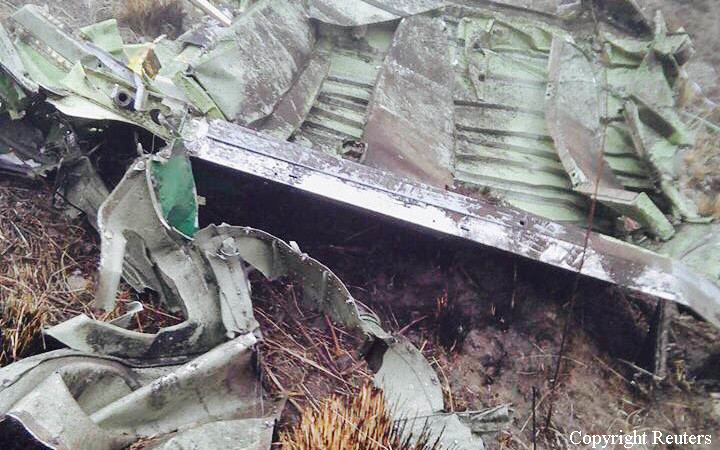
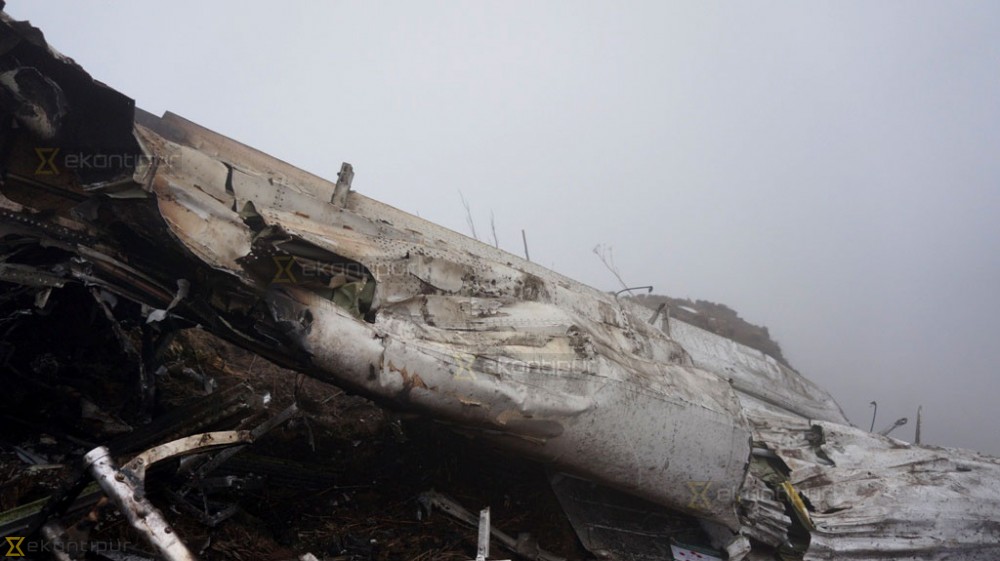
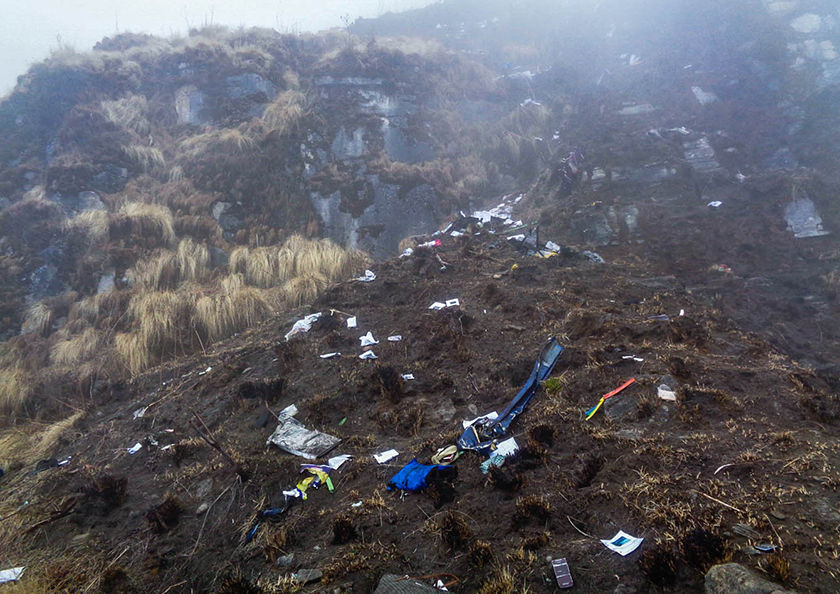
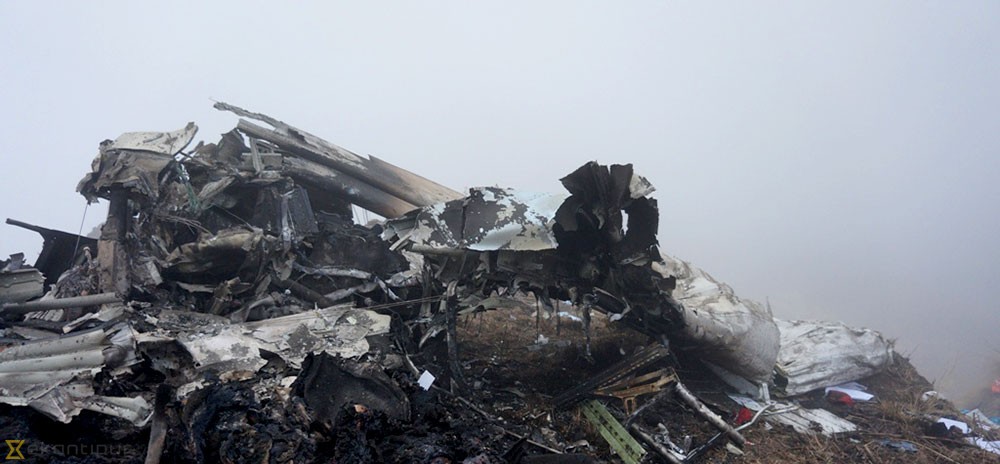
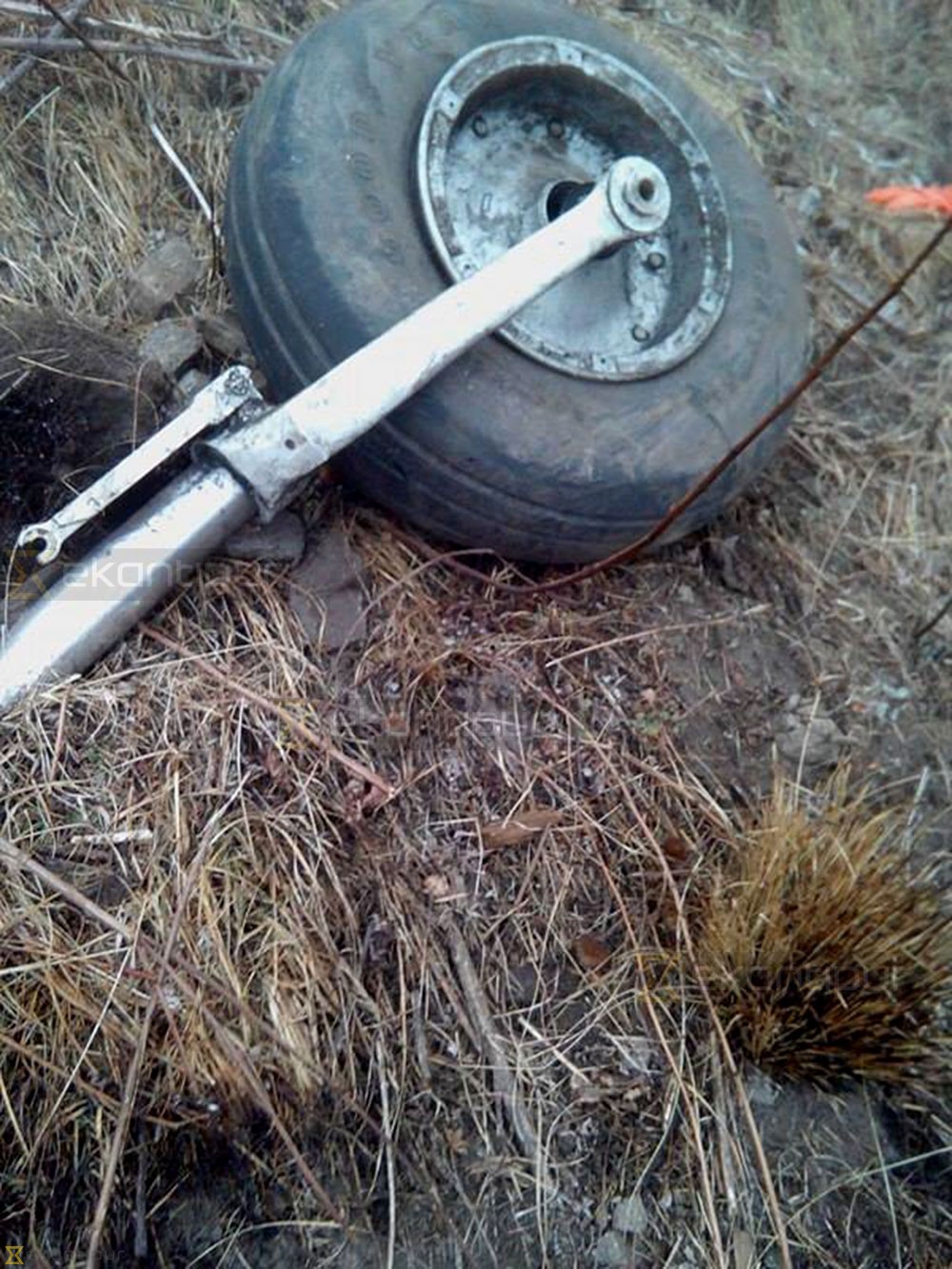
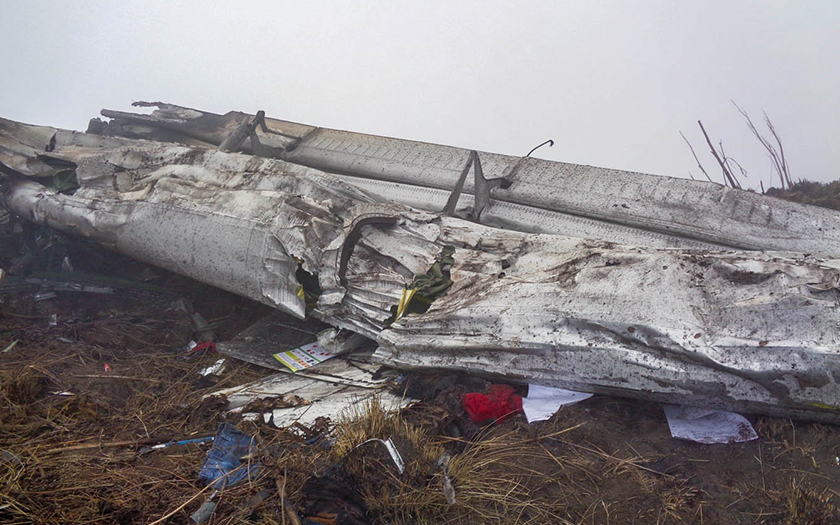
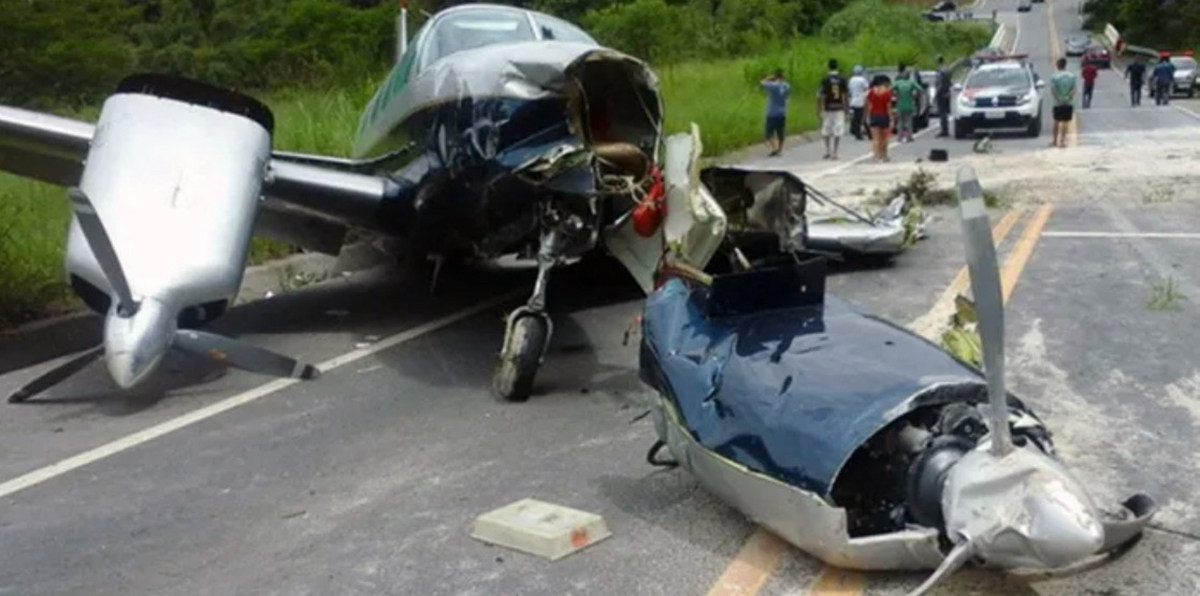
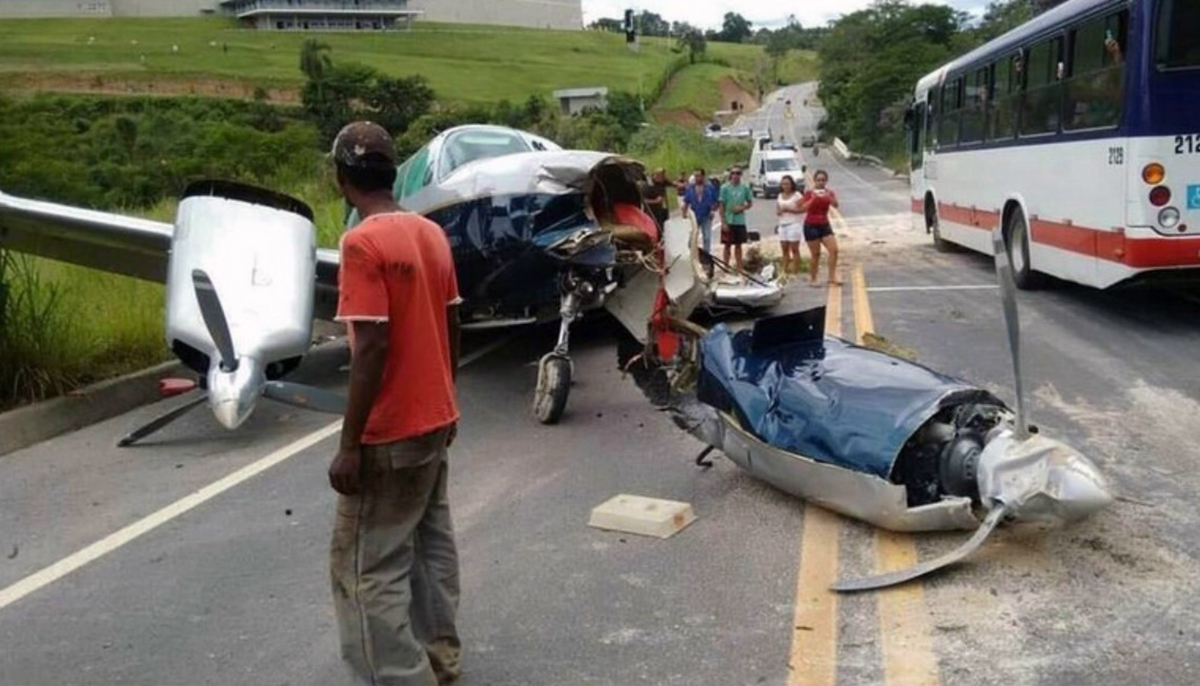
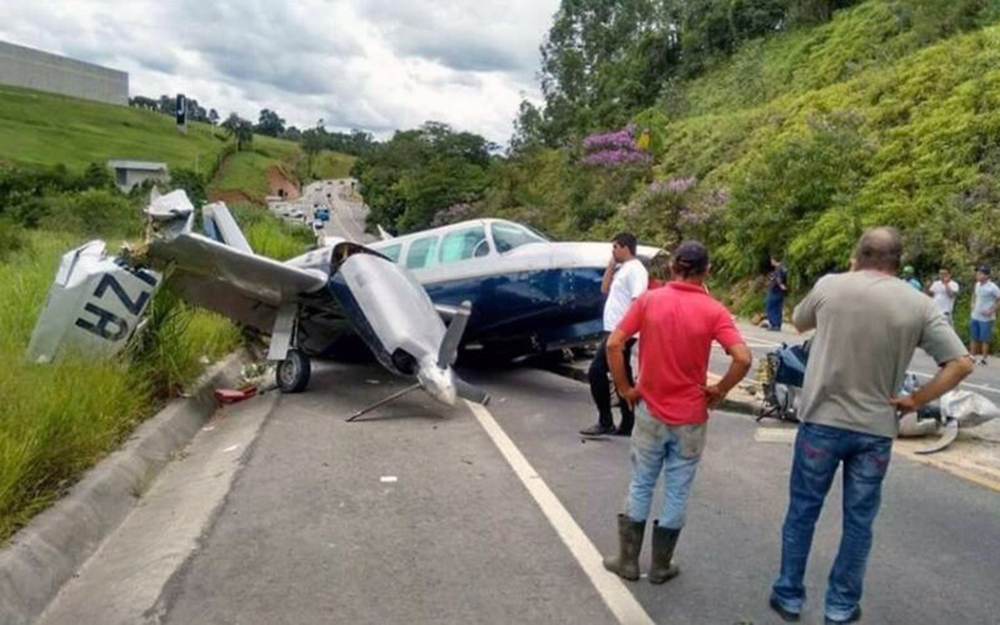
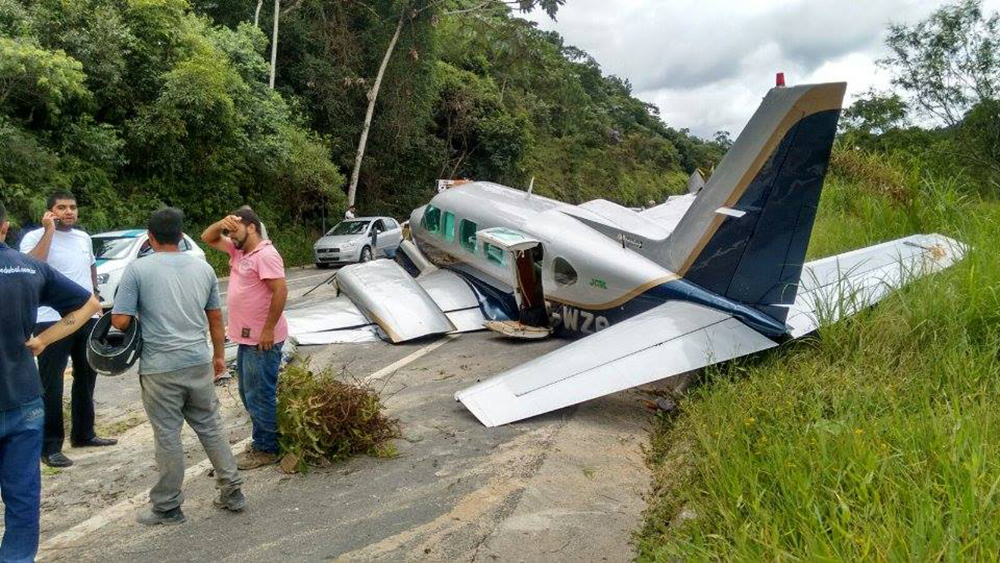
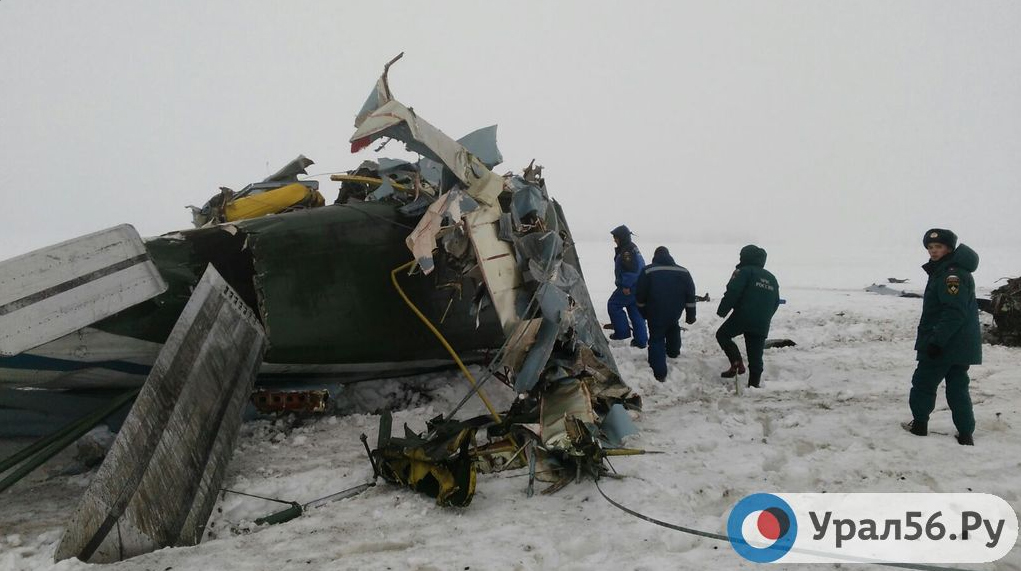
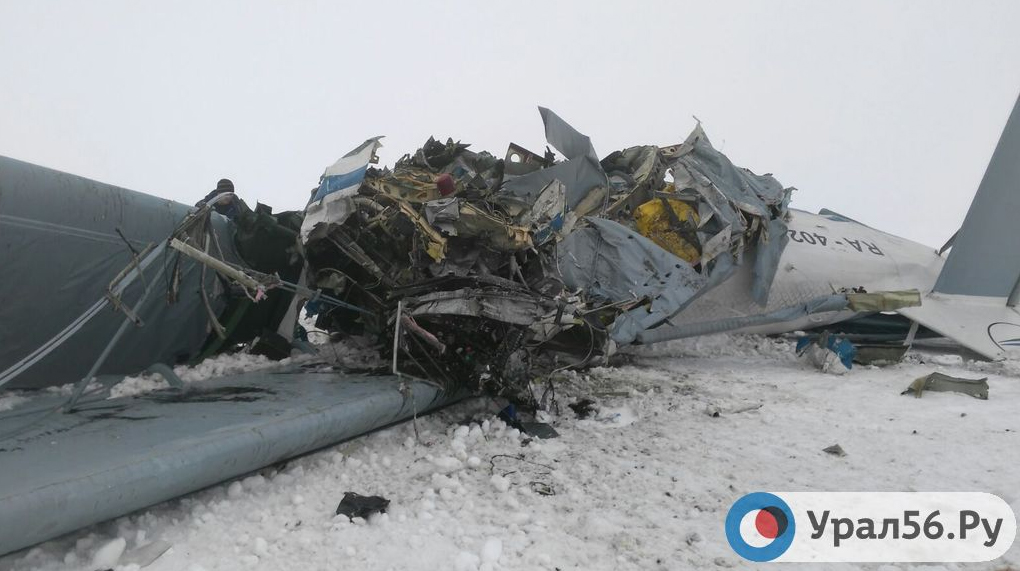
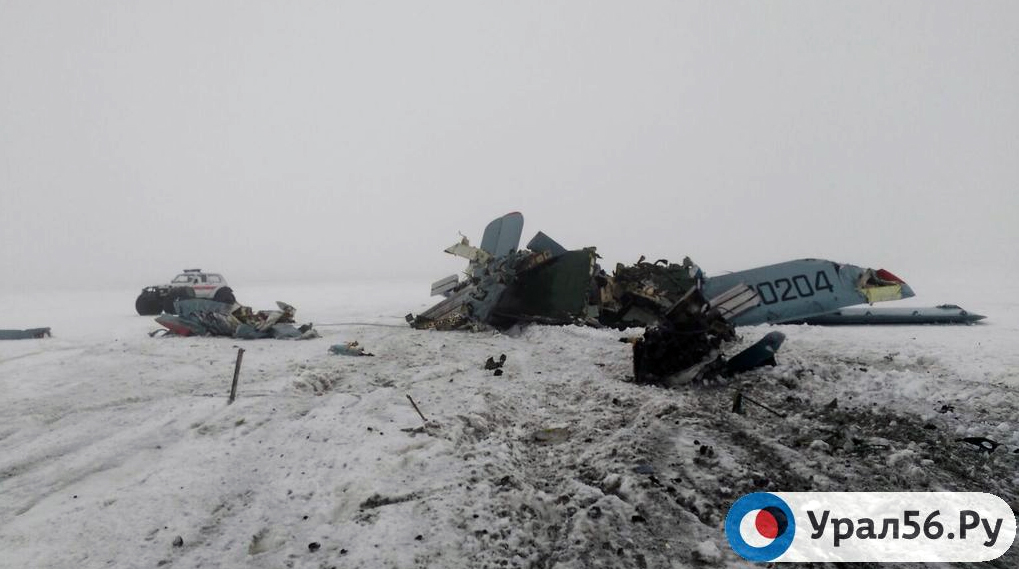
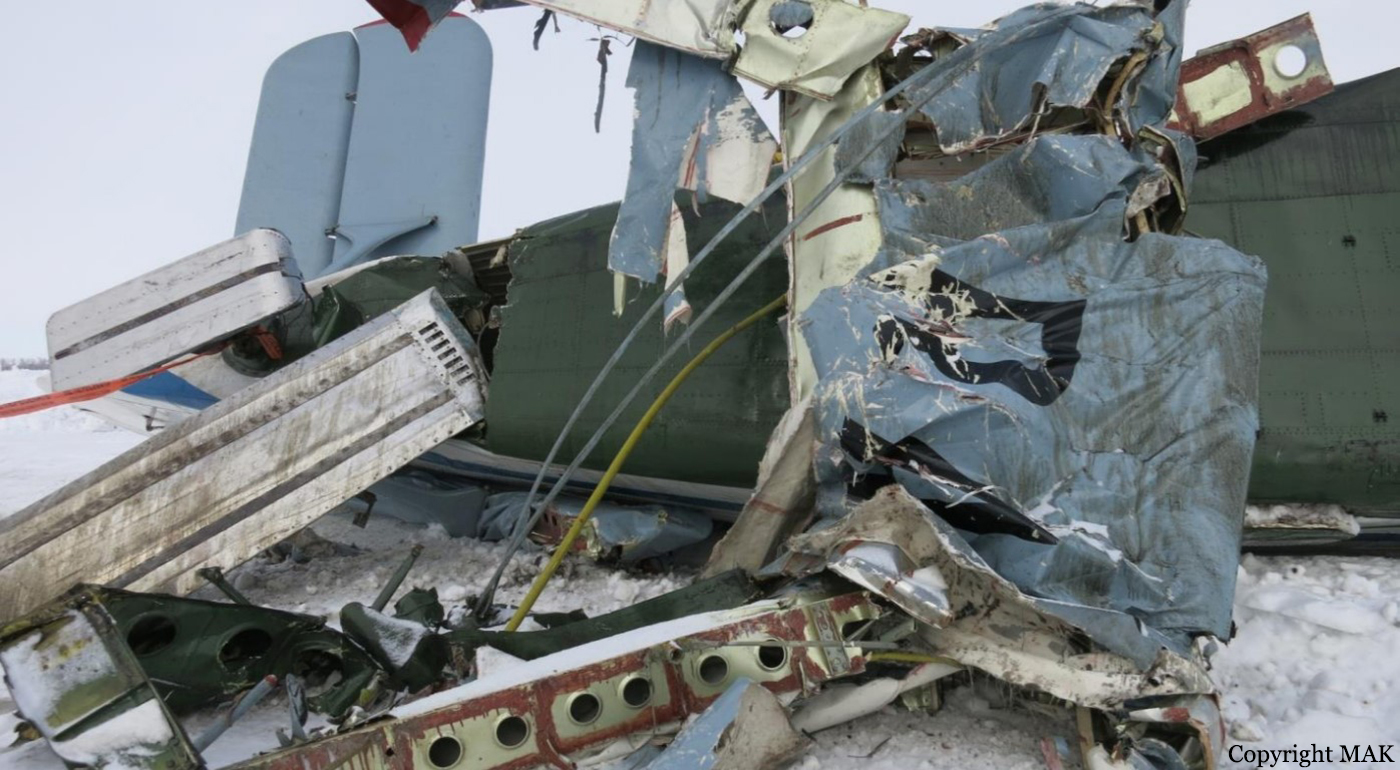
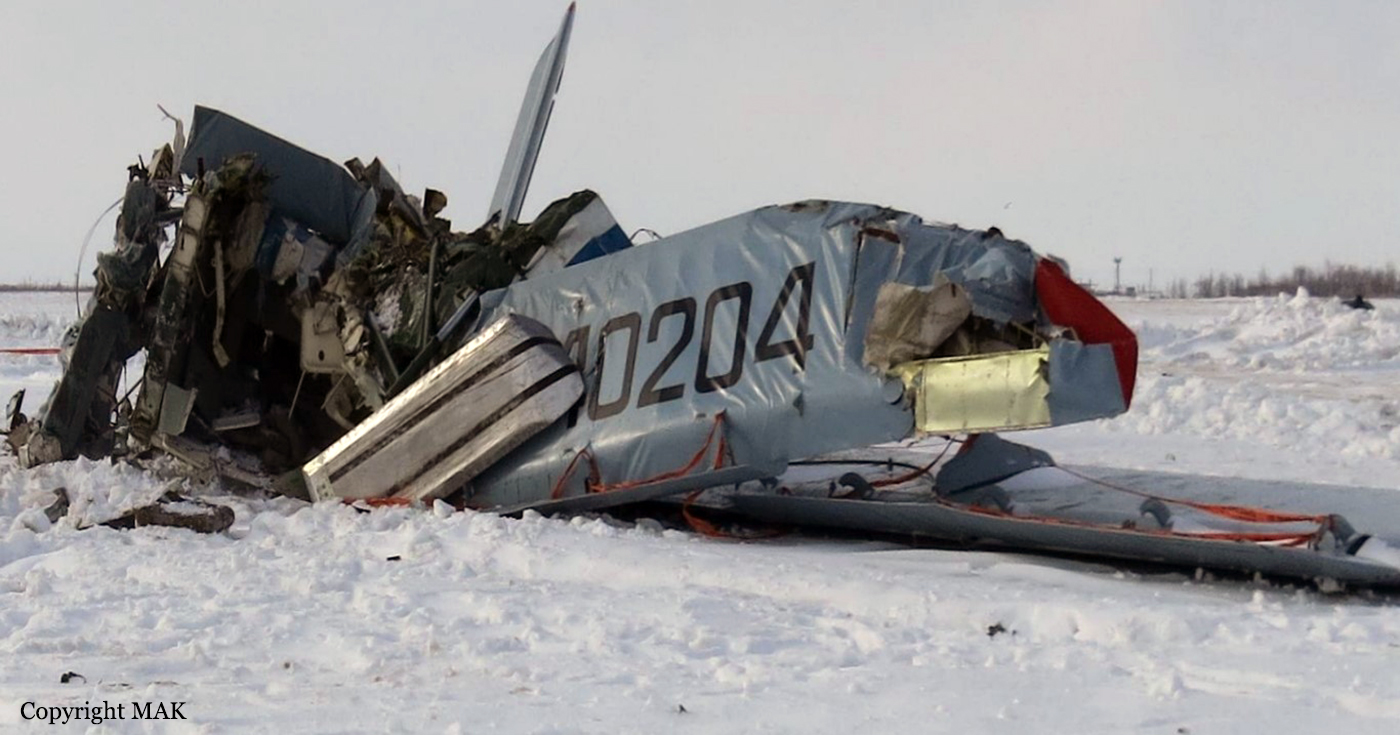
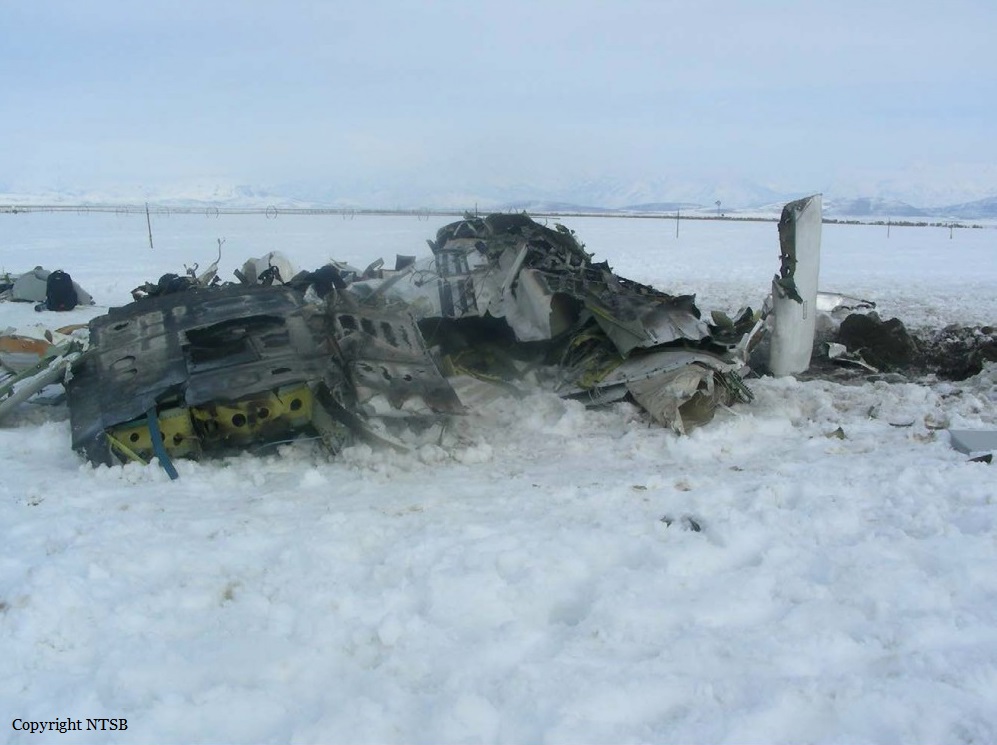
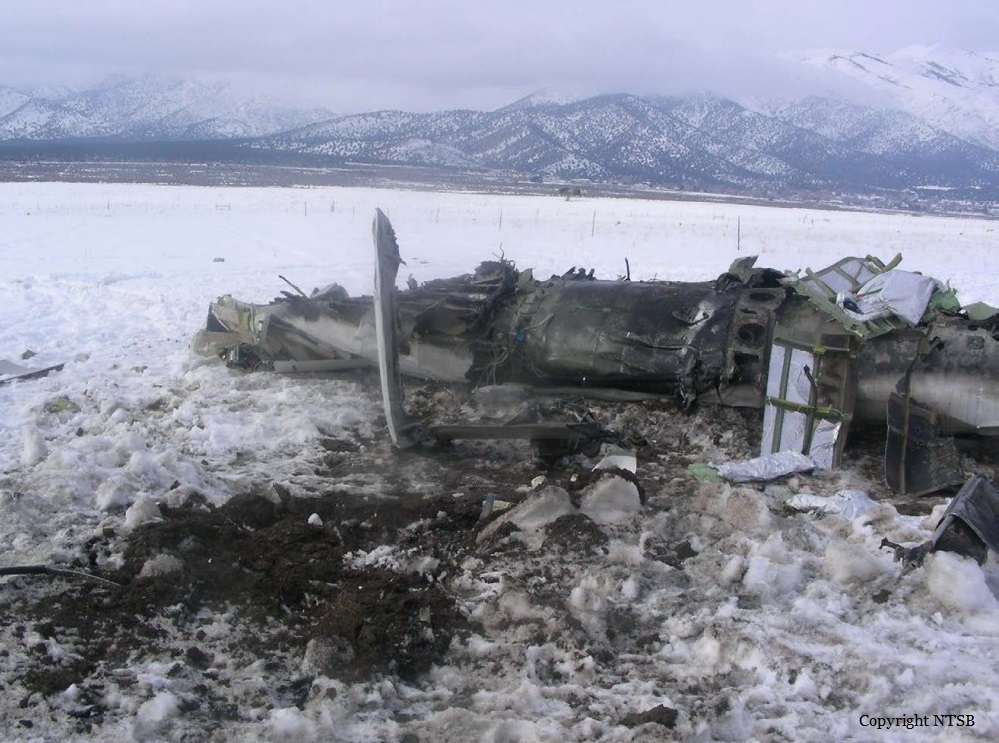
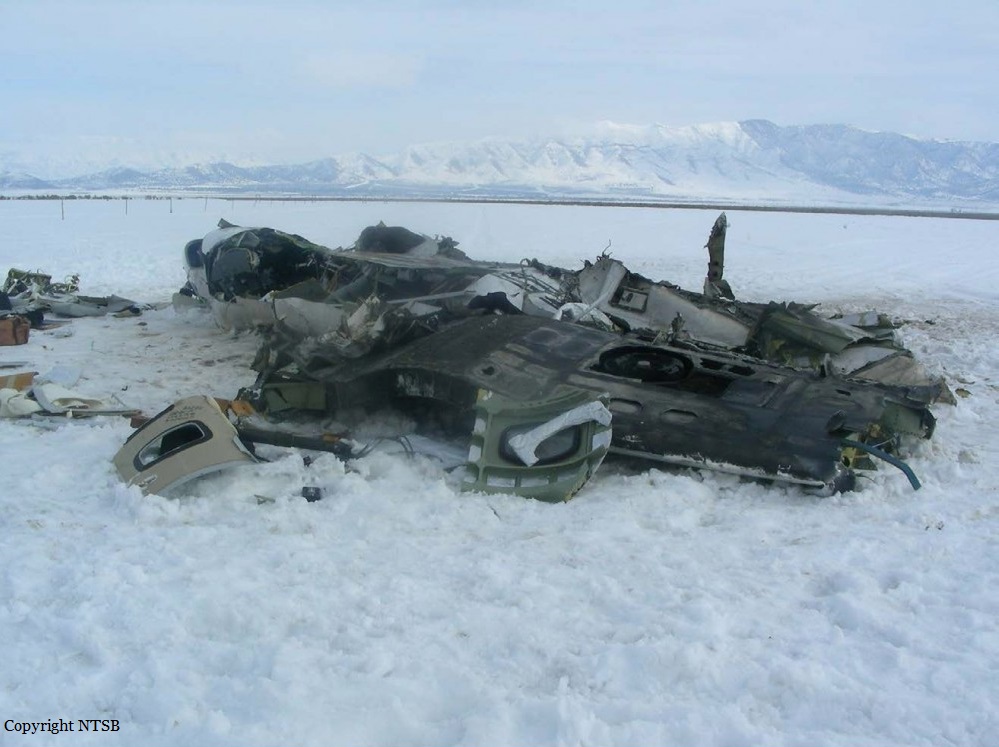
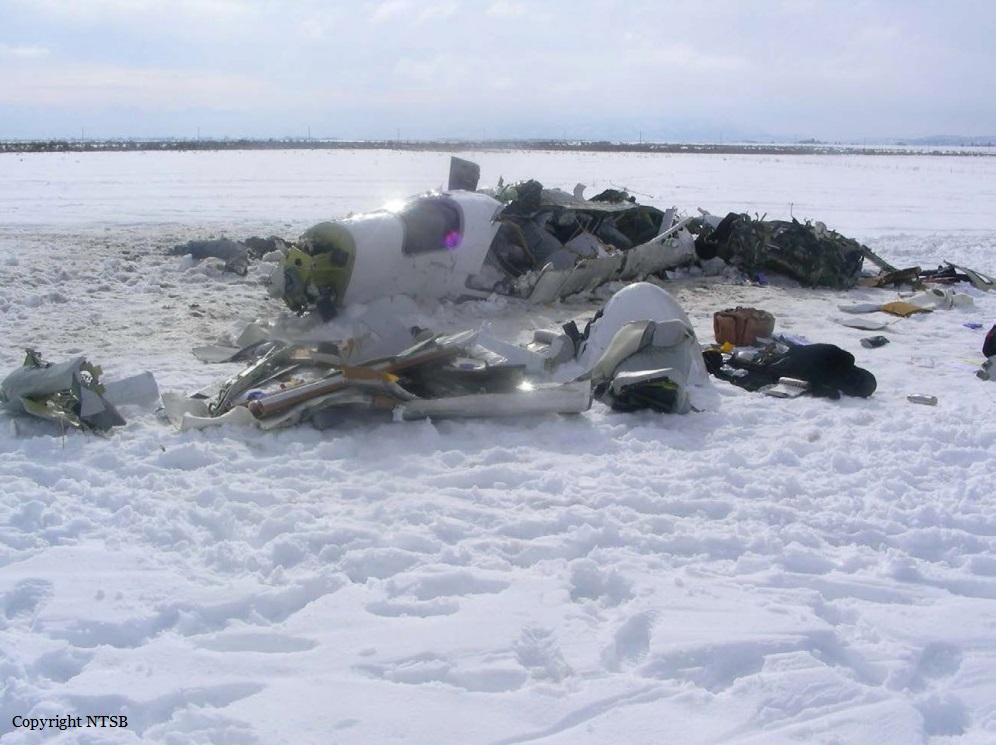
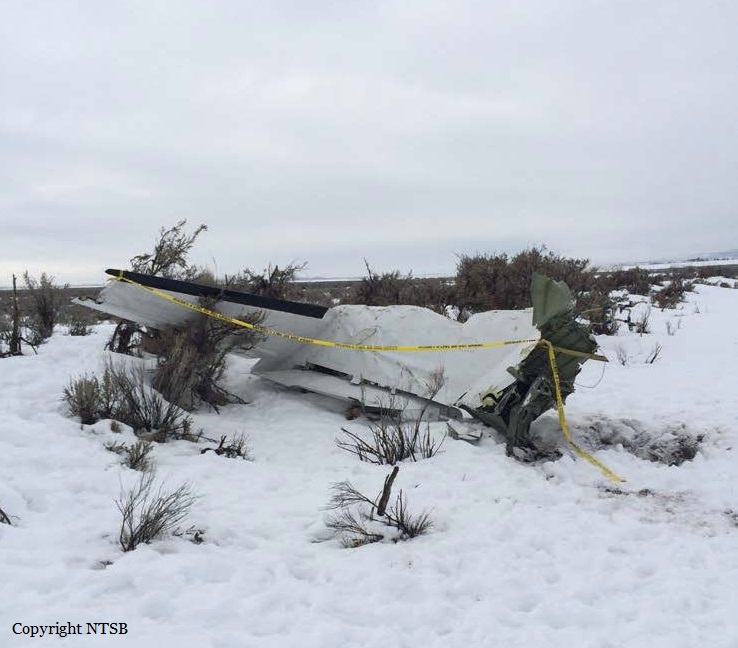
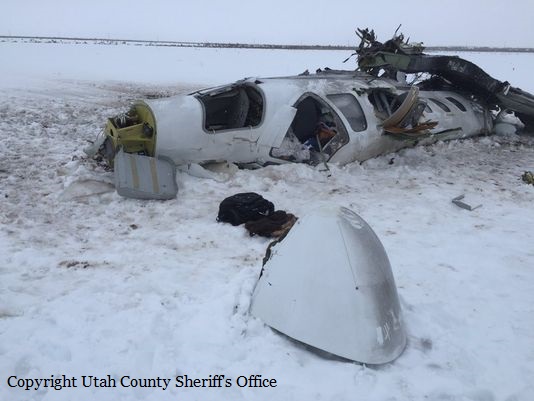
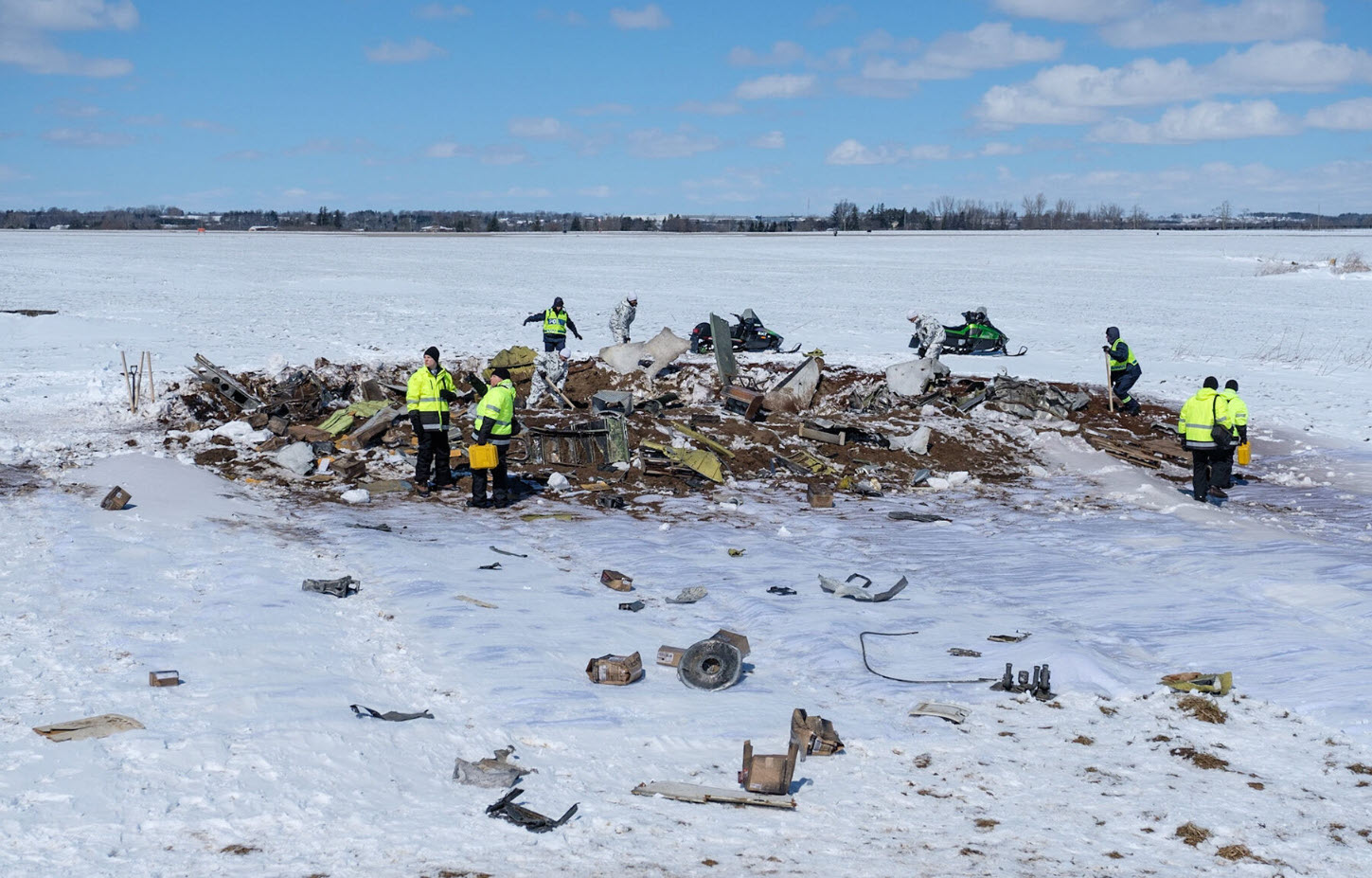
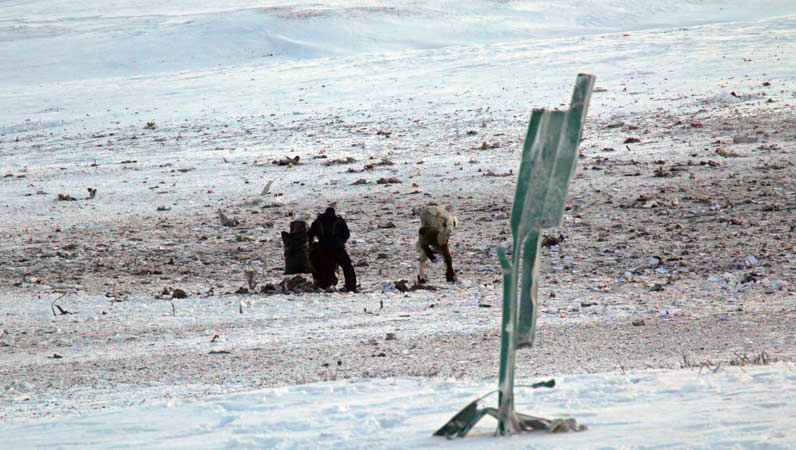
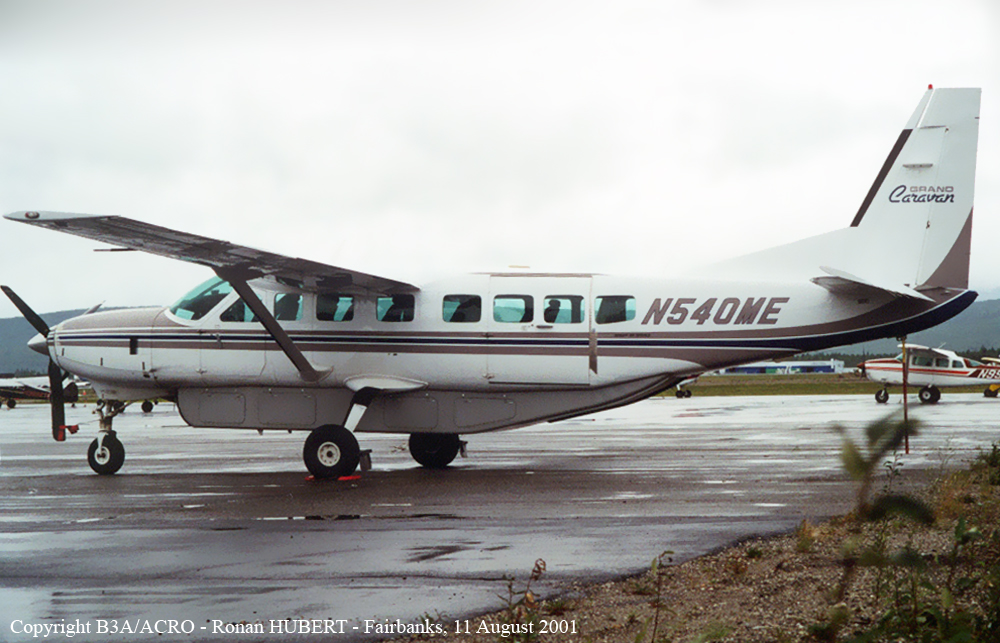
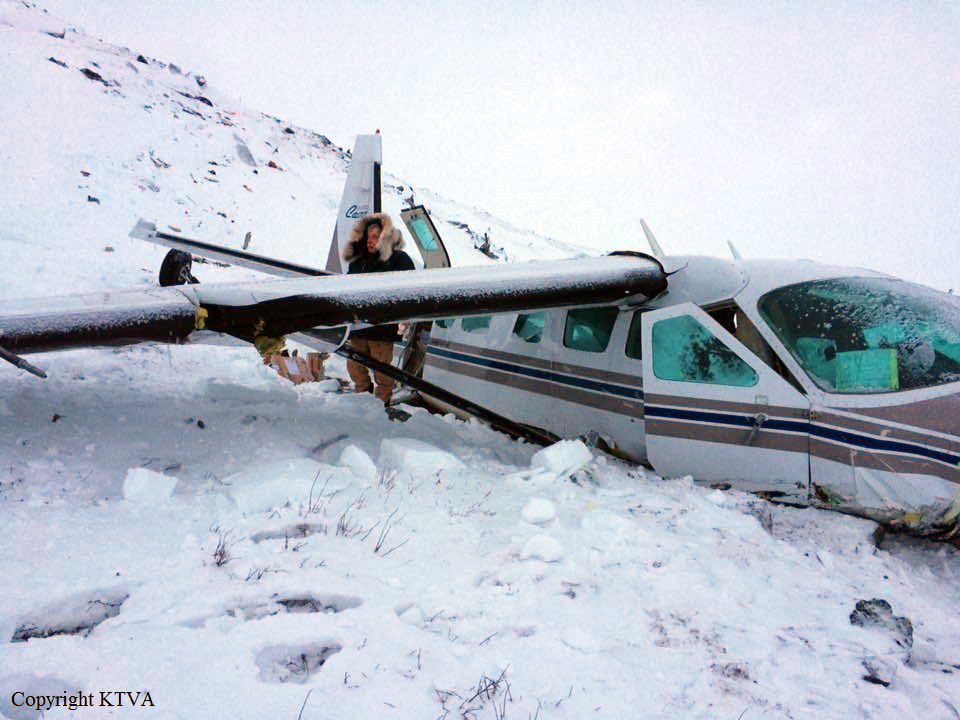
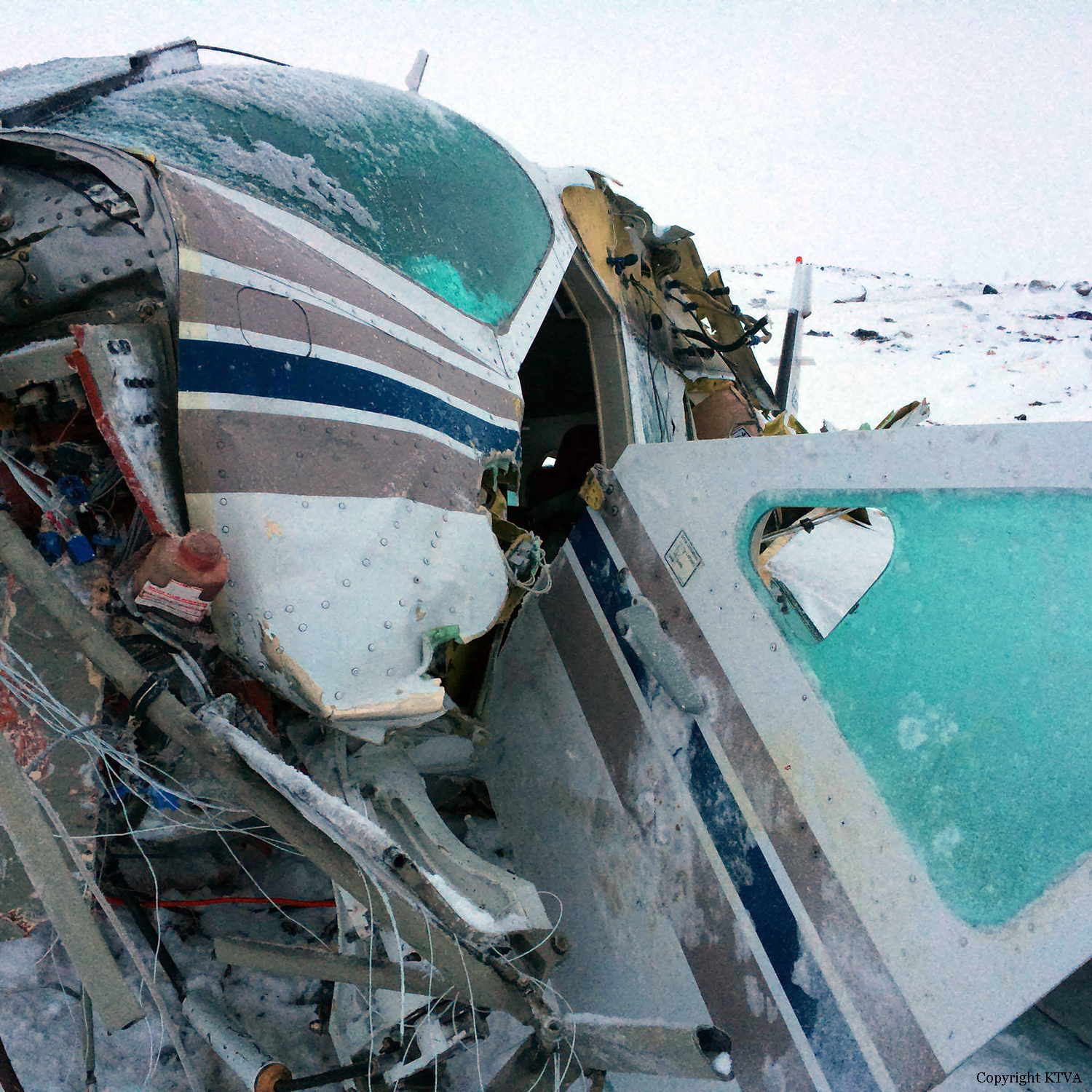
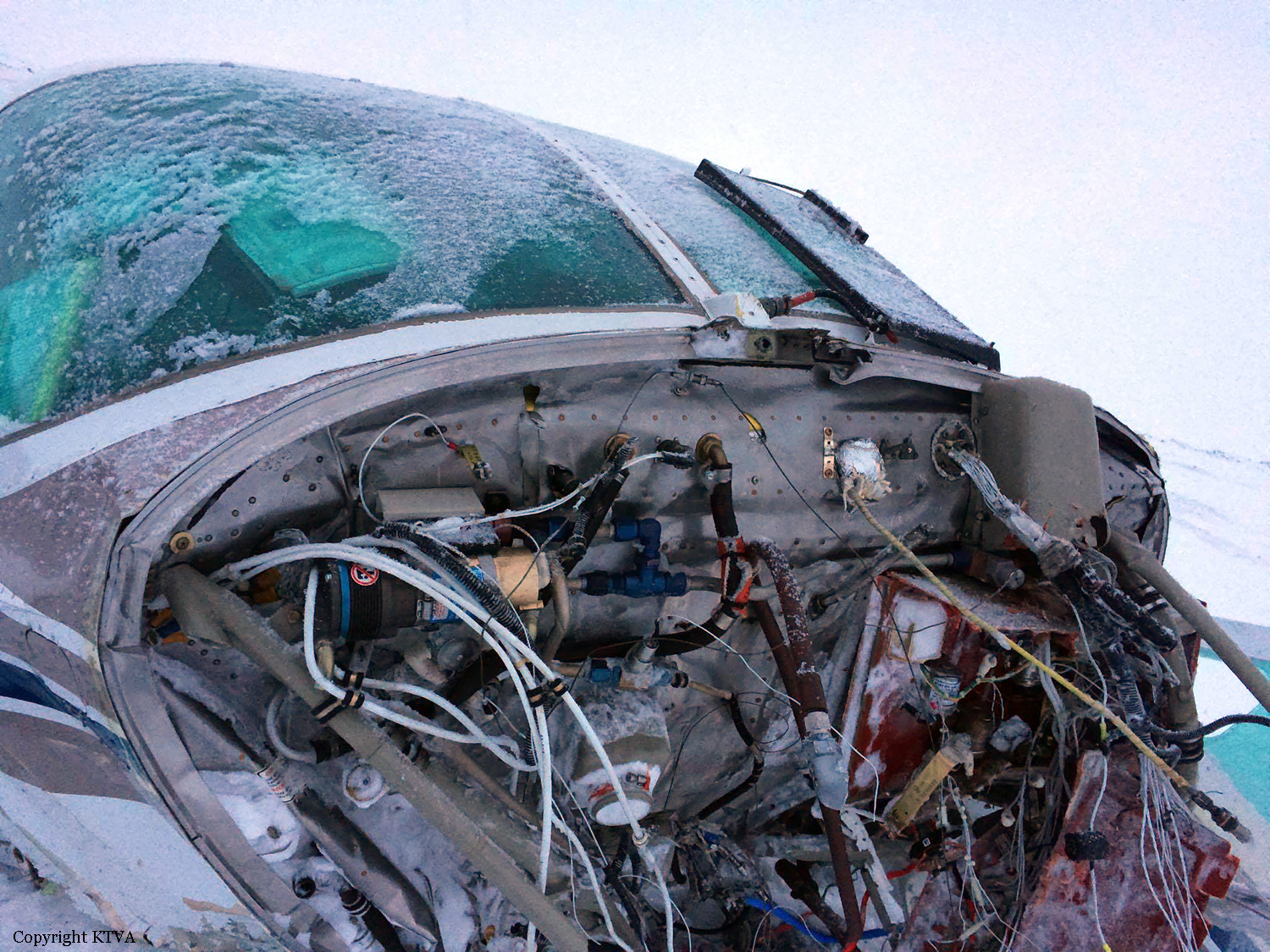
Circumstances:
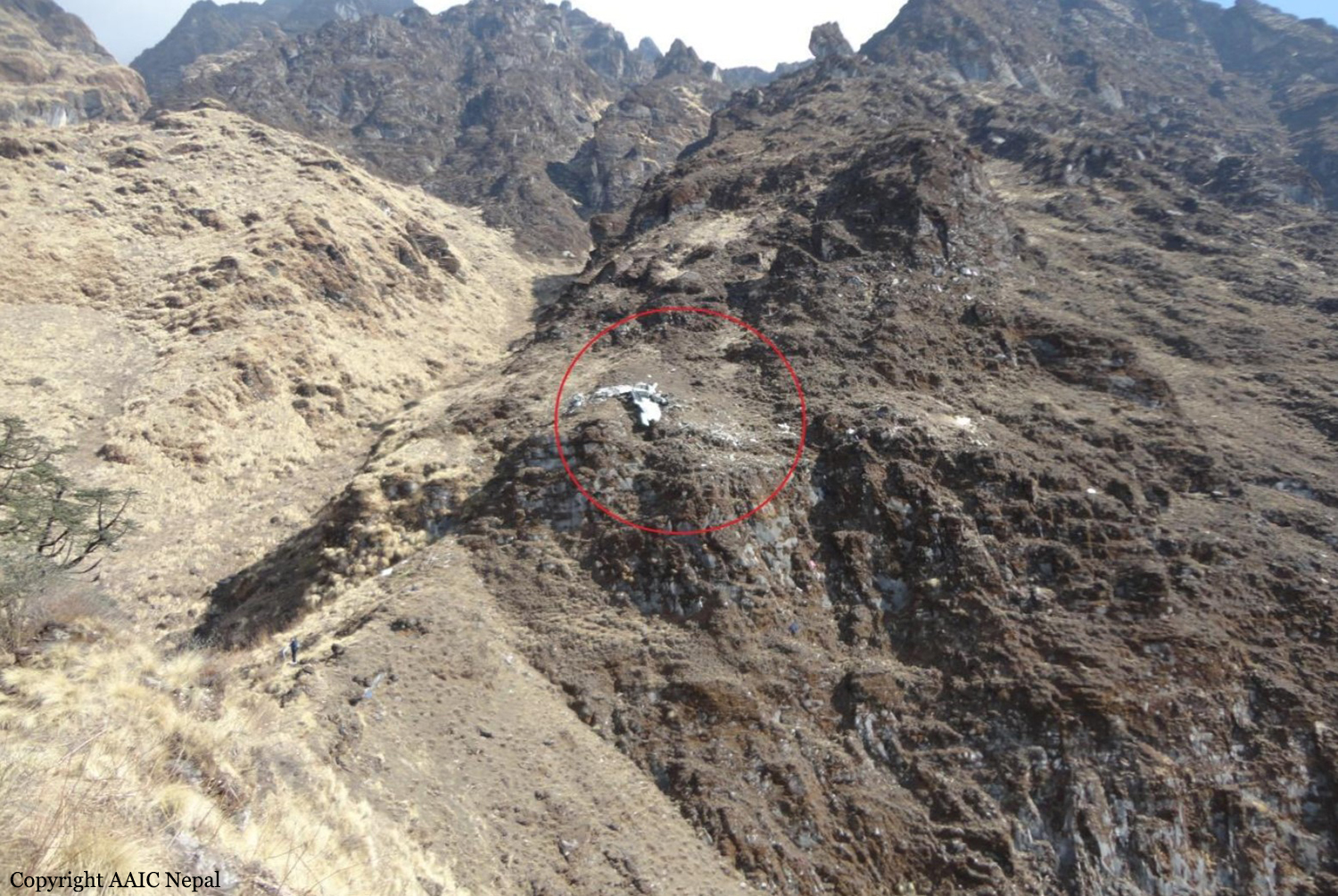
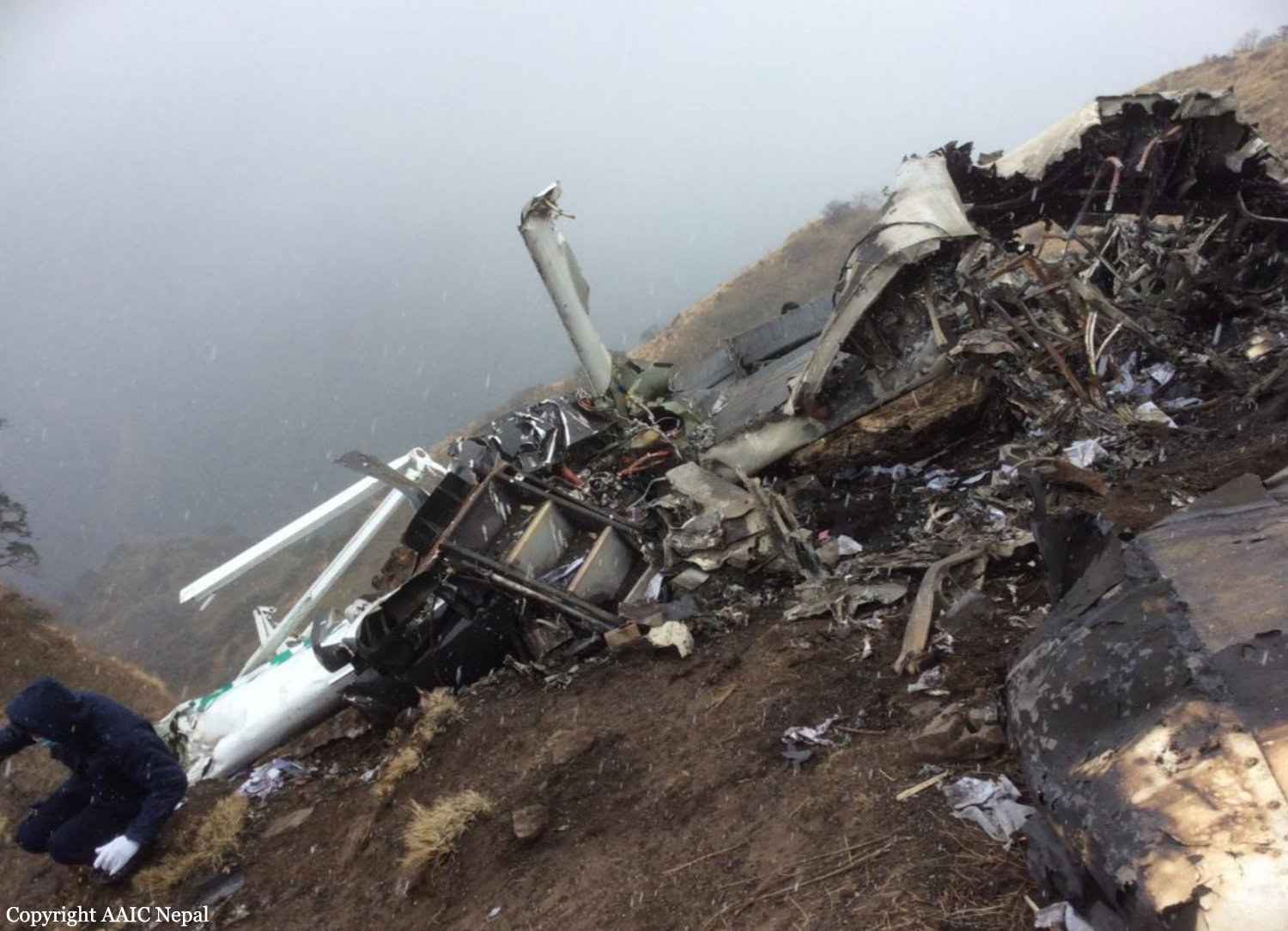
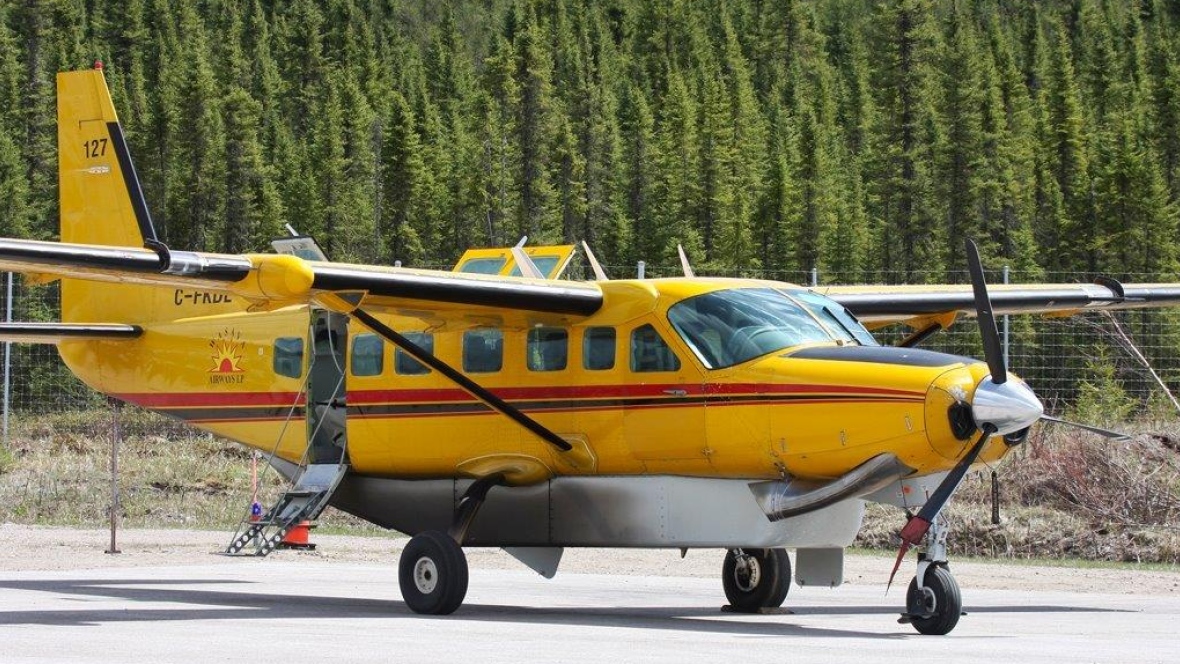
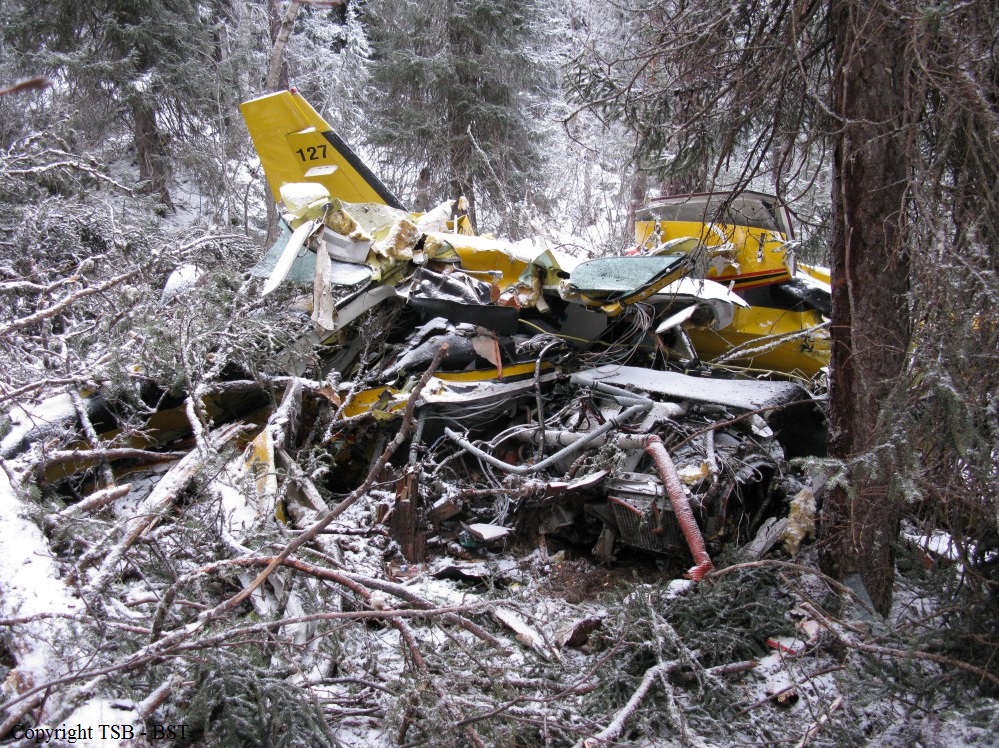
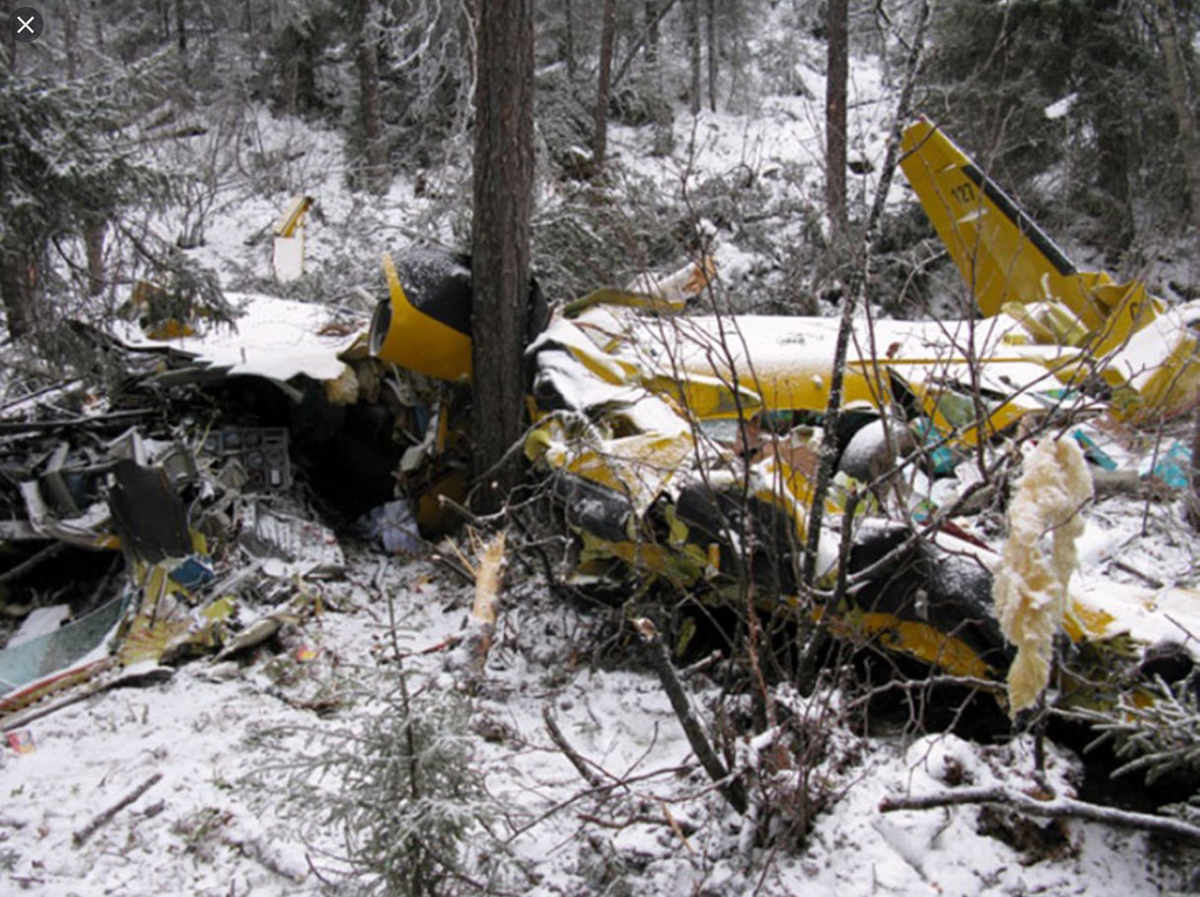
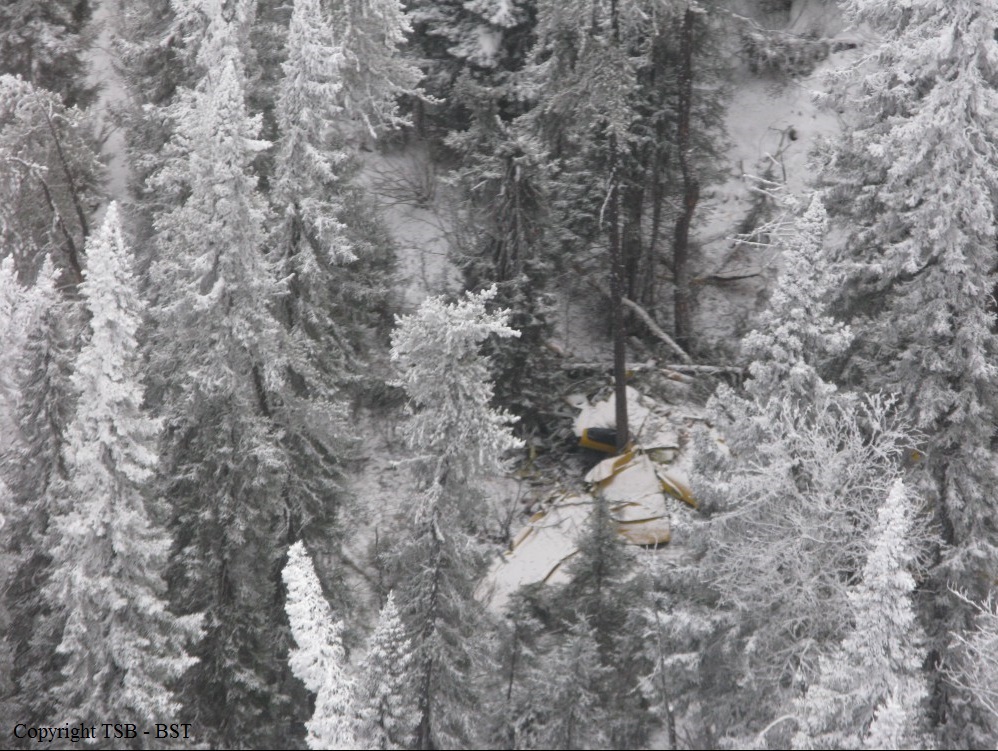
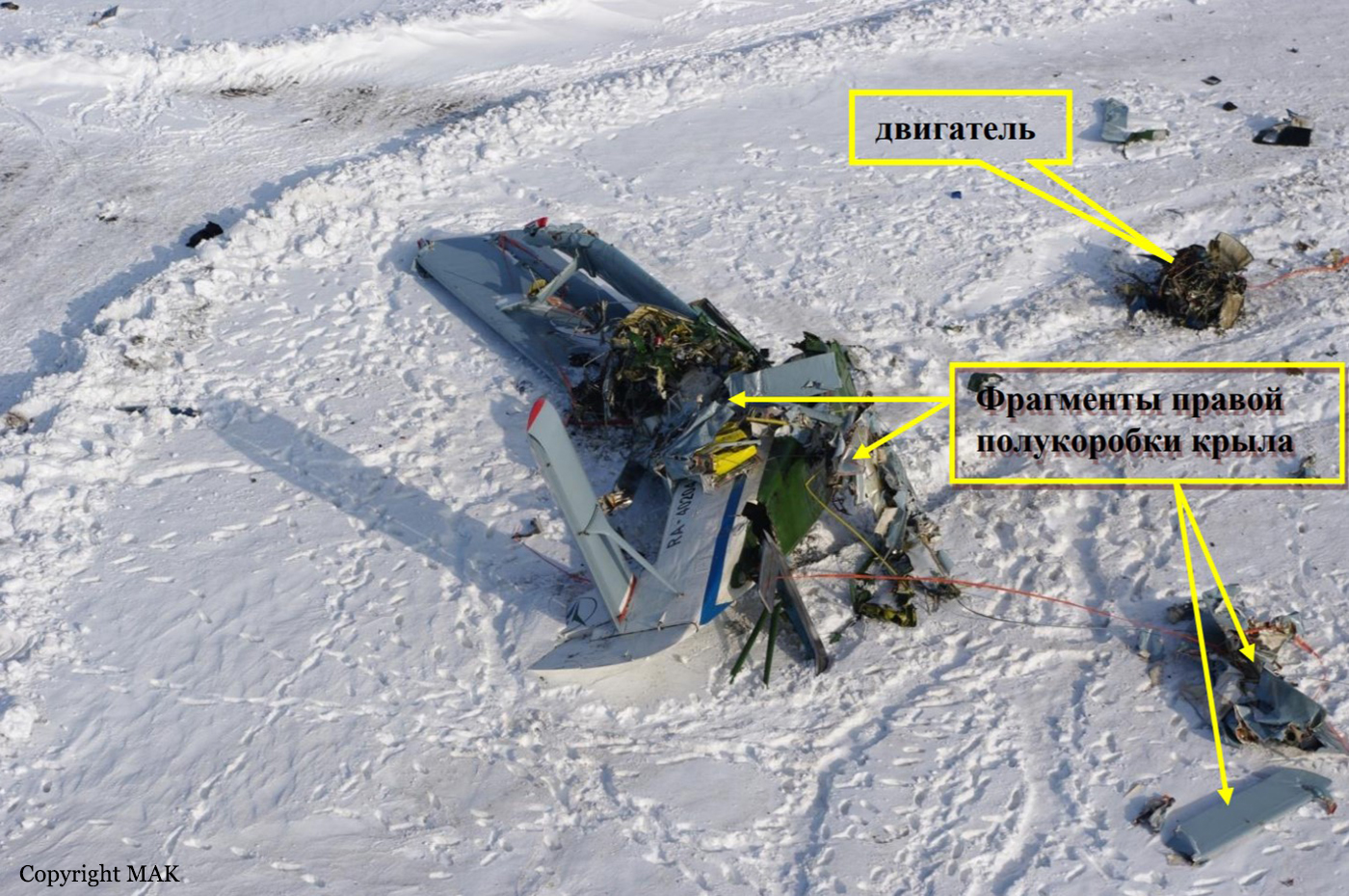
As per the flight plan submitted on 23rd February 2016, the aircraft was scheduled for VFR flight to Jomsom (VNJS) on 24th February with estimated off-block time of 01:00, intended cruising speed of 150 knots, intended level of 10,500 ft and via direct track. The first and second alternate aerodromes were Bhairahawa (VNBW) and Pokhara (VNPK) respectively and estimated elapsed time was 20 minutes with the fuel endurance of 2 hours and 30 minute. Based on the information from the CVR, FDR and ATC records, the following description of the history of the flight was reconstructed: At 01:55, the first-officer contacted Pokhara tower requesting Jomsom and Bhairahawa weather. Upon receiving Jomsom weather which was 8 km visibility towards Lete (arrival track) and foothill partially visible; at 01:56 F/O requested start-up for Jomsom. First-officer then briefed the weather to the captain, in response to this the captain responded by saying 'Let‘s have a look, if not possible we will return' (Translated from Nepali conversation). While performing the 'before start checklist', they received weather of Bhairahawa as closed. After completing the checklist and start-up the first-officer at 02:00 requested taxi clearance. The ATC informed runway change to 22 instead of runway 04 and gave taxi clearance. At 02:03 while taxiing the captain considering bad weather condition expressed his concern over the runway change with F/O but failed to express it to the ATC. As briefed by captain earlier, the control was transferred to F/O and at 02:04 F/O made a normal take-off. At 02:08 the captain reported 5 miles at 6,200 ft to ATC. At 02:09, while passing through 7,000 ft the captain informed the actual weather, which was light haze, mountain not visible but had ground contact, to an ultra-light aircraft upon his request. As per the cockpit conversation, the crew were comparing the base of the cloud which was higher than the day before and proposed to continue climb to 12,500 ft if not on-top of the cloud at 10,500 ft. Around 5 miles before Ghorepani passing 10,100 ft, the captain told that cells were still present so advised F/O to continue climb to 12,000 ft and told that they will proceed till TATOPANI and decide to continue or divert. At 02:14 approaching GHOREPANI and passing 11,400 ft, Captain told F/O to maintain level to be in between the cloud layers and briefed F/O that if they had to divert it would be a left turn. At the same time captain asked repeatedly to F/O if his side was raining for which F/O told and confirmed not visual, after which captain told they would see and decide (regarding continuation of flight). At 02:14:50 while over Ghorepani area at 11,500 ft the EGPWS TERRAIN alert and at 02:14:52 PULL UP warning came while they were not visual and at 02:15:01 it was stated that they were visual and by 02:14:53 the warning stopped. At 02:15 while maintaining 11,500 ft the captain reported ATC that they are at Ghorepani at level 10,500 ft after which frequency changeover to Jomsom tower was given. At 02:15:27 the captain instructed F/O to maintain heading of 3300 and flight level just below the cloud, after which a shallow descent was initiated. At this time captain asked F/O if his side was visual, in response F/O replied somewhat visual. The Captain then instructed F/O to descent to 10,000 ft. Once the descent was started at 02:15:55 passing 11,000 ft an OVERSPEED warning sounded in the cockpit for 2 seconds as the speed reached 152 knots. At 02:16 while passing 10,700 ft captain advised F/O to make a left turn so that it would be easy to turn if required as he was able to see his side. Then F/O asked if left side was visual for which the captain informed that not that side (towards the track) but somewhat visual to the left of him and told that the TRACK TO GO was TO THE LEFT whereas they were actually left of the track and had descended to 10,300 ft. At 02:17:58 EGPWS TERRAIN alert sounded when the aircraft was at 10,200 ft and descending on heading of 3210 with right bank angle of around 30 . At 02:18:06 when the aircraft had descended to 10,100 ft the PULL UP WARNING sounded for which the captain said not to worry and at 02:18:12; when the aircraft was at 10,000 ft the captain took-over the control, continued descent and asked F/O if his side was visual. The F/O informed that right side was not visual at all by which the aircraft had continued shallow descent on heading 3250 with right bank angle reaching up to 130 at 2:18:19 and by 02:18:23 the aircraft once again returned back to 0° bank angle. At 02:18:23 the captain started left bank followed by right bank again while still on a shallow descent until 02:18:27.Upon reaching 9,850 ft (lowest altitude) the aircraft started very shallow climb. At 02:18:35 when aircraft was 9,920 ft the captain told F/O that they reached Landslide (a checkpoint which is on track to Jomsom on the right side of the Kali-Gandaki River). At 02:18:44 when aircraft reached 10,150 ft captain told ―what I will do is now I will turn to heading of LETTE‖ (another way point on route to Jomsom); while the PULL-UP warning was continuously sounding. At 02:18:49 when the aircraft was at 10,300 ft right bank angle increased up to 16° with pitch up attitude of 7°. At 02:18:52 the captain told that he would start climb when the aircraft had reached 10,350 ft; pitch attitude of 10° and still on right bank. The aircraft reached zero degree bank at 02:18:53 and started shallow left bank with pitch attitude of 12° nose up. By 02:18:57 the bank angle reached 200 left with pitch attitude of 11.8 and altitude of 10,550 ft and captain was still questioning F/O about the visibility towards his side but F/O informed his side not visible completely. The last data recorded in FDR was at 02:19:03 when the altitude had reached around 10,700 ft; pitch attitude of 7° nose up and left bank angle of 25° heading of 335° with EGPWS PULL-UP warning ON.
Probable cause:
The Commission concludes that the probable cause of this accident was the fact that despite of unfavourable weather conditions, the crew‘s repeated decision to enter into cloud during VFR flight and their deviation from the normal track due to loss of situational awareness aggravated by spatial disorientation leading to CFIT accident.
The contributing factors for the accident are:
1. Loss of situational awareness,
2. Deteriorating condition of weather,
3. Skill base error of the crew during critical phases of flight,
4. Failure to utilize all available resources (CRM), especially insensitivity to EGPWS cautions/warnings.