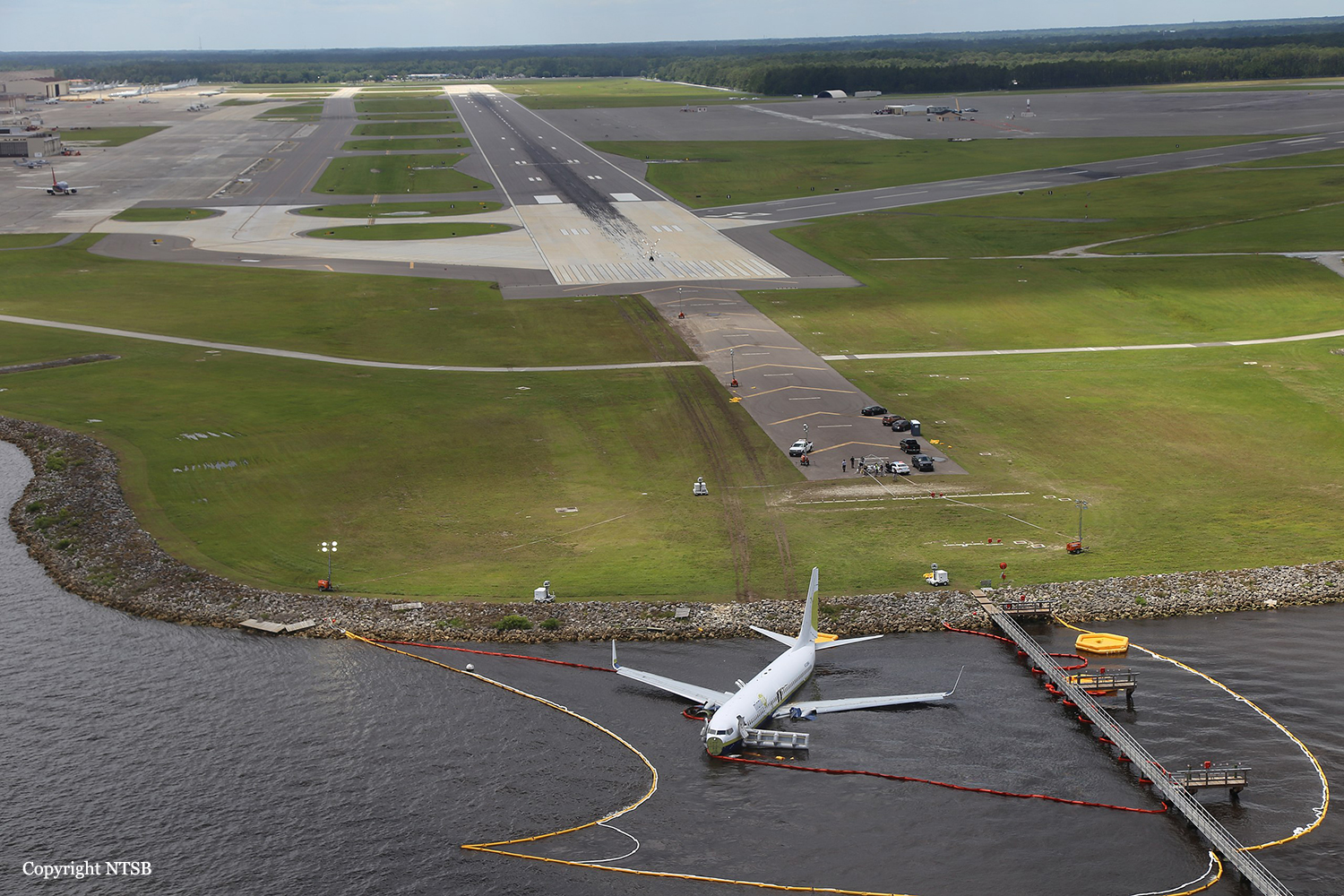Crash of a Boeing 737-81Q at Jacksonville NAS
Date & Time:
May 3, 2019 at 2142 LT
Registration:
N732MA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Guantánamo Bay - Jacksonville
MSN:
30618/830
YOM:
2001
Flight number:
LL293
Crew on board:
7
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
136
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2204.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
18
Aircraft flight hours:
38928
Aircraft flight cycles:
15610
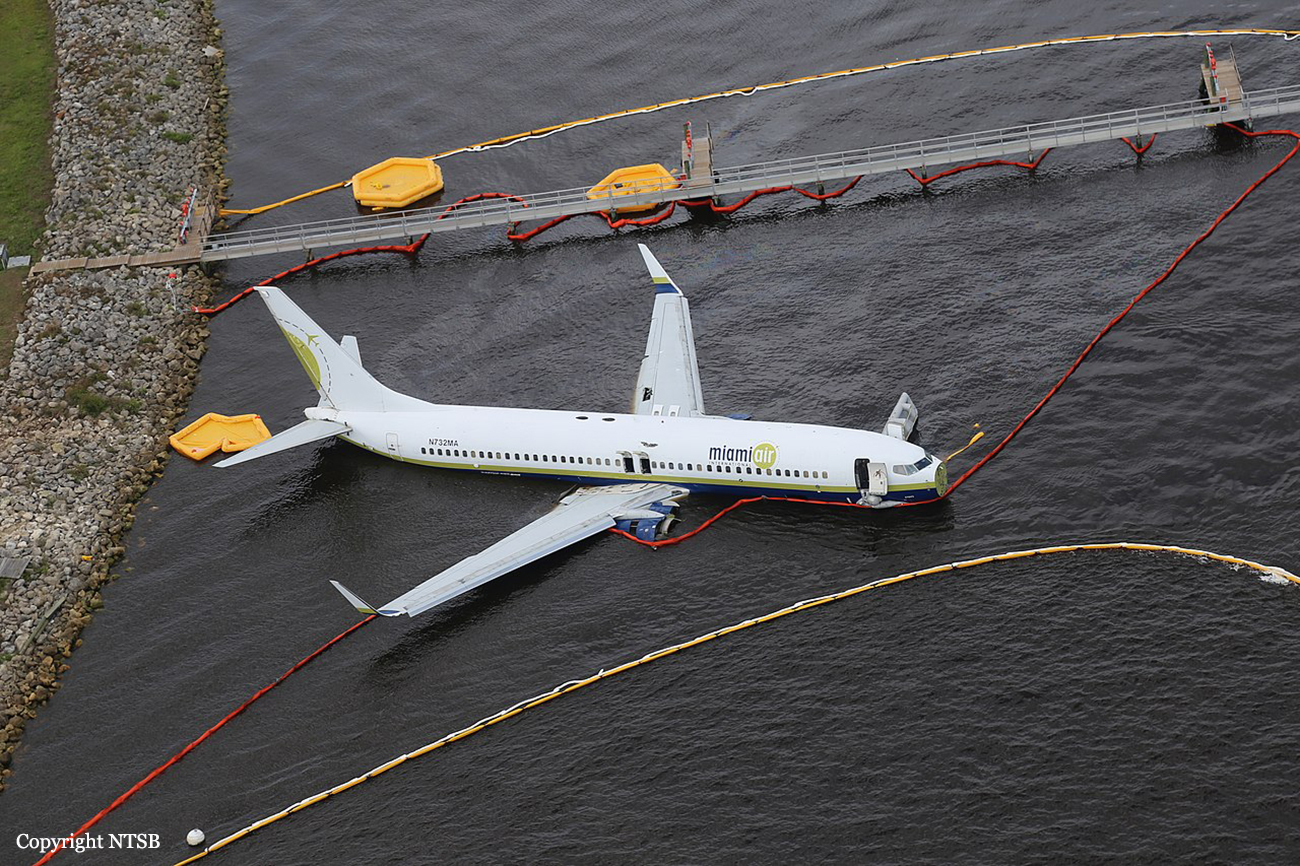
Circumstances:
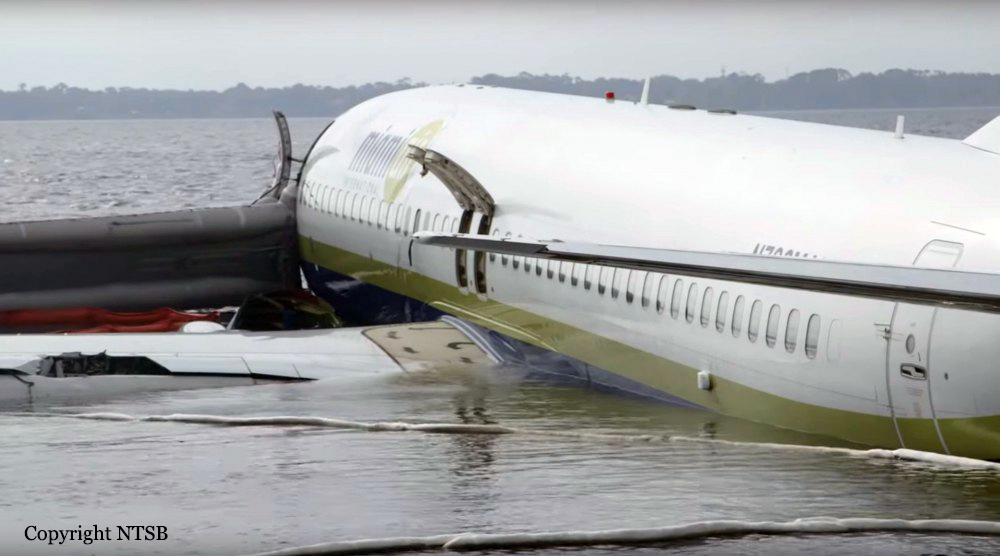
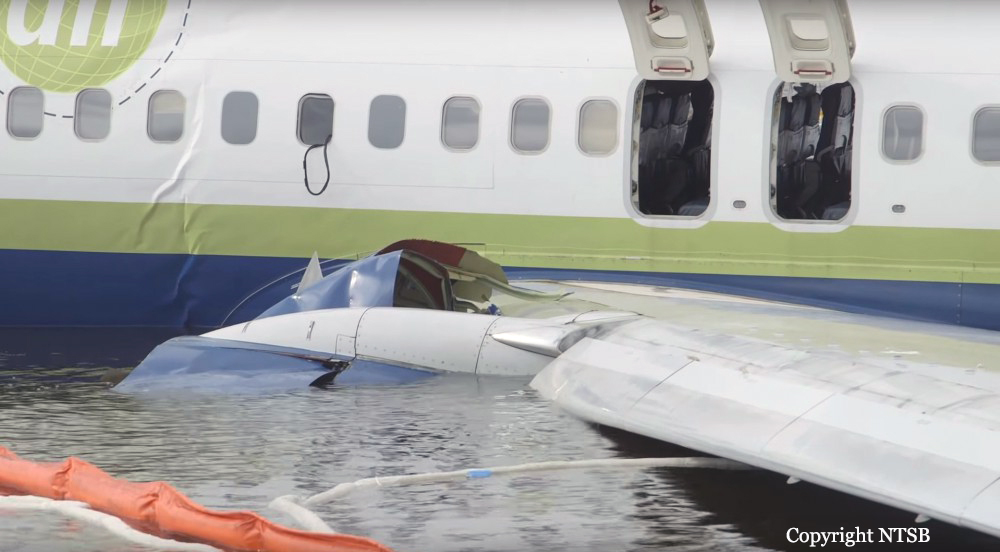
According to both pilots, the takeoff, climb, and cruise portions of the flight were uneventful. The No. 1 (left) thrust reverser was not operational and deferred for the flight in accordance with the airplane’s minimum equipment list. The captain was the pilot flying for the accident flight, and the first officer was the pilot monitoring. The captain was also performing check airman duties for the first officer who was in the process of completing operating experience training. During the approach to Jacksonville Naval Air Station (NIP), the flight crew had two runway change discussions with air traffic controllers due to reported weather conditions (moderate to heavy precipitation) near the field; the pilots ultimately executed the area navigation GPS approach to runway 10, which was ungrooved and had a displaced threshold 997 ft from the threshold, leaving an available landing distance of 8,006 ft. As the airplane descended through 1,390 ft mean sea level (msl), the pilots configured it for landing with the flaps set at 30º and the landing gear extended; however, the speedbrake handle was not placed in the armed position as specified in the Landing checklist. At an altitude of about 1,100 ft msl and 2.8 nm from the runway, the airplane was slightly above the glidepath, and its airspeed was on target. Over the next minute, the indicated airspeed increased to 170 knots (17 knots above the target approach speed), and groundspeed reached 180 knots, including an estimated 7-knot tailwind. At an altitude of about 680 ft msl and 1.6 nm from the threshold, the airplane deviated further above the 3° glidepath such that the precision approach path indicator (PAPI) lights would have appeared to the flight crew as four white lights and would retain that appearance throughout the rest of the approach. Eight seconds before touchdown, multiple enhanced ground proximity warning system alerts announced “sink rate” as the airplane’s descent rate peaked at 1,580 fpm. The airplane crossed the displaced threshold 120 ft above the runway (the PAPI glidepath crosses the displaced threshold about 54 ft above the runway) and 17 knots above the target approach speed, with a groundspeed of 180 knots and a rate of descent about 1,450 ft per minute (fpm). The airplane touched down about 1,580 ft beyond the displaced threshold, which was 80 ft beyond the designated touchdown zone as specified in the operator’s standard operating procedures (SOP). After touchdown, the captain deployed the No. 2 engine thrust reverser and began braking; he later reported, however, that he did not feel the aircraft decelerate and increased the brake pressure. The speedbrakes deployed about 4 seconds after touchdown, most likely triggered by the movement of the right throttle into the idle reverse thrust detent after main gear tire spinup. The automatic deployment of the speedbrakes was likely delayed by about 3 seconds compared to the automatic deployment that could have been obtained by arming the speedbrakes before landing. The airplane crossed the end of the runway about 55 ft right of the centerline and impacted a seawall 90 ft to the right of the centerline, 9,170 ft beyond the displaced threshold, and 1,164 ft beyond the departure end of runway 10. After the airplane came to rest in St. Johns River, the flight crew began an emergency evacuation.
Probable cause:
An extreme loss of braking friction due to heavy rain and the water depth on the ungrooved runway, which resulted in viscous hydroplaning. Contributing to the accident was the operator’s inadequate guidance for evaluating runway braking conditions and conducting en route landing distance assessments.
Contributing to the continuation of an unstabilized approach were
1) the captain’s plan continuation bias and increased workload due to the weather and performing check airman duties and
2) the first officer’s lack of experience.
Contributing to the continuation of an unstabilized approach were
1) the captain’s plan continuation bias and increased workload due to the weather and performing check airman duties and
2) the first officer’s lack of experience.
Final Report: