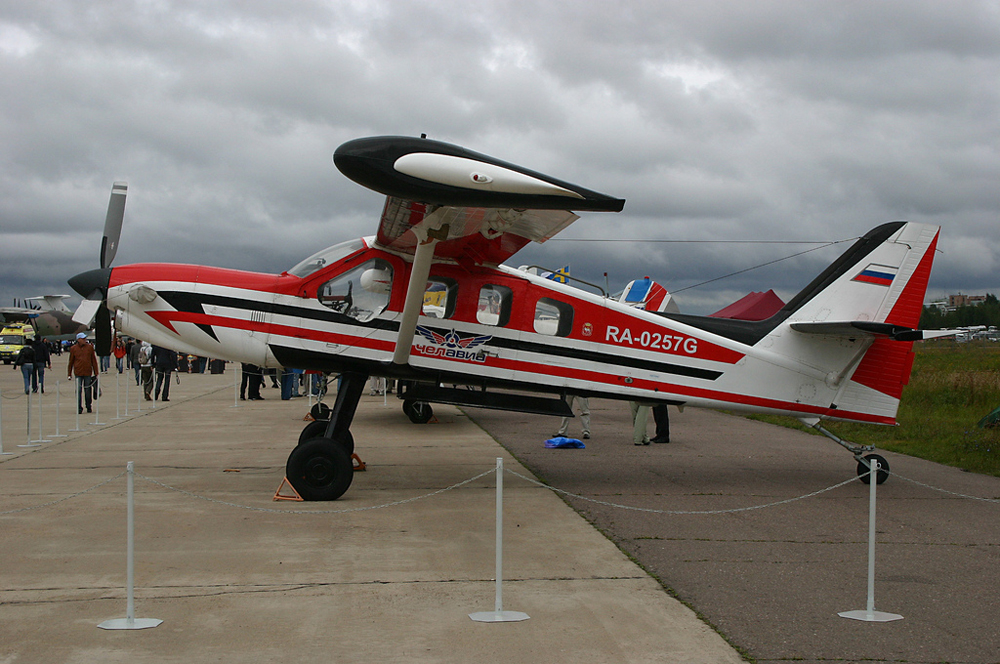
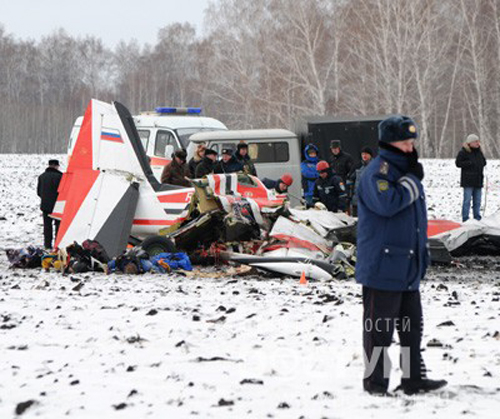
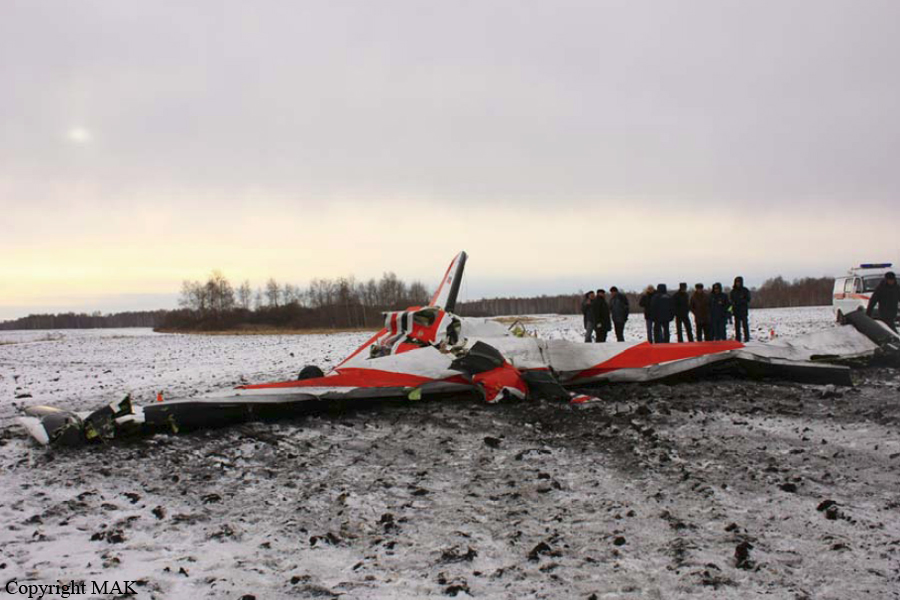
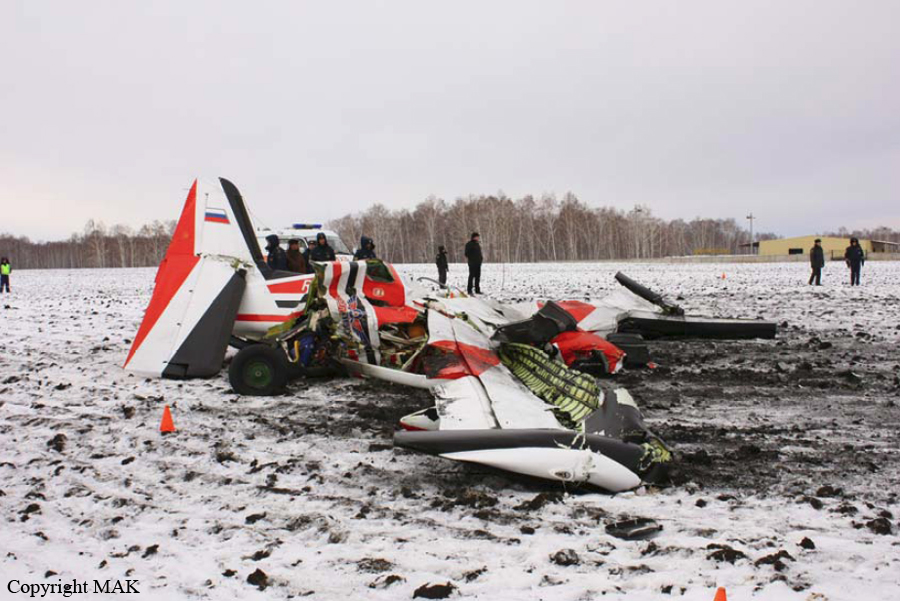
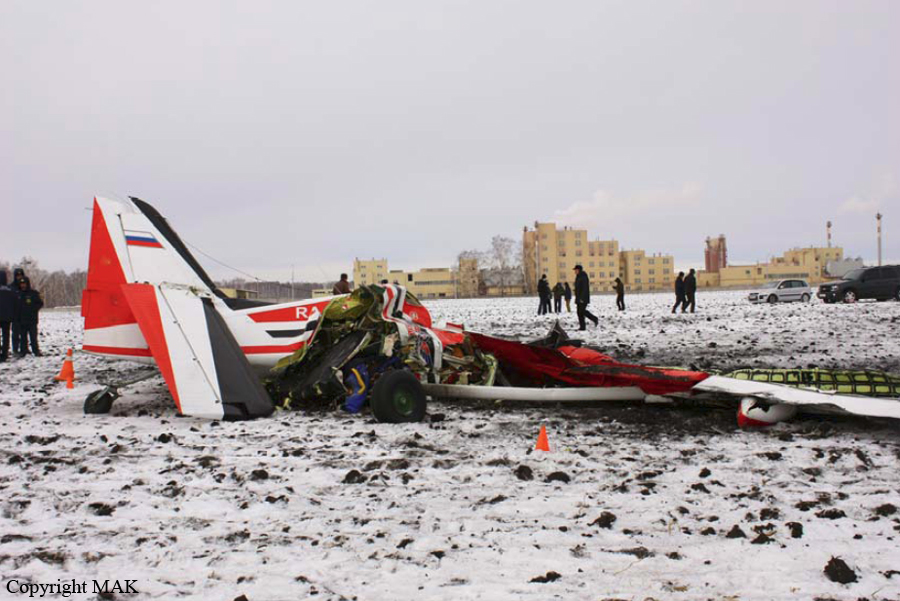
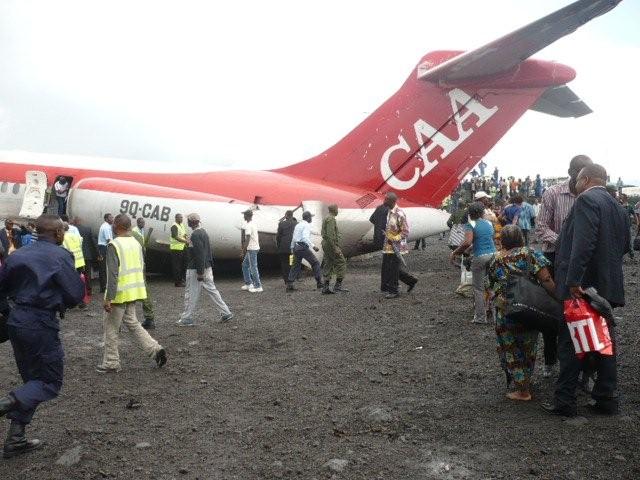
Crash of a Technoavia SM-92T Turbo Finist in Kalachevo: 8 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 13, 2009 at 1100 LT
Registration:
RA-0257G
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kalachevo - Kalachevo
MSN:
02-005
YOM:
1997
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
7
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
8
Captain / Total hours on type:
98.00
Aircraft flight hours:
536
Aircraft flight cycles:
1378
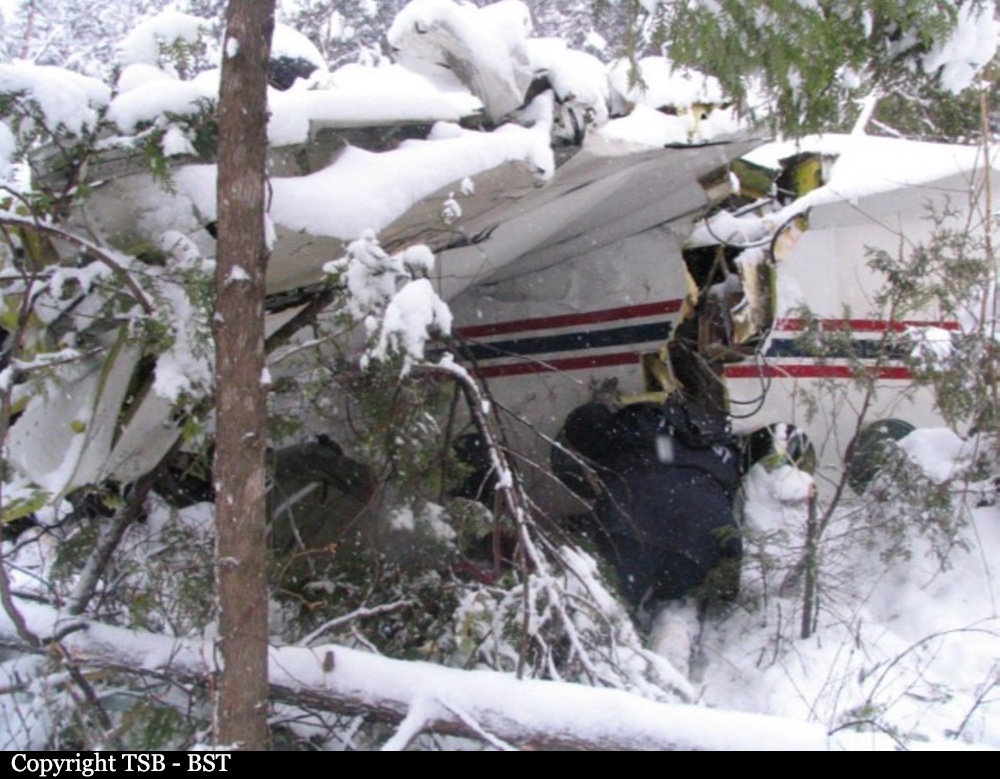
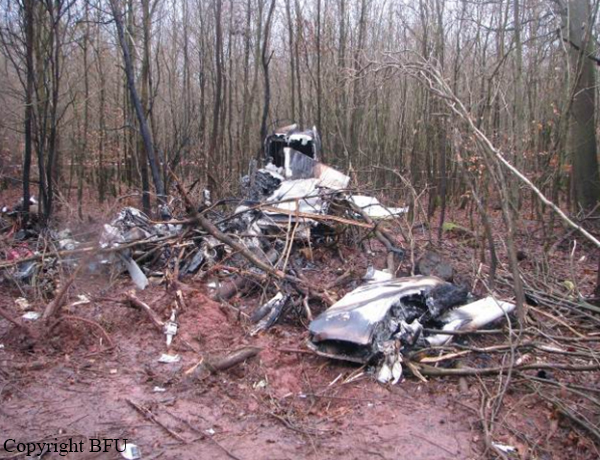
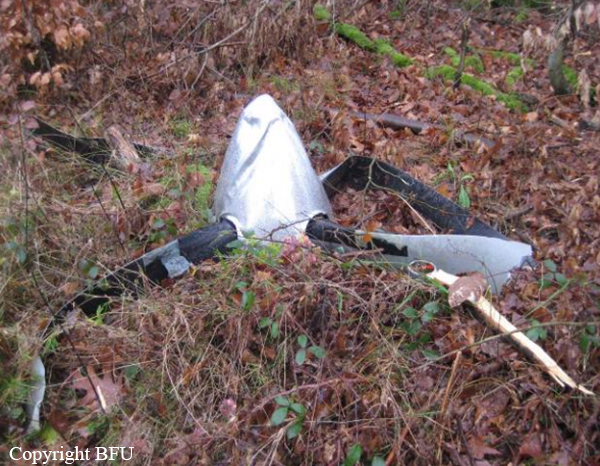
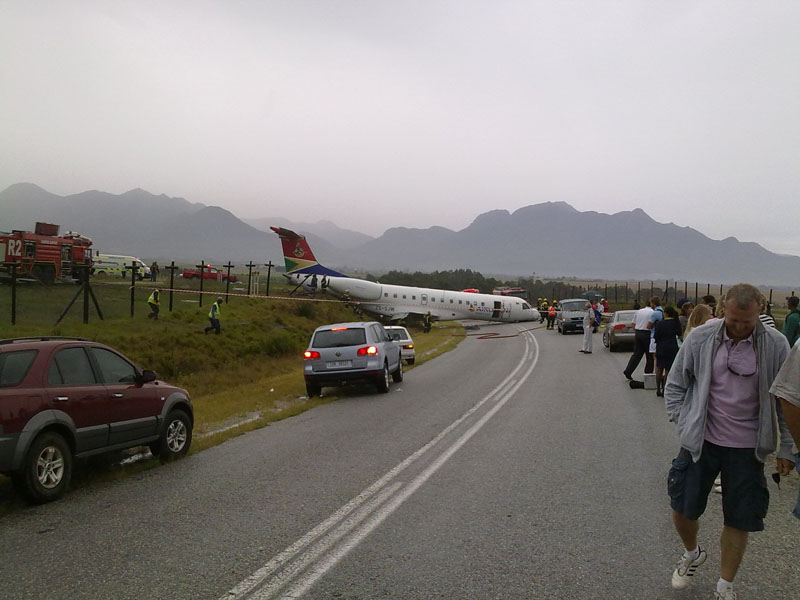
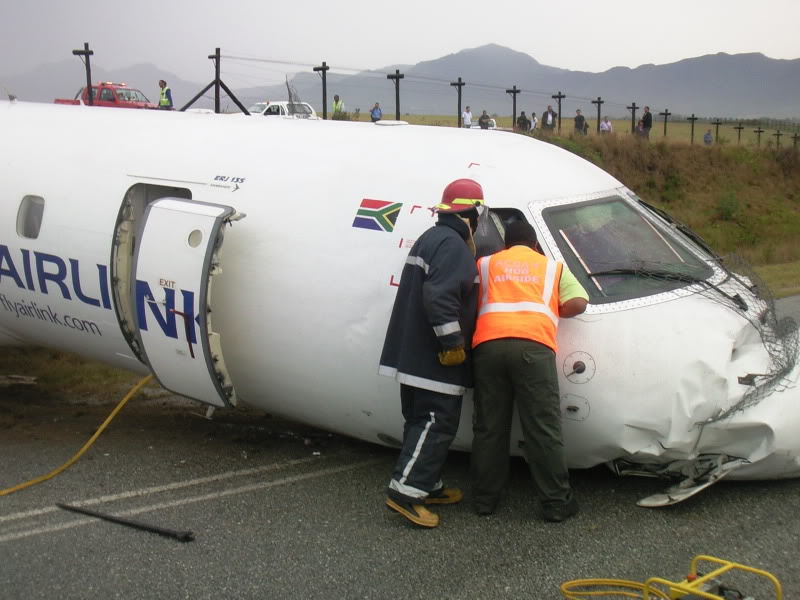
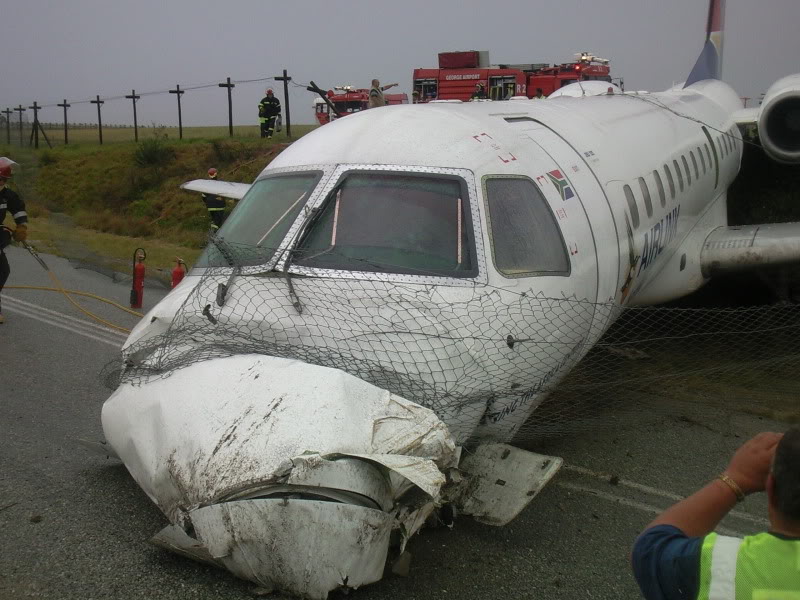
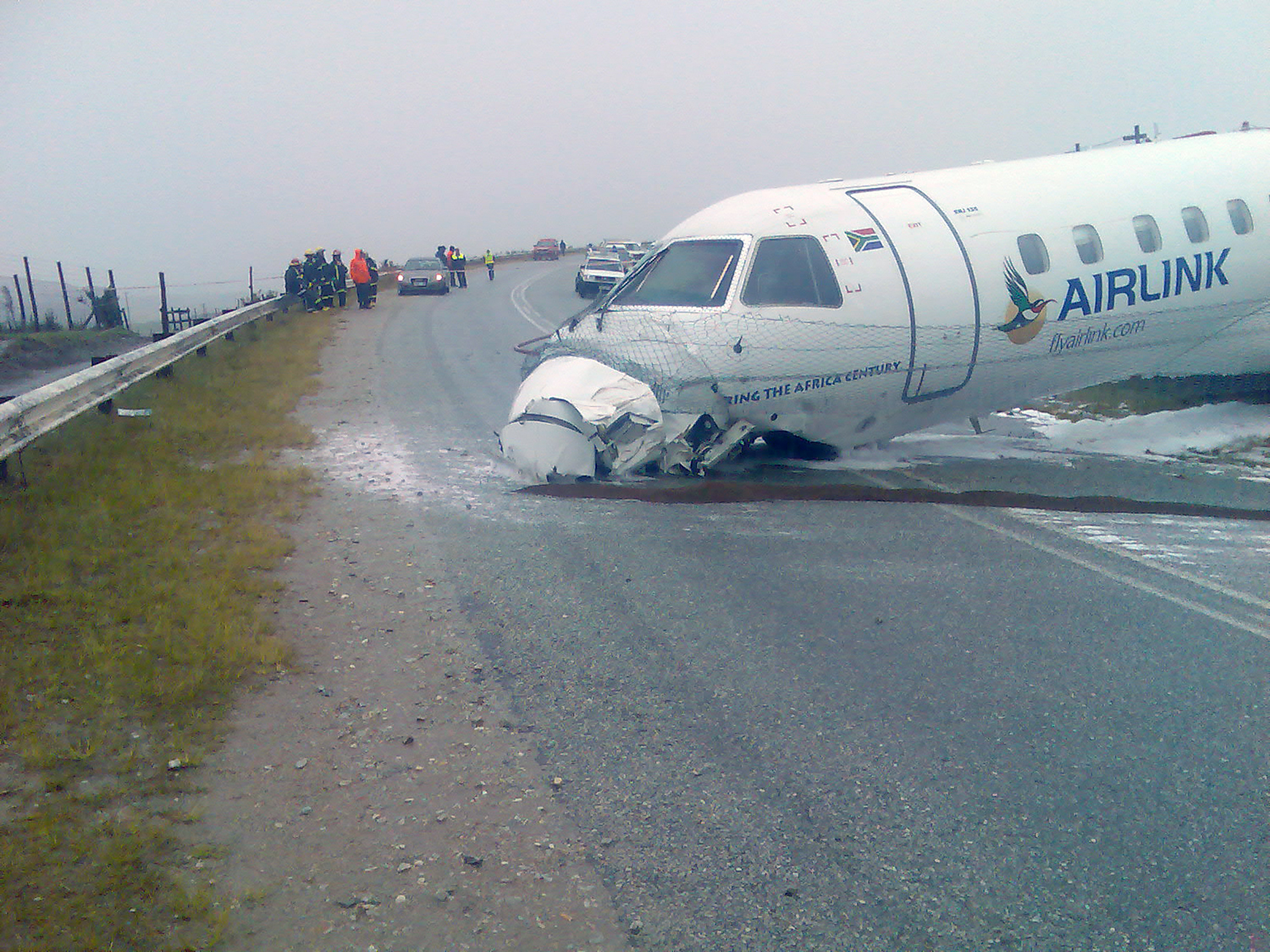
Circumstances:
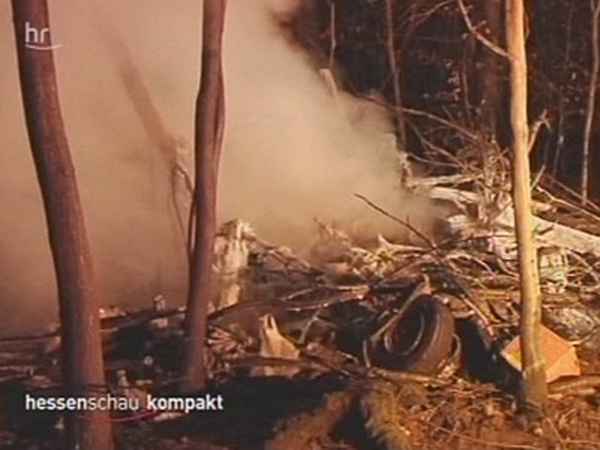
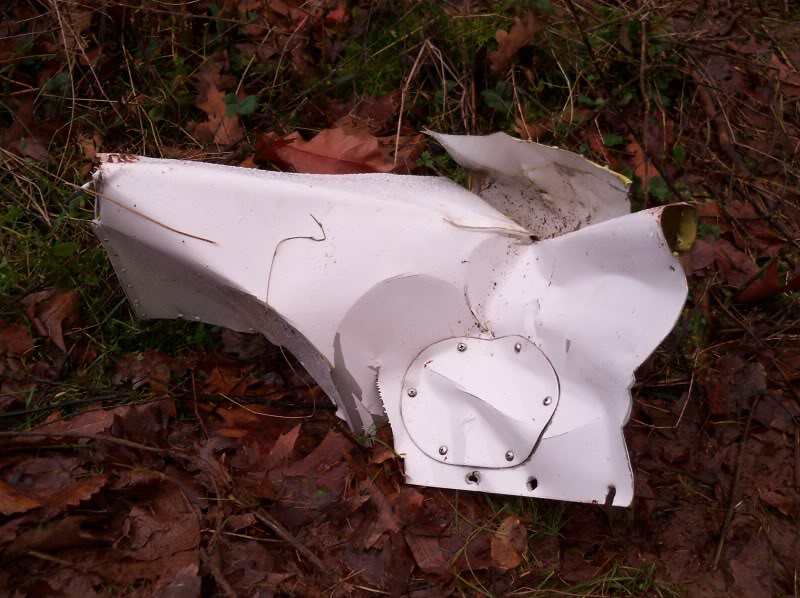
The single engine was completing local skydiving sorties at Kalachevo Airport, about 24 kkm south of Chelyabinsk. Shortly after takeoff, while climbing to a height of about 100 metres, the aircraft stalled and crashed in a snow covered field located 1,5 km north of the airfield. The aircraft was totally destroyed upon impact and all 8 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of a stall during initial climb due to the combination of the following factors:
- Violation of the climb procedures regarding the speed,
- Flight performances were not met as the aircraft was operated for skydiving purposes but not intended for such type of flight,
- The total weight of the aircraft was above the MTOW,
- The aircraft was not equipped with a system that could inform the pilot of the imminence of a stall,
- The aircraft stalled at a relative low altitude that could not allow the pilot to expect recovery.
- Violation of the climb procedures regarding the speed,
- Flight performances were not met as the aircraft was operated for skydiving purposes but not intended for such type of flight,
- The total weight of the aircraft was above the MTOW,
- The aircraft was not equipped with a system that could inform the pilot of the imminence of a stall,
- The aircraft stalled at a relative low altitude that could not allow the pilot to expect recovery.
Final Report: