Country
Operator Image

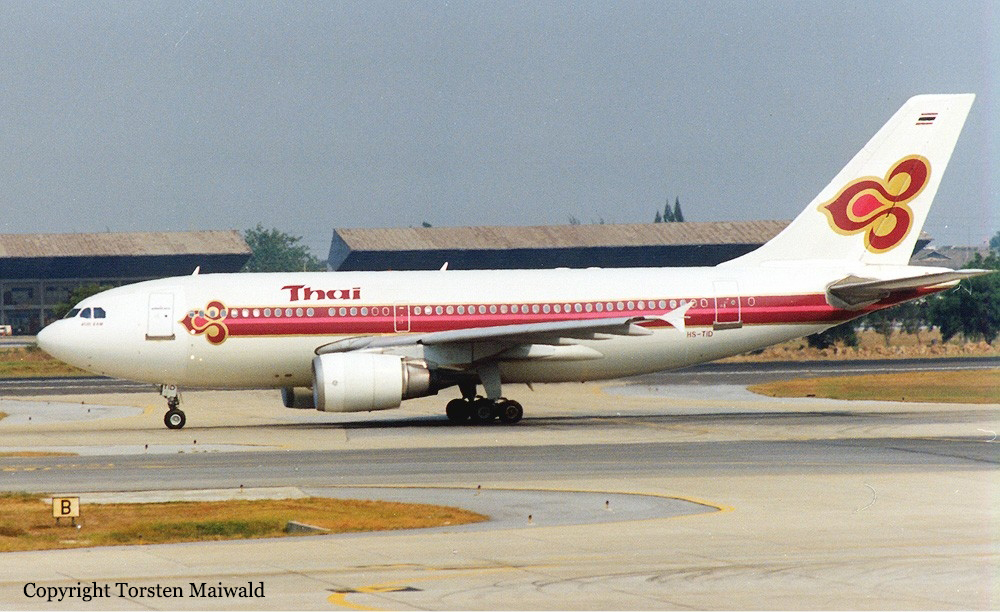
Crash of an Airbus A310-304 near Kathmandu: 113 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 31, 1992 at 1245 LT
Registration:
HS-TID
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bangkok - Kathmandu
MSN:
438
YOM:
1987
Flight number:
TG311
Crew on board:
14
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
99
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
113
Circumstances:
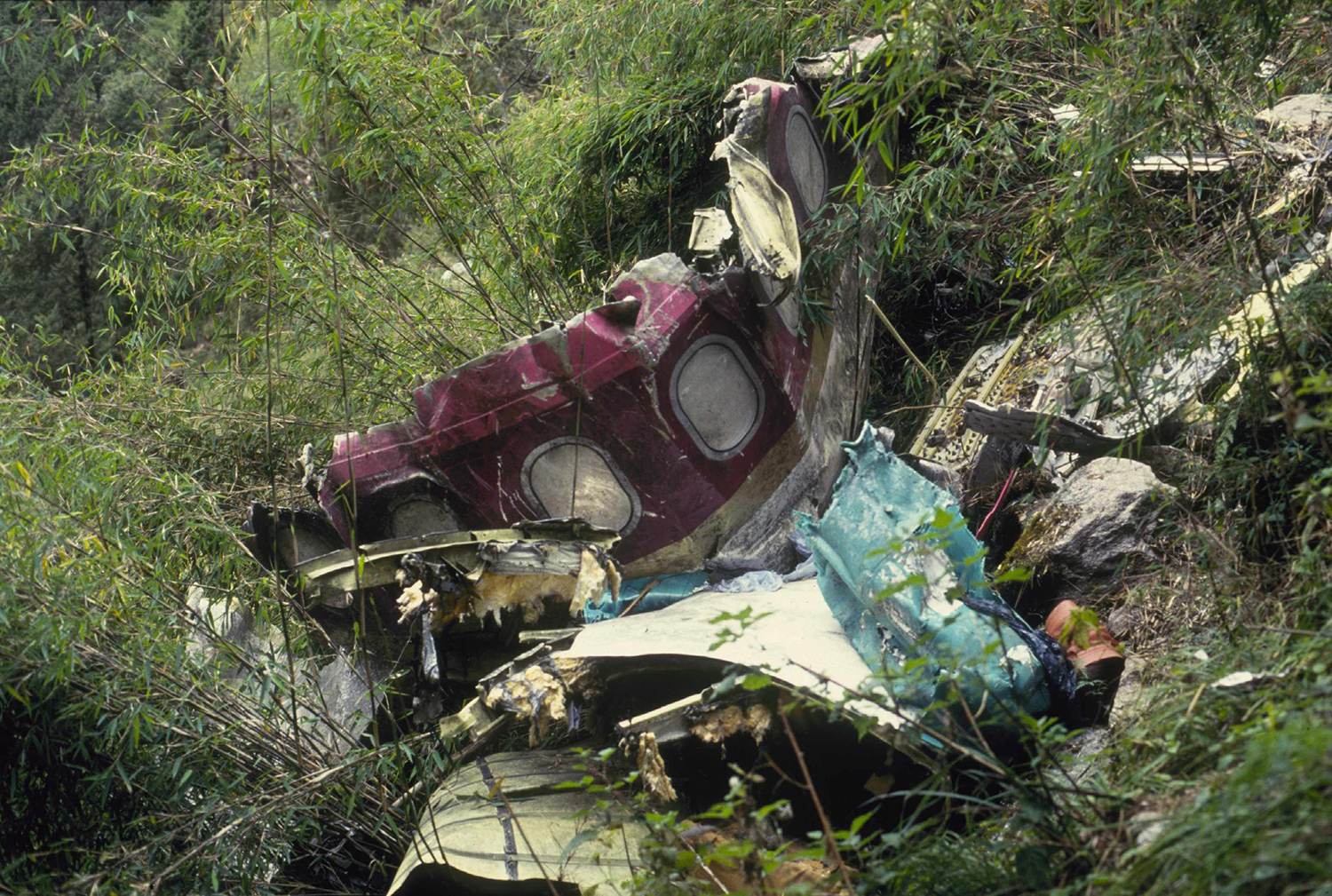
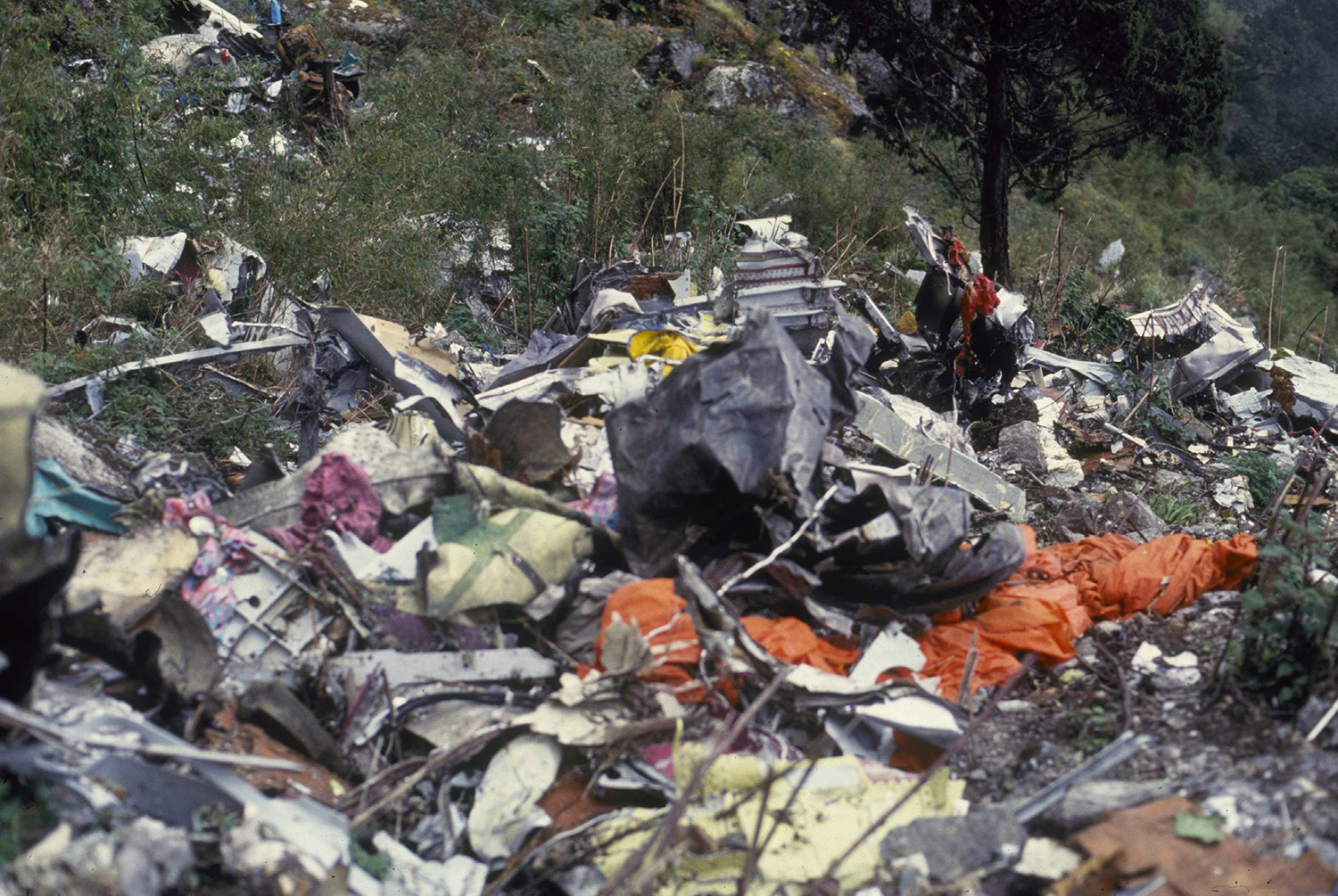
Thai Airways Flight 311 was conducting the Sierra (VOR/DME) approach to runway 02 at Tribhuvan International Airport, in instrument weather conditions. A flap fault occurred while the flight was on the approach; this caused the crew to ask for clearance back to Calcutta, a decision that was in keeping with both Company and performance requirements, which necessitate the use of full flaps for the steep final approach. Shortly (21 seconds) after making this request, at a distance of approximately 12 nm from the Kathmandu VOR, the flap fault was rectified by retracting and then reselecting the flaps. The crew determined that it was not possible to continue the straight-in approach, due to the steep descent angles required and the position of the aircraft. The crew stated to the control tower that they wished to start their approach again and requested a left turn back to the Romeo fix, which is 41 nm south south-west (202 radial) of the Kathmandu VOR. The Controller, in the non-radar environment, responded by clearing the flight to make the Sierra approach, which starts at the 202 radial and 16 nautical miles from the VOR. The crew response to the clearance was to report that, at the moment, they couldn't land and to ask again for left turn back to Romeo to start their approach again. After further dialogue with the controller, which included requests for a left turn, the crew unilaterally initiated a right turn from the aircraft's 025° heading and commenced a climb from an altitude of 10,500 feet to FL180, when the flight was about 7 nm south of the Kathmandu VOR. The crew reported to the tower controller that the flight was climbing and the controller replied by instructing the crew to report at 16 nm for the Sierra approach. During the turn, there was more discussion between the tower controller and the flight, where it was established that the aircraft was to maintain an altitude of FL115 and was to 'proceed to Romeo' and contact the Area Control Center (ACC) controller. The flight, commencing a descent while in the turn, completed a 360° turn, momentarily rolling out on headings of 045° and 340°, and again proceeded toward the north on a heading of 025° magnetic. When the flight was about 5 nm south-west of the Kathmandu VOR, the crew contacted the ACC and stated that the aircraft was 'heading 025' and they wished to proceed to Romeo to start their approach again; adding they had 'technical problems concerned with the flight.' It was again established that the flight was to proceed to Romeo and the crew agreed to 'report over Romeo.' It was determined from the cockpit voice recorder that the crew was in the process of inserting 'Romeo' and other related navigational information in the Flight Management System, but were experiencing difficulties. The flight continued towards the north on a heading of 025° and then, at about 16 nm north, the heading was altered to the left to 005°. Slightly over one minute later, the Ground Proximity Warning System (GPWS) sounded the warning 'terrain, terrain' followed by 'whoop whoop pull-up'; the aural warning continued until impact approximately 16 seconds later. Engine thrust was increasing and 'Level Change' had been announced on the cockpit, just before the impact occurred at the 11,500-foot level of a 16,000-foot peak; the accident site was located on the 015 radial (north-north east) at 23.3 nm from the Kathmandu VOR. The aircraft was destroyed and all 113 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
TG311 flight crew's management of the aircraft flight path wherein the flight proceeded in a northerly direction which was opposite to the cleared point Romeo to the South; ineffective radio communication between the area control centre and the TG311 flight crew which allowed the flight to continue in the wrong direction, in that the TG311 crew never provided the aircraft's VOR radial when stating DME and the controller never solicited this information and thus the aircraft's position was not transmitted at any time; and ineffective cockpit crew coordination by the TG311 crew in conducting flight navigation duties. Contributing factors were: the misleading depiction of Romeo on the operator's approach chart used by the flight crew; a flap fault, although corrected, required that the initial approach be discontinued; and radio communication difficulties between the TG311 crew and the air traffic controllers that stemmed from language difficulties and ineffective discussion of apparent unresolved problems.



Crash of an Avro 748-243-2A in Udon Thani
Date & Time:
Dec 7, 1987
Registration:
HS-THH
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
1707
YOM:
1971
Crew on board:
0
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
After landing, the aircraft was unable to stop within the remaining distance, overran and came to rest. There were no casualties but the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.

Crash of a Boeing 737-2P5 off Phuket: 83 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 31, 1987 at 1536 LT
Registration:
HS-TBC
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Hat Yai - Phuket
MSN:
22267
YOM:
1980
Flight number:
TG365
Crew on board:
9
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
74
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
83
Captain / Total hours on type:
5576.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
156
Aircraft flight hours:
16963
Aircraft flight cycles:
20864
Circumstances:
Thai Airways Flight 365 was approaching Phuket VOR/DME on radial 119 after a flight from Hat Yai. At the same time Dragon Air Flight 203 (a Boeing 737 registered VR-HYL, carrying 62 occupants) also approached Phuket VOR/DME on radial 090. At 08:34 UTC Dragonair 203 reported at 2500 feet with Thai 365 in sight in front of them. The Thai Boeing was flying at 3000 feet at the time, and was 13 miles from Phuket VOR/DME. Dragonair 203, first priority in approach sequence, then turned right at 12 DME and was going to turn inbound for finals for runway 27. The Thai crew surmised that the other crew were making a false position report to gain landing priority and reported hurriedly that they were at 8 DME inbound and requested visual approach, though they hadn't reached 8 DME yet. This forced Phuket Approach to give Thai 365 landing priority at 08:35. The Dragonair crew (flying IFR) immediately warned that the Thai plane couldn't descend through their flight level. Concentrating on the conflicting traffic the speed decayed to 163 knots until the stick shaker activated. The Thai crew then applied power and raised the landing gear, but the aircraft entered a stall crashed into the sea, disintegrating on impact. All 83 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The pilot slowed the aircraft and it stalled while the pilot prepared to be number one on landing as advised by Phuket approach control. It appears that he was worrying and not sure whether he could make number one landing because the pilot if number two aircraft in sequence gave warning that the number one aircraft ahead was above him and could not descend passing through his level. The pilot added power and raised the gear after stick shaker activated but didn't execute a recovery before hitting the sea.

Crash of an Avro 748-243-2 in Chiang Rai
Date & Time:
Apr 28, 1987 at 1005 LT
Registration:
HS-THI
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Chiang Mai - Chiang Rai
MSN:
1708
YOM:
1971
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
39
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
Following an uneventful flight from Chiang Mai, the crew initiated the approach to Chiang Rai Airport in good weather conditions. The copilot was the pilot-in-command when the aircraft completed a gear up landing. It slid on runway for about 1,075 meters before coming to rest on the runway. All 43 occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the crew failed to extend the landing gear on approach. The following contributing factors were reported:
- The crew failed to follow the approach checklist,
- Lack of crew coordination,
- The captain failed to supervise properly the copilot's actions.
- The crew failed to follow the approach checklist,
- Lack of crew coordination,
- The captain failed to supervise properly the copilot's actions.

Crash of a Boeing 737-2P5 in Phuket: 11 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 15, 1985 at 2329 LT
Registration:
HS-TBB
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bangkok - Phuket
MSN:
21810
YOM:
1979
Crew on board:
7
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
11
Circumstances:
Following an uneventful flight from Bangkok, the crew started the descent to Phuket Airport by night and good weather conditions. Four minutes after being cleared to descend to 3,000 feet, the pilot reported that he was unable to receive the DME signal. ATC asked the crew if he wanted to conduct a VOR approach to runway 09 but the captain preferred to attempt a visual approach to runway 27. On final, the aircraft struck a hill (800 feet high) and crashed about 18 km short of runway. The aircraft was destroyed and all 11 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
Decision of the crew to continue the approach below MDA until the aircraft struck the ground.
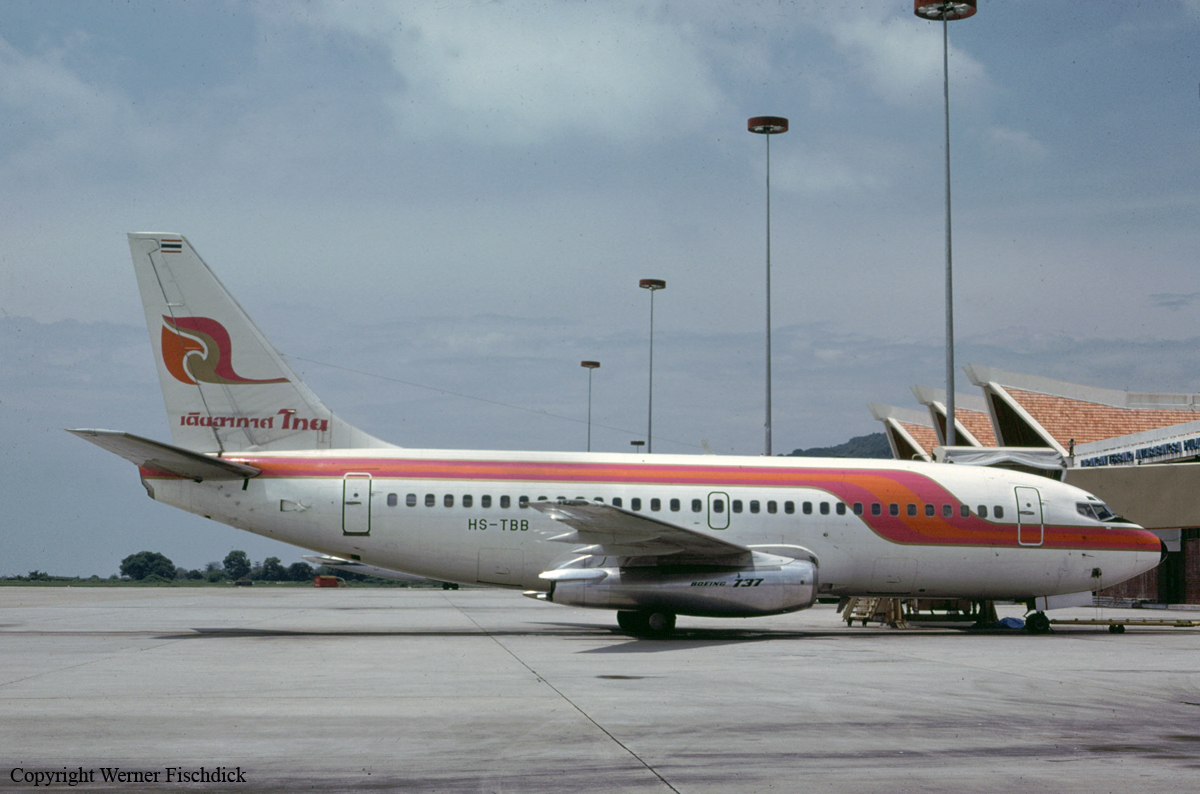
Crash of an Avro 748-2-243 in Chiang Rai
Date & Time:
Jun 21, 1980
Registration:
HS-THG
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Chiang Mai - Chiang Rai
MSN:
1693
YOM:
1970
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
16
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
After touchdown at Chiang Rai Airport, the airplane encountered difficulties and was unable to stop within the remaining distance. It overran and came to rest in a ditch. All 21 occupants were evacuated, some of them were injured.

Crash of an Avro 748-2-207 in Bangkok: 44 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 27, 1980 at 0655 LT
Registration:
HS-THB
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Nakhon Phanom – Udon – Khon Kaen – Bangkok
MSN:
1568
YOM:
1964
Flight number:
TG231
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
49
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
44
Captain / Total hours on type:
7796.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
11899
Aircraft flight hours:
12791
Circumstances:
On 27 April 1980, HS-748 Series 11, HS-THB was on a scheduled domestic passenger flight. The flight operated the route Bangkok - Khon Kaen - Udon - Nakhon Phanom - Udon - Khon Kaen - Bangkok. The departure flight was flight number TG221 which departed Bangkok International Airport at 0101 h, arrived Khon Kaen Airport at 0210 h, departed Khon Kaen Airport at 0233 h, arrived Udon Airport at 0251 h, departed Udon Airport at 0309 h, arrived Nakhon Phanom Airport at 0349 h. The return flight, flight number TG231, departed Nakhon Phanom Airport at 0408 h, arrived Udon Airport at 0448 h, departed Udon Airport at 0507 h, arrived Khon Kaen Airport at 0532 h, departed Khon Kaen Airport at 0550 h, ETA Bangkok International Airport at 0656 h. At 0559 h, after take-off from Khon Kaen Airport, the pilot reported to Bangkok Area Control Centre that he was climbing to 6 000 ft, ETA Korat at 0626 h, ETA Bangkok International Airport at 0656 h and requested ATC clearance to Bangkok International Airport via W6 - KT - W1 - BKK. Bangkok Area Control Centre cleared HS-THB to Bangkok International Airport via this route, to maintain FL 120 and asked the pilot to report when the aircraft reached FL 120.
- At 0614 h the pilot reported that HS-THB reached FL 120.
- At 0626 h the pilot reported that the aircraft was over KT.
- AT 0627 h Bangkok Area Control Centre informed the pilot that HS-THB was in radar contact, 5 miles northwest of KT.
- At 0642 h Bangkok Area Control Centre cleared HS-THB to descend to 8 000 ft and informed the pilot that the altimeter setting was 1 008 mb. This was acknowledged by the pilot.
- At 0644 h, Bangkok Area Control Centre advised the pilot to contact Bangkok Approach Control on 119.1 MHz.
- At 0644 h, the pilot contacted Bangkok Approach Control and reported that he was maintaining 8 000 ft. Bangkok Approach Control advised the pilot to descend to 6 000 ft and informed him that the altimeter setting was 1 008 mb. This was acknowledged by the pilot.
- At 0648 h Bangkok Approach Control advised HS-THB to descend to 6 000 ft.
- At 0651 h Bangkok Approach Control advised HS-THB to descend to 1 500 ft.
- At 0653 h the pilot reported that HS-THB had reached 1 500 ft.
- At 0654 h Bangkok Approach Control informed the pilot that HS-THB was 7 miles from the Outer Marker and cleared the aircraft to make an ILS approach to runway 21R. This was acknowledged by the pilot.
- At 0656 h Bangkok Approach Control advised the pilot to contact Bangkok Tower on 118.1 MHz but no answer from the pilot was received. Bangkok Approach Control tried to contact HS-THB until 0709 h but no answer was received. HS-THB operated in good weather conditions on both the outbound and return flights until, descending to runway 21R nearly at the airport, it encountered an area of rain. Later, HS-THB lost altitude rapidly. Many things in the passenger cabin fell to the cabin floor. It was raining with hail. Looking through the windows, some passengers saw grey clouds. Then the aircraft could maintain altitude. Thirty seconds later it again lost altitude, more severely than the first time. Finally it crashed into a paddy field and skidded forward about 510 feet. Fire occurred in both wings for a while. The accident site was 8 NM northeast of Bangkok International Airport.
- At 0614 h the pilot reported that HS-THB reached FL 120.
- At 0626 h the pilot reported that the aircraft was over KT.
- AT 0627 h Bangkok Area Control Centre informed the pilot that HS-THB was in radar contact, 5 miles northwest of KT.
- At 0642 h Bangkok Area Control Centre cleared HS-THB to descend to 8 000 ft and informed the pilot that the altimeter setting was 1 008 mb. This was acknowledged by the pilot.
- At 0644 h, Bangkok Area Control Centre advised the pilot to contact Bangkok Approach Control on 119.1 MHz.
- At 0644 h, the pilot contacted Bangkok Approach Control and reported that he was maintaining 8 000 ft. Bangkok Approach Control advised the pilot to descend to 6 000 ft and informed him that the altimeter setting was 1 008 mb. This was acknowledged by the pilot.
- At 0648 h Bangkok Approach Control advised HS-THB to descend to 6 000 ft.
- At 0651 h Bangkok Approach Control advised HS-THB to descend to 1 500 ft.
- At 0653 h the pilot reported that HS-THB had reached 1 500 ft.
- At 0654 h Bangkok Approach Control informed the pilot that HS-THB was 7 miles from the Outer Marker and cleared the aircraft to make an ILS approach to runway 21R. This was acknowledged by the pilot.
- At 0656 h Bangkok Approach Control advised the pilot to contact Bangkok Tower on 118.1 MHz but no answer from the pilot was received. Bangkok Approach Control tried to contact HS-THB until 0709 h but no answer was received. HS-THB operated in good weather conditions on both the outbound and return flights until, descending to runway 21R nearly at the airport, it encountered an area of rain. Later, HS-THB lost altitude rapidly. Many things in the passenger cabin fell to the cabin floor. It was raining with hail. Looking through the windows, some passengers saw grey clouds. Then the aircraft could maintain altitude. Thirty seconds later it again lost altitude, more severely than the first time. Finally it crashed into a paddy field and skidded forward about 510 feet. Fire occurred in both wings for a while. The accident site was 8 NM northeast of Bangkok International Airport.
Probable cause:
The pilot directed the aircraft into a thunderstorm in an early dissipating stage. The aircraft was severely affected by a downdraft and lost altitude rapidly. At that time the altitude of the aircraft was only 1500ft and the pilot could not maintain altitude of the aircraft. The aircraft crashed into the ground and ran forward.
Factors which caused the pilot to direct the aircraft into the thunderstorm were:
1. During flight prior to the accident, the pilot did not tune his radio to the ATIS frequency, so he did not receive the special weather report (SPECI) broadcast four minutes before the accident advising that there was a thunderstorm in the area he would soon encounter.
2. The pilot did not make use of airborne weather radar.
3. While the pilot was approaching at high altitude, he could see the thunderstorm, but it was not in his flight path to Bangkok International Airport. When the pilot was descending in compliance with Bangkok Approach Control instruction, he was not aware that the rain area which he was entering was a thunderstorm which was moving and developing severely. The thunderstorm which had developed to the severe stage was moving and intercepted the aircraft.
4. The pilot assumed that flying by radar vector would be safe as he thought that the Approach Control Radar could detect the thunderstorm and Bangkok Approach Control would not vector the aircraft into the thunderstorm.
Factors which caused the pilot to direct the aircraft into the thunderstorm were:
1. During flight prior to the accident, the pilot did not tune his radio to the ATIS frequency, so he did not receive the special weather report (SPECI) broadcast four minutes before the accident advising that there was a thunderstorm in the area he would soon encounter.
2. The pilot did not make use of airborne weather radar.
3. While the pilot was approaching at high altitude, he could see the thunderstorm, but it was not in his flight path to Bangkok International Airport. When the pilot was descending in compliance with Bangkok Approach Control instruction, he was not aware that the rain area which he was entering was a thunderstorm which was moving and developing severely. The thunderstorm which had developed to the severe stage was moving and intercepted the aircraft.
4. The pilot assumed that flying by radar vector would be safe as he thought that the Approach Control Radar could detect the thunderstorm and Bangkok Approach Control would not vector the aircraft into the thunderstorm.
Final Report:

Crash of a Douglas DC-8-33 in Kathmandu: 1 killed
Date & Time:
May 10, 1973
Registration:
HS-TGU
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Bangkok - Kathmandu
MSN:
45526/89
YOM:
1960
Crew on board:
10
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
100
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Circumstances:
After touchdown at Kathmandu-Tribhuvan Airport, the four engine airplane was unable to stop within the remaining distance. It overran, lost its undercarriage and one engine before coming to rest in a dump. Onee people on the ground was killed and four passengers were injured. The aircraft was written off.
Probable cause:
Wrong approach configuration on part of the pilot-in-command who landed too far down the runway, causing the braking distance to be insufficient.