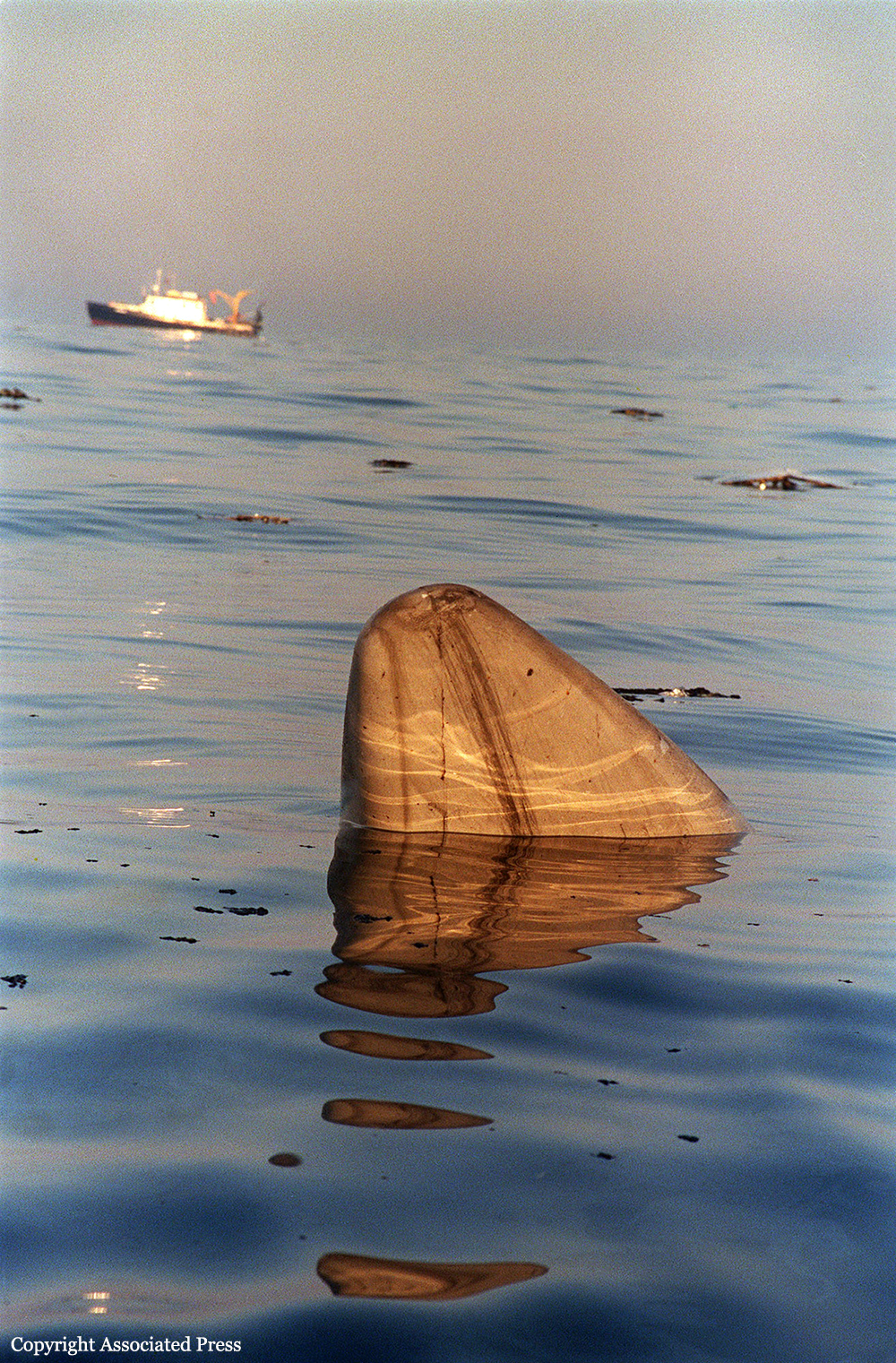
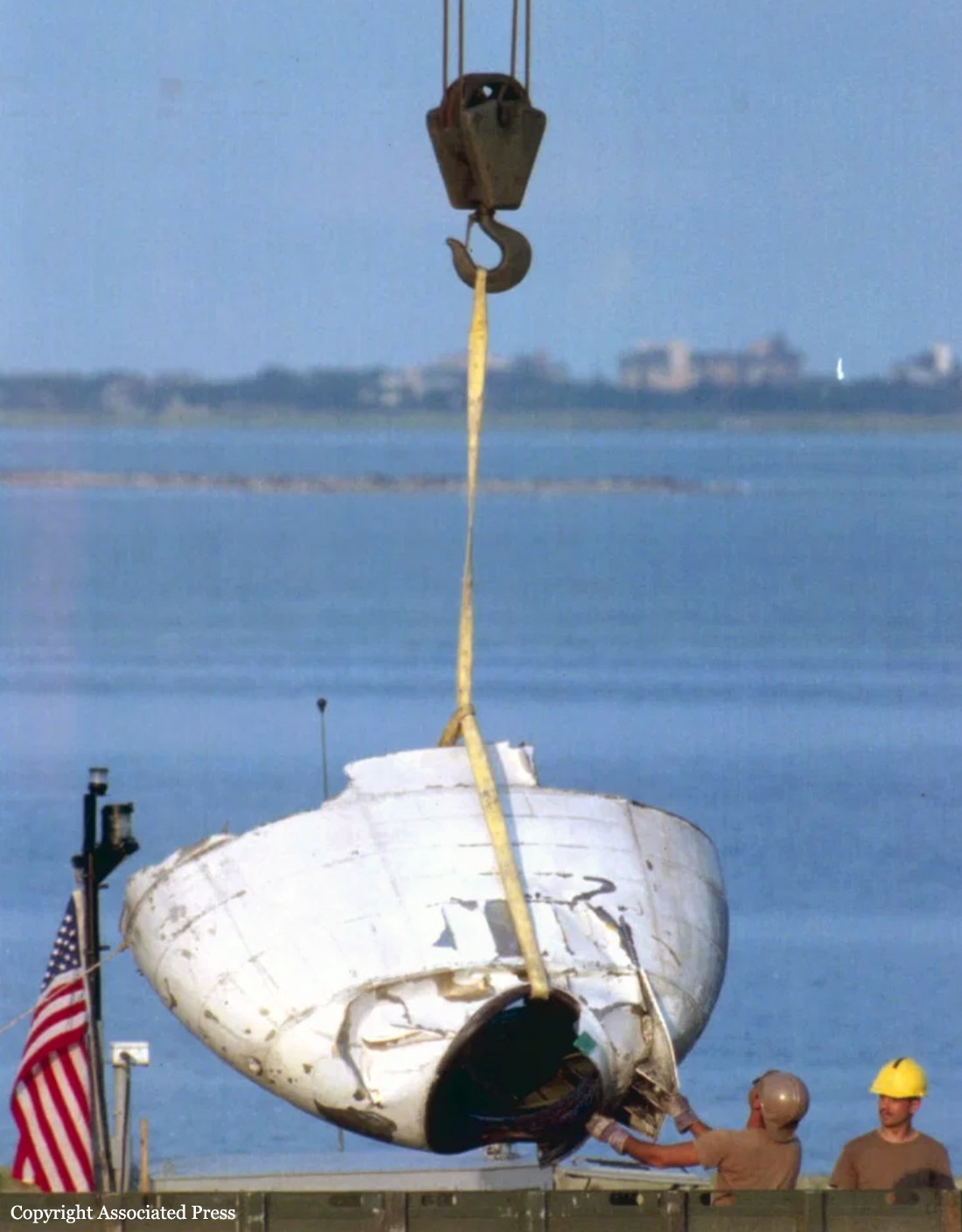
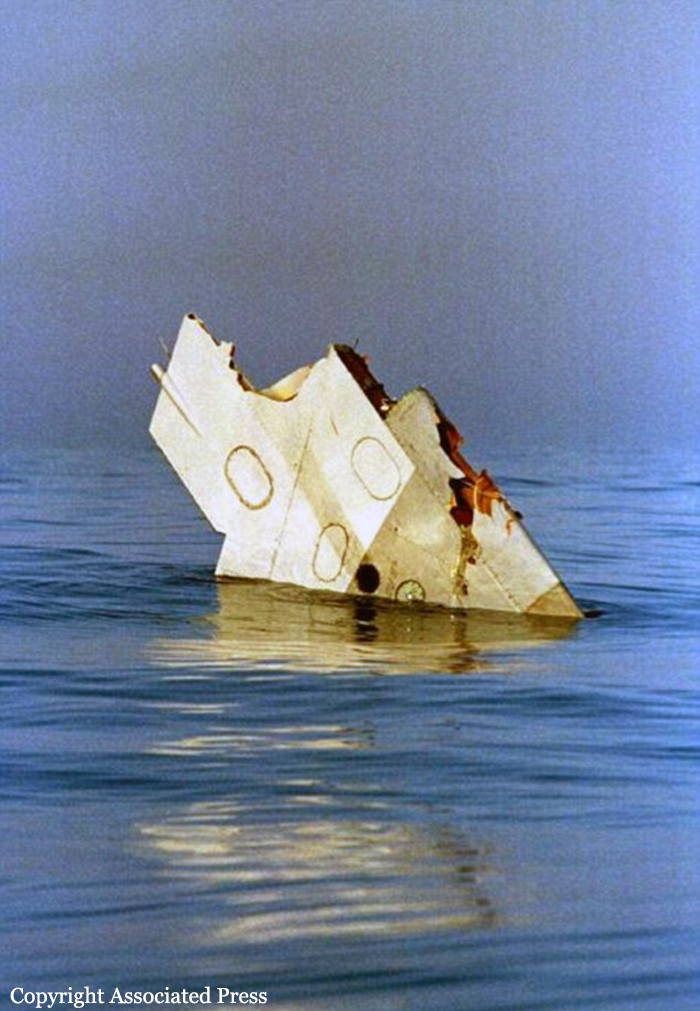
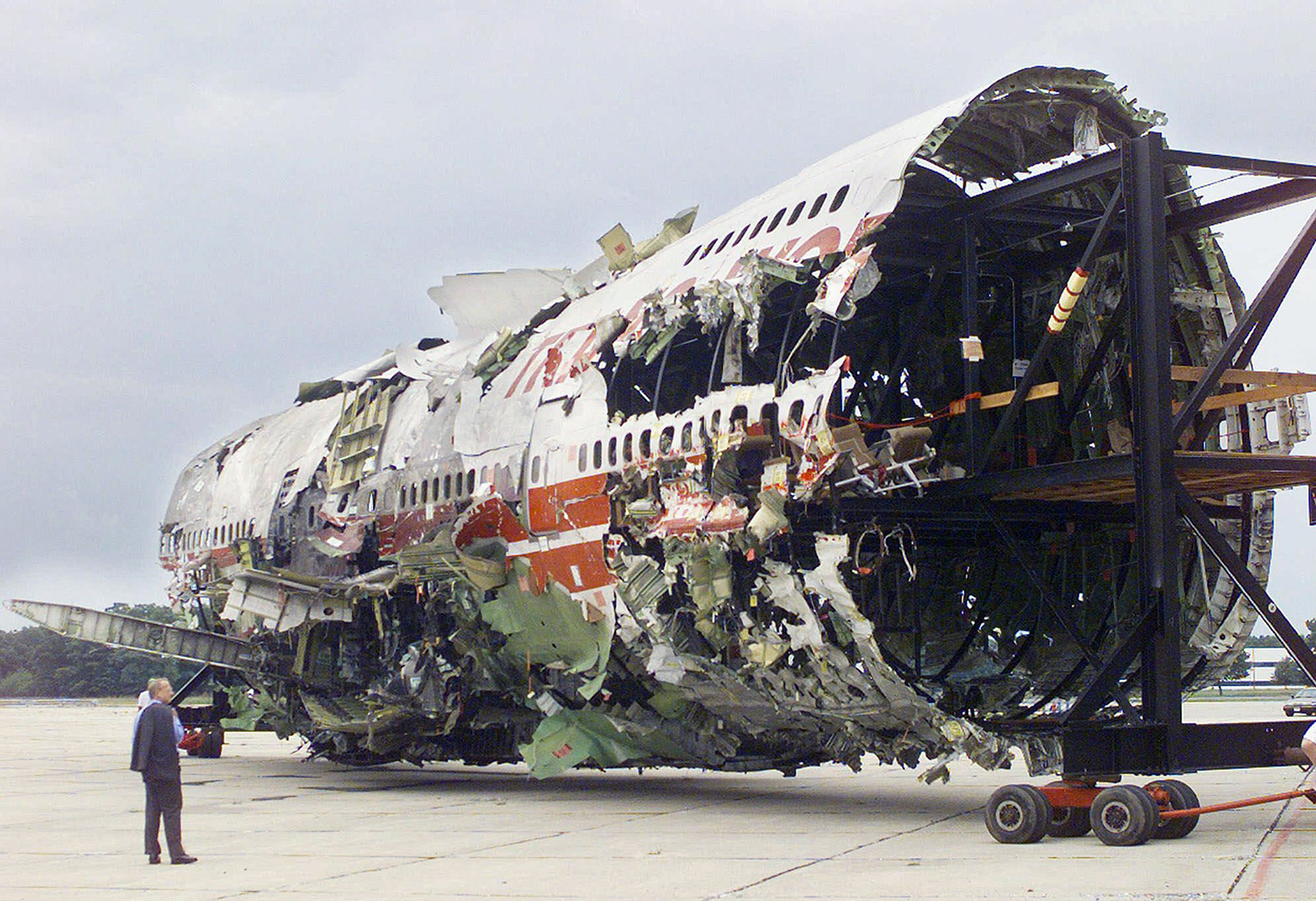
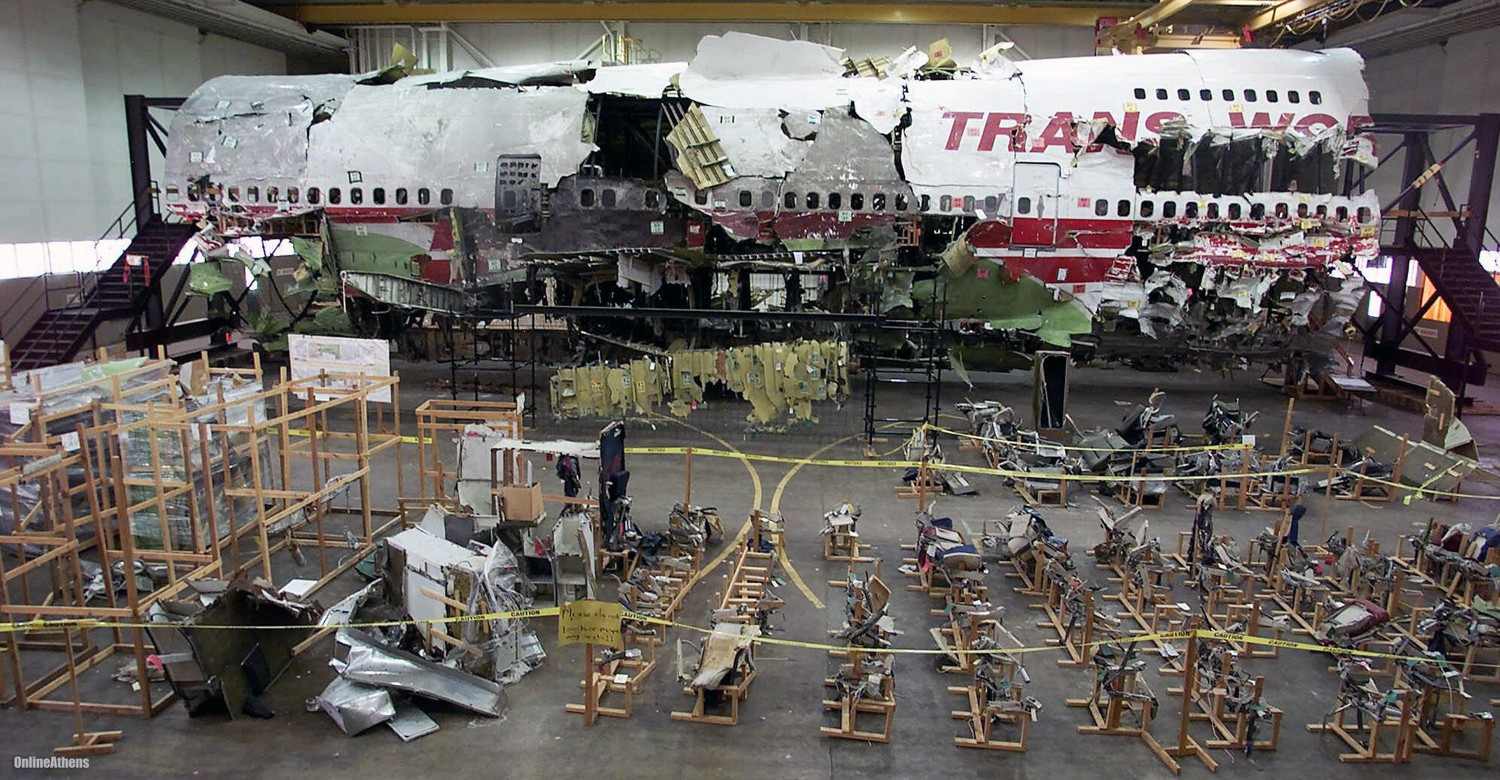
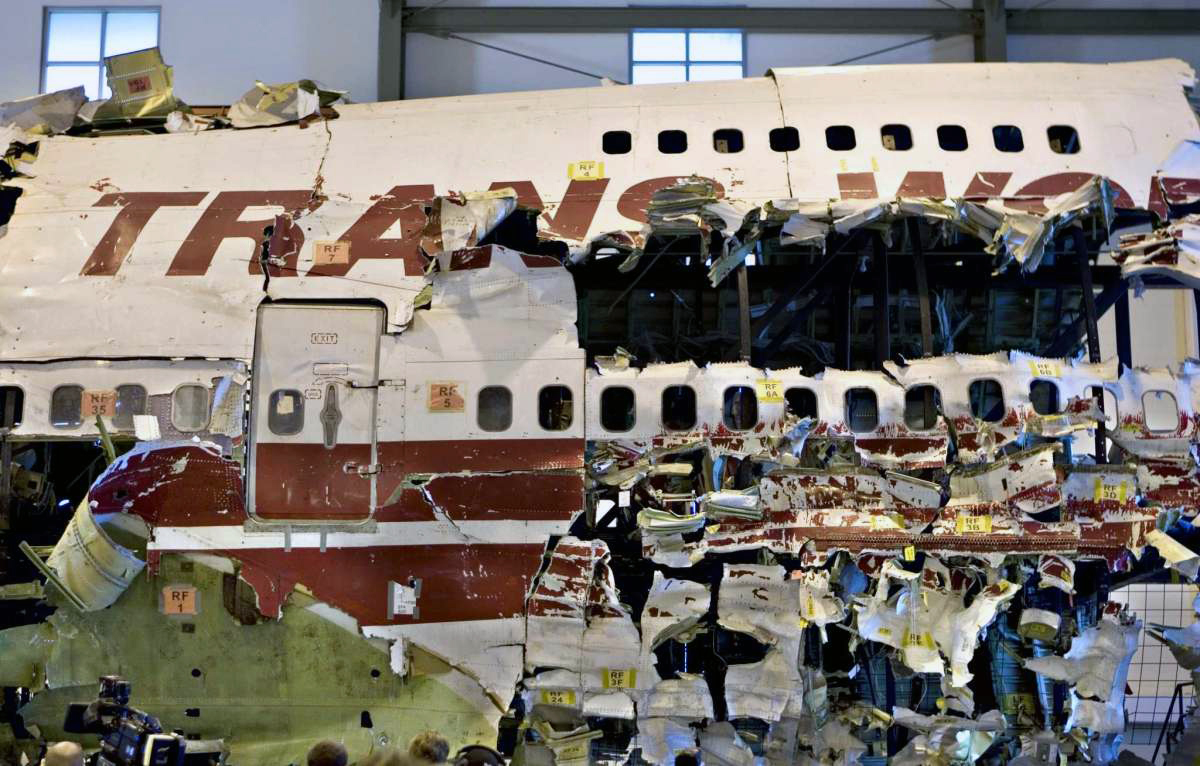
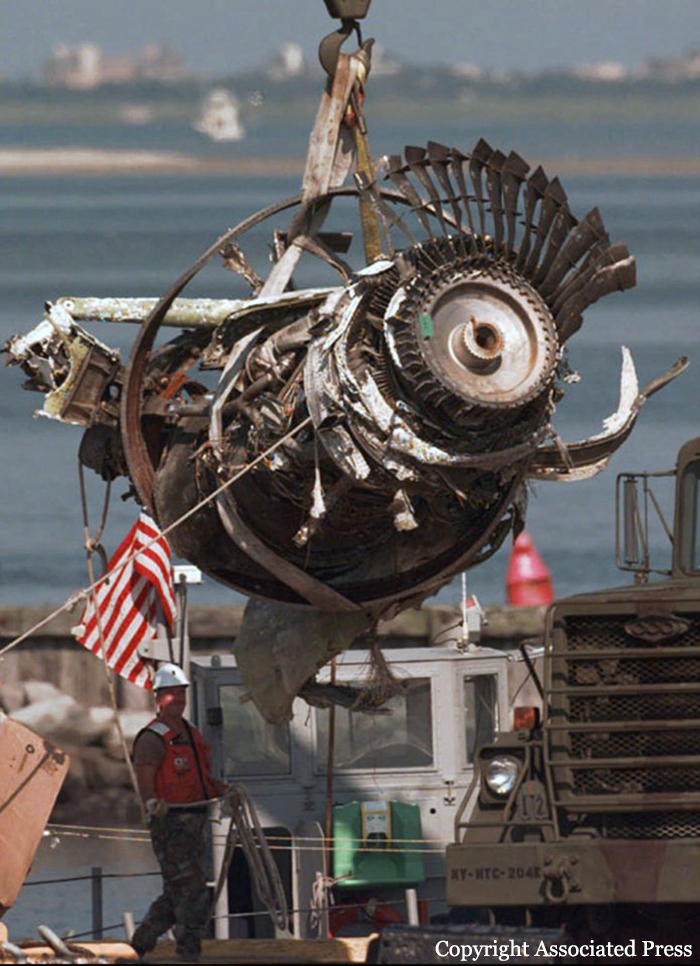
Crash of a Boeing 747-131 off East Moriches: 230 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 17, 1996 at 2031 LT
Registration:
N93119
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
New York – Paris
MSN:
20083
YOM:
1971
Flight number:
TW800
Crew on board:
18
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
212
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
230
Captain / Total hours on type:
5490.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
4700
Aircraft flight hours:
93303
Aircraft flight cycles:
16869
Circumstances:
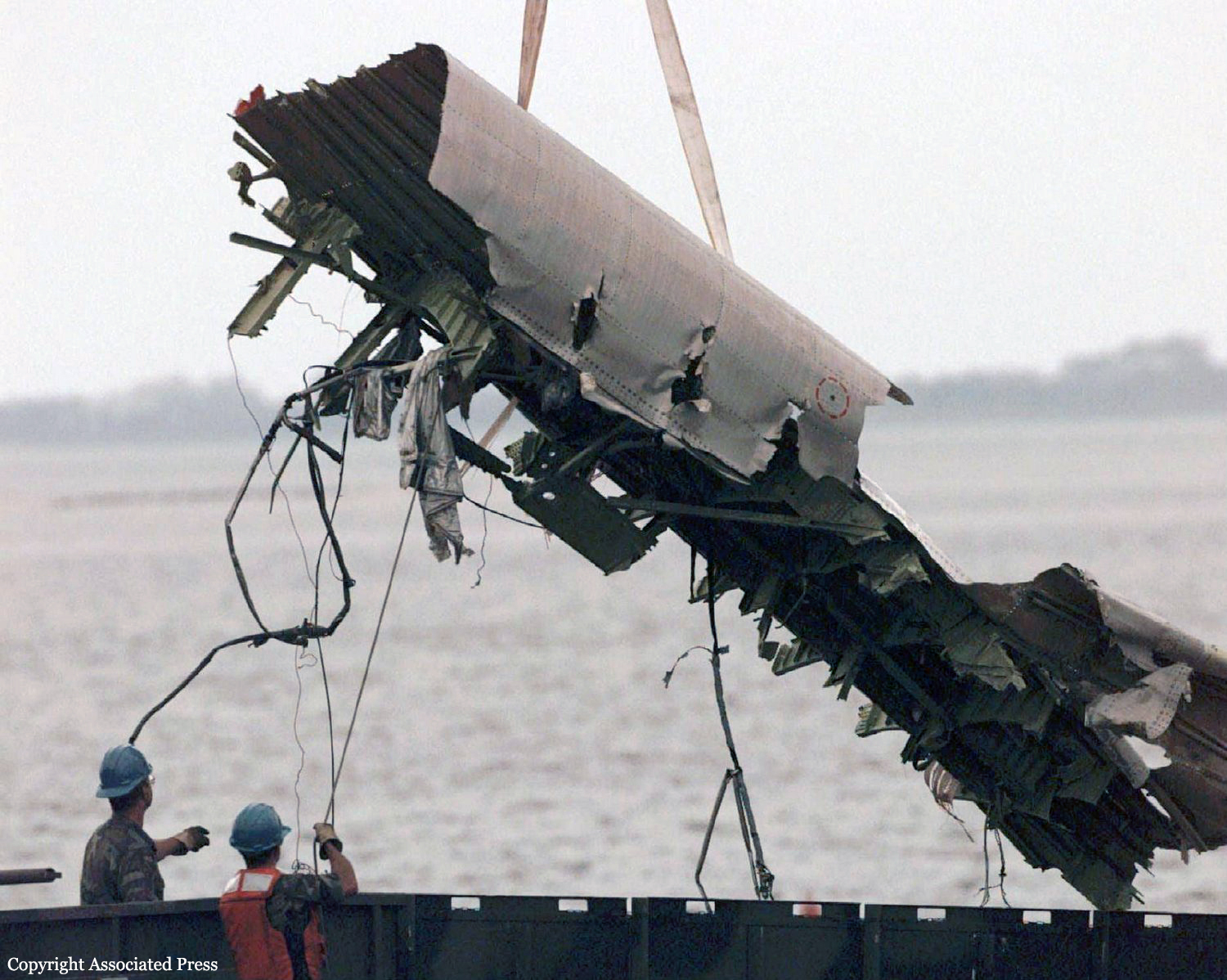
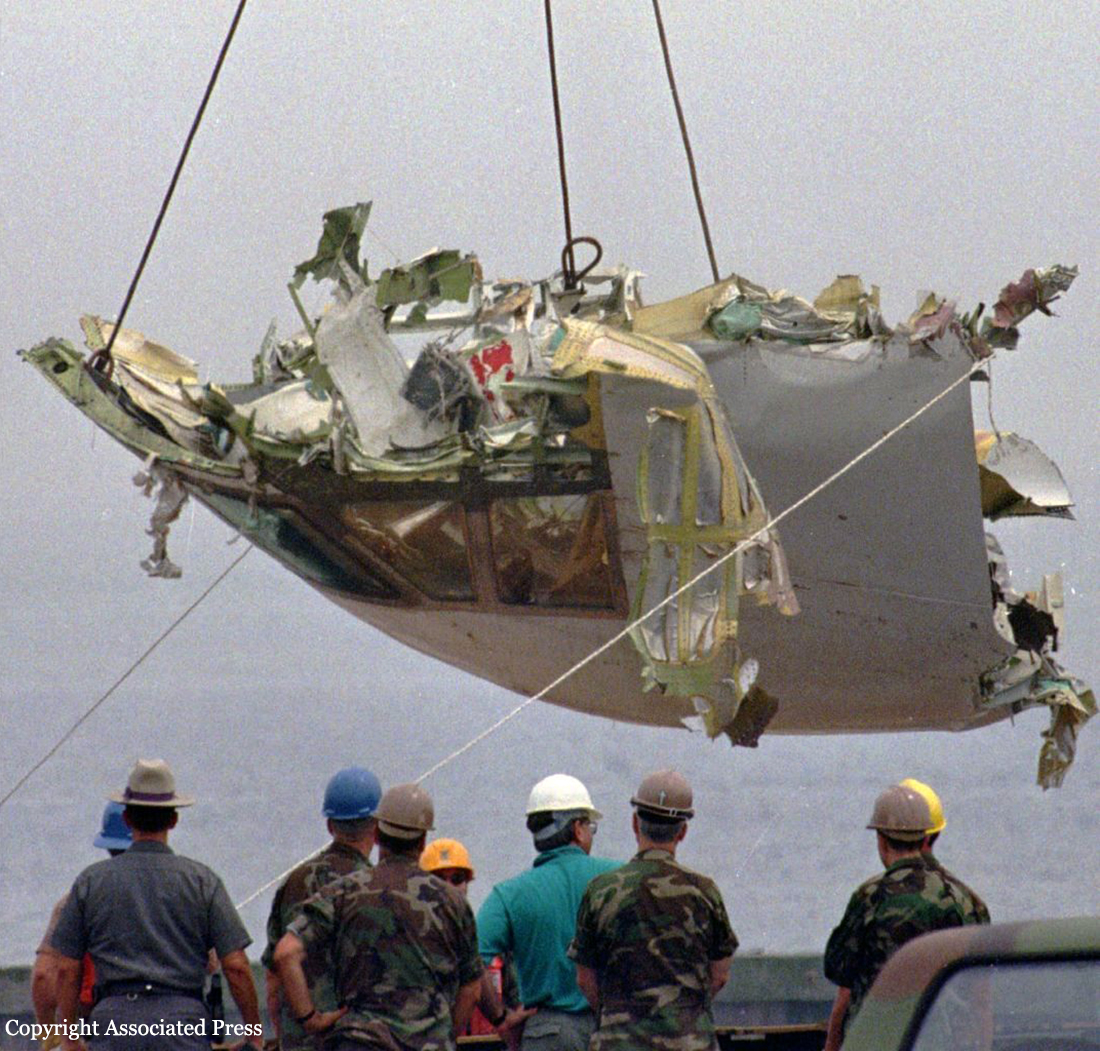
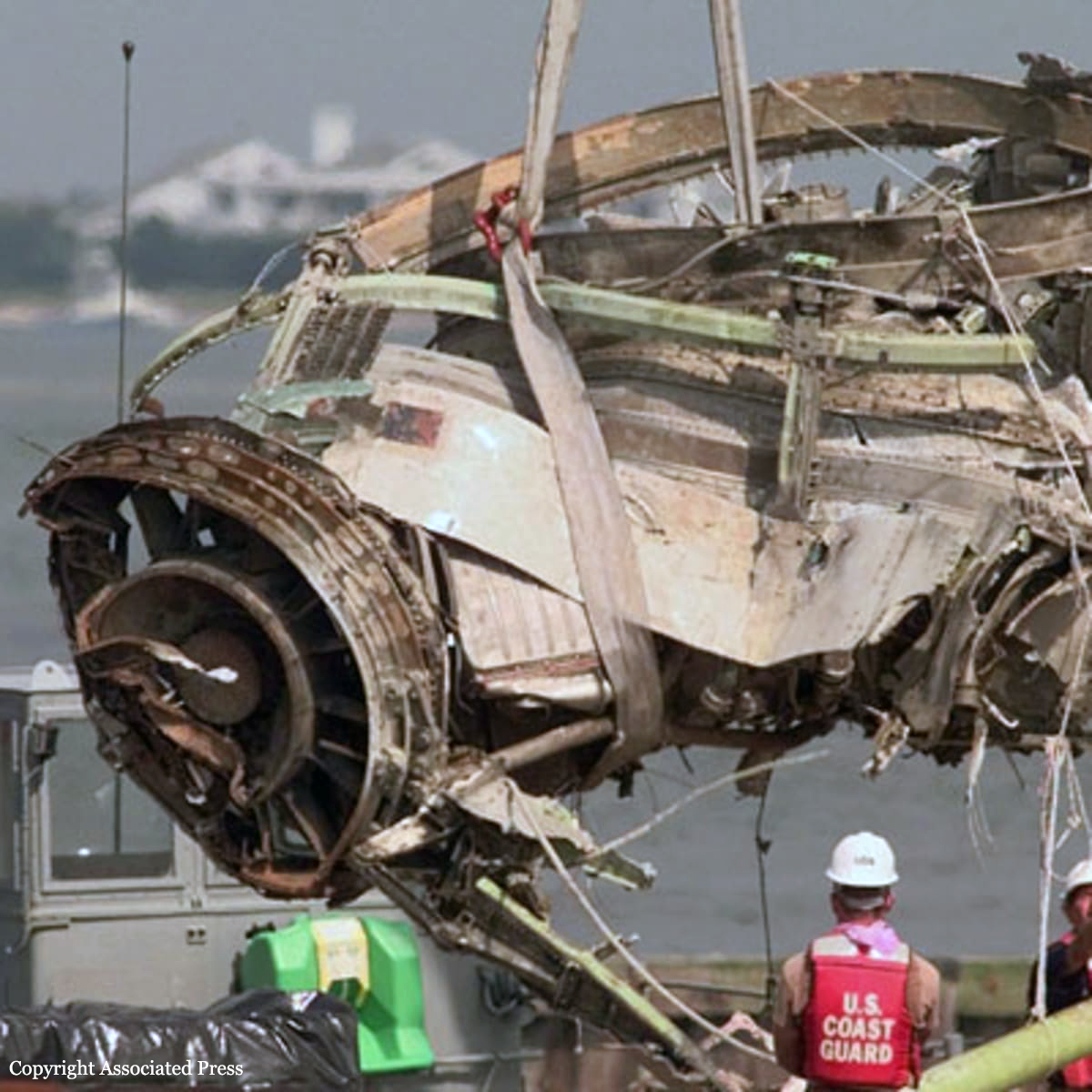
On July 17, 1996, about 2031 eastern daylight time, Trans World Airlines, Inc. (TWA) flight 800, a Boeing 747-131, N93119, crashed in the Atlantic Ocean near East Moriches, New York. TWA flight 800 was operating under the provisions of 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 121 as a scheduled international passenger flight from John F. Kennedy International Airport (JFK), New York, New York, to Charles De Gaulle International Airport, Paris, France. The flight departed JFK about 2019, with 2 pilots, 2 flight engineers, 14 flight attendants, and 212 passengers on board. All 230 people on board were killed, and the airplane was destroyed. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed for the flight, which operated on an instrument flight rules flight plan. The investigation revealed that the crash occurred as the result of a fuel/air explosion in the airplane's center wing fuel tank (CWT) and the subsequent in-flight breakup of the airplane. The investigation further revealed that the ignition energy for the CWT explosion most likely entered the CWT through the fuel quantity indication system wiring; neither the ignition energy release mechanism nor the location of the ignition inside the CWT could be determined from the available evidence. There was no evidence of a missile or bomb detonation.
Probable cause:
An explosion of the center wing fuel tank (CWT), resulting from ignition of the flammable fuel/air mixture in the tank. The source of ignition energy for the explosion could not be determined with certainty, but, of the sources evaluated by the investigation, the most likely was a short circuit outside of the CWT that allowed excessive voltage to enter it through electrical wiring associated with the fuel quantity indication system. Contributing factors to the accident were the design and certification concept that fuel tank explosions could be prevented solely by precluding all ignition sources and the design and certification of the Boeing 747 with heat sources located beneath the CWT with no means to reduce the heat transferred into the CWT or to render the fuel vapor in the tank non flammable.
Final Report: