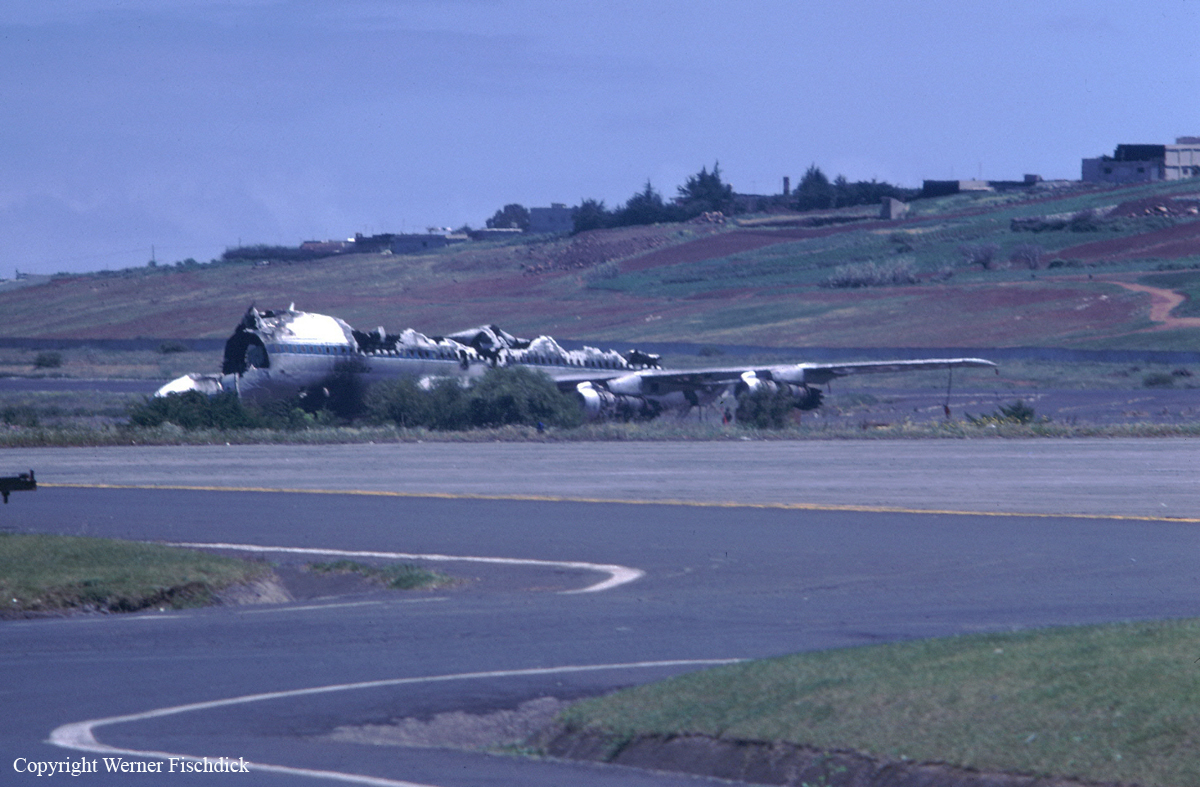
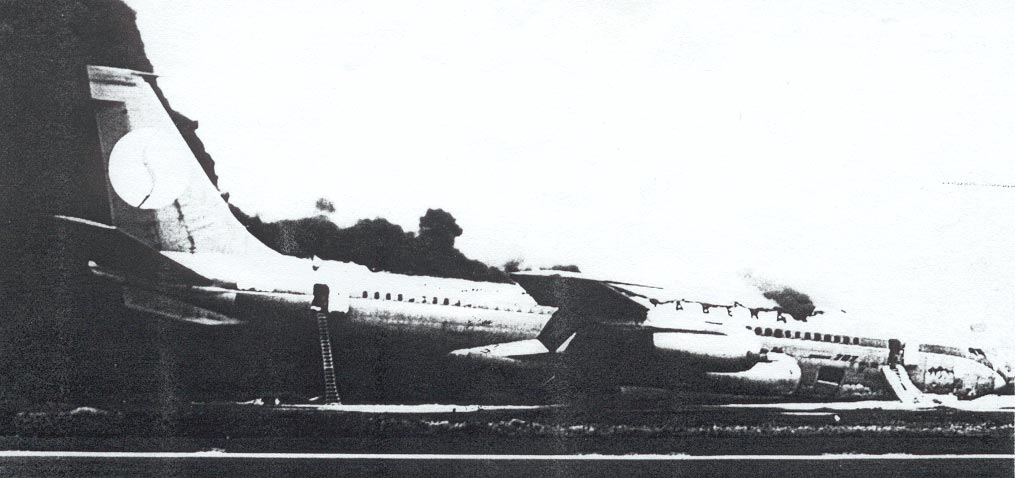
Circumstances:
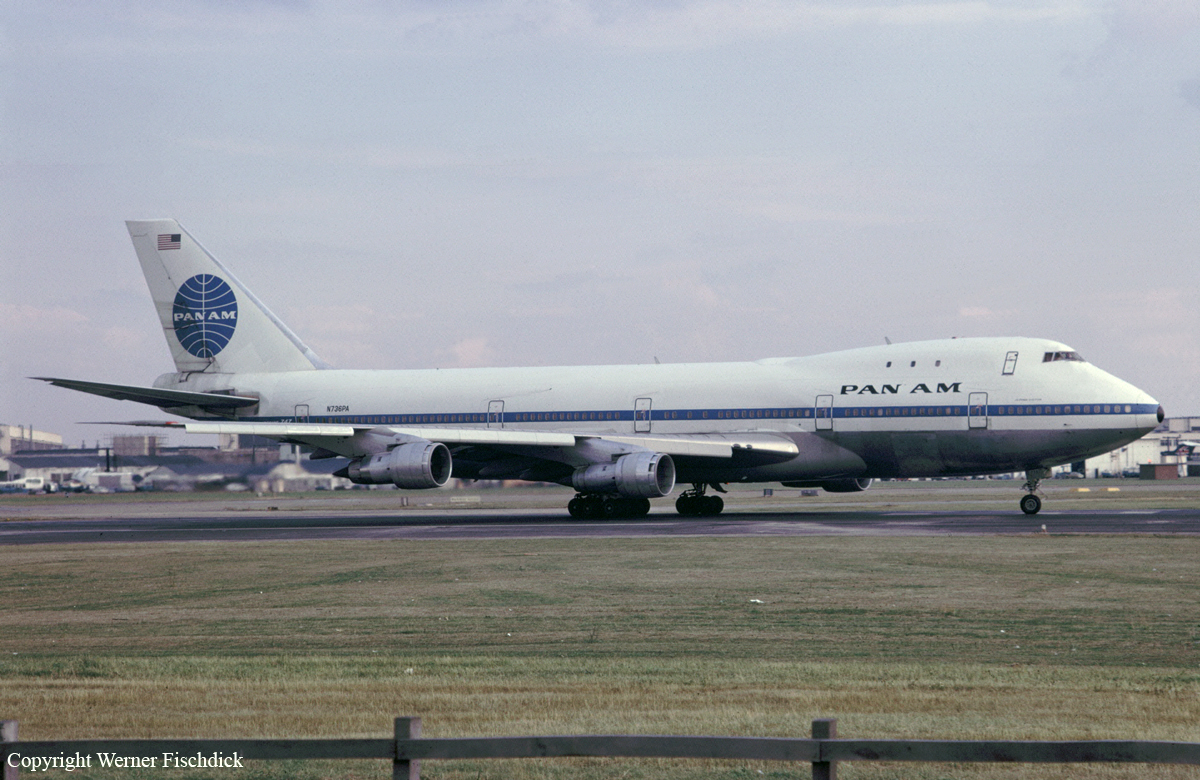
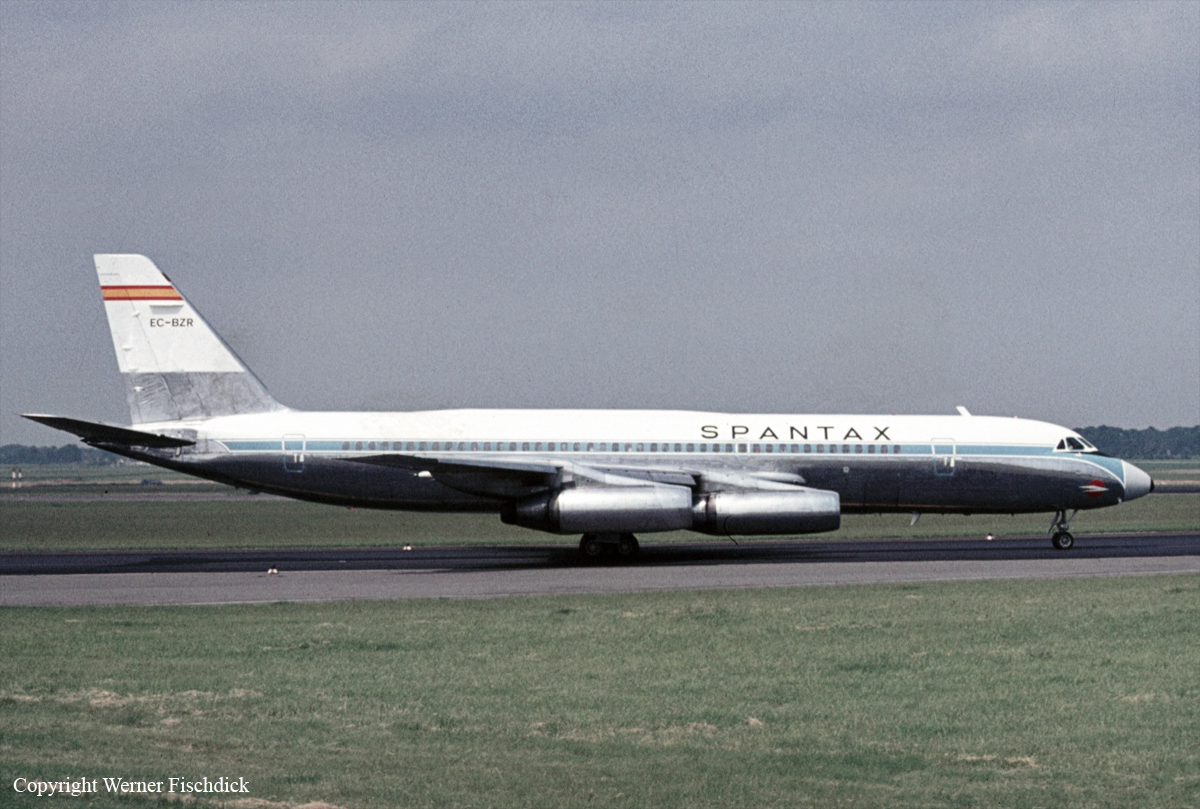
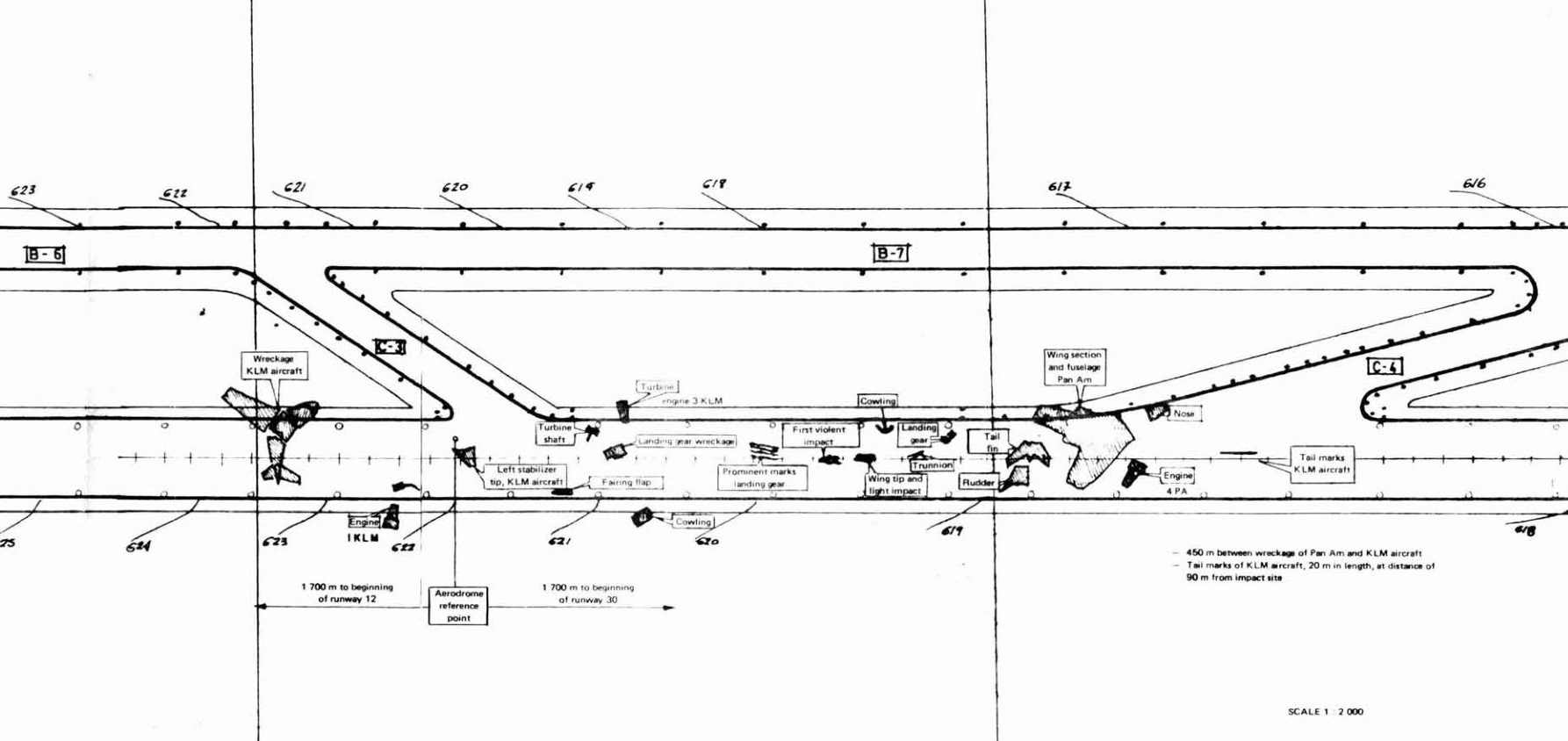
The KLM Boeing 747, registration PH-BUF, took off from Schipol Airport (Amsterdam) at 0900 hours on 27 March 1977, en route to Las Palmas de Gran Canaria. This flight was part of the Charter Series KL4805/4806 Amsterdam-Las Palmas (Canary Islands) - Amsterdam operated by KLM on behalf of the Holland International Travel Group (H.I.N.T.), Rijswijk-Z.H. The Boeing 747 registration N736PA, flight number 1736, left Los Angeles International Airport, California, United States, on 26 March 1977, local date, at 0129Z hours, arriving at John F. Kennedy International Airport at 0617Z hours. After the aeroplane was refuelled and a crew change effected, it took off for Las Palmas de Gran Canaria (Spain) at 0742Z. While the aeroplanes were en route to Las Palmas, a bomb exploded in the airport passenger terminal. On account of this incident and of a warning regarding a possible second bomb, the airport was closed. Therefore, KLM 4805 was diverted to Los Rodeos (Tenerife) Airport, arriving at 1338Z on 27 March 1977. For the same reason, PAA1736 proceeded to the same airport, which was its alternate, landing at 1415. At first the KLM passengers were not allowed to leave the aeroplane, but after about twenty minutes they were all transported to the terminal building by bus. On alighting from the bus, they received cards identifying them as passengers in transit on Flight KL 4805. Later, all the passengers boarded KLM 4805 expect the H.I.N.T. Company guide, who remained in Tenerife. When Las Palmas Airport was opened to traffic once more, the PAA 1736 crew prepared to proceed to Las Palmas, which was the flight's planned destination. When they attempted to taxi on the taxiway leading to runway 12, where they had been parked with four other aeroplanes on account of the congestion caused by the number of flights diverted to Tenerife, they discovered that it was blocked by KLM Boeing 747, Flight 4805, which was located between PAA 1736 and the entrance to the active runway. The first officer and the flight engineer left the aeroplane and measured the clearance left by the KLM aircraft, reaching the conclusion that it was insufficient to allow PAA 1736 to pass by, obliging them to writ until the former had started to taxi. The passengers of PAA 1736 did not leave the aeroplane during the whole time that it remained in the airport. KLM 4805 called the tower at 1656 requesting permission to taxi. It was authorized to do so and at 1658 requested to backtrack on runway 12 for take-off on runway 30. The tower controller first cleared the KLM flight to taxi to the holding position for runway 30 by taxiing down the main runway and leaving it by the (third) taxiway to its left. KLM 4805 acknowledged receipt of this message from the tower, stating that it was at that moment taxiing on the runway, which it would leave by the first taxiway in order to proceed to the approach end of runway 30. The tower controller immediately issued an amended clearance, instructing it to continue to taxi to the end of the runway, where it should proceed to backtrack. The KLM flight confirmed that it had received the message, that it would backtrack, and that it was taxiing down tile main runway. The tower signalled its approval, whereupon KLM 4805 immediately asked the tower again if what they had asked it to do was to turn left on taxiway one. The tower replied in the negative and repeated that it should continue on to the end of the runway and there backtrack. Finally, at 1659, KLM 4805 replied, "O.K., sir." At 1702, the PAA aeroplane called the tower to request confirmation that it should taxi down the runway. The tower controller confirmed this, also adding that they should leave the runway by the third taxiway to their left. At 1703:00, in reply to the tower controller's query to KLM 4805 as to how many runway exits they had passed, the latter confirmed that at that moment they were passing by taxiway C4. The tower controller told KLM 4805, "O.K., at the end of the runway make one eighty and report ready for ATC clearance ." In response to a query from KLM 4805, the tower controller advised both aeroplanes - KLM 4805 and PAA 1736 - that the runway centre line lights were out of service. The controller also reiterated to PAA 1736 that they were to leave the main runway via the third taxiway to their left and that they should report leaving the runway. At the times indicated, the following conversations took place between the tower and the KLM 4805 and PAA 1736 aeroplanes. Times taken from KLM CVR.
1705:44.6 KLM 4805: The KLM four eight zero five is now ready for take-off and we are waiting for our ATC clearance. (1705:50.77).
1705:53.41 Tower: KLM eight seven zero five you are cleared to the Papa Beacon, climb to and maintain flight level nine zero, right turn after take-off, proceed with heading four zero until intercepting the three two five radial from Las Palmas VOR. (1706 :08.09).
1706:09.61 KLM 4805: Ah - Roger, sir, we are cleared to the Papa Beacon, flight level nine zero until intercepting the three two five. We are now (at take-off). (1706:17.79).
1706:18.19 Tower : O.K..... Stand by for take-off, I will call you. (1706: 21.79).
Note: A squeal starts at: 1706:19.39 The squeal ends at: 1706:22.06
1706:21.92 PAA 1736: Clipper one seven three six. (1706 : 23.39).
1706:25.47 Tower: Ah - Papa Alpha one seven three six report the runway clear. (1706: 28.89).
1706:29.59 PAA 1736: O.K., will report when we're clear. (1706:30.69).
1706:31.69 Tower: Thank you.
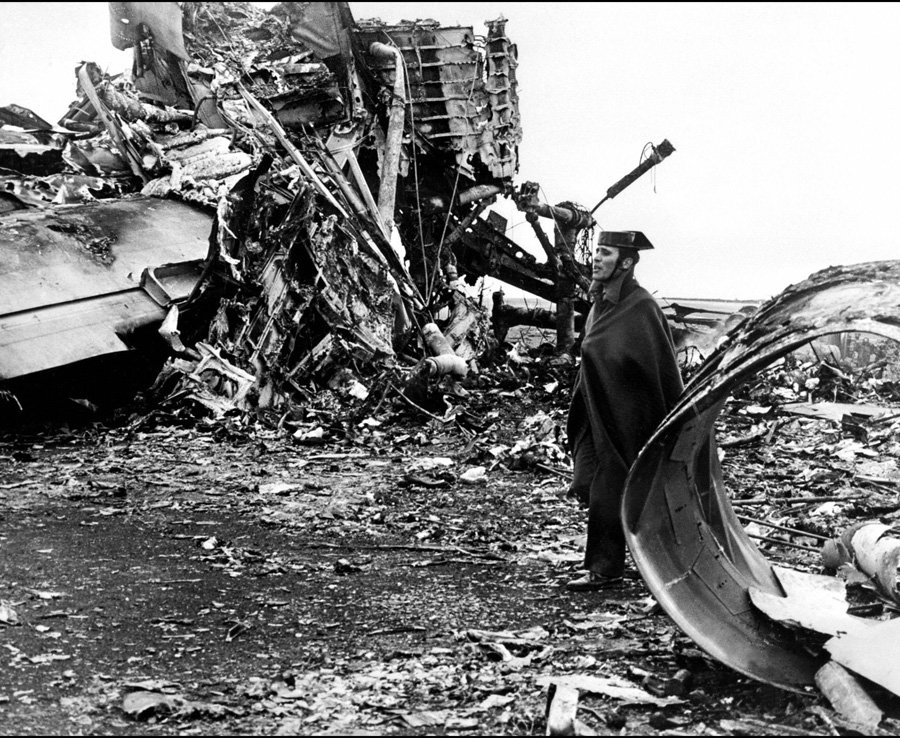
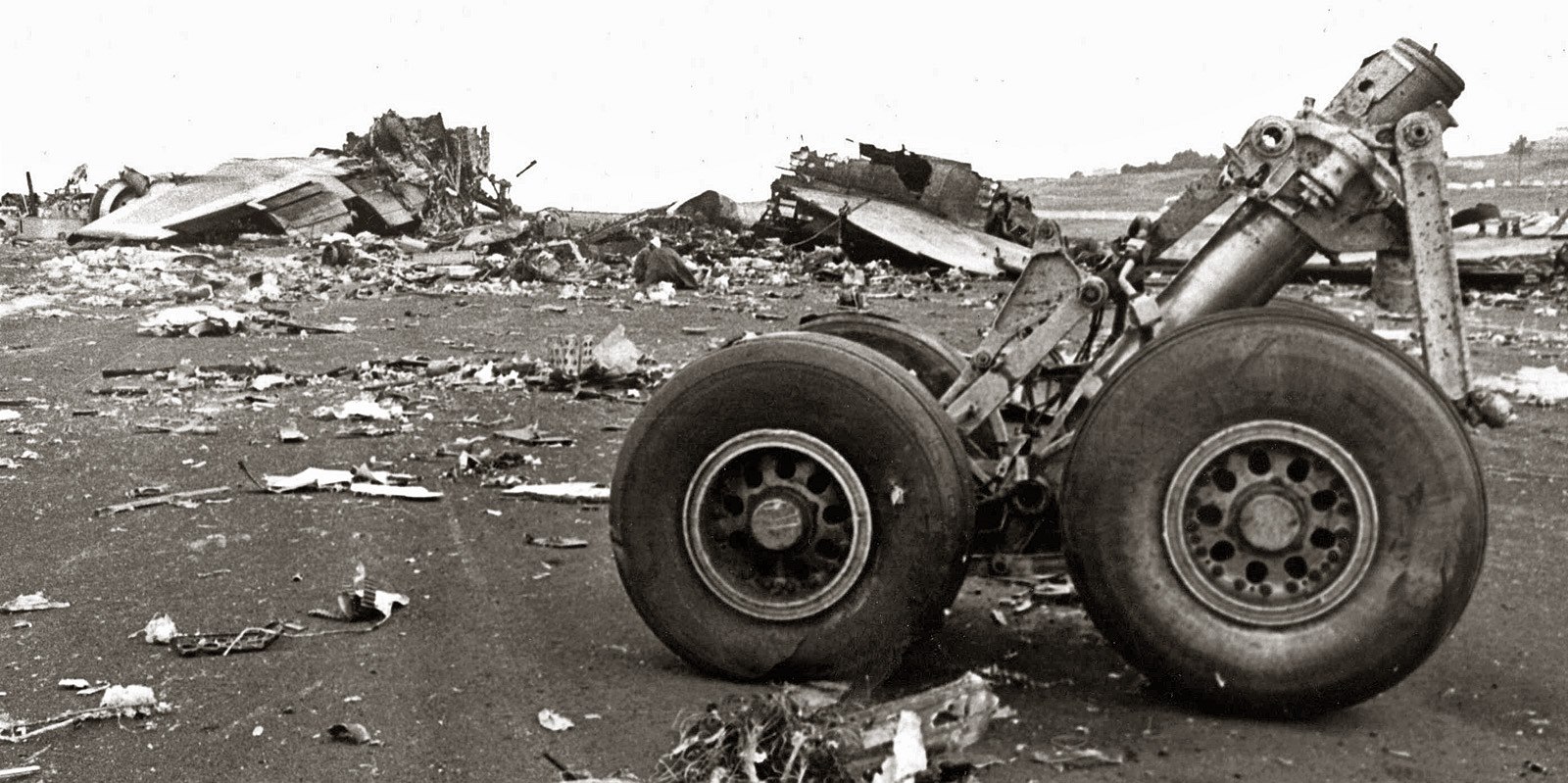
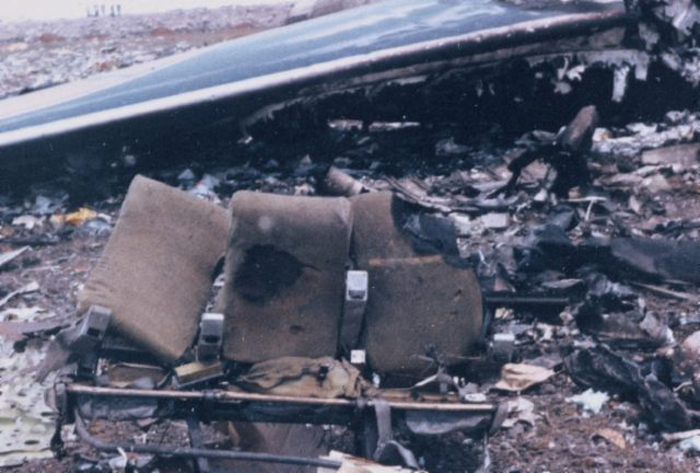
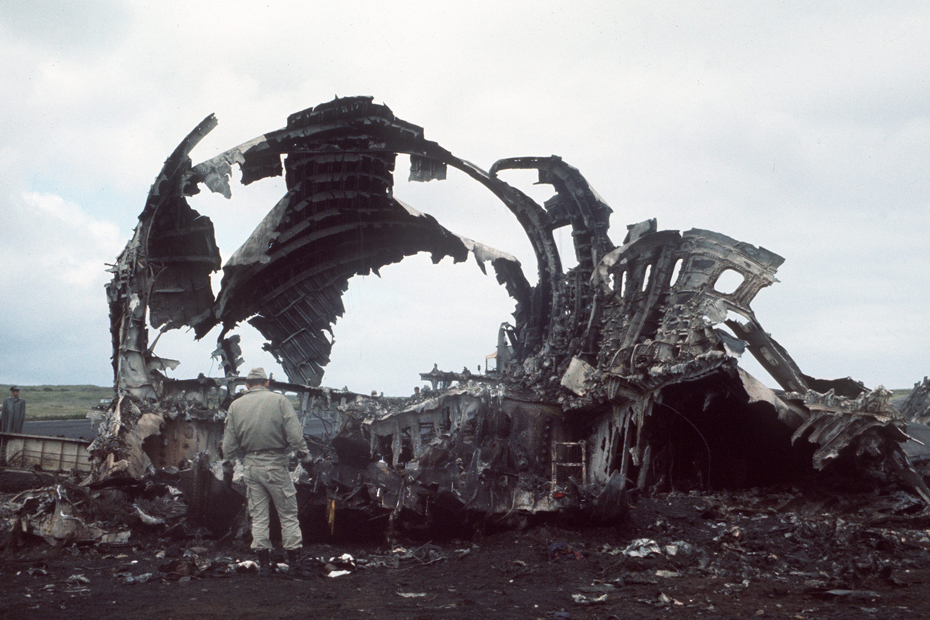
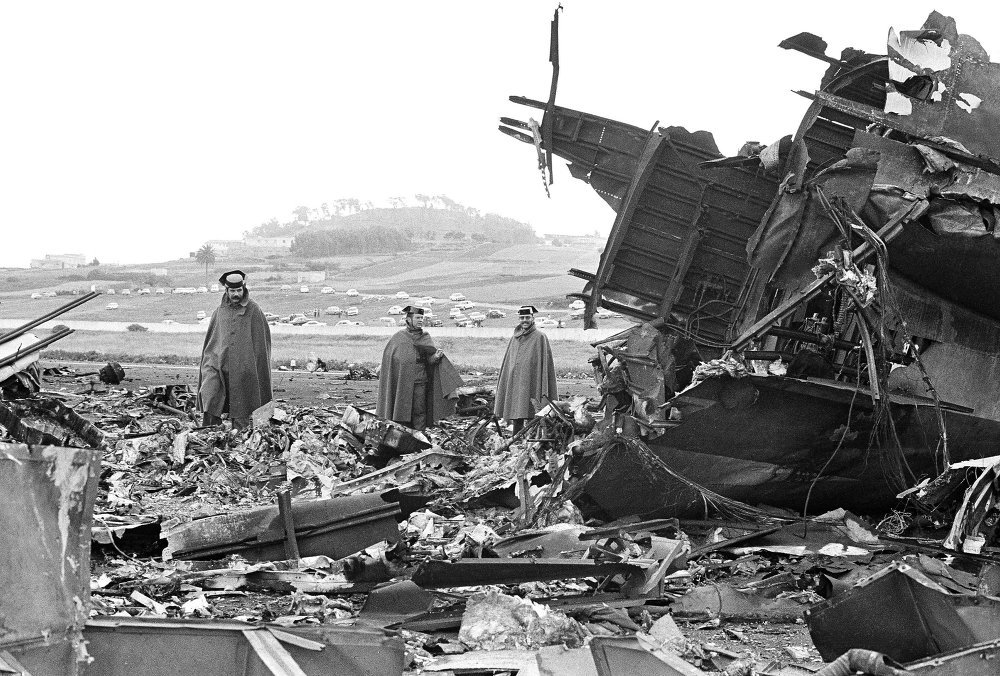
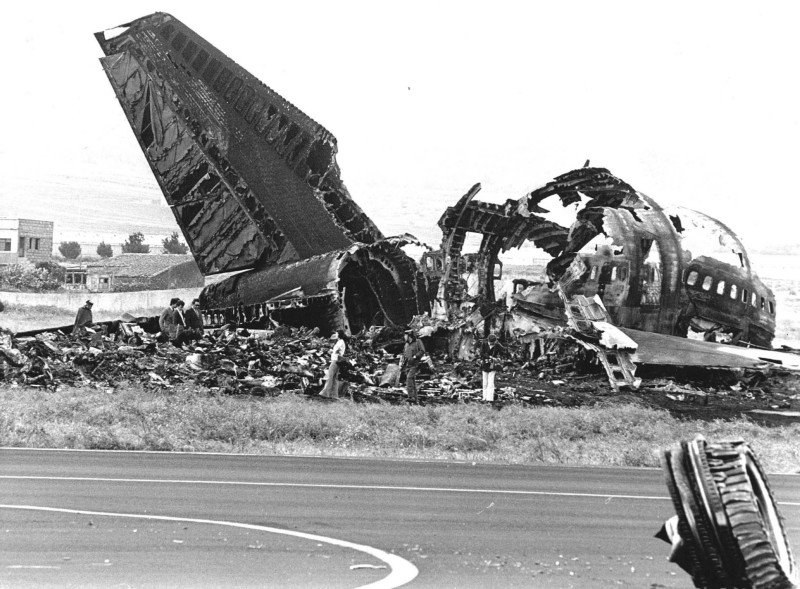
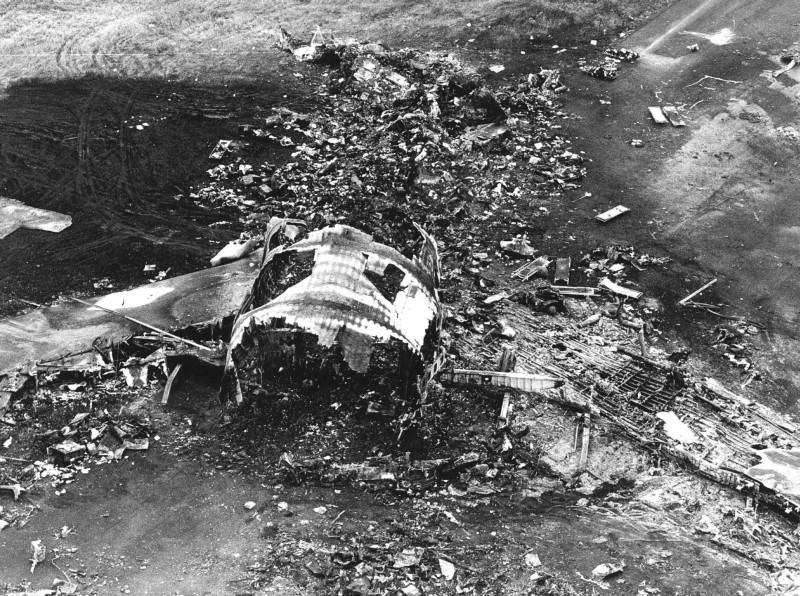
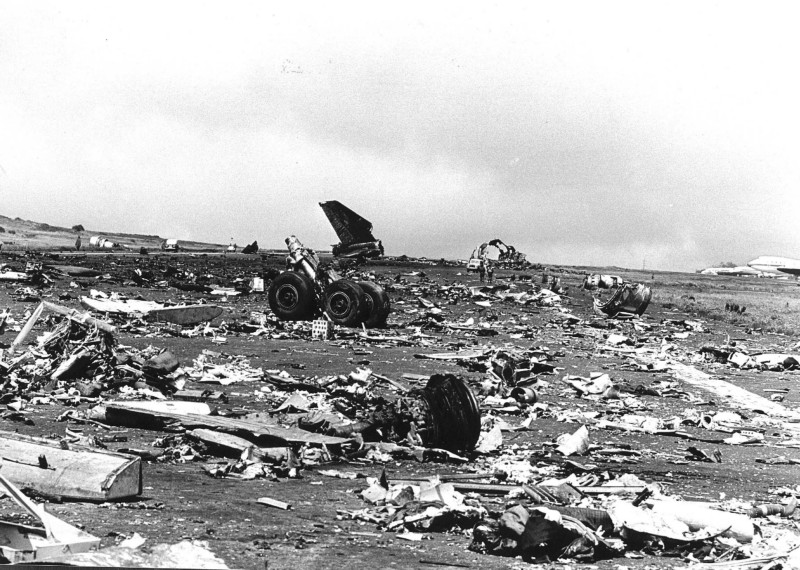
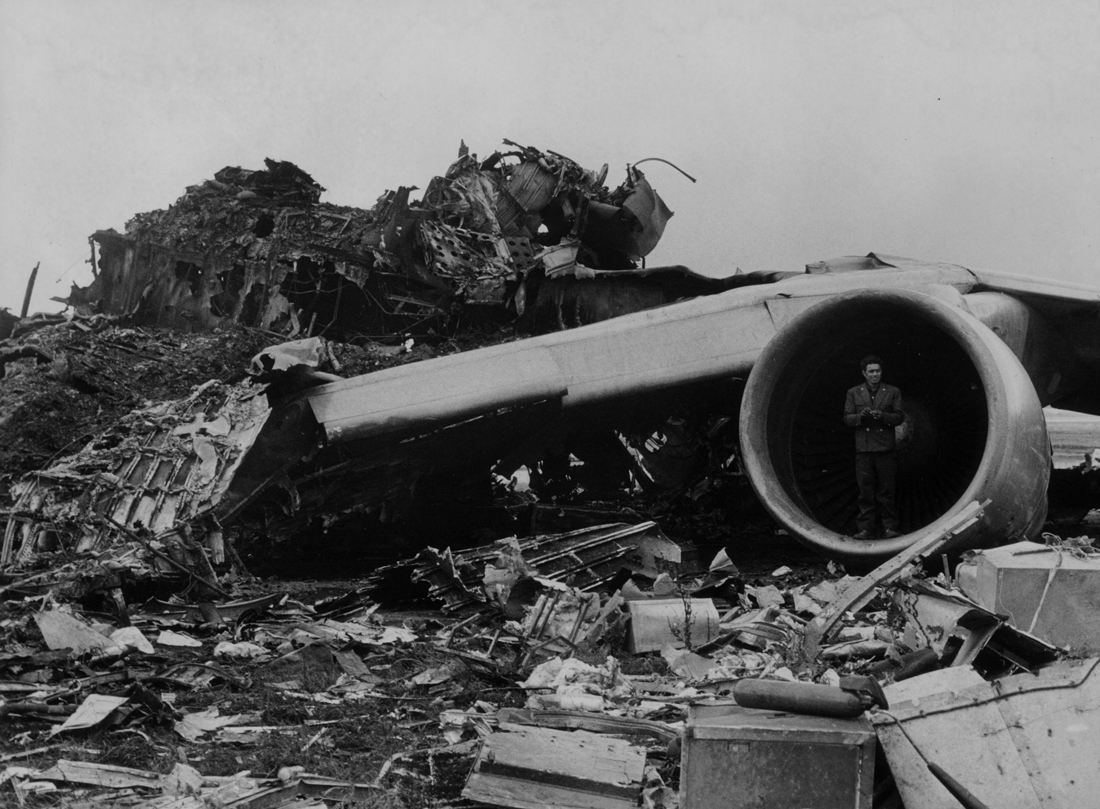
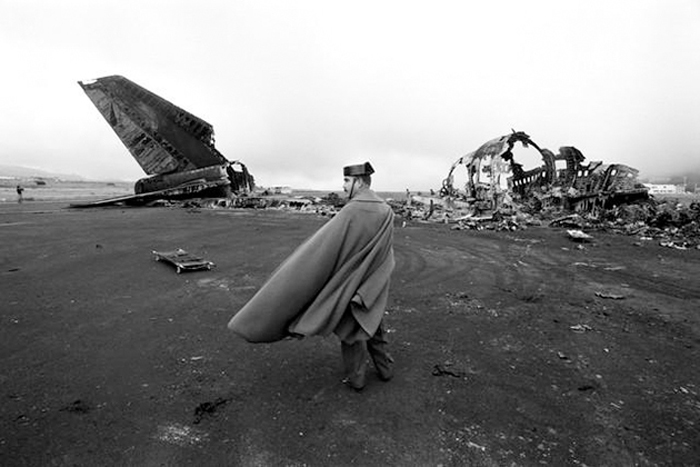
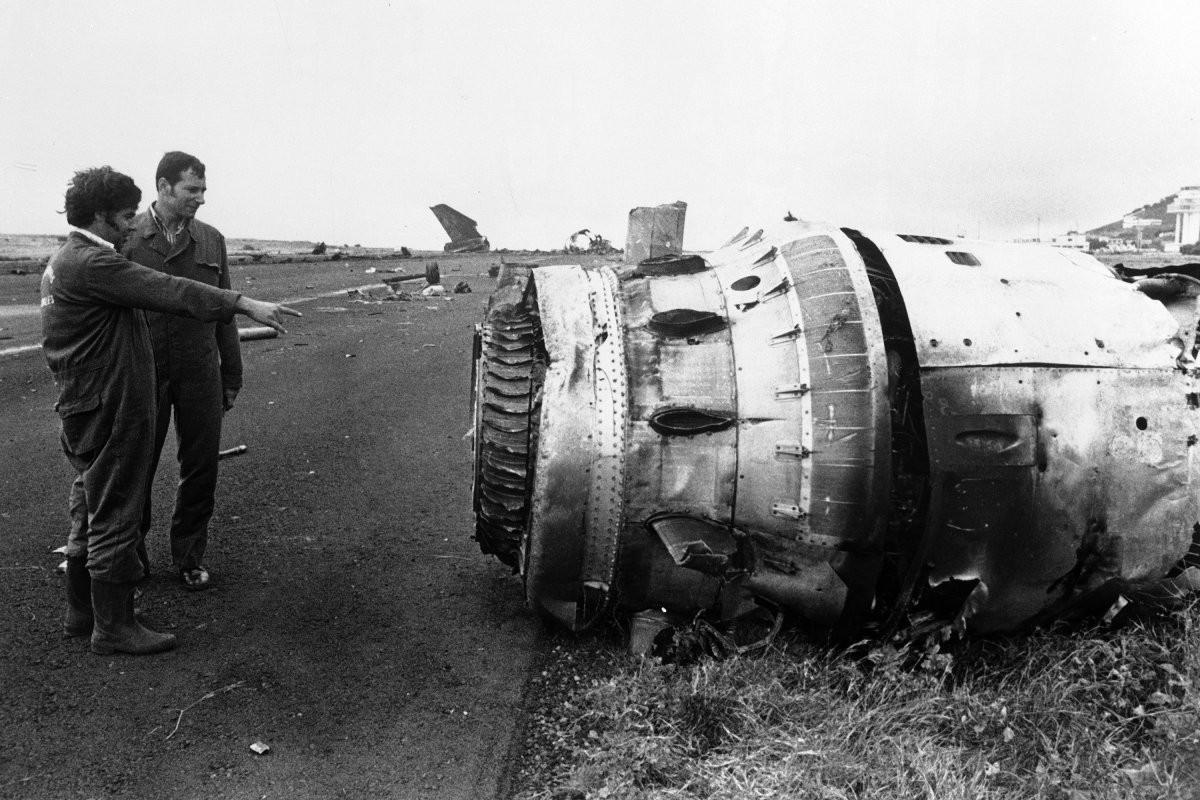
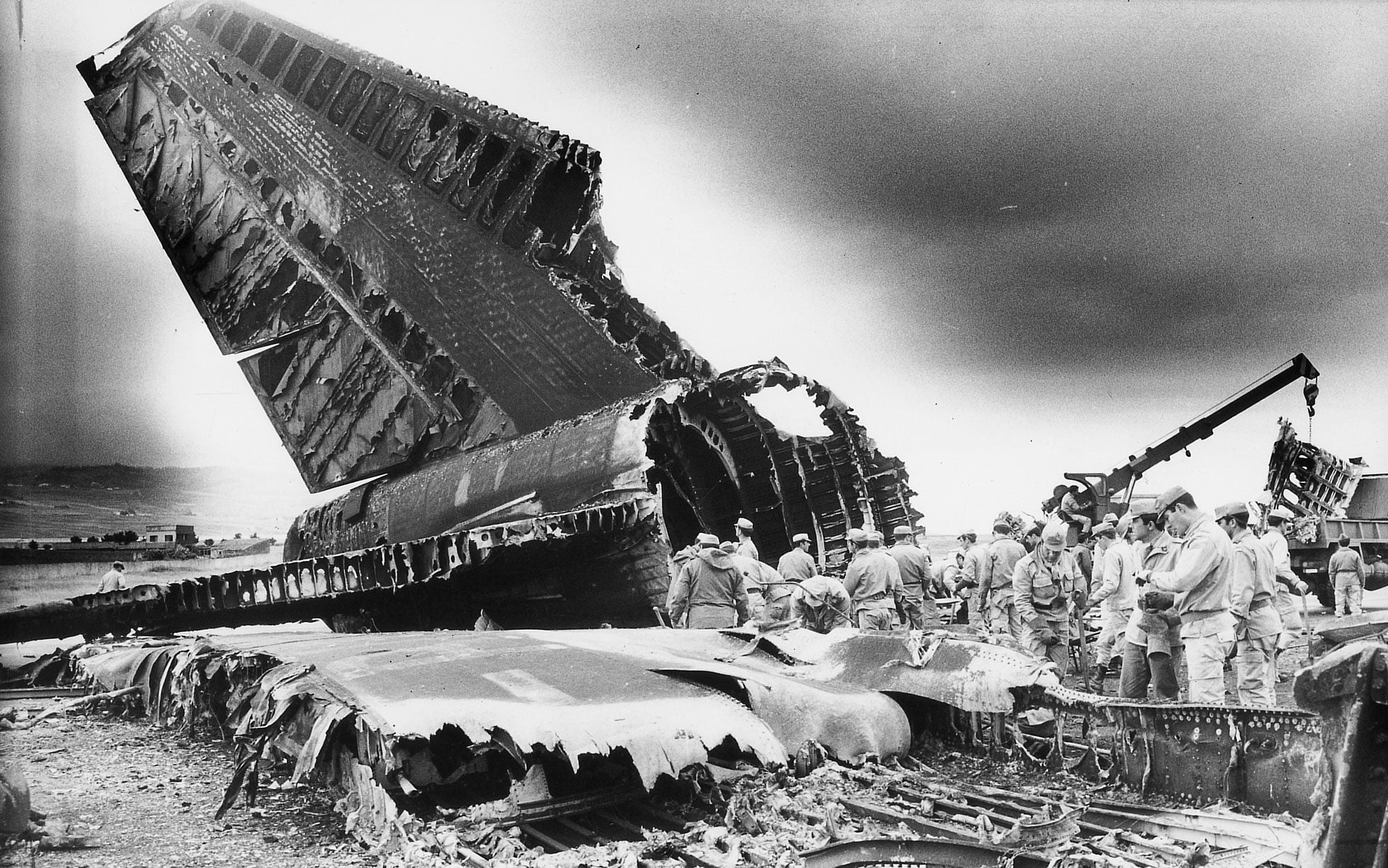
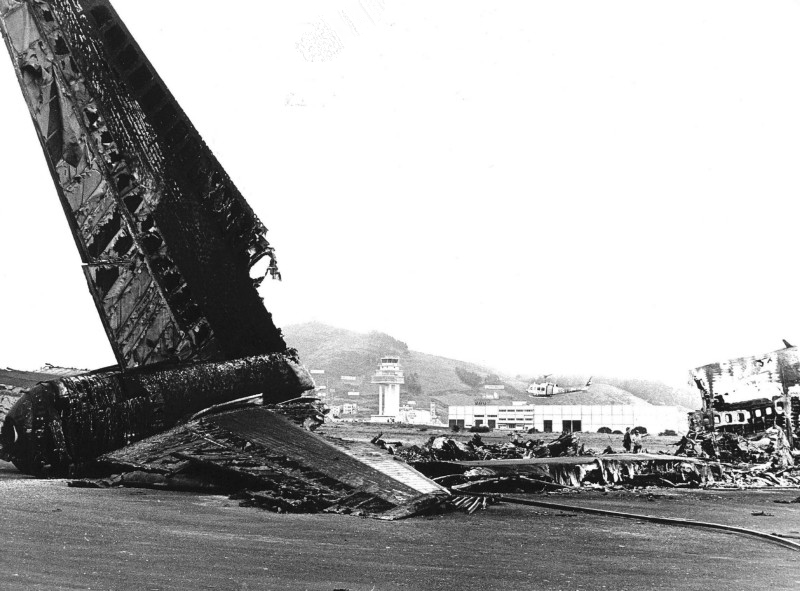
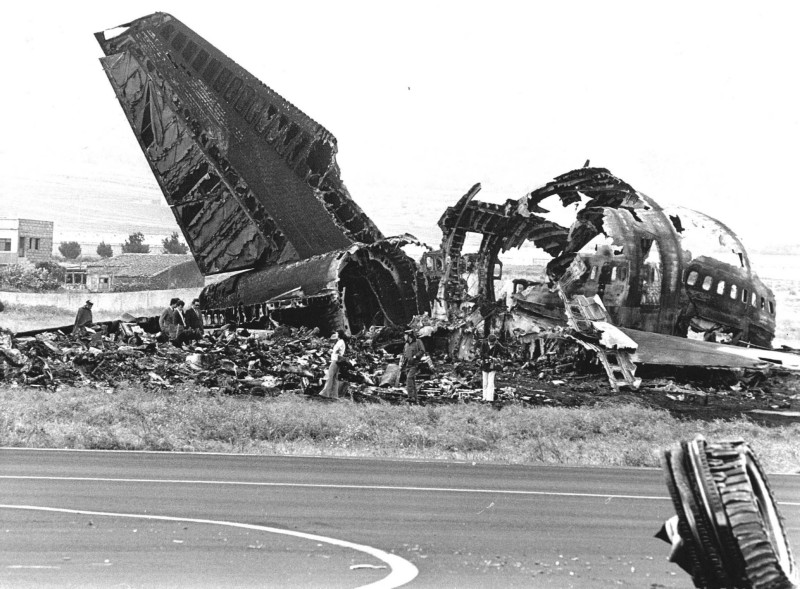
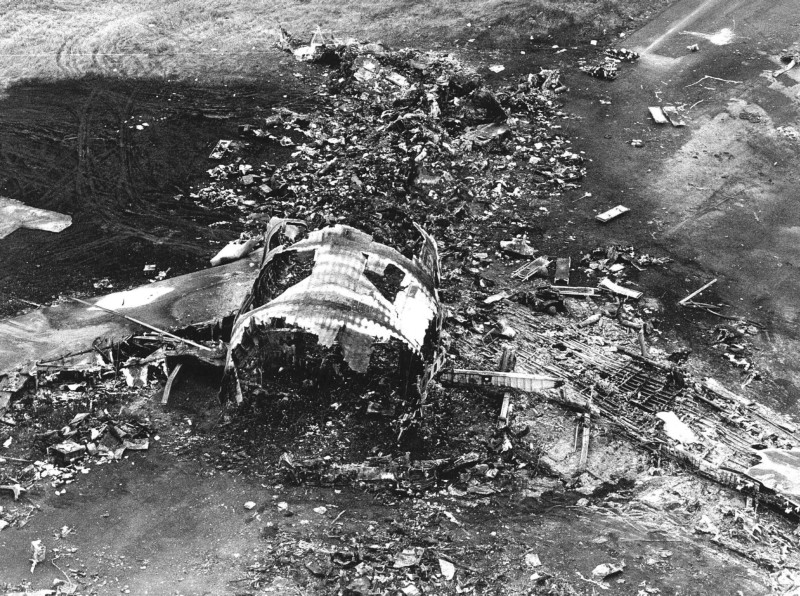
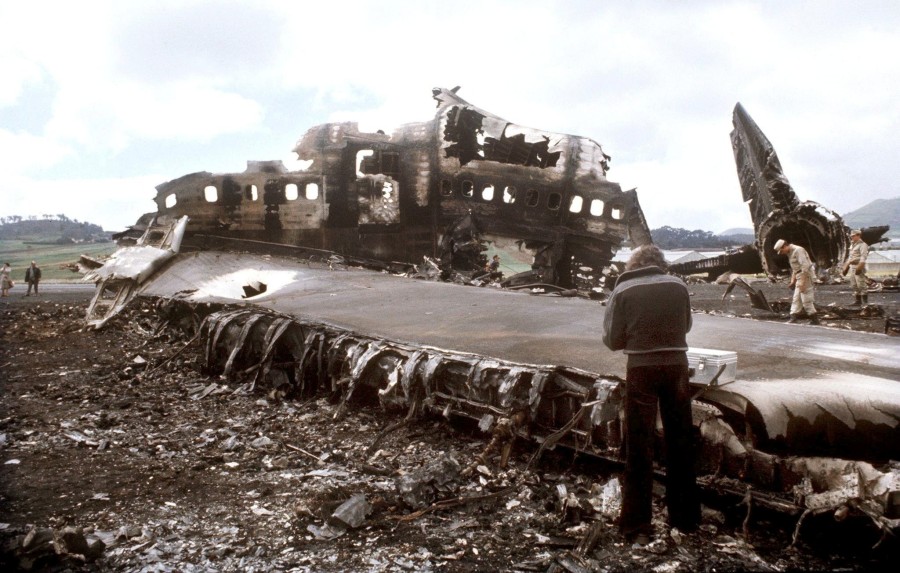
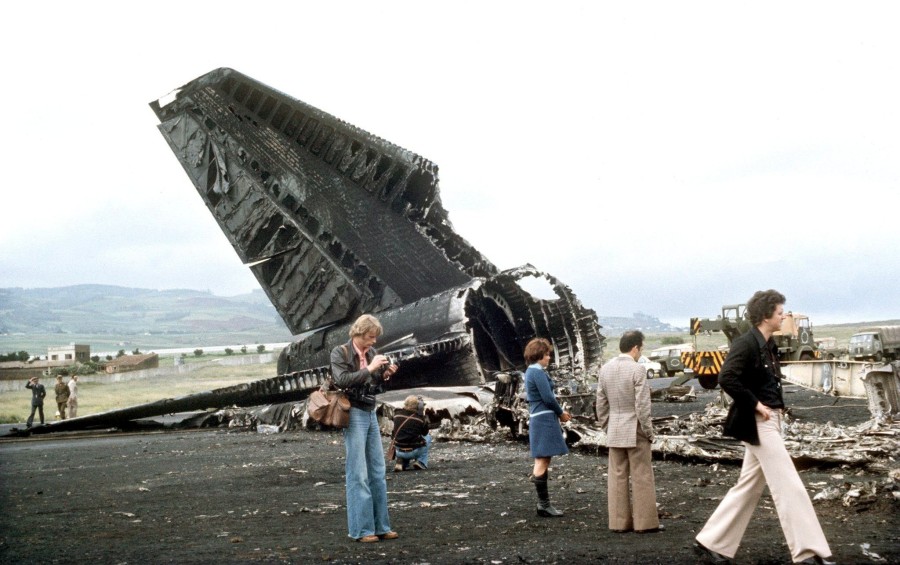
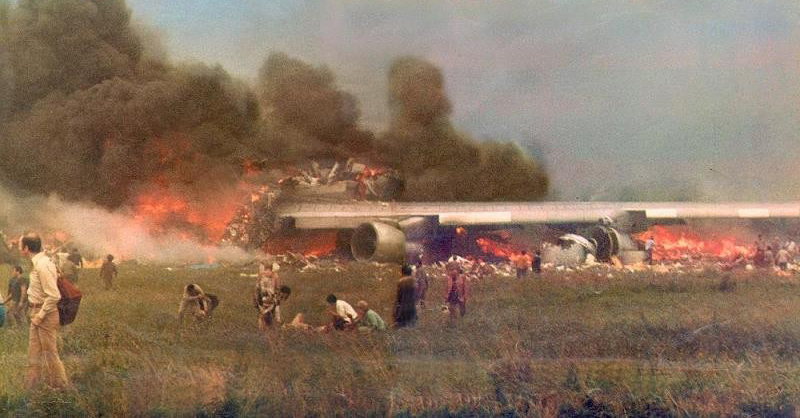
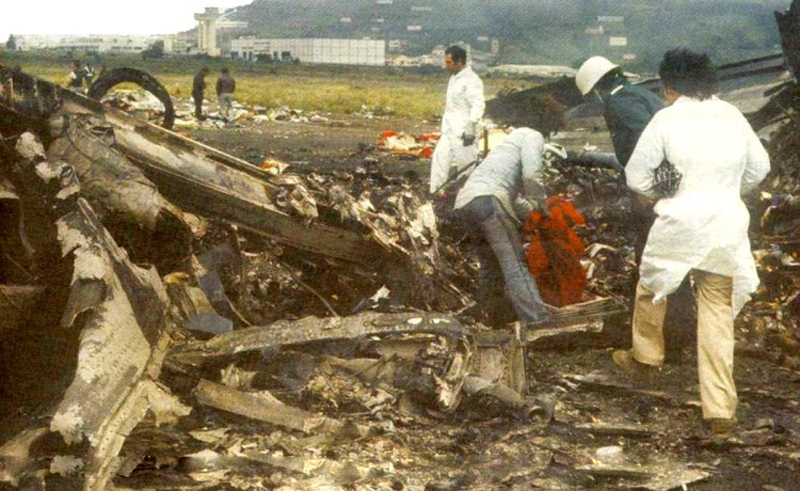
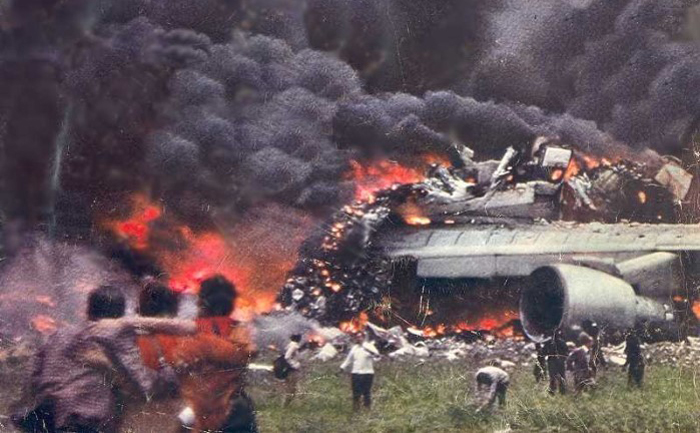
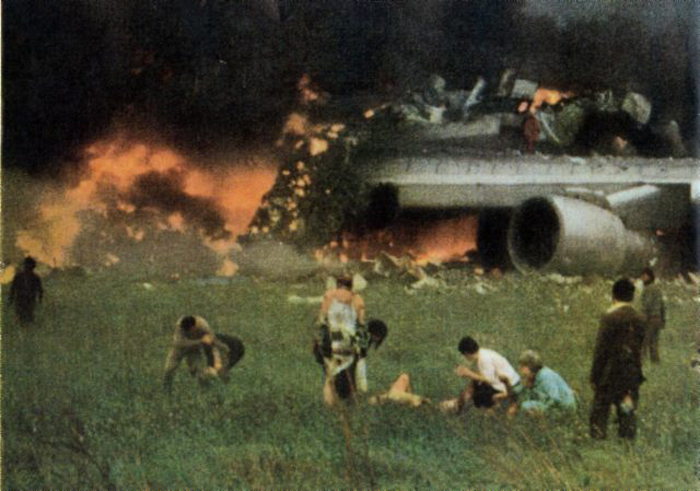
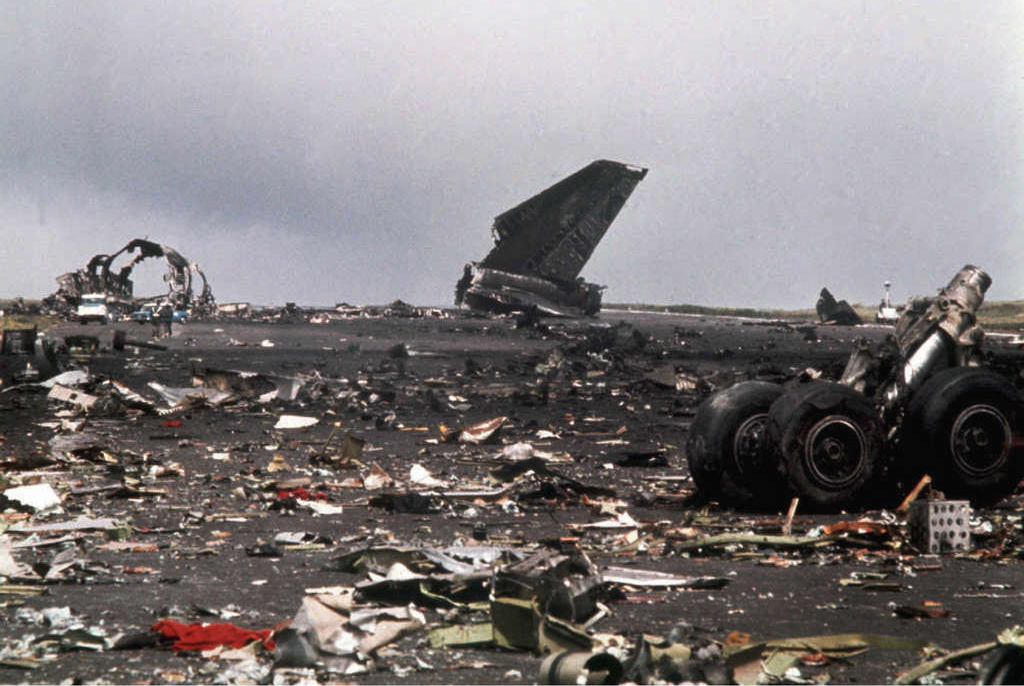
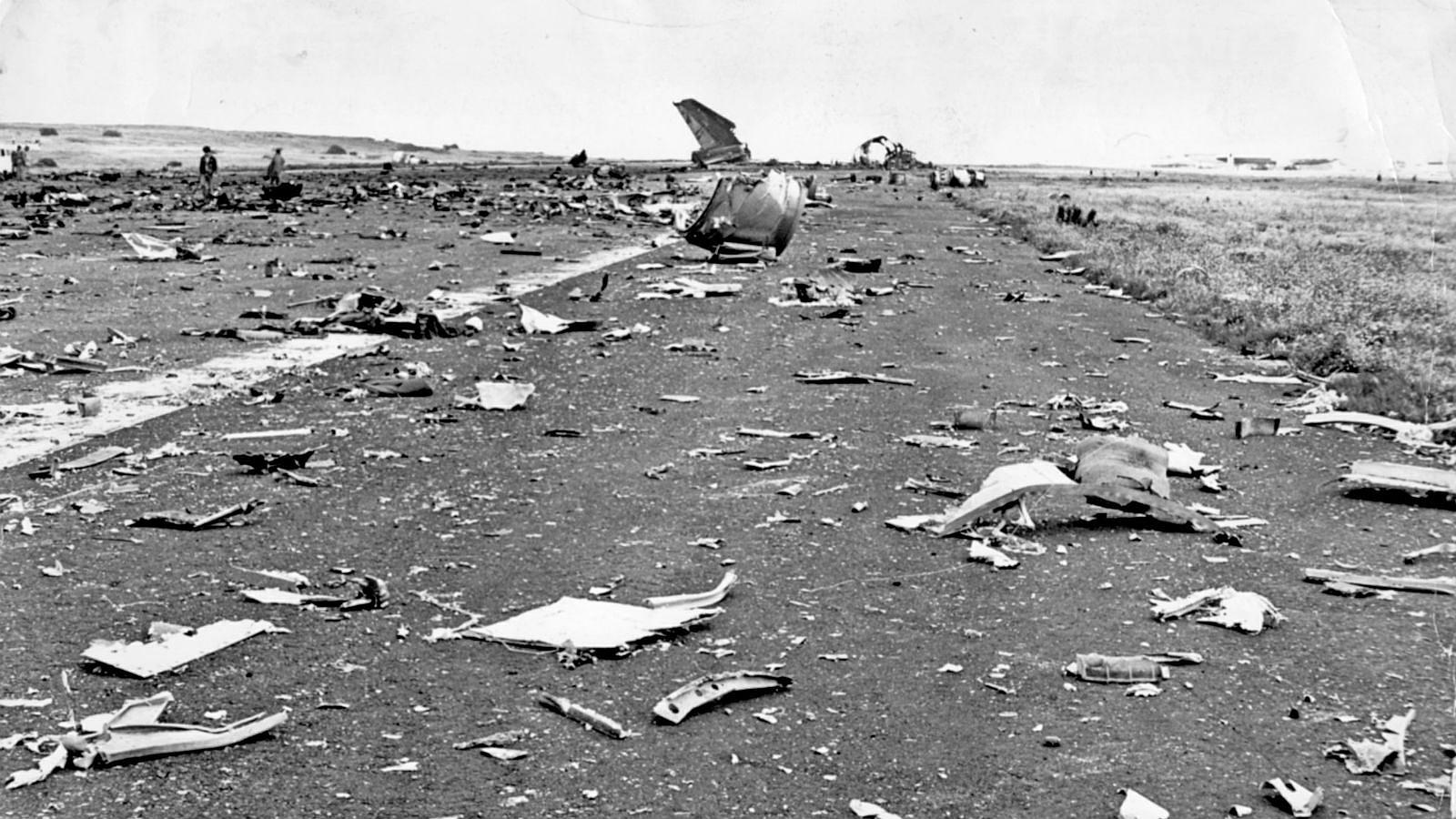
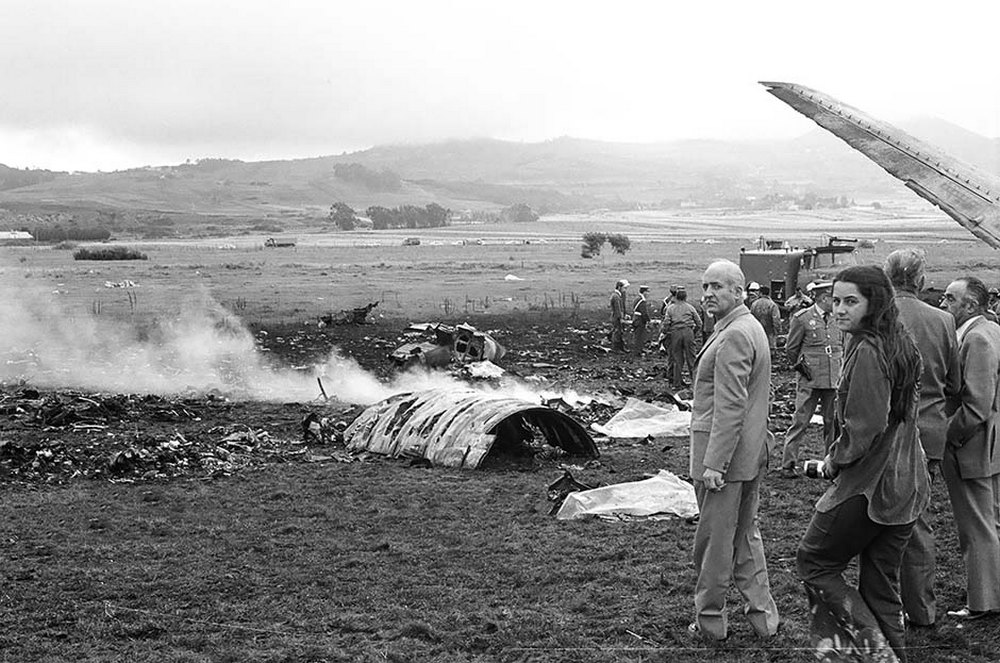
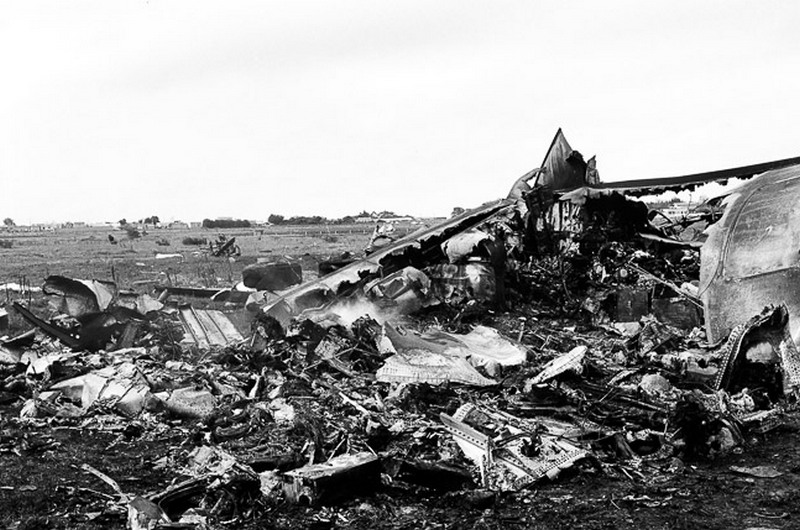
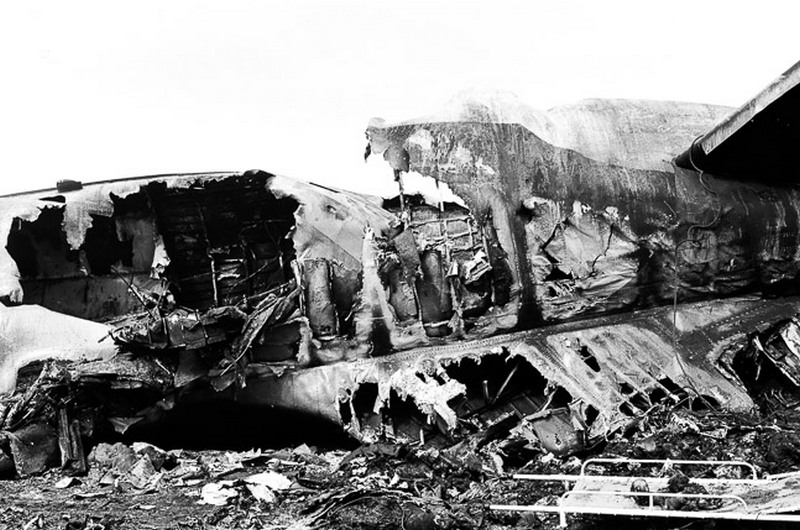
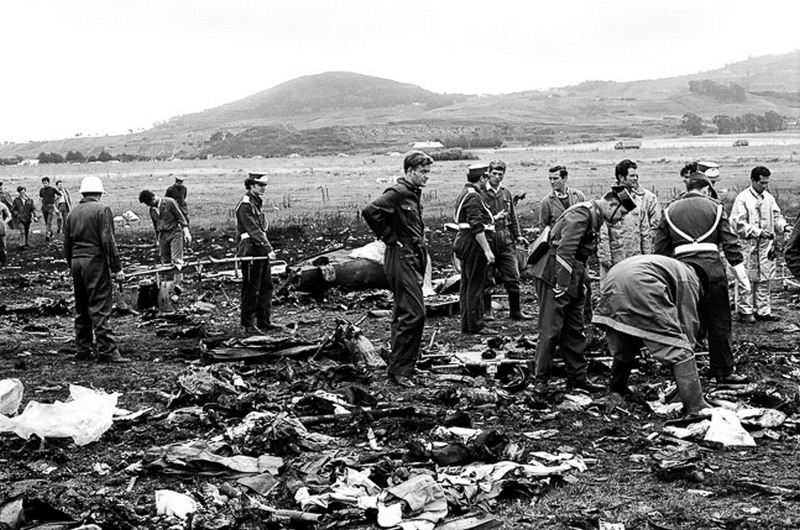
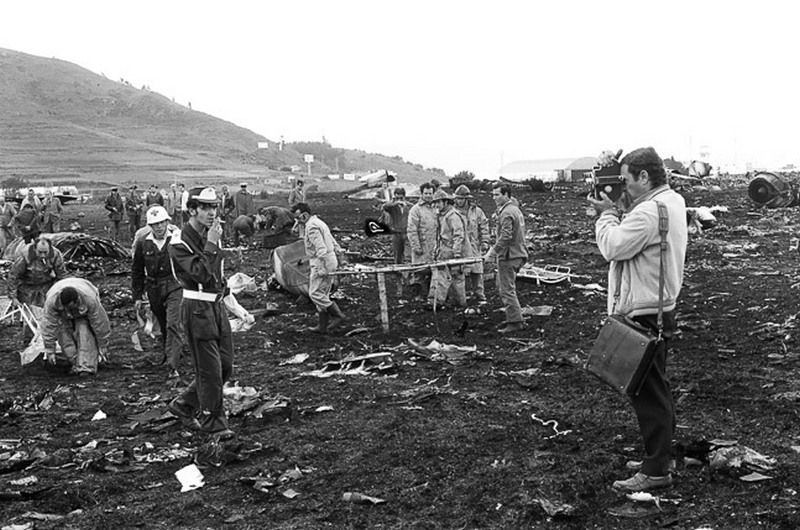
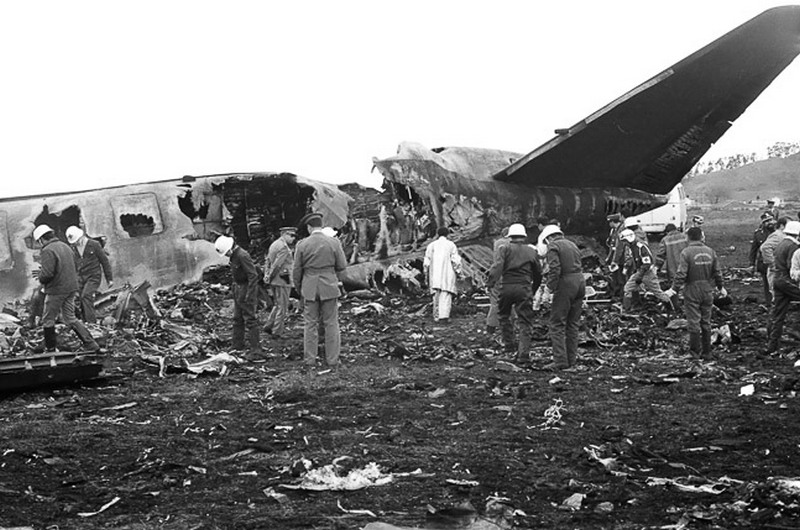
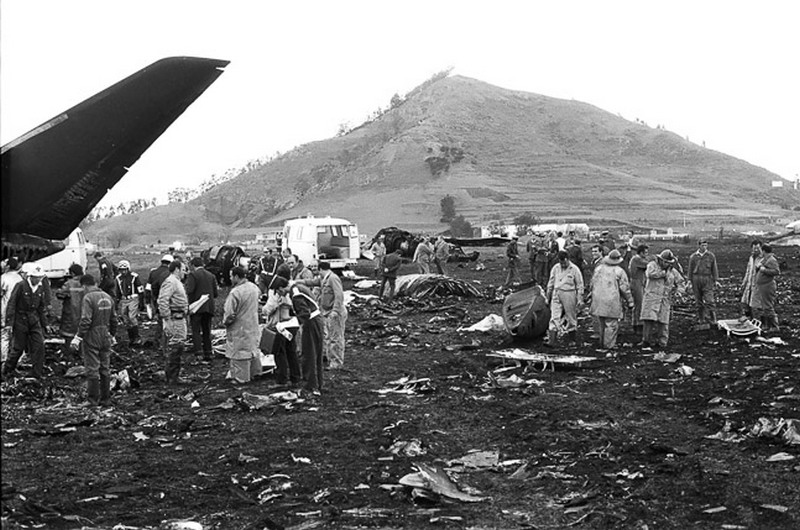
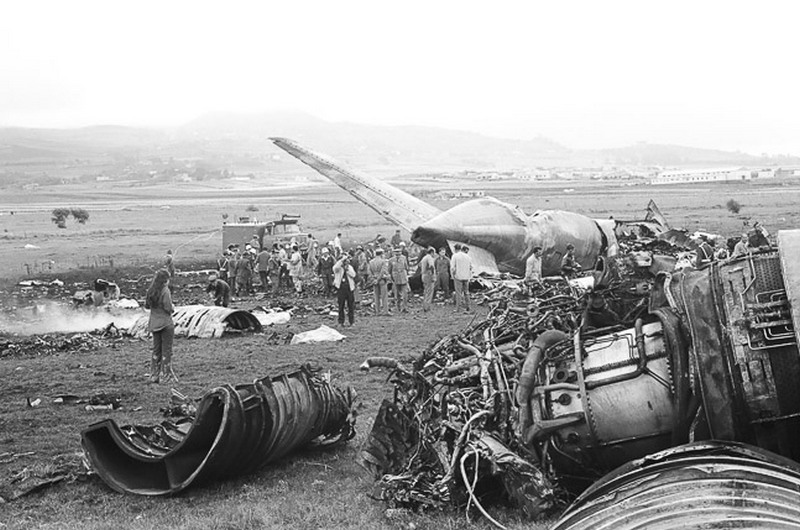
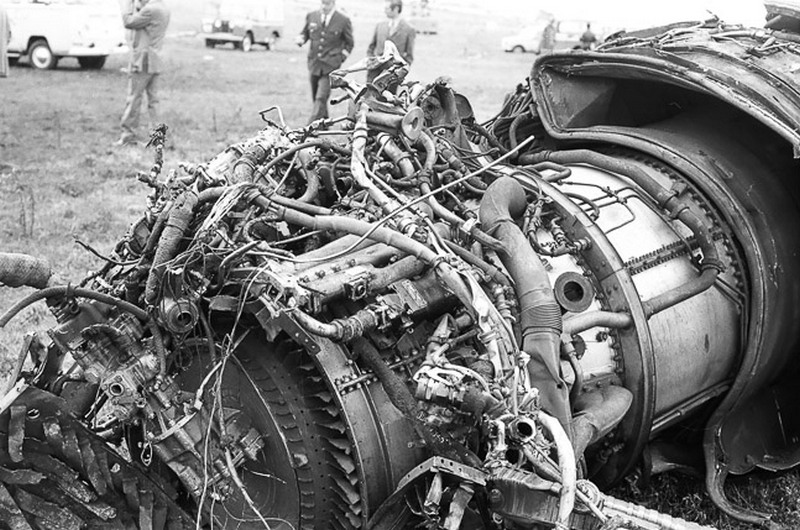
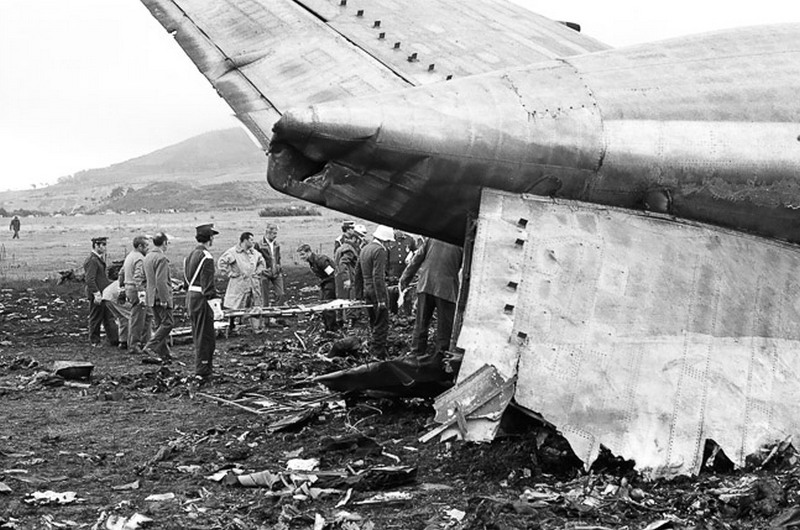
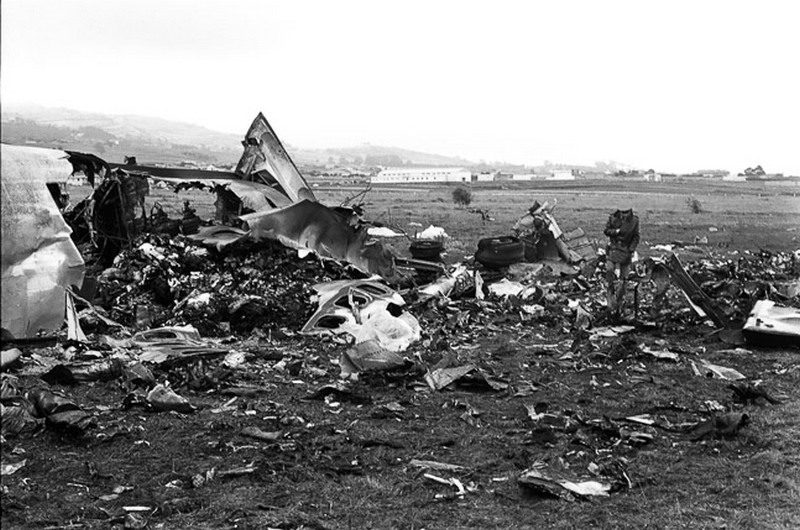
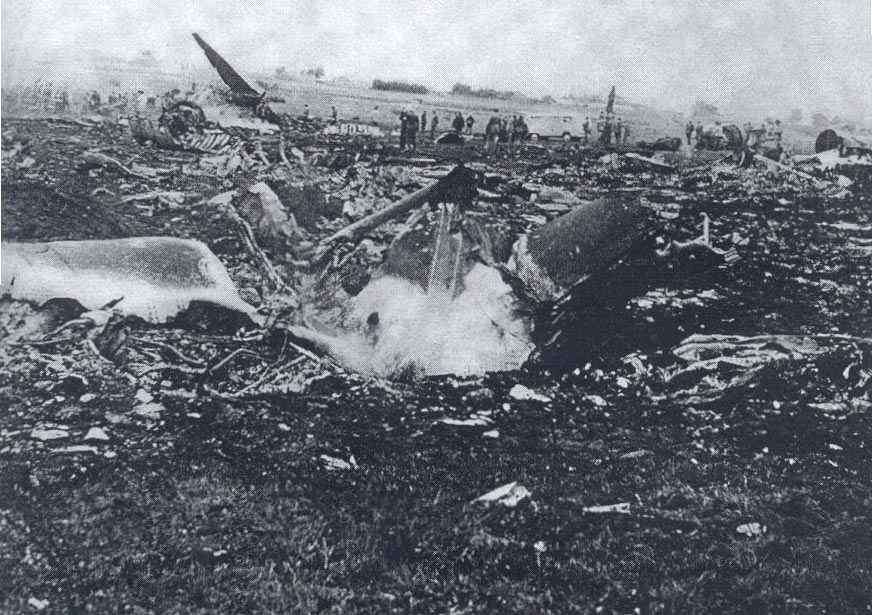
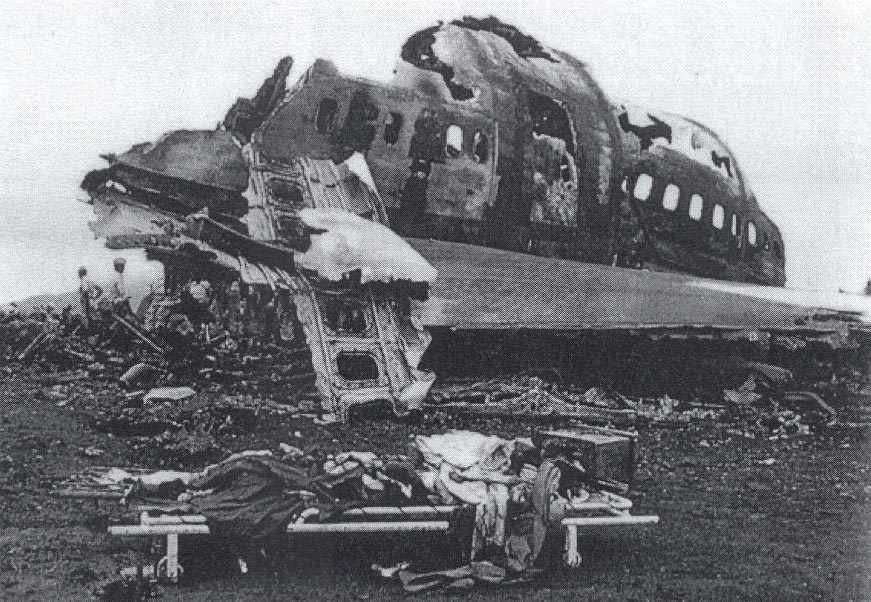
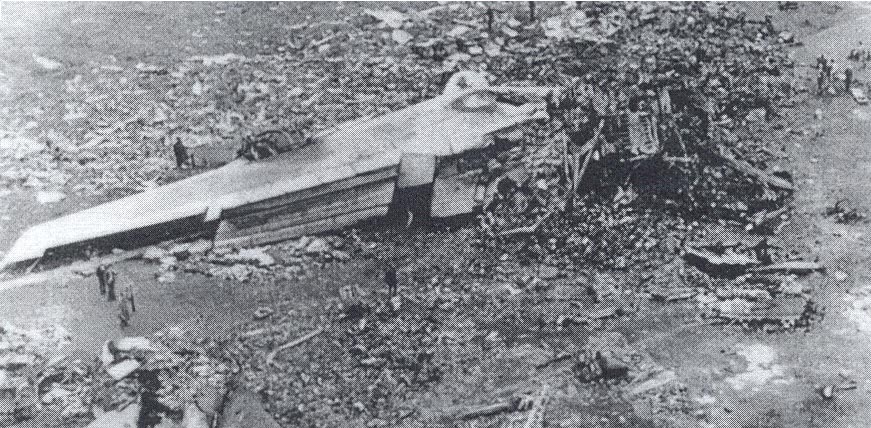
Subsequently, KLM 4805, which had released its brakes to start take-off run 20 seconds before this communication took place, collided with the PAA aeroplane. The control tower received no further communications from PAA 1736, nor from KLM 4805. There were no eyewitnesses to the collision. All 248 occupants on board the KLM 747 were killed. Among the 396 people on board the Pan Am 747, 335 were killed (among them nine crew members) and 61 others were injured.
Probable cause:
The KLM aircraft had taken off without take-off clearance, in the absolute conviction that this clearance had been obtained, which was the result of a misunderstanding between the tower and the KLM aircraft. This misunderstanding had arisen from the mutual use of usual terminology which, however, gave rise to misinterpretation. In combination with a number of other coinciding circumstances, the premature take-off of the KLM aircraft resulted in a collision with the Pan Am aircraft, because the latter was still on the runway since it had missed the correct intersection.