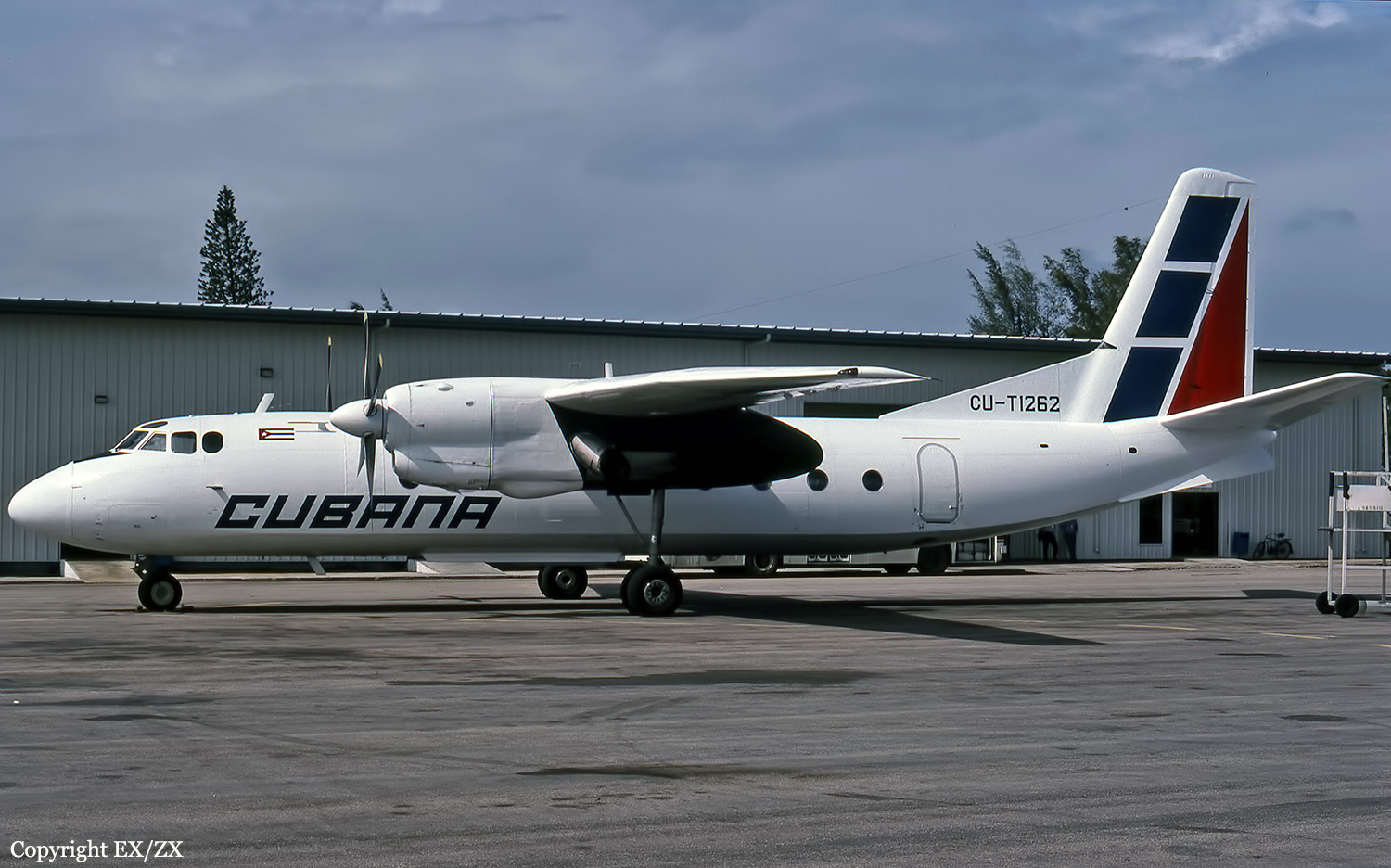
Crash of an Antonov AN-24RV off Santiago de Cuba: 44 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 11, 1997 at 2156 LT
Registration:
CU-T1262
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Santiago de Cuba - Havana
MSN:
27307610
YOM:
1972
Flight number:
CU787
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
39
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
44
Circumstances:
Shortly after takeoff from Santiago de Cuba-Antonio Maceo Airport, while climbing by night at an altitude of 500 feet, the aircraft entered an uncontrolled descent and crashed in the sea few hundred metres offshore. The aircraft disintegrated on impact and all 44 occupants were killed, among them six Spanish and two Brazilian citizens.
Probable cause:
Loss of control following the failure of the left engine for unknown reasons.