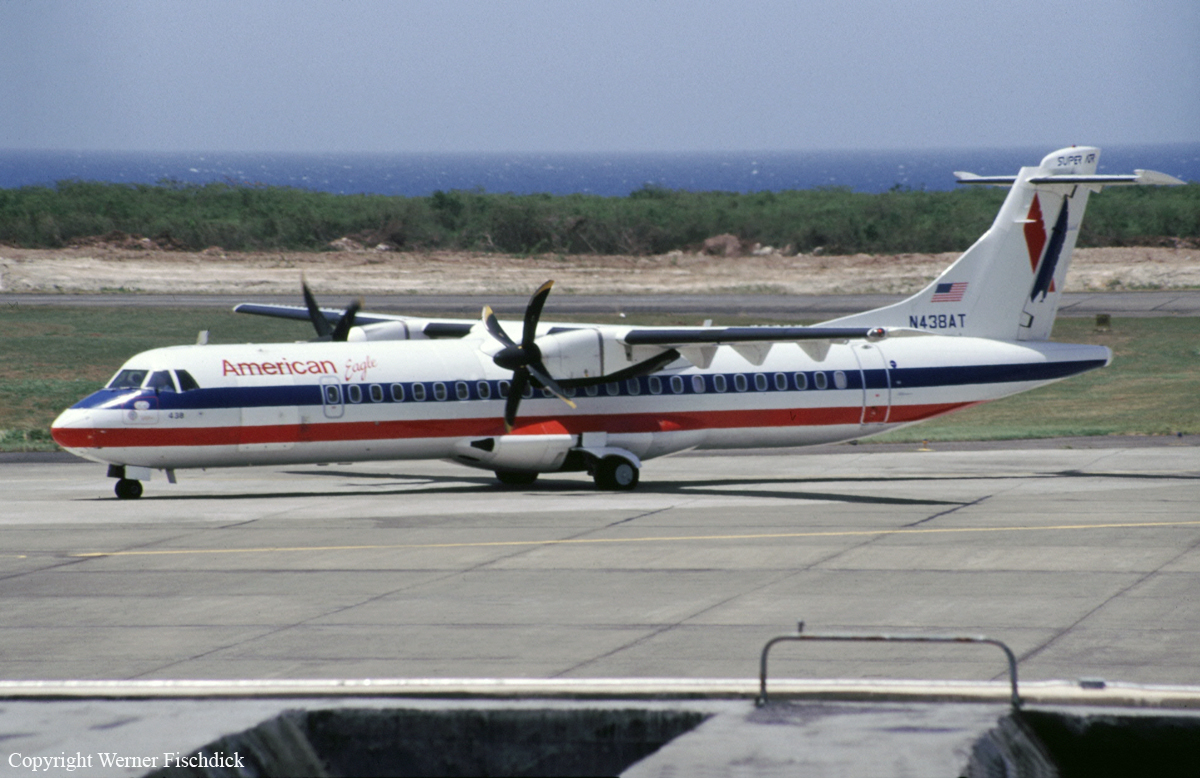
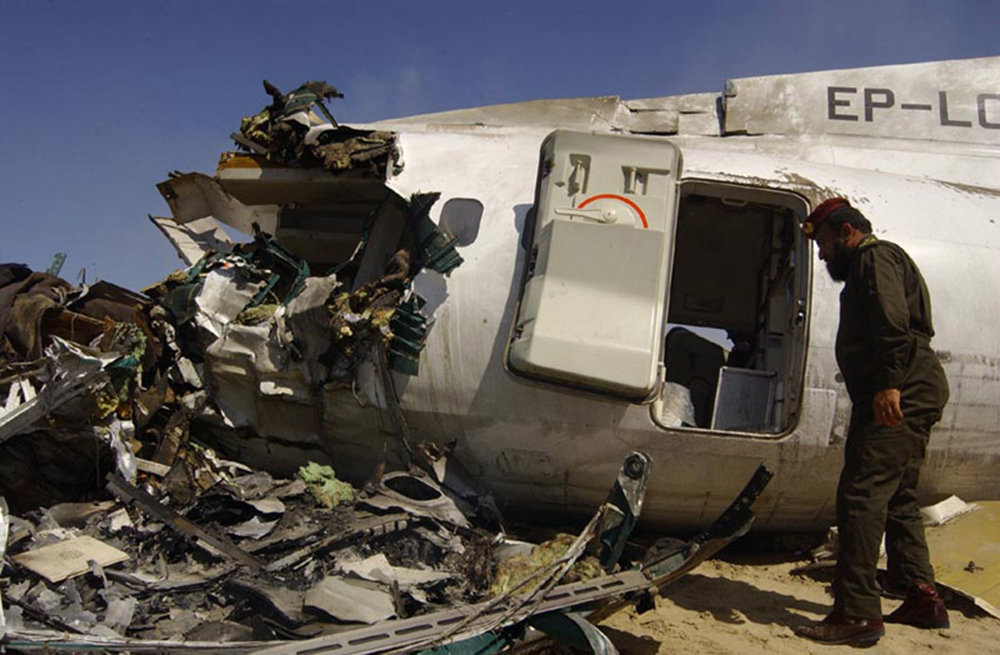
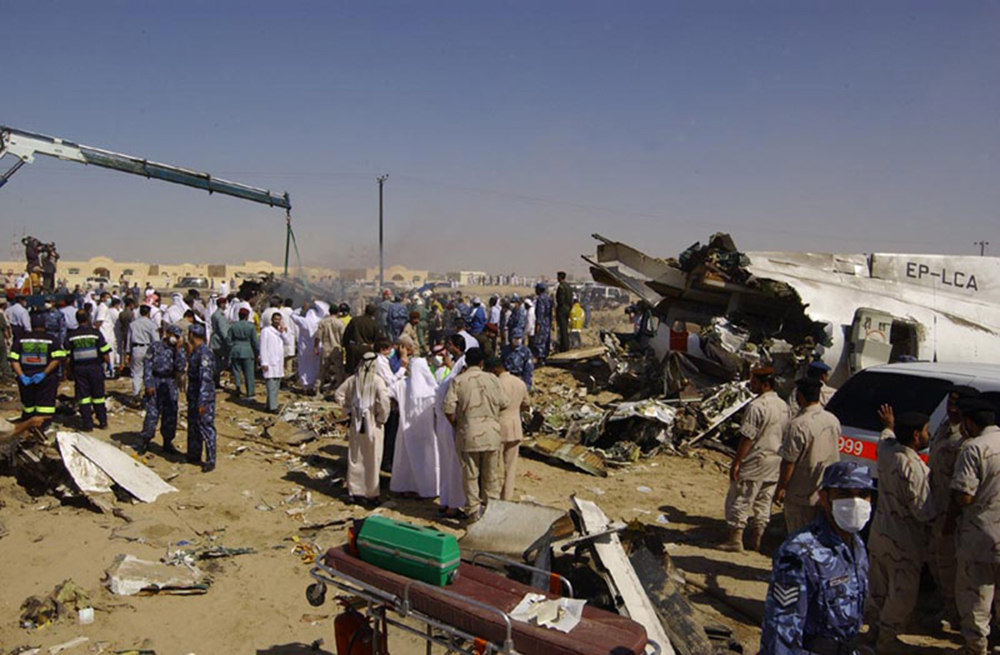
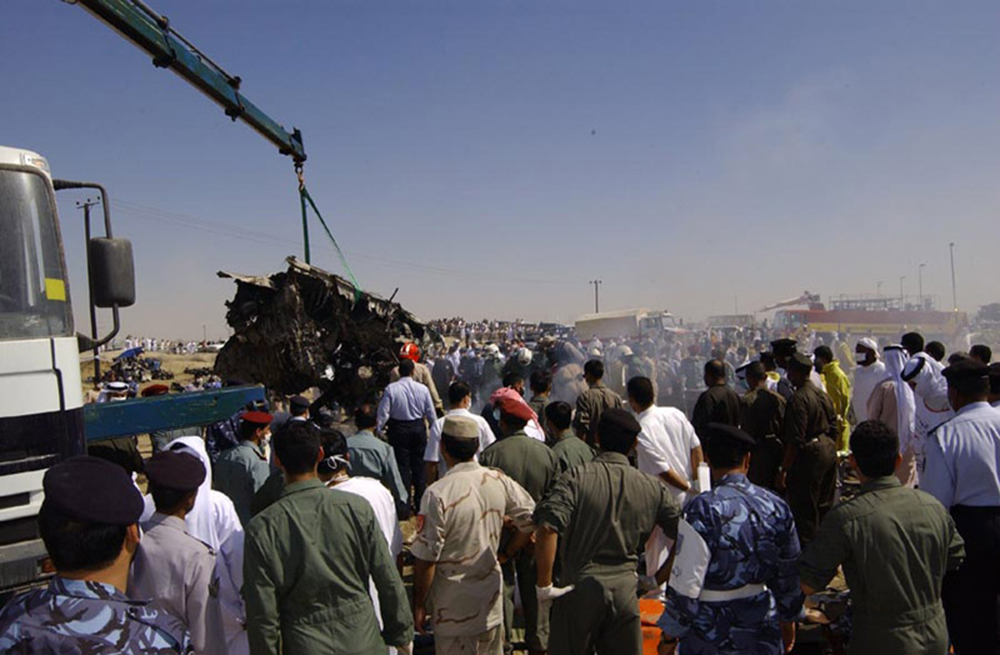
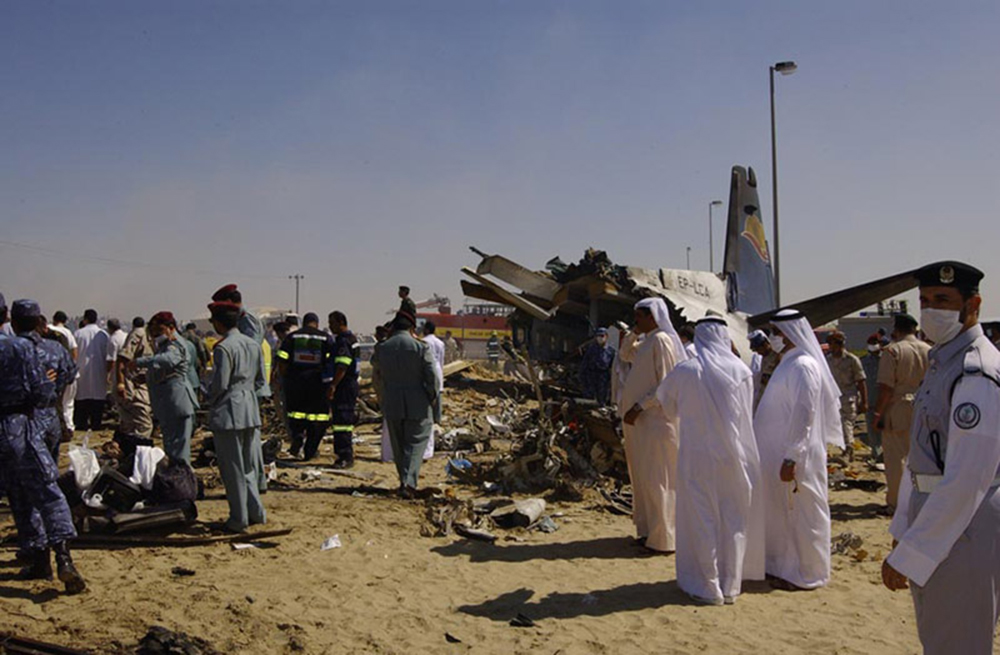
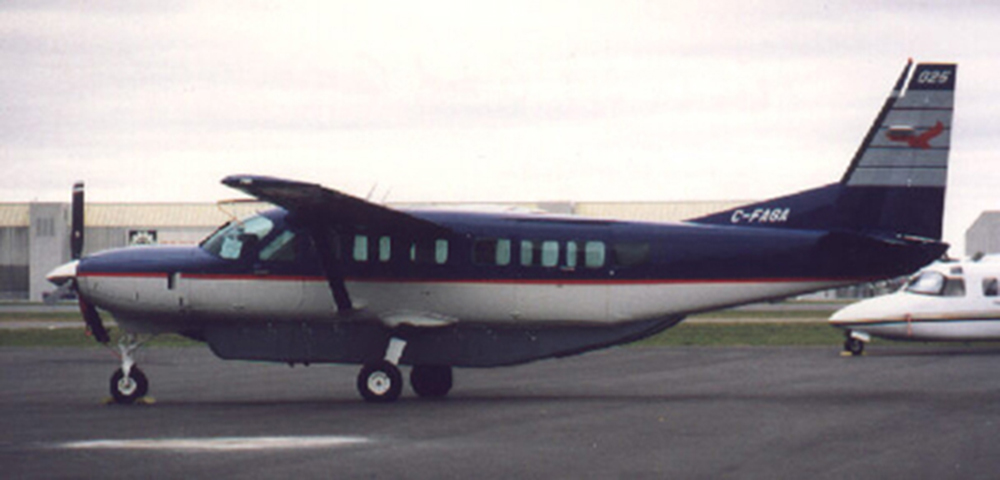
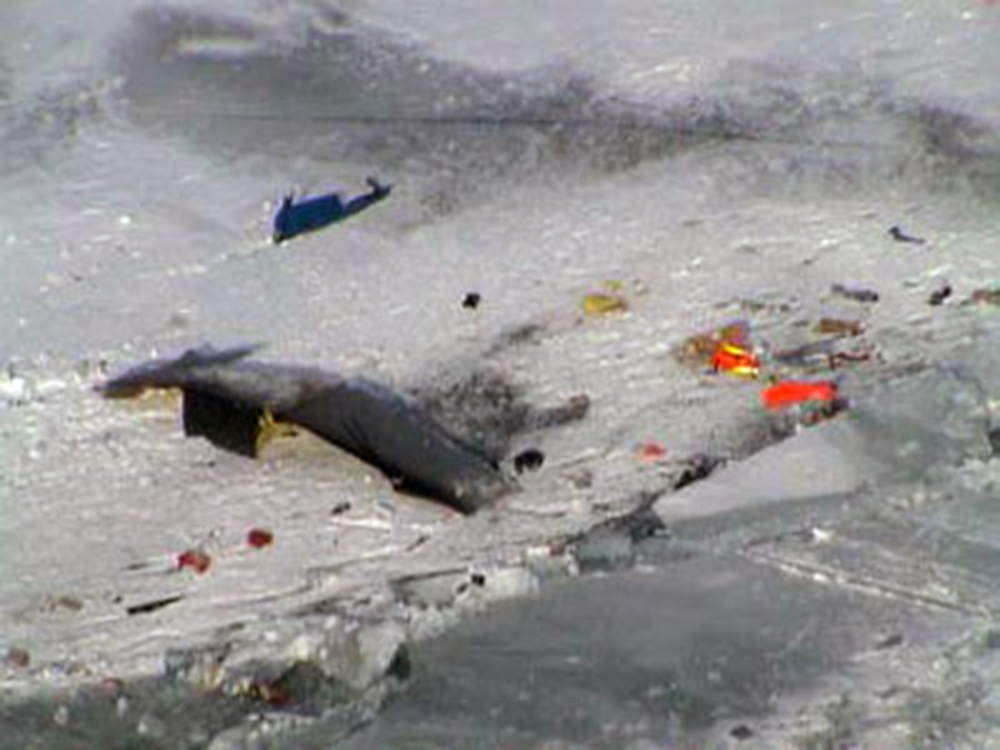
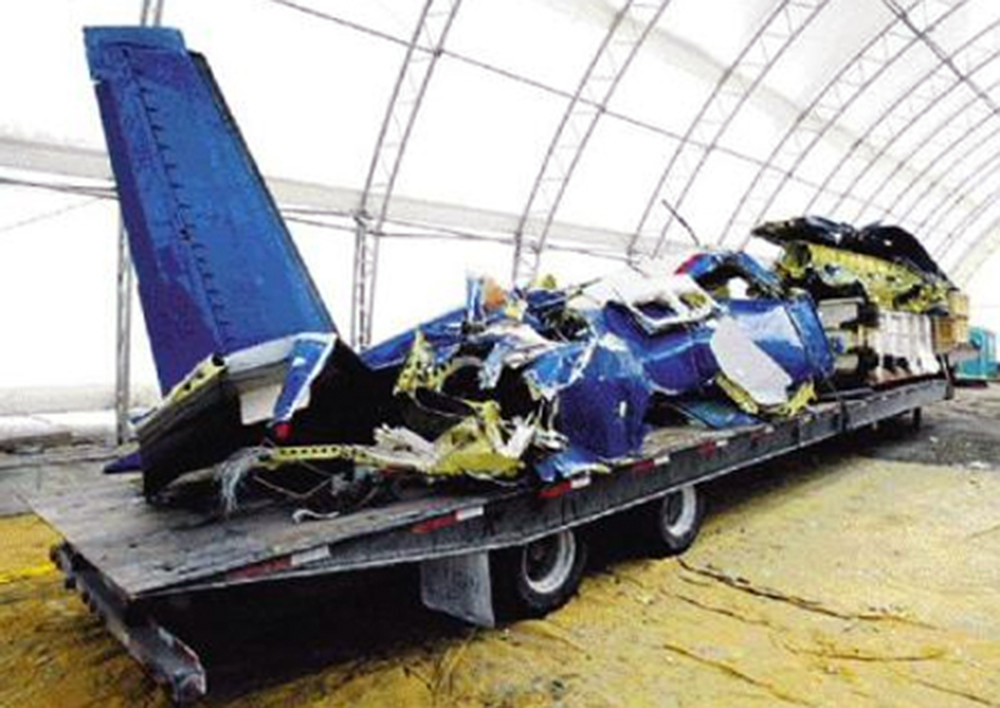
Crash of an ATR72-212 in San Juan
Date & Time:
May 9, 2004 at 1450 LT
Registration:
N438AT
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Mayaguez - San Juan
MSN:
438
YOM:
1995
Flight number:
AA5401
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
22
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
3814.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
20
Aircraft flight hours:
19276
Aircraft flight cycles:
18086
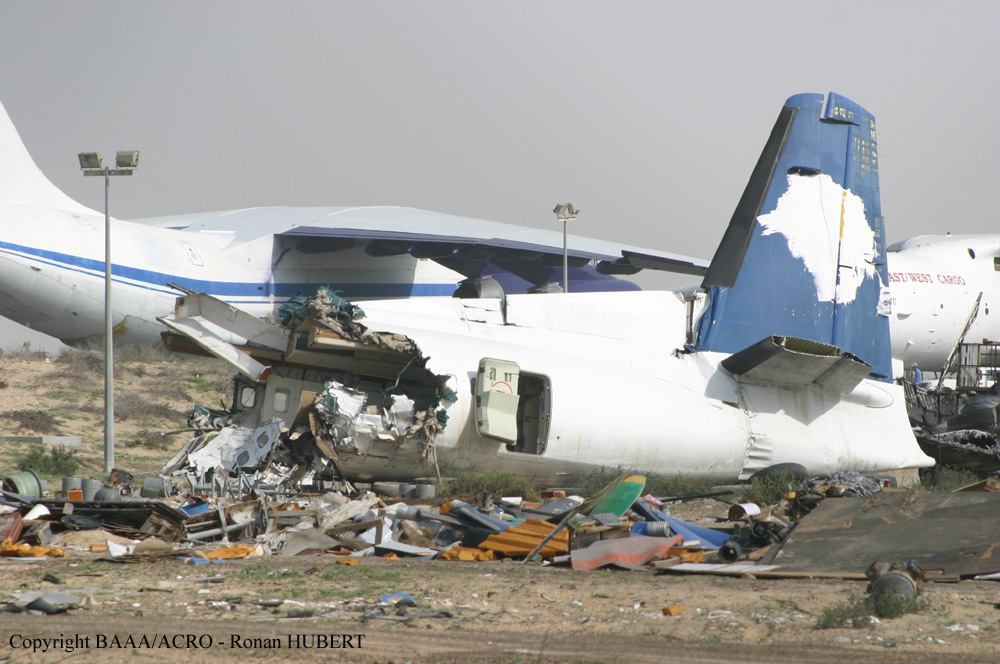
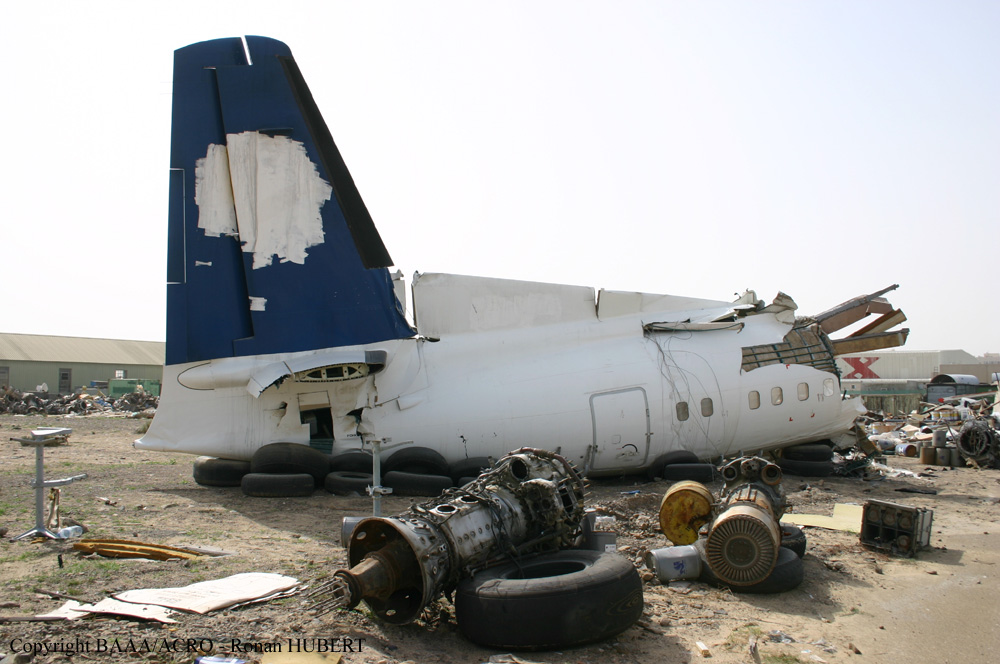
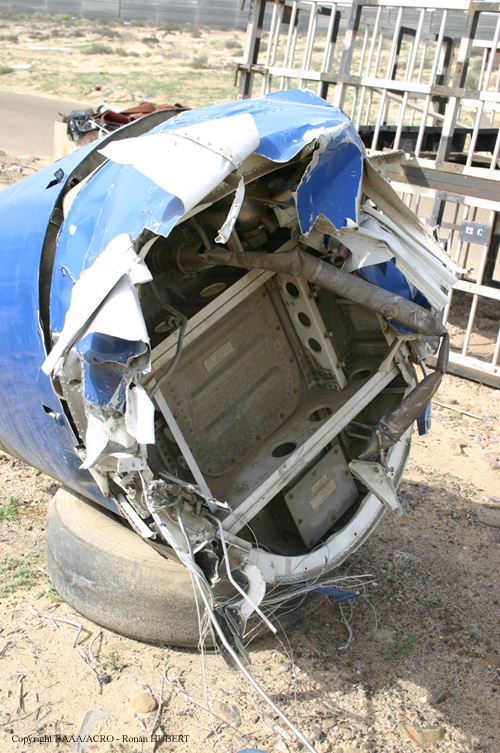
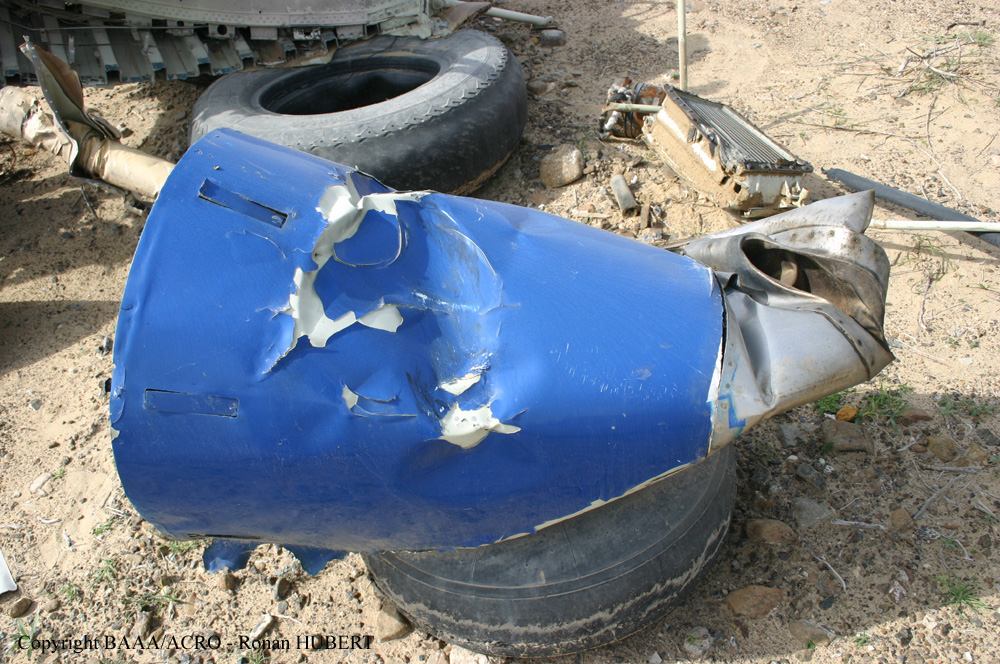
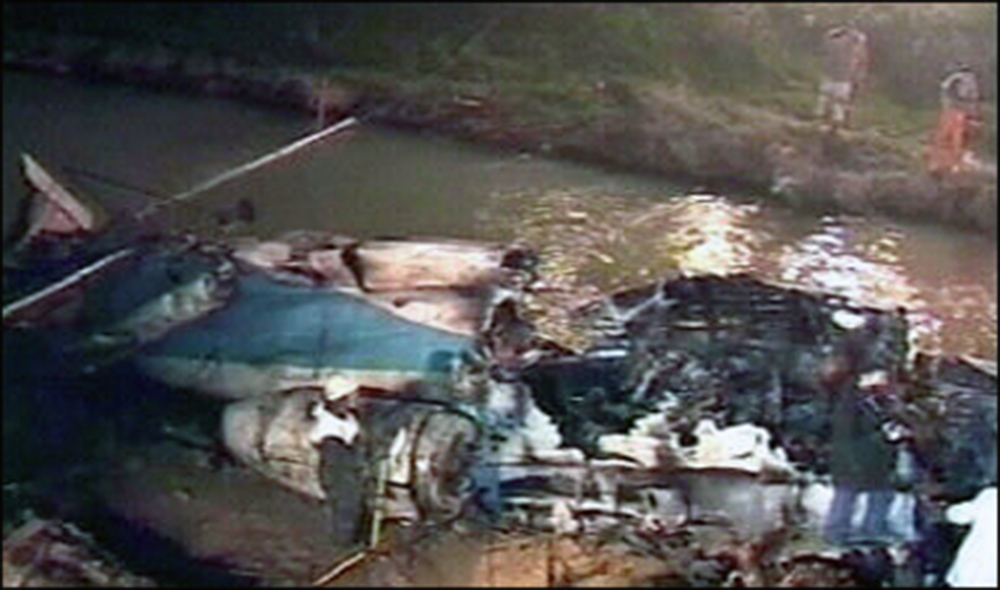
Circumstances:
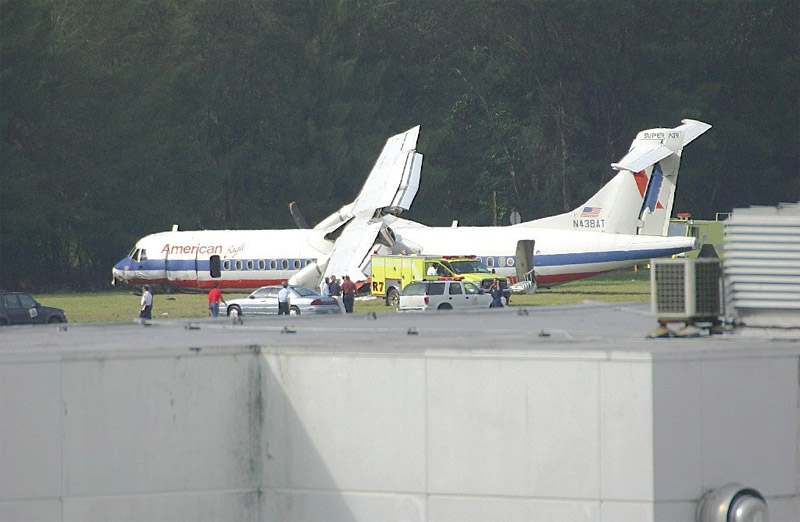
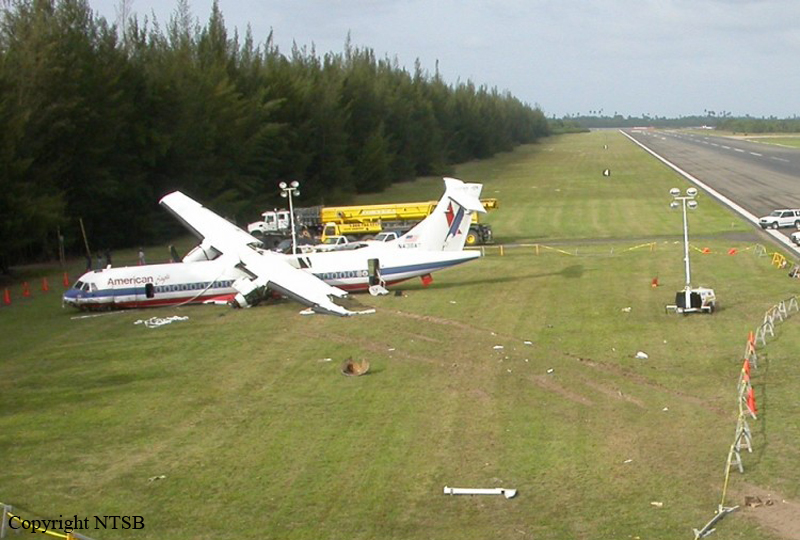
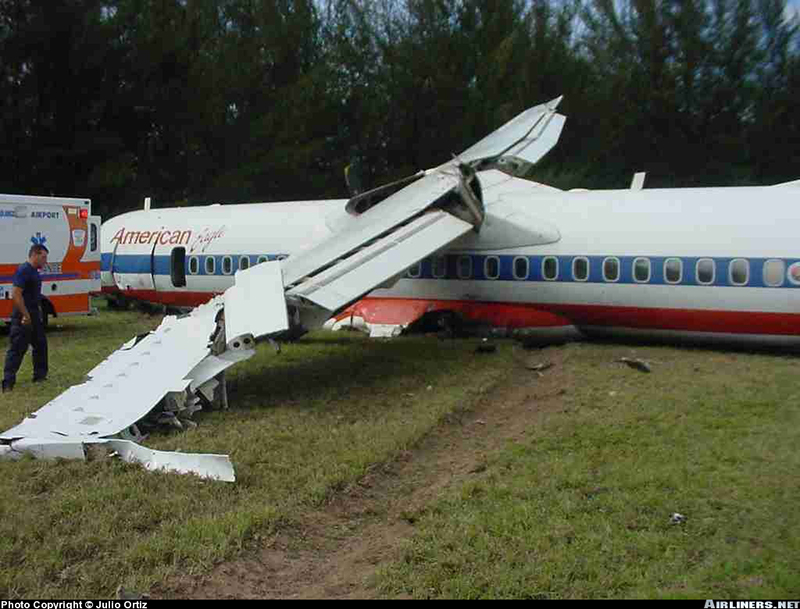
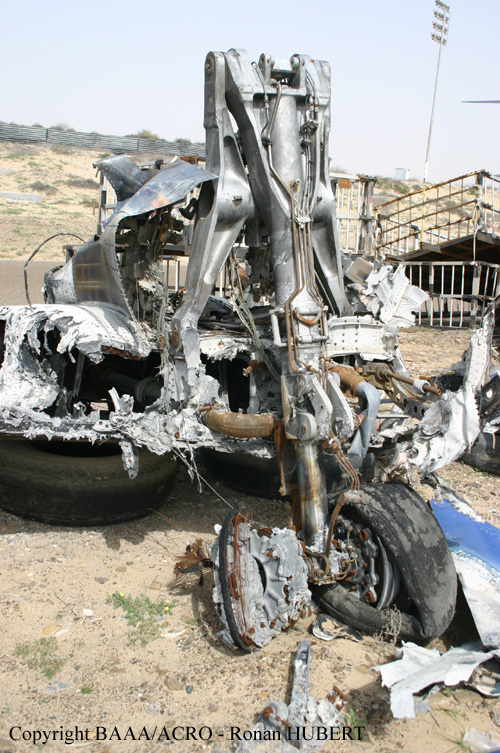
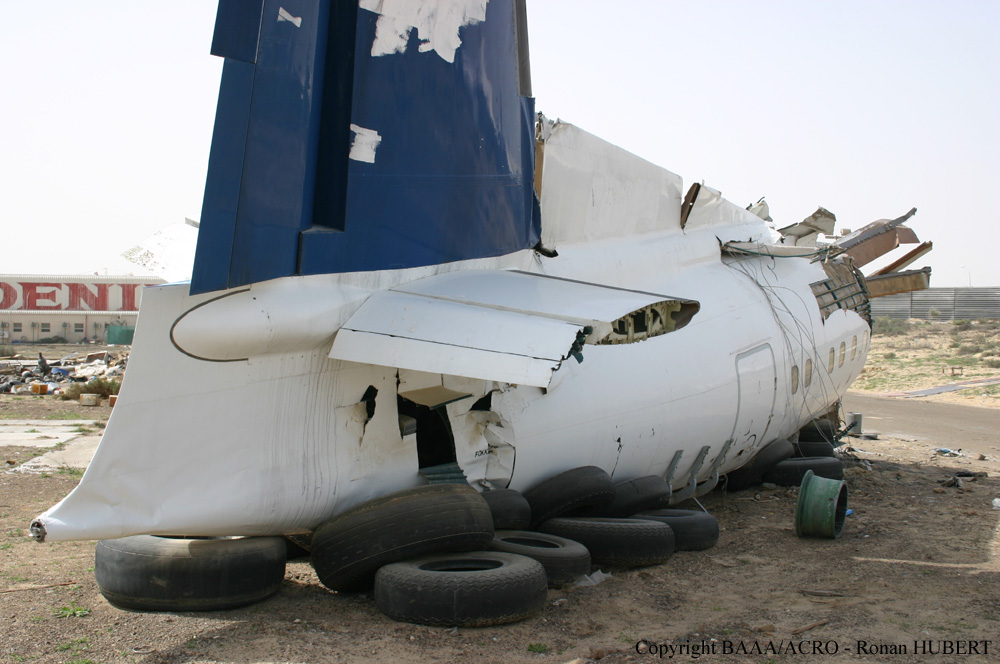
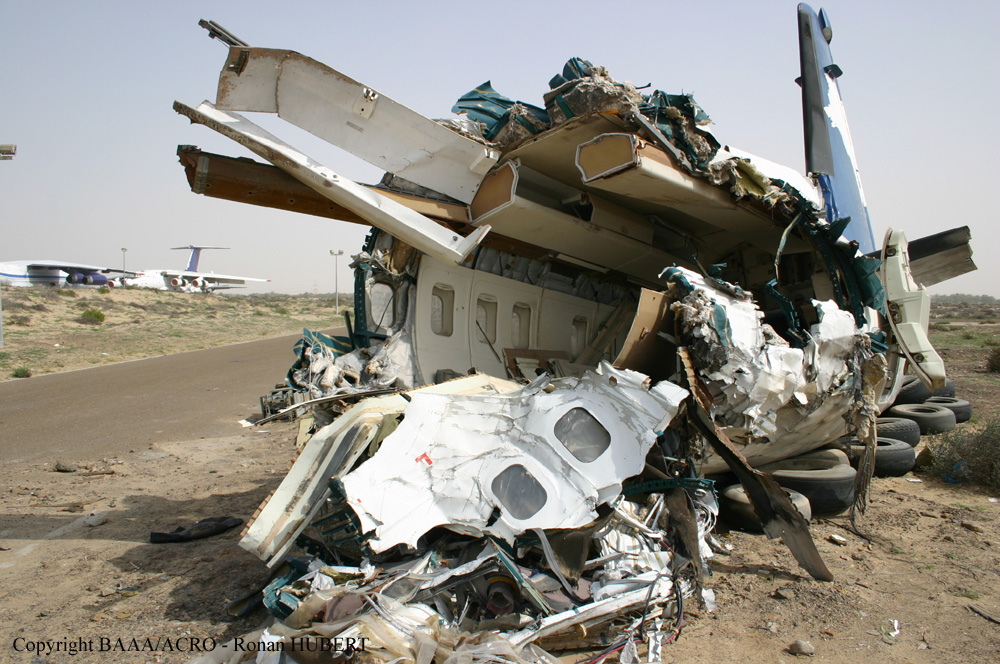
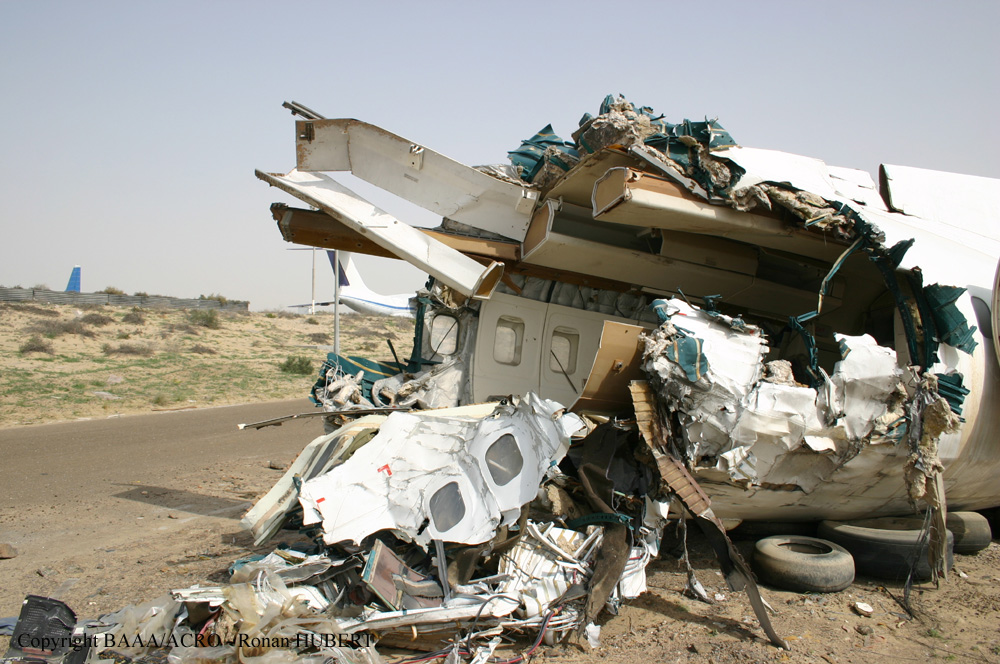
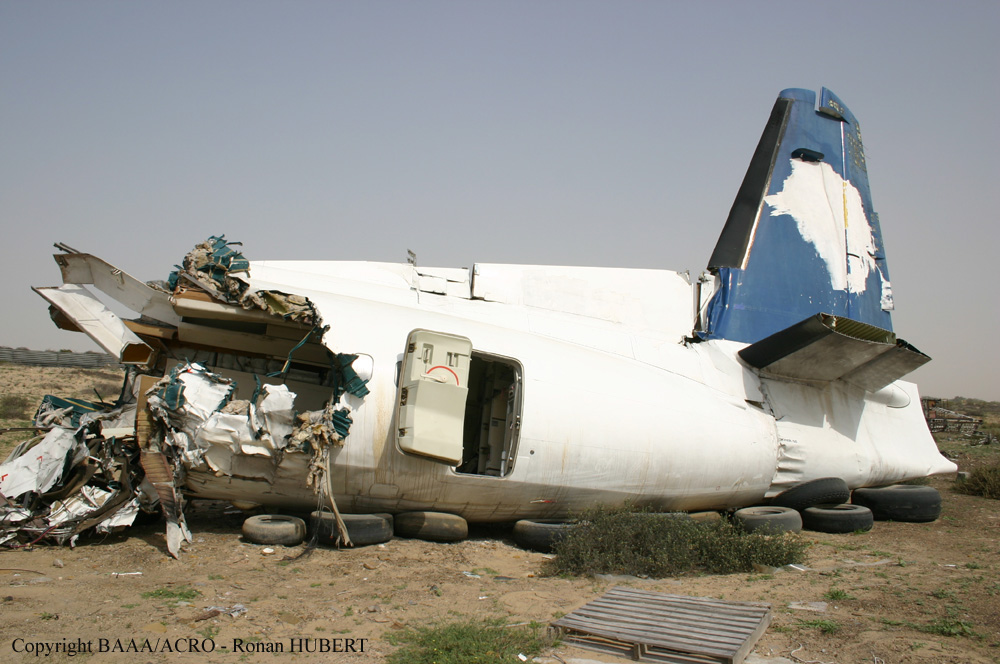
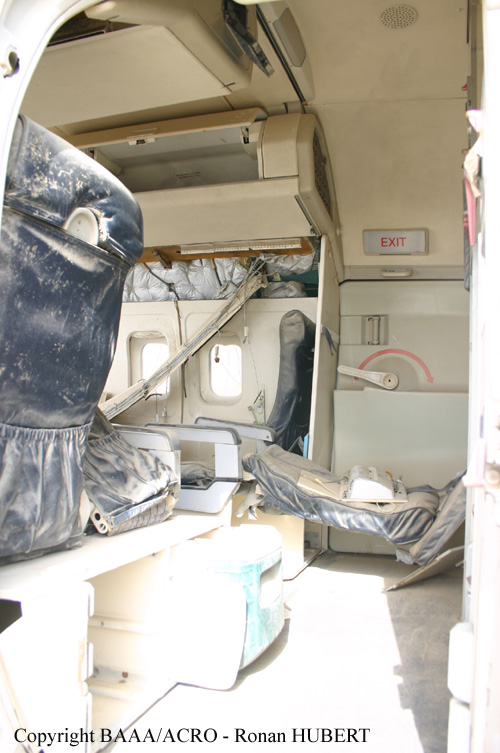
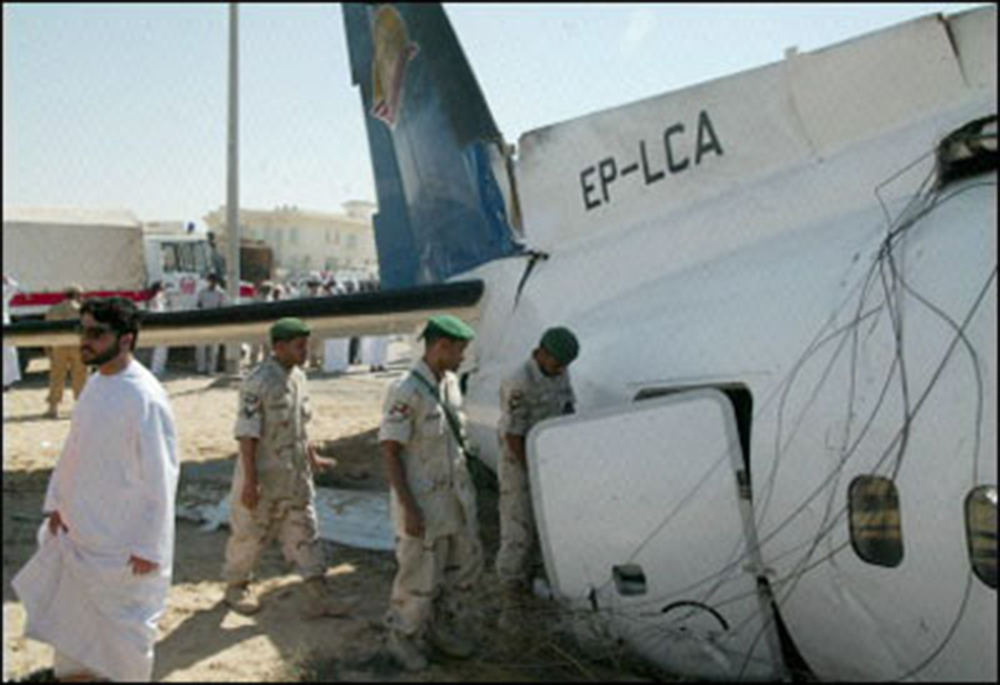
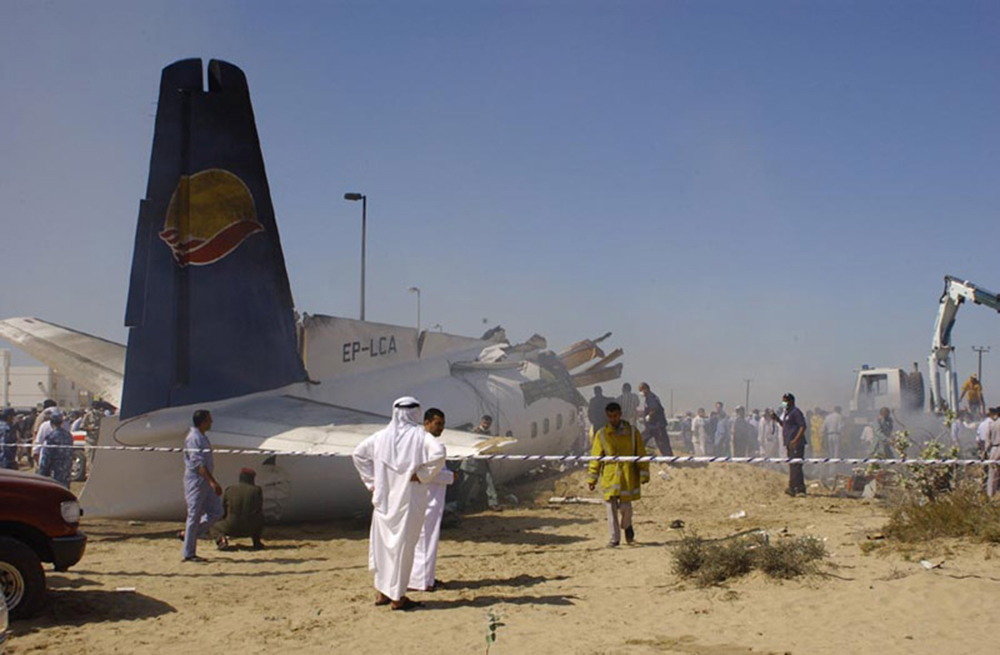
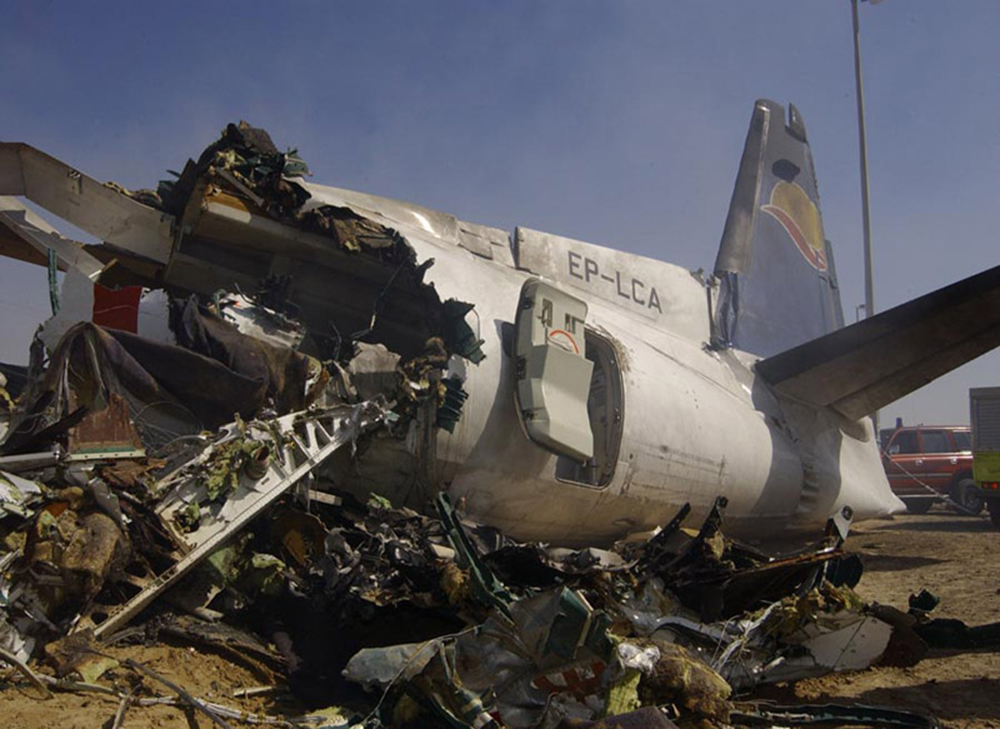
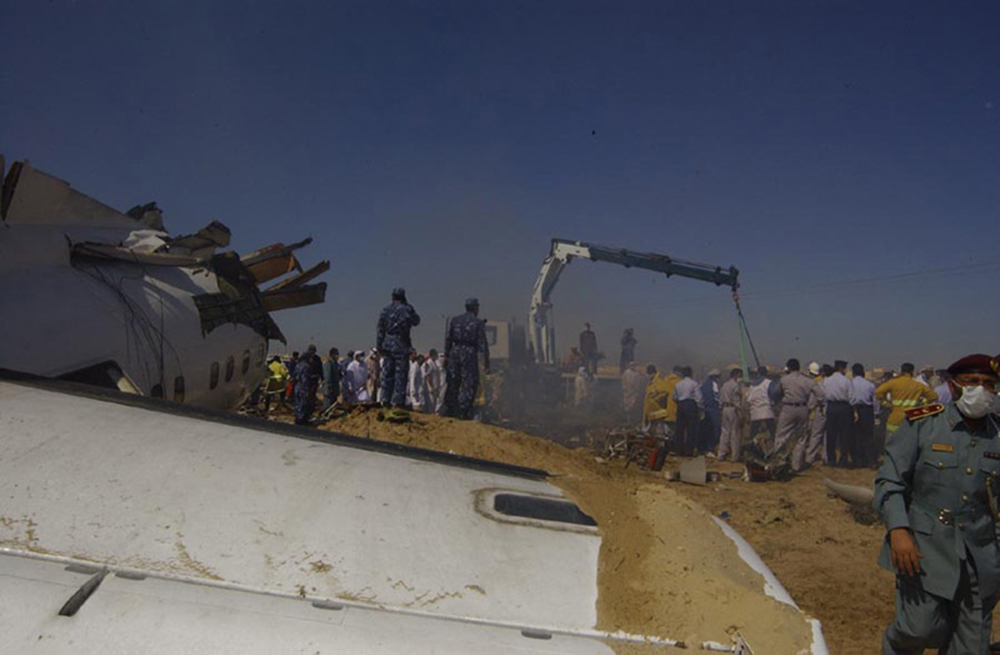
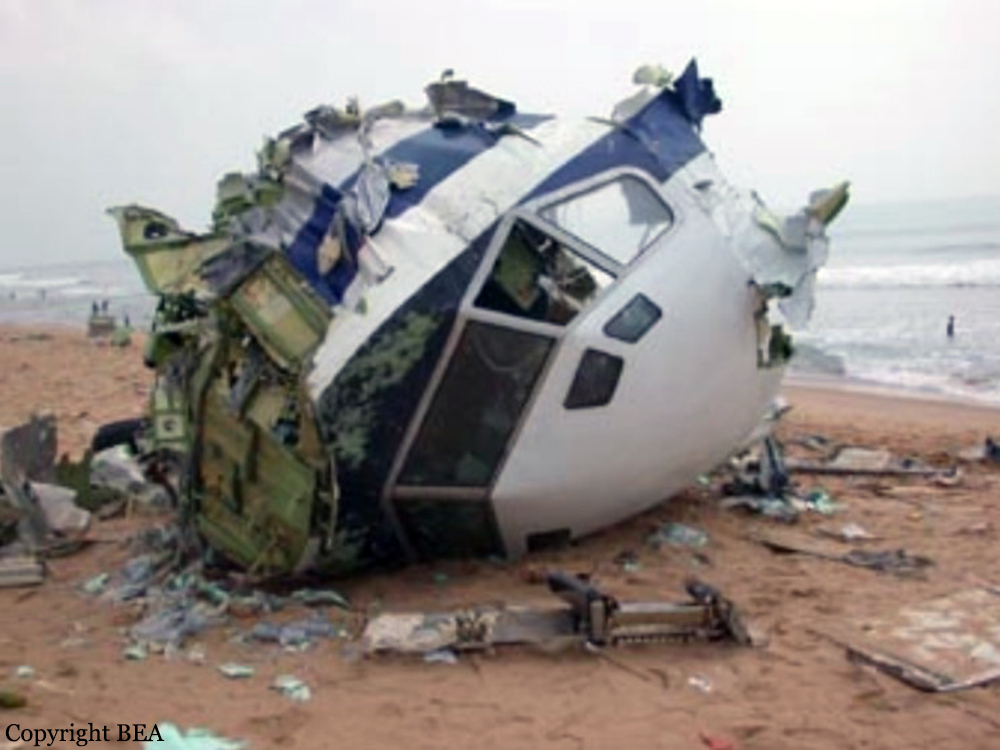
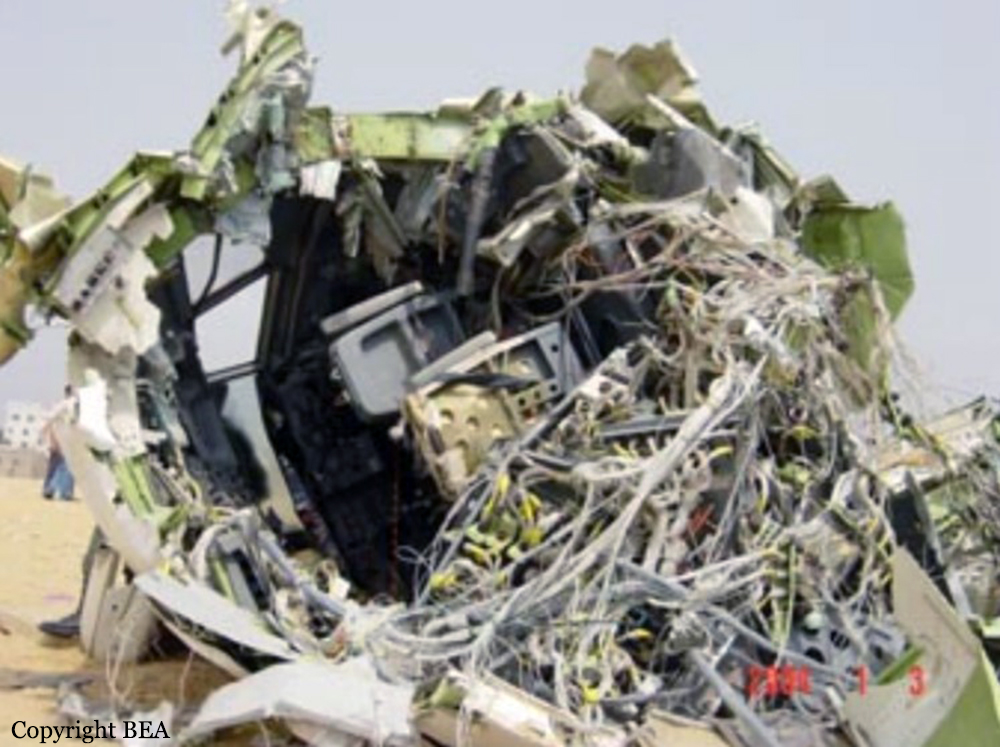
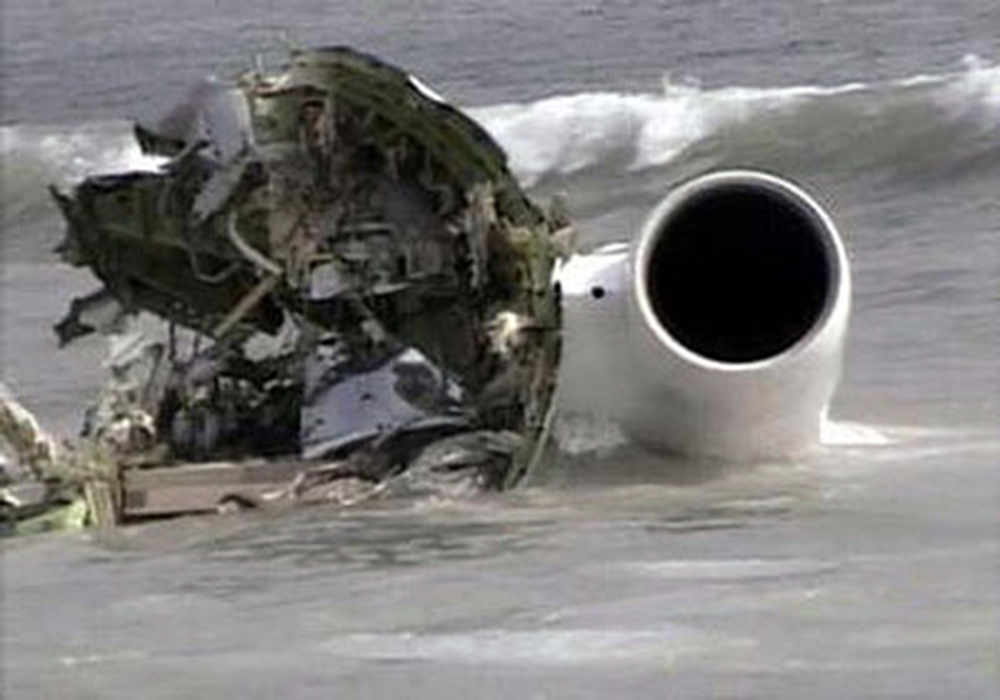
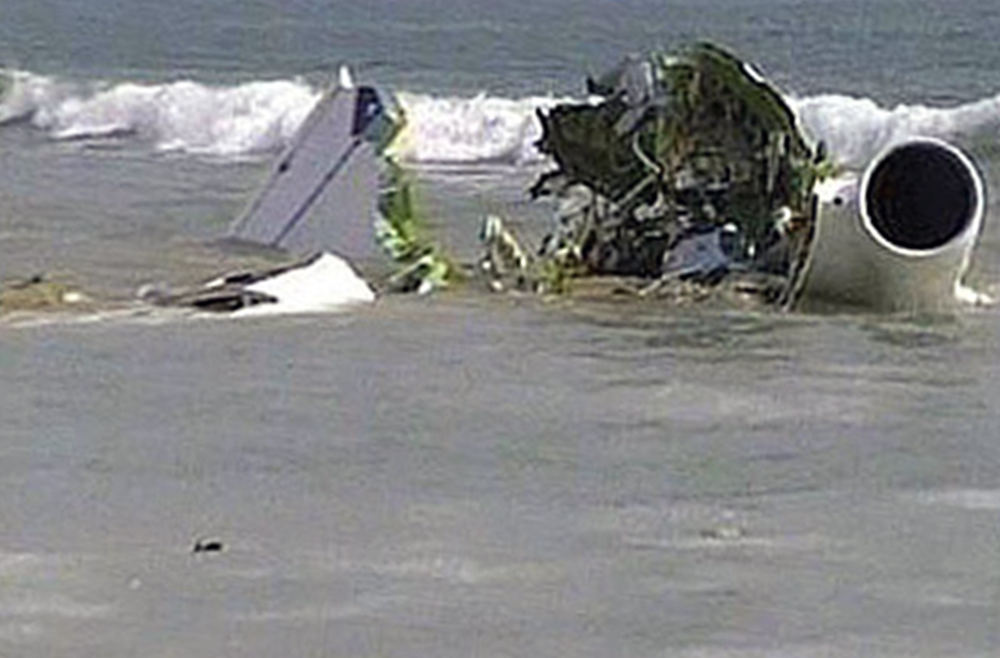
Flight 5401 departed Mayagüez, Puerto Rico, for San Juan about 14:15. The captain was the nonflying pilot for the flight, and the first officer was the flying pilot. The takeoff, climb, and en route portions of the flight were uneventful. At 14:37, as the flight approached the San Juan traffic area, the ATIS reported that winds were 060 degrees at 17 knots and gusting at 23 knots. Shortly thereafter, the captain briefed a Vref (the minimum approach airspeed in the landing configuration before the airplane reaches the runway threshold) of 95 knots and told the first officer to "stand by for winds." At 14:43 SJU Terminal Radar Approach Control cautioned the pilots of possible wake turbulence from a preceding Boeing. The captain told the first officer to slow down to about 140 kts. At 14:46, the local controller cleared the airplane to land on runway 08. The first officer turned the airplane left toward runway 08 and transitioned to the visual approach slope indicator. At 14:49, the captain stated, "you better keep that nose down or get some power up because you're gonna balloon." The airplane descended below the glideslope, causing a GPWS "glideslope" alert. The airplane was about 45 feet above ground level and traveling at 110 knots indicated airspeed when it crossed the runway 08 threshold. After the airplane crossed the runway threshold, the captain stated, "power in a little bit, don't pull the nose up, don't pull the nose up." At 14:49:39, the captain stated, "you're ballooning," and the first officer replied, "all right." The airplane touched down for the first time about 14:49:41 and about 1,600 feet beyond the runway 08 threshold with vertical and lateral loads of about 1.3 Gs and -0.10 G, respectively. Upon touchdown the captain stated, "get the power," and, 1 second later, "my aircraft." The first officer responded, "your airplane." The airplane had skipped to an altitude of about 4 feet and touched down again two seconds later about 2,200 feet beyond the runway 08 threshold. The airplane then pitched up to an angle of 9° while climbing to an altitude of 37 feet and the engine torque increased from 10 to 43 percent. About 14:49:49, the pitch angle decreased to -3°, and the engine torque started to decrease to 20 percent with the pitch angle decreasing to -10°. The airplane touched down a third time about 14:49:51 at a bank angle of 7° left wing down and about 3,300 feet beyond the runway 08 threshold and with vertical and lateral loads of about 5 Gs and 0.85 G. The ATR pitched up again to 24 feet and landed a fourth time about 14:49:56 (about 15 seconds after the initial touchdown) and about 4,000 feet beyond the runway 08 threshold. This time the airplane pitched down to -7° and that it was banked 29° left wing down. The airplane came to a complete stop on a grassy area about 217 feet left of the runway centerline and about 4,317 feet beyond the runway threshold.
Probable cause:
The captain’s failure to execute proper techniques to recover from the bounced landings and his subsequent failure to execute a go-around.
Final Report: