Country
code
CO
Crash of a Piper PA-31-350 Navajo Chieftain in Hayden: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 28, 1998 at 0858 LT
Registration:
N35533
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Colorado Springs - Hayden
MSN:
31-8052047
YOM:
1980
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
375.00
Aircraft flight hours:
12411
Circumstances:
The Part 135 cargo flight was approaching its destination on an IFR flight plan. The pilot had requested the ILS-DME approach to runway 10, but 2 minutes later, he changed his request to the VOR-B approach to runway 28. ARTCC cleared him for the approach to the non-towered airport. The pilot contacted the airport's Unicom, and requested that the ramp personnel be standing by with fuel and oxygen. The airplane was found 5.8 nm from the approach end of runway 28, at 7,900 feet. The approach minimums for the VOR-B was 7,900 feet, which the pilot could descend to at 8.7 nm. The VOR was located 285 degrees at 13.6 nm from the accident site, and the ILS-DME transmitter was located 285 degrees at 5.6 nm from the accident site. The airplane was equipped with a single DME display head, and it had a Nav 1/Nav 2 selector switch.
Probable cause:
The pilot not following instrument procedures and subsequently descended to minimums prematurely. Factors were the mountainous terrain and the falling snow.
Final Report:
Crash of a Beechcraft A100 King Air in Colorado Springs: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 21, 1997 at 0626 LT
Registration:
N100BE
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Eden Prairie - Colorado Springs
MSN:
BB-221
YOM:
1976
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Captain / Total hours on type:
65.00
Aircraft flight hours:
8651
Circumstances:
The pilot was cleared for an ILS DME approach to runway 17L. During the final stage of the approach, the aircraft entered fog and disappeared from view of the control tower personnel. Radar and radio communications were lost also. After searching for 31 minutes, the aircraft was found by airport operations personnel over half way down the runway and 600 feet east of the runway. There was no evidence the aircraft touched down on the runway. The aircraft was configured with the landing gear up and the flaps deployed. Missed approach procedures require the flaps and landing gear to be retracted after initiating the procedure. The decision
height for the approach is 6,384 feet msl (200 feet above ground level) and the required RVR for a 14 CFR Part 135 flight to commence and approach is 2400 (1/2 mile). When on the glide slope, the decision height is 0.4 miles from the runway touchdown zone. Examination of the airplane did not disclose evidence of mechanical malfunction.
height for the approach is 6,384 feet msl (200 feet above ground level) and the required RVR for a 14 CFR Part 135 flight to commence and approach is 2400 (1/2 mile). When on the glide slope, the decision height is 0.4 miles from the runway touchdown zone. Examination of the airplane did not disclose evidence of mechanical malfunction.
Probable cause:
Failure of the pilot to follow IFR Procedures and maintain the minimum descent altitude (MDA). A related factor was fog.
Final Report:
Crash of a Swearingen SA226T Merlin III in Byers: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 19, 1997 at 2017 LT
Registration:
N950TT
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Front Range - Aspen
MSN:
T-225
YOM:
1973
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
479.00
Aircraft flight hours:
6599
Circumstances:
The pilot departed Front Range Airport (elevation 5512 feet) at approximately 2008, climbed to 7,000 feet msl, accelerated to 270 knots, and requested his IFR clearance. Weather at the time of N950TT's departure was 500 feet overcast; witnesses reported the tops of the thin cloud condition were 8,500 feet msl and it was very dark on top (no stars or moon). The pilot made several changes in airspeed and climb rate until radar indicated that he had entered an 8,500 fpm decent. The pilot reported to ATC that he had 'stalled' the airplane. Radar indicated that he then climbed at 7,500 fpm until his estimated airspeed was 10 knots, and then subsequently descended again at 8,400 fpm until he impacted the frozen ground. The pilot had flown 4 times for 7 hours in the previous 40 days. Five airline pilots, each of who had 3,000 to 5,000 hours in Swearingens, stated individually that even though the airplane is single pilot certified, they believed that 'its a two pilot airplane--because the work load is too high.'
Probable cause:
The pilot inadvertently stalling the airplane and his subsequent spatial disorientation which prevented him from maintaining airplane control. Factors were excessive workload on the pilot and the dark night light conditions.
Final Report:

Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in the Uncompahgre National Forest: 9 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 8, 1997 at 0723 LT
Registration:
N12022
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Montrose - Page
MSN:
208B-0432
YOM:
1995
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
8
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
9
Captain / Total hours on type:
1546.00
Aircraft flight hours:
2599
Aircraft flight cycles:
3680
Circumstances:
The airplane departed under visual flight rules (VFR) for a flight over mountainous terrain. It was tracked by radar from the departure area to the accident site. While climbing at the normal rate of climb to 15,400 feet, the airplane abruptly disappeared from radar. The wreckage was located among pine trees and exhibited evidence of a steep flight path angle and damage consistent with a stall/spin event. Investigation revealed no indication of airframe or flight control anomalies, and the powerplant and propeller damage was consistent with engine operation at moderate to high power. Evidence indicated that the airplane was free of airframe ice at impact. Postaccident calculations indicate that the airplane was near the maximum certificated gross weight and aft center of gravity limit. The pilot did not maintain instrument flying currency and reportedly avoided instrument meteorological conditions (IMC). Evidence indicated that the pilot did not use oxygen, as required (when flying above 12,000 feet). Ground observations and satellite and Doppler radar imagery indicated widespread cloudiness over the mountains west of Montrose on the day of the accident. Satellite data showed variable cloud tops higher than the airplane's flight altitude in the vicinity of the accident. The radar plot of the aircraft during the climb above 10,000 feet indicated course changes from the southwest to the northwest, back to the southwest and then a sharp turn to the right just prior to the rapid descent.
Probable cause:
the pilot's failure to maintain sufficient airspeed for undetermined reasons while maneuvering the airplane near the maximum gross weight and aft cg in or near instrument meteorological conditions, resulting in the loss of control and entry into a stall/spin. Factors contributing to the accident were the pilot's improper in-flight planning and decision-making and his failure to use proper stall/spin recovery techniques.
Final Report:


Ground accident of a Boeing 727-51C in Denver
Date & Time:
Oct 1, 1997 at 0436 LT
Registration:
N414EX
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Denver – San Francisco
MSN:
18899/256
YOM:
1966
Flight number:
RYN607
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
7305.00
Aircraft flight hours:
47098
Aircraft flight cycles:
45215
Circumstances:
As the cargo jet was taxiing for takeoff in a non movement area, it was struck by an airport employee shuttle bus. The airplane captain was seriously injured. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed, and the collision occurred during predawn hours. The bus driver said he stopped at the stop sign, turned on the 4-way flasher lights, and looked both ways. He saw one inbound aircraft to the right that had stopped. He did not see the airplane approaching from the left as he started across the cargo ramp. The airplane crew stated they did not see the bus until seconds before impact. Airplane skid marks, measuring 22 and 24 feet in length, were noted on the taxiway. No bus skid marks were noted on the roadway.
Probable cause:
Failure of the bus driver to yield the right of way to oncoming traffic due to his inadequate visual lookout. Factors were visibility restrictions, inadequate driver training by management, and the flight crew's inadequate visual lookout due to their attention being diverted by performing the pre takeoff checklist.
Final Report:
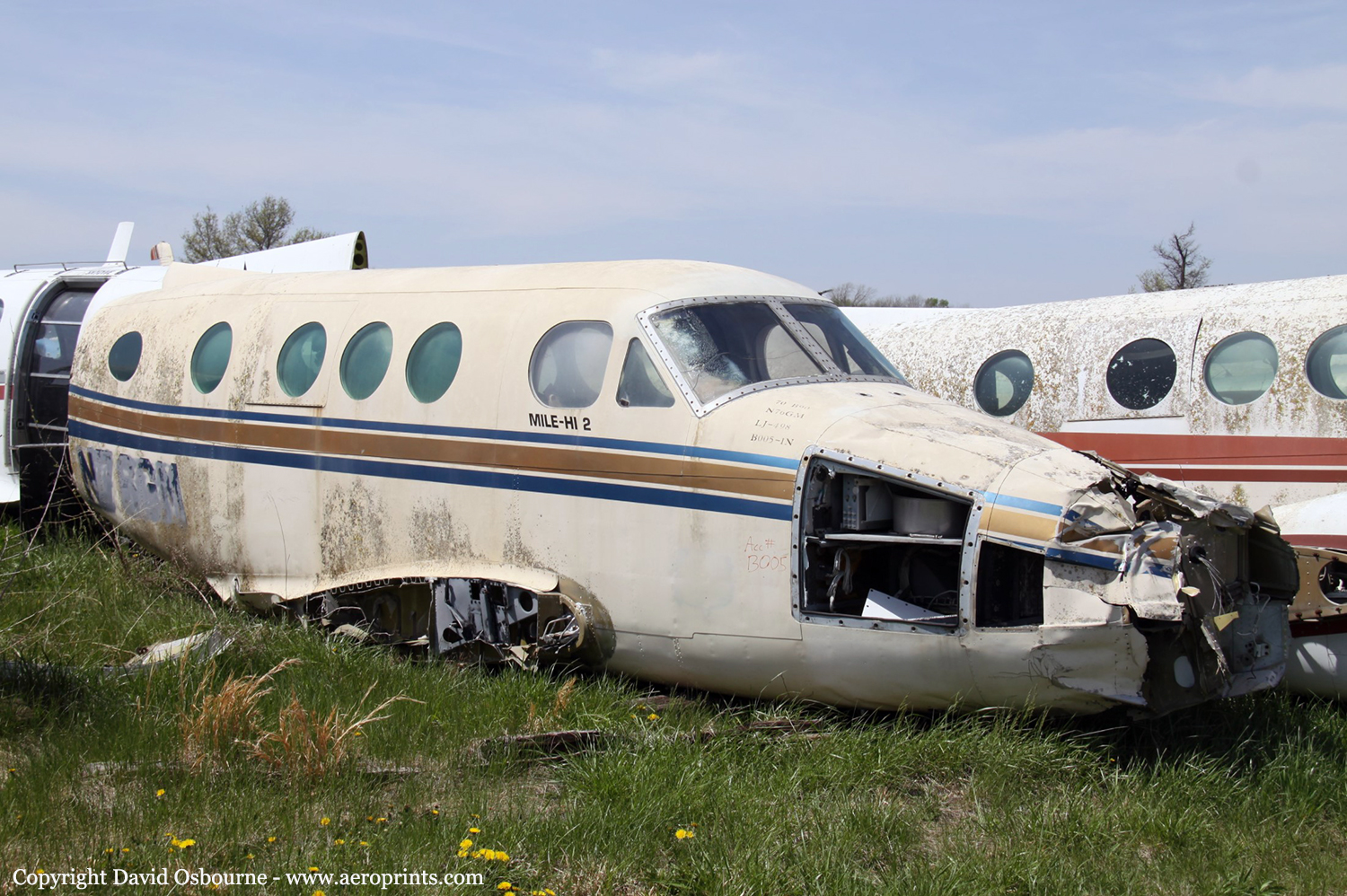
Crash of a Beechcraft B90 King Air in Longmont
Date & Time:
Jan 23, 1997 at 2050 LT
Registration:
N76GM
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Louisberg – Louisville – Vandalia – Longmont
MSN:
LJ-498
YOM:
1970
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
42.00
Aircraft flight hours:
10530
Circumstances:
The pilot had made a refueling stop at Vandalia, Illinois. She did not observe the refueling process, but the FBO also operated a King Air and she felt he knew the proper procedure to follow. The airplane was reportedly serviced with 235 gallons of Jet-A fuel (total capacity is 384 gallons). The pilot flew between 7,500 and 10,500 feet. When the airplane was 45 minutes from its destination, the fuel transfer pump lights illuminated, indicating the wing tanks were empty. The nacelle tank gauges registered 3/4 full and the pilot determined she had sufficient fuel to complete the flight. When the airplane was three minutes from its destination, both engines flamed out and the pilot made a wheels up forced landing. When the salvage company recovered the airplane, they reported finding no evidence of fuel aboard. The pilot was provided and used performance charts for the Beech 65-A90 instead of the Beech B90.
Probable cause:
Failure of the pilot to refuel the airplane, resulting in fuel exhaustion. Factors were the pilot's reference to similar but different aircraft performance charts, and the operator's failure to provide the pilot with the proper performance charts.
Final Report: