Circumstances:
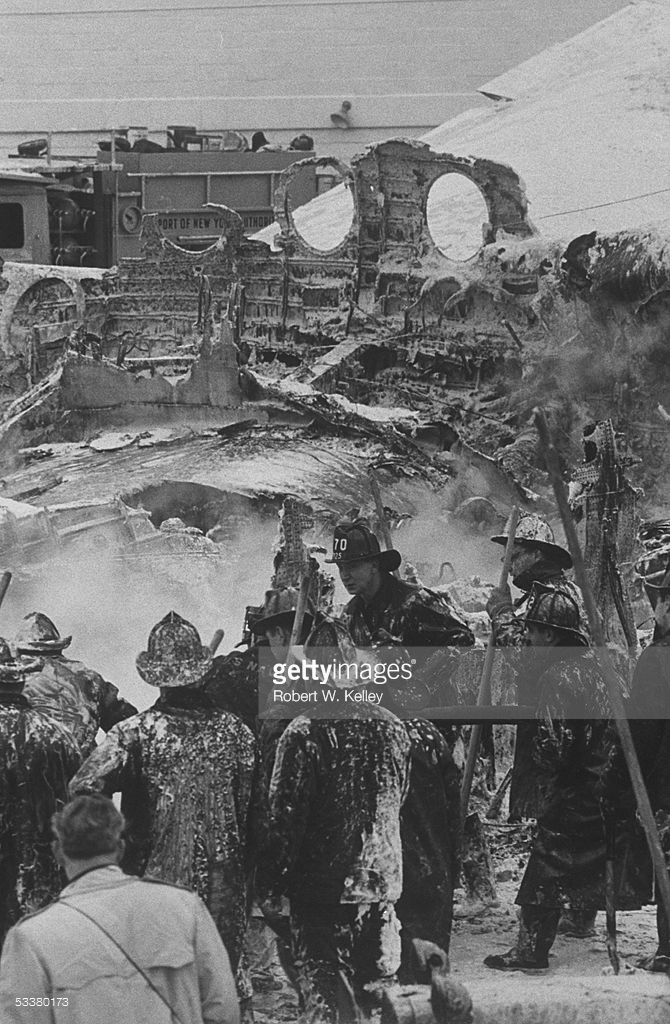
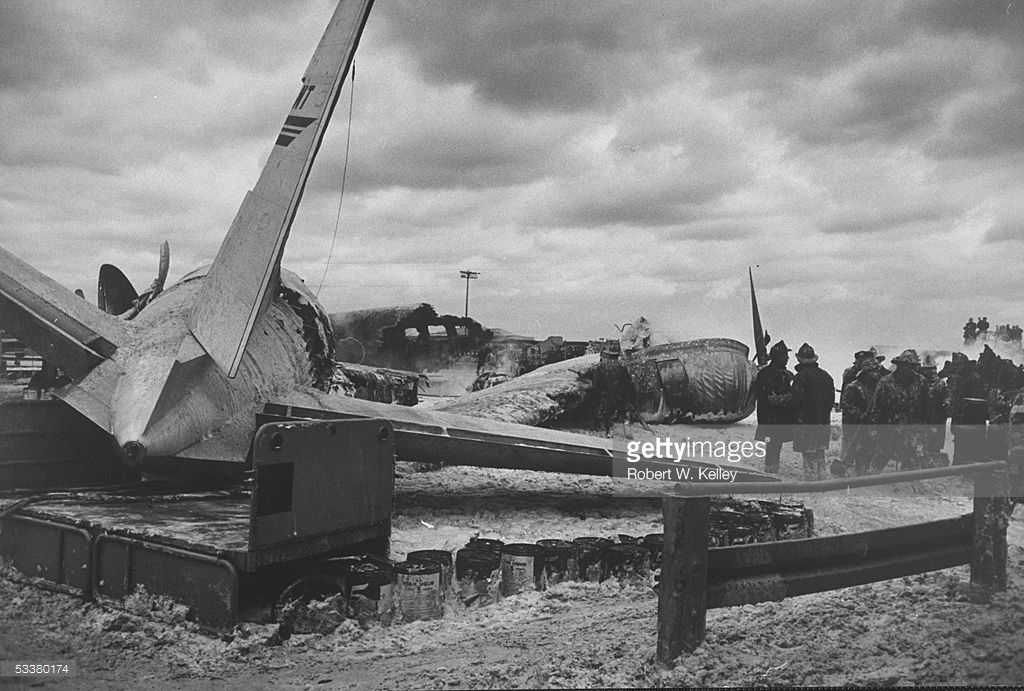
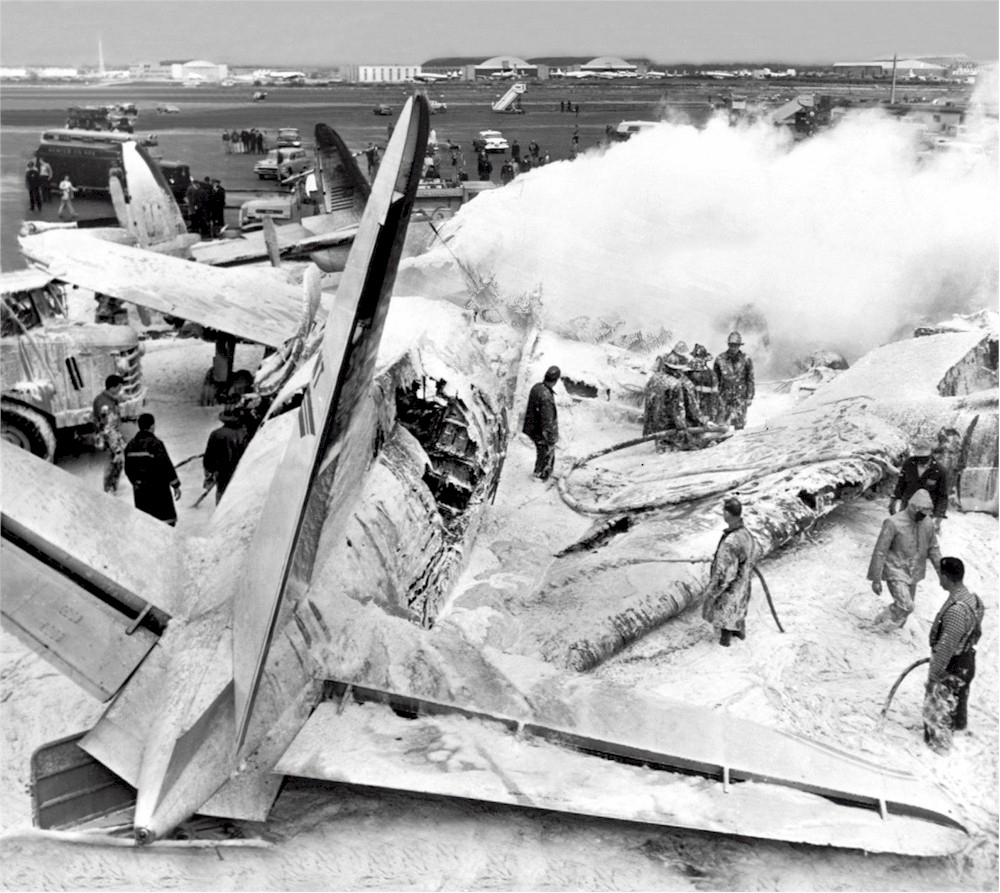
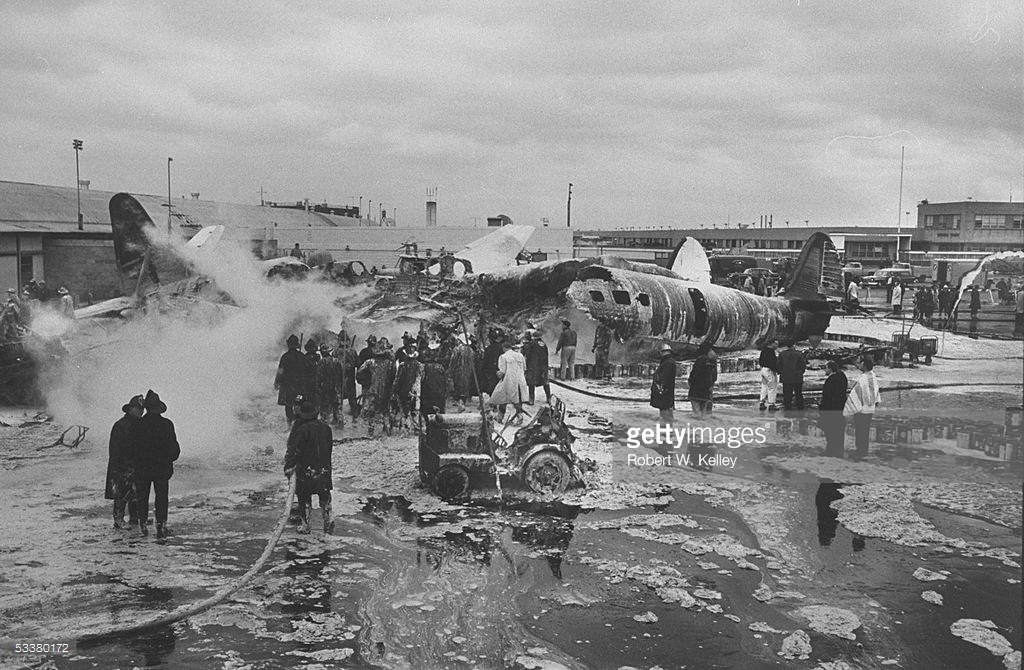
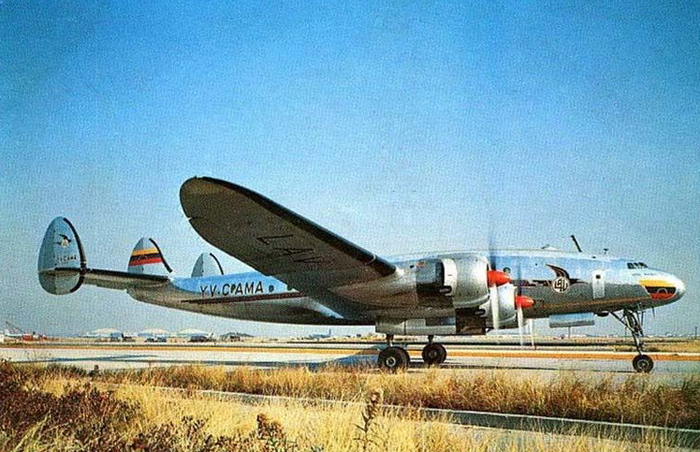
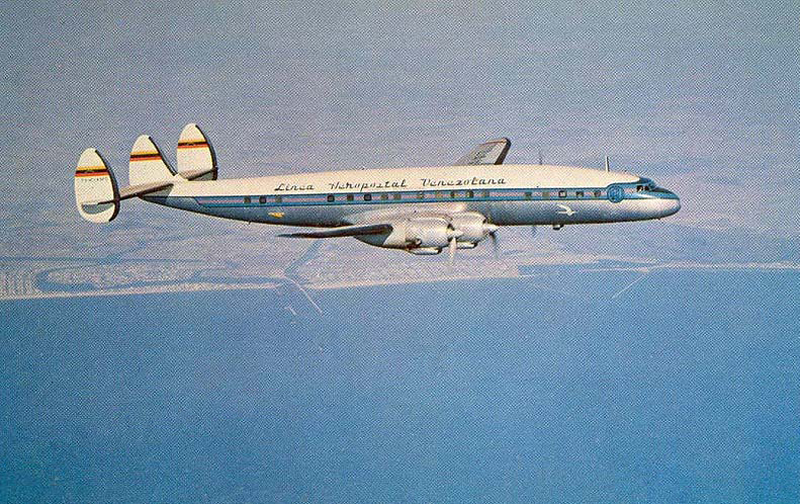
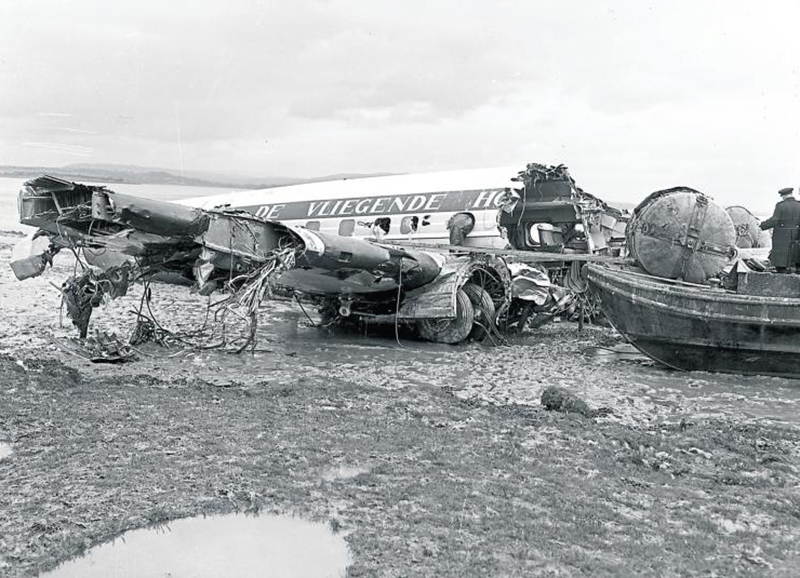
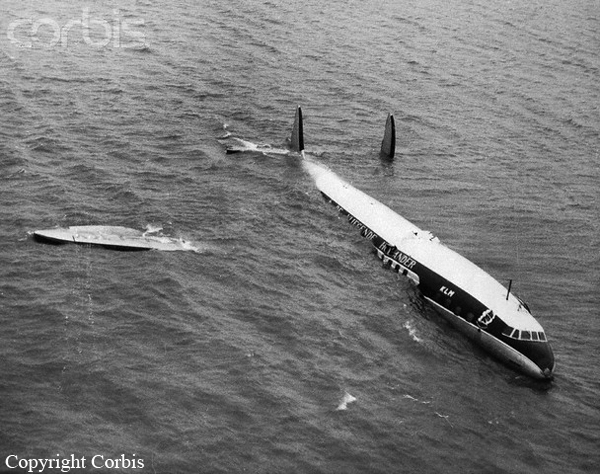
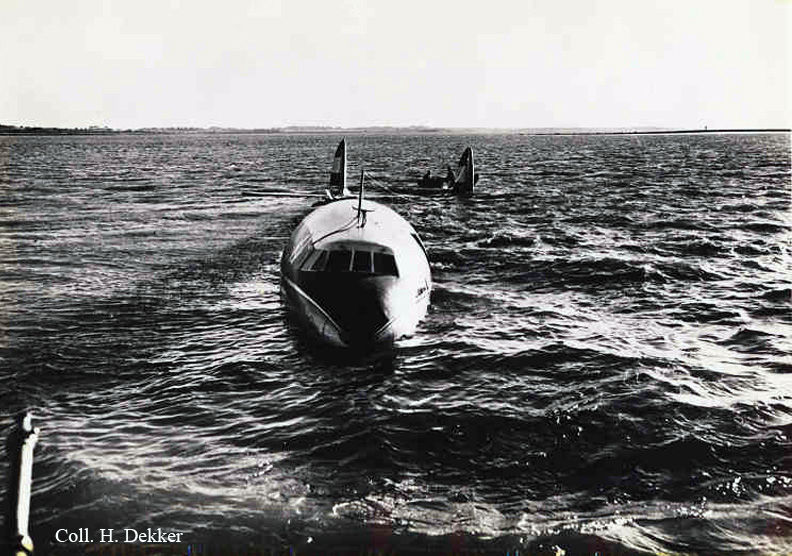
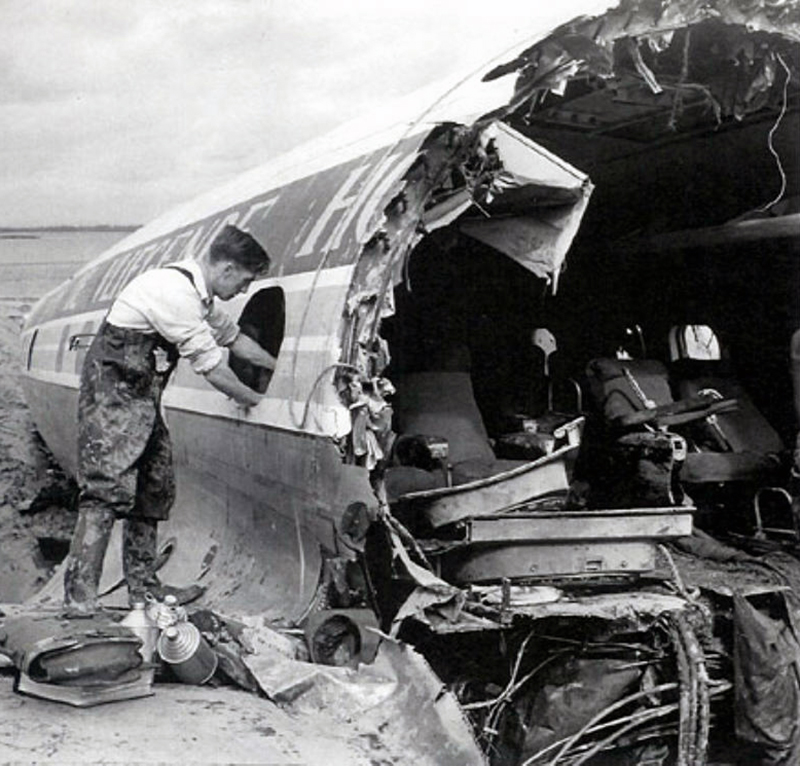
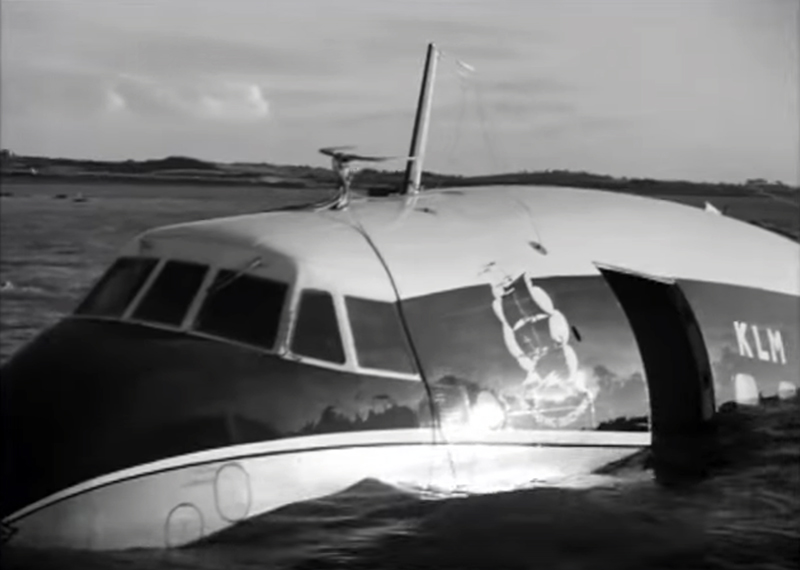
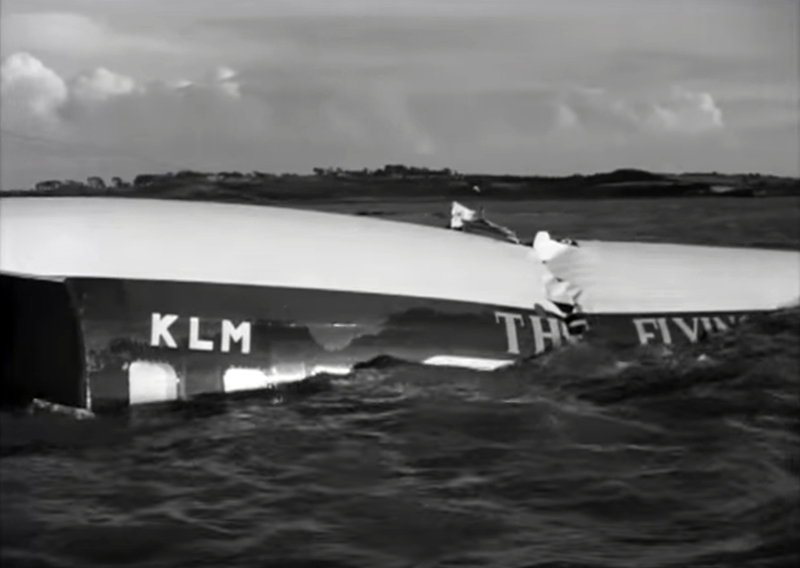
The crew of Flight 627 consisted of Captain C. C. Foxworth Captain E. M. Engle, (first officer), Flight Engineer L. P. Devries, Flight Attendant A. J. Folli, and Flight Attendant A. L., Krause. On departure from the ramp, the gross weight of the aircraft was 95,838 pounds; allowable gross takeoff weight was 105,530 pounds. The load was distributed so that the center of gravity of the aircraft was within the approved limits. Flight 627 initially taxied out at 2345, bar 18, for takeoff from Runway 7R. This flight and a preceding flight returned to the ramp because fog drifted in and reduced visibility below the approved minimum of one-fourth mile while they were awaiting clearance for takeoff. 2 Neither flight was issued off clearance, although according to Captain Foxworth, they held at Runway 7R about 15 minutes. The captains of flights reported that when they arrived at Runway 7R the existing visibility was well over the required one-quarter mile, as they could ace beyond the far end of the 8,200-foot runway, and so advised the control tower. About 15 minutes after returning to the ramp, Captain Foxworth was advised by Eastern Operations that visibility had improved, and the flight again taxied out, following another Eastern aircraft, Flight 623W. While they were taxing, the tower suggested that takeoff be made on Runway 22L and advised that visibility to the south-southeast, from tower location, was three miles. Since both flights had taxied beyond this runway at the time this information was conveyed to them, they turned around and Captain Foxworth, now in the lead, took position for takeoff near the end of Runway 22L. The tower advised Flight 627 that the weather was now being reported as thin obscuration, one and one-half miles visibility, fog, and smoke. 4 Captain Foxworth opened the left side "clear-view" window for maximum visibility. The runway lights were turned to full intensity, and the landing lights of the aircraft were on. Captain Foxworth observed that visibility appeared to be at least one-fourth mile, and stare could be seen. He could see the runway border lights and down the runway centerline for some distance. He said that he was unable to see past the intersection. The engines were run up, cockpit checks completed, and airways clearance via Long Beach, Sully, and Woolf intersections was received. Takeoff clearance was issued at 0055, October 19. Captain Foxworth, flying from the left, made the takeoff using the runway border lights and centerline as visual reference guides. The first officer also maintained visual reference except when he briefly directed his attention to retraction of the landing gear. In the takeoff run the captain noticed that visibility was variable due to fog and seemed to get progressively worse, but later stated that he had "expected to come out on top almost any second" after becoming airborne; he did not go on instruments. Takeoff seemed normal. Shortly after calling for retraction of the gear. Captain Foxworth observed that air speed was approaching 110 knots. He said that he lost all ground references at about the intersection of Runways 19L, 25L, and 22L, at or shortly after becoming airborne. A few seconds later he heard the first officer shout a warning and they struck the ground while at takeoff power. A second or two after the first officer moved the landing gear handle to retract position and again directed his attention outside, he saw they were quite low, grabbed for the control wheel to pull the nose up, and simultaneously shouted a warning. He did not recall whether he got his hands on the wheel before impact. The aircraft struck the ground to the left of Runway 22L at Taxiway F. It bounced, and following the second impact skidded to a stop in an undeveloped part of the airport south of Taxiway G. An intense fire immediately developed in the left wing at No. 2 engine position. The pilots, flight engineer, and one passenger left through the crew door, located just to the rear of the cockpit on the right side; all other occupants exited in orderly fashion through the main cabin door at the left rear side of the aircraft.
Probable cause:
The Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was the captain's loss of visual reference and orientation when he encountered drifting fog shortly after becoming airborne on takeoff, and the resultant inadvertent assumption of a descending flight path. The following findings were reported:
- The general visibility figure given to the flight at about the tine clearance was issued for takeoff was ceiling unlimited, visibility one and one-half miles,
- From his position at the end of the runway, the captain estimated visibility to be about one-fourth mile, which was within the CAA-approved limits,
- A visual takeoff was made by the captain with the first officer also maintaining visual reference to the ground,
- Near the main intersection, slightly more than one-fourth mile from start of the takeoff run, the aircraft encountered fog which greatly reduced visibility,
- Although the aircraft became airborne, it did not penetrate the top of the fog
- The first officer saw the ground an instant before impact, but the aircraft struck before corrective action could be taken,
- There was no evidence of failure or malfunction of the aircraft, engines, or propellers before impact.