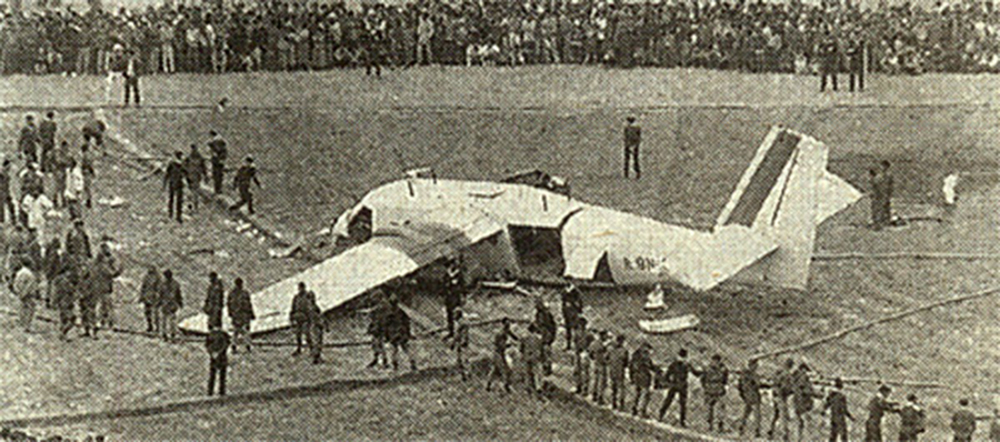
Crash of an Antonov AN-24B in Arkhangelsk
Date & Time:
Feb 6, 1995 at 1852 LT
Registration:
RA-46564
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Naryan-Mar - Arkhangelsk
MSN:
87304703
YOM:
1968
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
34
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
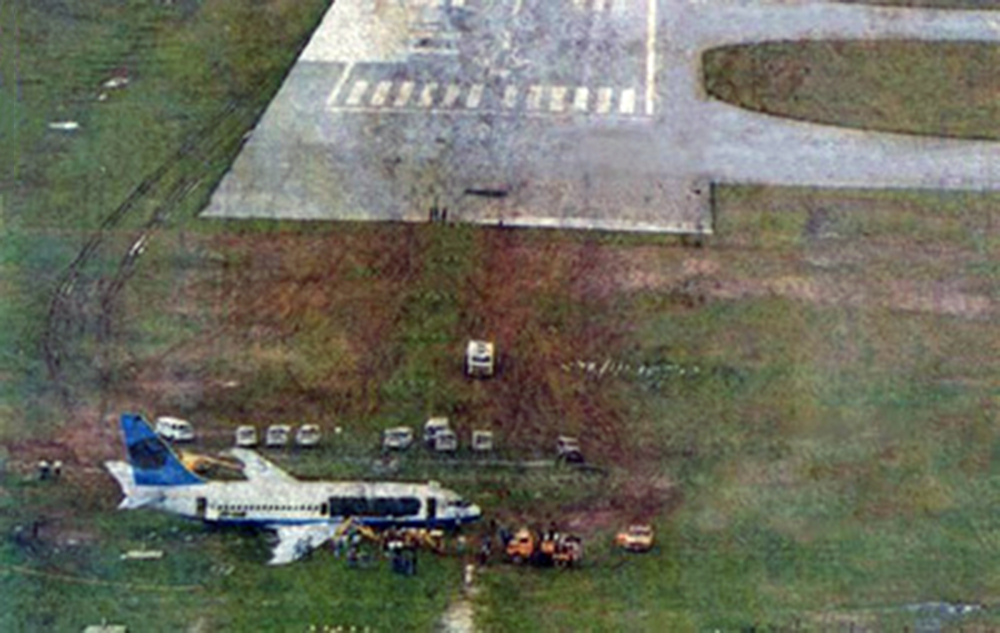
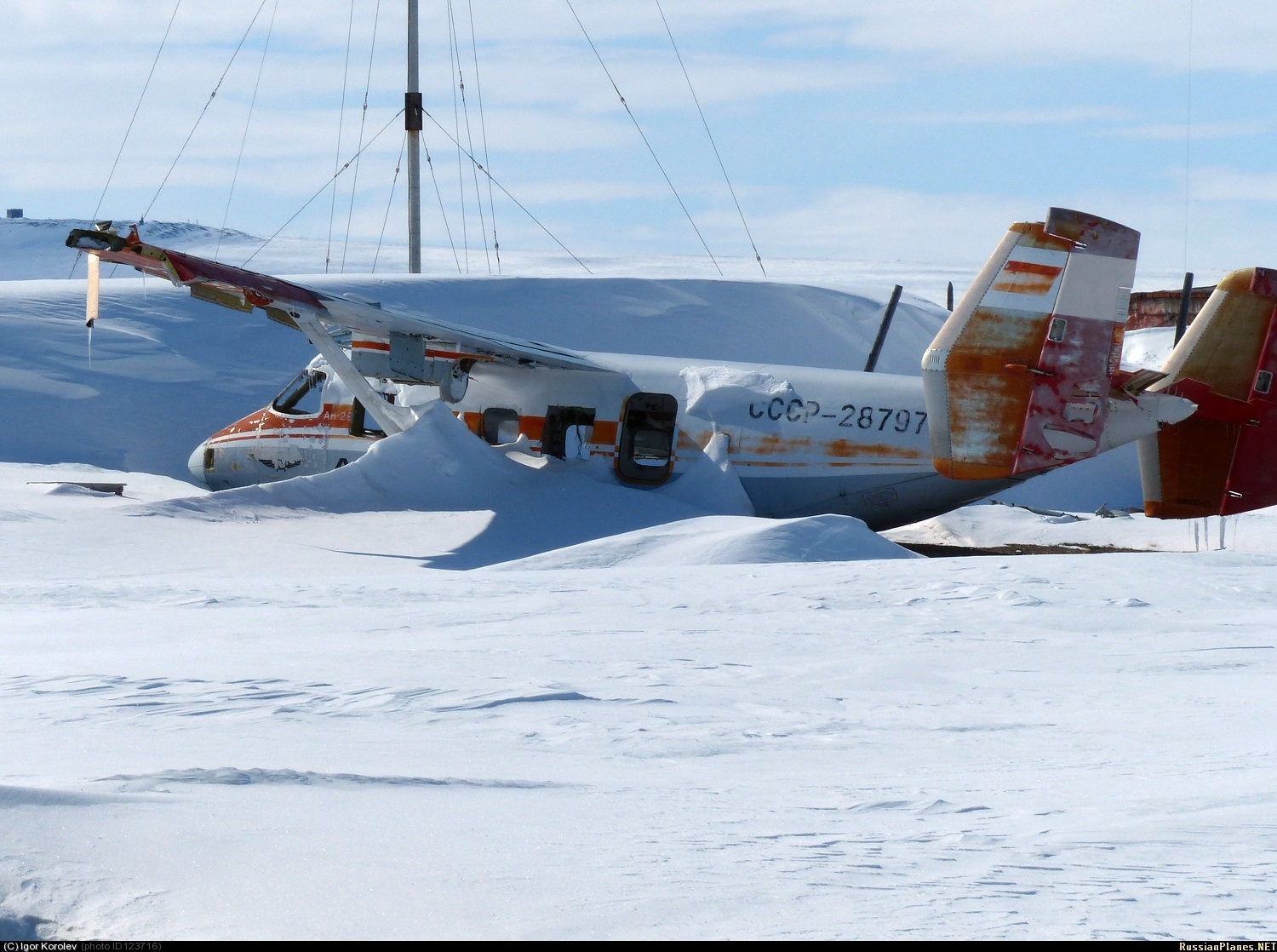
Circumstances:
On final approach to Arkhangelsk-Vaskovo Airport, the crew encountered marginal weather conditions with snow showers. The captain lost visual contact with the runway but continued the approach when he realized, too late, that the aircraft was misaligned with the runway. This caused the aircraft to land to the right of the runway and to collide with a snow bank. All 38 occupants evacuated safely while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.