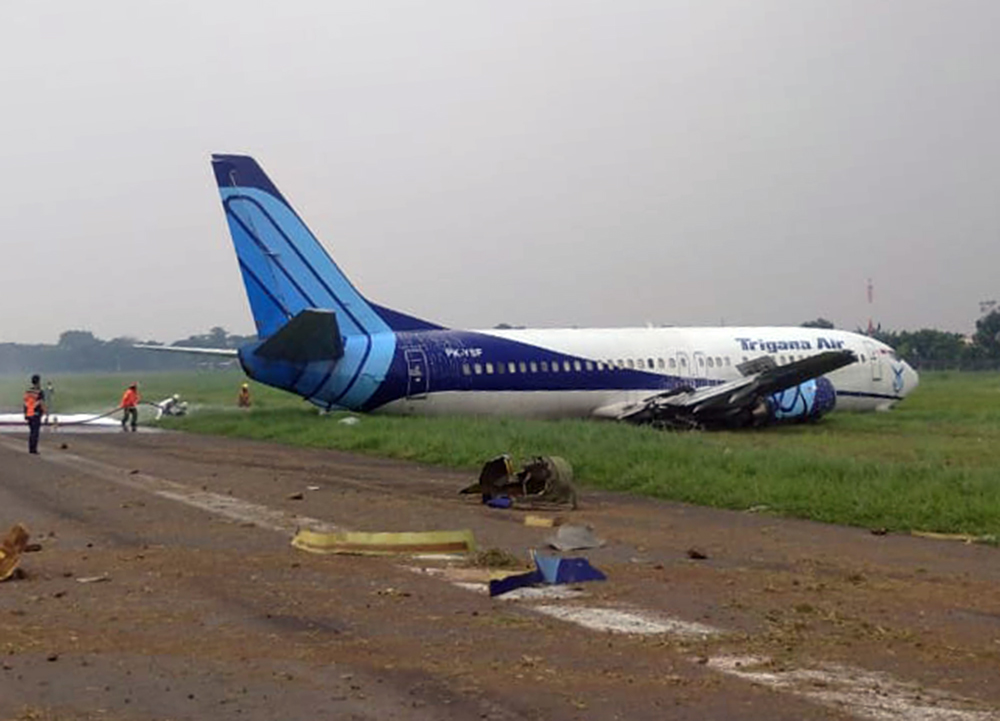
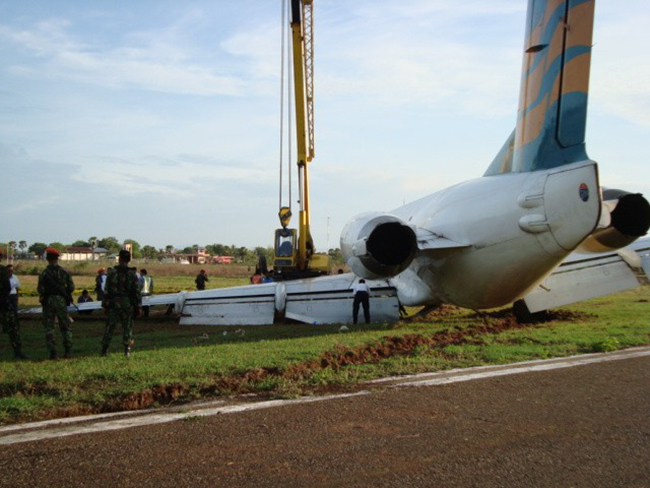
Crash of a Boeing 737-4Y0 in Jakarta
Date & Time:
Mar 20, 2021 at 1126 LT
Registration:
PK-YSF
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Jakarta - Makassar
MSN:
23869/1639
YOM:
1988
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
5208.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1084
Aircraft flight hours:
55982
Aircraft flight cycles:
65005
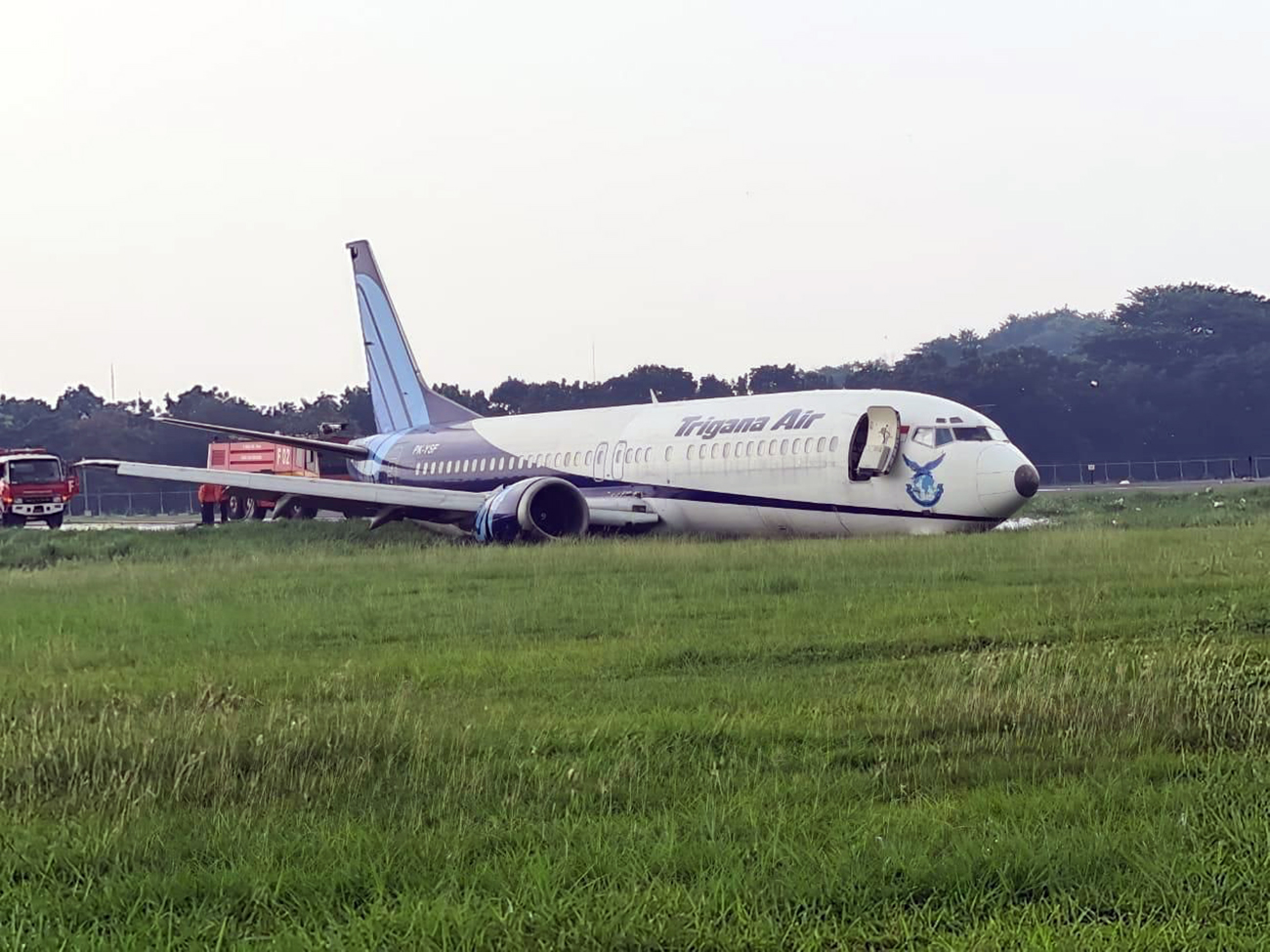
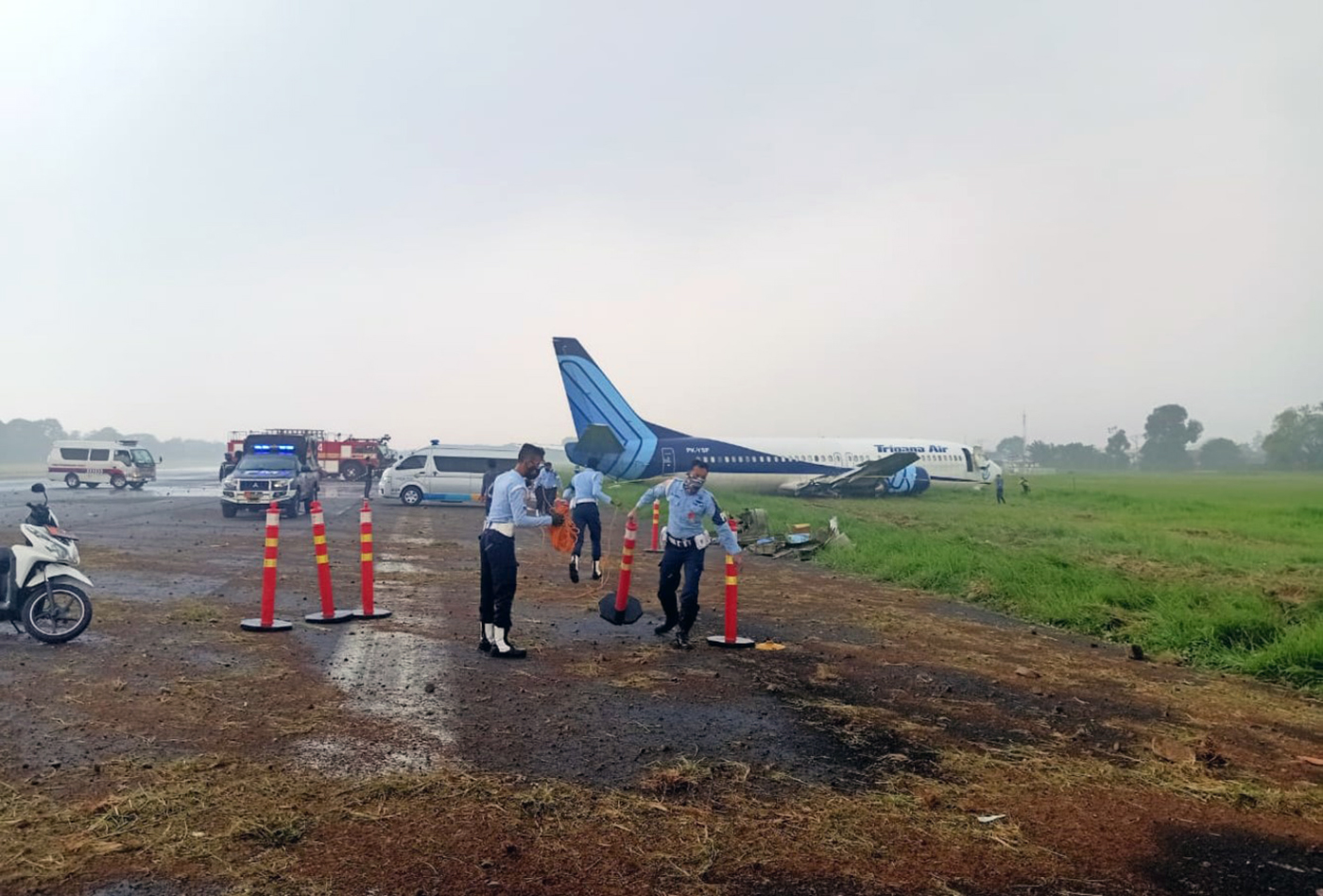
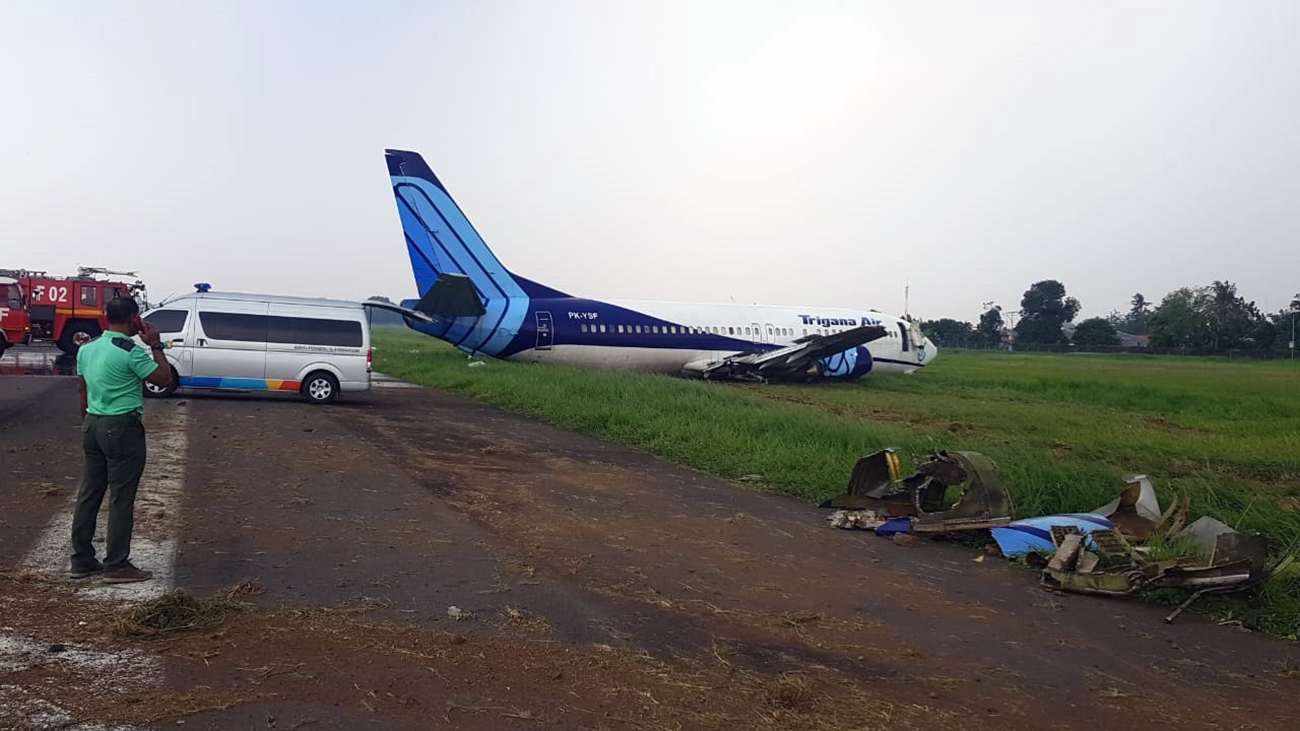
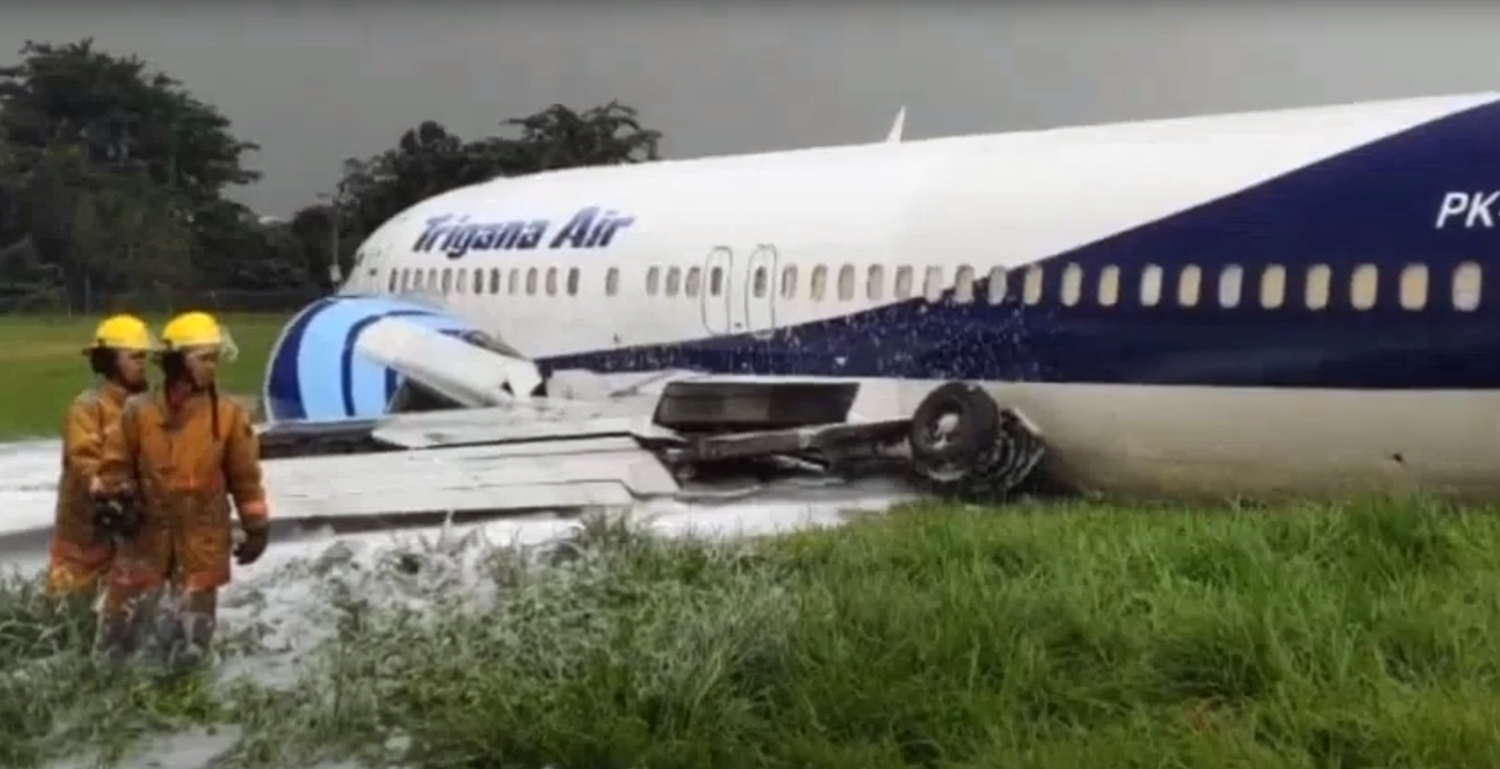
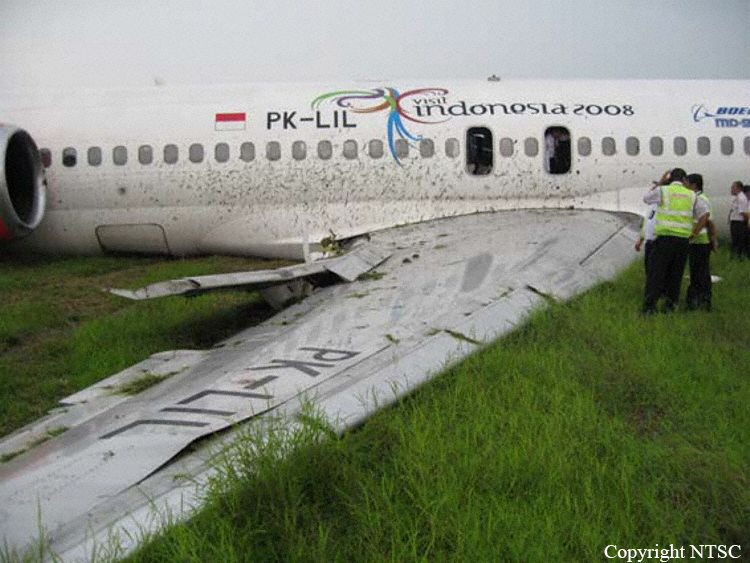
Circumstances:
On 20 March 2021, a Boeing 737-400F, registered PK-YSF, was being operated by Trigana Air Service on a non-schedule cargo flight from Halim Perdanakusuma International Airport (WIHH), Jakarta, Indonesia with intended destination of Sultan Hasanuddin International Airport (WAAA), South Sulawesi, Indonesia. On board in this flight was two pilots, one engineer and one Flight Operation Officer (FOO). According to the weight and balance sheet, the flight carried 16,672 kgs of general cargo, takeoff fuel of 11,100 kg and the takeoff weight was 60,695 kg (133,835 lbs). The Pilot in Command (PIC) acted as Pilot Flying (PF) and the Second in Command (SIC) acted as Pilot Monitoring (PM). At 0328 UTC (1028 LT), the PM requested clearance to Halim Tower controller (the controller) to pushback and start the engines. At 1031 LT, the PM requested to the controller for taxi clearance. There was no report of aircraft system abnormality prior to the aircraft departure. At 1047 LT, the controller issued clearance to the PK-YSF pilot to enter and to backtrack Runway 24. At 1051 LT, the PM reported ready for departure to the controller. The controller issued takeoff clearance with additional departure clearance that after takeoff, turn left to heading 180° and initially climb to altitude of 3,000 feet. The PM acknowledged the clearance. The takeoff was conducted with reduced takeoff thrust by assumed temperature of 40°C and the aircraft became airborne at 10:52:57 LT. At 1055 LT, the controller advised the pilot to report when established on heading 180°. The PM reported that they were experiencing right engine failure and requested to fly to AL NDB . The controller advised the PM to turn left heading 060° and to climb to 2,500 feet. Furthermore, the controller asked the pilot intention whether to hold over AL NDB or direct for landing approach. The PM replied that they would hold over AL NDB and added the information that no fire was detected. The controller issued clearance to fly to AL NDB at altitude of 2,500 feet. The controller assumed that PK-YSF would return to Halim and advised the Airport Rescue and Fire-Fighting (ARFF) personnel that PK-YSF experienced right engine failure and would return to Halim. At 1058 LT, the controller requested the information of time required for holding over AL NDB and was replied by the PM that holding would require about 15 minutes. Furthermore, the controller requested whether the pilot able to hold at a point about 15 to 20 Nm from AL NDB and was replied by the PM that they did not objection to the proposal. The controller instructed the pilot to maintain outbound heading up to 15 Nm, at altitude of 2,500 feet. This was intended by the controller to manage the departure and arrival aircraft to and from Halim. At 1116 LT, the PM reported that they were ready to turn left for approach. The controller advised the pilot to turn left and to intercept localizer of the Instrument Landing System (ILS) Runway 24. At 1125 LT, the PM reported to the controller that the Runway was in sight. The controller advised that the wind was from 060° at velocity of 6 knots, QNH 1,007 mbs and issued landing clearance. The aircraft touched down on the touchdown zone and shortly after, both wheels of the right main landing gear detached. The controller noticed spark appeared from the aircraft and pressed the crash bell. At 1127 LT, the controller informed pilots of the other aircraft that the runway blocked by the landing aircraft and identified fire on one of the engines. Few seconds later, the PM called the controller whether any fire and was replied by the controller that fire was visible on the left side of the aircraft.