Crash of a Beechcraft C90 King Air in Columbia
Date & Time:
Jan 27, 2014 at 0530 LT
Registration:
N350WA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Sacramento - Columbia
MSN:
LJ-762
YOM:
1978
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
1784.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2237
Aircraft flight hours:
9501
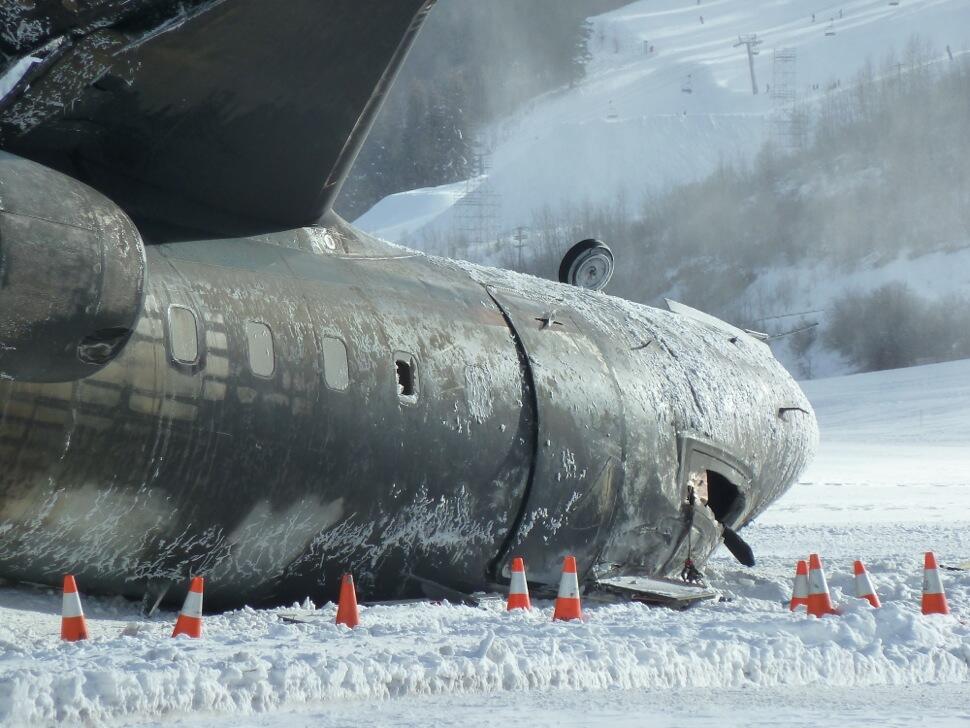
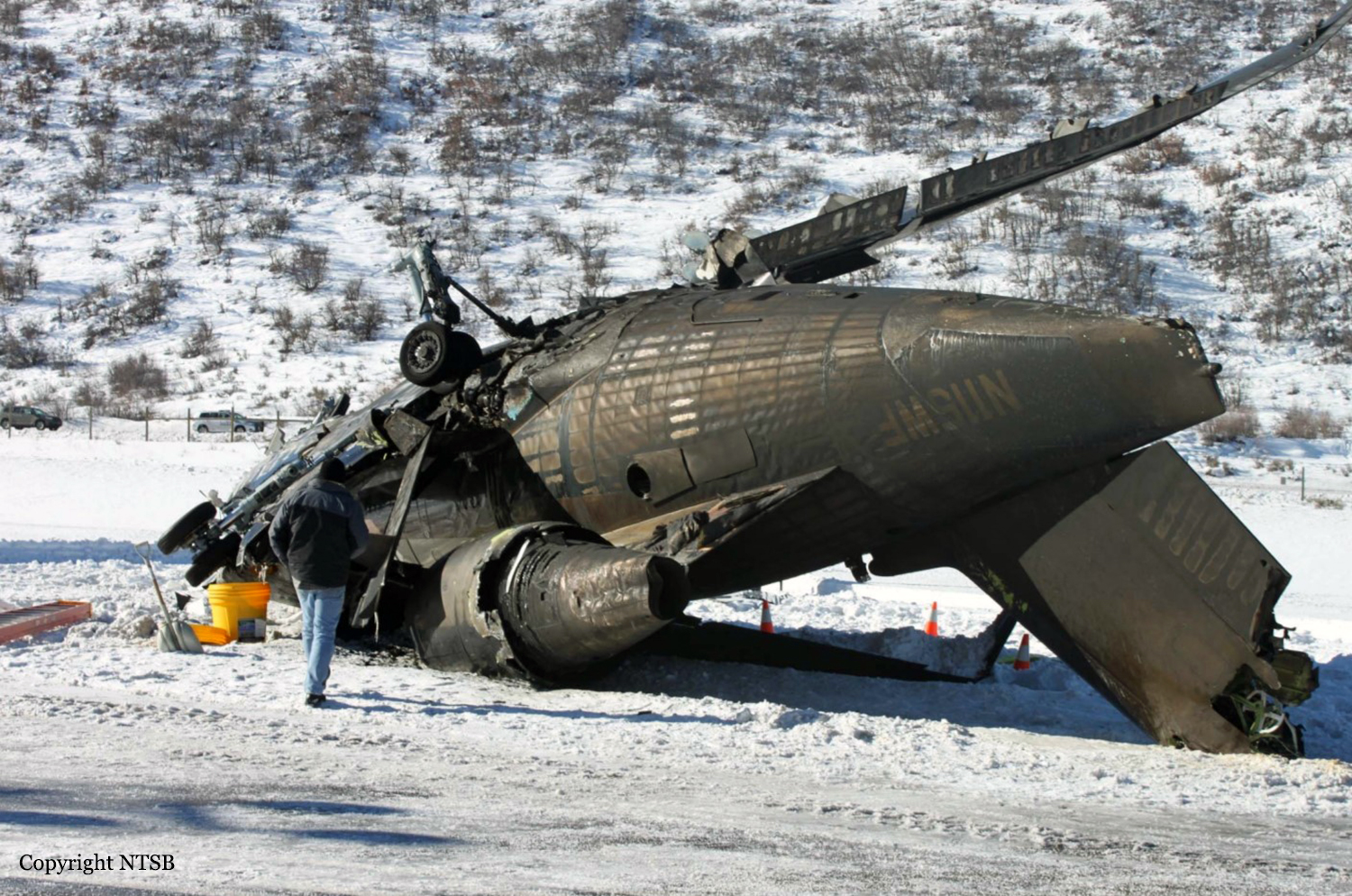
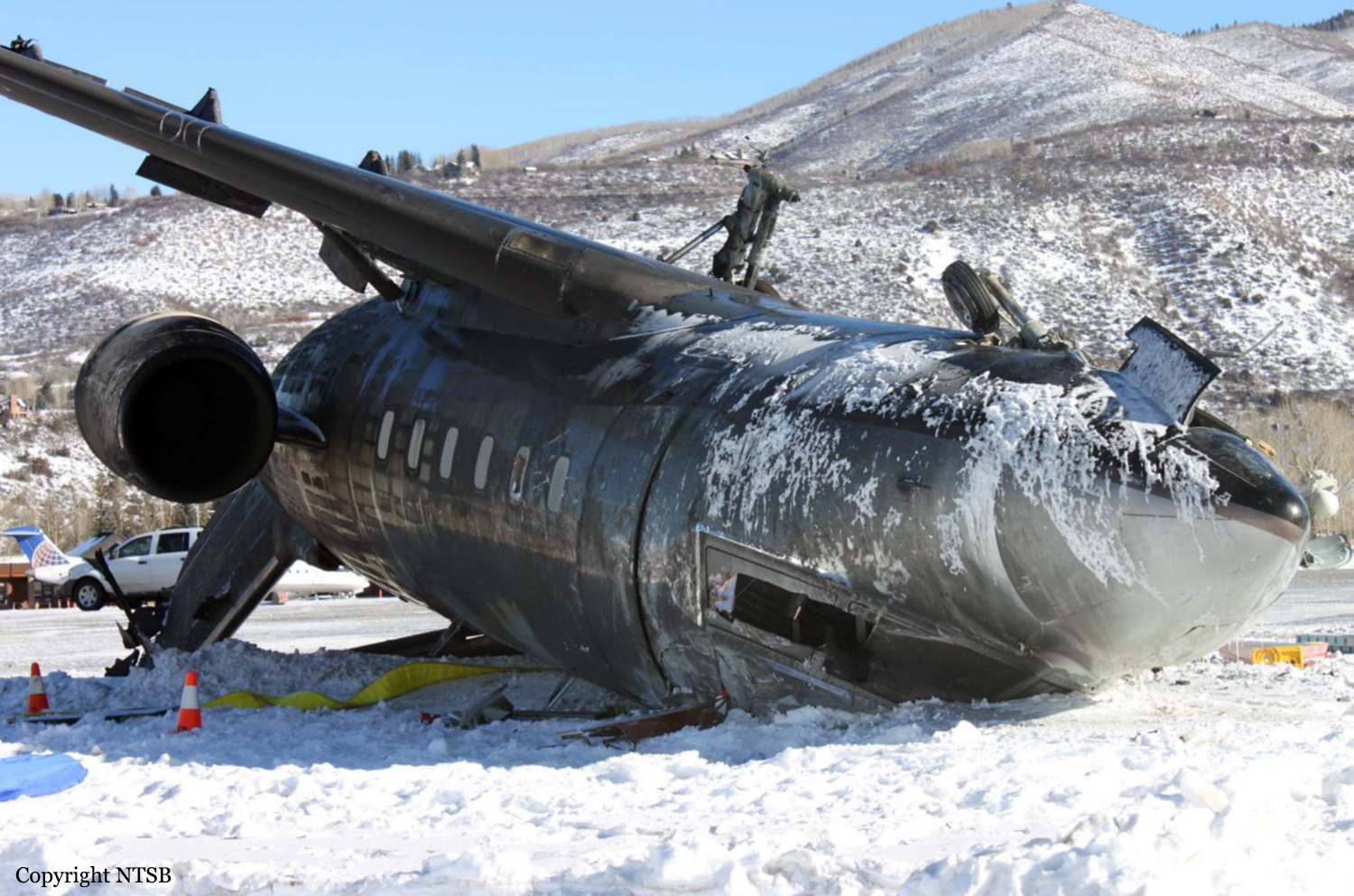
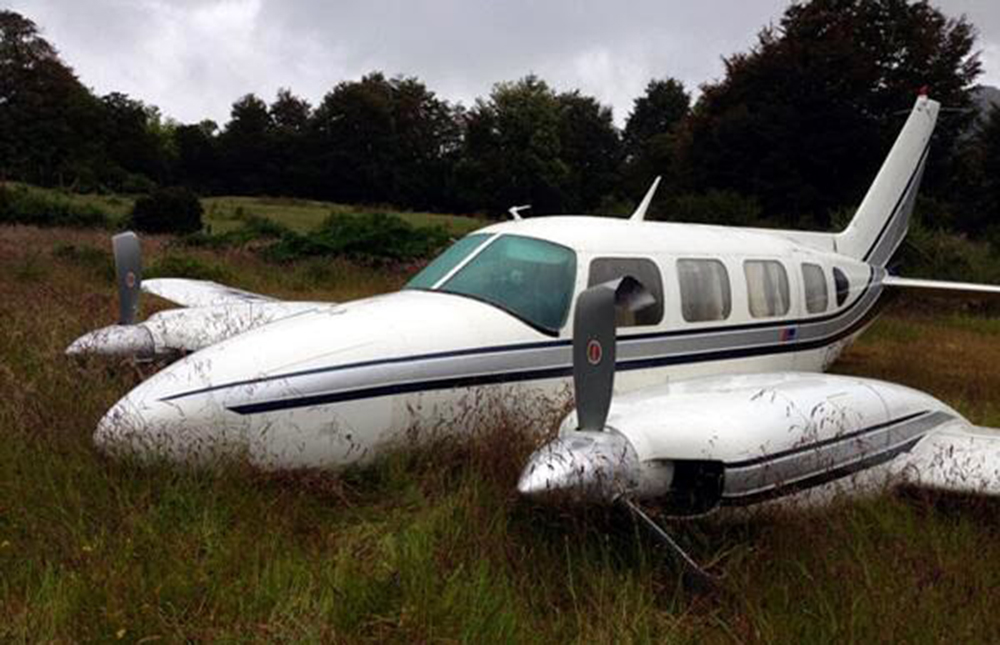
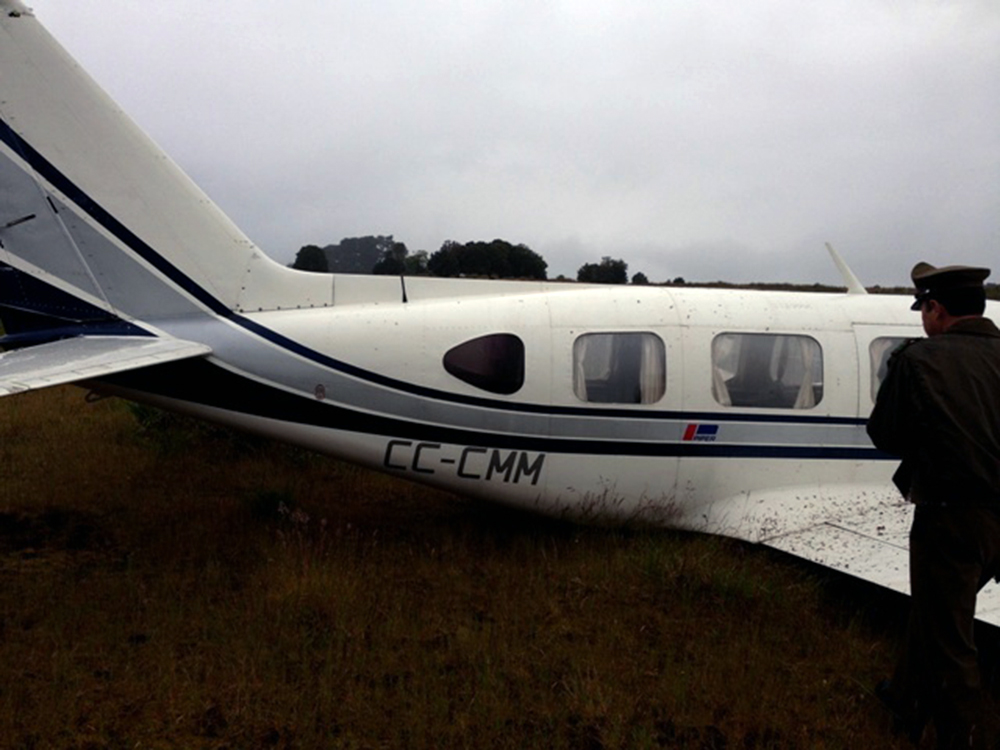
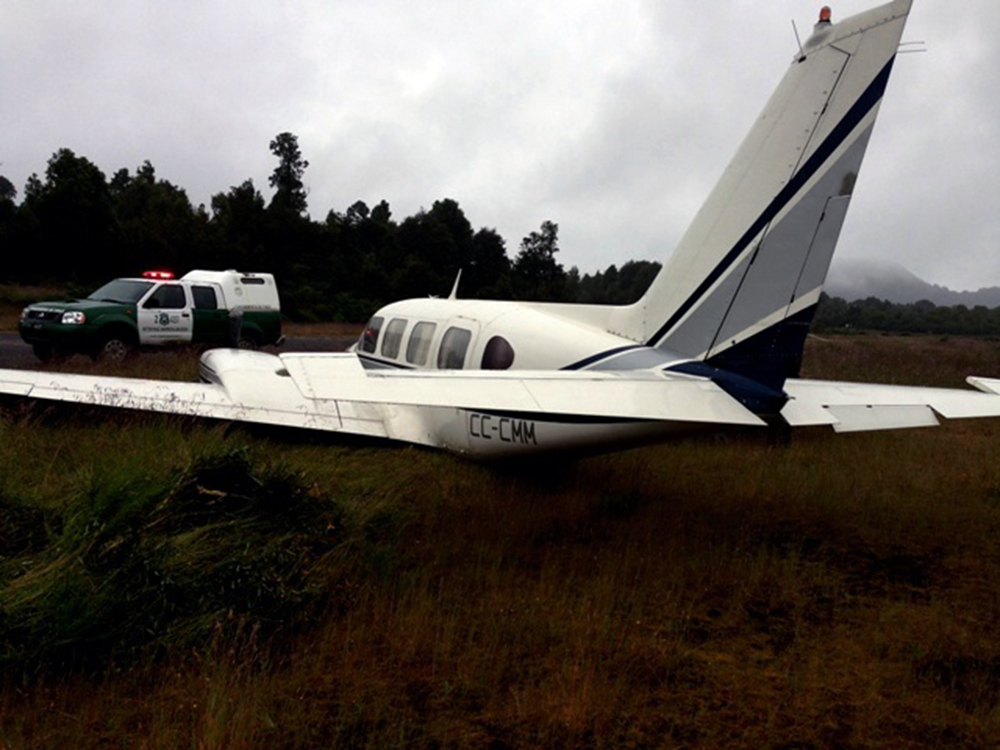
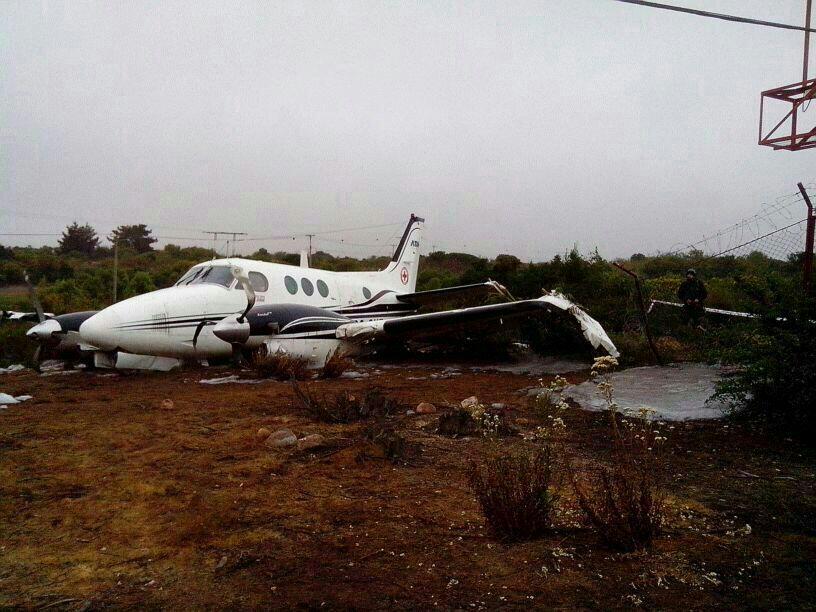
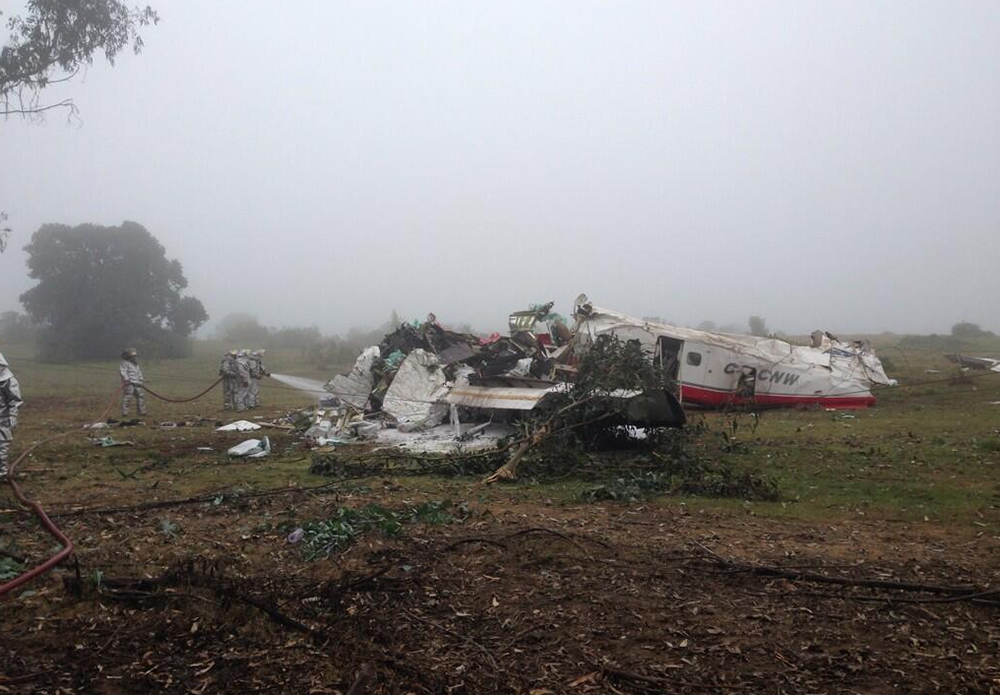
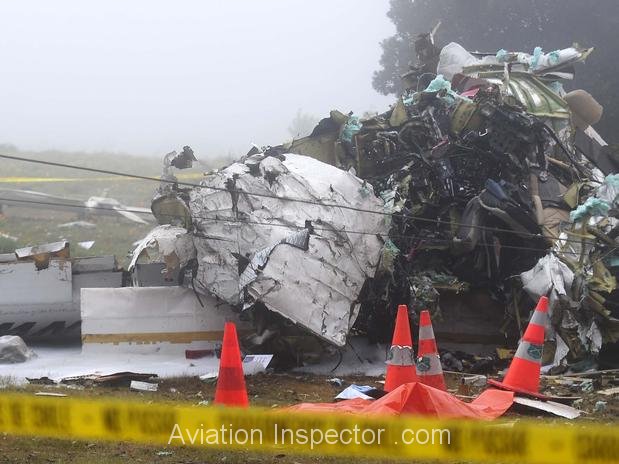
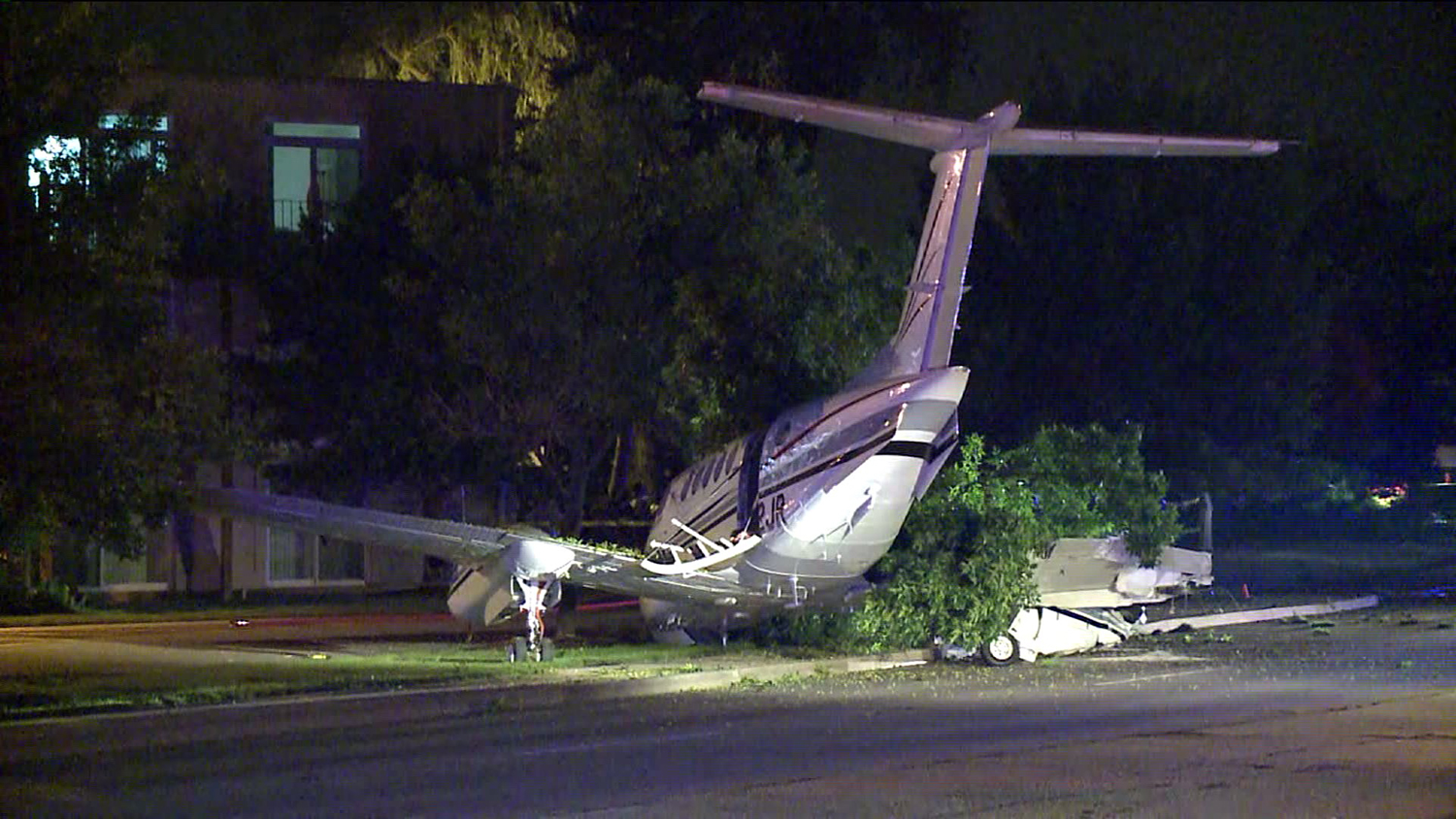
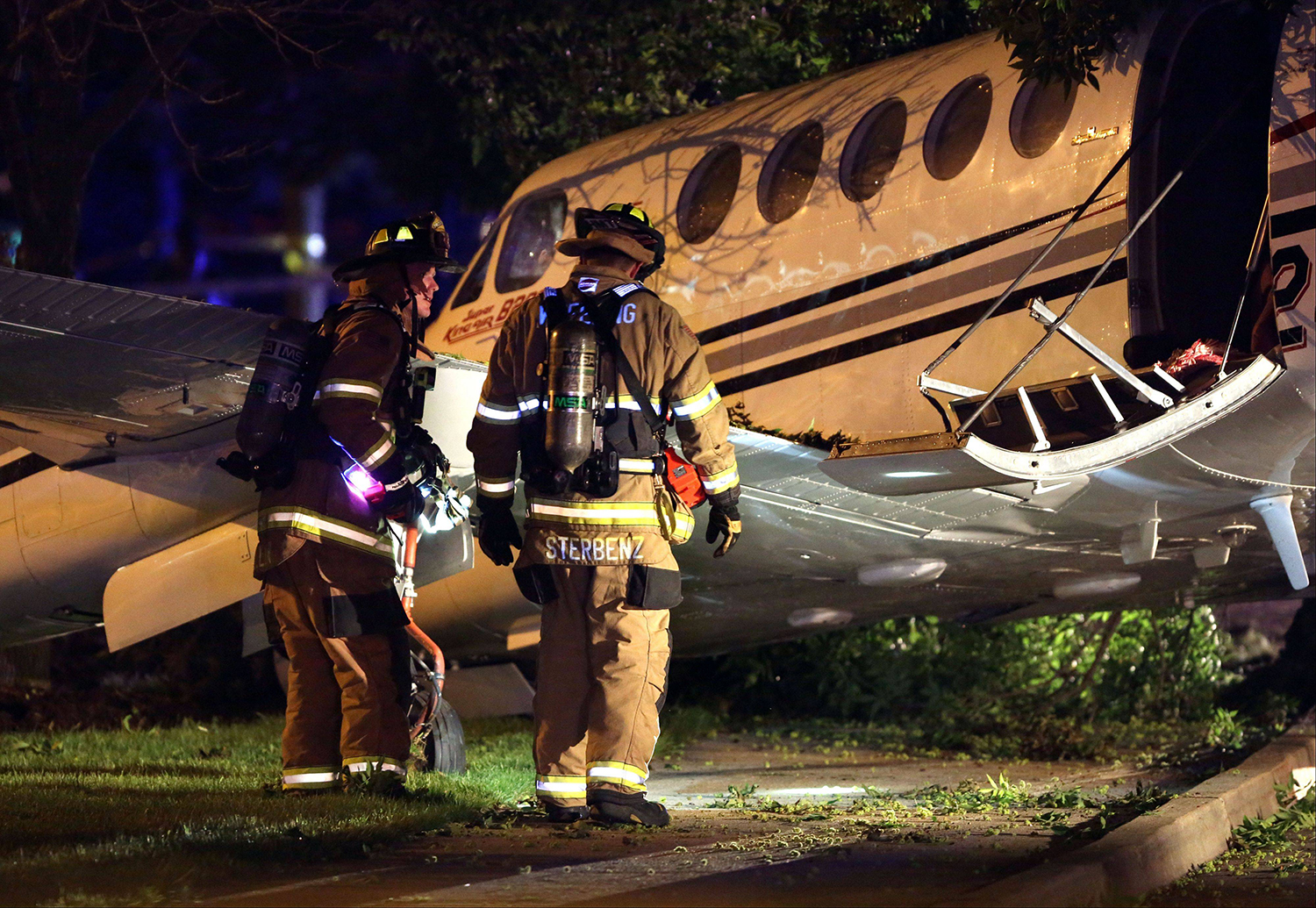
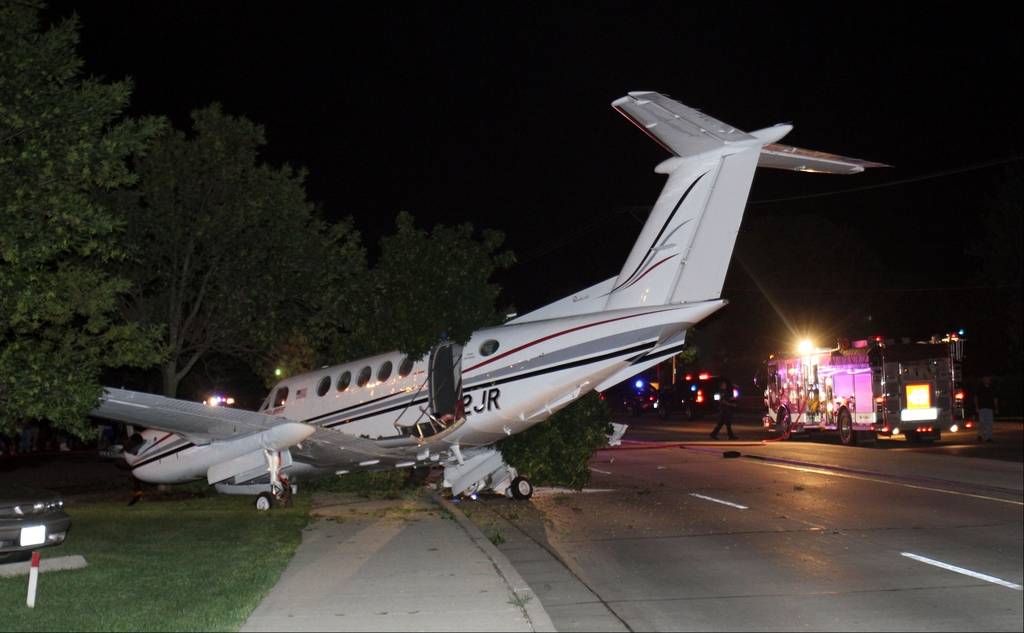
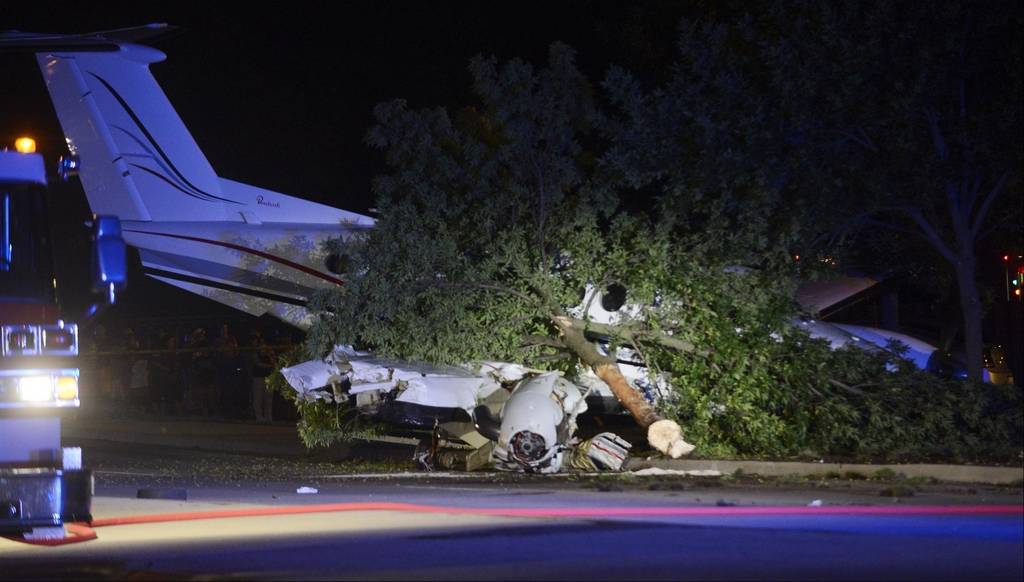
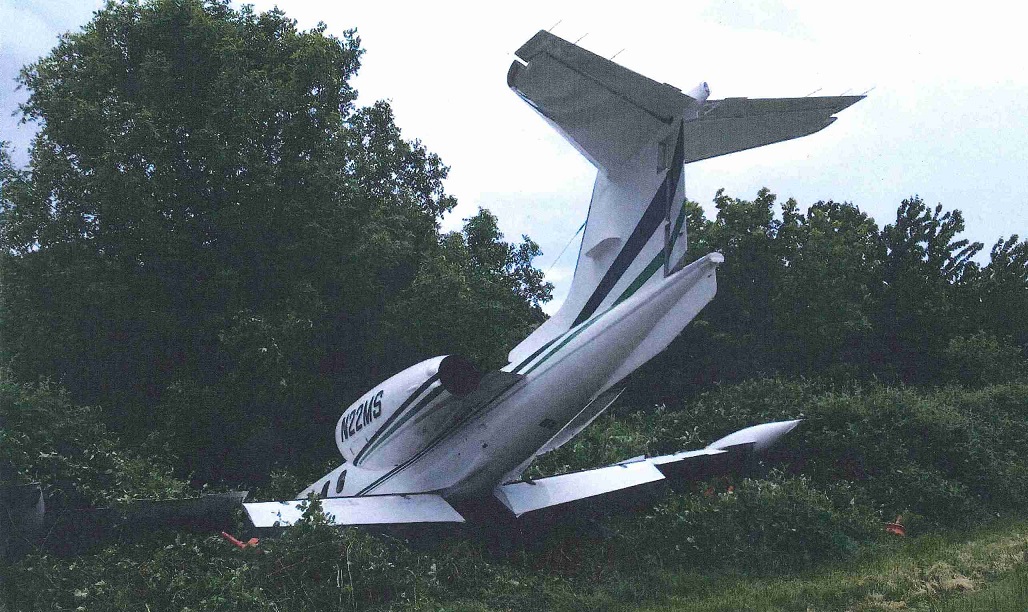
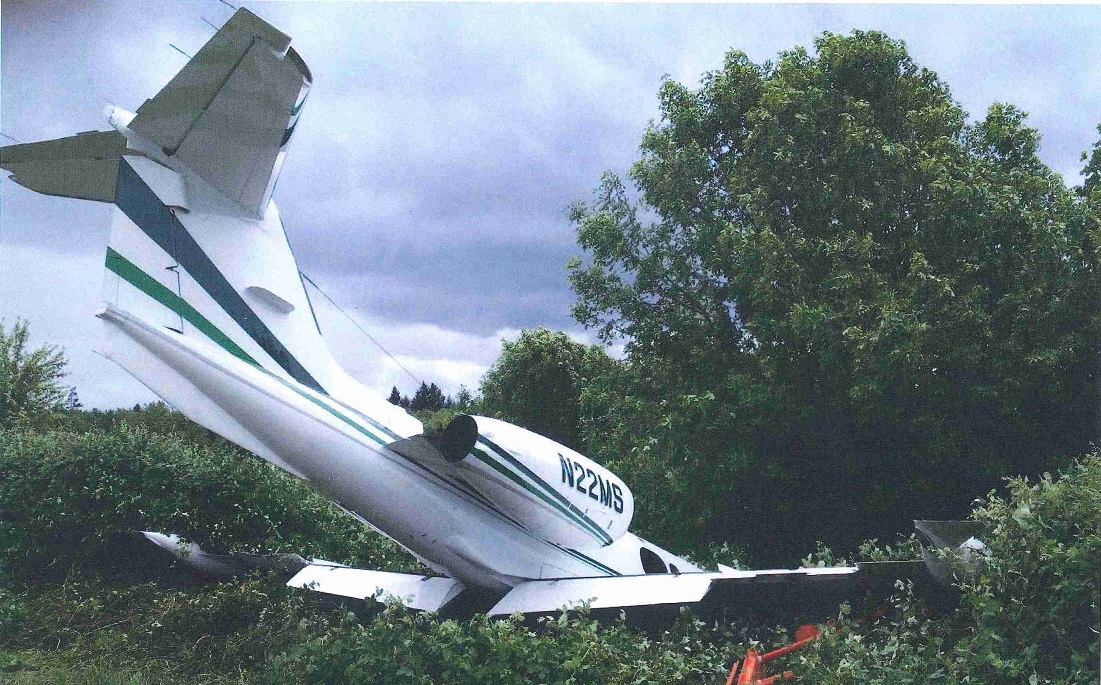
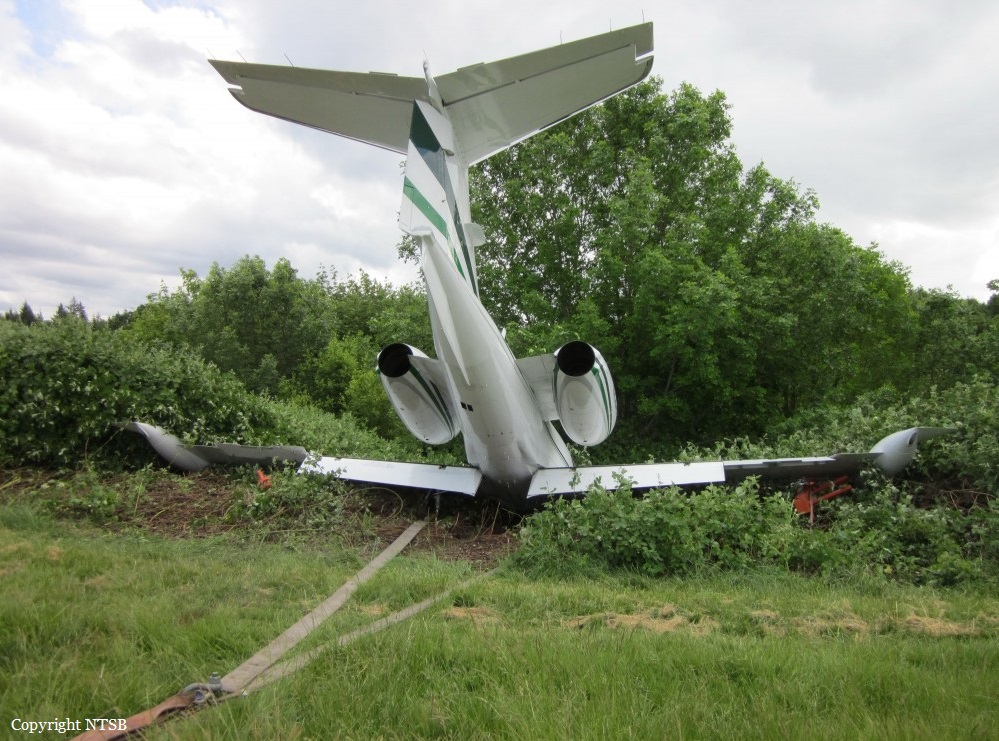
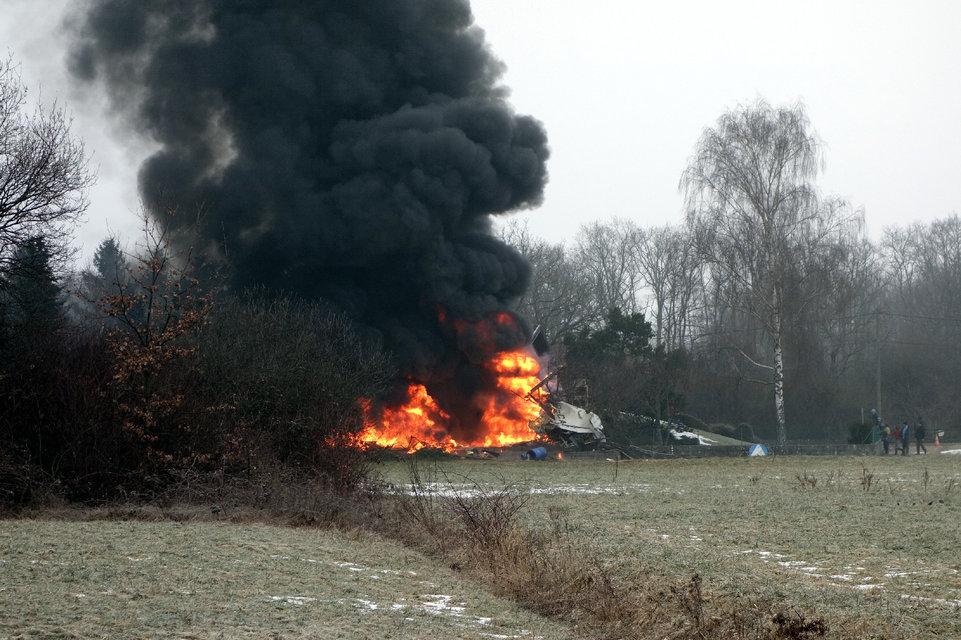
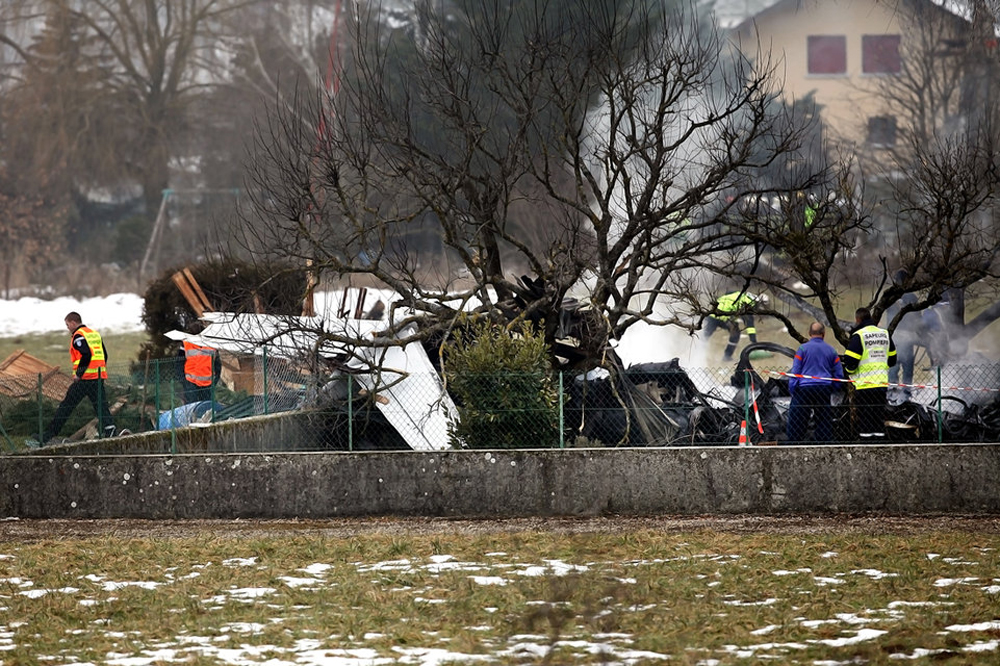
Circumstances:
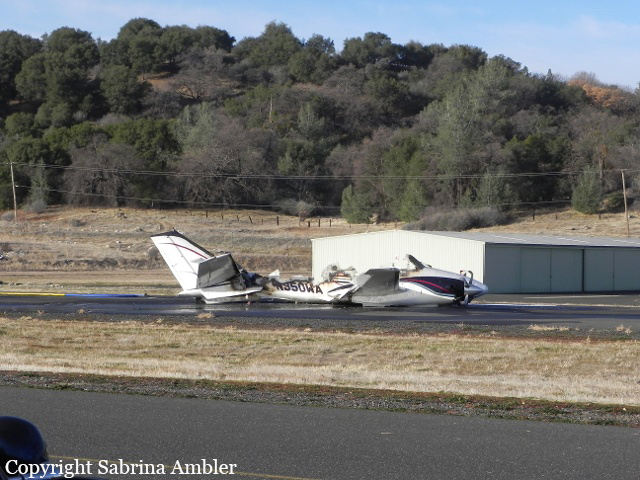
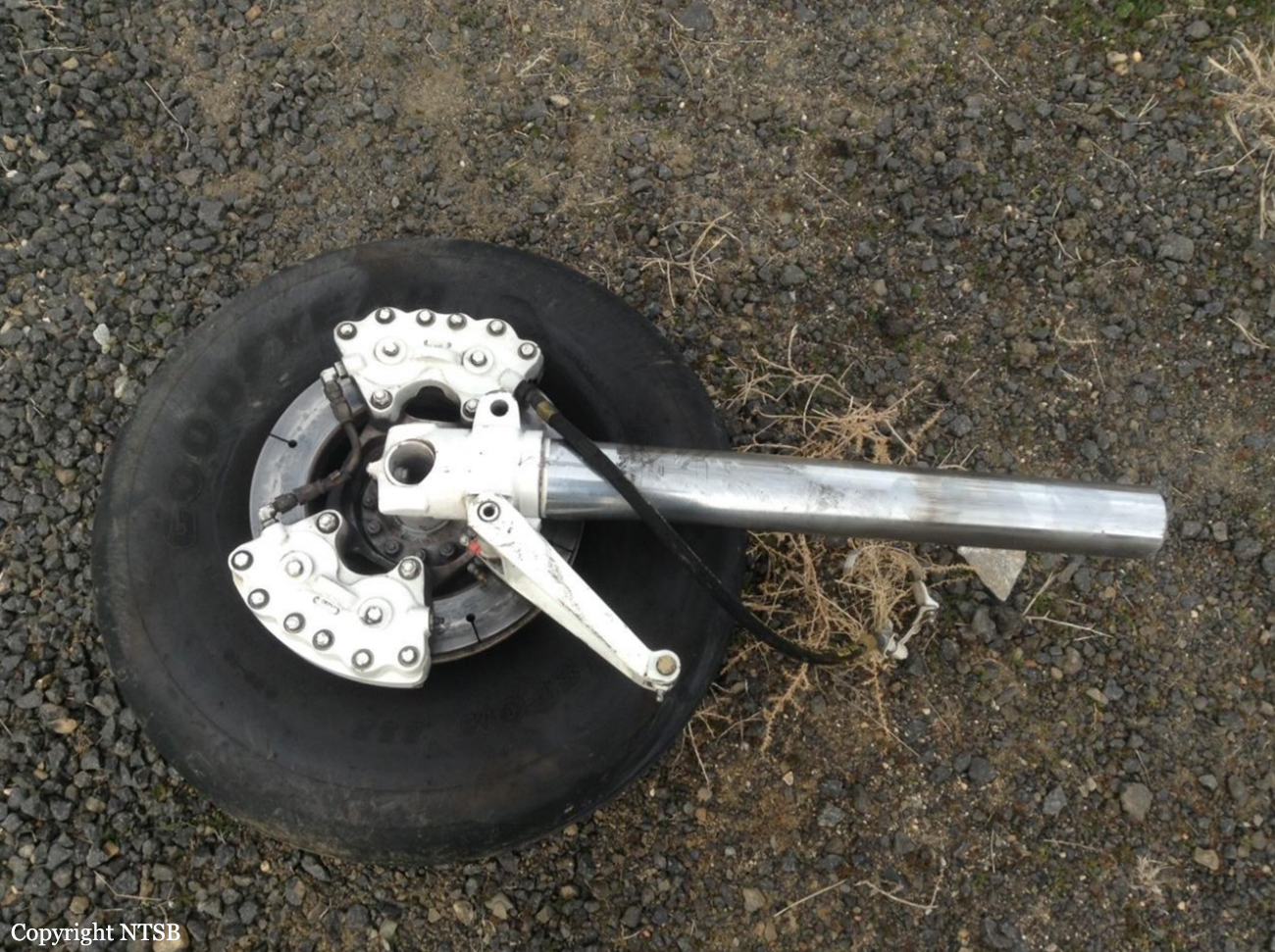
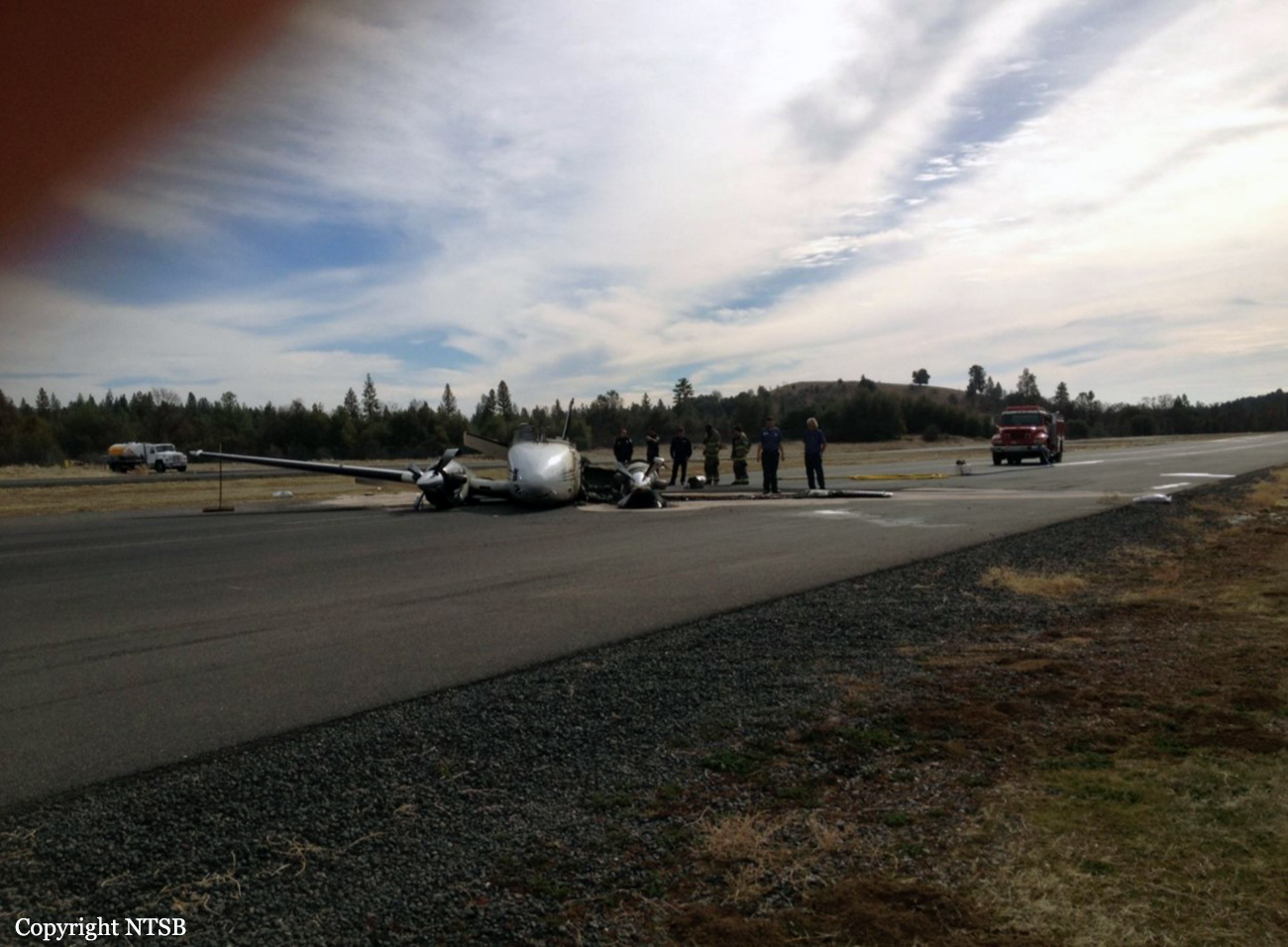
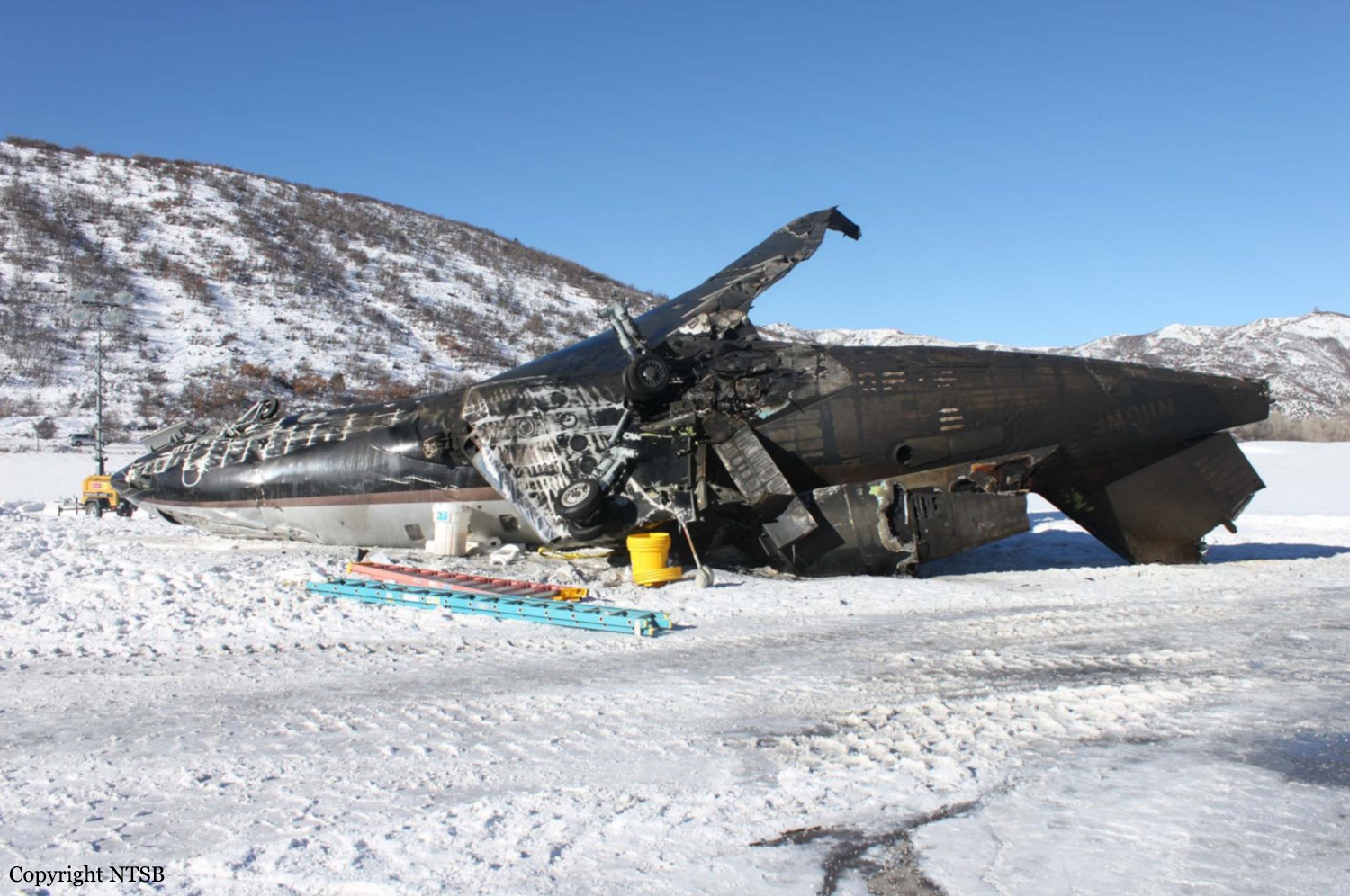
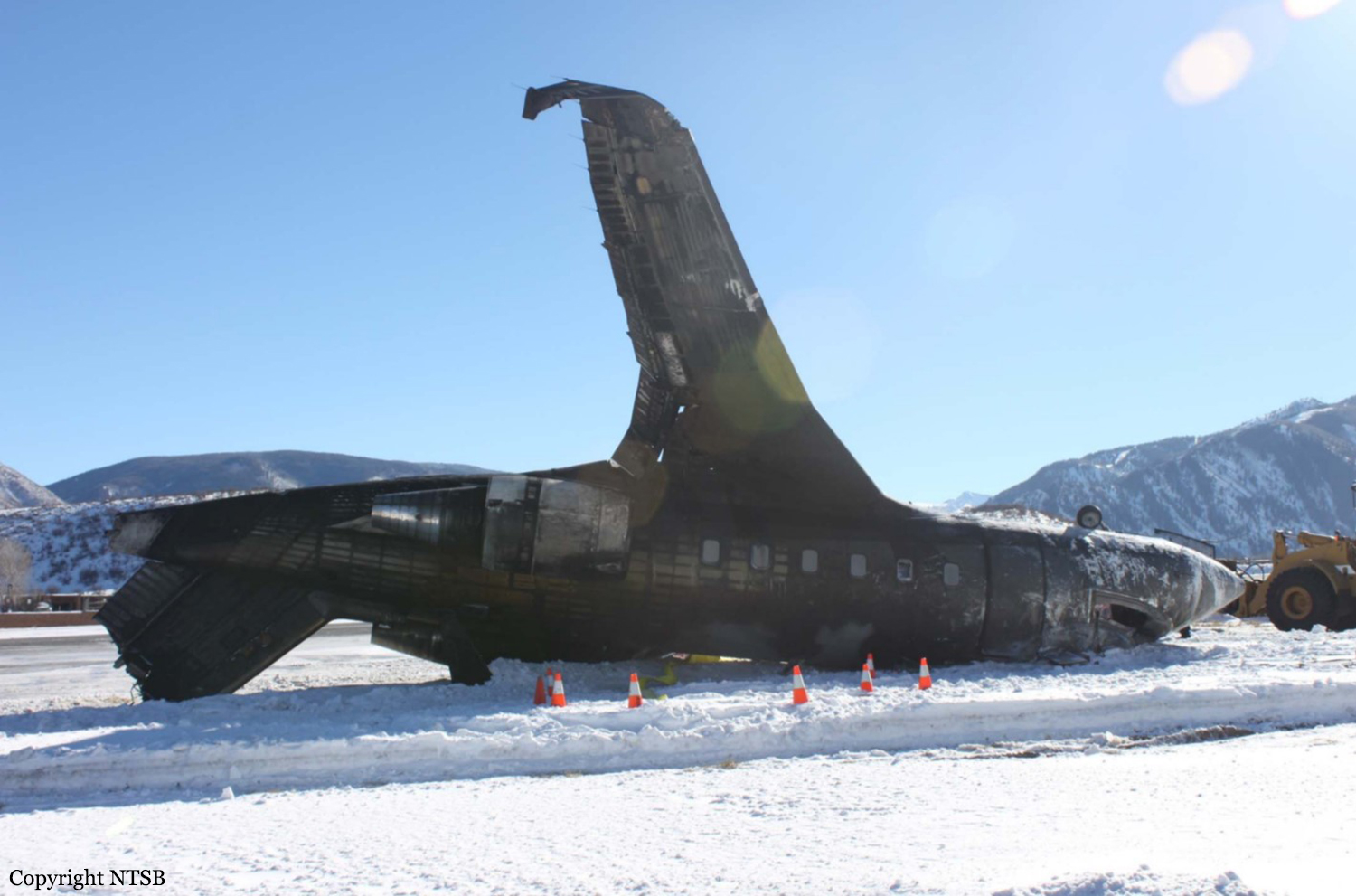
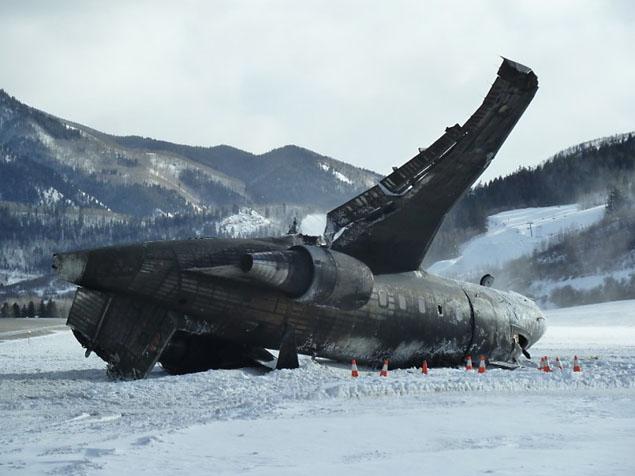
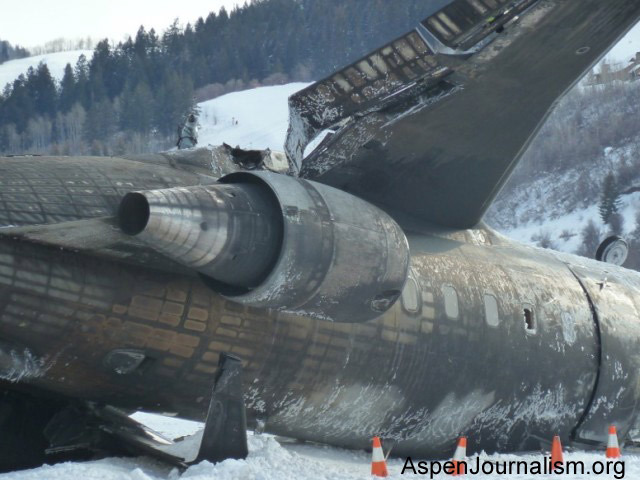
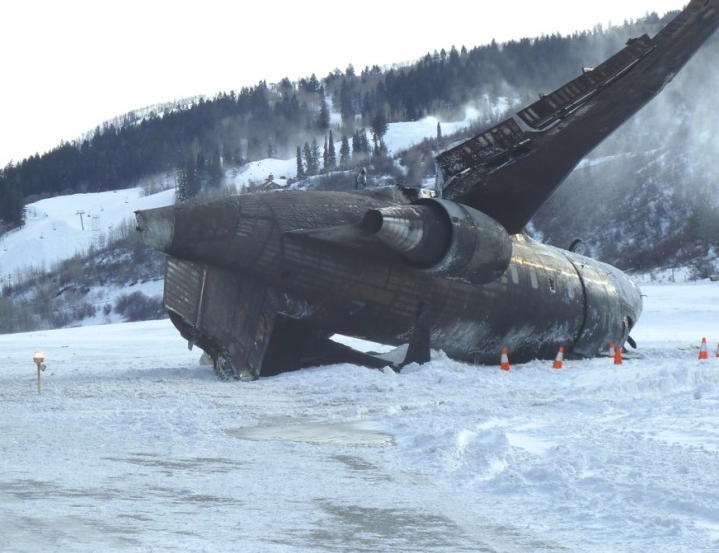
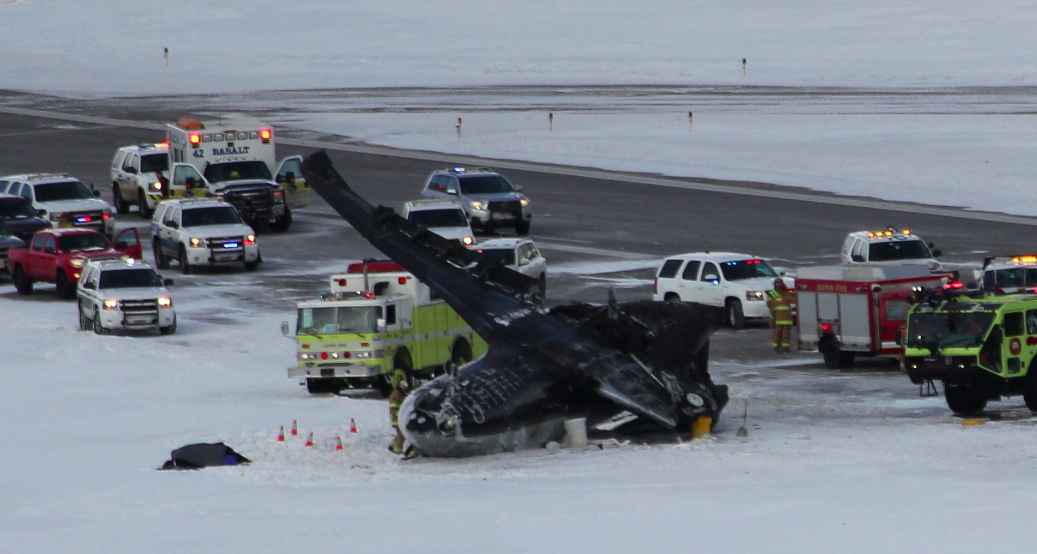
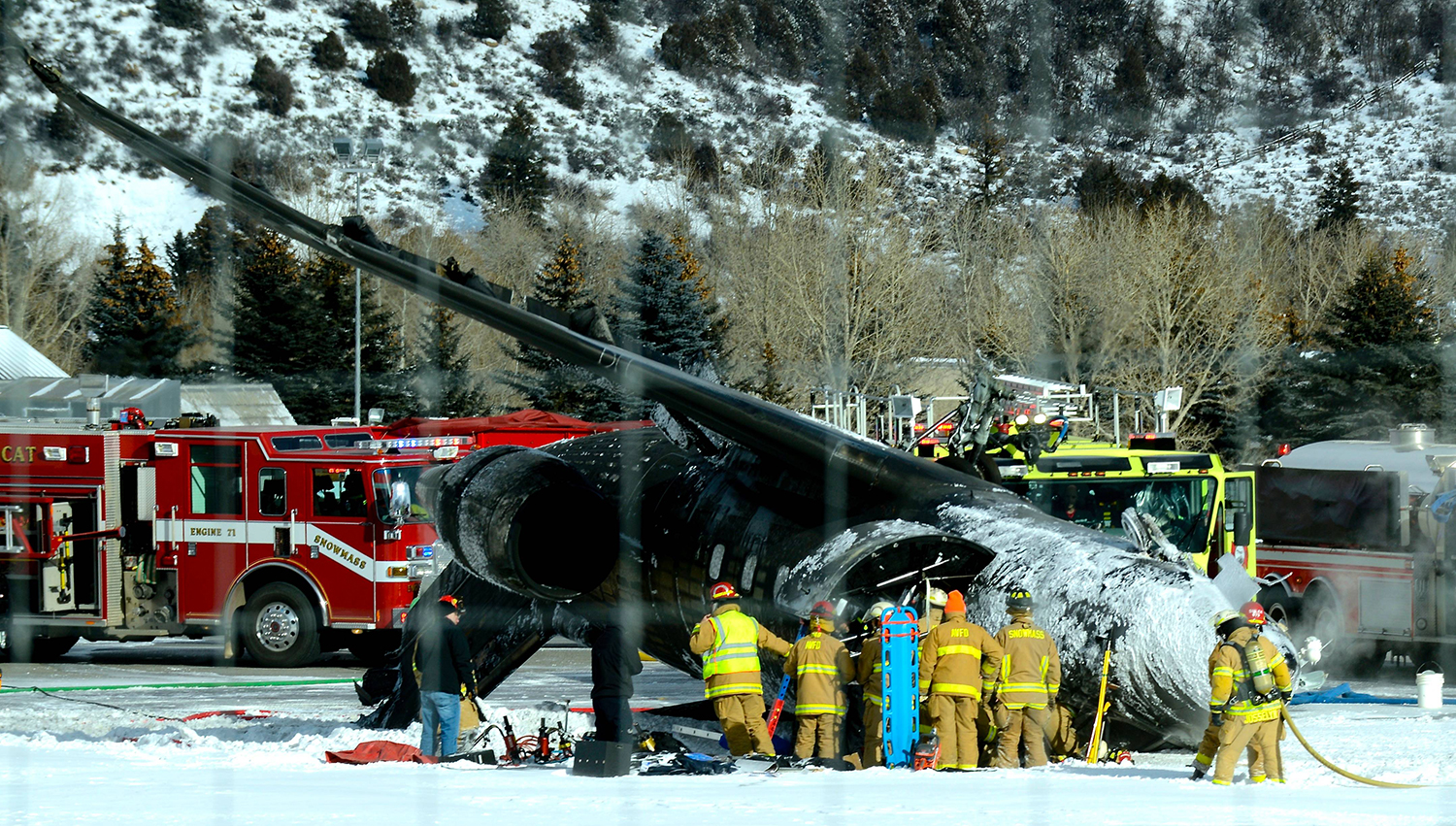
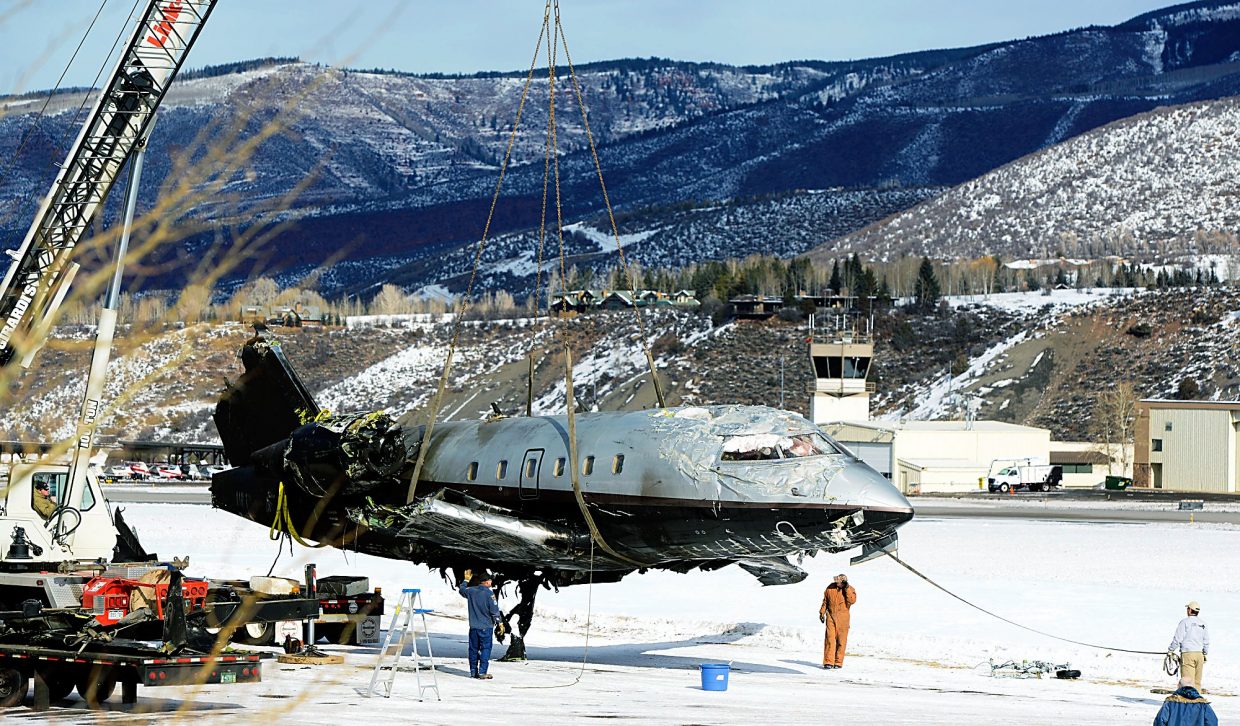
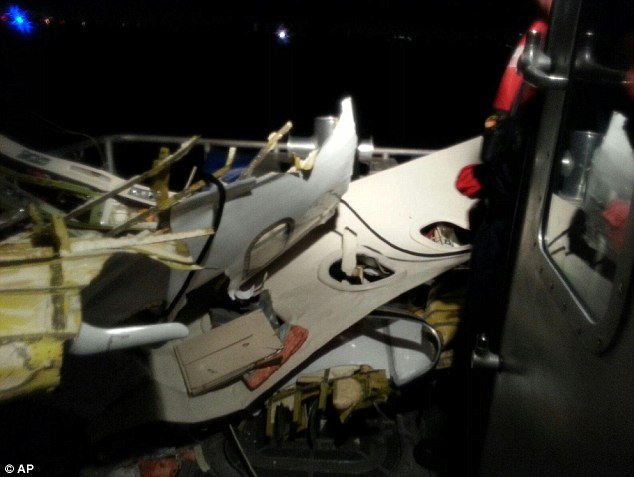
The commercial pilot, who was the pilot flying (PF), and the airplane transport pilot, who was the pilot not flying (PNF), were conducting an aeromedical positioning flight. The pilots reported that, during a night approach, they visually identified the airport, activated the runway lighting system, and then canceled the instrument flight plan for a visual approach. The PNF reported that, after turning onto the final approach, the flaps were fully lowered and that the airplane was in a “wings level, stabilized approach.” The PF reported that he was initially using the vertical approach slope indicator (VASI) for guidance but that the airplane drifted below the glidepath during the approach, and he did not correct back to the glidepath. On short final, the pilots verified that the landing gear were in the down-and-locked position by noting the illumination of the three green landing gear indicator lights, and the airspeed indicator indicated 110 knots. Both pilots reported that the landing was “firm” and that it was followed by a loud bang and the subsequent failure of all three landing gear. The airplane slid on its belly for about 825 ft down the runway before coming to rest. Both pilots evacuated the airplane, which was subsequently consumed by a postaccident fire. Both pilots reported that the airplane was operating normally with no discrepancies noted. Postaccident examination of the wreckage at the accident site revealed that the airplane impacted the runway about 100 ft short of its displaced threshold. Broken components of the landing gear were located along the debris field, which extended about 565 ft beyond the initial impact point. It is likely that the PF's failure to correct and maintain the VASI glidepath after allowing the airplane to descend below the glidepath and the touchdown at a high descent rate resulted in a hard landing and the subsequent failure of all three landing gear.
Probable cause:
The pilot’s unstabilized night visual approach, which resulted in a hard landing and the collapse of all three landing gear.
Final Report: