Circumstances:
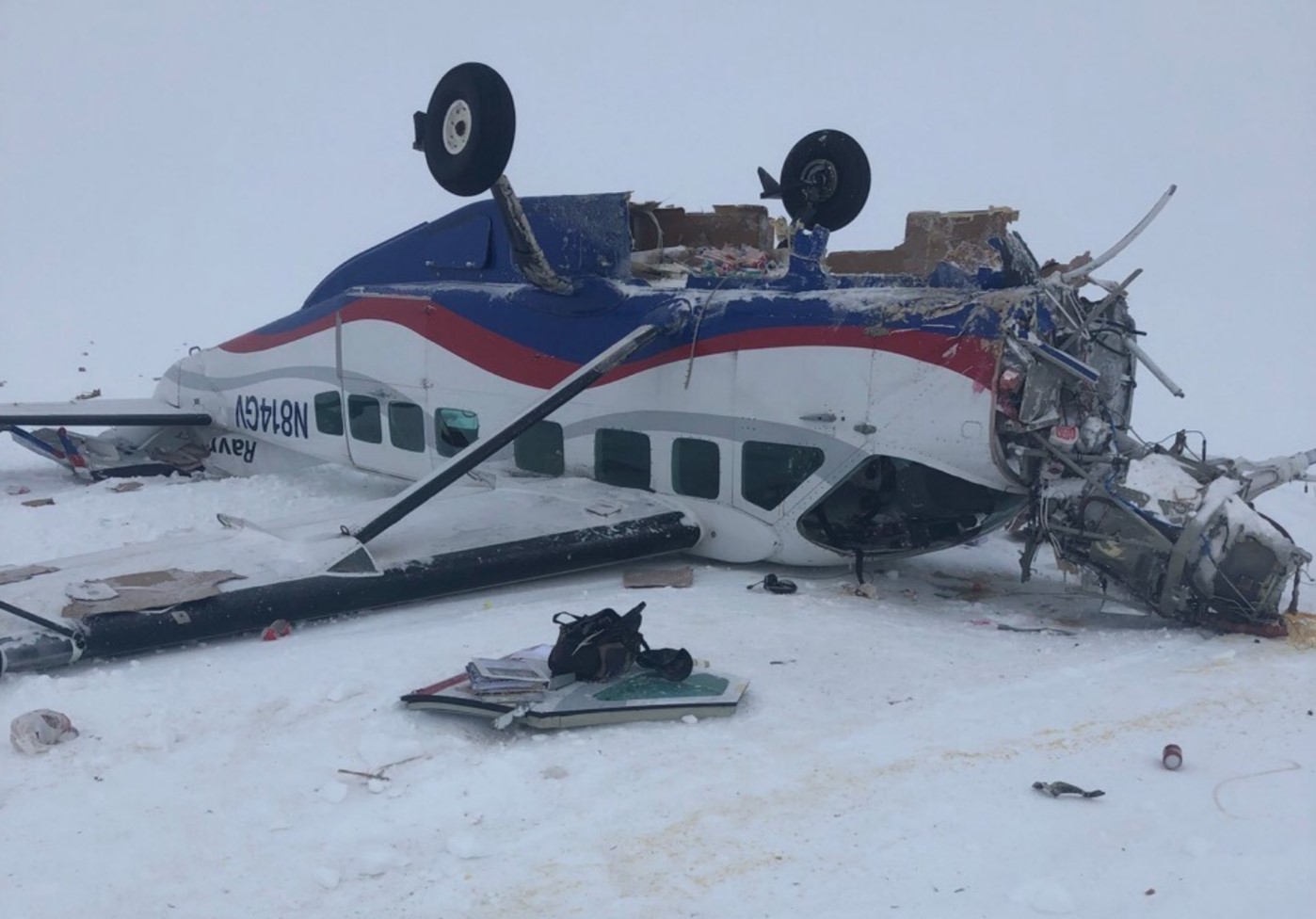
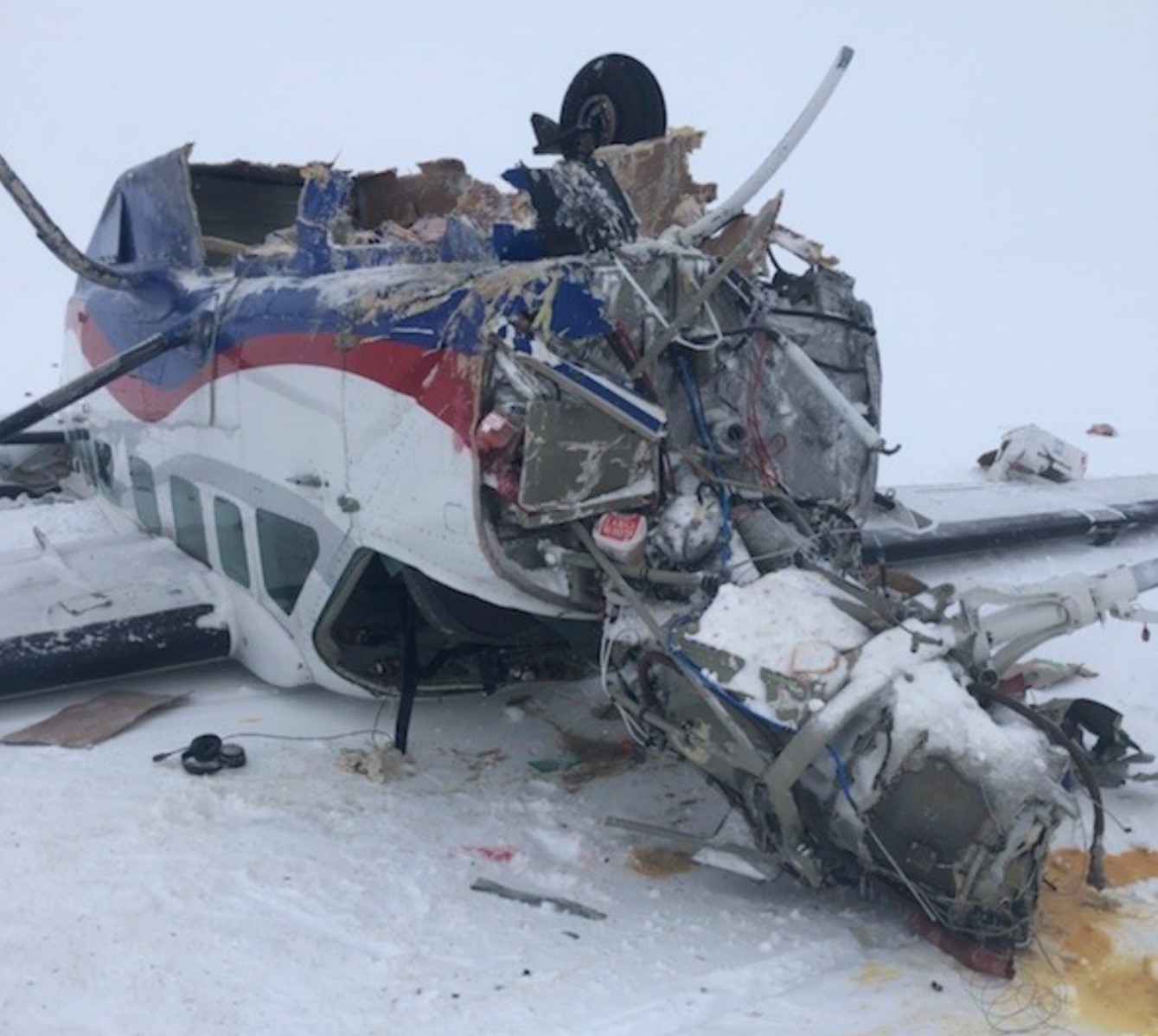
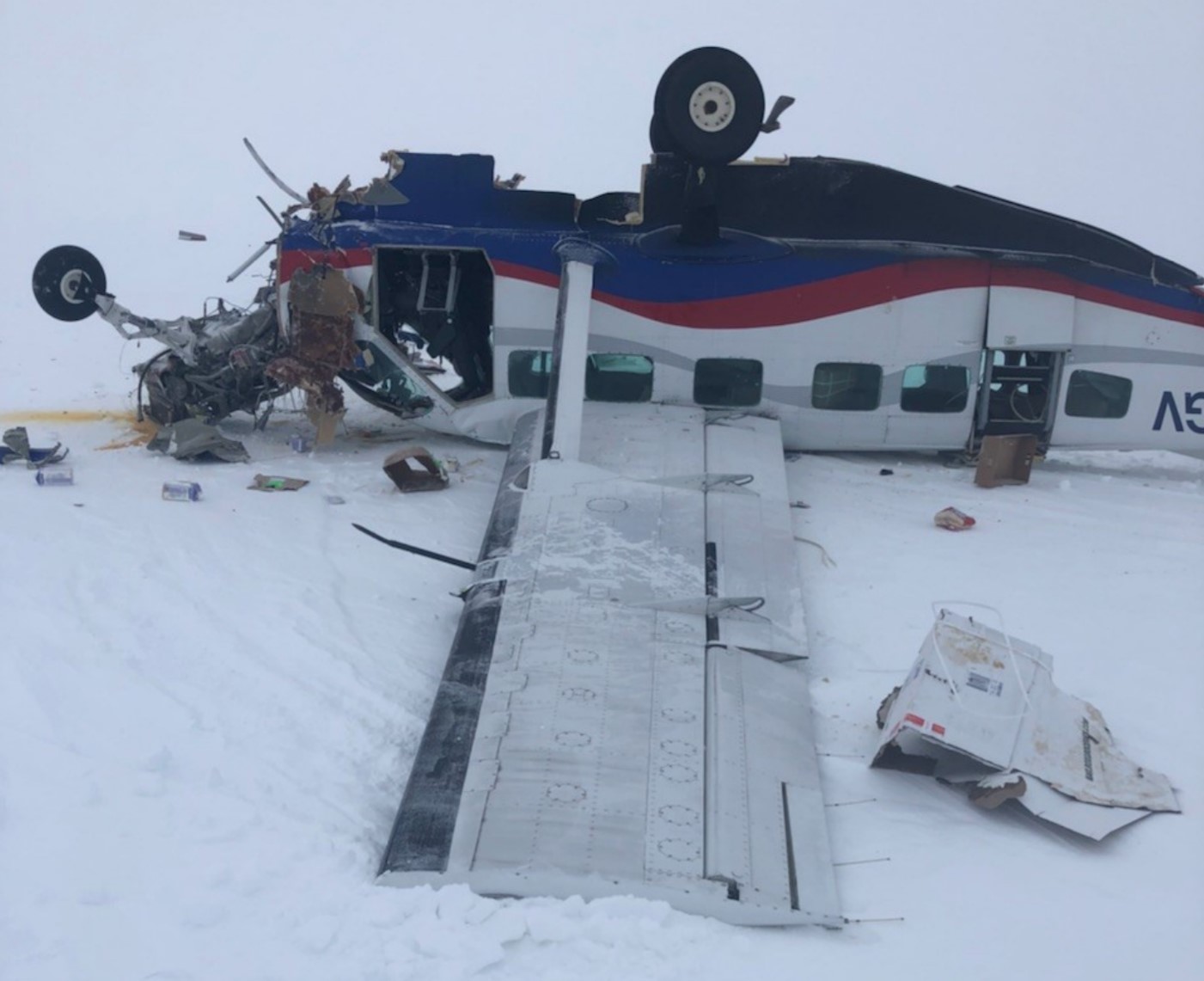
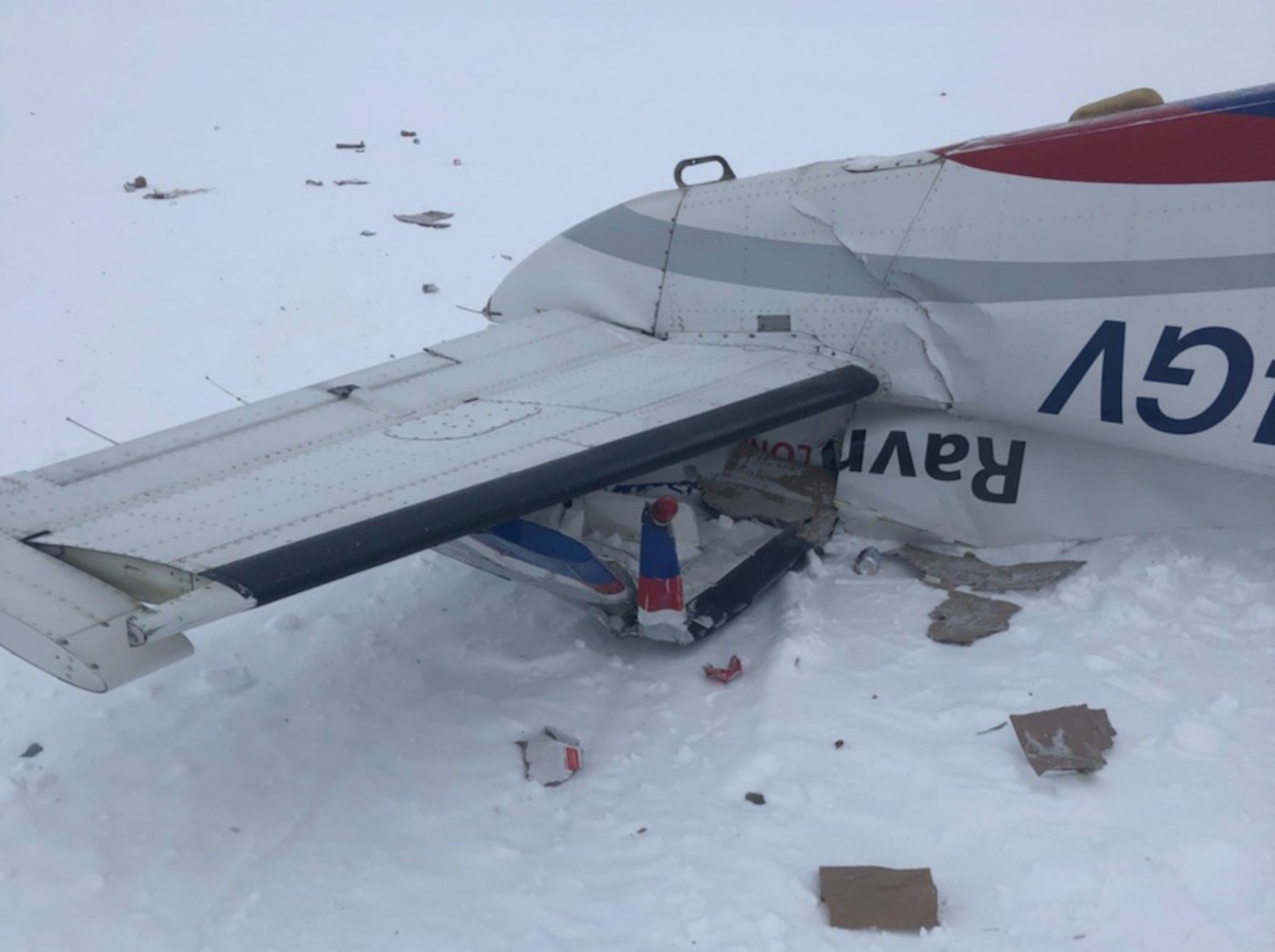
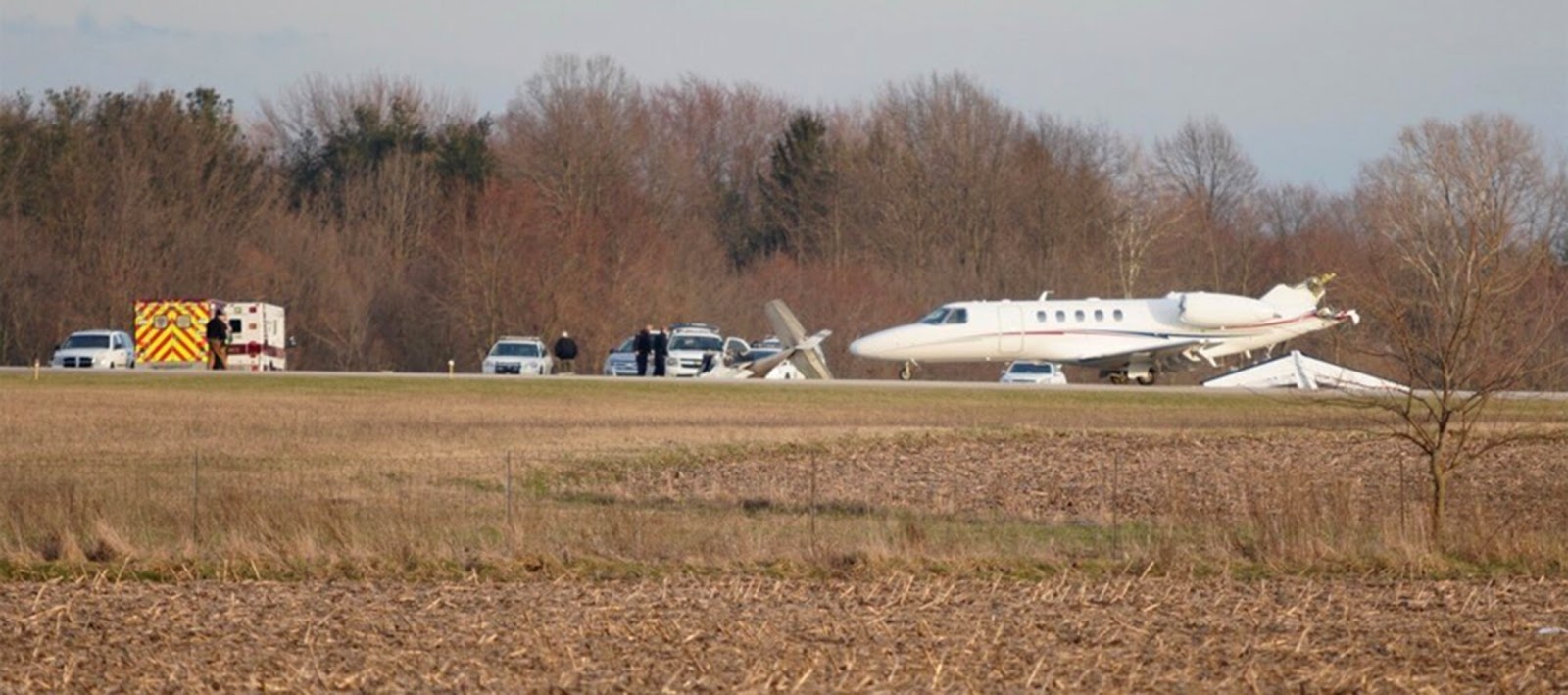
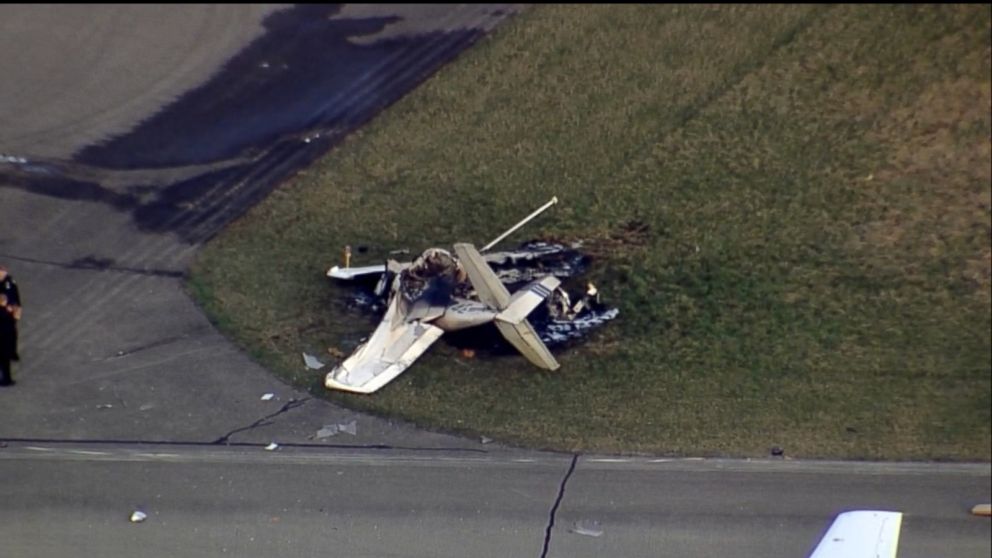
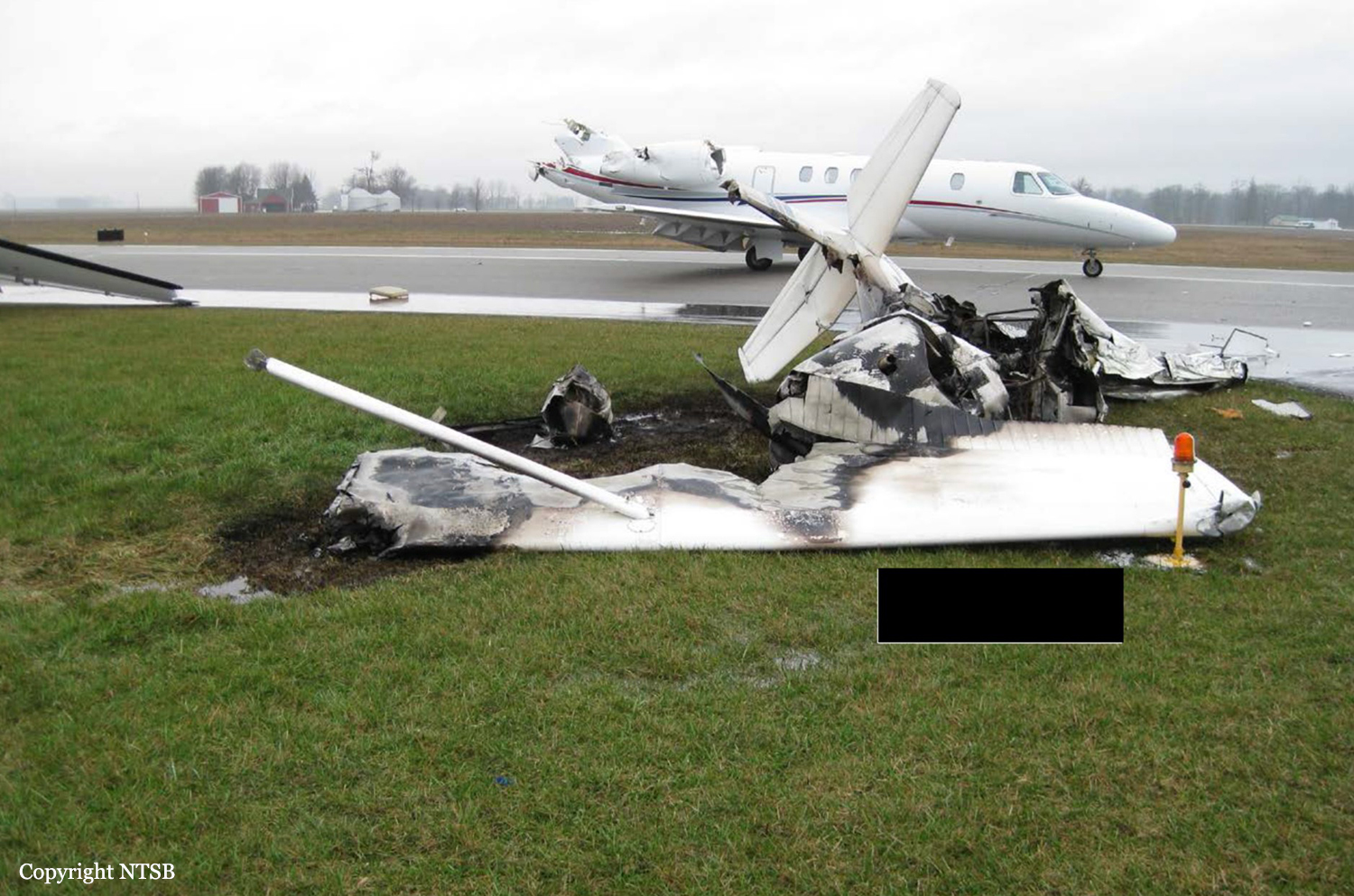
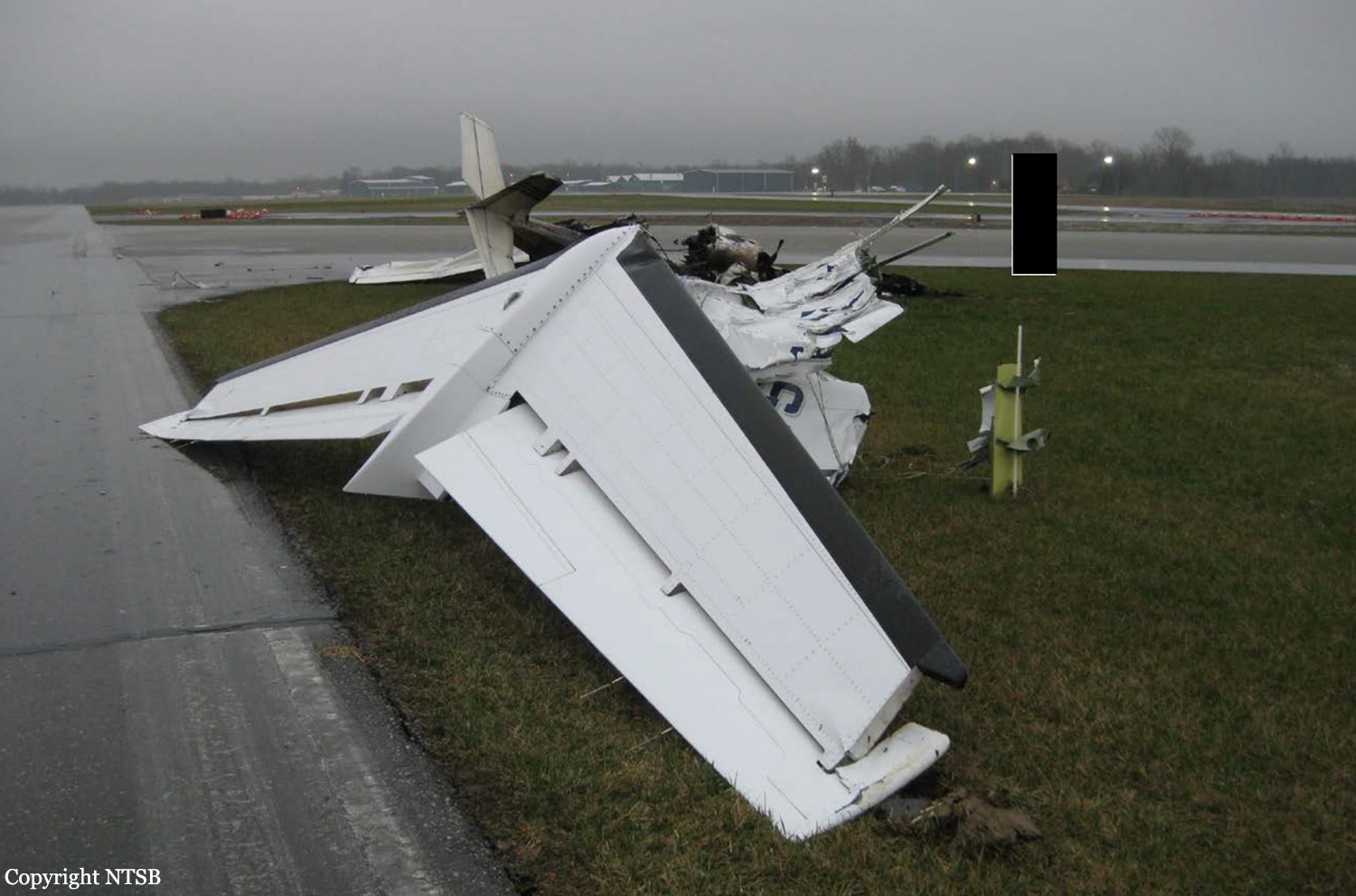
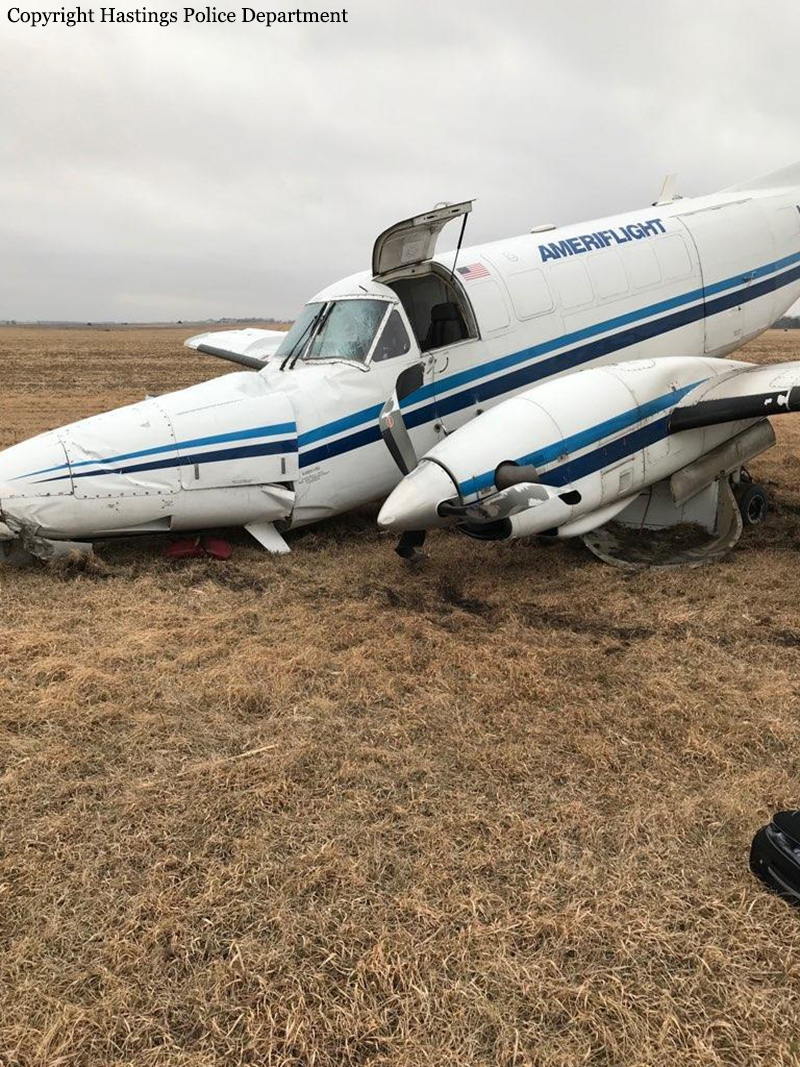
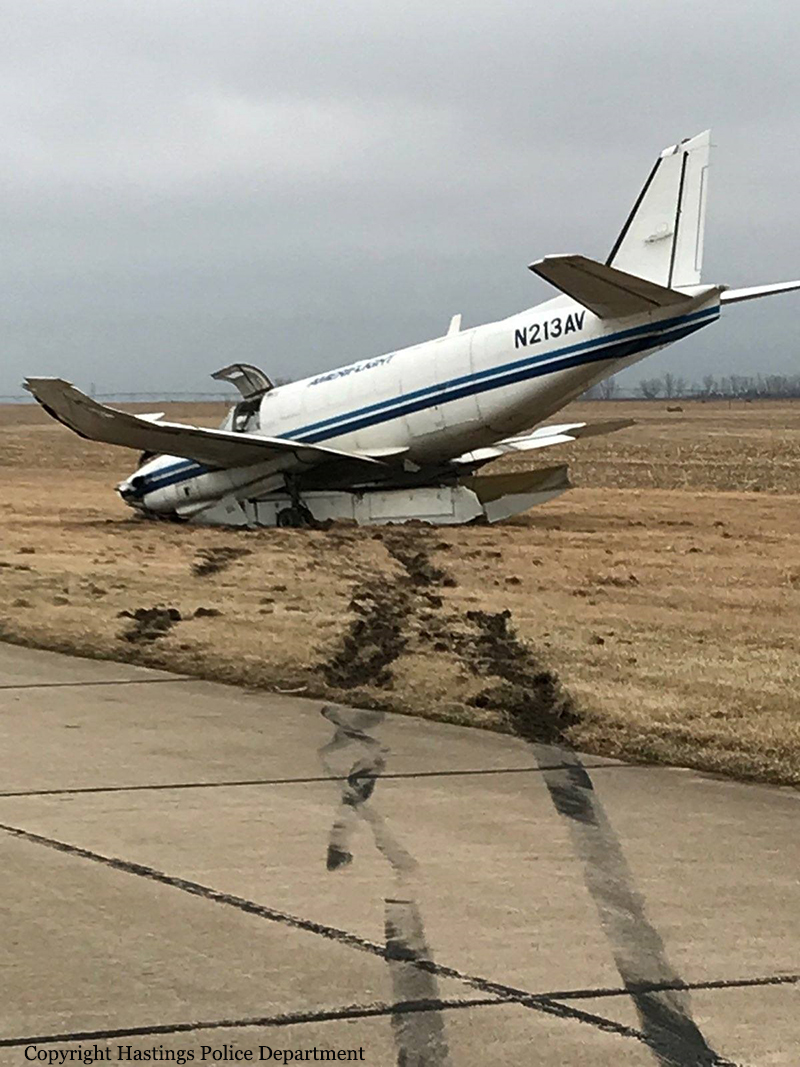
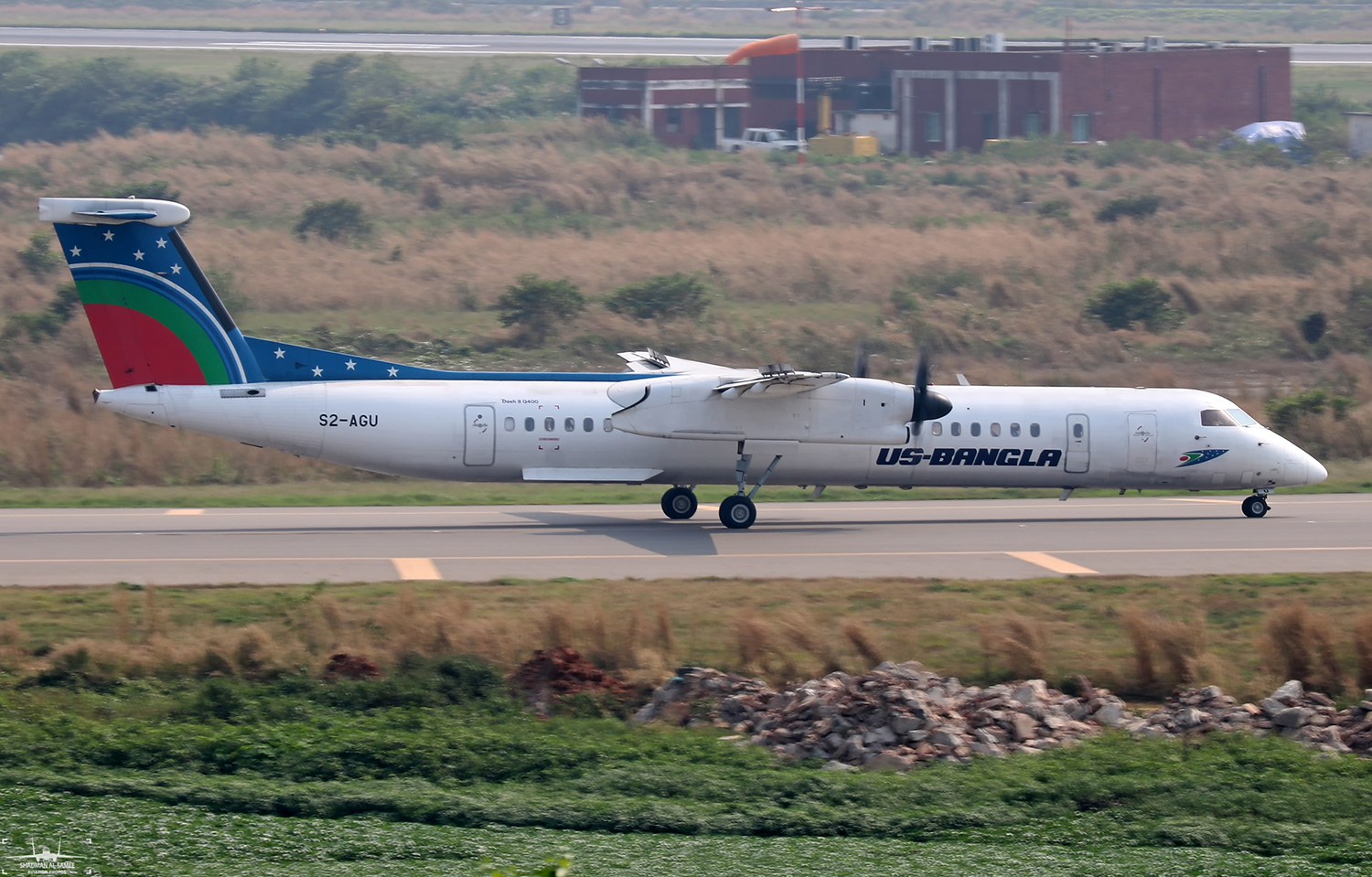
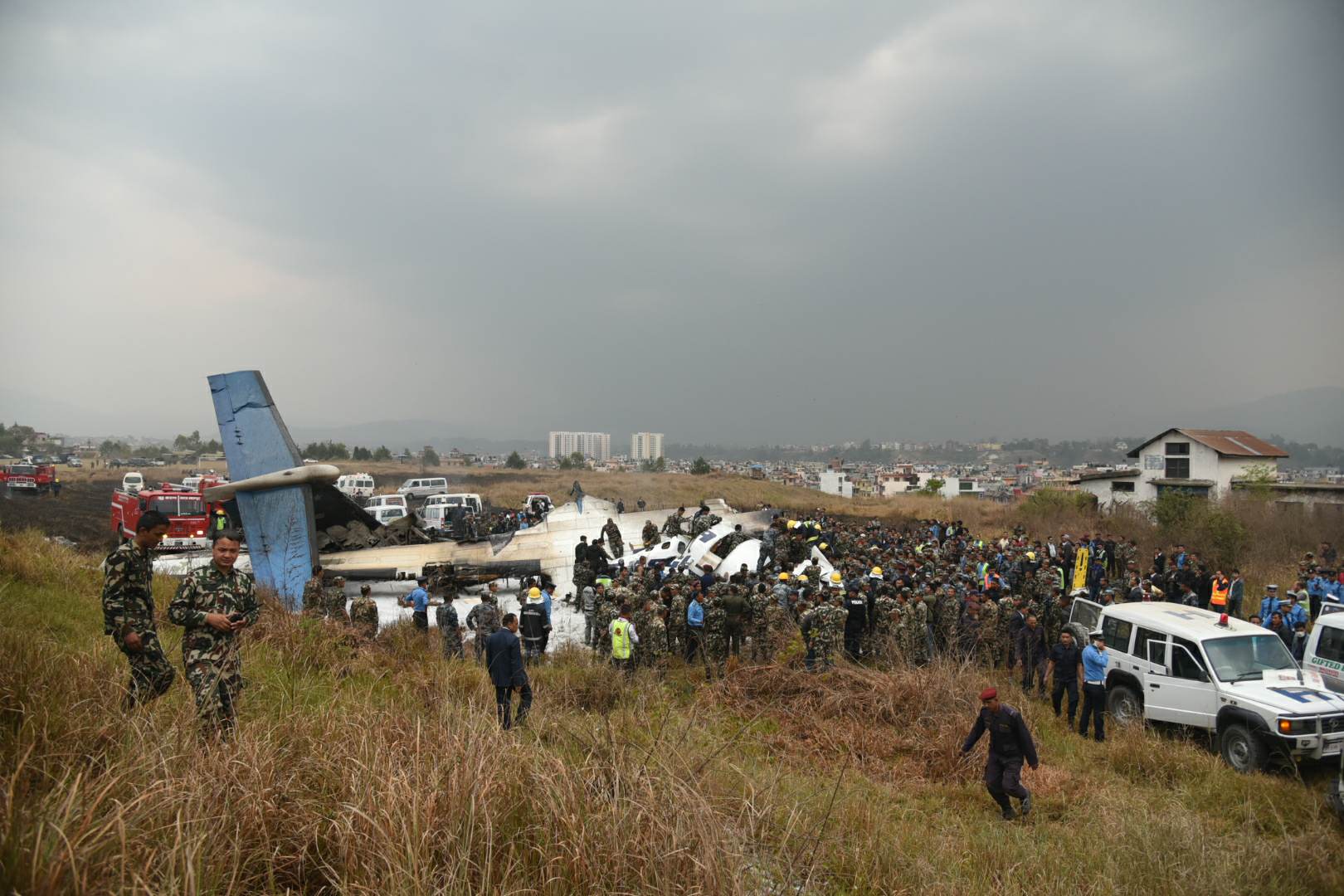
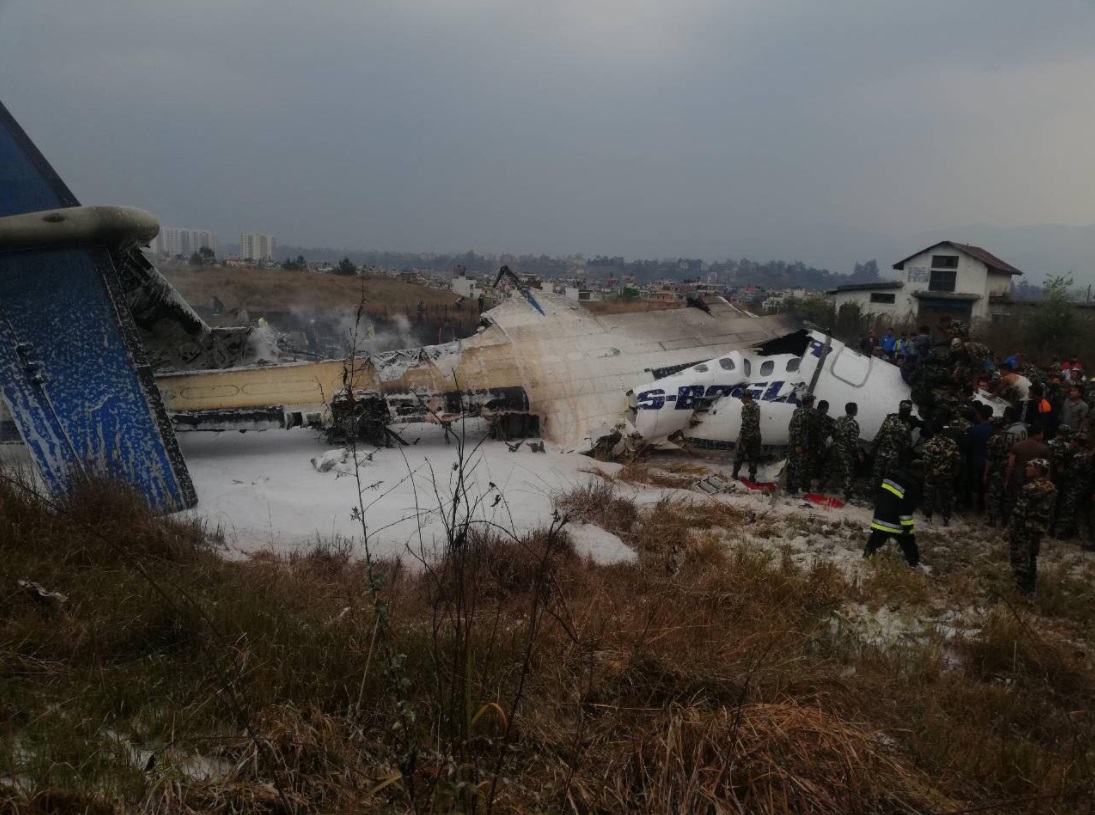
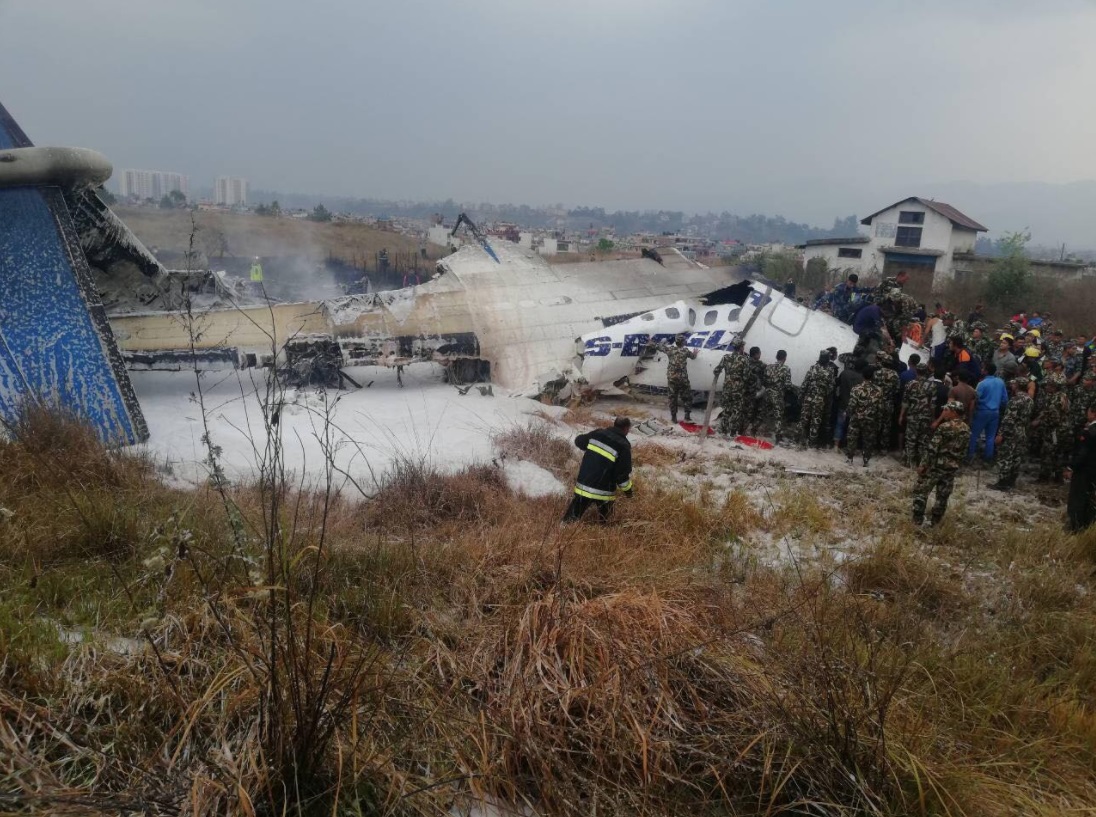
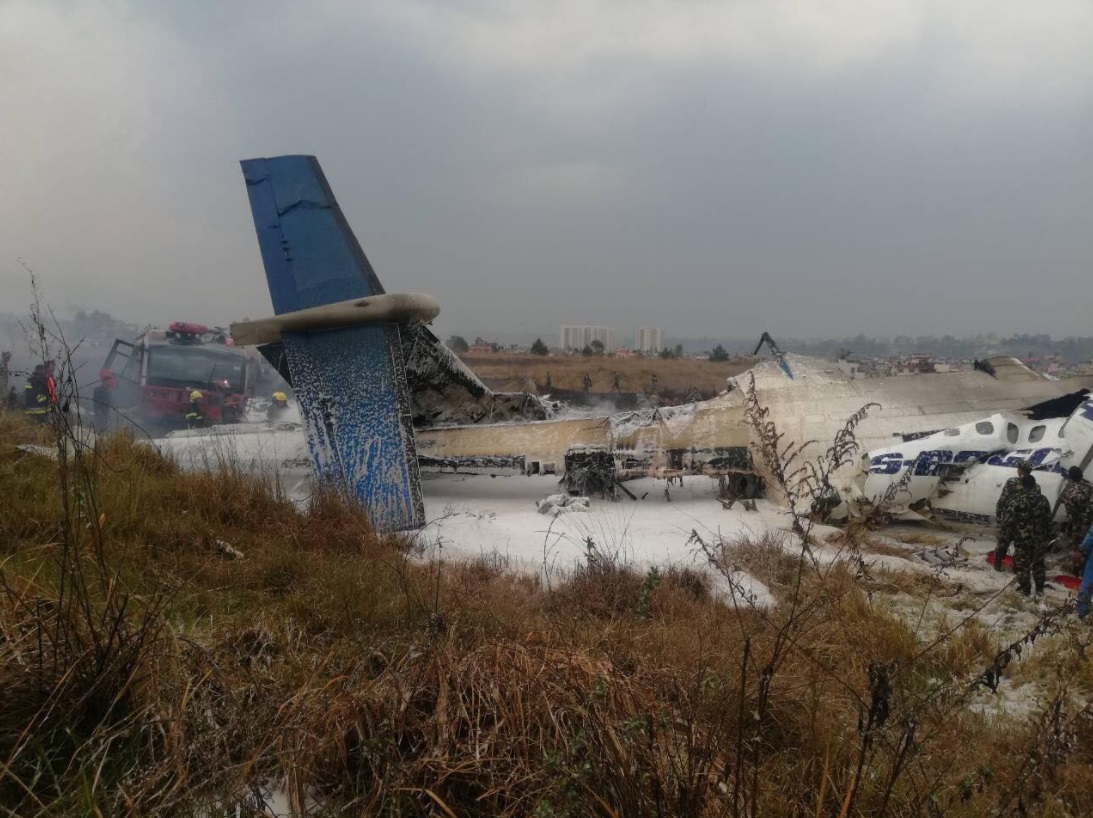
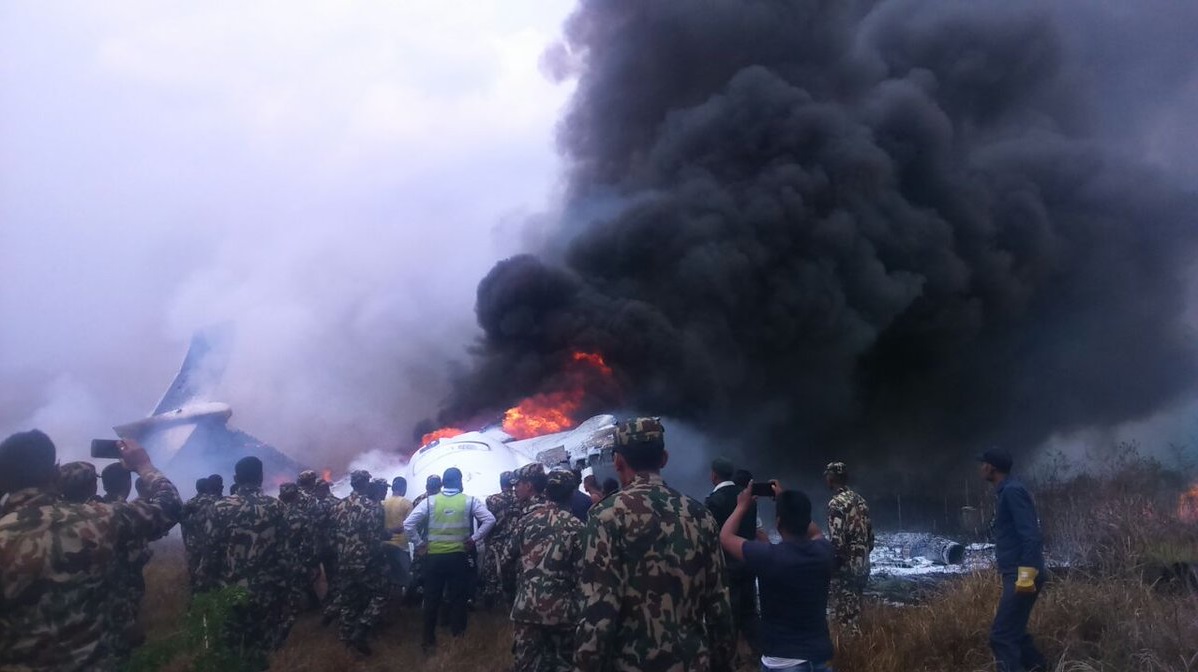
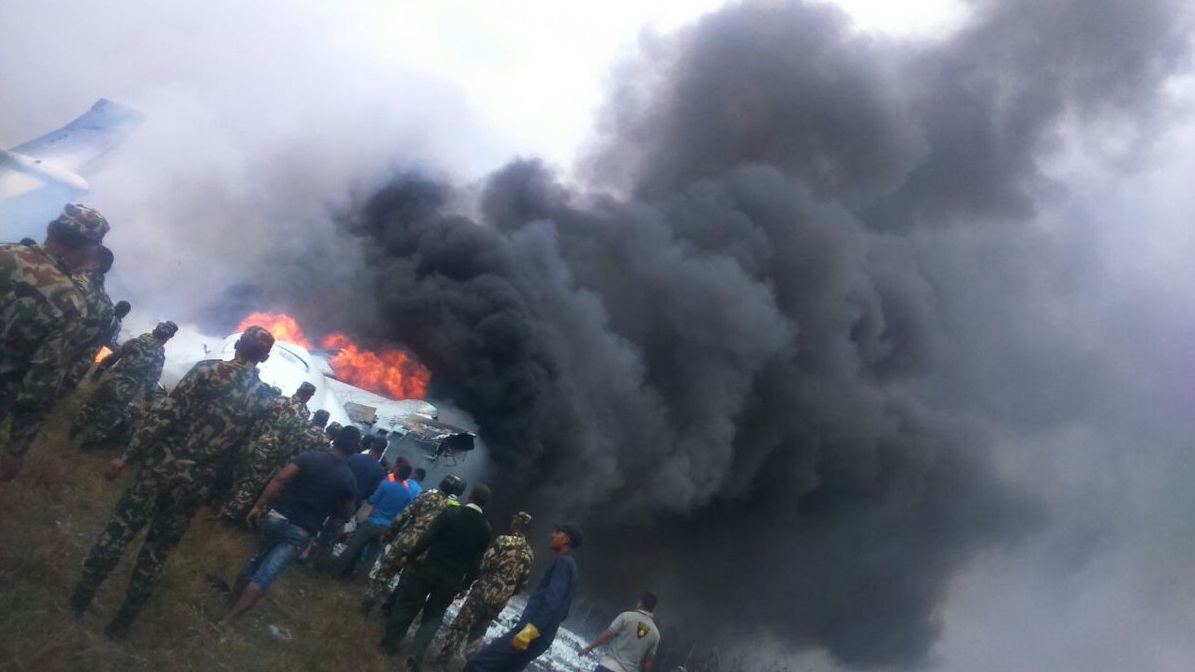
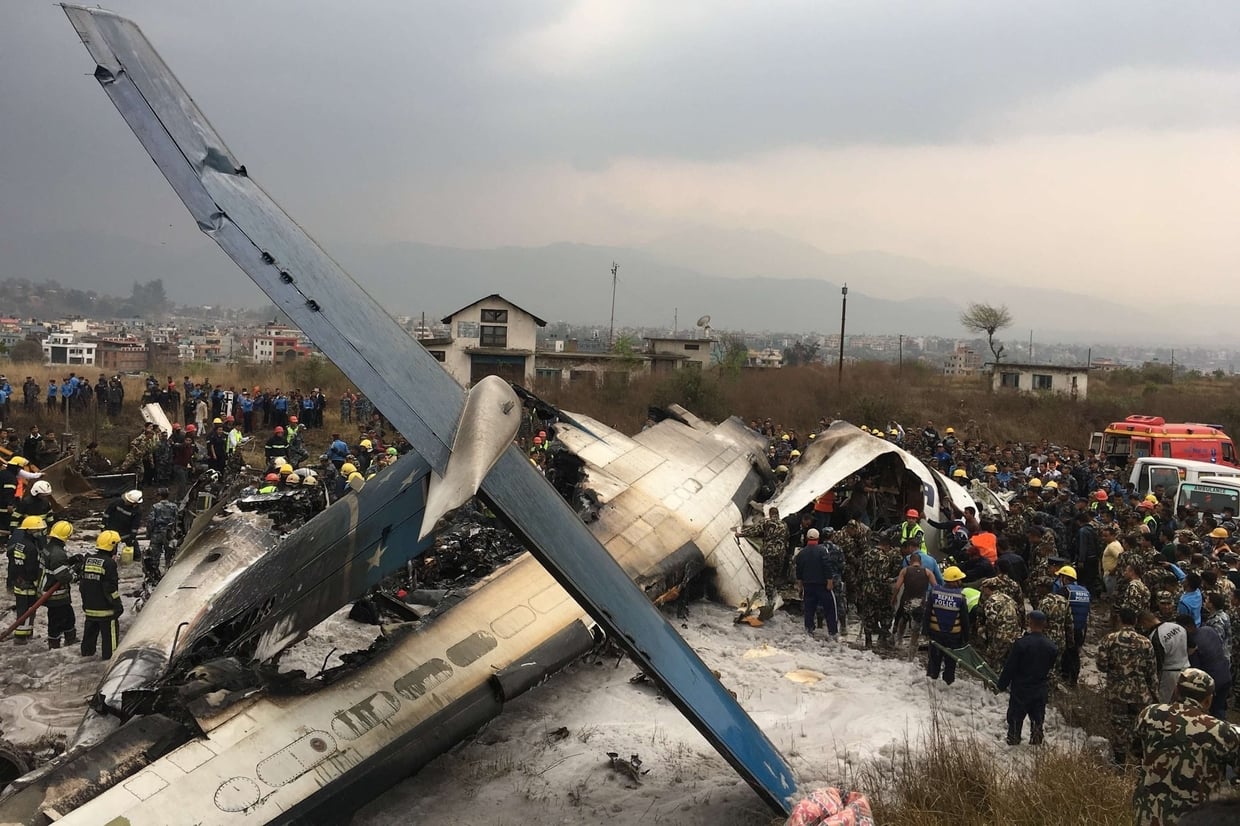
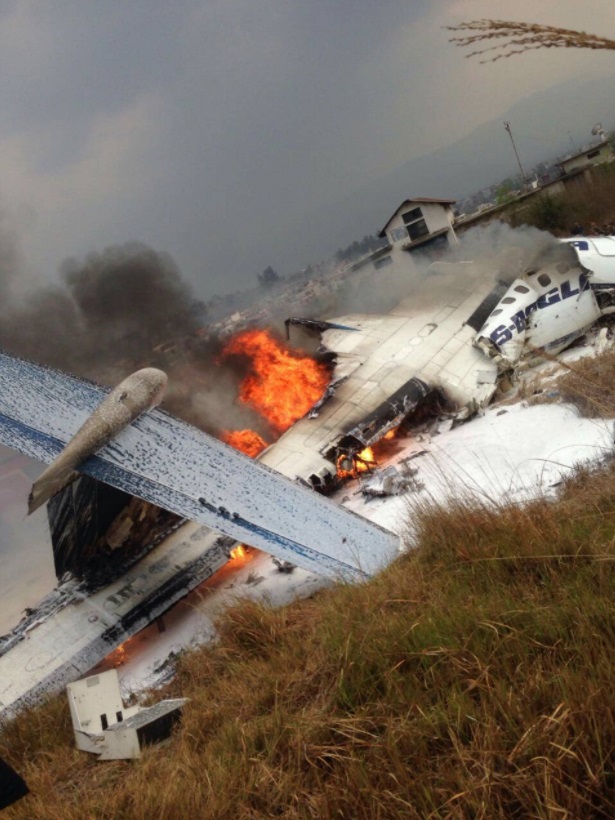
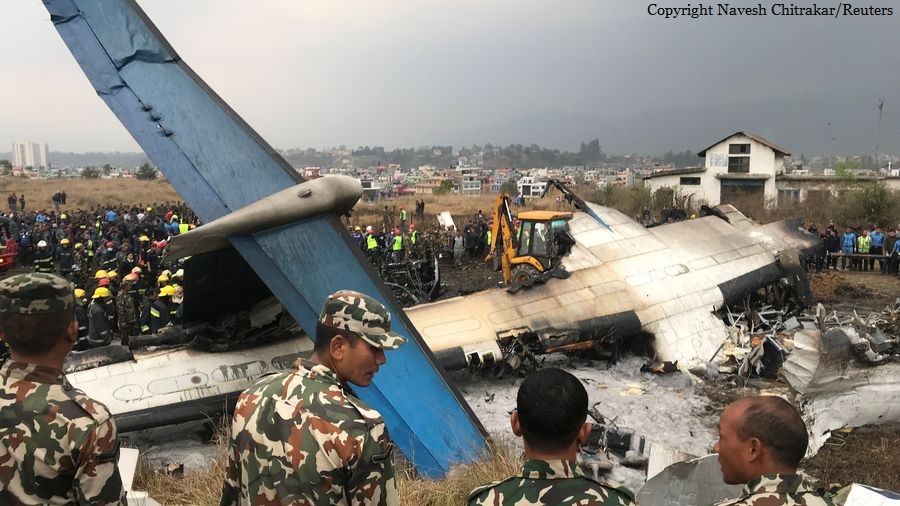
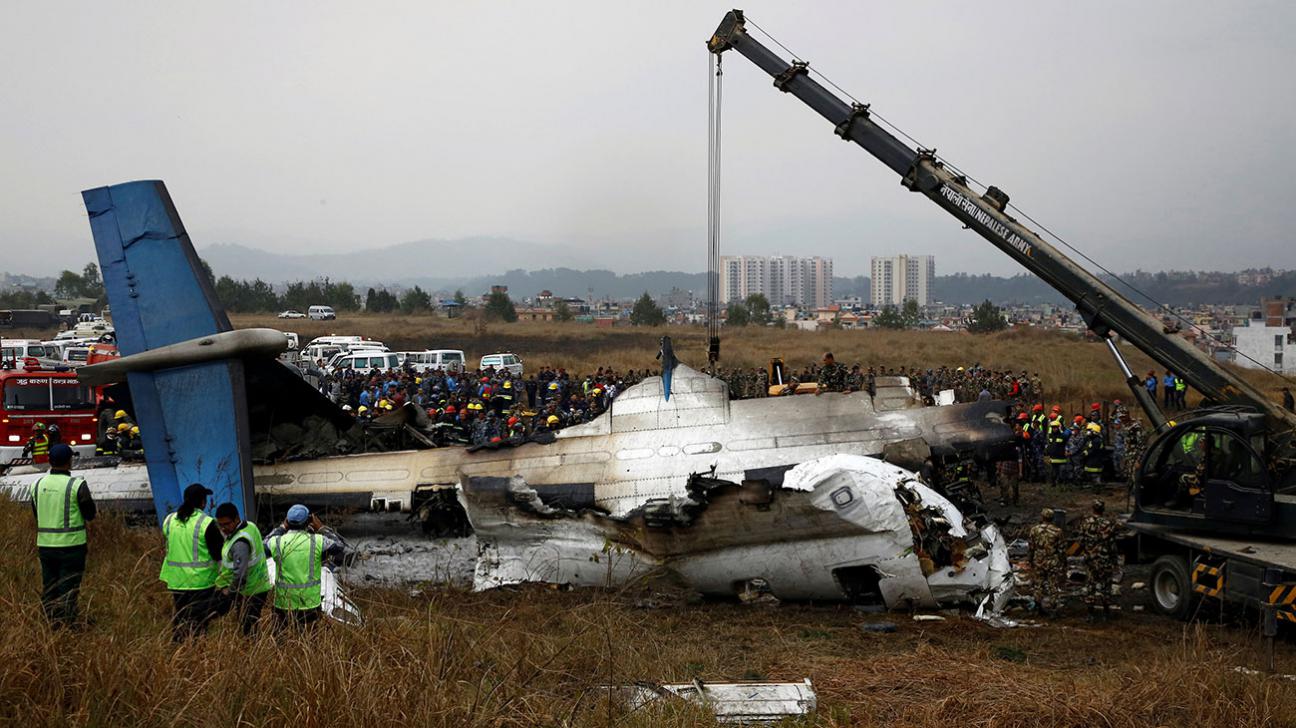
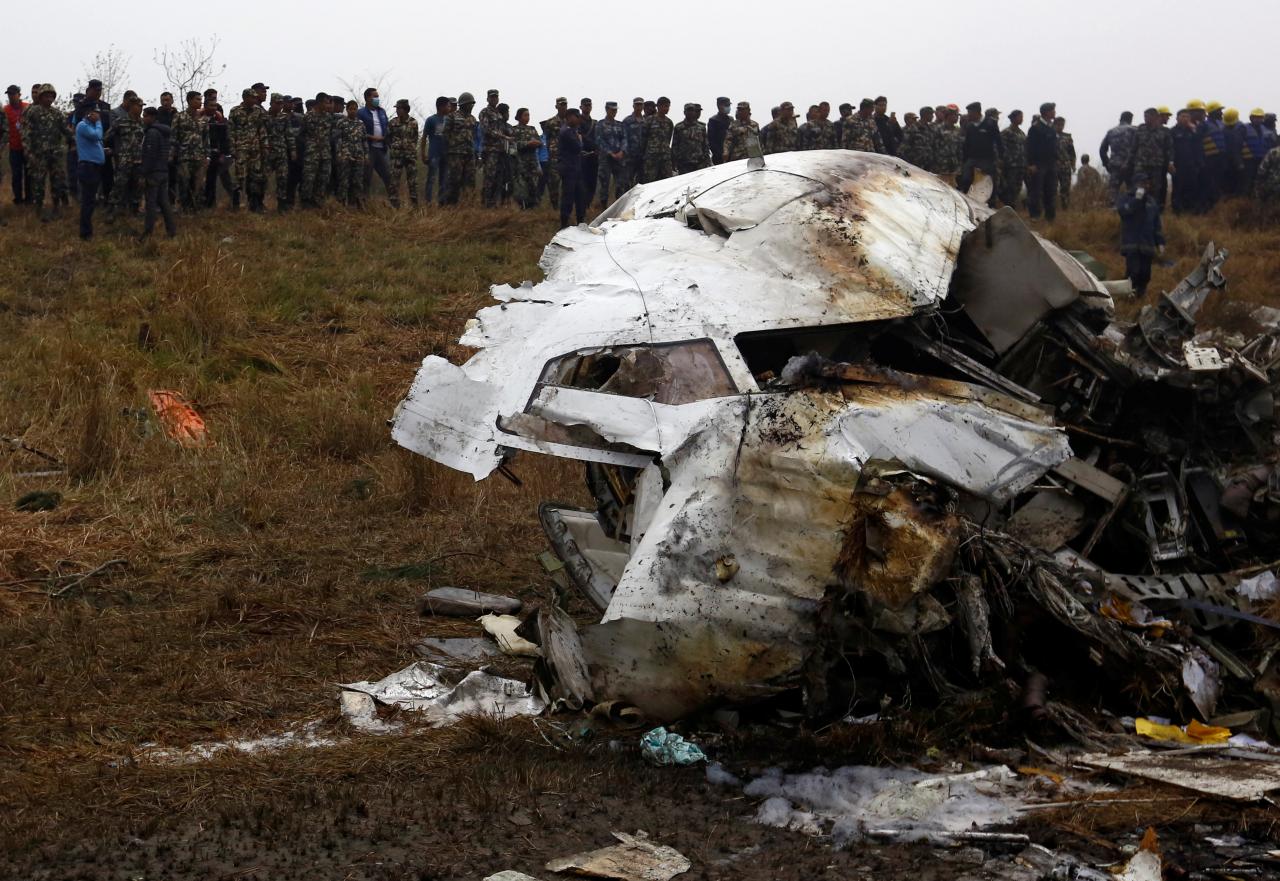
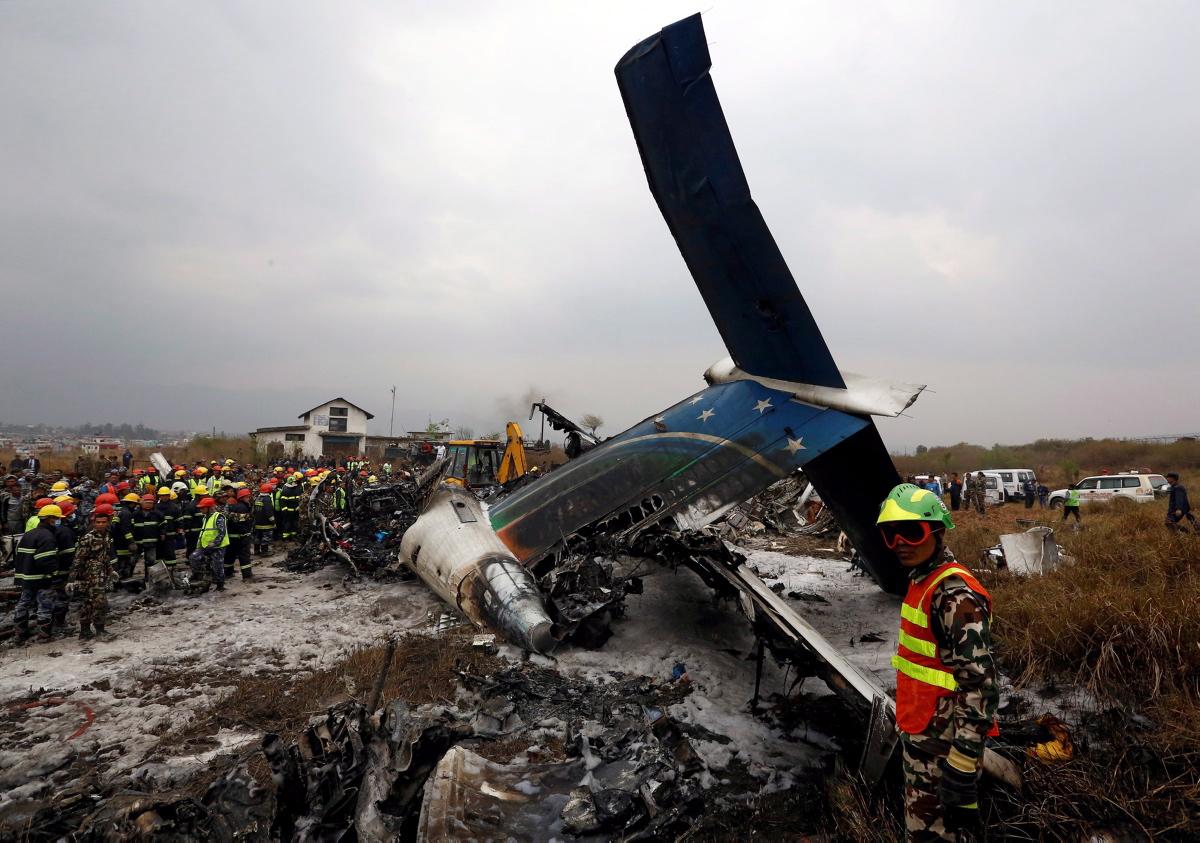
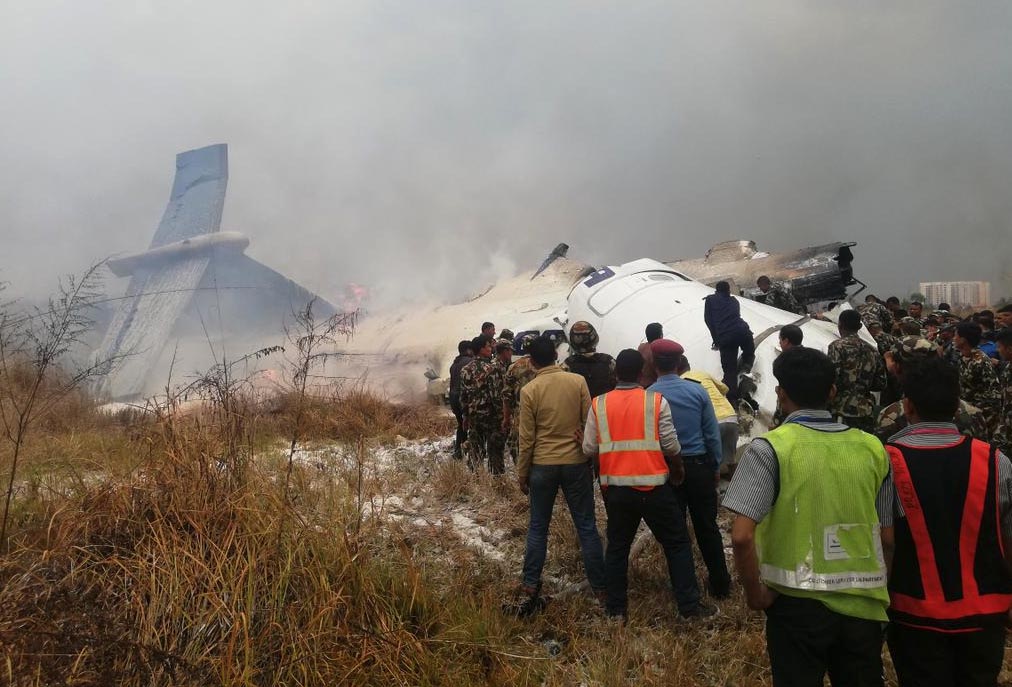
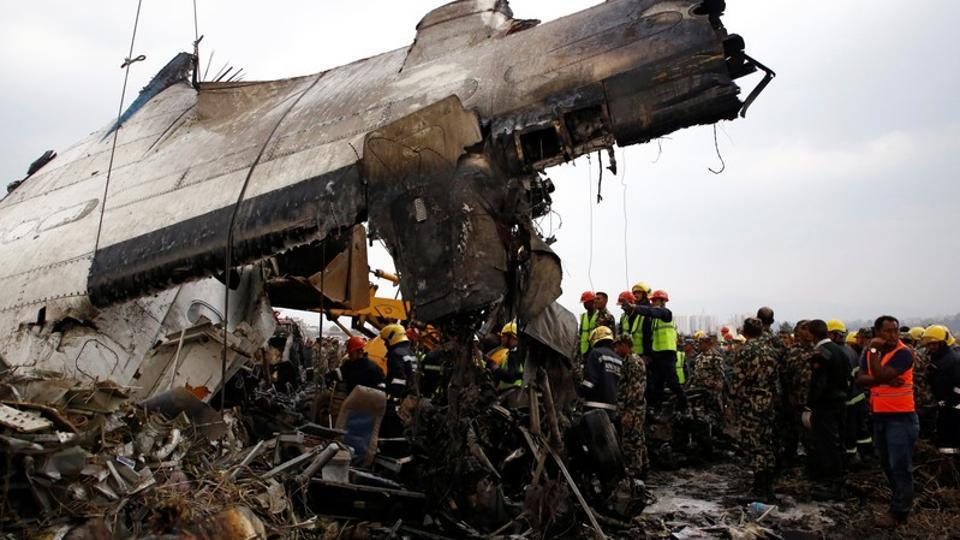
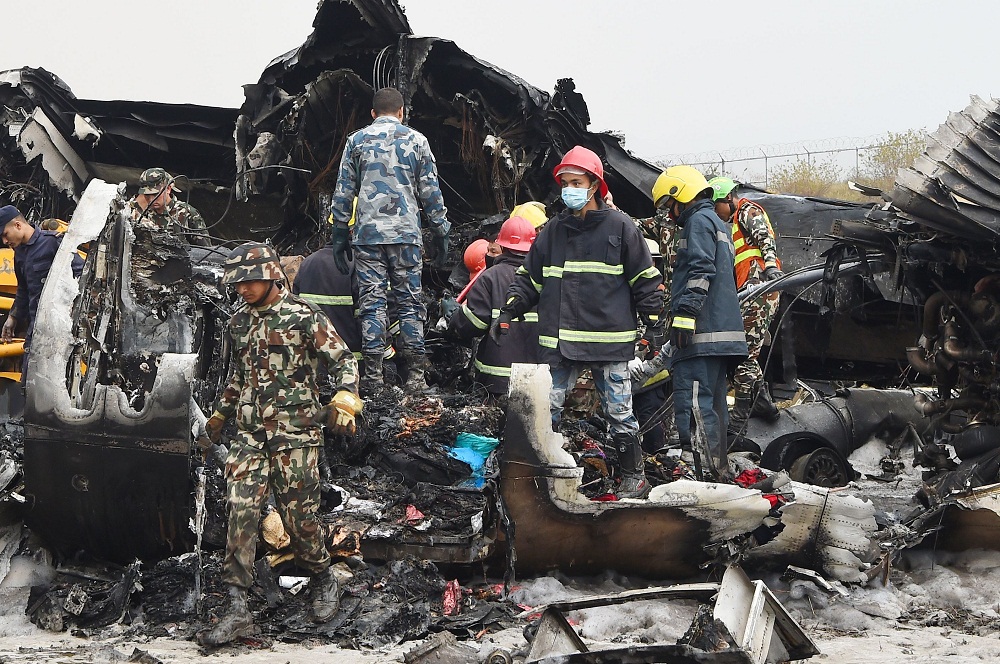
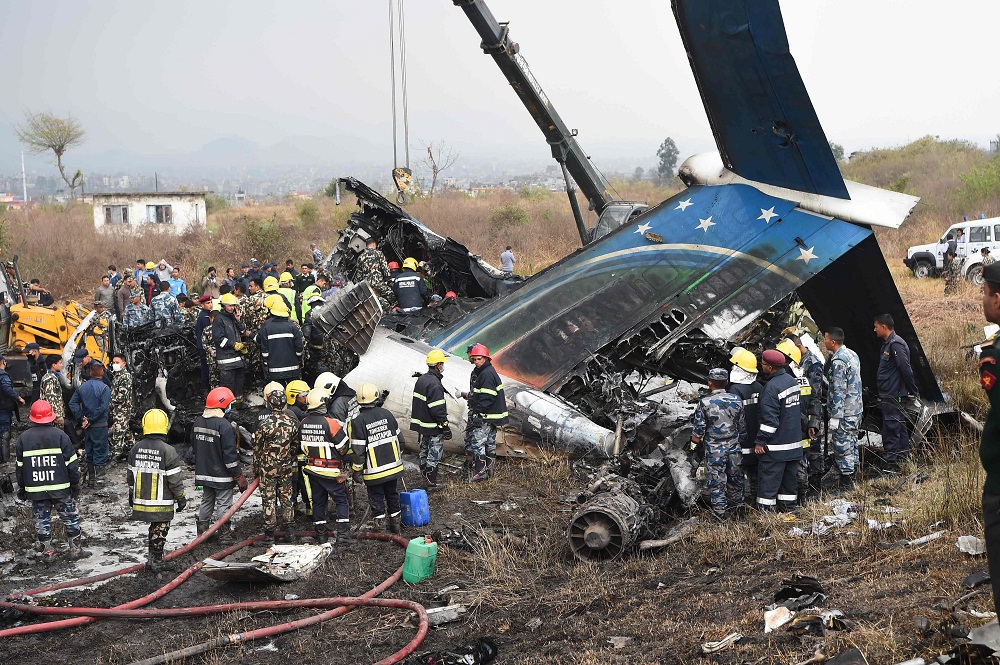
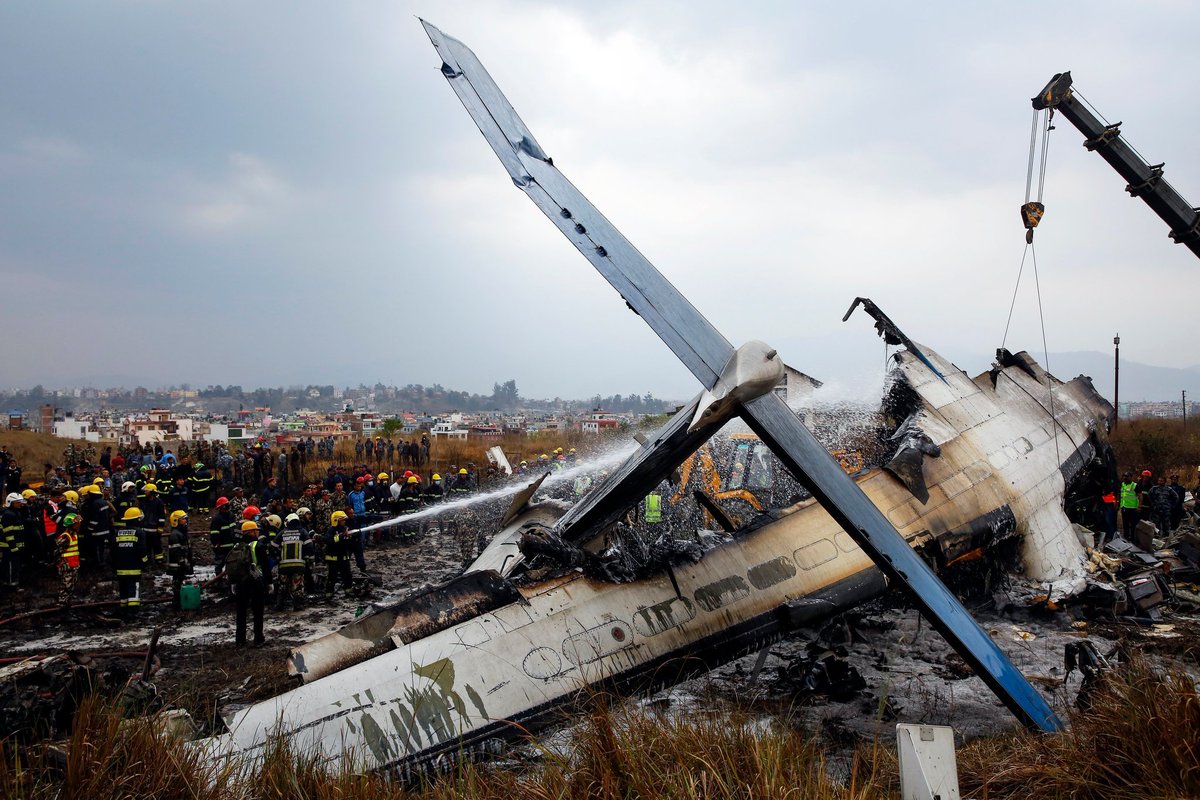
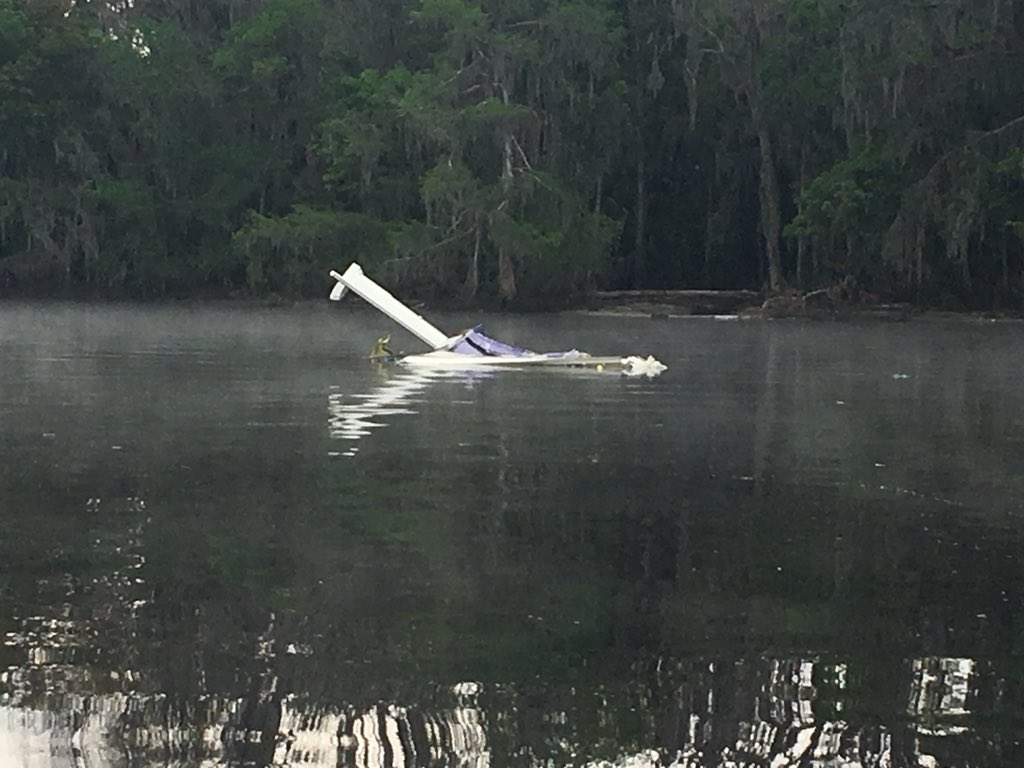
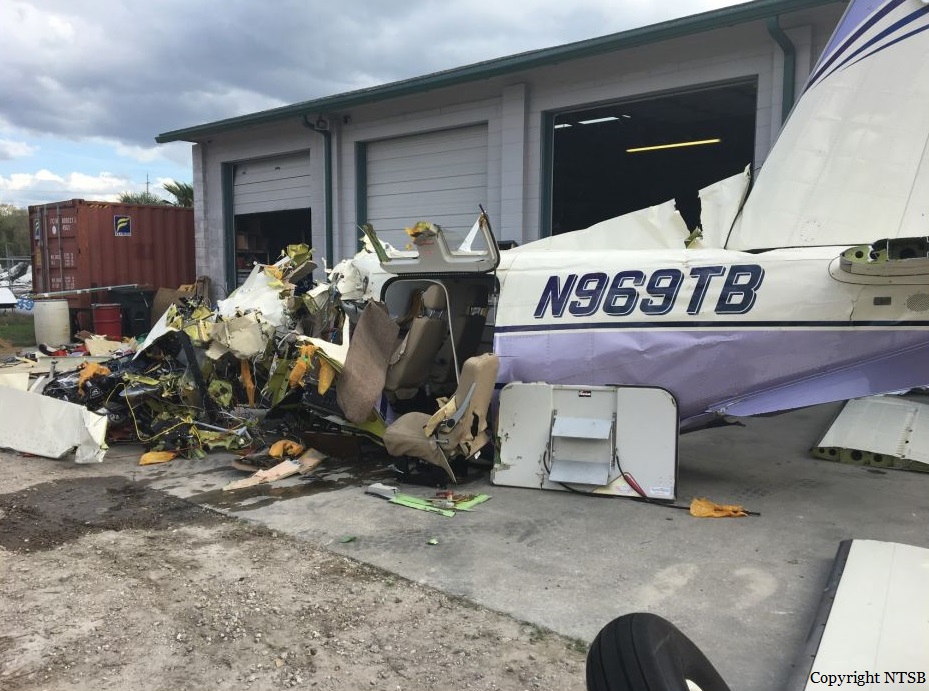
On March 12, 2018, a US Bangla Airlines, Bombardier DHC-8-402, S2-AGU, flight number BS211 departed Hazrat Shahjalal International Airport, Dhaka, Bangladesh at 06:51 UTC on a schedule flight to Tribhuvan International Airport (TIA), Kathmandu, Nepal. The aircraft overflew part of Bangladesh and Indian airspace en-route to Nepal. At 0641, Dhaka Ground Control contacted the aircraft requesting for its Bangladesh ADC number which was recently made mandatory a few weeks ago by Bangladesh authority for all international outbound flights. The crew provided the ADC number as 2177 as provided in the Flight Plan. The Ground Controller again asked the crew if they had the ADC for Bangladesh. At 0642, PIC then contacted the Operations to confirm the Bangladesh ADC number. As per the CVR records, changes in the PIC’s vocal pitch and language used indicated that he was agitated and experiencing high levels of stress at the time while communicating with Dhaka Ground Control and airlines operations. The aircraft finally took off at 0651. As the aircraft was in a climb phase, the PIC overheard a communication between Operations and another US Bangla aircraft regarding the fuel onboard but the PIC without verifying whether the message was meant for him or not, engaged in some unnecessary conversation with the Operations staff. The Captain's vocal pitch and language used indicated that he was very much emotionally disturbed and experiencing high level of stress. The aircraft established its first contact with Kathmandu Control at 0752:04. At 0807:49 the First Officer contacted Kathmandu Control and requested for descent. Kathmandu Control gave descend clearance to FL160 with an estimated approach time of 0826 which was acknowledged by the First Officer. At 0810 the flight was handed over to Kathmandu Approach. At 0811, Kathmandu Approach instructed the aircraft to descend to 13,500 ft and hold over GURAS. The crew inserted the HOLD in the Flight Management System. At 0813:41 Kathmandu Approach further instructed the aircraft to reduce its speed and descend to 12500 ft. At 0816 Kathmandu Approach instructed the aircraft to further descend to 11500 ft., and cleared for VOR approach RWY 02 maintaining minimum approach speed. Both the crew forgot to cancel the hold on the FMS as they were engaged in some unnecessary conversation. Upon reaching GURAS, the aircraft turned left to enter the holding pattern over GURAS, it was noticed by PIC and FO and immediately PIC made correction and simultaneously this was alerted to the crew by Approach Control also. Once realizing the aircraft flying pattern and ATC clearance, the PIC immediately selected a heading of 027° which was just 5° of interception angle to intercept the desired radial of 202° inbound to KTM. The spot wind recorded was westerly at 28kt. The aircraft continued approach on heading mode and crossed radial 202° at 7 DME of KTM VOR. The aircraft then continued on the same heading of 027° and deviated to the right of the final approach course. Having deviated to the right of the final approach path, the aircraft reached about 2-3 NM North east of the KTM VOR and continued to fly further northeast. At 0827, Kathmandu Tower (TWR) alerted the crew that the landing clearance was given for RWY 02 but the aircraft was proceeding towards RWY 20. At 0829, Tower Controller asked the crew of their intention to which the PIC replied that they would be landing on RWY 02. The aircraft then made an orbit to the right. The Controller instructed the aircraft to join downwind for RWY 02 and report when sighting another Buddha Air aircraft which was already on final for RWY 02. The aircraft instead of joining downwind leg for RWY 02, continued on the orbit to the right on a westerly heading towards Northwest of RW 20. The controller instructed the aircraft to remain clear of RWY 20 and continue to hold at present position as Buddha air aircraft was landing at RW 02 (from opposite side) at that time. After the landing of Buddha Air aircraft, Tower Controller, at 08:32 UTC gave choice to BS211 to land either at RW 20 or 02 but the aircraft again made an orbit to the right, this time northwest of RWY 20. While continuing with the turn through Southeastern direction, the PIC reported that he had the runway in sight and requested tower for clearance to land. The Tower Controller cleared the aircraft to land but when the aircraft was still turning for the RWY it approached very close to the threshold for RWY 20 on a westerly heading and not aligned with the runway. At 08:33:27 UTC, spotting the aircraft maneuvering at very close proximity of the ground and not aligned with the RWY. Alarmed by the situation, the Tower Controller hurriedly cancelled the landing clearance of the aircraft by saying, "Takeoff clearance cancelled". Within the next 15-20 seconds, the aircraft pulled up in westerly direction and with very high bank angle turned left and flew over the western area of the domestic apron, continued on a southeasterly heading past the ATC Tower and further continued at a very low height, flew over the domestic southern apron area and finally attempted to align with the runway 20 to land. During this process, while the aircraft was turning inwards and momentarily headed towards the control tower, the tower controllers ducked down out of fear that the aircraft might hit the tower building. Missing the control tower, when the aircraft further turned towards the taxi track aiming for the runway through a right reversal turn, the tower controller made a transmission by saying, "BS 211, I say again...". At 08:34 UTC the aircraft touched down 1700 meters down the threshold with a bank angle of about 15 degrees and an angle of about 25 degrees with the runway axis (approximately heading Southeast) and to the left of the center line of runway 20, then veered southeast out of the runway through the inner perimeter fence along the rough down slope and finally stopped about 442 meters southeast from the first touchdown point on the runway. All four crew members (2 cockpit crew and 2 cabin crew) and 45 out of the 67 passengers onboard the aircraft were killed in the accident. Two more passengers succumbed to injury later in hospital during course of treatment. The aircraft caught fire after 6 seconds of touchdown which engulfed major portions of the aircraft.
Probable cause:
The Accident Investigation Commission determines that the probable cause of the accident is due to disorientation and a complete loss of situational awareness in the part of crewmember. Contributing to this the aircraft was offset to the proper approach path that led to maneuvers in a very dangerous and unsafe attitude to align with the runway. Landing was completed in a sheer desperation after sighting the runway, at very close proximity and very low altitude. There was no attempt made to carry out a go around, when a go around seemed possible until the last instant before touchdown on the runway.
The following contributing factors were reported:
- Improper timing of the pre-flight briefing and the commencement of the flight departure in which the operational pre-flight briefing was given in early morning but the flight departure time was around noon and there were four domestic short flights scheduled in between.
- The PIC, who was the pilot flying, seemed to be under stress due to behavior of a particular female colleague in the company and lack of sleep the preceding night.
- A very steep gradient between the crew.
- Flight crew not having practiced visual approach for runway 20 in the simulator.
- A poor CRM between the crew.
An investigation into the captain's behaviour showed that he had history of depression while serving in the Bangladesh Air Force in 1993 and was removed from active duty after evaluation by a psychiatrist. He was re-evaluated by a psychiatrist in January 2002 and was declared to be fit for flying. Examinations in successive annual medical checks were not focused on his previous medical condition of depression, possibly because this was not declared in the self-declaration form for annual medicals. During the flight the captain was irritable, tensed, moody, and aggressive at various times. He was smoking during the flight, contrary to company regulations. He also used foul language and abusive words in conversation with the junior female first officer. He was engaged in unnecessary conversation during the approach, at a time when sterile cockpit rules were in force. The captain seemed very unsecure about his future as he had submitted resignation from this company, though only verbally. He said he did not have any job and did not know what he was going to do for living.