Crash of an Airbus A310 in Vienna, Austria
Date & Time:
Jul 12, 2000 at 1334 LT
Registration:
D-AHLB
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Hania - Hanover
MSN:
0528
YOM:
1990
Flight number:
HF3378
Crew on board:
8
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
143
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Aircraft flight hours:
41307
Aircraft flight cycles:
13789
Circumstances:
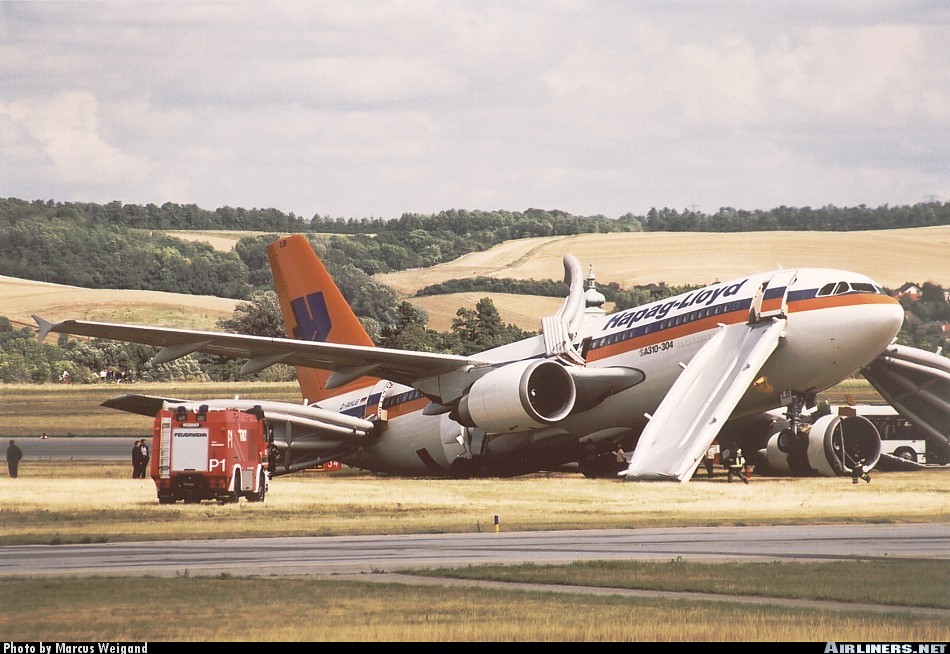
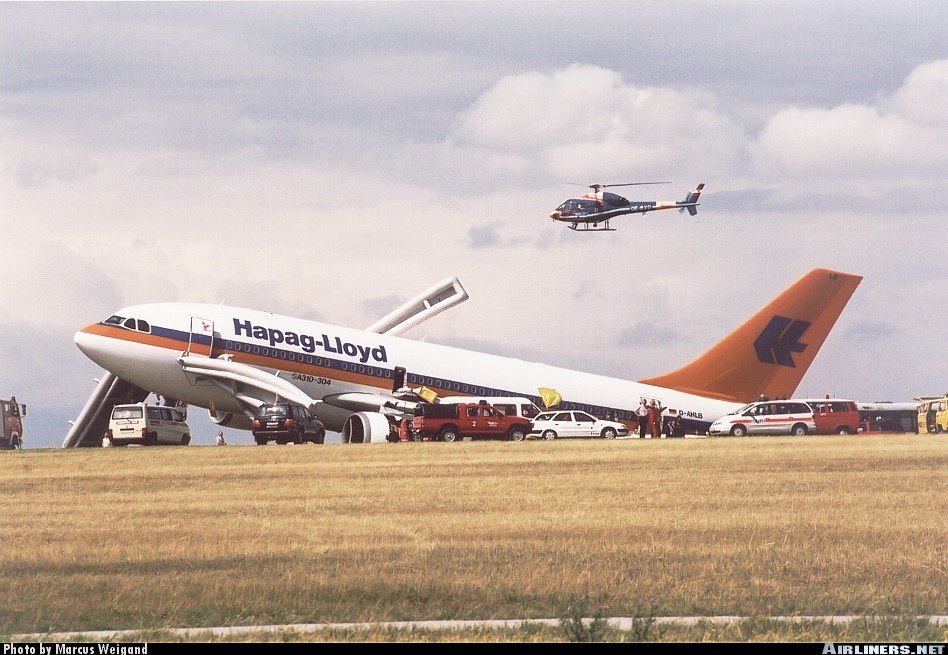
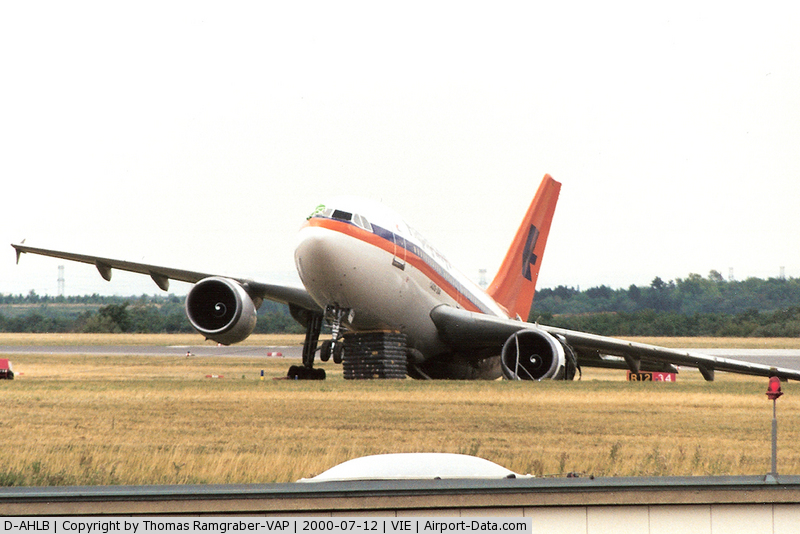
After takeoff from Chania-Souda Airport, the crew reported technical problems with the right main gear that could not be raised properly in its wheel well. The captain decided to continue to Munich in a gear down configuration but the fuel consumption increased. En route, the crew realized he could not make it to Munich so diverted to Vienna-Schwechat Airport. At a distance of about 12 NM from the airport, at an altitude of 4,000 feet, both engines failed due to fuel exhaustion. One of the engine could be restarted for a short period of time but on short final, the aircraft stalled and struck the ground (a grassy area) about 500 metres short of runway 34. The left main gear broke off, the aircraft slid for some 600 metres then veered to the left and came to rest on its left wing. All 151 occupants were rescued, among them 26 passengers were slightly injured. The aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Continuation of the flight with a landing gear problem until the engines failed due to fuel exhaustion.
The following findings were identified:
Crew:
- Failure to comply with the company's rules on fuel reserves, caused by several human factors, with extreme workload and stress being the important factor (loss of situational awareness).
- Determination of the fuel reserves using only the FMS, which, due to its characteristics did not take into account the additional fuel consumption.
- Failure to develop alternative strategies to curb the fuel problem.
- Failure to comply with a fuel warning (low fuel level warning) and decision to continue the flight to Vienna International Airport, although the plane was in the immediate vicinity of Zagreb Airport.
Manufacturer:
- Inadequate and misleading documentation (FMS scheme, altitude, terms) for this specific case, particularly in relation to the restriction of FMS.
Operator:
- Inadequate documentation for "abnormal landing gear up indication" of the abnormal checklist.
- Lack of review of the fuel needs by the Operations Division.
Contributing factors:
- Missing or inadequate preventive measures by manufacturers, approving authority and airlines following the previous publications of ICAO and EU DG VII about problems which, with the introduction of aircraft equipped with modern technologies, occurred and had been identified.
- Anthropo-technical construction deficiencies, which favour a misinterpretation of the FMS EFOB display.
The following findings were identified:
Crew:
- Failure to comply with the company's rules on fuel reserves, caused by several human factors, with extreme workload and stress being the important factor (loss of situational awareness).
- Determination of the fuel reserves using only the FMS, which, due to its characteristics did not take into account the additional fuel consumption.
- Failure to develop alternative strategies to curb the fuel problem.
- Failure to comply with a fuel warning (low fuel level warning) and decision to continue the flight to Vienna International Airport, although the plane was in the immediate vicinity of Zagreb Airport.
Manufacturer:
- Inadequate and misleading documentation (FMS scheme, altitude, terms) for this specific case, particularly in relation to the restriction of FMS.
Operator:
- Inadequate documentation for "abnormal landing gear up indication" of the abnormal checklist.
- Lack of review of the fuel needs by the Operations Division.
Contributing factors:
- Missing or inadequate preventive measures by manufacturers, approving authority and airlines following the previous publications of ICAO and EU DG VII about problems which, with the introduction of aircraft equipped with modern technologies, occurred and had been identified.
- Anthropo-technical construction deficiencies, which favour a misinterpretation of the FMS EFOB display.
Final Report: