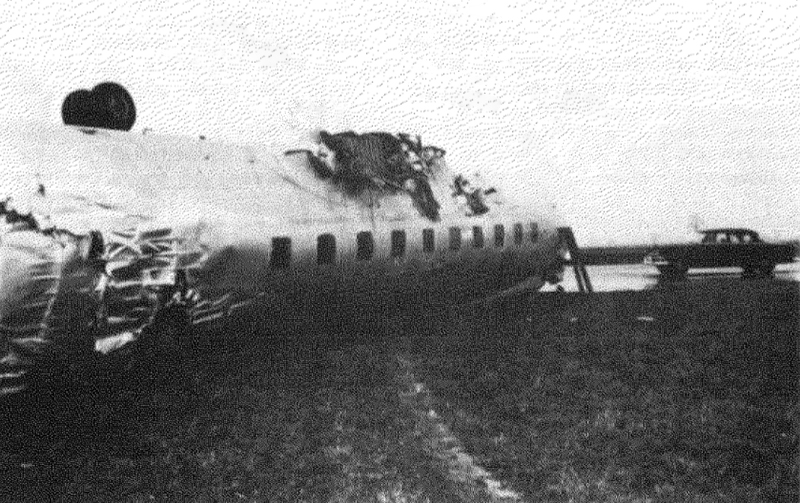
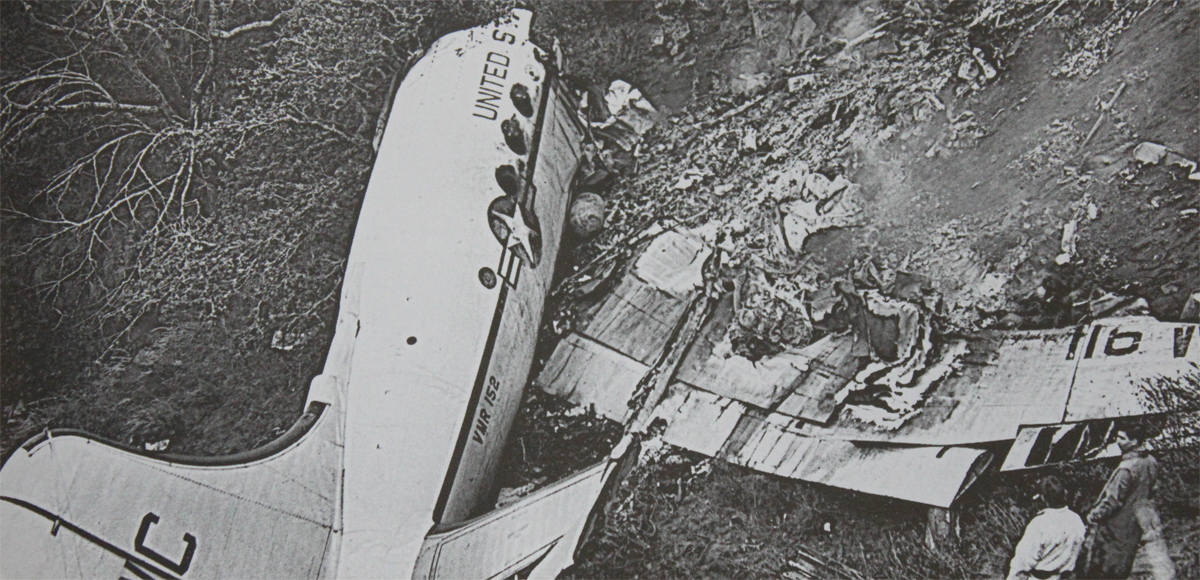
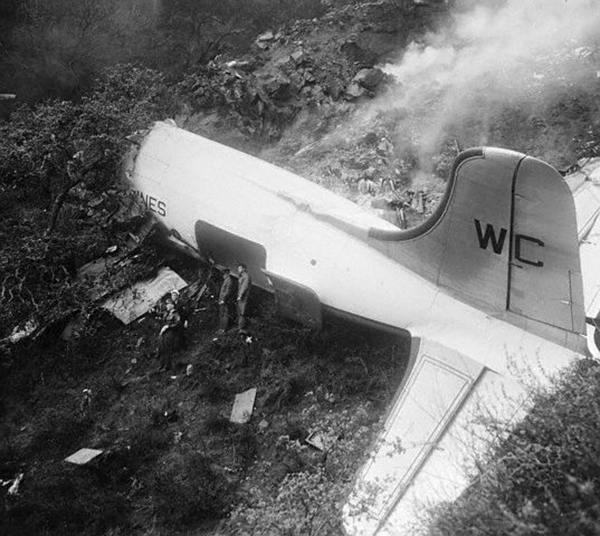
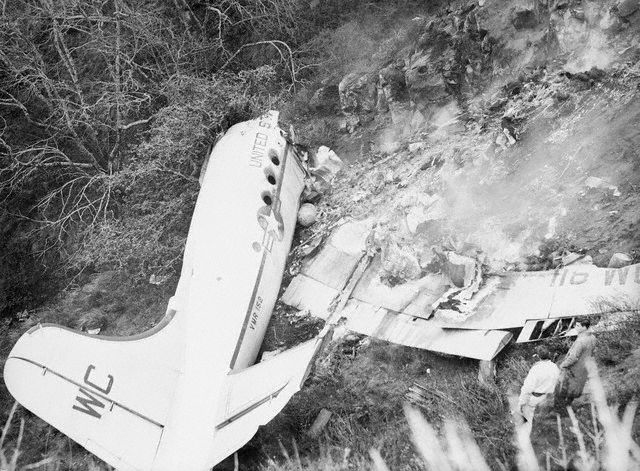
Crash of a Martin 404 in Owensboro
Date & Time:
Feb 17, 1956 at 1458 LT
Registration:
N445A
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Evansville – Owensboro – Louisville – Chicago
MSN:
14122
YOM:
1951
Flight number:
EA156
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
20
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
3182.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2616
Aircraft flight hours:
12373
Circumstances:
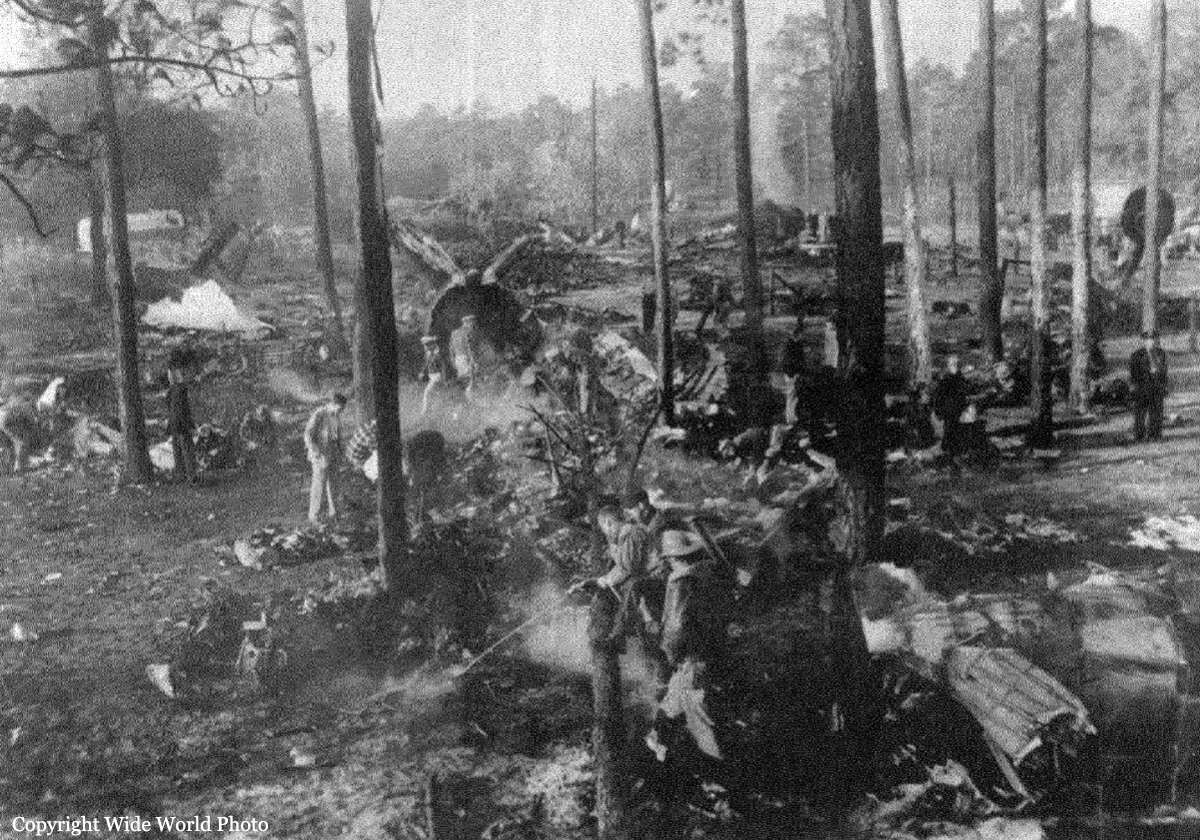
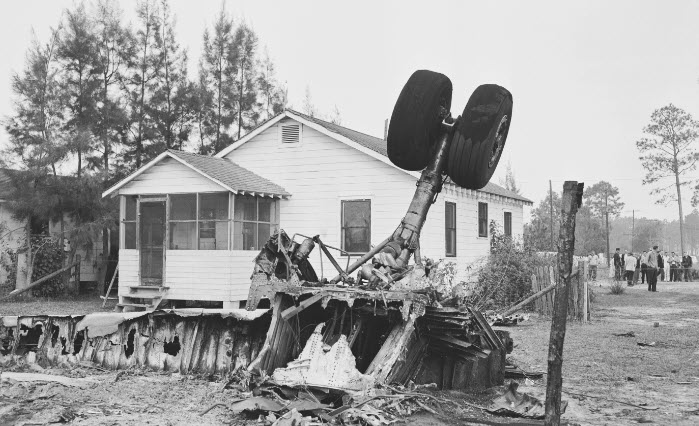
Eastern Air Lines Flight 156 of February 17 was a scheduled operation between Evansville, Indiana, and Chicago, Illinois, with intermediate stops at Owensboro and Louisville, Kentucky. It utilized the aircraft and flight crew of Trip 157 from Chicago, which terminated at Evansville. The crew consisted of Captain Charles R. Hard, Pilot Raymond F. Rozman, and Flight Attendant Robert T. Schroeter. The Chicago to Evansville flight arrived at 1422, 43 minutes late because of traffic and ground delays. It was reported routine in all other respects. During the short ground time at Evansville Captain Bard reviewed the weather forecasts for the flight Evansville to Chicago, and received the latest weather observation reports for Owensboro, the first stop. These indicated the flight to Owensboro would be in accordance with Instrument Flight Rules and that an instrument approach to the airport there would be necessary. Accordingly, an IFR flight plan was filed and an instrument clearance was given the crew before departure. Clearance was direct to Owensboro at 2,000 feet. Flight 156 departed at 1441. Gross takeoff weight was 41,471 pounds, which was less than the maximum allowable, 43,306 pounds. The load was properly distributed with respect to the center of gravity limits of the aircraft. The crew reported its position en mute to ATC (Air Traffic Control) according to its clearance and thereafter at 1447 called the company radio located on the Owensboro Airport. Routine information exchanged between flight and ground personnel included giving the flight the latest weather and altimeter information. There being no control tower at Owensboro, the company there advised the flight that surface wind favored landing on runway 05. A few minutes later N445A was observed to descend below the clouds just north of the airport, flying on a southerly heading toward the field. It was observed to level out and turn right onto a downwind leg for runway 05. In the limited visibility, reported as one mile in rain and fog, the aircraft disappeared from view near the southwest boundary of the airport while still, on its downwind leg. Shortly thereafter it came back into view, proceeding toward the landing runway. It suddenly struck the ground, right wing down, rolled to an inverted position, and slid to a stop beside runway 05. The aircraft lost its both wings and was partially destroyed. All 23 occupants were evacuated.
Probable cause:
The Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was an improperly executed final approach, resulting in a stall, during a steep left turn at an altitude too low to permit recovery. The following findings were reported:
- Weather conditions reported were above the minimums for the flight to execute an ADF approach, circle, and land,
- Weather conditions experienced by the flight were equal to or better than those reported,
- The flight established visual contact with the ground at a position which was normal following the completion of the specified instrument approach procedure,
- A circling approach was begun to land on runway 05,
- The position on the downwind leg from which a left turn was begun to align with runway 5 resulted in little or no straight-in portion of the approach and an abnormally steep turn,
- During the latter phase of the approach while at low altitude the aircraft rolled from a steep left bank to the right in a continuous motion,
- The aircraft struck the ground short of and to the right of the runway of intended landing in an uncontrolled attitude,
- There was no evidence of malfunction or failure of the aircraft, its engines, or propellers,
- Thunderstorm turbulence, wind shift, and lightning were not factors in the accident.
- Weather conditions reported were above the minimums for the flight to execute an ADF approach, circle, and land,
- Weather conditions experienced by the flight were equal to or better than those reported,
- The flight established visual contact with the ground at a position which was normal following the completion of the specified instrument approach procedure,
- A circling approach was begun to land on runway 05,
- The position on the downwind leg from which a left turn was begun to align with runway 5 resulted in little or no straight-in portion of the approach and an abnormally steep turn,
- During the latter phase of the approach while at low altitude the aircraft rolled from a steep left bank to the right in a continuous motion,
- The aircraft struck the ground short of and to the right of the runway of intended landing in an uncontrolled attitude,
- There was no evidence of malfunction or failure of the aircraft, its engines, or propellers,
- Thunderstorm turbulence, wind shift, and lightning were not factors in the accident.
Final Report: