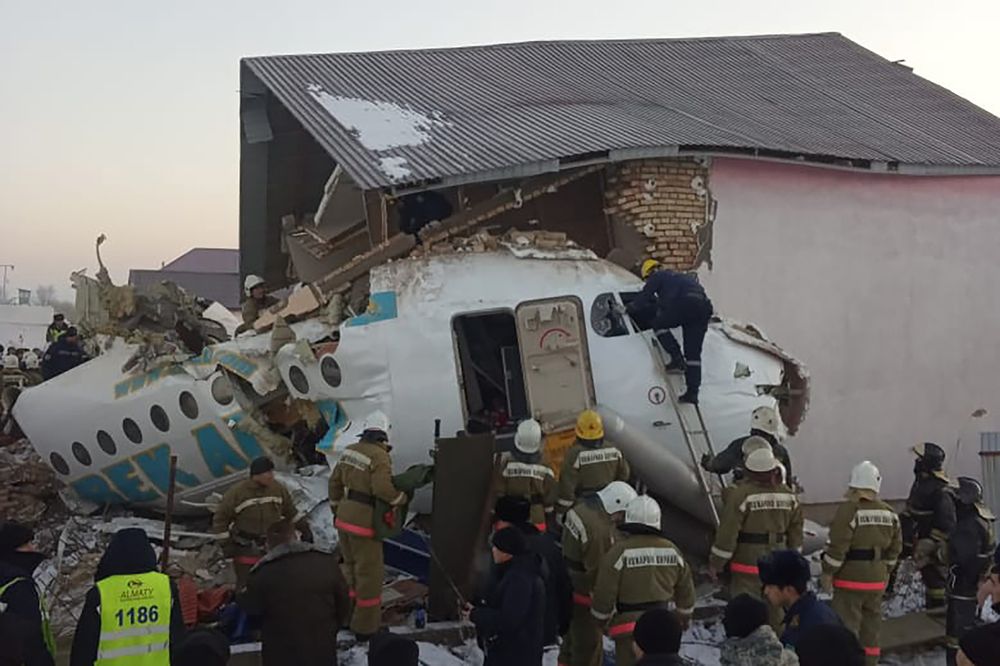
Shortly after takeoff from Bogotá-Guaymaral Airport, while in initial climb, the crew informed ATC about the failure of the right engine. He was cleared to return for an emergency and completed a circuit to land on ruwnay 11. On final, the airplane lost height and crashed in a wooded area located about 800 metres short of runway, bursting into flames. The aircraft was destroyed by a post crash fire and all four occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The investigation determined that the accident was caused by the following probable cause(s):
- Loss of in-flight control as a result of slowing below Minimum Control Speed and drag, generated by the failure of the right engine (No. 2).
- Failure of engine No. 2, due to lack of lubrication, possibly caused by oil leakage through an 11.5 mm fracture, found in one of the sides of cylinder No. 2 at the height of the intake valves.
- Inappropriate application by the crew of the emergency procedure for landing with an inoperative engine, by not declaring the emergency, not feathering the propeller of the inoperative engine and configuring the aircraft early for landing (with landing gear and flaps) without having a safe runway, making it difficult to control the aircraft and placing it in a condition of loss of lift and control.
Contributing Factors:
- Failure of the operator to emphasize in the crew training program the techniques and procedures to be followed in the event of engine failure, among others, the declaration of emergency to ATC, the flagging of the propeller of the inoperative engine, the care in the application of power to the good engine so as not to increase yaw and not to configure the aircraft until landing has been assured.
- Lack of emergency calls by the crew, which denotes deficiencies in the Operator's Safety Management System, and which prevented the early warning of the aerodrome support services and deprived the crew of possible assistance from other aircraft or from the same operator.
- Loss of in-flight control as a result of slowing below Minimum Control Speed and drag, generated by the failure of the right engine (No. 2).
- Failure of engine No. 2, due to lack of lubrication, possibly caused by oil leakage through an 11.5 mm fracture, found in one of the sides of cylinder No. 2 at the height of the intake valves.
- Inappropriate application by the crew of the emergency procedure for landing with an inoperative engine, by not declaring the emergency, not feathering the propeller of the inoperative engine and configuring the aircraft early for landing (with landing gear and flaps) without having a safe runway, making it difficult to control the aircraft and placing it in a condition of loss of lift and control.
Contributing Factors:
- Failure of the operator to emphasize in the crew training program the techniques and procedures to be followed in the event of engine failure, among others, the declaration of emergency to ATC, the flagging of the propeller of the inoperative engine, the care in the application of power to the good engine so as not to increase yaw and not to configure the aircraft until landing has been assured.
- Lack of emergency calls by the crew, which denotes deficiencies in the Operator's Safety Management System, and which prevented the early warning of the aerodrome support services and deprived the crew of possible assistance from other aircraft or from the same operator.
Final Report: