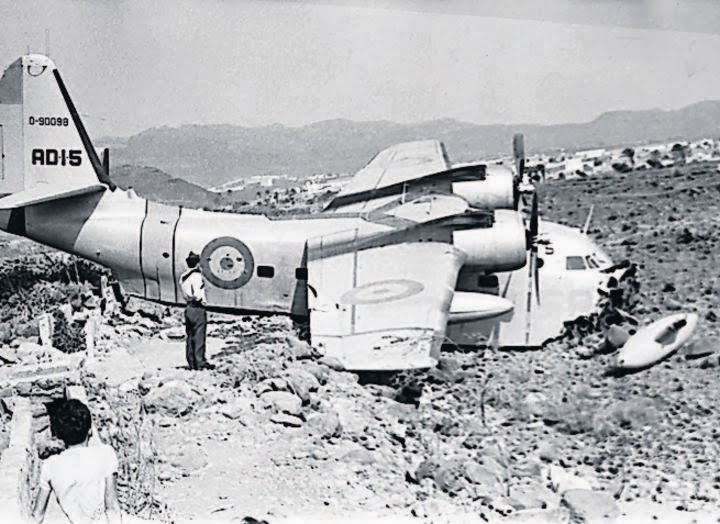
Crash of a Canadair CL-215-1A10 near Pontevedra: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Sep 8, 1976 at 1800 LT
Registration:
UD.13-7
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Santiago de Compostela - Santiago de Compostela
MSN:
1035
YOM:
1974
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Circumstances:
The crew departed Santiago de Compostela on a fire fighting mission in the region of Pontevedra. In unknown circumstances, the airplane crashed on the slope of Mt Xiabre and was destroyed. All three crew members were killed.