Date & Time:
Nov 20, 2014 at 0721 LT
Operator:

Schedule:
Yellowknife – Fort Simpson
Crew fatalities:
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Captain / Total flying hours:
3500
Captain / Total hours on type:
1800.00
Aircraft flight hours:
25637
Circumstances:
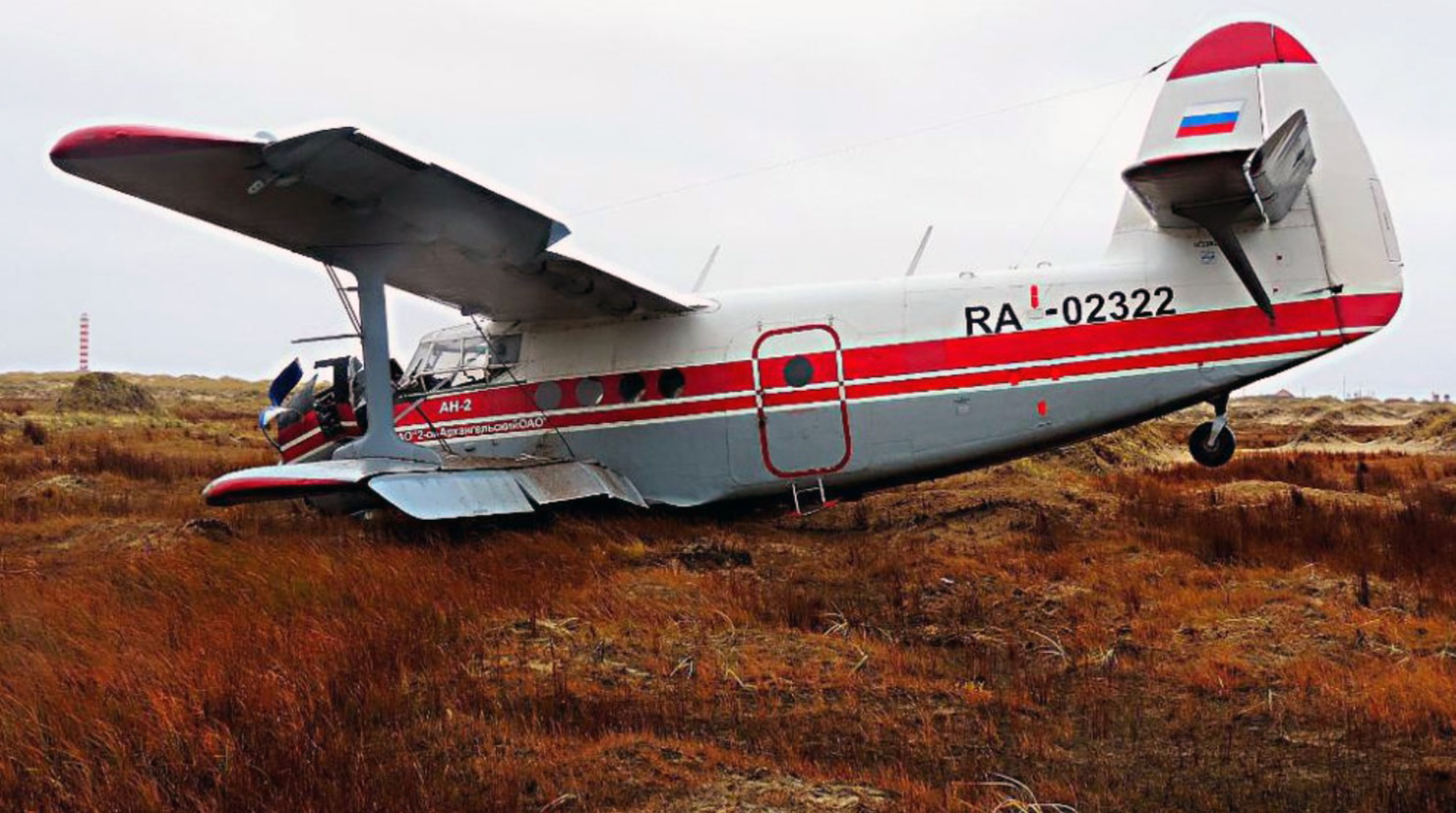
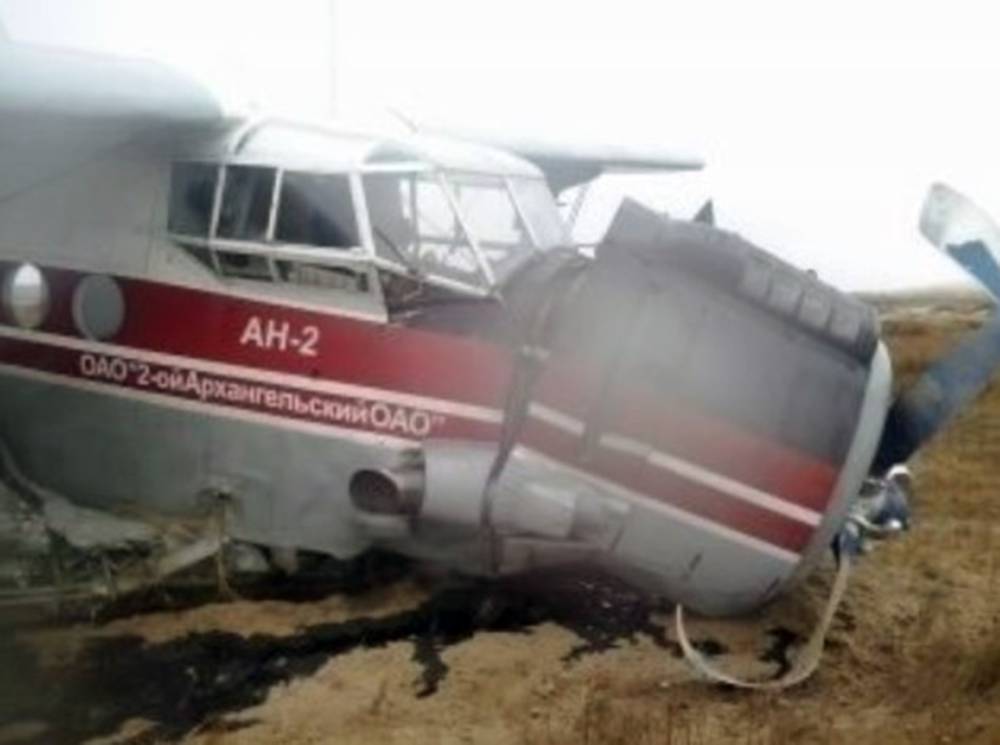
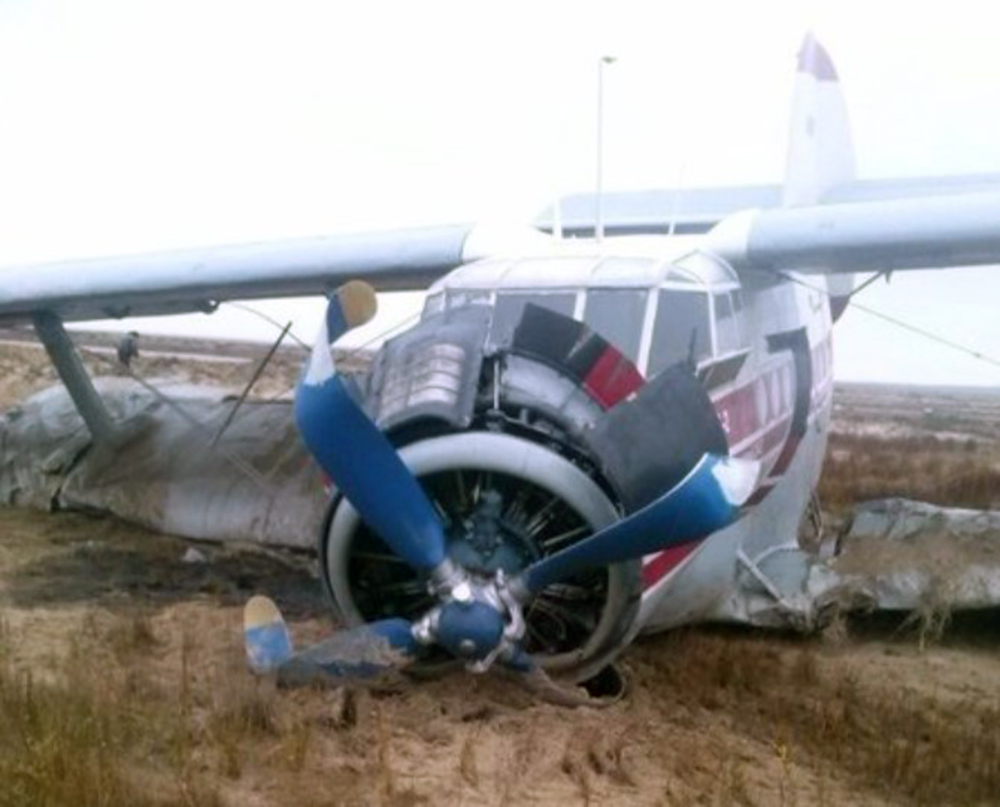
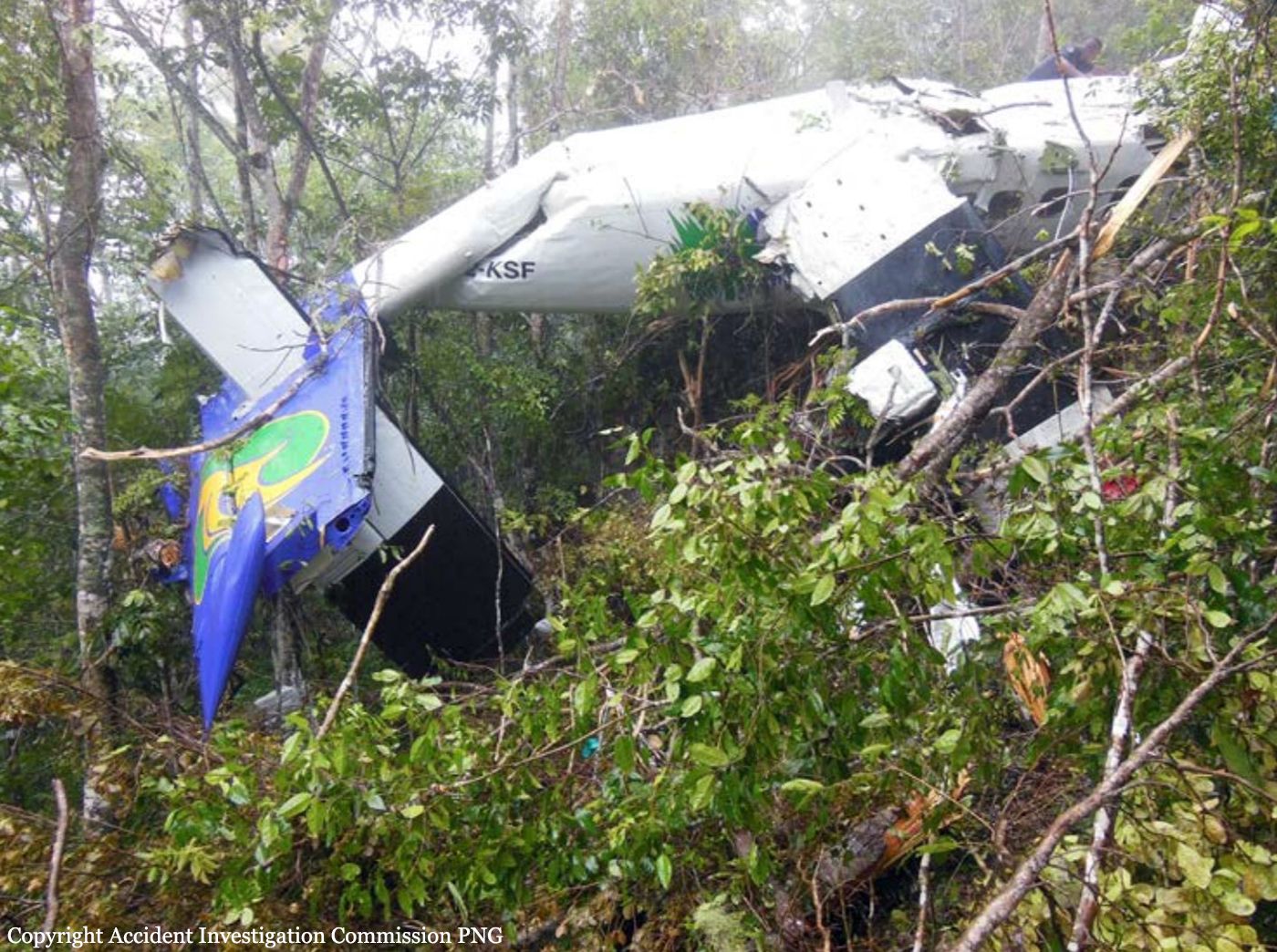
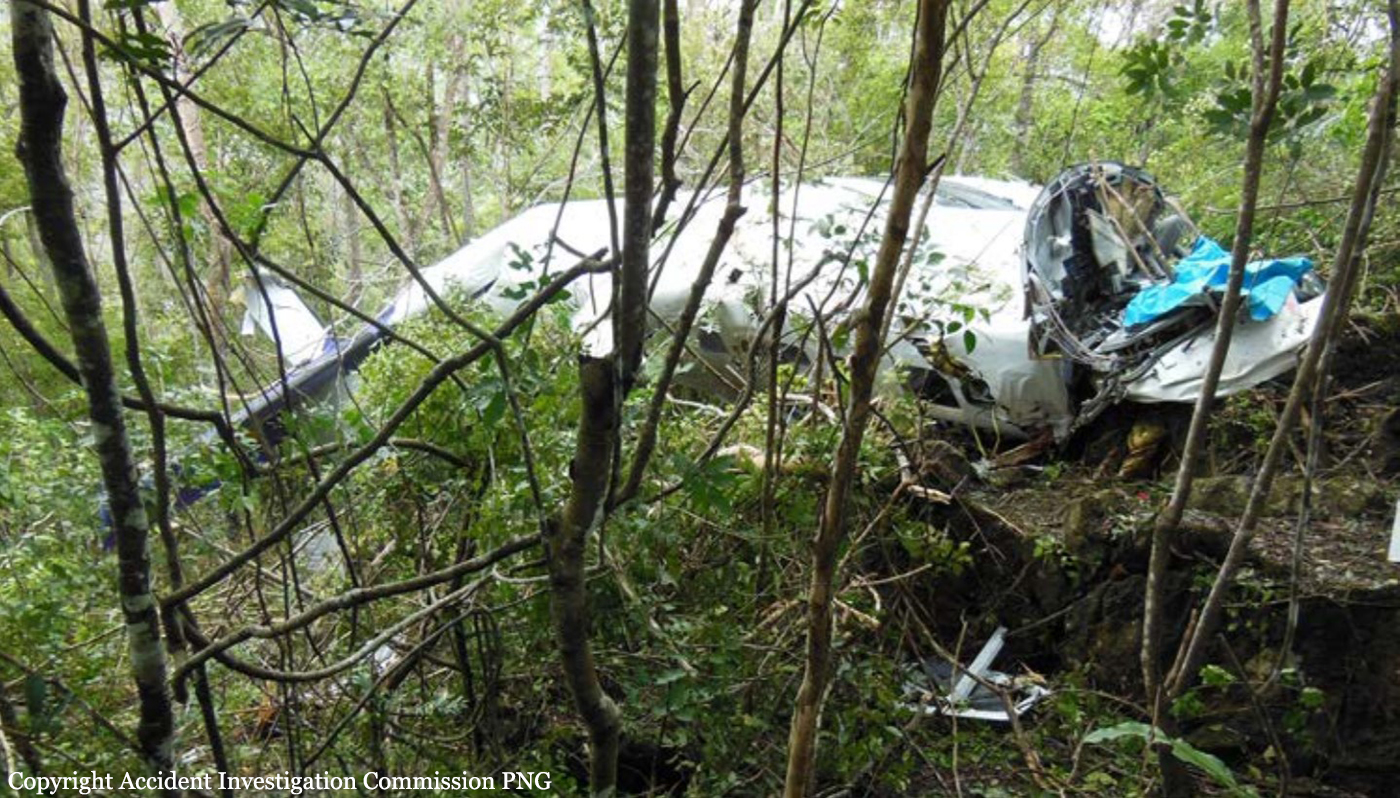
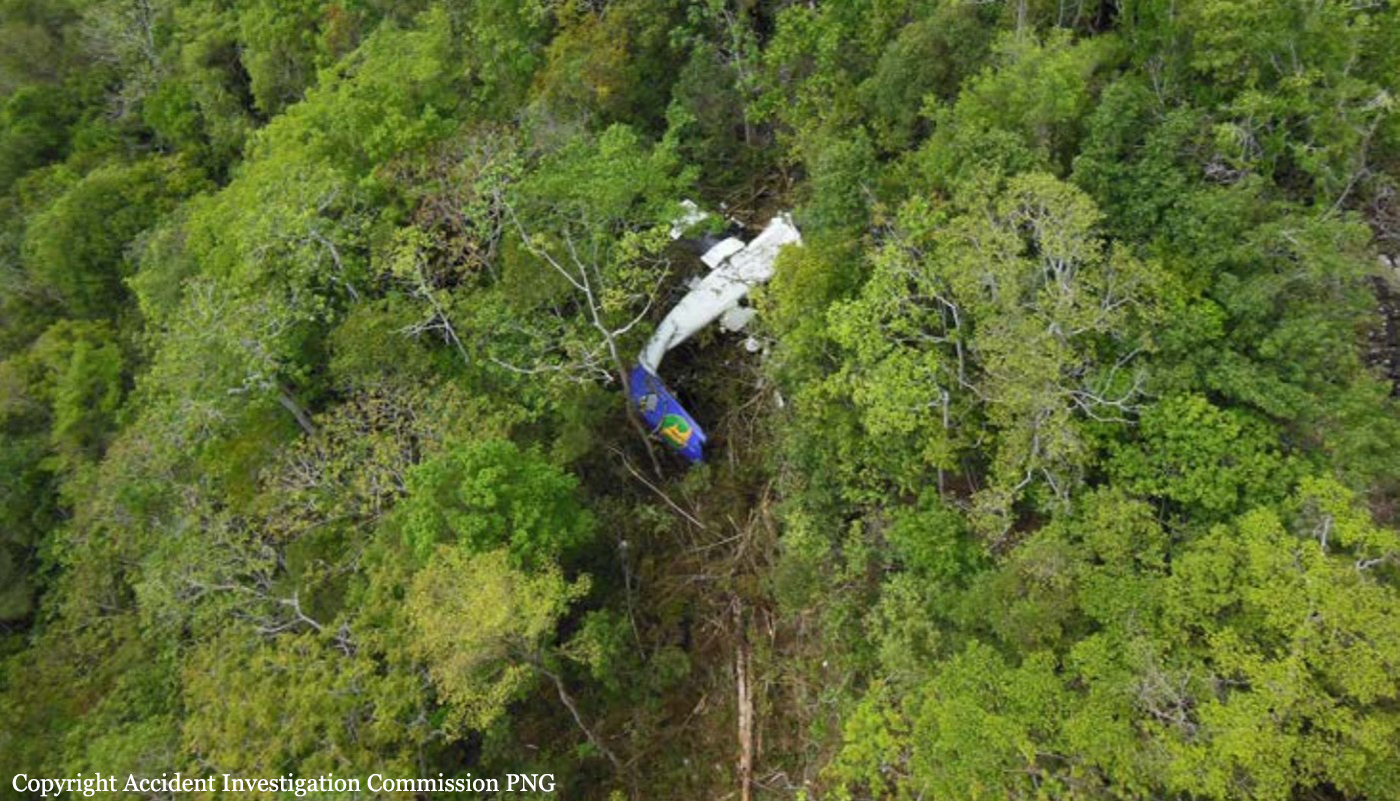
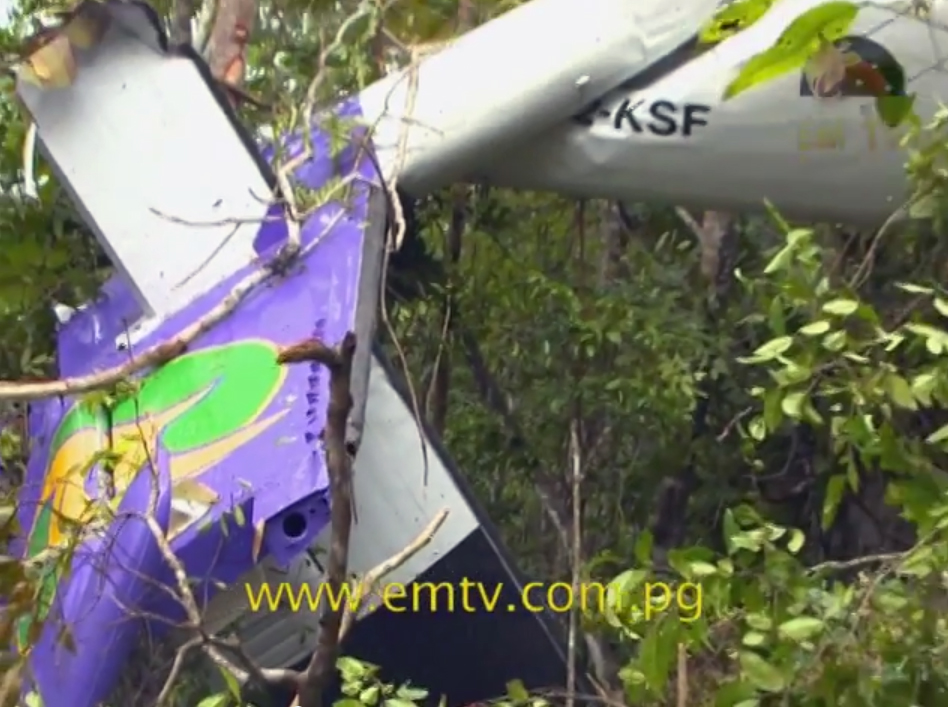
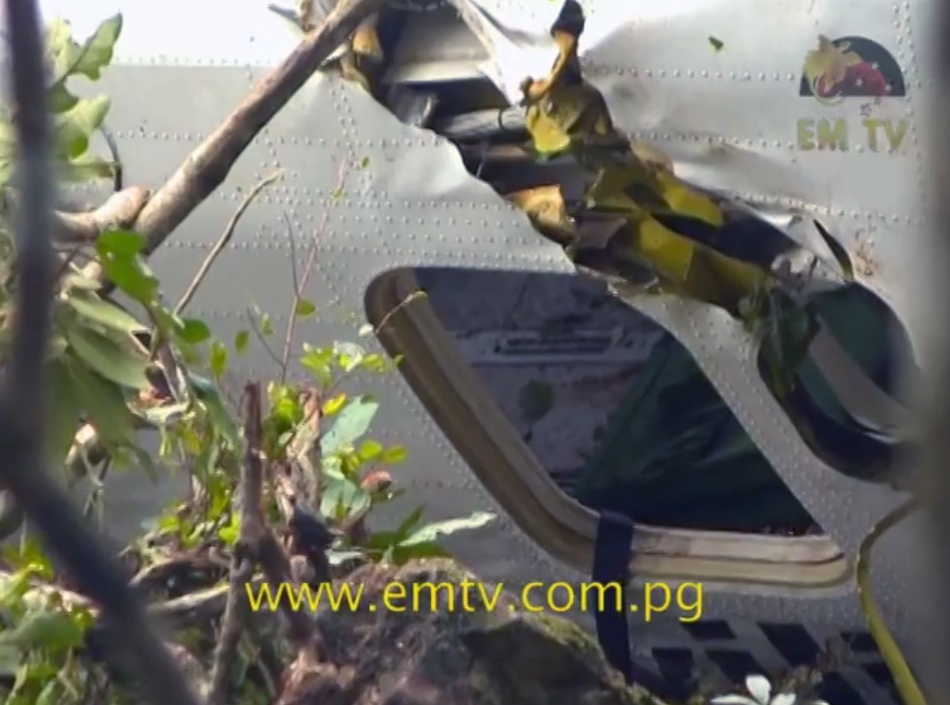
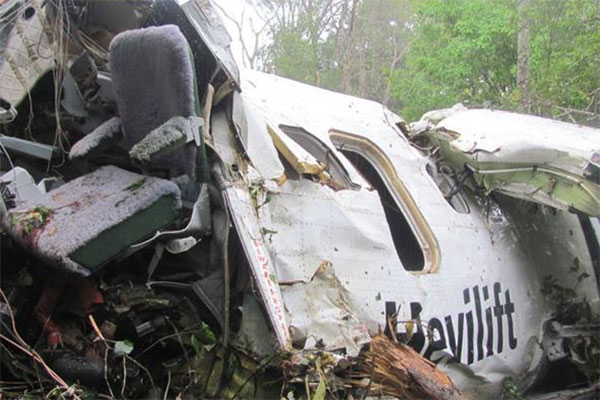
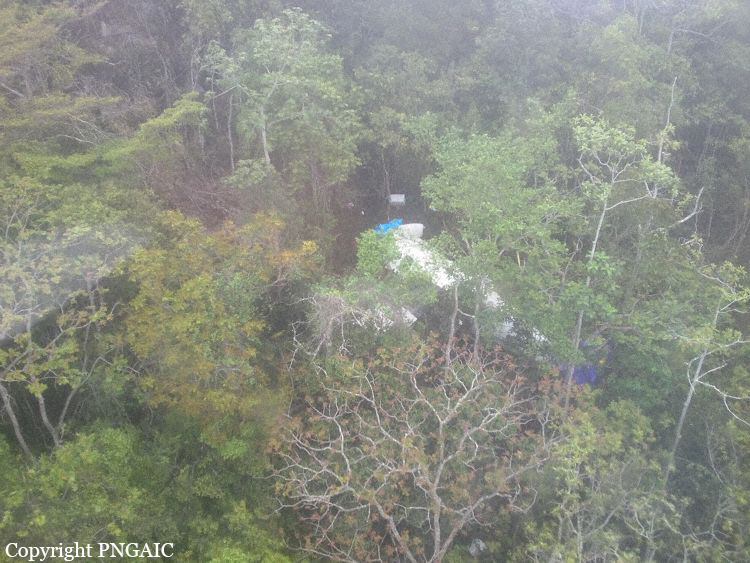
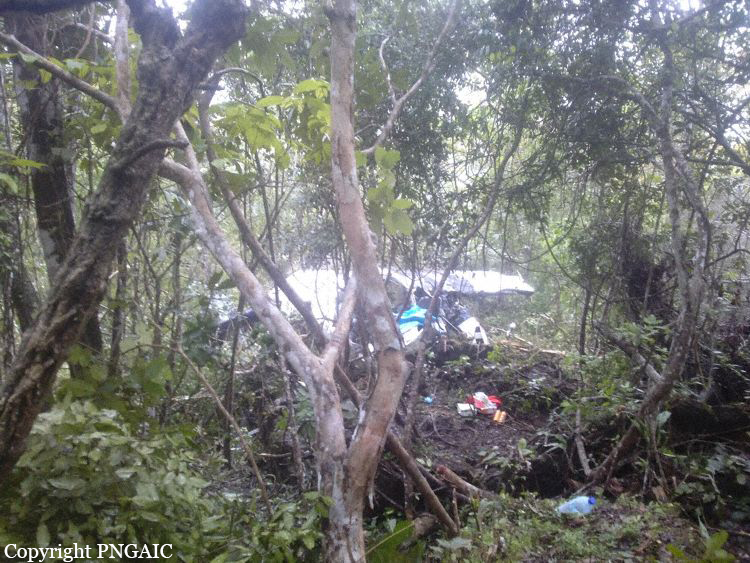
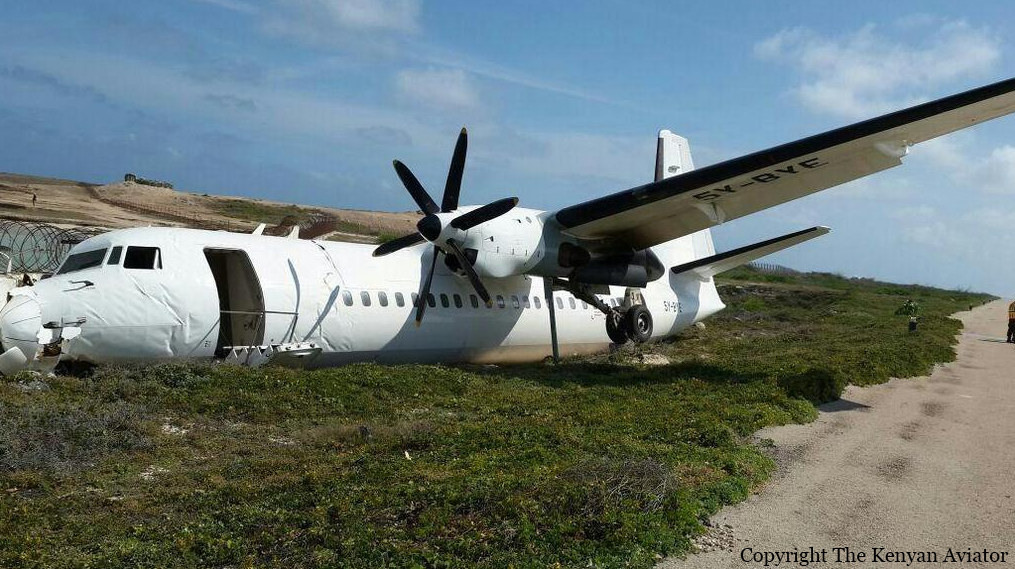
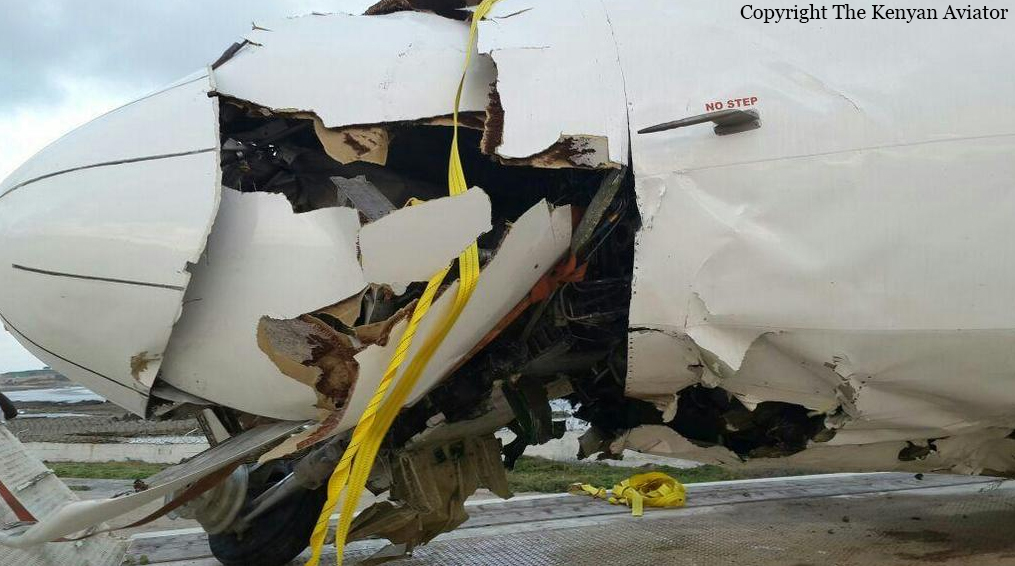
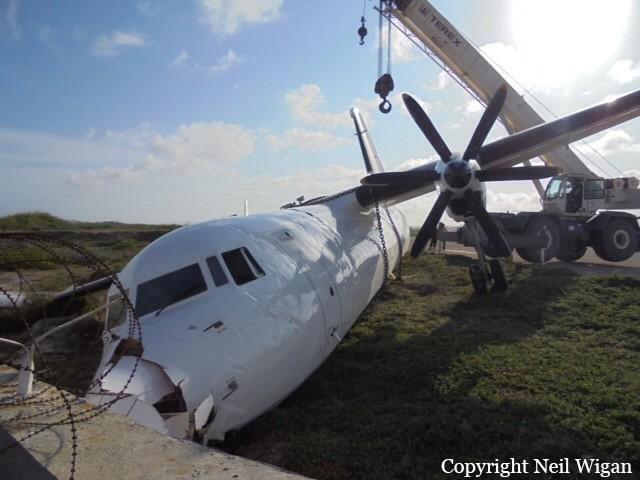
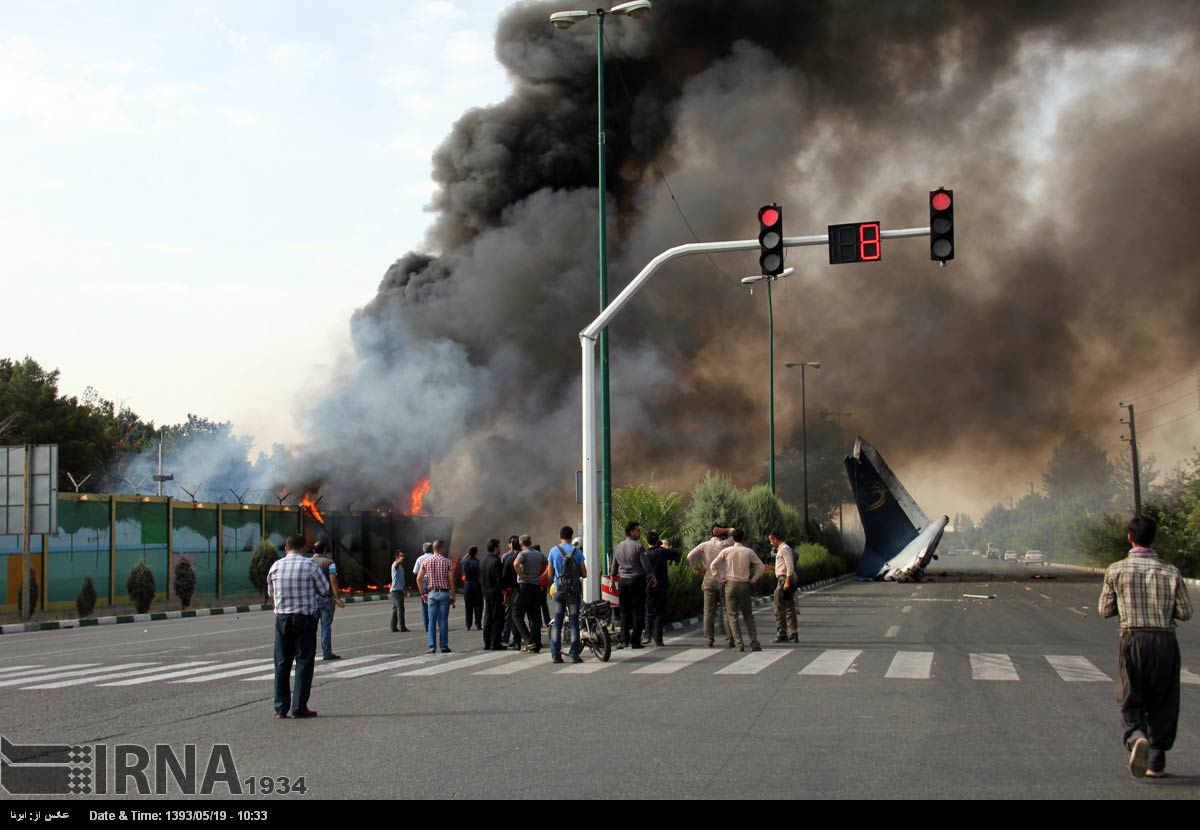
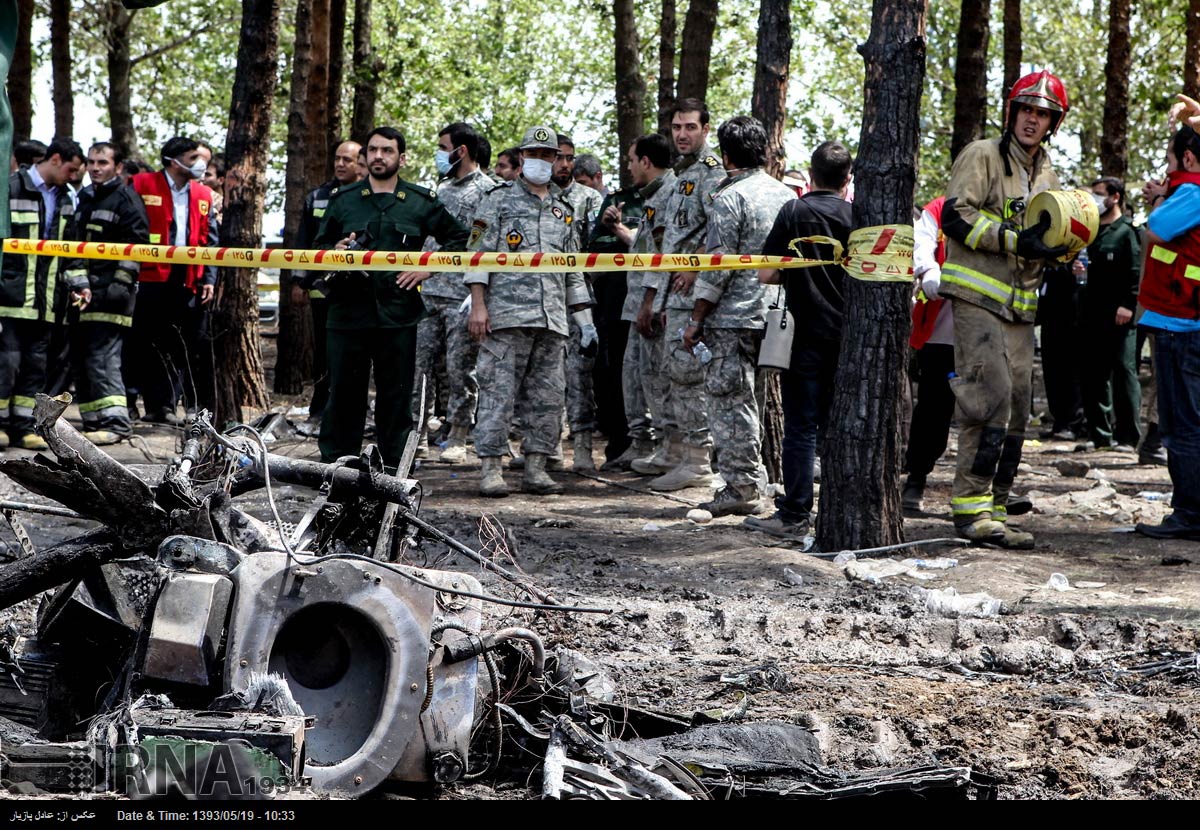
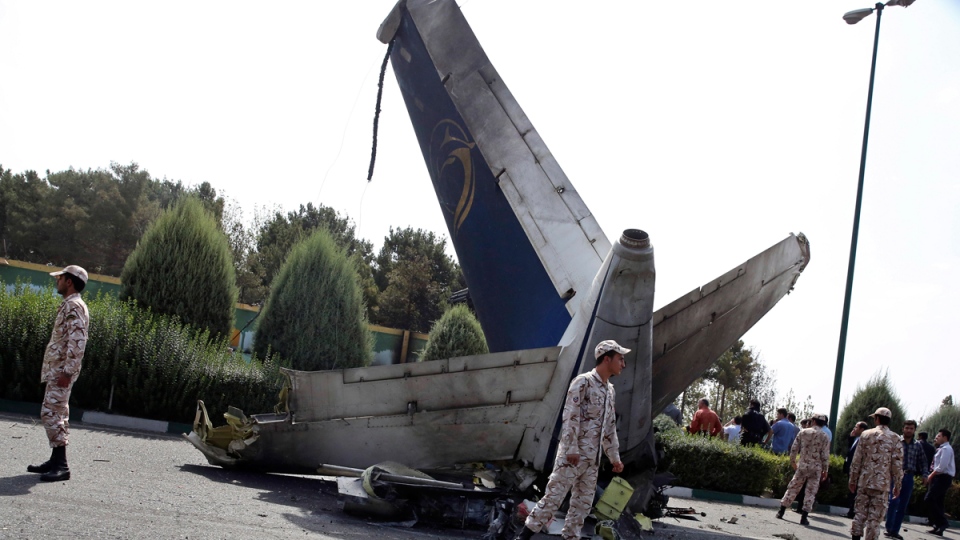
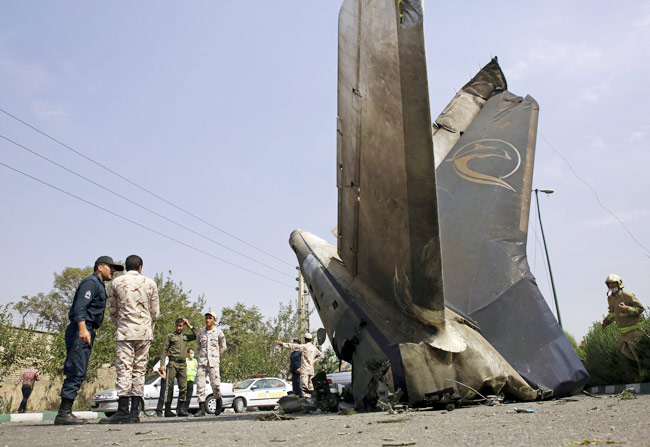
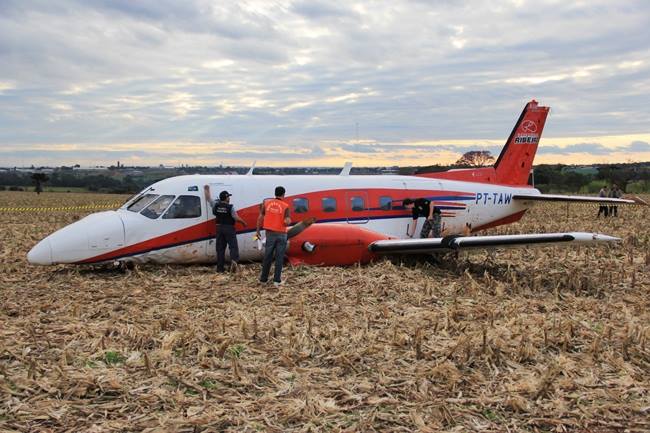
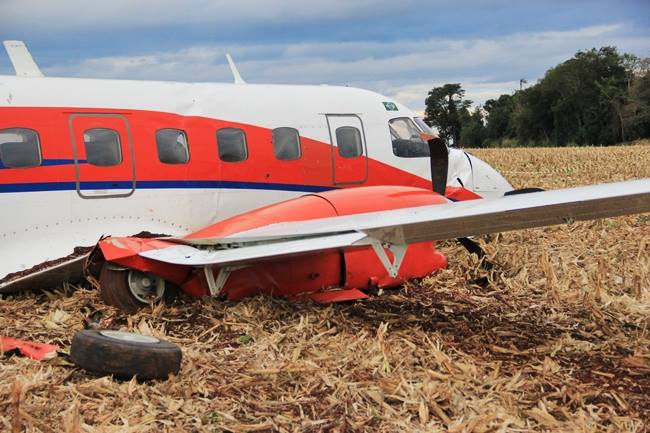
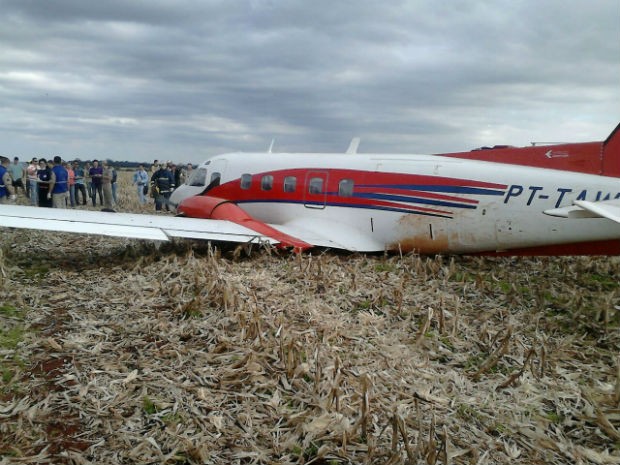
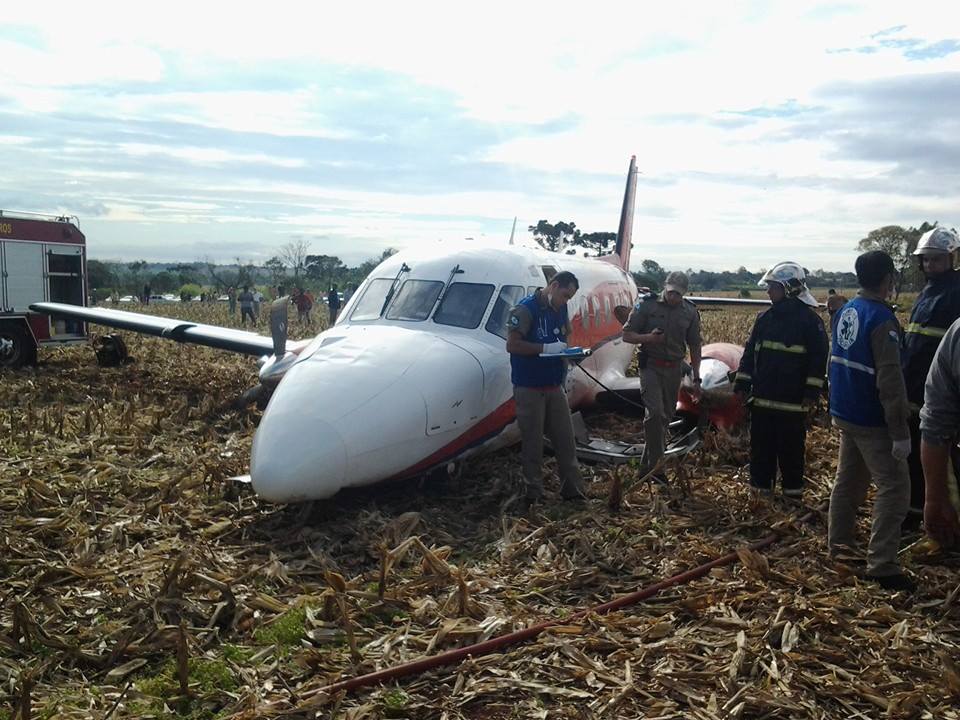
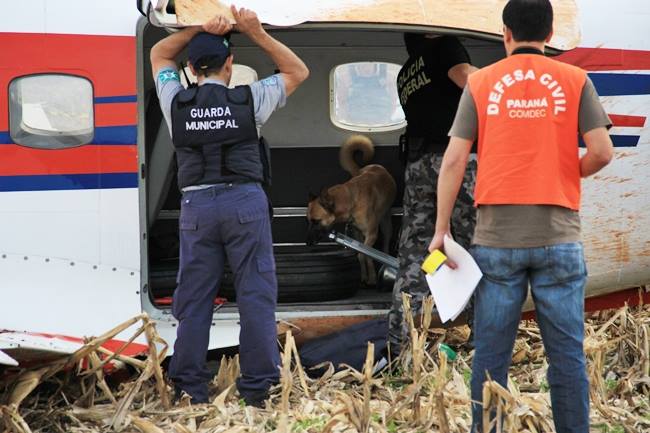
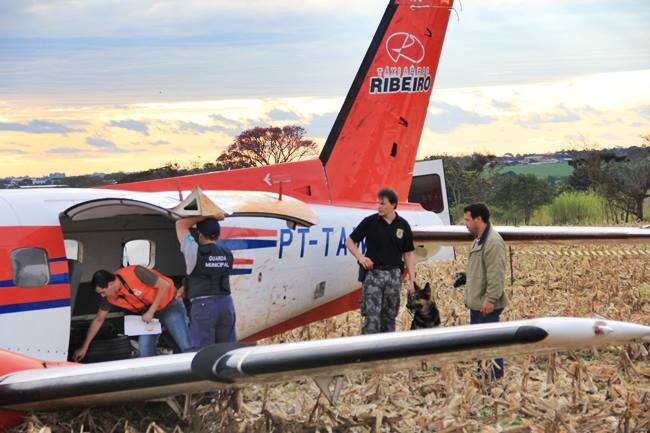
The Air Tindi Ltd. Cessna 208B Caravan departed Yellowknife Airport, Northwest Territories, on 20 November 2014 at 0642 Mountain Standard Time under instrument flight rules as Discovery Air flight DA223 to Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The flight had been rescheduled from the previous night because of freezing drizzle at Fort Simpson. During the climb to 8000 feet above sea level, DA223 encountered icing conditions that necessitated a return to Yellowknife. On the return to Yellowknife, DA223 was unable to maintain altitude. At 0721, flying in darkness approximately 18 nautical miles west of Yellowknife, it contacted the frozen surface of the North Arm of Great Slave Lake. The aircraft sustained substantial damage when it struck a rock outcropping, but there were no injuries to the pilot or to the 5 passengers. The pilot established communication with Air Tindi via satellite phone, and the pilot and passengers were recovered approximately 4 hours after the landing. The emergency locator transmitter did not activate during the landing, but was activated manually by the pilot.
Probable cause:
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
1. Not using all enroute information led the pilot to underestimate the severity and duration of the icing conditions that would be encountered.
2. Inadequate awareness of aircraft limitations in icing conditions and incomplete weight-and-balance calculations led to the aircraft being dispatched in an overweight state for the forecast icing conditions. The aircraft centre of gravity was not within limits, and this led to a condition that increased stall speed and reduced aircraft climb performance.
3. The pilot’s expectation that the flight was being undertaken at altitudes where it should have been possible to avoid icing or to move quickly to an altitude without icing conditions led to his decision to continue operation of the aircraft in icing conditions that exceeded the aircraft’s performance capabilities.
4. The severity of the icing conditions encountered and the duration of the exposure resulted in reductions in aerodynamic performance, making it impossible to prevent descent of the aircraft.
5. The inability to arrest descent of the aircraft resulted in the forced landing on the surface of Great Slave Lake and the collision with terrain.
6. The Type C pilot self-dispatch system employed by Air Tindi did not have quality assurance oversight or adequate support systems. This contributed to the aircraft being dispatched in conditions not suitable for safe flight.
Findings as to risk:
1. If passenger briefings on cabin door operations are ineffective, there is a risk of passenger egress in an accident being compromised, affecting survivability.
2. If survival equipment is stowed in a location that may be inaccessible following an accident, such as the belly pod, there is a risk of survival being compromised if search and rescue is delayed.
Other findings:
1. The aircraft was under control and in a level attitude when it contacted the ice. This minimized structural damage and increased survivability for the aircraft’s occupants.
2. The survival skills of the crew and passengers were indispensable in a situation in which access to the survival equipment on the aircraft was limited.
Final Report: