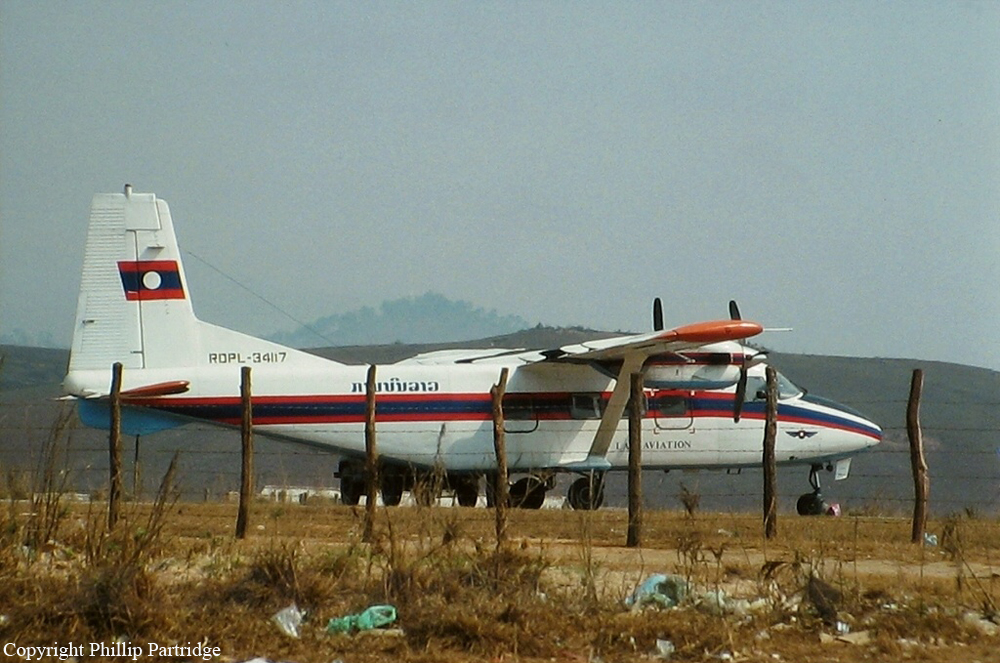
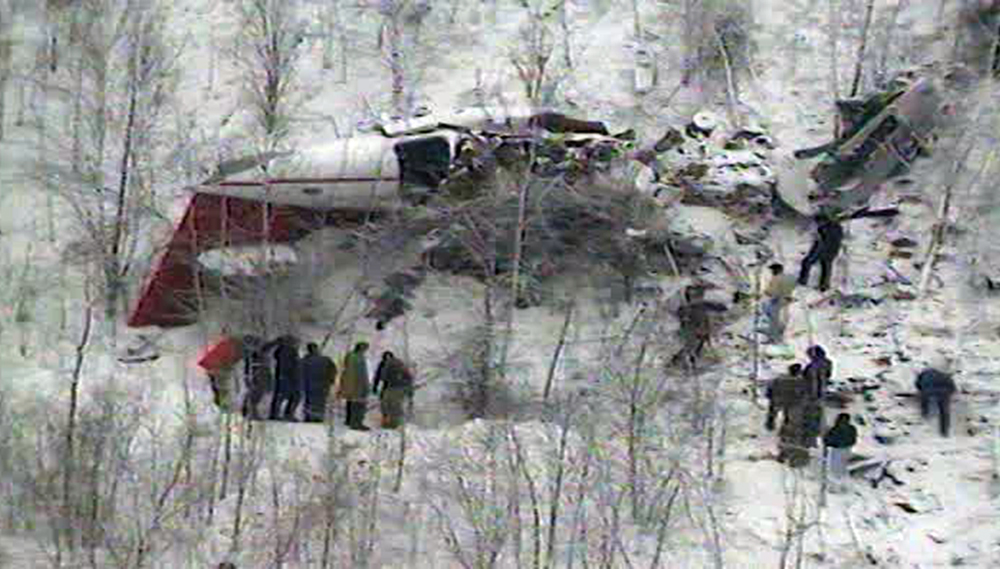
Crash of a Harbin Yunsunji Y-12-II near Phônsavan: 18 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 13, 1993 at 0920 LT
Registration:
RDPL-34117
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Vientiane – Phônsavan
MSN:
0042
YOM:
1991
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
16
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
18
Circumstances:
While descending to Phônsavan Airport, the crew encountered below minima weather conditions due to fog. On approach, the pilot failed to realize his altitude was too low when the aircraft struck trees and crashed in a hilly and wooded terrain located 28 km from the airport, bursting into flames. All 18 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
Controlled flight into terrain after the crew decided to continue the approach below the minimum safe altitude in below minima weather conditions.