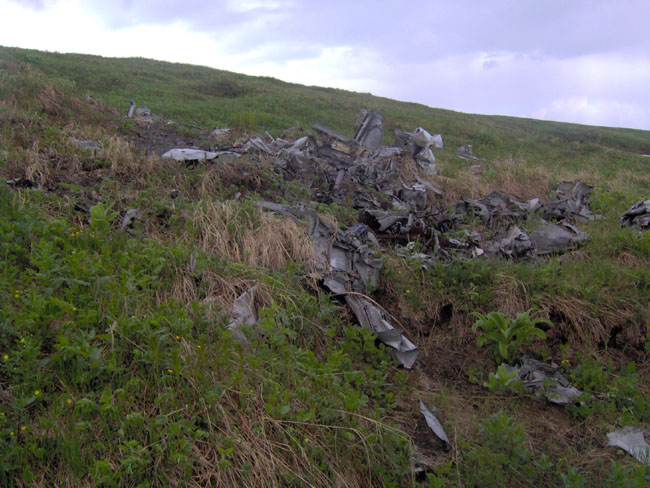
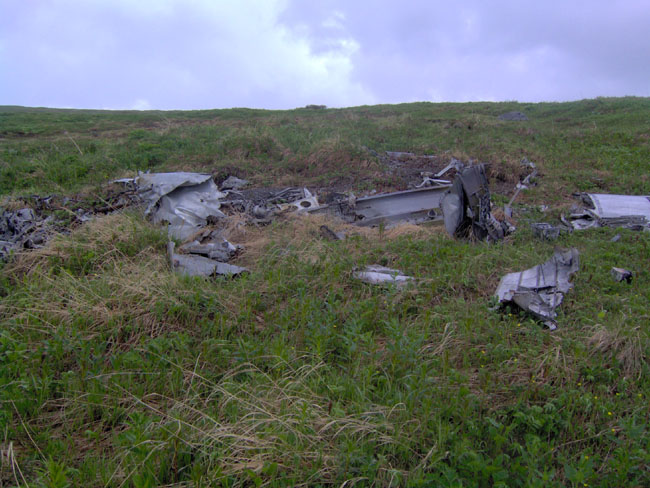
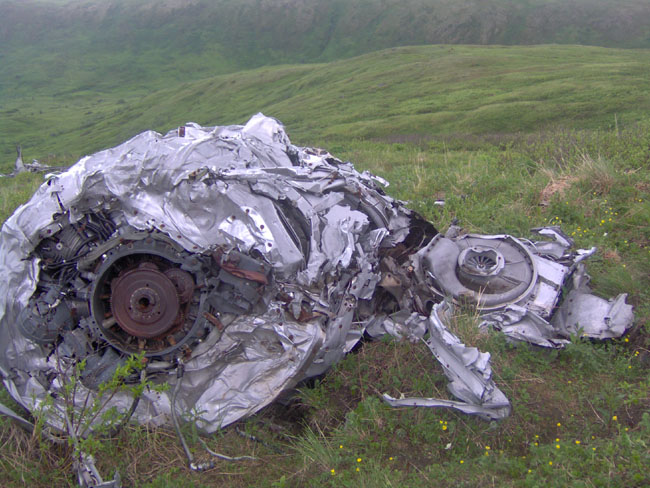
Circumstances:
Flight 327 was scheduled between Providence, Rhode Island, and Tulsa, Oklahoma, with intermediate stops including Chicago, Illinois; and St. Louis, Springfield, and Joplin, Missouri. The flight to Chicago was routine; however, the crew, when securing the cockpit, observed that the fire-warning light for the forward cargo and electrical accessory compartments flickered. This was called to the attention of both the ground crew and the relieving crew (a routine crew change was made) and was written in the aircraft log. Because of necessary repairs to the fire-warning system the flight was delayed 1 hour, 40 minutes and it departed Chicago at 1950. The new crew consisted of Captain Wesley G. Mims, First Officer Paul H. Johnson, and Stewardess Shirley D. Walker. Flight 327 was routine to Joplin and it departed there at 2323 with seven passengers aboard. Leaving Joplin the aircraft weighed 35,940 pounds, which was well under the allowable gross takeoff weight; the load was properly distributed. The flight was cleared by ARTC (Air Route Traffic Control) to the Owasso “H” facility, 2 via airway V-88, to maintain 4,000 feet, and to contact Tulsa approach control on crossing the south course of Chanute low frequency range for further clearance. At approximately 2333, 10 minutes after takeoff from Joplin, ARTC, through the company radio, advised the flight to climb to 4,500 feet, to maintain 4,500 feet, and to report leaving 4,000. This transmission was acknowledged and flight 327 reported leaving 4,000 feet at 2334. Approximately 10 minutes later company radio at Tulsa gave the flight the Tulsa 2328 weather sequence. The company then gave the flight the local altimeter setting as 30.15 and field pressure as 460 feet above zero. This was acknowledged and flight 327 reported it was changing over to Tulsa approach control frequency. At 2347 the flight reported crossing the south leg of Chanute low frequency range and was immediately cleared by approach control direct to Owasso, to descend to and maintain 3,500 feet, and to report when over Owasso. The 2328 Tulsa weather was given the flight as: Measured ceiling 600 feet, overcast; visibility 2-1/2 miles; very light drizzle and fog; wind calm. Liter, the flight reported it was 1-1/2 minutes from Owasso and asked if any delay was expected. Approach control advised no delay was expected since the only local traffic was then making an ILS (Instrument Landing System) approach. Shortly thereafter approach control advised flight 327 that the visibility was then 1-3/4 miles, that the U.S. Weather Bureau was checking the ceiling, and asked if an Owasso approach straight in to runway 17 was to be mad or if an ILS approach was preferred. The flight advised it would make the Owasso approach and at 2357 was cleared accordingly. It was asked to report when over the Owasso facility inbound. At 2400 flight 327 reported over Owasso, inbound, and was cleared to land on runway 17L. Two minutes later a special 2355 weather observation was transmitted to the flight as: Measured 200, overcast; visibility 1-3/4; very light drizzle and fog. This transmission was not acknowledged and nothing further was heard from the flight. Repeated efforts by approach control and other facilities to contact the flight were unsuccessful.
Probable cause:
The Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was the captain's lack of alertness in allowing the first officer to continue an instrument descent to an altitude too low to permit terrain clearance. The following findings were reported:
- This flight was the first time the captain and first officer had flown together,
- The first officer flew the aircraft from Joplin and during the instrument approach,
- The aircraft and its components, including altimeters, functioned in a normal manner throughout the flight and approach,
- The last weather report received by the flight indicated weather conditions were rapidly deteriorating,
- The captain told the first officer he could descend to 700 feet, without specifying mean sea level or above the elevation of the airport,
- The captain allowed the aircraft to be flown below the company’s approved landing minimums for this type approach and to an altitude precluding terrain clearance.