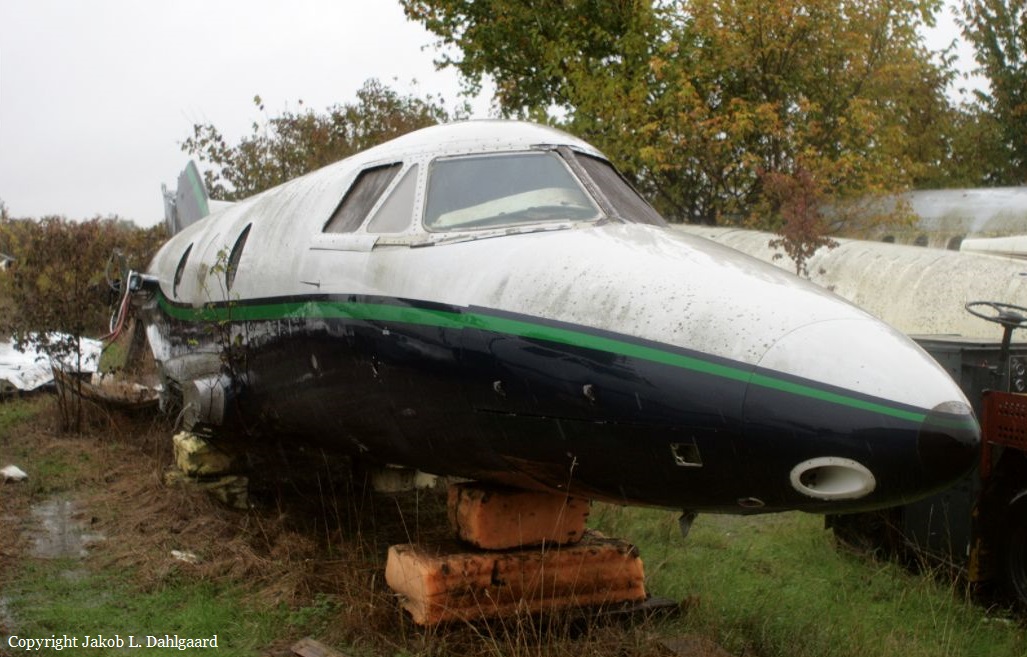
Crash of a Dassault Falcon 10 in White Plains
Date & Time:
Jun 30, 1997
Registration:
N10YJ
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
57
YOM:
1975
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Aircraft flight hours:
6784
Circumstances:
On approach to White Plains-Westchester County Airport, the crew noted a left main gear unsafe light. The gear was recycled and the crew agreed with ATC to perform a low pass to check the gear. Few minutes later, upon landing, the left main gear collapsed. All four occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
No investigations were conducted on this event.