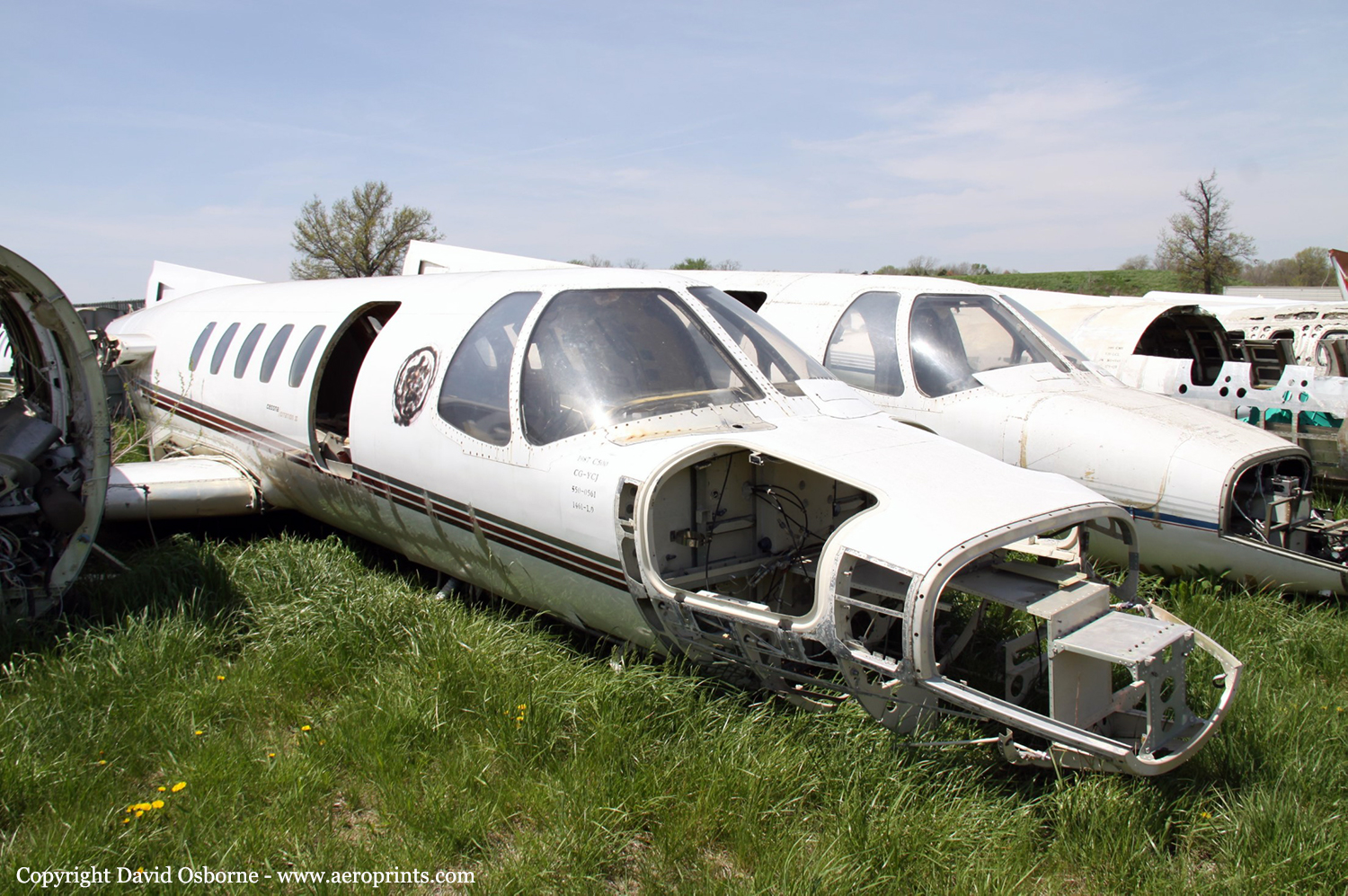
Crash of a Cessna 550 Citation II in Sandspit
Date & Time:
Nov 12, 2002 at 2052 LT
Registration:
C-GYCJ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Vancouver - Sandspit
MSN:
550-0561
YOM:
1987
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
1450.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
850
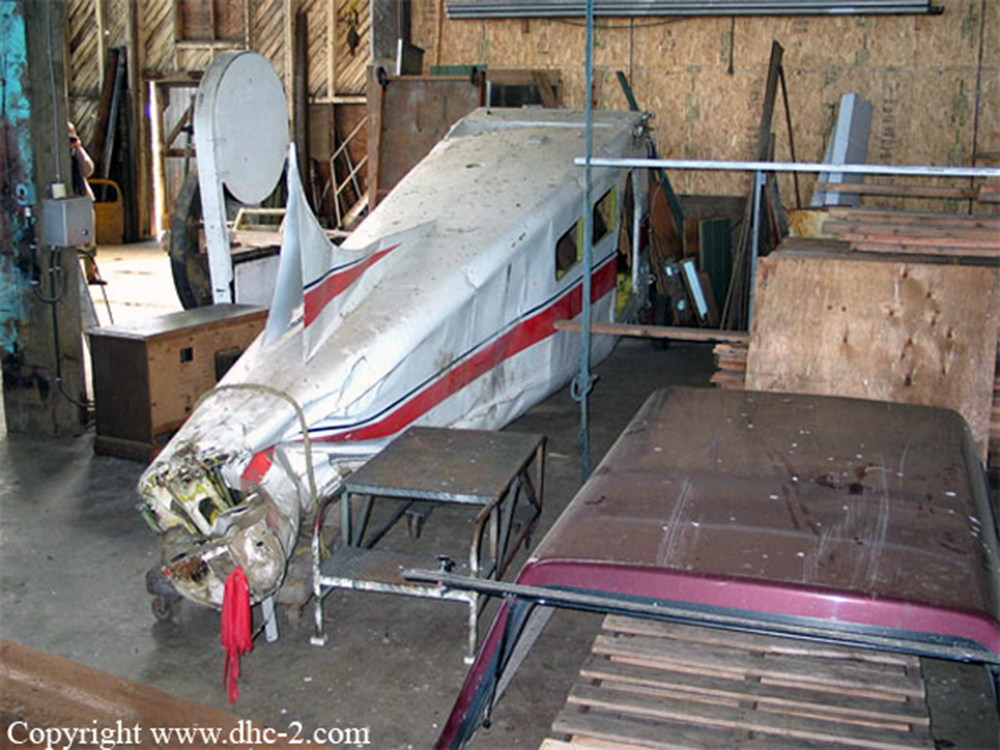
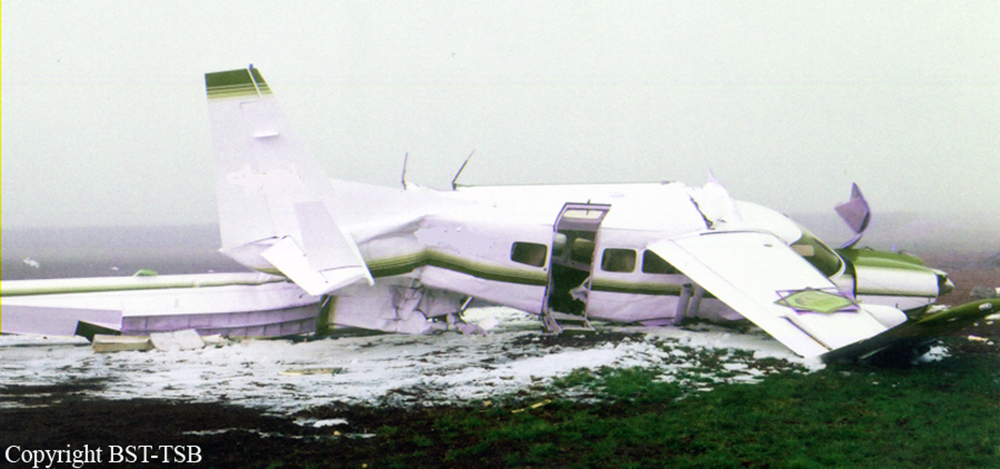
Circumstances:
The aircraft departed Vancouver International Airport, British Columbia, on a medical evacuation flight to the Sandspit Airport in the Queen Charlotte Islands, British Columbia. On board the aircraft were two pilots and a team of two Advanced Life Support Paramedics. When the aircraft arrived at Sandspit, the surface wind was strong, gusty, and across the runway. The crew conducted an instrument approach to Runway 30, and just before touchdown the aircraft's nose pitched down; the captain believed that the nosewheel, and then the main gear, collapsed as the aircraft slid on its belly. The crew carried out an evacuation and proceeded to the airport terminal building. When they returned to the aircraft to retrieve their belongings, the crew discovered that the gear was in the up position, as was the landing gear selector. The accident occurred at 2052 Pacific standard time. There were no injuries. The aircraft was substantially damaged.
Probable cause:
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
1. The crew did not complete the before-landing checks, ignored aural warnings, and did not lower the landing gear, which resulted in a gear-up landing.
Findings as to risk:
1. The aircraft was not equipped with a GPWS, which could have prevented this accident.
2. The before-landing checklist in use did not reflect the AFM requirement that the speed brakes should be retracted prior to 50 feet.
1. The crew did not complete the before-landing checks, ignored aural warnings, and did not lower the landing gear, which resulted in a gear-up landing.
Findings as to risk:
1. The aircraft was not equipped with a GPWS, which could have prevented this accident.
2. The before-landing checklist in use did not reflect the AFM requirement that the speed brakes should be retracted prior to 50 feet.
Final Report: