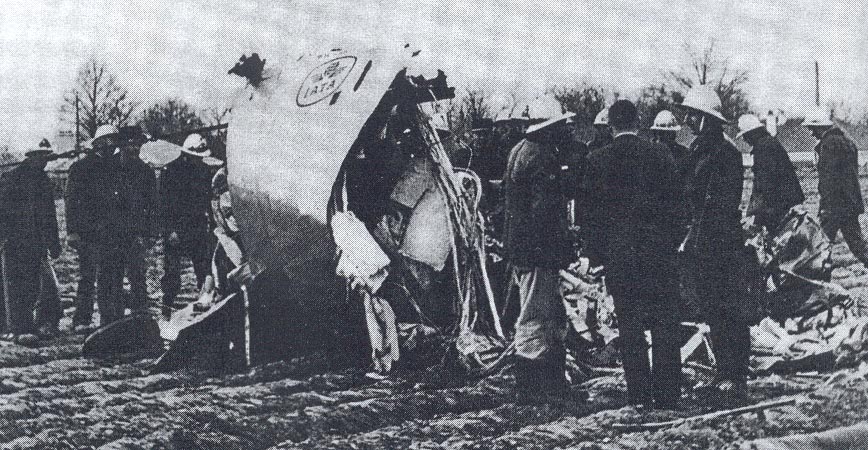
Circumstances:
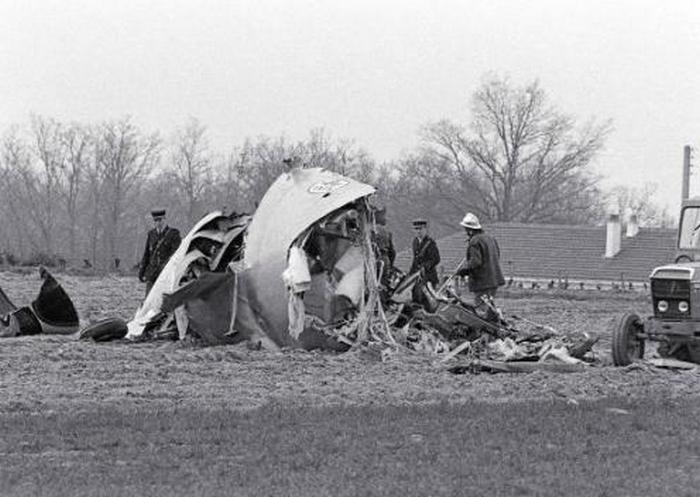
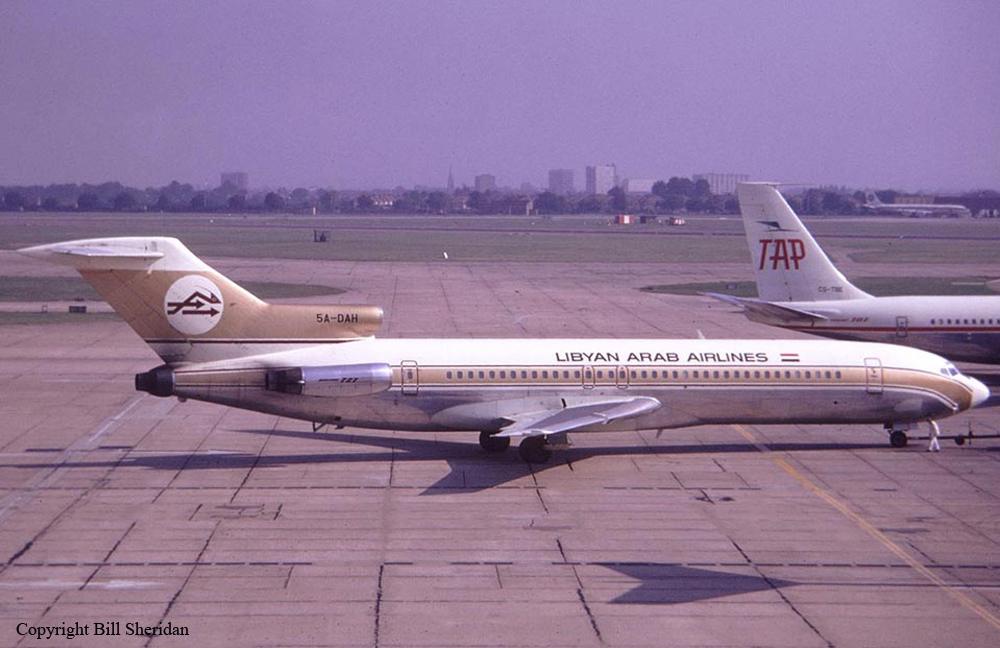
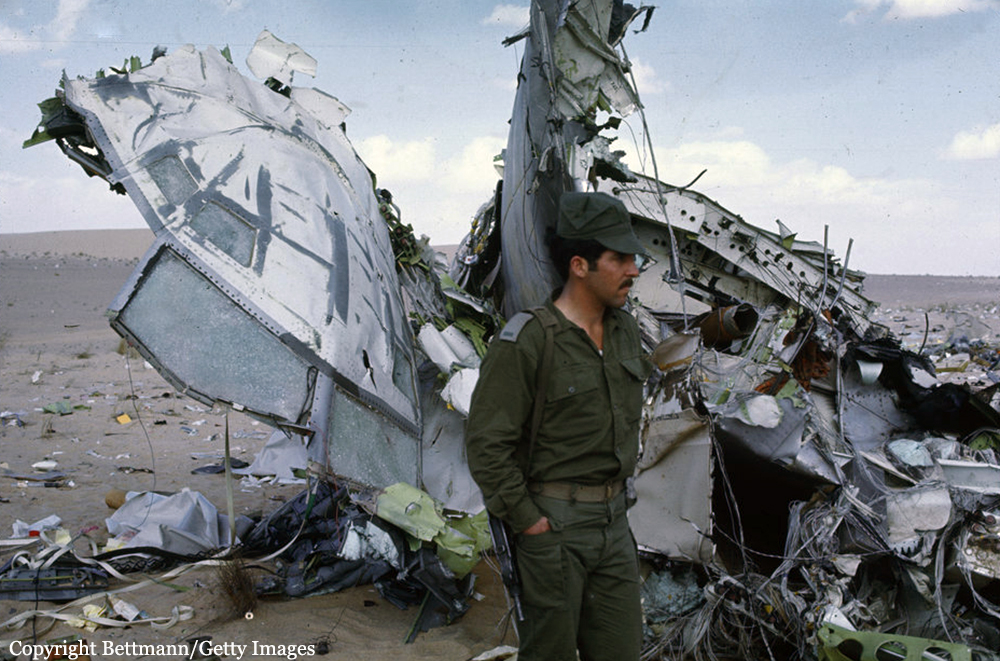
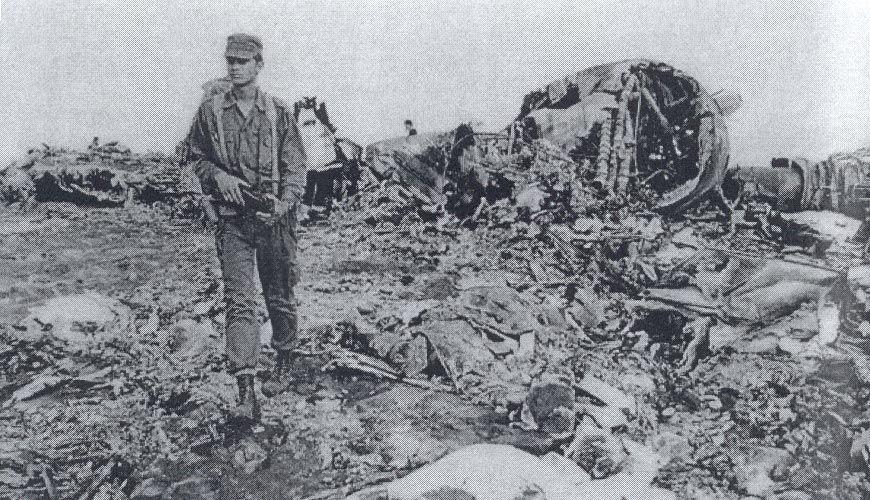
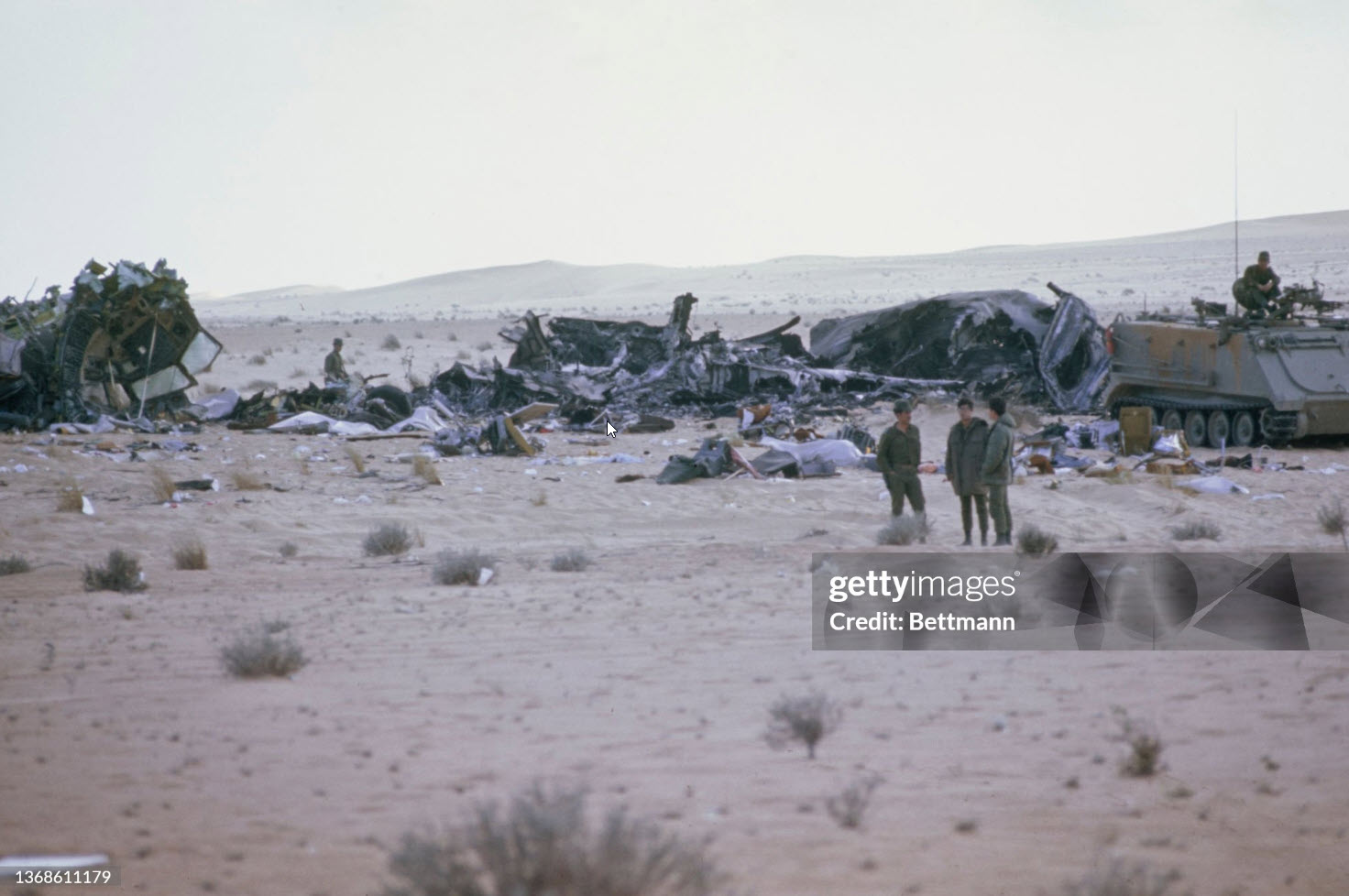
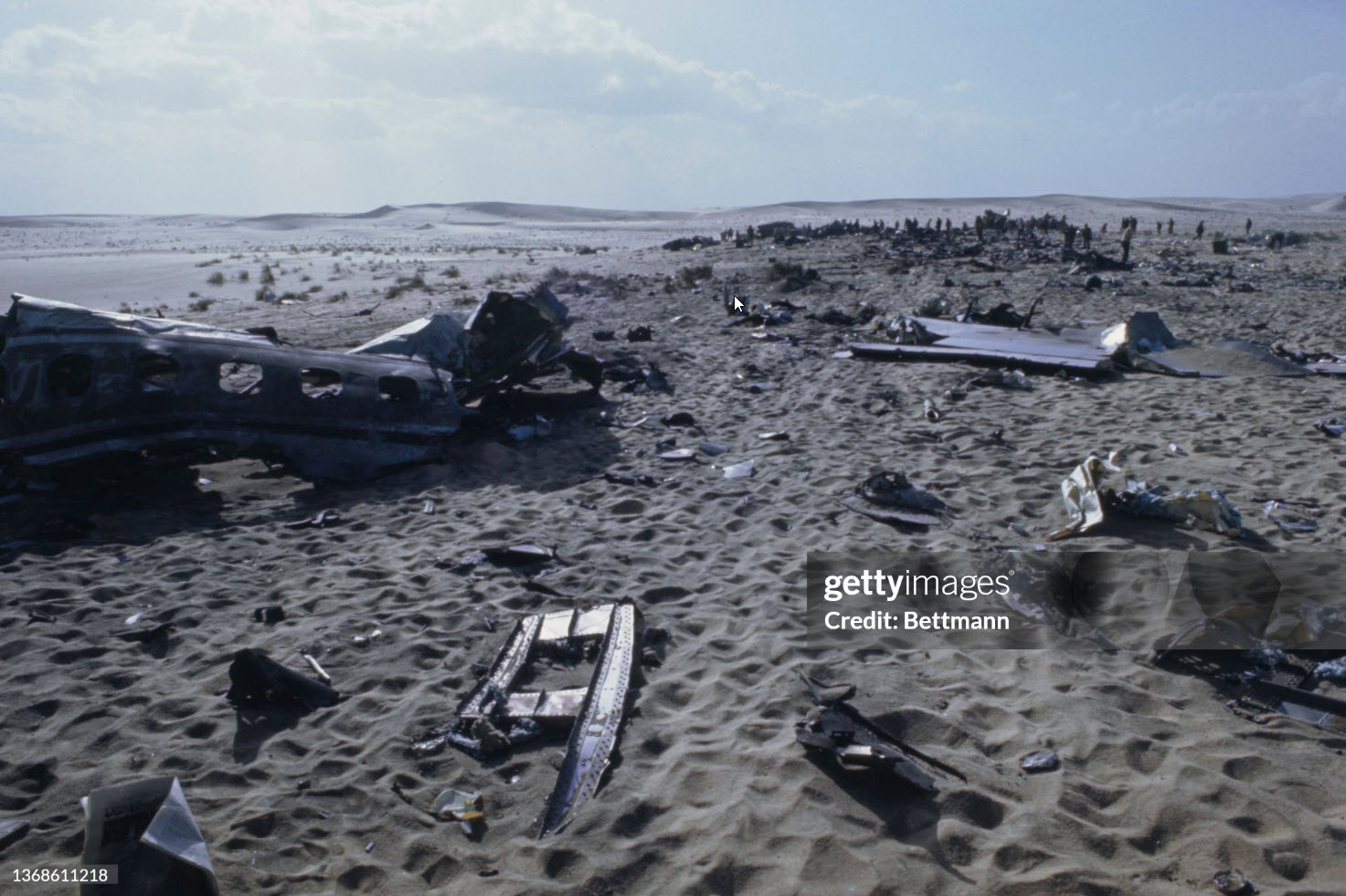
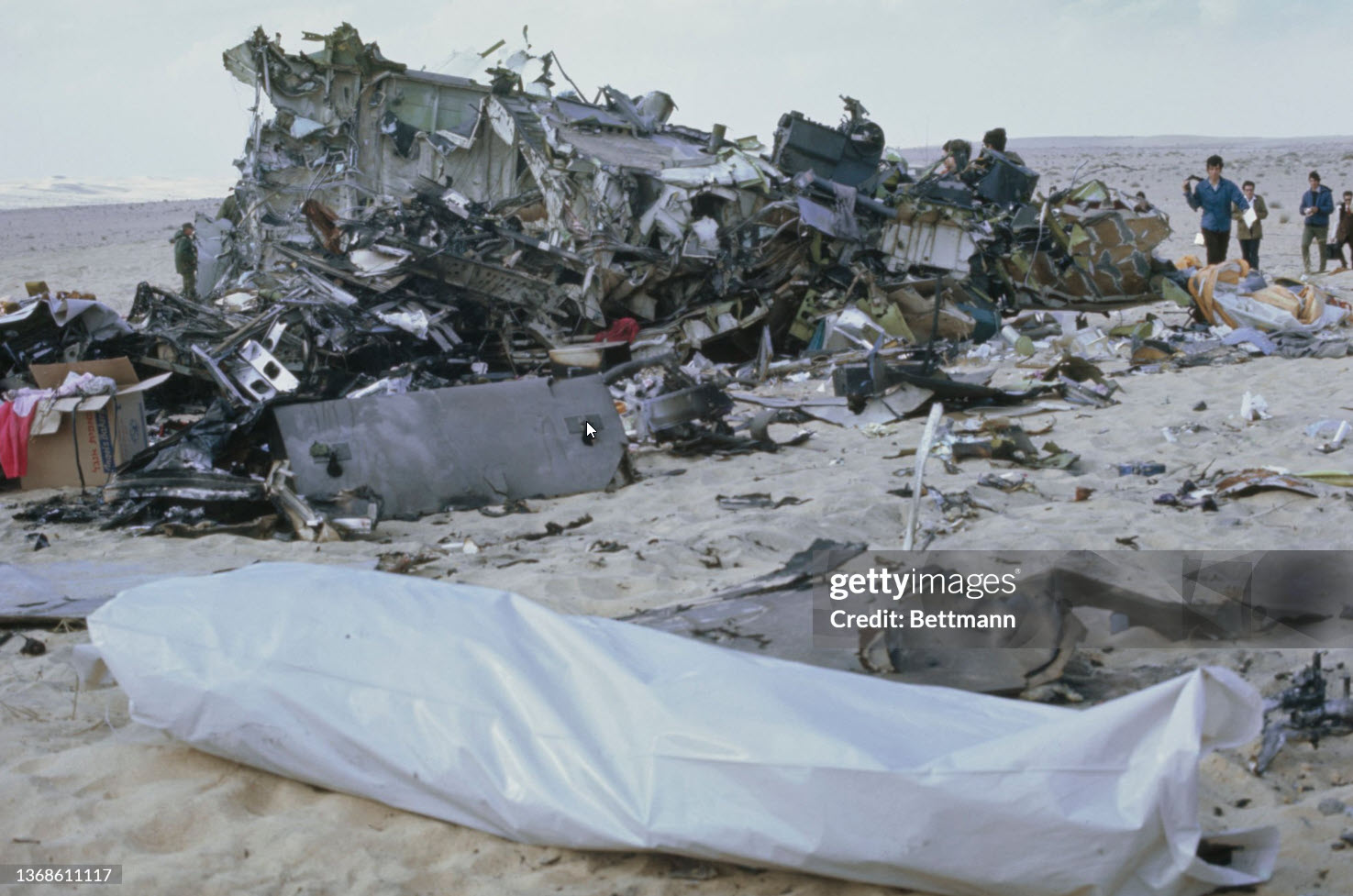
Flight 114 was an international scheduled service from Tripoli to Bahrain with intermediate stops in Benghazi and Cairo. On board were 104 passengers and a crew of nine, five from Air France, among them the captain, Mr. Jacques Bourgès, aged 42. Normally, the Benghazi – Cairo route was flown eastwards along the Libyan coast until reaching the city of Sidi Barrani in Egypt, where the airway turned inland to the VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) and Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) area located west of Lake Qarun. The entry to the Cairo terminal area was made on a north-easterly heading over a 71-nautical-mile (131 km) long path that separated Lake Qarun from the Cairo VOR. At 13:45 the Cairo traffic control (CTC) saw the aircraft approaching from the west. Permission was granted to land in runway 23. CTC surprisingly saw the Boeing heading eastward towards the Suez Canal at 13:50. Evidence from both the recovered Boeing 727 voice recorders and the Israeli authorities' flight data recorder later showed that the Libyan aircraft was likely to had been already off course when it reported its position over Qarun, probably due to strong westerly upper-level winds associated to a low level sandstorm. The crew was forced to rely on instrument navigation because of this sandstorm. Both instrument and navigational error caused the aircraft to go off course, entering airspace dominated by Israel when flying over the Sinai Peninsula. By this time the aircraft had been lost from the Egyptian air traffic control. The crew believed they were close to the destination airport and started the descent. At 13:55 the aircraft was detected in the radar by the Israelis as it was entering Israeli airspace; it was located south-east of Suez at an altitude of 15,000 feet (4,600 m). Two Israeli Air Force Phantoms were sent to intercept the then unidentified aircraft. Following the re-establishment of communications with CTC the pilot of the Libyan aircraft looked through the cabin's port window and saw the fighters, but he mistook them for Egyptian MiGs. The Libyan aircraft continued flying deeper into the Sinai at a speed of 325 miles per hour (523 km/h), but it suddenly veered to the west. It was at that time that the Boeing's crew realised they were having problems with their instruments. The Israeli fighter pilots attempted to make visual contact with the passenger airliner's crew, and tried to communicate to them by signaling with their hands and dipping their wings. The 727 crew's response was interpreted as a denial of that request. The 727 adopting a westward course was interpreted by the Israeli pilots as an attempt to flee. The Israeli Phantom pilots fired bursts from their 20 mm M61 cannons, severely damaging the airliner's control surfaces, hydraulic systems, and wing structure. Flight 114 attempted an emergency landing in an area covered with sand dunes, but crashed, with an explosion near the right main landing gear. Four passengers and the copilot survived while 108 other occupants were killed. The copilot later said that the flight crew knew the Israeli jets wanted them to land but relations between Israel and Libya made them decide against following instructions. In direct contradiction to the co-pilot's own account, the Libyan government stated that the attack occurred without warning. Israel's air force perceived Flight 114 as a security threat, and that among the possible tasks it could have been undertaking was an aerial spy mission over the Israeli air base at Bir Gifgafa. The Israeli government also revealed that LN114 was shot down with the personal authorization of David Elazar, the Israeli Chief of Staff. Israel's argument was that the heightened security situation and the erratic behaviour of the jet's crew made the actions taken prudent. The United Nations did not take any action against Israel. The 30 member nations of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) voted to censure Israel for the attack. The United States did not accept the reasoning given by Israel, and condemned the incident. Israel's Defense Minister, Moshe Dayan, called it an "error of judgment", and Israel paid compensation to the victims' families.