Circumstances:
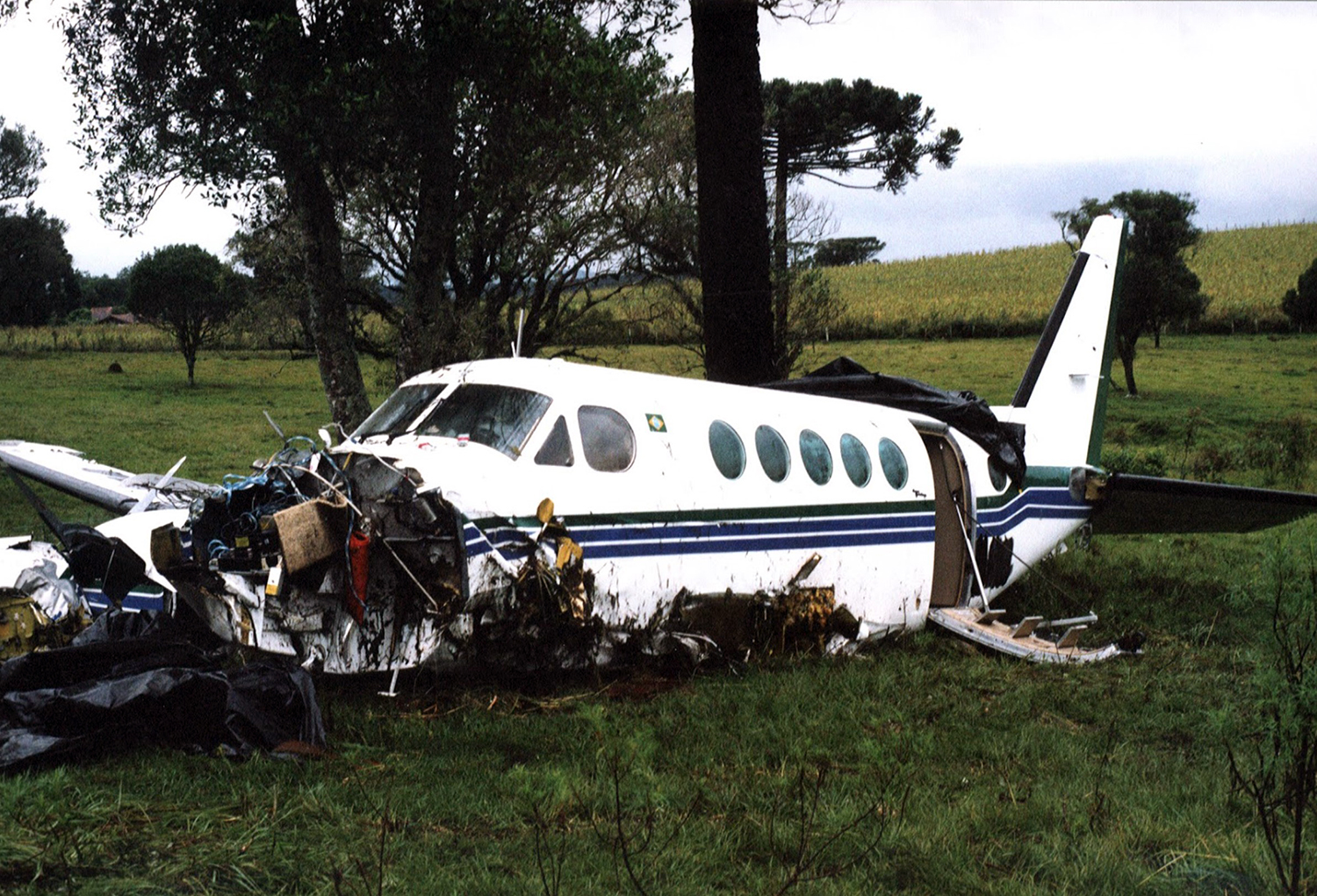
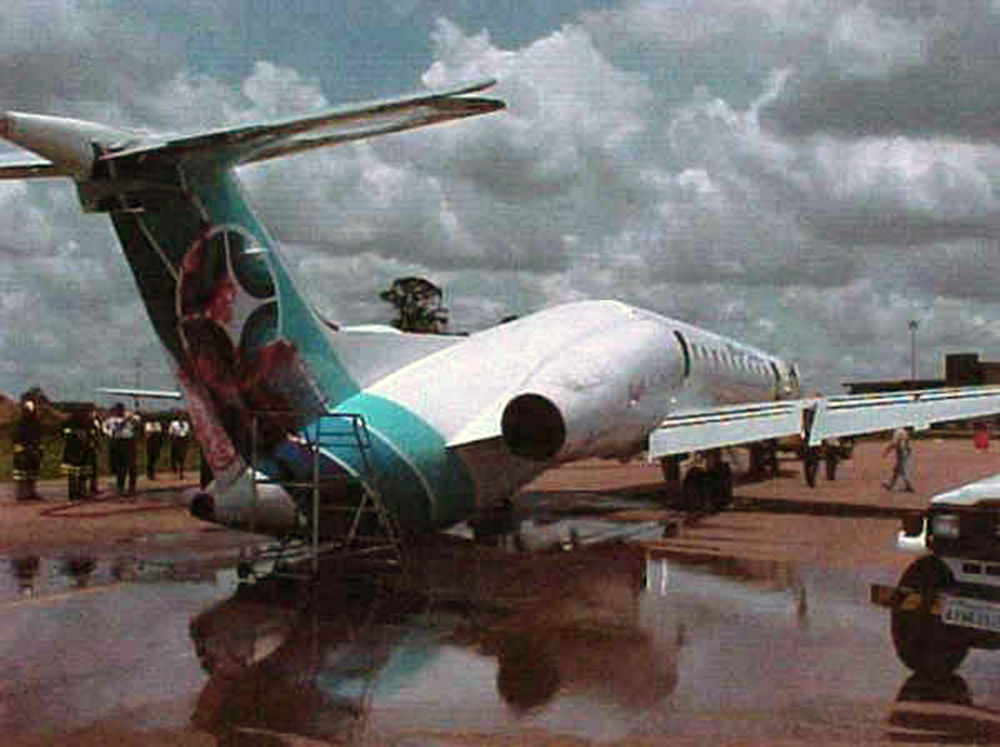
On final approach to runway 15, after passing through the last cloud layer, the pilot-in-command realized he was too high on the glide. Rather than initiating a go-around procedure, the captain increased the rate of descent at 1,800 feet per minute and continued with a wrong approach configuration. The aircraft landed with a positive acceleration of 11 gm causing the fuselage to break in two after the wings. The crew continued the braking procedure and vacated the runway before stopping the aircraft on a taxiway. All 40 occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
- There was the participation of factors, with their own characteristics, that caused failures of attention, judgment and perceptual evaluation of distances and temporality. The qualitative training deficiency, the lack of cabin resource management and the low situational alert were significant contributing factors to the accident.
- PF has performed poorly in the use of the correct piloting technique in the combination of Speed x Ratio of Descent parameters.
- The instructor assigned by the company to supervise the acquisition of operational experience on route had not received specific instruction for the performance of this task. Technical and operational supervision was lacking.
- PF had good flight experience, but not in this type of aircraft. It was in the phase of acquiring operational experience in route. The inadequate action was also due to the little experience in the aircraft and in the circumstance of the operation, which required a quick correction close to the ground.
- The pilots did not adequately utilize the resources available in the cockpit for the proper operation of the aircraft. PF did not make the necessary corrections to modify the aircraft's trajectory, which was its assignment. The instructor (PNF), in turn, did not effectively correct or interfere with the PF flight, which would have been his responsibility since he was the supervisor of the operation. The pilots did not observe, yet, the technical-operational procedure foreseen in the Flight Operations Manual (MOV), regarding the GPWS warning. The crew did not observe that the warning determined an unsafe condition close to the touch. It was characterized an ineffective fulfillment of the tasks assigned to each crew member, besides the non-observance of the operational rules.
- On the IMC approach made, the PF varied the parameters, remaining high on the ramp. Upon reaching visual conditions, the PF increased the descent rate of the aircraft. The PNF, concerned with locating the runway, did not consider an inadequate PF correction.
- The PF, with the intention of reducing the drop ratio, did not apply correctly, in amplitude and in time, the power available in the engines. Near the touch, the PF increased the pitch angle, trying to reduce the drop ratio. Considering the low height (approximately 80 ft) and engine power (IDLE), the aircraft continued with a high rate of descent (approximately 1,800 ft/min), without the action taken by the PF altering its path. The PNF did not interfere in the application of the commands. Therefore, there was inadequate use of the aircraft commands by the crew members, in conditions for which they were qualified.
- The PF, even being alerted by the PNF about the low speed and high rate of descent, thought it was applying an adequate correction, however it kept the aircraft in an incompatible performance for landing. The PNF, despite having experience in flight and in the aircraft, showed a lack of knowledge of its limits regarding the point of irreversibility of an unsafe situation. The PNF was limited to alerting the PF about the situation, not guiding it on the correct way to make the corrections.
The PNF overestimated PF's capacity and did not take or try to take over the controls.
- The pilots were not aware of the maximum rate of descent during the touch for which the aircraft was certified, nor were they aware of the variation of that rate with respect to weight. The availability of the autopilot to the MDA could have minimized the ramp deviation observed.