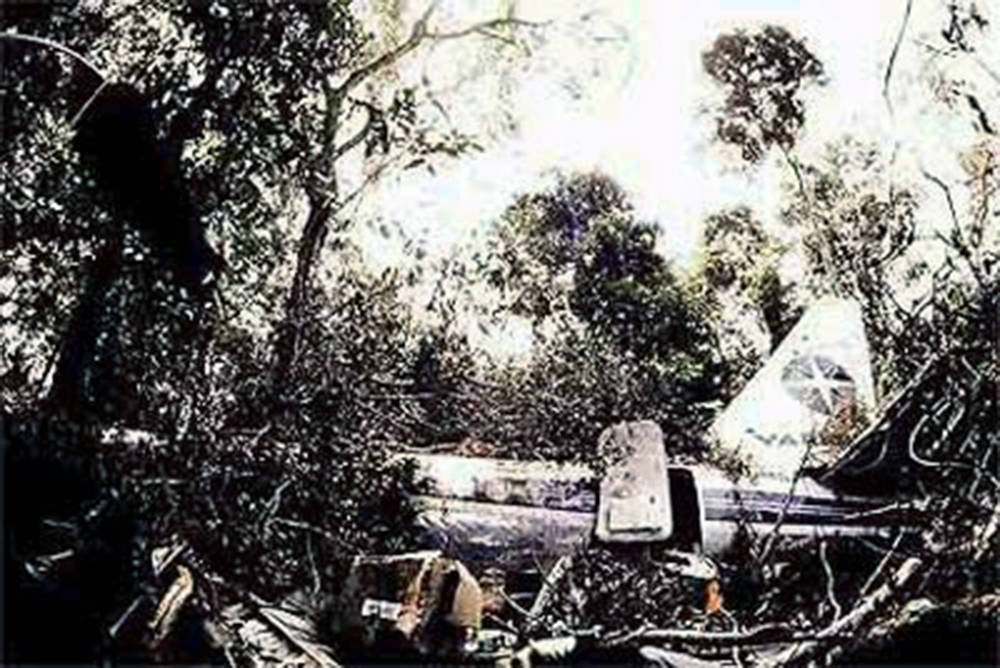
Crash of a Boeing 737-2C3 in Carajás: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 14, 1997 at 1234 LT
Registration:
PP-CJO
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Belém – Marabá – Carajás – Brasília
MSN:
21013
YOM:
1974
Flight number:
RG265
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
48
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
2478.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1464
Circumstances:
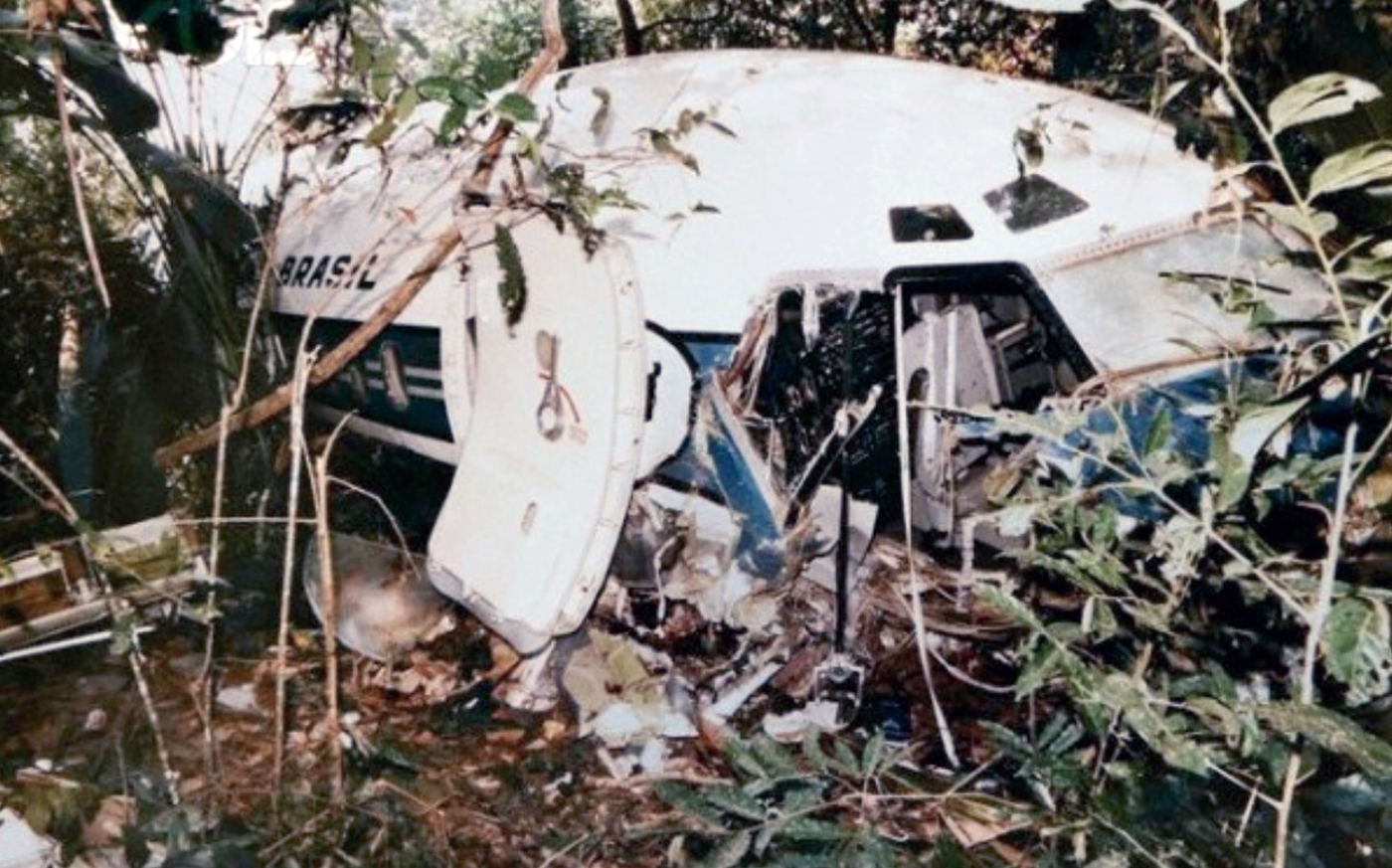
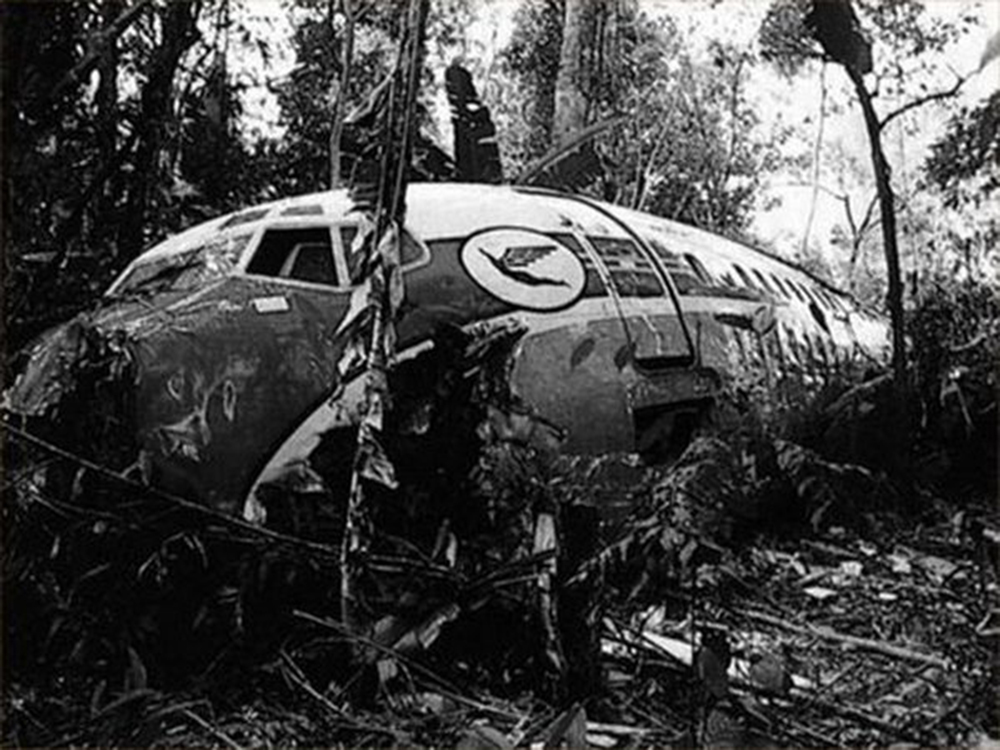
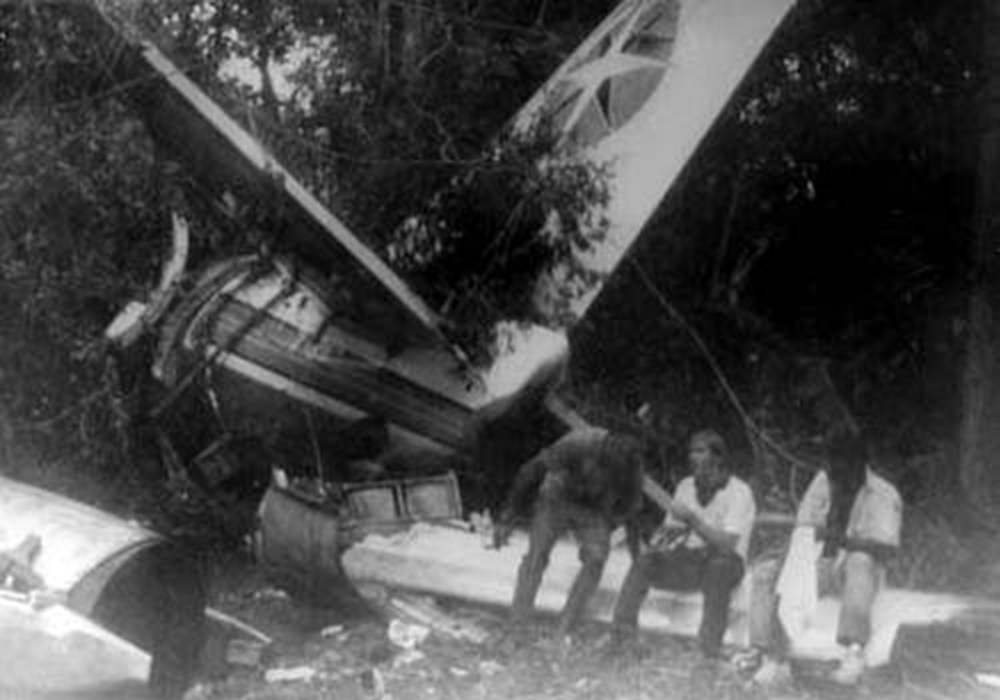
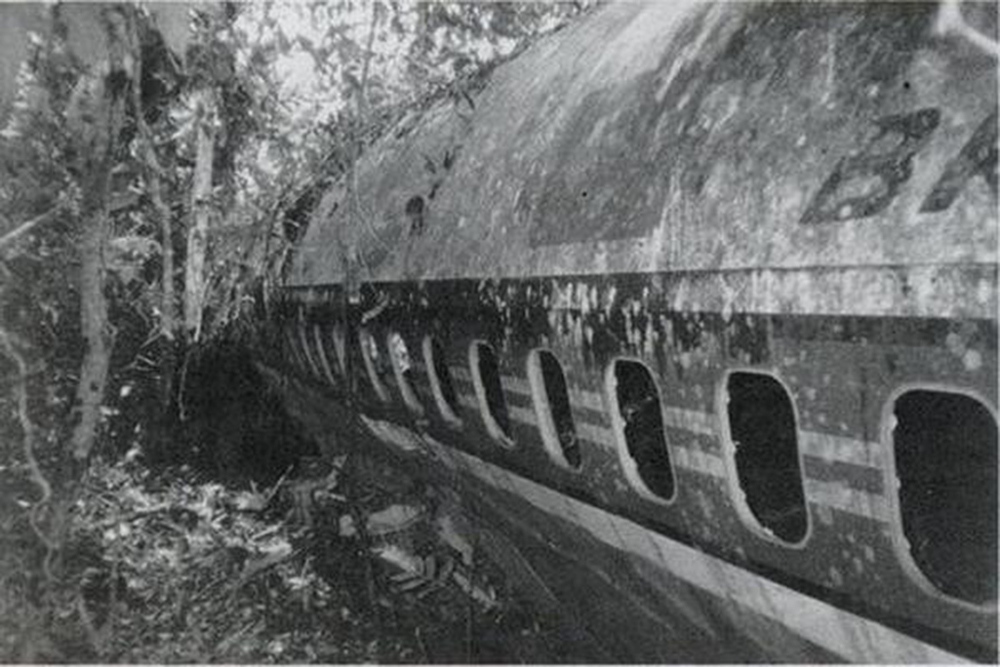
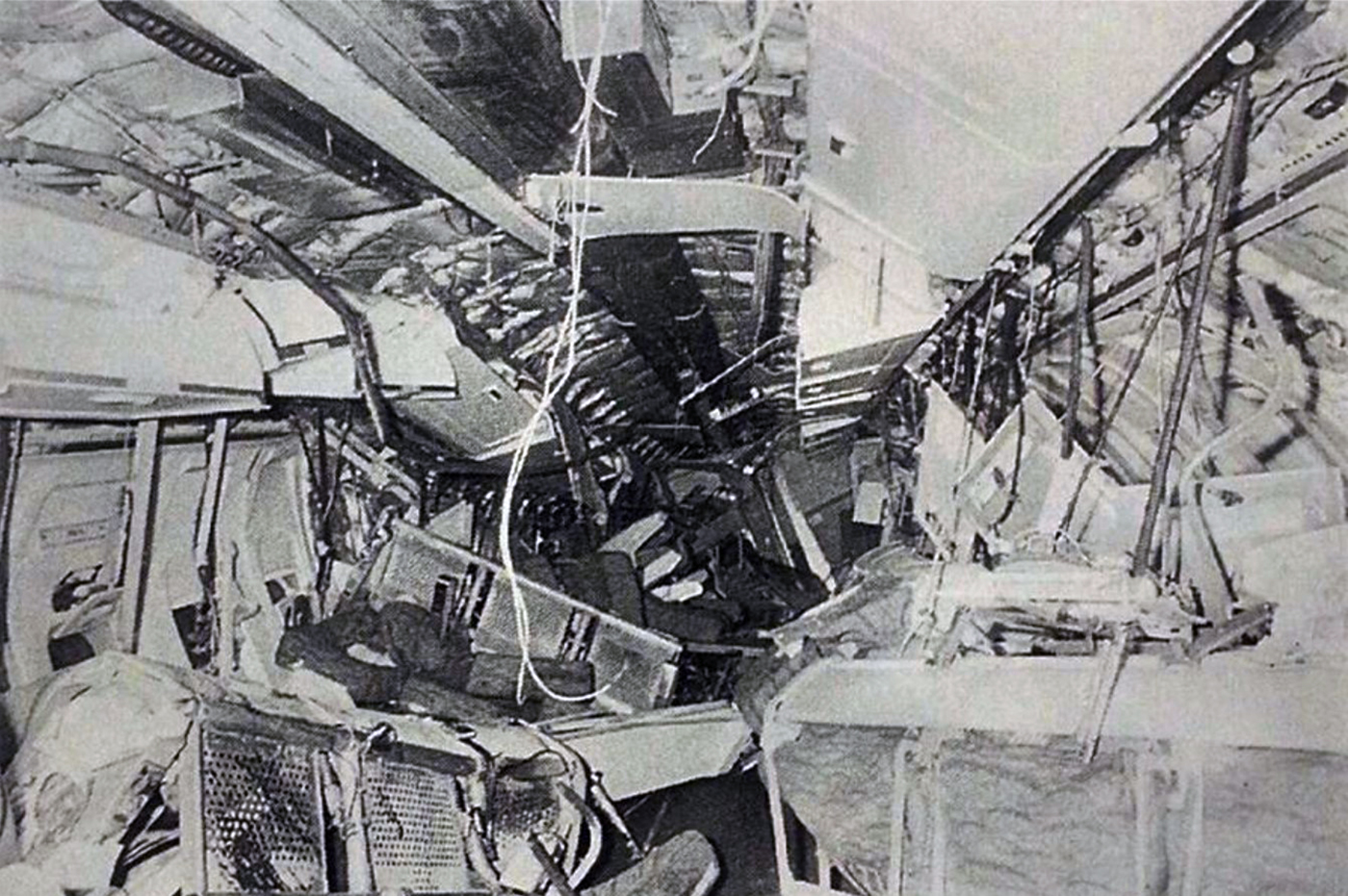
The aircraft departed Belém-Val de Cans Airport on a flight to Brasília with intermediate stops in Marabá and Carajás, carrying 48 passengers and a crew of six. The approach to Carajás-Parauapebas Airport was completed in poor weather conditions with rain falls, clouds down to 120 metres and a limited visibility due to rain and fog. On final the aircraft was unstable and landed hard on runway 10. On touchdown, the right main gear was torn off and the aircraft went out of control. It veered off runway to the right, collided with trees and eventually came to rest in a wooded area. The copilot was killed as the right side of the cockpit was destroyed upon impact. Ten other people were injured and 43 escaped unhurt. The aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
- Lack of crew coordination,
- The captain was overconfident,
- The copilot showed a lack of self confidence,
- The environment developed in the cockpit on approach allowed the pilots to deviate from the operational tasks primarily related to mutual controls,
- Poor approach and landing planning which required a higher sink rate than normal,
- The crew failed to make an approach briefing,
- Insufficient application of controls,
- The crew completed an unstable approach,
- Weather conditions were below minimums,
- The runway was not equipped with a lighting system but only with PAPIs,
- The crew failed to initiate a go-around procedure as the landing was obviously missed.
- Lack of crew coordination,
- The captain was overconfident,
- The copilot showed a lack of self confidence,
- The environment developed in the cockpit on approach allowed the pilots to deviate from the operational tasks primarily related to mutual controls,
- Poor approach and landing planning which required a higher sink rate than normal,
- The crew failed to make an approach briefing,
- Insufficient application of controls,
- The crew completed an unstable approach,
- Weather conditions were below minimums,
- The runway was not equipped with a lighting system but only with PAPIs,
- The crew failed to initiate a go-around procedure as the landing was obviously missed.
Final Report: