Crash of a Boeing 737-2A8 in New Delhi
Date & Time:
Jun 19, 1988 at 1726 LT
Registration:
VT-EAI
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Srinagar – Jammu – Chandigarh – New Delhi
MSN:
20482/272
YOM:
1970
Flight number:
IC422
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
128
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
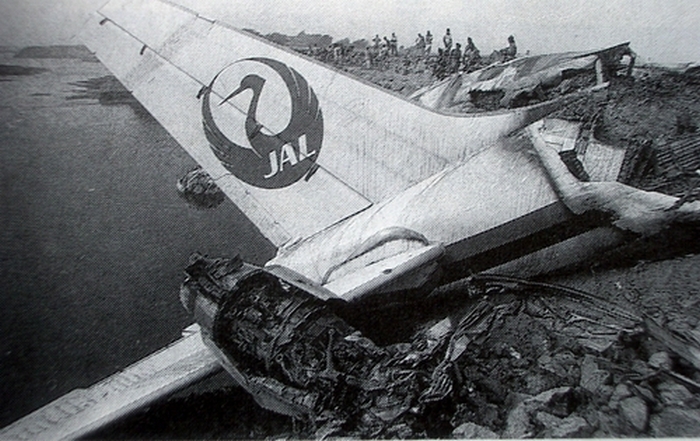
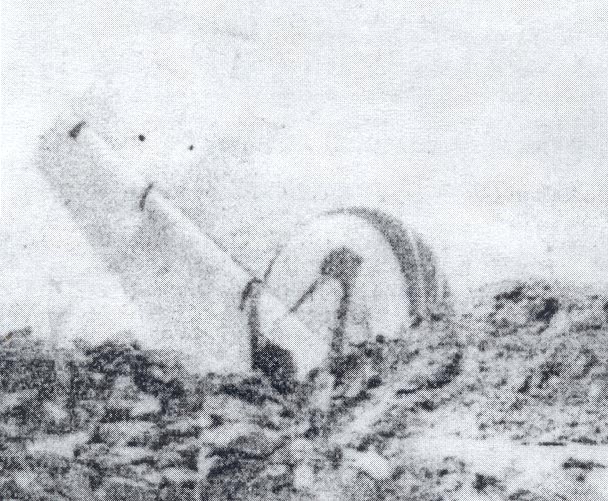
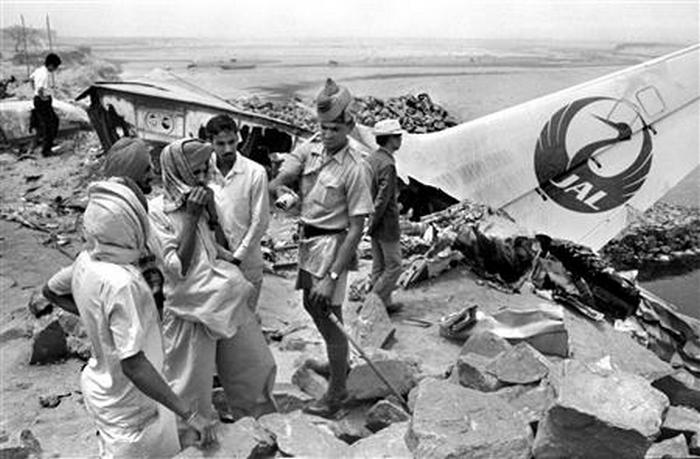
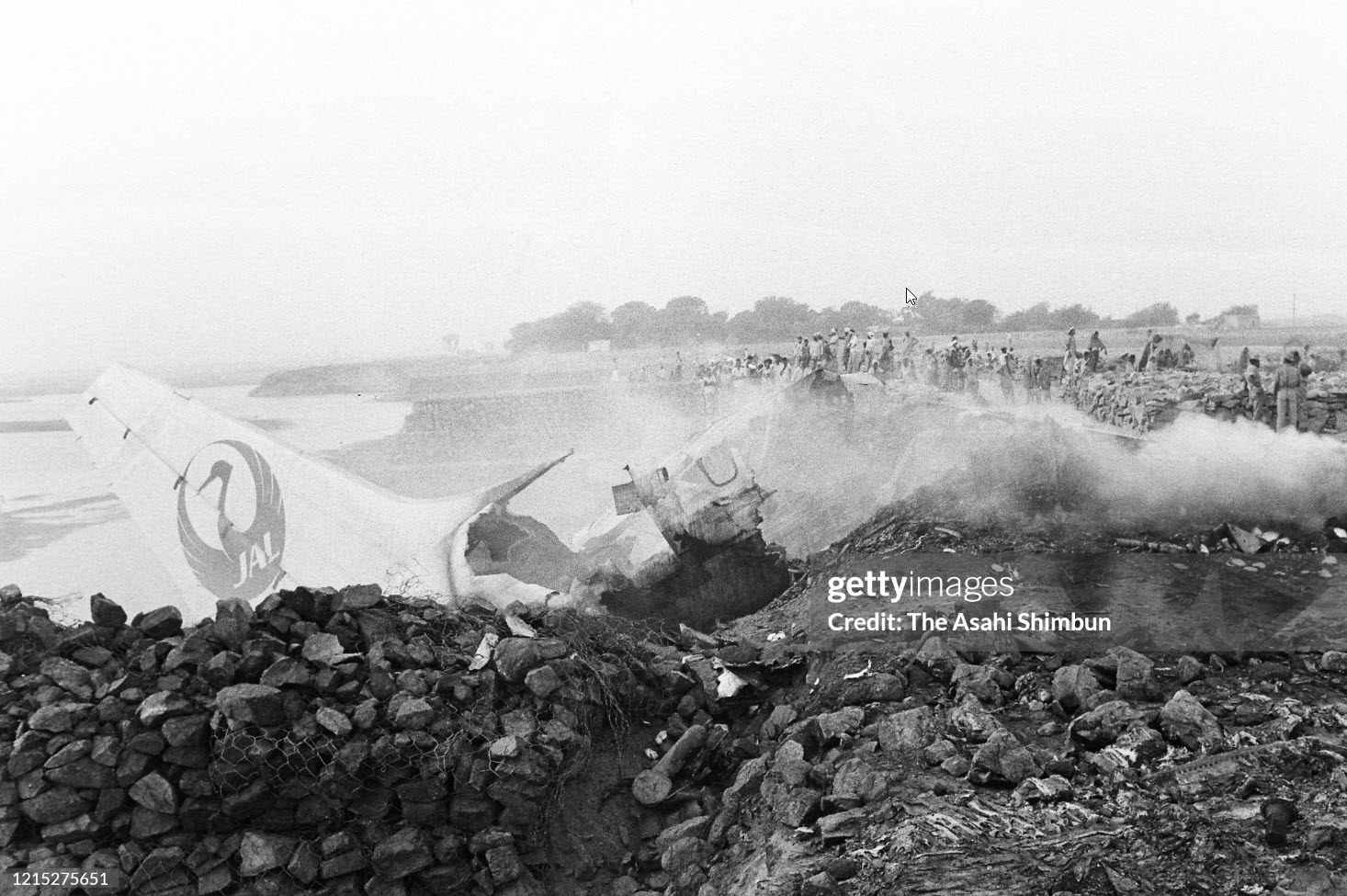
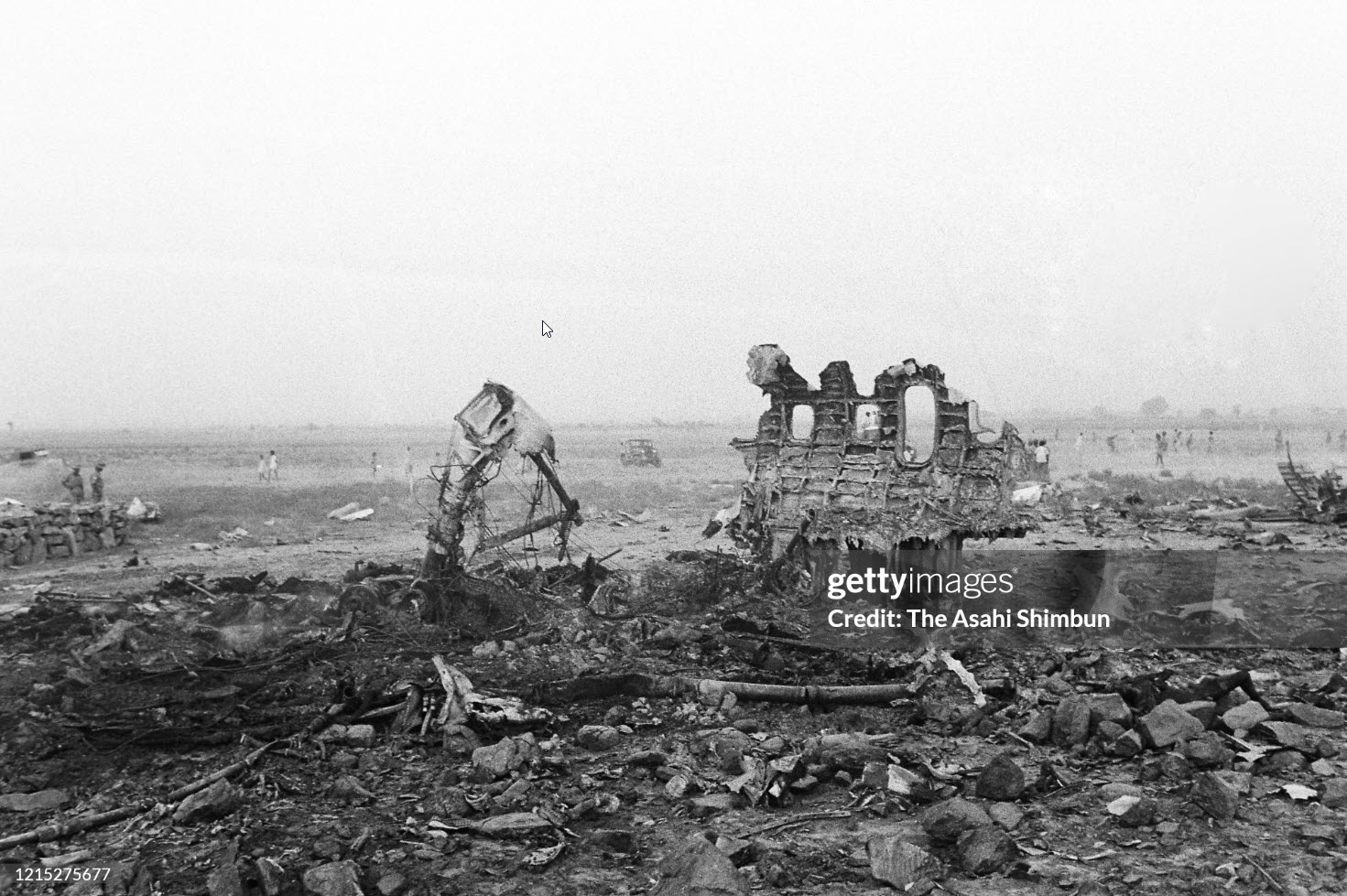
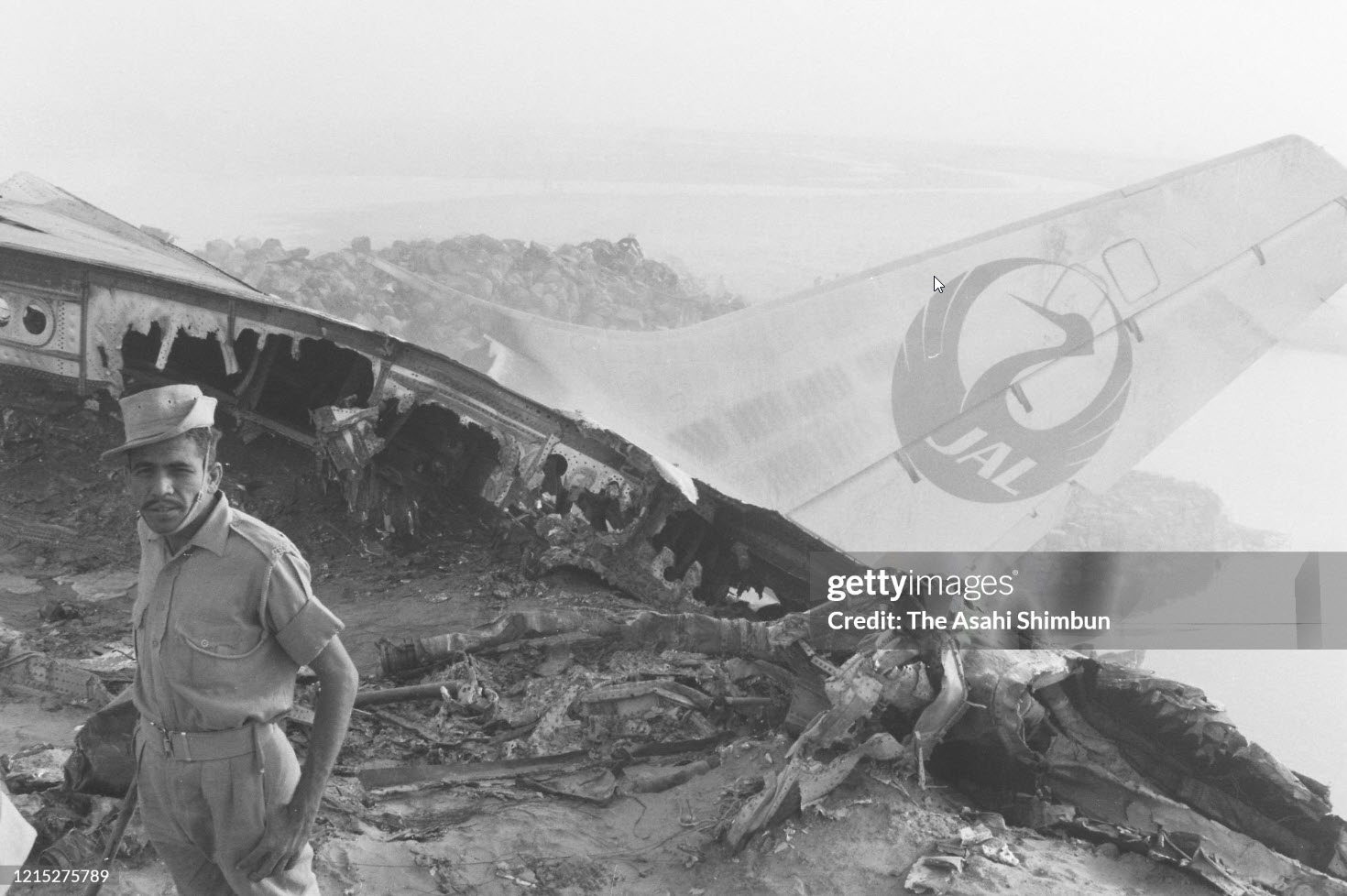
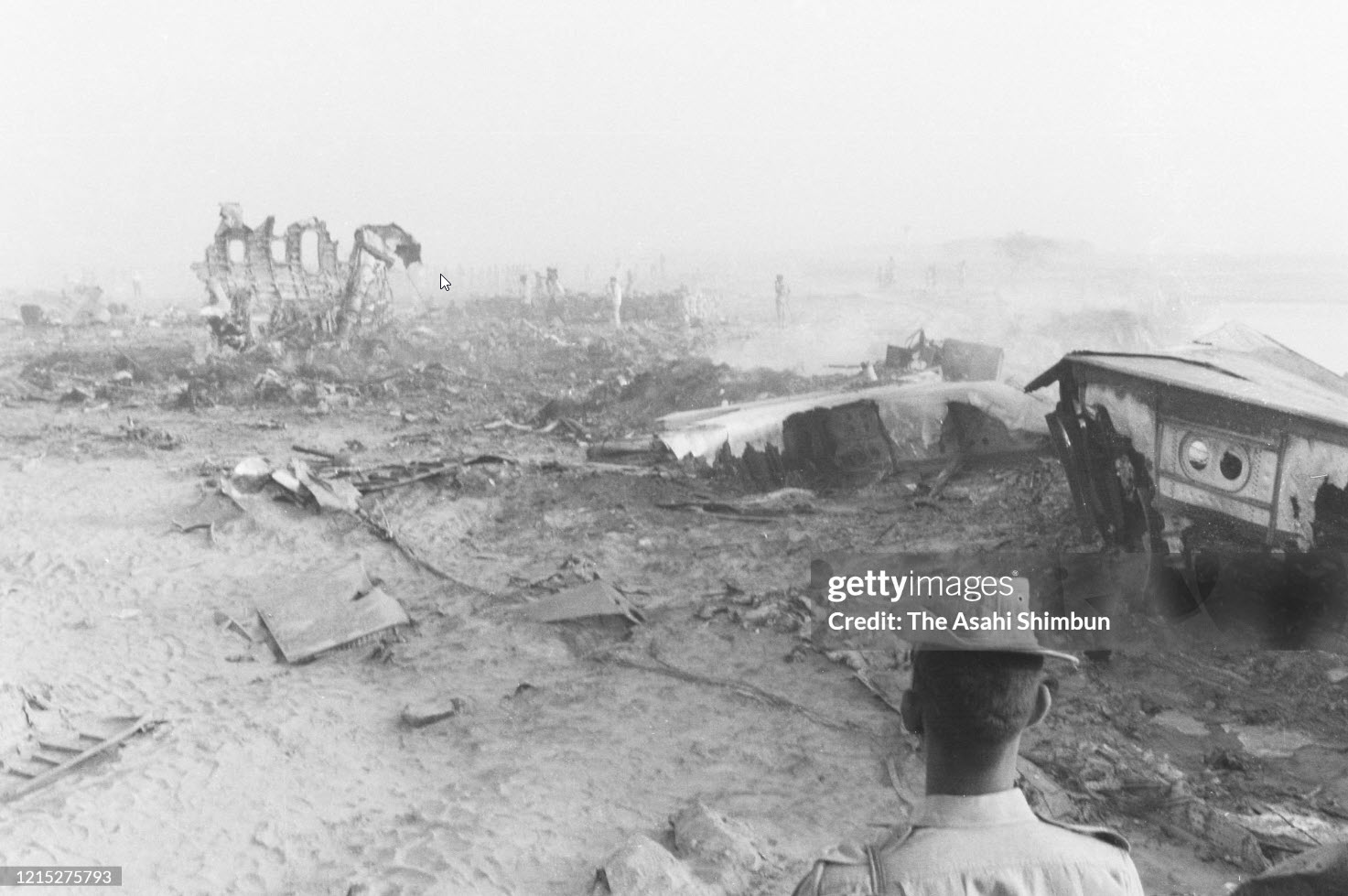
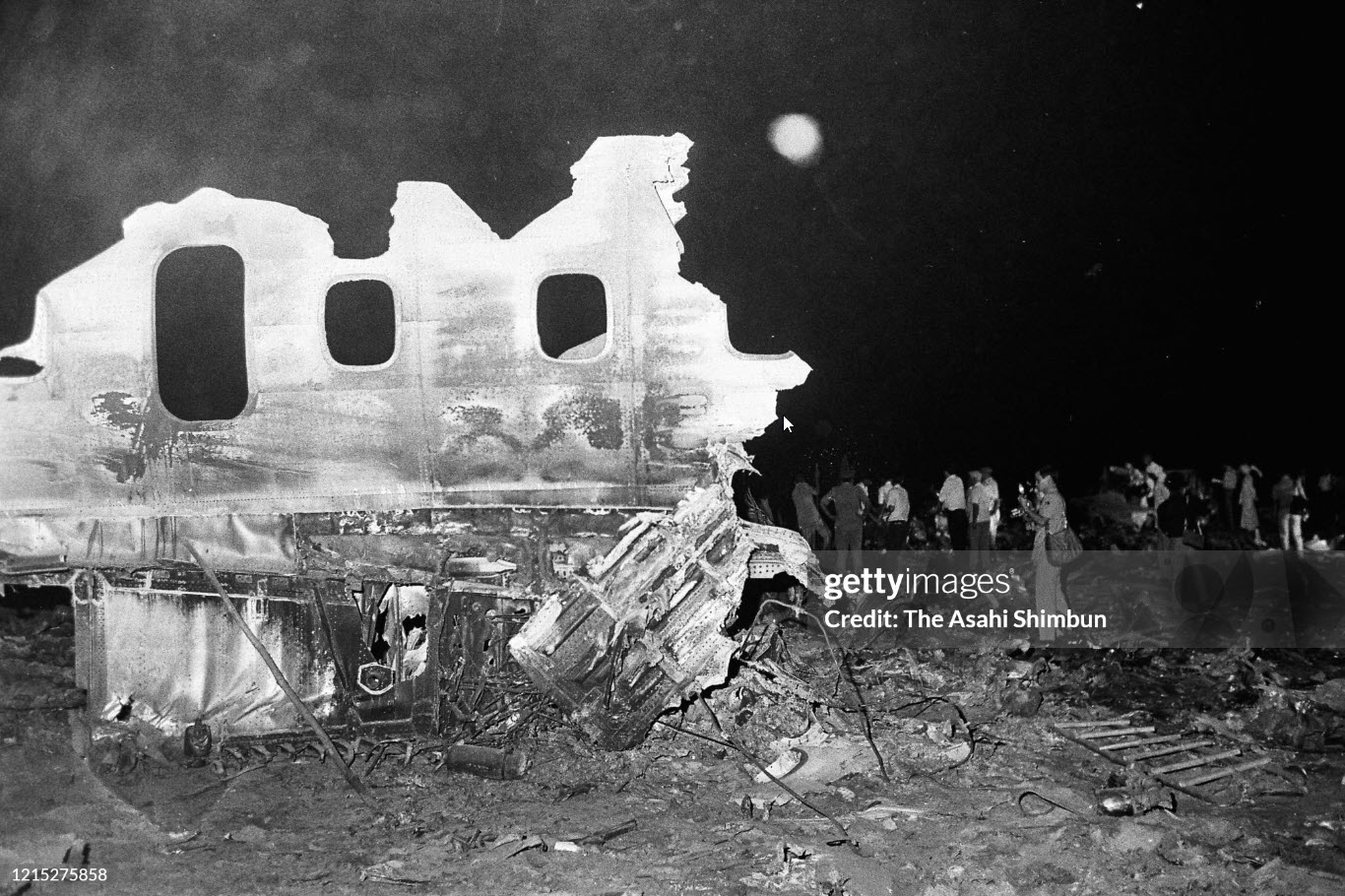
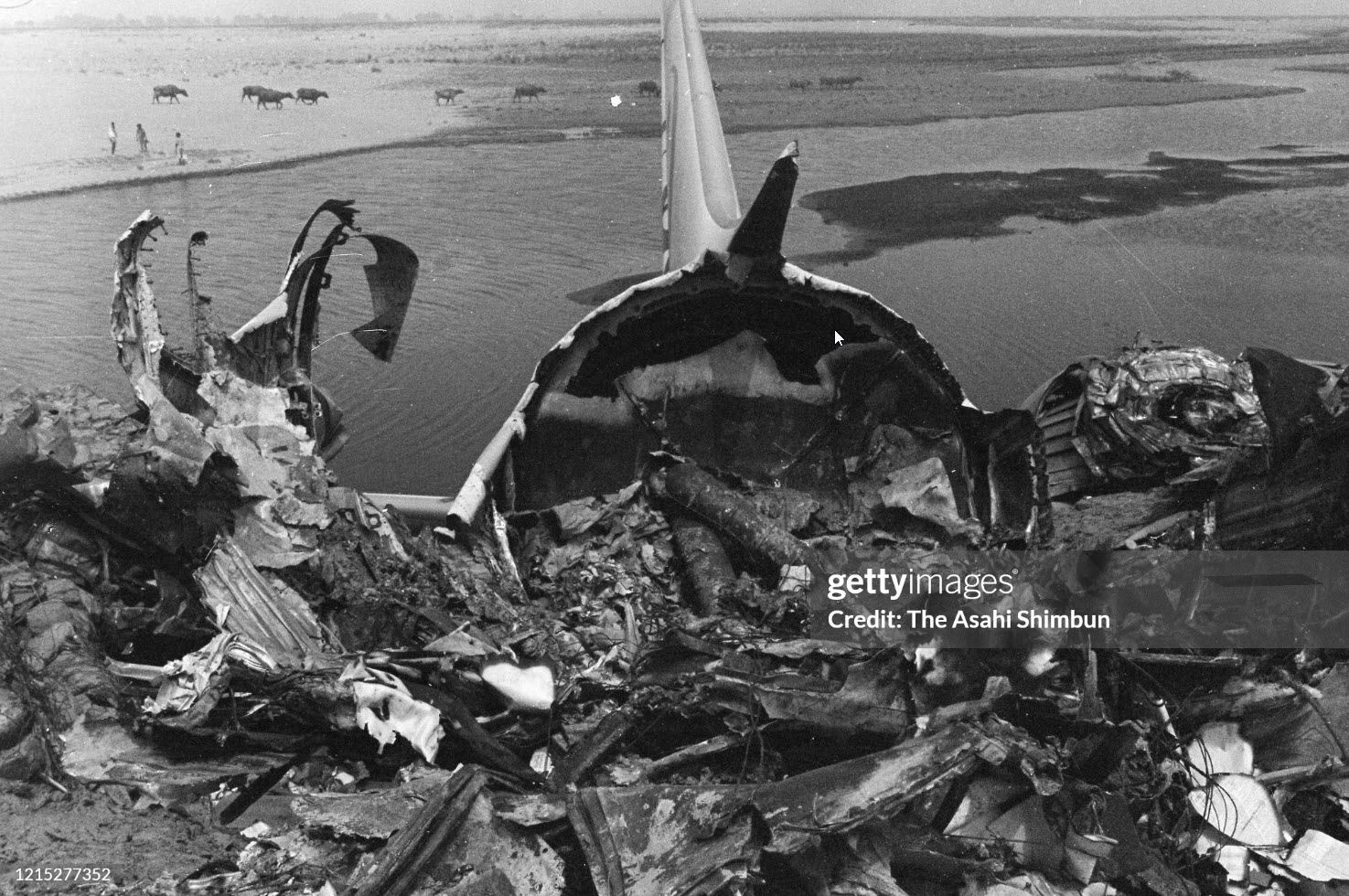
Indian Airlines flight IC422 was a domestic service from Srinagar to Delhi via Jammu and Chandigarh, India. The aircraft, a Boeing 737-200, landed gear up on runway 10 at Delhi-Indira Gandhi International Airport. The left engine then caught fire due to a fuel leak from ruptured fuel lines and a broken fuel control unit. The fire was quickly put out by fire services. All 134 occupants evacuated safely.
Probable cause:
The accident occurred because of commander's negligent flying contrary to laid down procedures and failure to ensure that the landing gears were down and locked before landing. The co-pilot's failure to bring to the notice of the commander the deviations from the laid down procedures and to verify and cross-check that the gears were down, was a contributory factor to the accident.