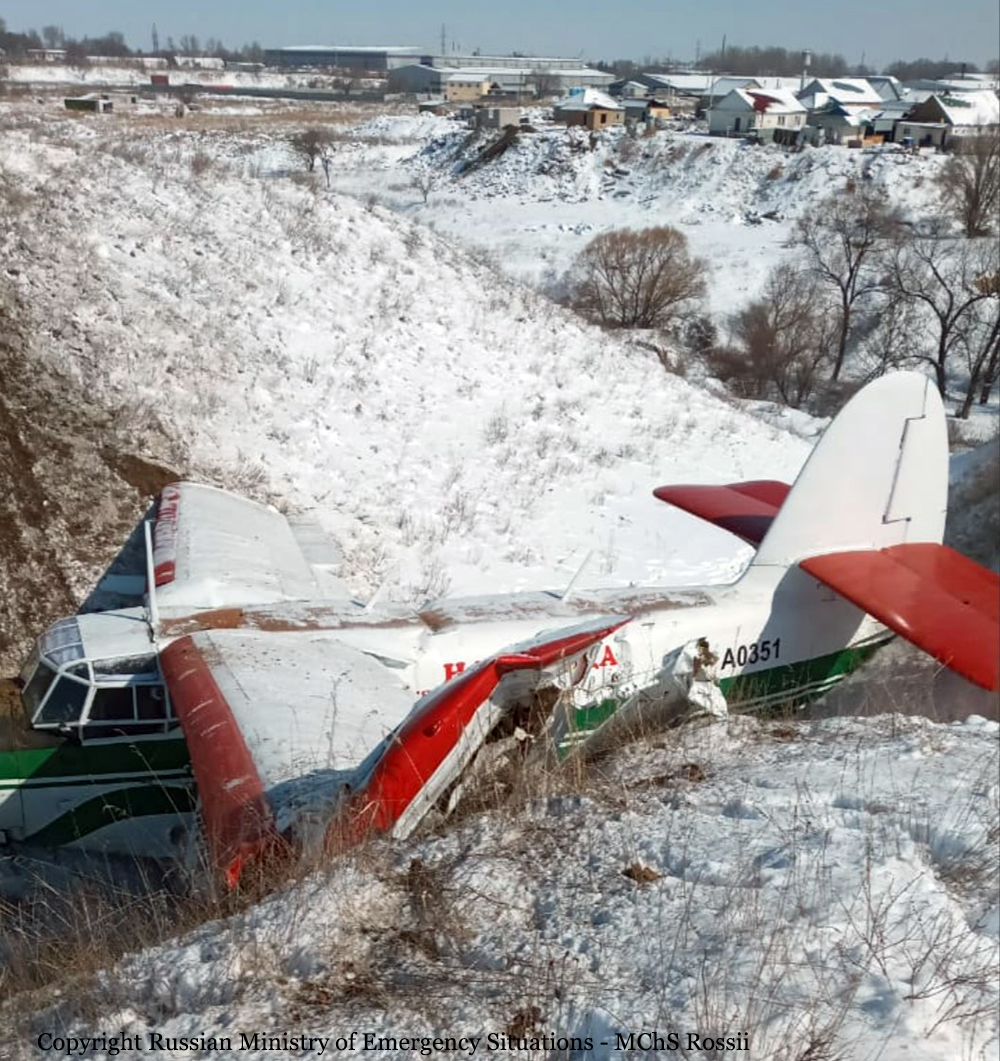
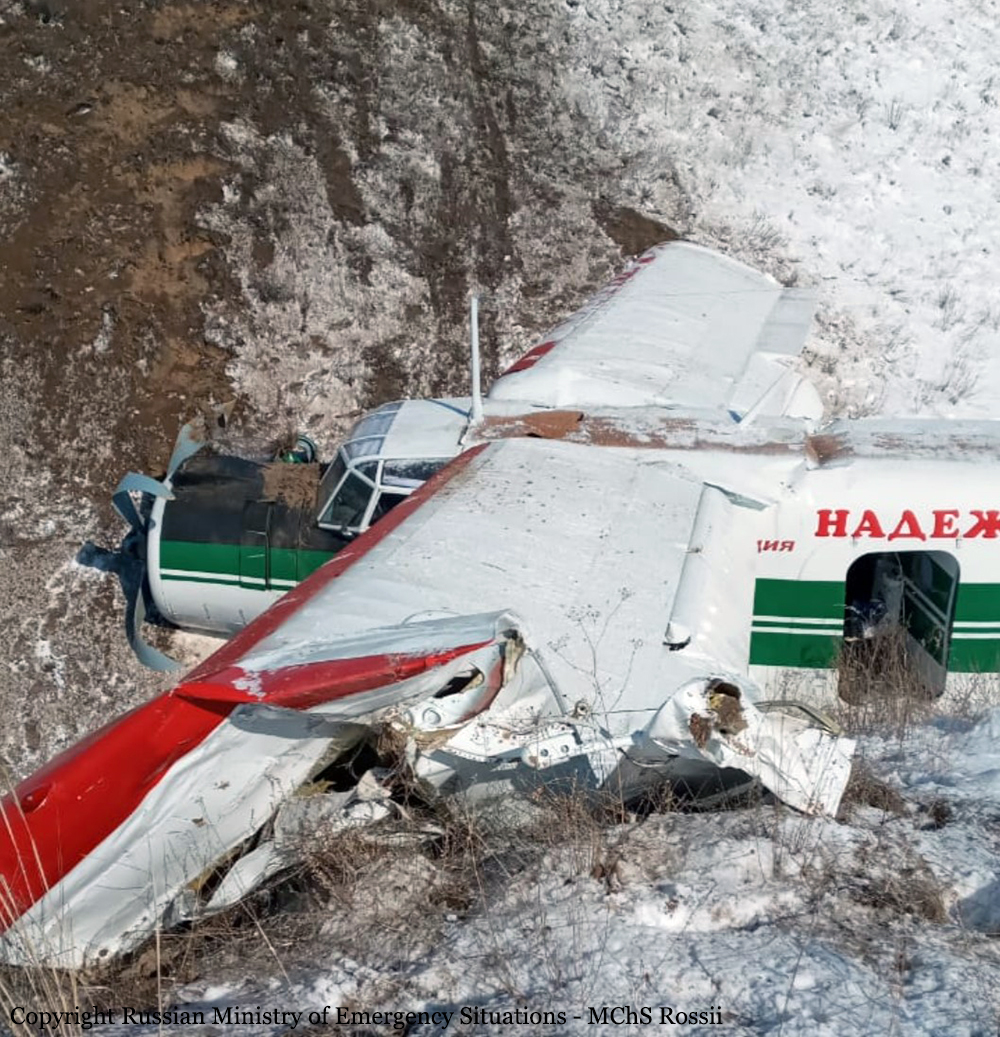
Crash of a PZL-Mielec AN-2T in Boralday
Date & Time:
Feb 26, 2021 at 1226 LT
Registration:
UP-A0351
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Boralday - Kegen
MSN:
1G194-19
YOM:
1981
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
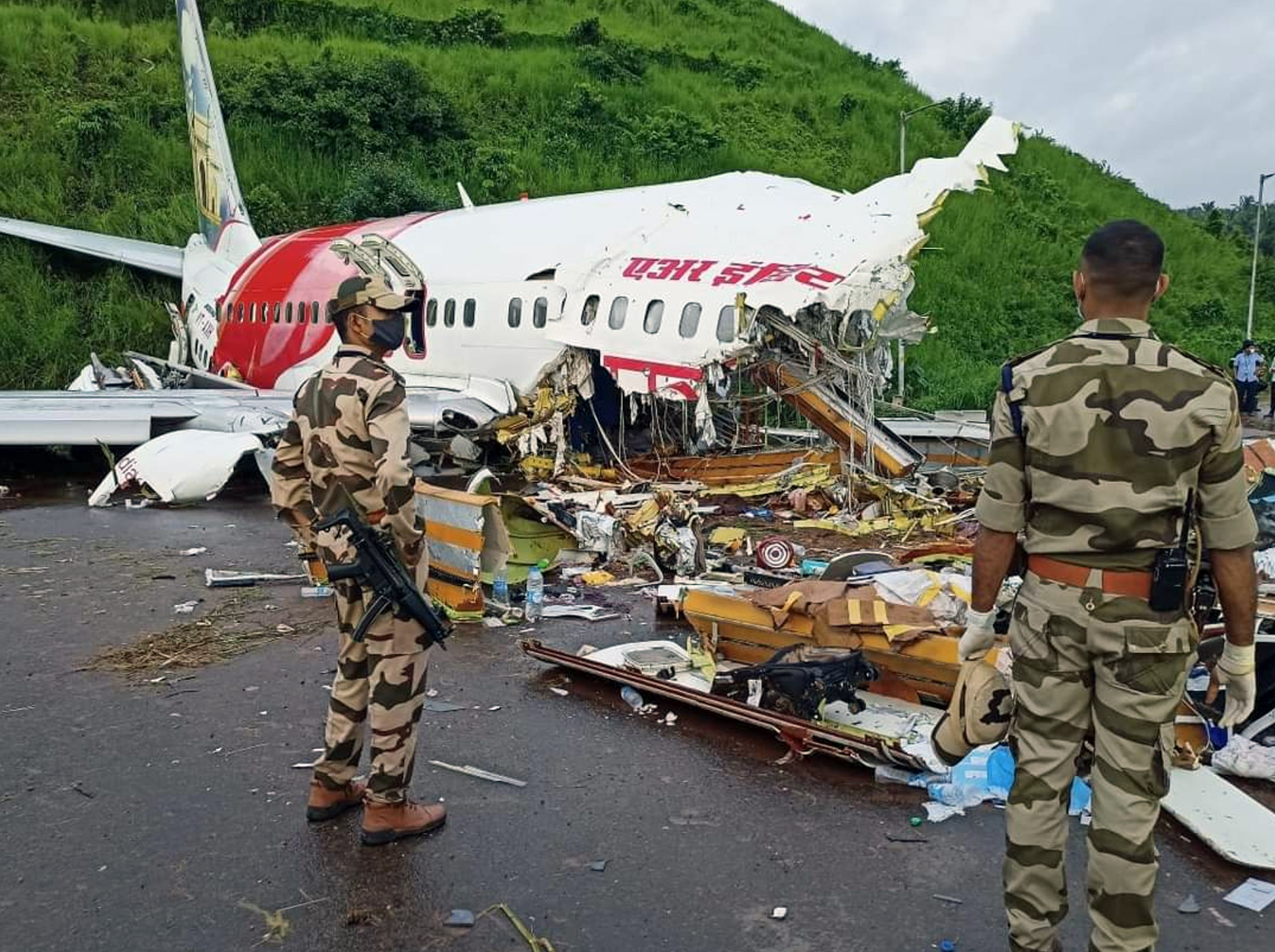
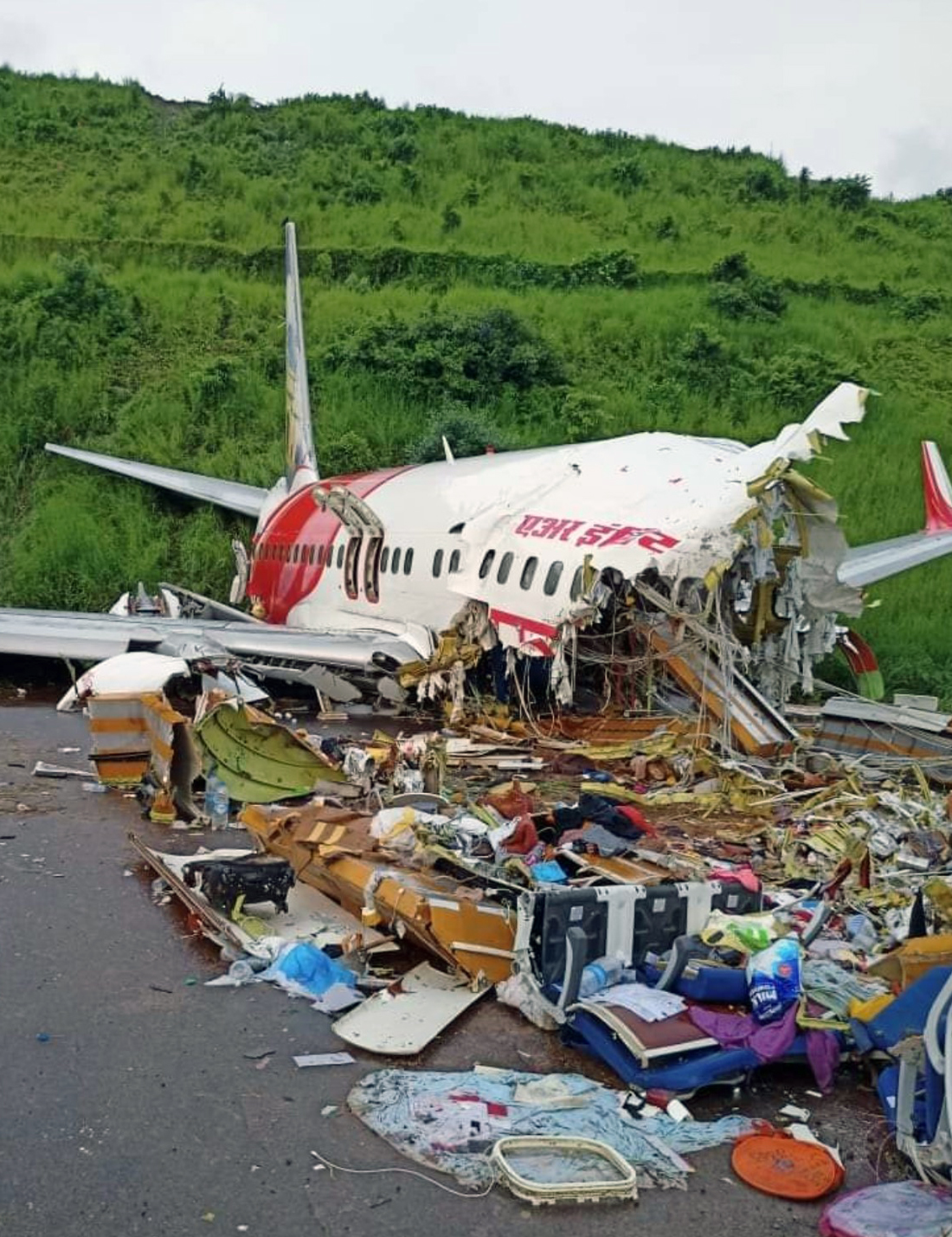
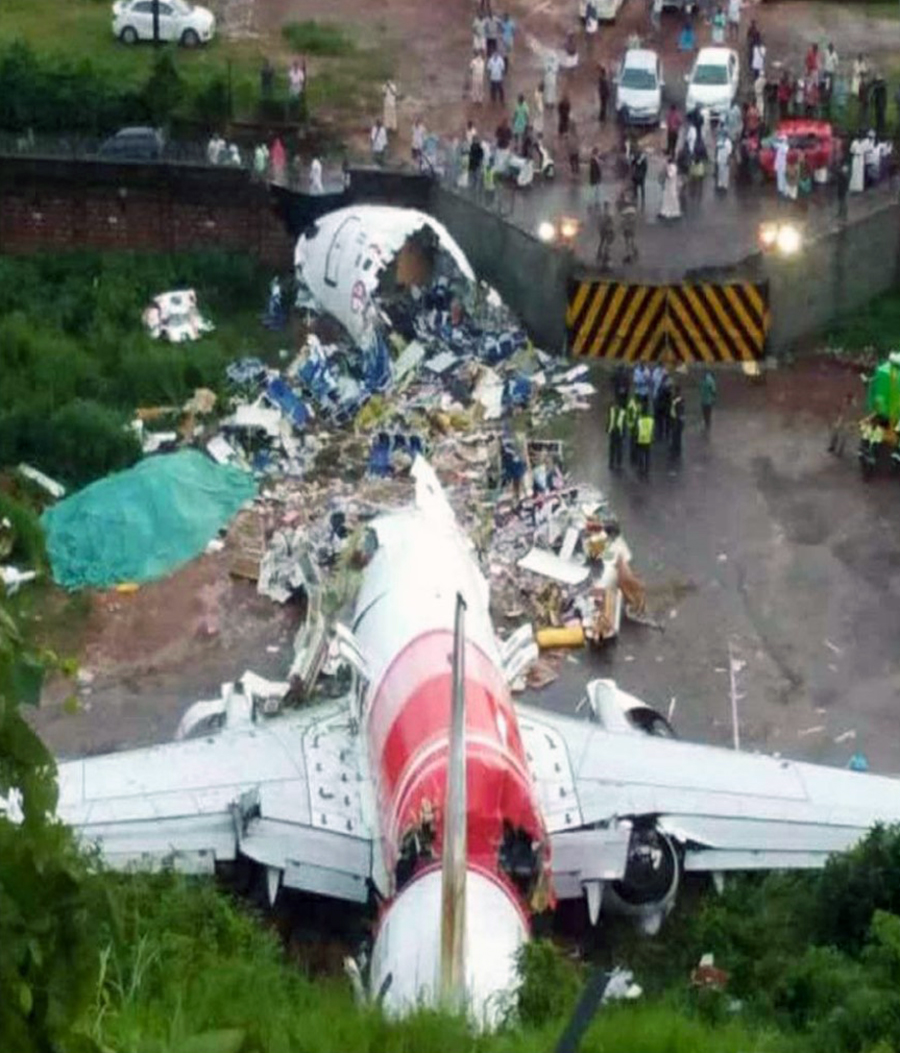
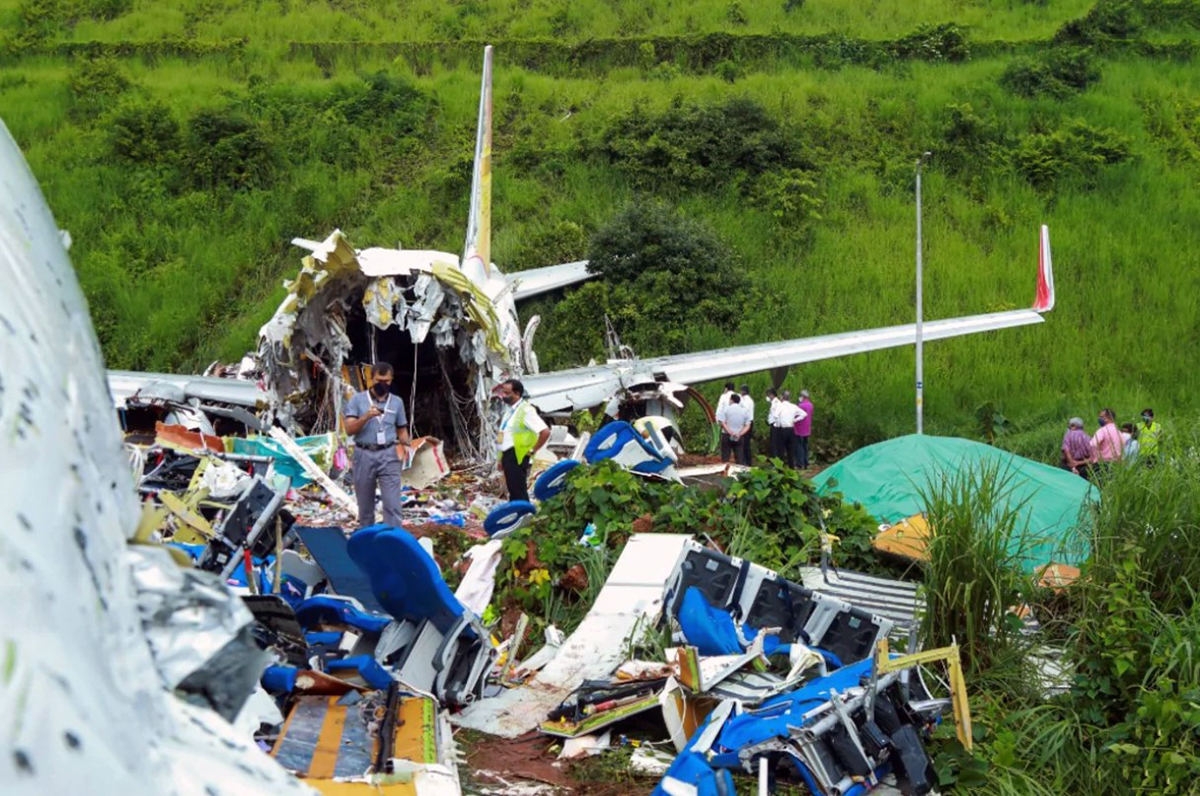
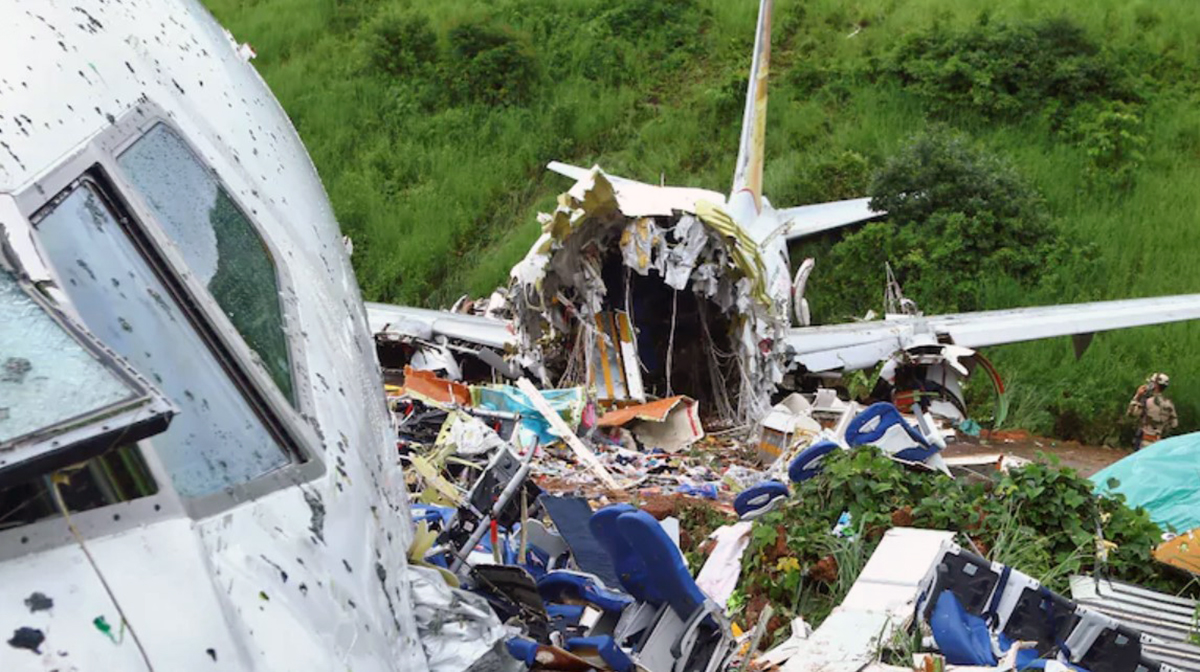
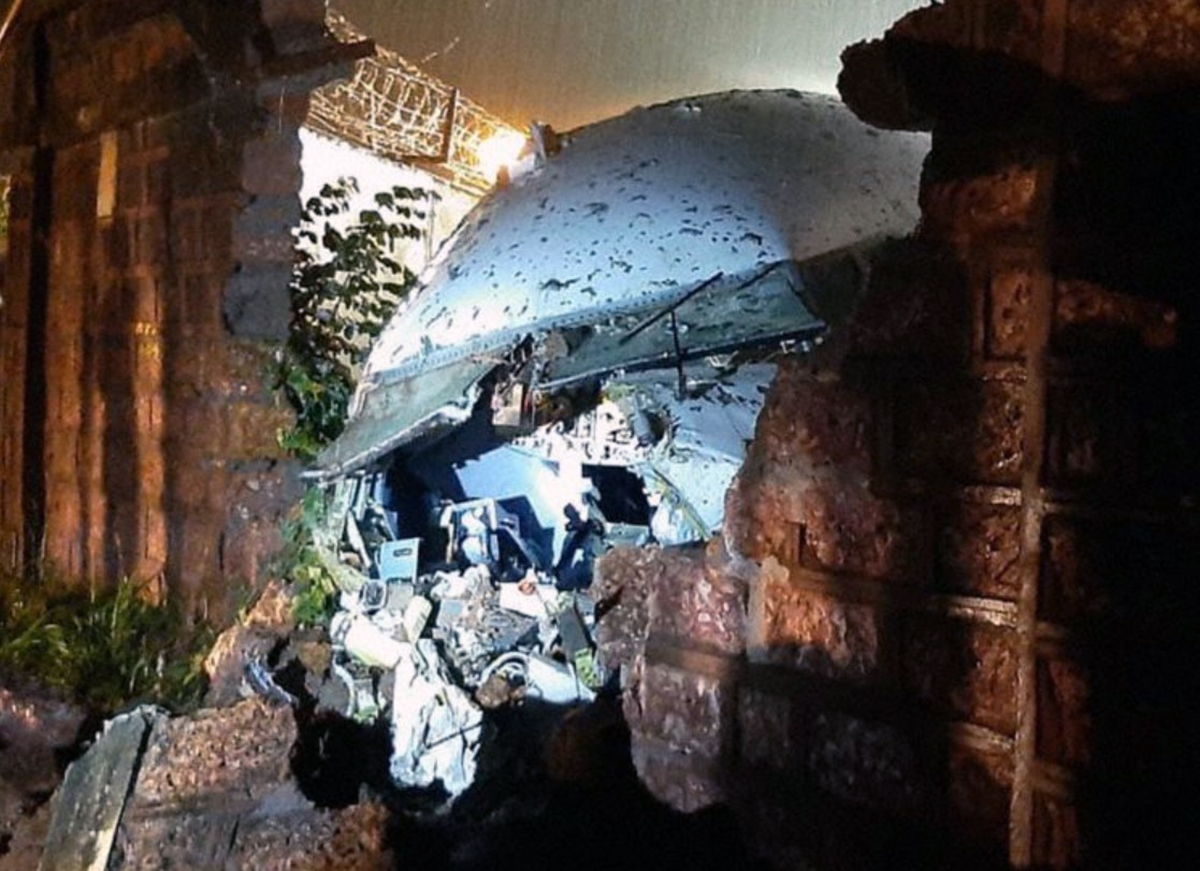
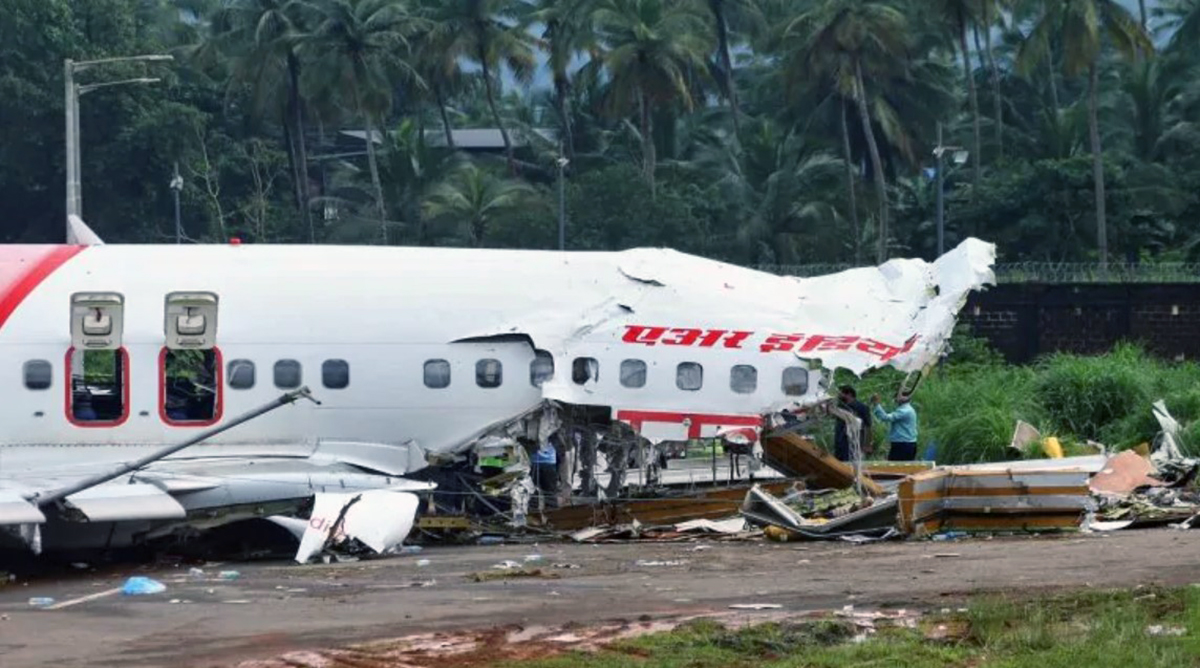
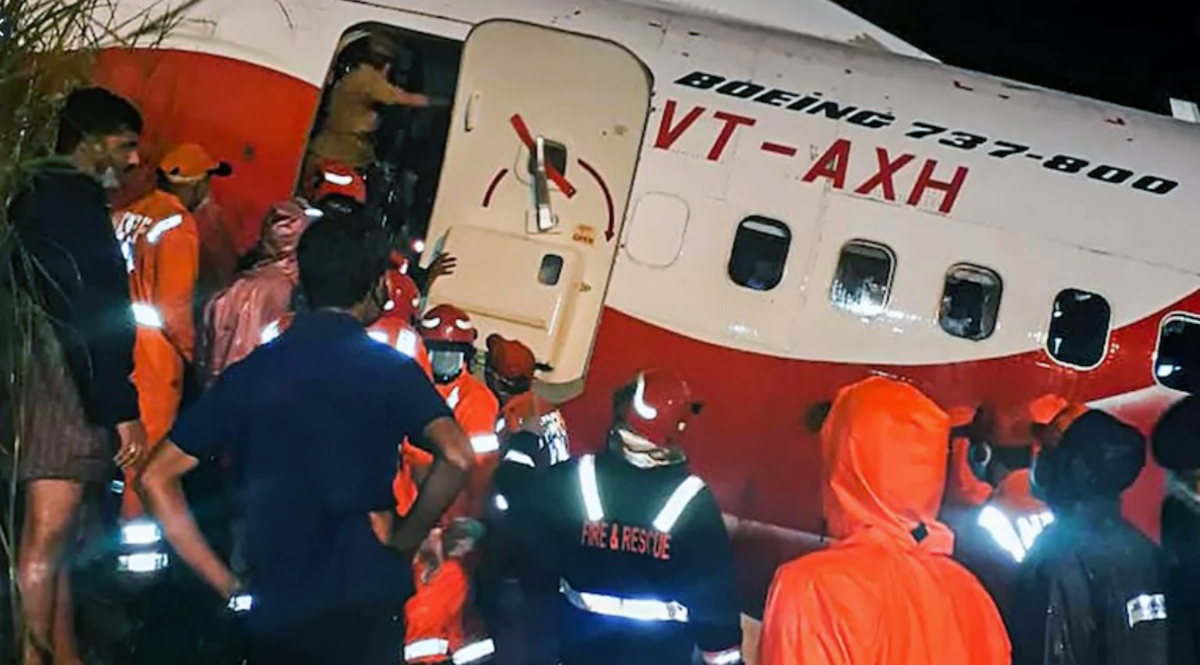
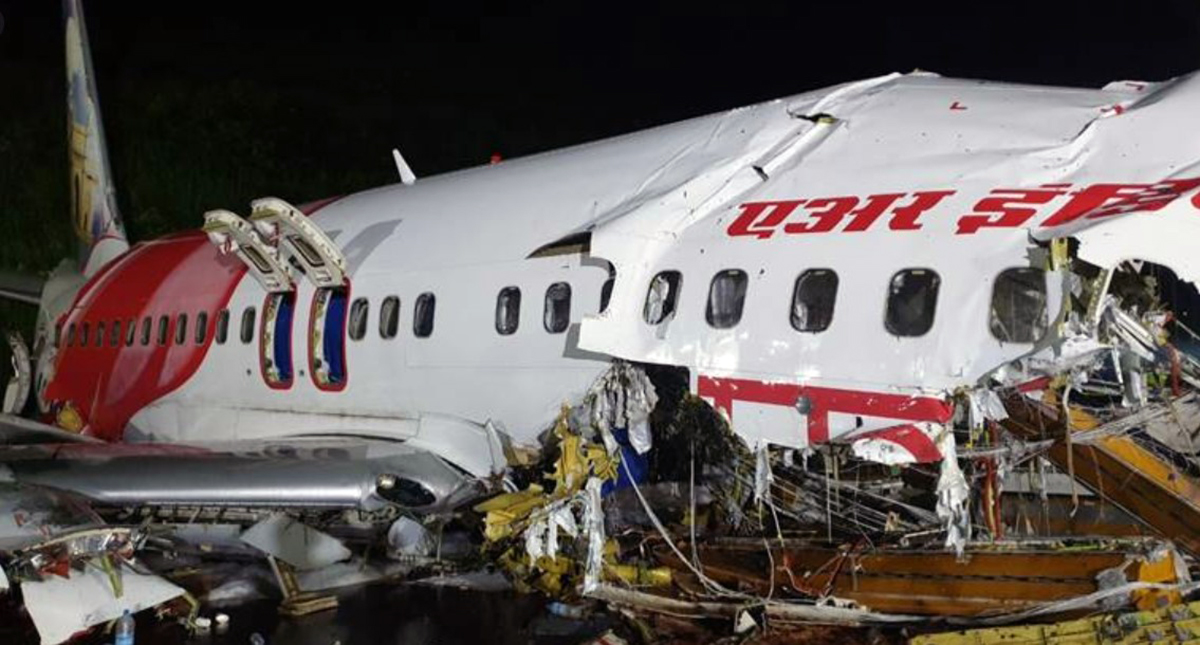
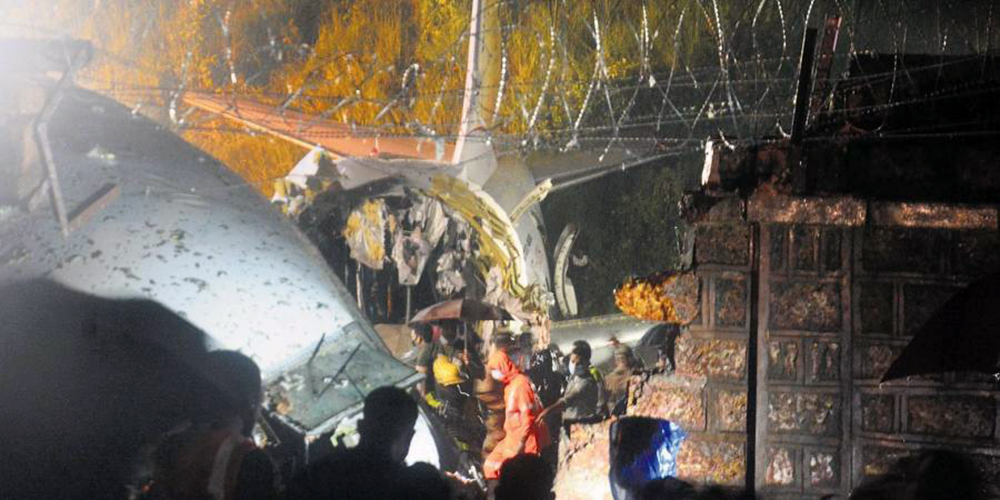
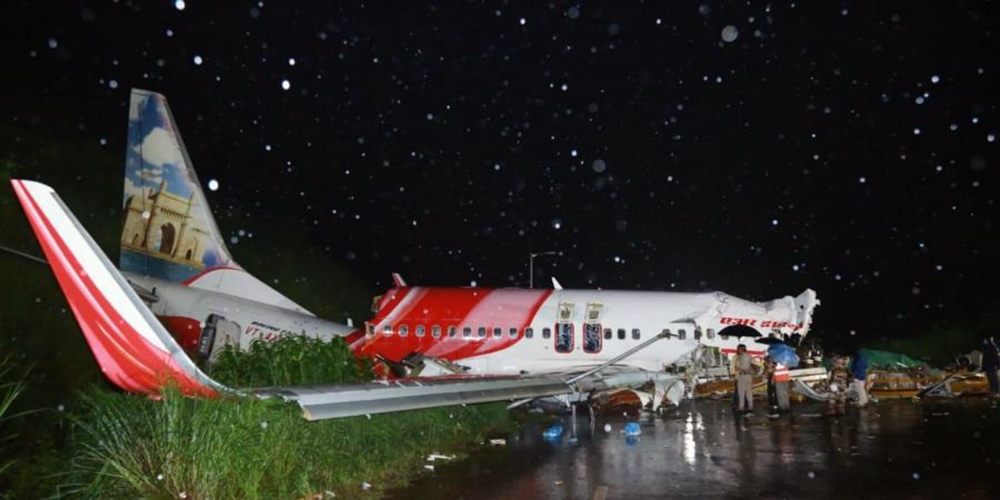
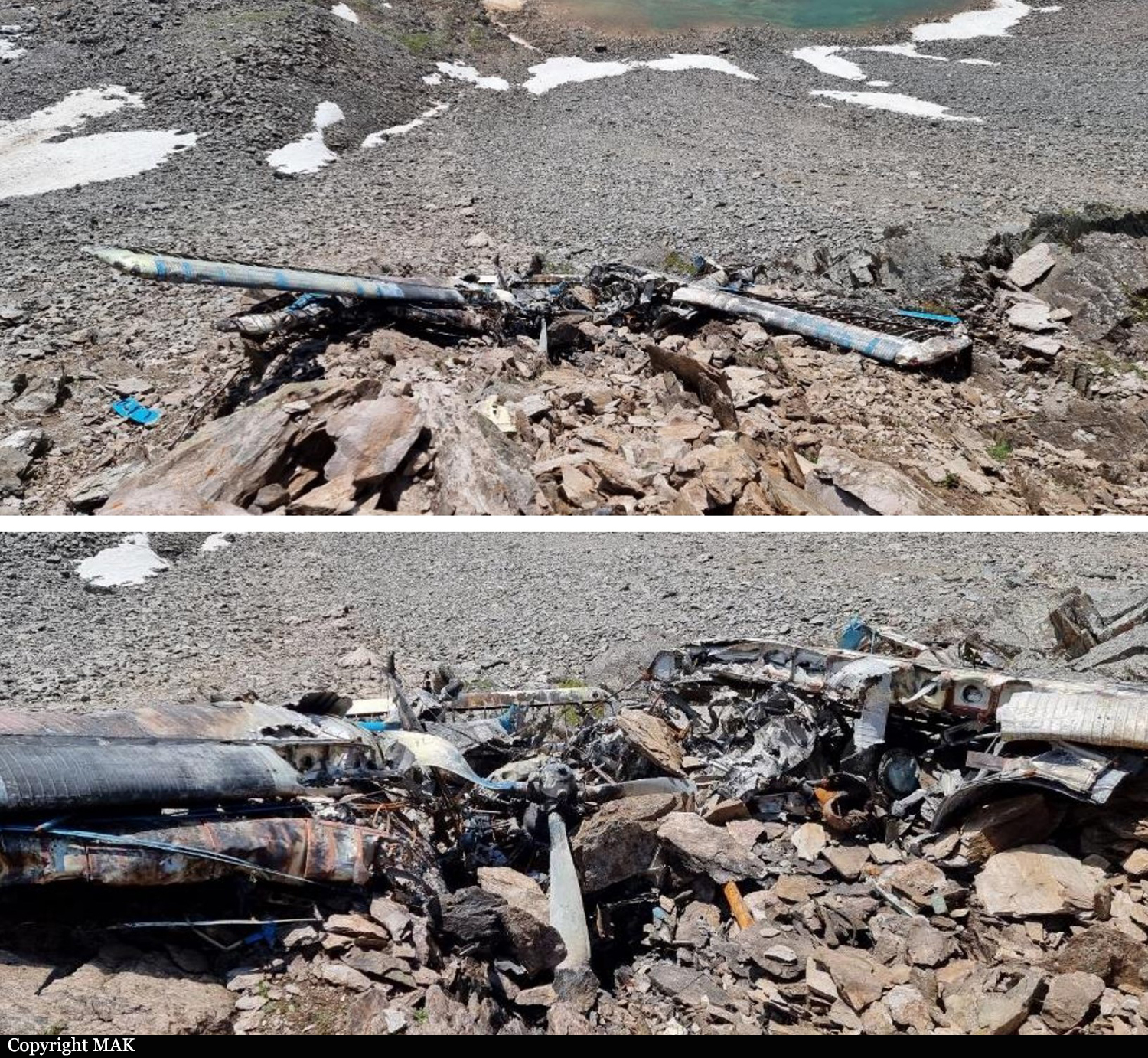
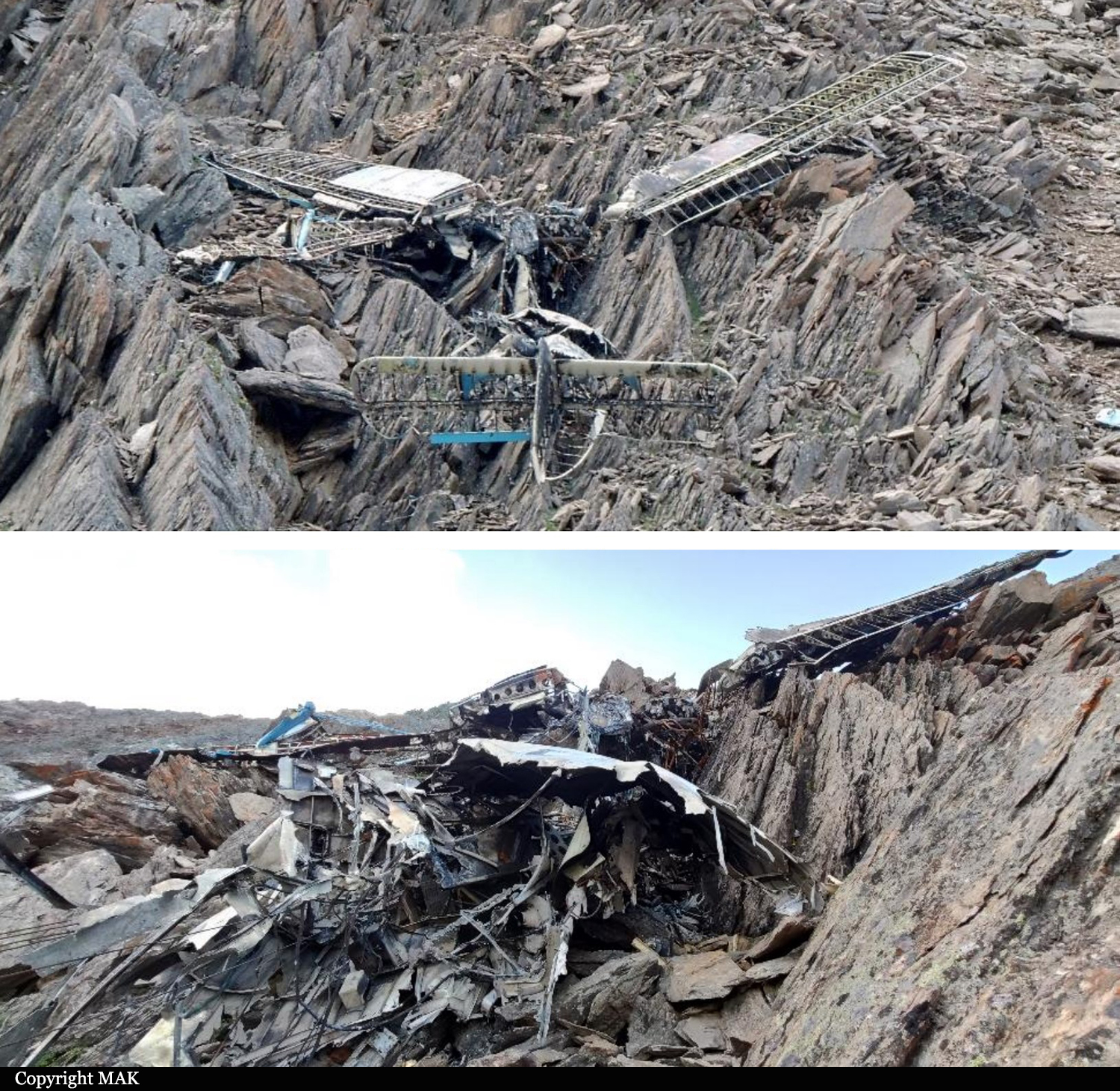
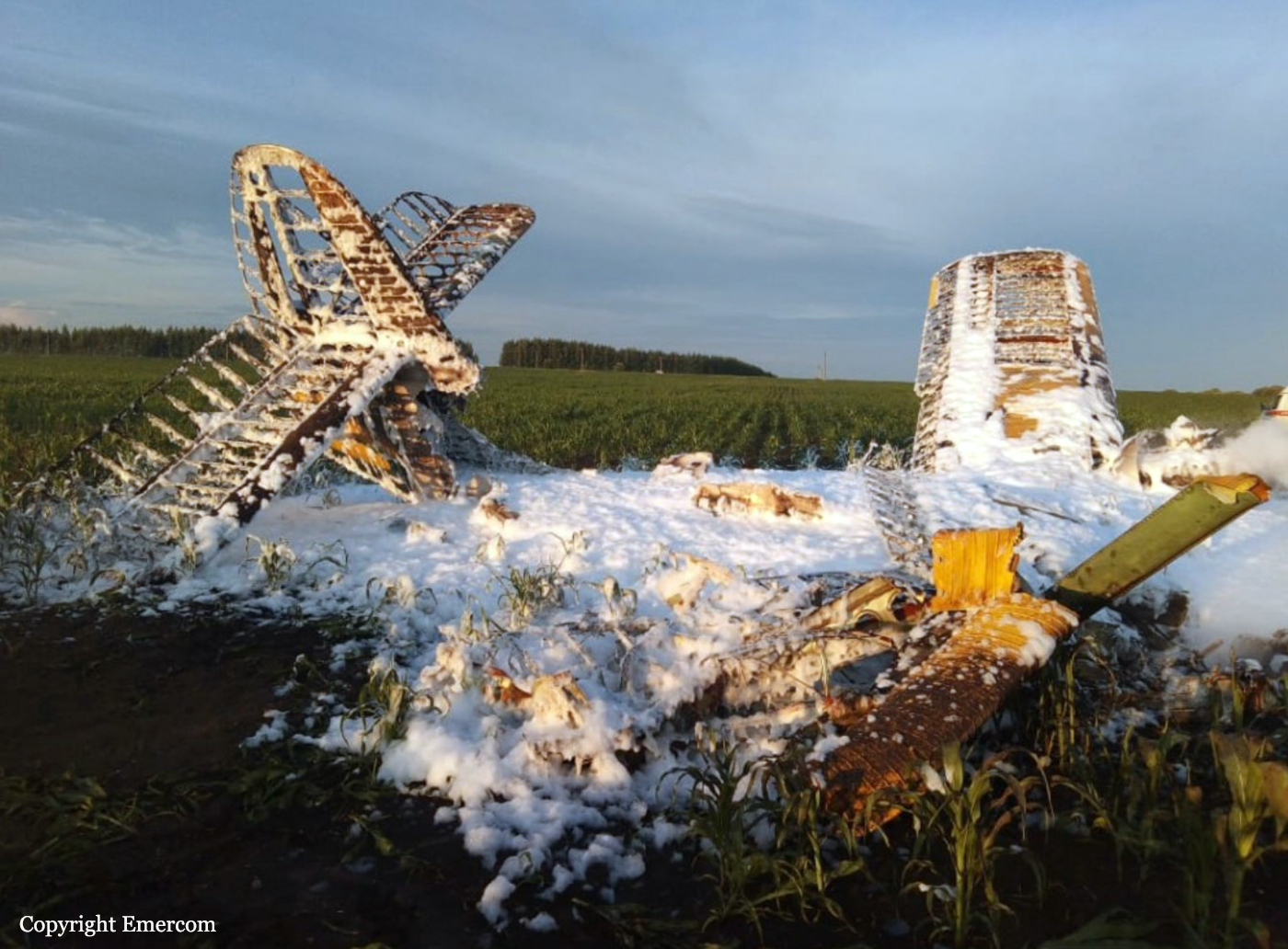
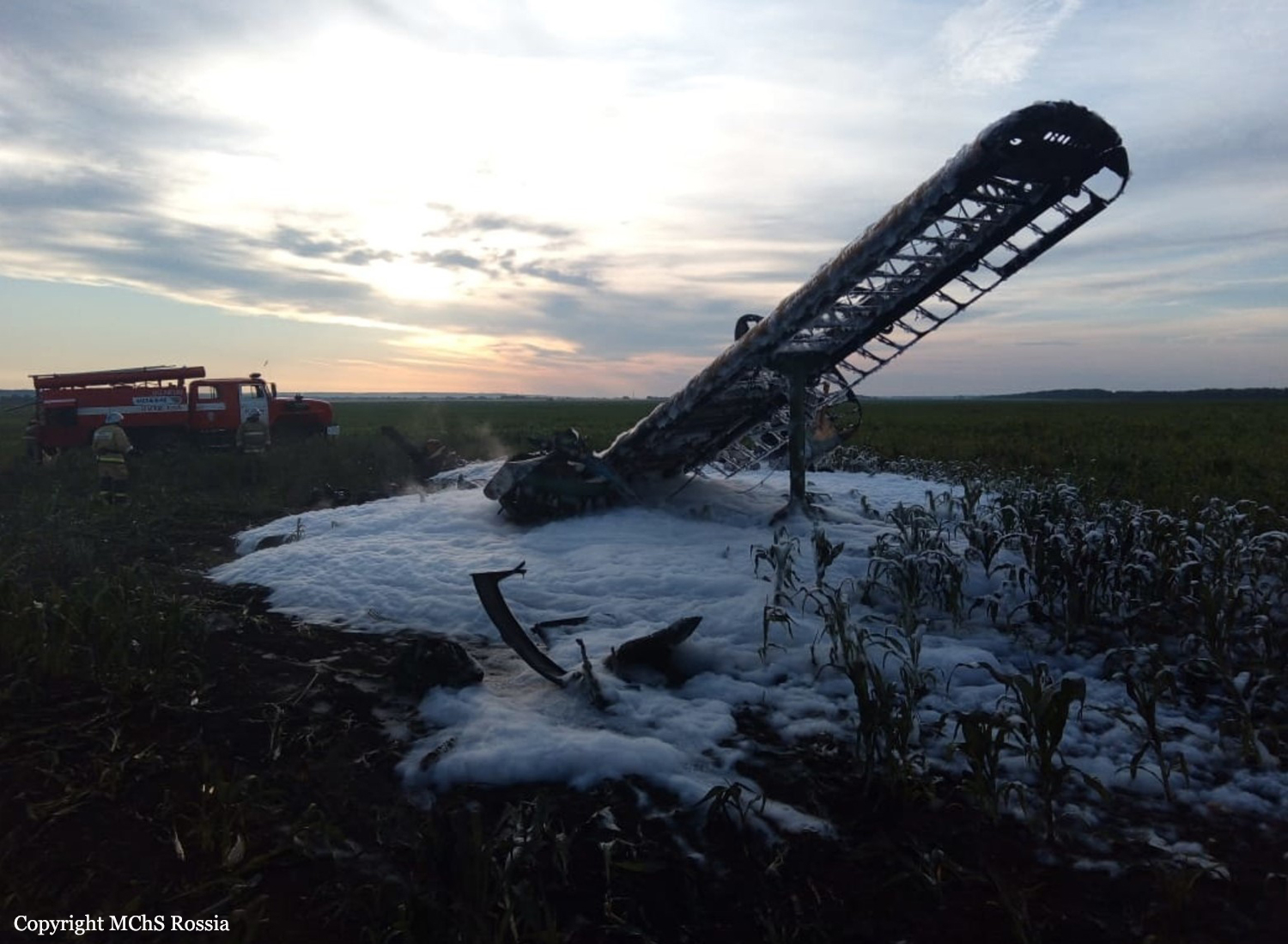
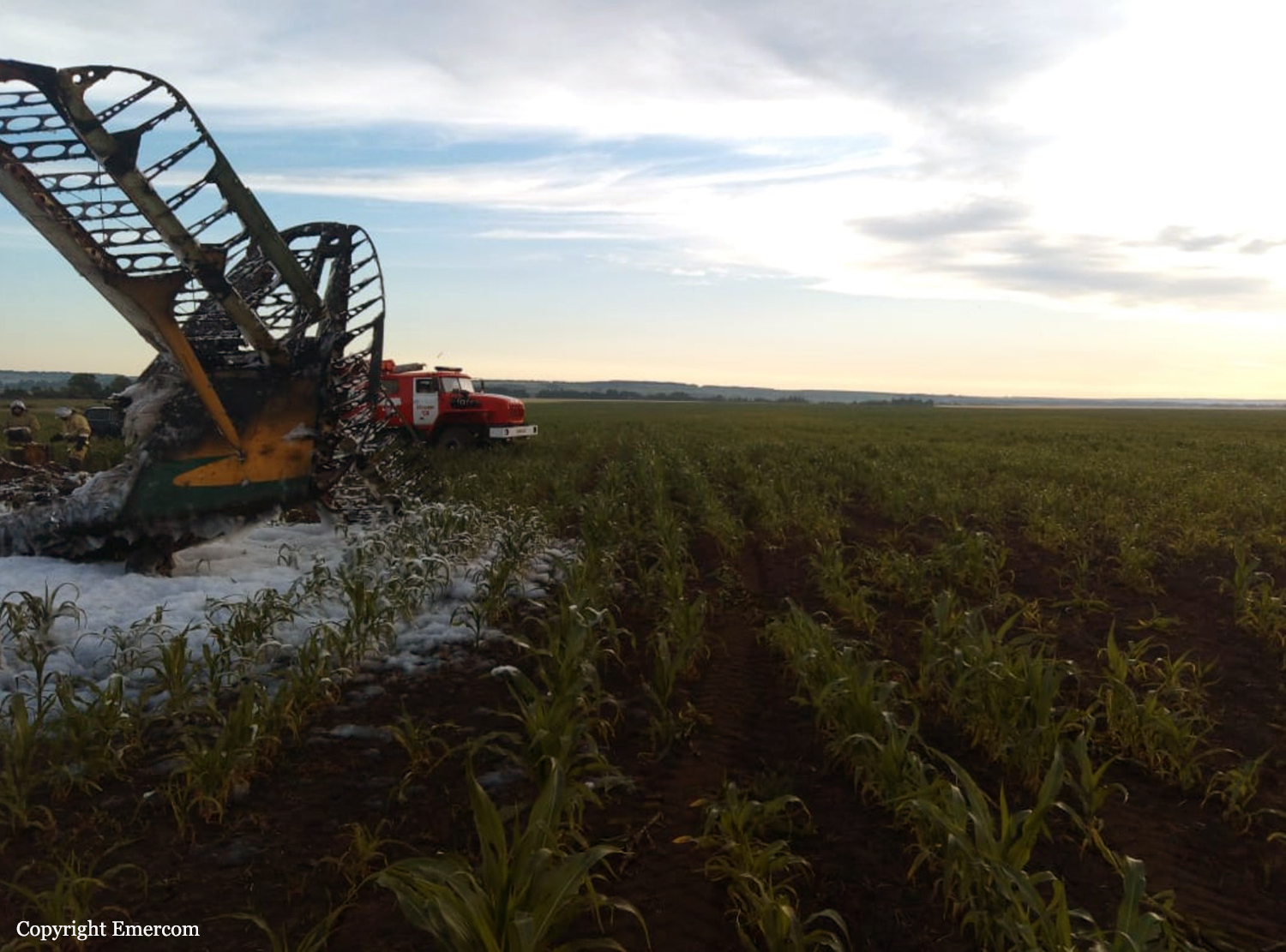
Circumstances:
The single engine aircraft departed Boralday Airport in the suburb of Almaty on an ambulance flight to Kegen with five people on board. Shortly after takeoff, while climbing, the engine suffered a loss of power. The crew attempted an emergency landing when the aircraft lost height and crashed in hilly terrain. All five occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair. Operator reported as Asia Continental Airlines.