Circumstances:
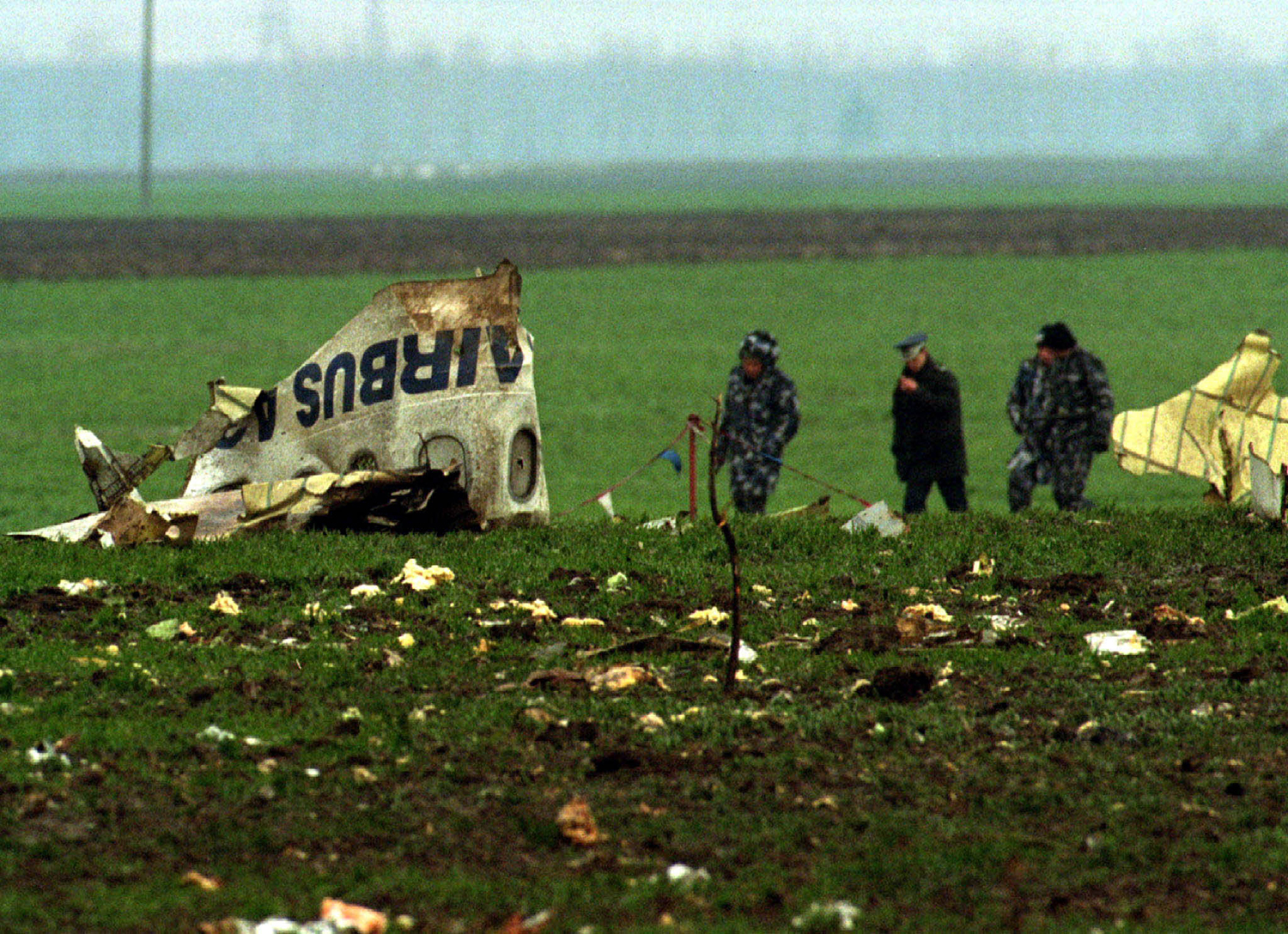
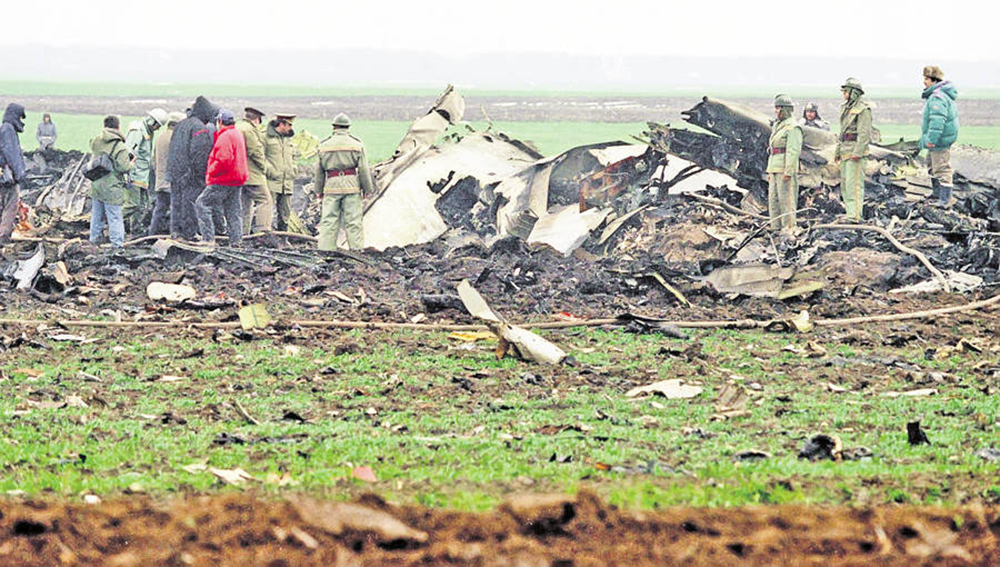
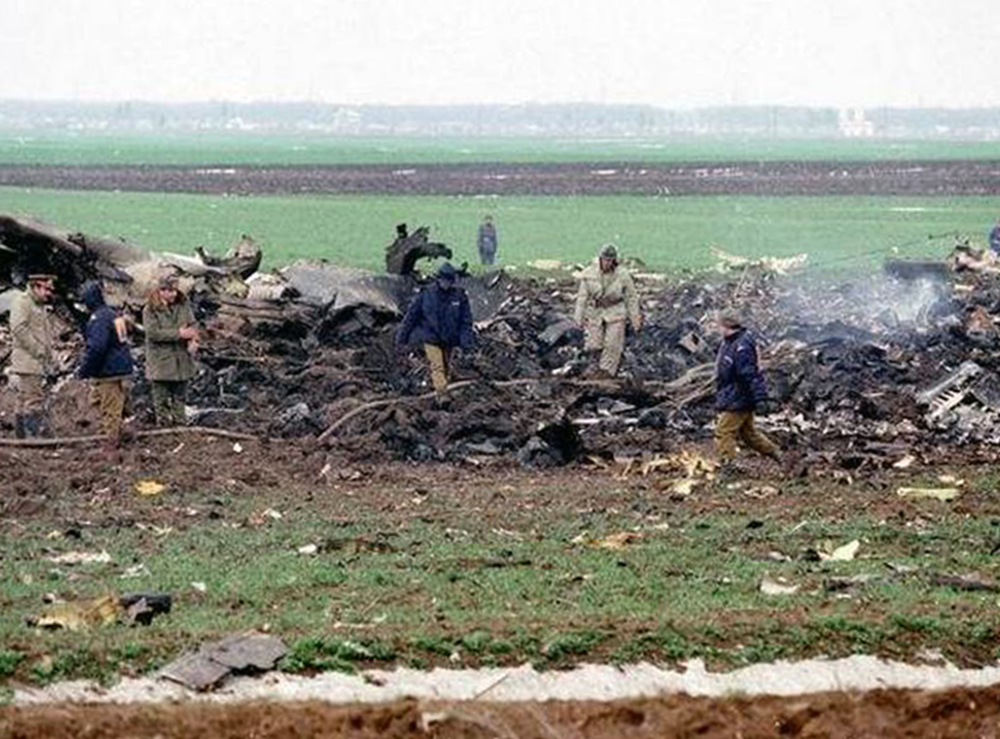
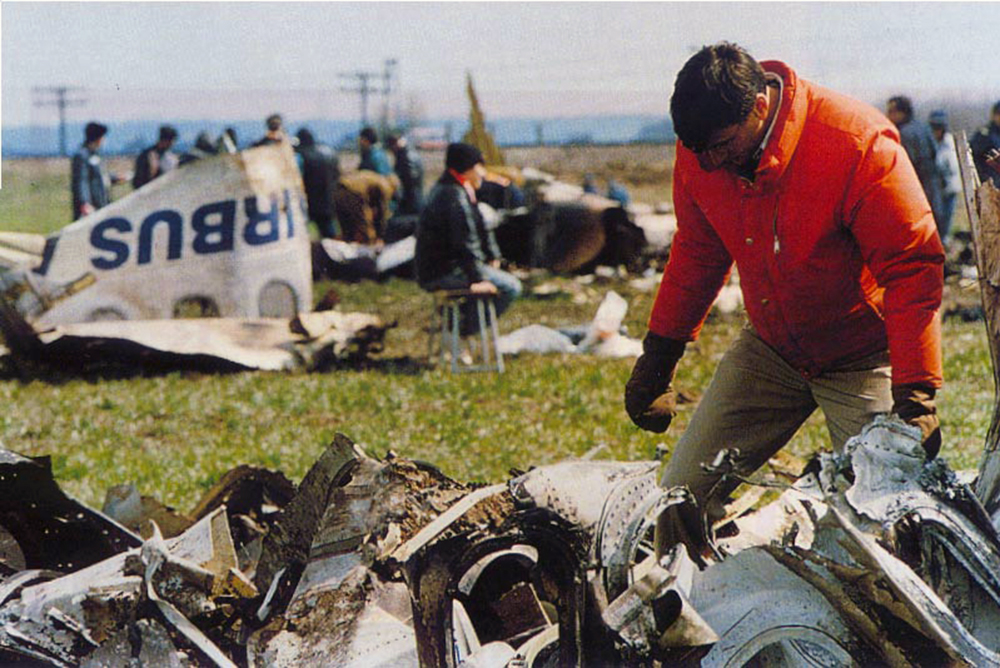
Tarom flight 371 was a scheduled passenger service from Bucharest Otopeni Airport (OTP) in Romania to Brussel Airport (BRU), Belgium. On board were 49 passengers and eleven crew members. The first officer was pilot flying, the captain was pilot monitoring. Following de-icing, the Airbus A310 taxied to runway 08R for departure. The flight was cleared via the Strejnic 'STJ' VOR/DME beacon and an initial climb to flight level 260. Takeoff was initiated at 09:04 hours local time. When airborne, the captain announced positive climb and co-pilot requested to retract the landing gear. At 09:07:20 the captain called the Otopeni Approach controller and received a clearance to turn left and proceed direct to STJ. The co-pilot asked the captain to select direct STJ on FMS. The captain confirmed a direct STJ selection and requested the co-pilot to move the control wheel slightly. At an altitude of 1700 feet and speed a 187 knots, with flaps 15/slats 15 and pitch angle of 17.6 degrees, the aircraft was turning left, with a bank angle of 12 degrees, flying towards STJ. At 09:07:36, when the aircraft crossed 2000 feet at 188 knots, an engine thrust asymmetry started developing with continuous decrease of the left engine thrust, approximately 1 degree TRA (throttle resolver angle)/second. At 09:07:53, when the aircraft was crossing 3300 feet altitude at 195 kts turning with a decreasing bank angle of 20 degrees, the first officer called "250 in sight" and asked the captain to retract the flaps. This was carried out. At that moment, the engine thrust asymmetry reached 14.5 TRA degrees and 0.19 for EPRs. The first officer then requested slats retraction, but this action which was not carried out by the captain. At this moment the aircraft was passing through 013 degrees magnetic heading, at 3800 feet altitude and a decreasing speed of 185 kts. The aircraft pitch angle was 16,5 degrees, decreasing, and the left bank angle was 18 degrees, also decreasing. At that time the thrust asymmetry reached was 28 TRA degrees and 0.27 for EPRs. At 09:08:02, the first officer asked the captain: "Are you all right?" The aircraft was passing through 330 degrees magnetic heading, 4200 ft altitude, a decreasing speed of 181 kts, and an increasing 17 degrees left bank angle. At 09:08:08, a noise like an uttering of pain or a metallic noise was heard. The aircraft was crossing 4460 ft altitude, 179 kts speed and an increasing bank angle of 22 degrees. At that time the engines thrust asymmetry reached 0.36 for EPRs. The bank angle continued to increase to 28 degrees and the engine thrust asymmetry reached 0.41 for EPRs. At 09:08:15, the first officer, with a stressed and agitated voice, requested engagement of autopilot no. 1. The aircraft was crossing 4620-ft altitude, continuing its turn at an increasing bank angle of 43 degrees and a steadily decreasing pitch angle of 3.5 degrees. One of the pilots attempted to engage autopilot no. 1 The aircraft started a descent with 45 degrees bank angle and the engine thrust asymmetry had reached the maximum value of 0.42 for EPRs, followed by a continuous thrust reduction of engine n°2. One second later, there was recorded autopilot disengagement followed by the aural warning a level 3 "cavalry charge" lasting several moments. From that moment on, the aircraft started diving, the speed increased and the aircraft performed a complete rotation around its roll axis. At 09:08.28, first officer cried out "THAT ONE HAS FAILED!" without any other comments. The aircraft was descending through 3600 ft at 258 kts speed and an increasing nose down pitch angle at 61.5 degrees. The aircraft continued until it impacted the ground at a nose down attitude of approximately 50 degrees pitch angle with both engines at idle power. The airplane was destroyed and all 60 occupants were sustained fatal injuries.
Probable cause:
The following factors were reported:
- Thrust asymmetry,
- Possible incapacitation of the captain,
- Insufficient corrective action from the copilot in order to cover the consequences of the first factors.
The French Ministry of Transport commented on the Romanian investigation report, stating that the pilot flying's actions that led to the loss of control could have been caused by the fact that the artificial horizon between Eastern and Western built aircraft is inverted in roll and that the first officer spent the majority of his career on Eastern-built aircraft.