Circumstances:
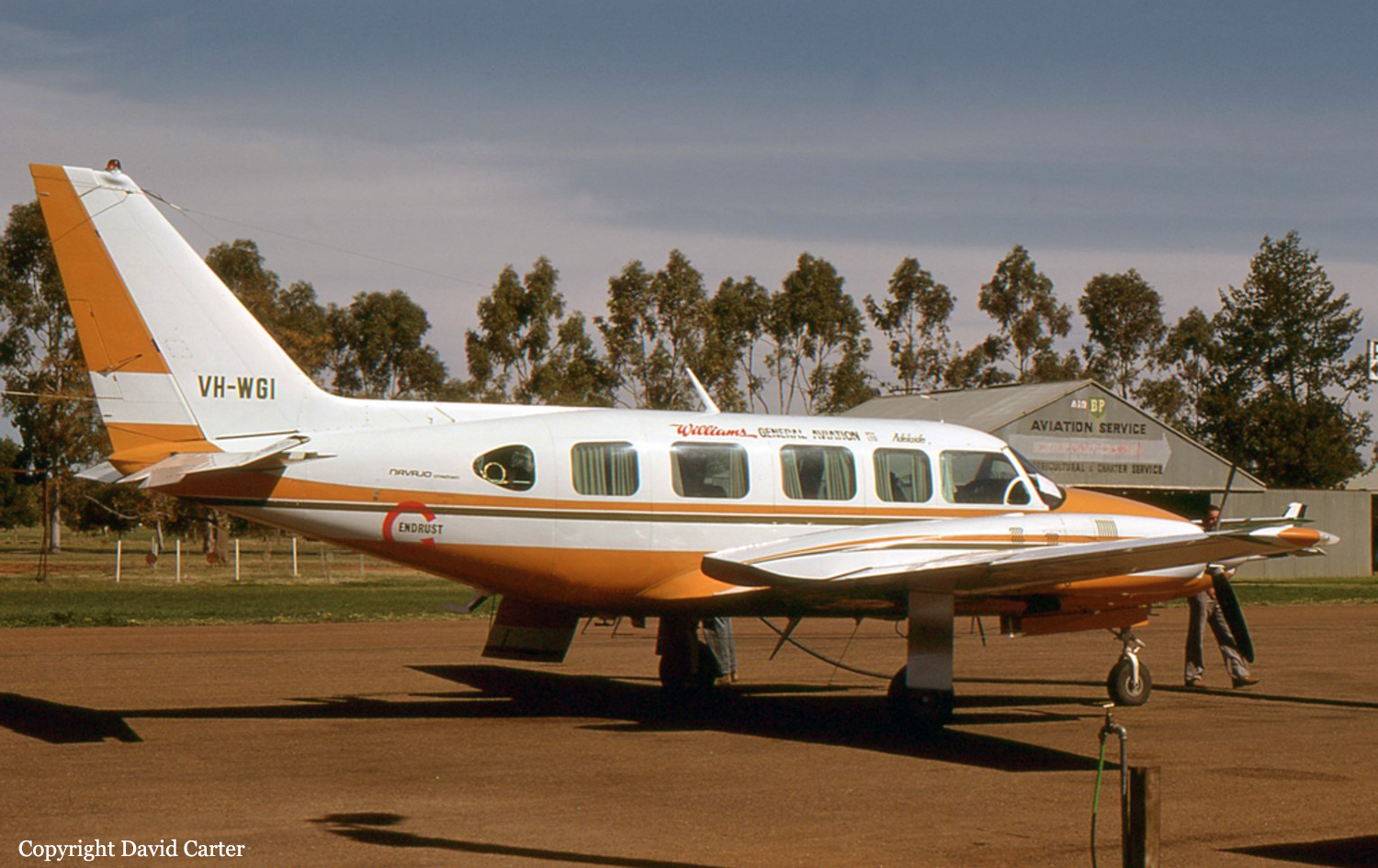
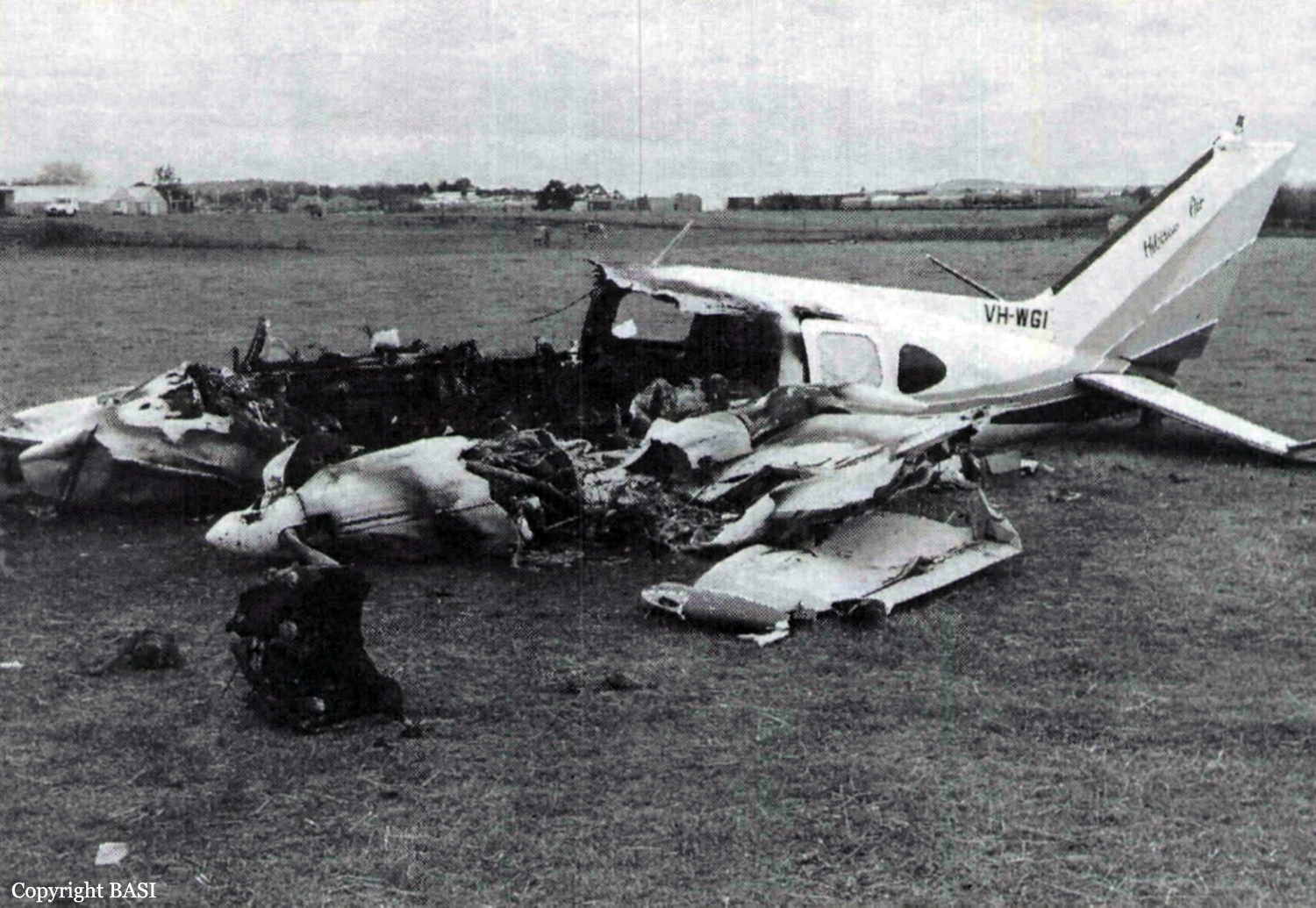
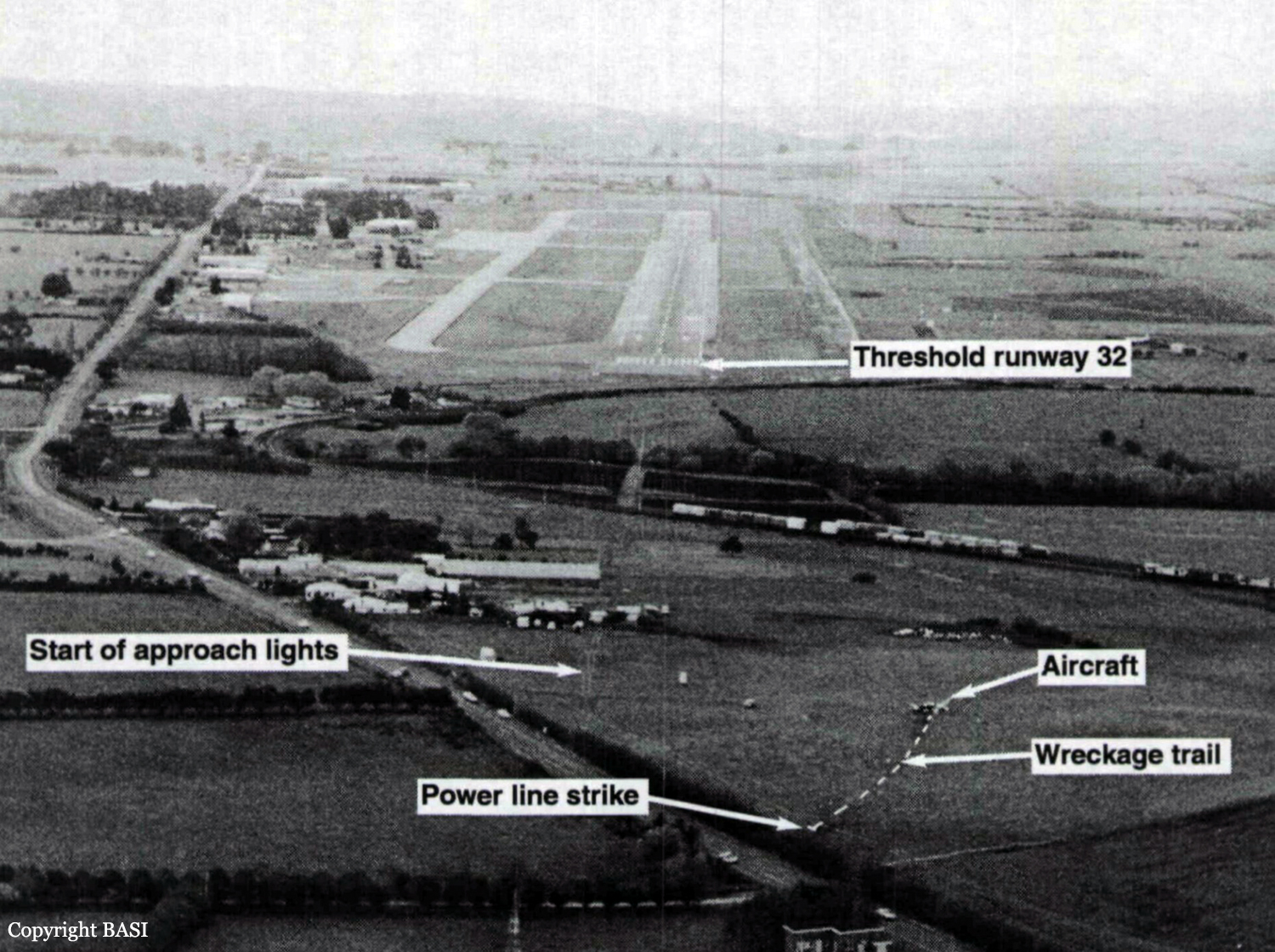
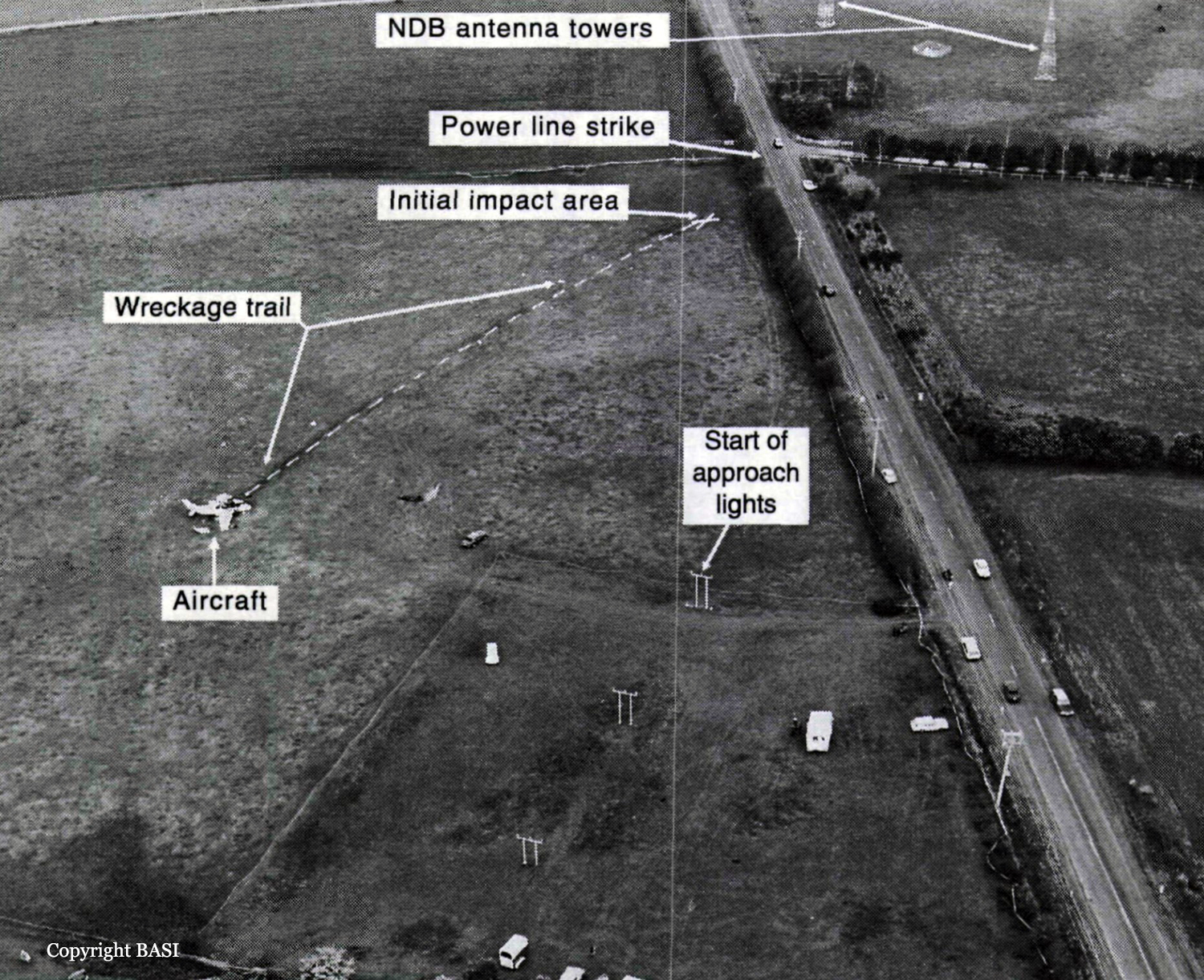
Members of a football club had planned to visit Launceston, travelling by light aircraft. Three aircraft were needed to carry the group, with all passengers and pilots contributing to the cost of the aircraft hire. One of the club members, who was a pilot, organised the required aircraft and additional pilots for departure from Moorabbin Airport on the afternoon of 17 September 1993. The operator from whom the aircraft were hired, who also employed the organising pilot as an instructor, arranged for one Piper PA-23 (VH-PAC), a Piper PA-31-310 (VH-NOS) and a Piper PA-31-350 (VH-WGI) to be available for the trip, with the organising pilot to fly VH-WGI. On the day of the flight the pilot of VH-WGI carried out pre-flight inspections, obtained the weather forecasts and submitted flight plans for all three aircraft. The flight plans for the two PA-31 aircraft were for flights operated in accordance with IFR procedures. The PA-23 was to operate in accordance with VFR procedures. The TAF for Launceston predicted 2 octas of stratocumulus cloud, base 2,000 ft and 3 octas of stratocumulus cloud, base 3,500 ft. The flight plan for VH-WGI (see fig. 2) indicated that the aircraft would track Moorabbin Wonthaggi-Bass-Launceston and cruise at an altitude of 9,000 ft. A cruise TAS of 160 kts, total plan flight time of 90 minutes, endurance 155 minutes and Type of Operation 'G' (private category flight) were specified. No alternate aerodrome was nominated and none was required. The estimated time of departure was 1730. The flight plan was submitted to the CAA by facsimile at 1529. Last light at Launceston was 1919. VH-WGI departed Moorabbin at 1817 and climbed to an en-route cruise altitude of 9,000 ft. The pilot was required to report at Wonthaggi but passed this position at 1832 without reporting. Melbourne ATC tried unsuccessfully to contact the pilot because of this missed report. Later, the Melbourne radar controller noticed the aircraft deviating left of track but was unable to make contact. Communications were re-established at 1858 when the pilot called Melbourne FS saying he had experienced a radio problem. By this time the aircraft heading had been corrected to regain track. At 1927 the pilot called Launceston Tower and was cleared for a DME arrival along the inbound track of the Launceston VOR 325 radial. The Launceston ATIS indicated 2 octas of cloud at 800 ft, QNH 1,012 hPa, wind 320° at 5-10 kts, temperature +10° and runway 32 in use. At 1930 the ADC advised the pilot that the 2 octas of cloud were clear of the inbound track, but that there was some lower cloud forming just north of the field, possibly on track. He informed the pilot that there was a chance he might not be visual by the VOR, in which case he would need to perform an ILS approach via the Nile locator beacon. The ADC contacted the airport meteorological observer at 1933, inquiring as to what the 1930 searchlight check of cloud height had revealed. He was told the observation indicated 7 octas of cloud at about 800 ft. At 1935.52 (time in hours, minutes and seconds) the ADC asked the pilot for his DME (distance) and level. The pilot responded that he was at 12 DME and 3,300 ft. The ADC told the pilot that conditions were deteriorating with probably 4 octas at 800 ft at the field. He then told the pilot he would hopefully get a break in the cloud, but then restated that if he was not visual by the VOR to make a missed approach, track to Nile and climb to 3,000 ft. At 1939.45 the pilot was again asked for his DME and level. He indicated that he was at 1,450 ft and 2-3 DME. He then also confirmed that he was still in IMC. There were three other aircraft inbound for Launceston and the ADC made an all-stations broadcast that conditions were deteriorating at Launceston, with 4 octas at 800 ft, and to expect an ILS approach. At 1940.56 the pilot stated that he was overhead the field, but did not have it sighted and was going around. At 1941.07 the pilot reported that he had the airfield in sight and at 1941.16 that he was positioned above the final approach for runway 32. Fifteen seconds later the pilot reported that he was opposite the tower and was advised by the ADC that he was cleared for a visual approach, or a missed approach to Nile as preferred. The pilot indicated he would take the visual approach and was then told to manoeuvre as preferred for runway 32. This was acknowledged at 1941.48. No further communications were received from the pilot. The ADC made a broadcast to two other inbound aircraft at 1942.32, advising that VH-WGI was in the circuit ahead of them, that it had become visual about half a mile south of the VOR, that it was manoeuvring for a visual approach and was just in and out of the base of the cloud. After the pilot of VH-WGI reported over the field, and the aircraft first appeared out of cloud, witnesses observed it track to about the south-east end of the aerodrome at a height of about 500-800 ft. It then turned left to track north-west on the north-east side of the main runway and approximately over the grass runway. The aircraft was seen to be travelling at high speed, and passing through small areas of cloud. North of the main terminal building a left turn was initiated onto a close downwind leg for runway 32. The aircraft appeared to descend while on this leg. As the base turn was started, at a height estimated as 300-500 ft, the aircraft briefly went through cloud. Some of the witnesses reported that the engine noise from the aircraft during the approach was fairly loud, suggestive of a high power setting. Late on a left base leg the aircraft was observed to be in a steep left bank, probably in the order of 60°, at a height of about 200 ft. It then descended rapidly and struck a powerline with the right wing, approximately 28 ft AGL, resulting in an airport electrical power failure at 1943.02. Almost simultaneously the left wing struck bushes. A short distance beyond the powerlines the aircraft struck the ground and slid to a stop. A fierce fire broke out immediately. Airport fire services responded to the accident and the fire was quickly extinguished. Six of the occupants received fatal injuries and the others, including the pilot, were seriously injured.
Probable cause:
The following findings were reported:
1. The actual weather at Launceston at the time of arrival of VH-WGI was significantly worse than forecast.
2. The pilot did not have the required recent experience to conduct either an IFR flight or an ILS approach. The operator's procedures did not detect this deficiency.
3. The pilot's inexperience and limited endorsement training did not adequately prepare him for IFR flight in the conditions encountered.
4. The CAA did not specify adequate endorsement training or minimum endorsement time requirements for aircraft of the class of the PA-31-350, particularly in regard to the endorsement of inexperienced pilots.
5. An absence of significant decision-making training requirements contributed to the poor decision-making action by the pilot who decided to continue with a visual circling approach at Launceston in conditions that were unsuitable for such an approach.
6. As a consequence of continuing the approach, the pilot subjected himself to an overwhelming workload. This was due to a combination of adverse weather conditions, his lack of training and experience in IFR approach procedures on the type, and a misinterpretation of (or non-compliance with) the AIP/DAP-IAL instructions, a combination which appears to have influenced the pilot to fly a close-in, descending circuit at low altitude. The carriage of alcohol-affected passengers may have also added to the level of difficulty.
7. Because of workload, and possibly also due to distractions, the pilot inadvertently allowed the aircraft to enter a rapid descent at a critical stage of the approach, at an altitude from which recovery could not be effected.