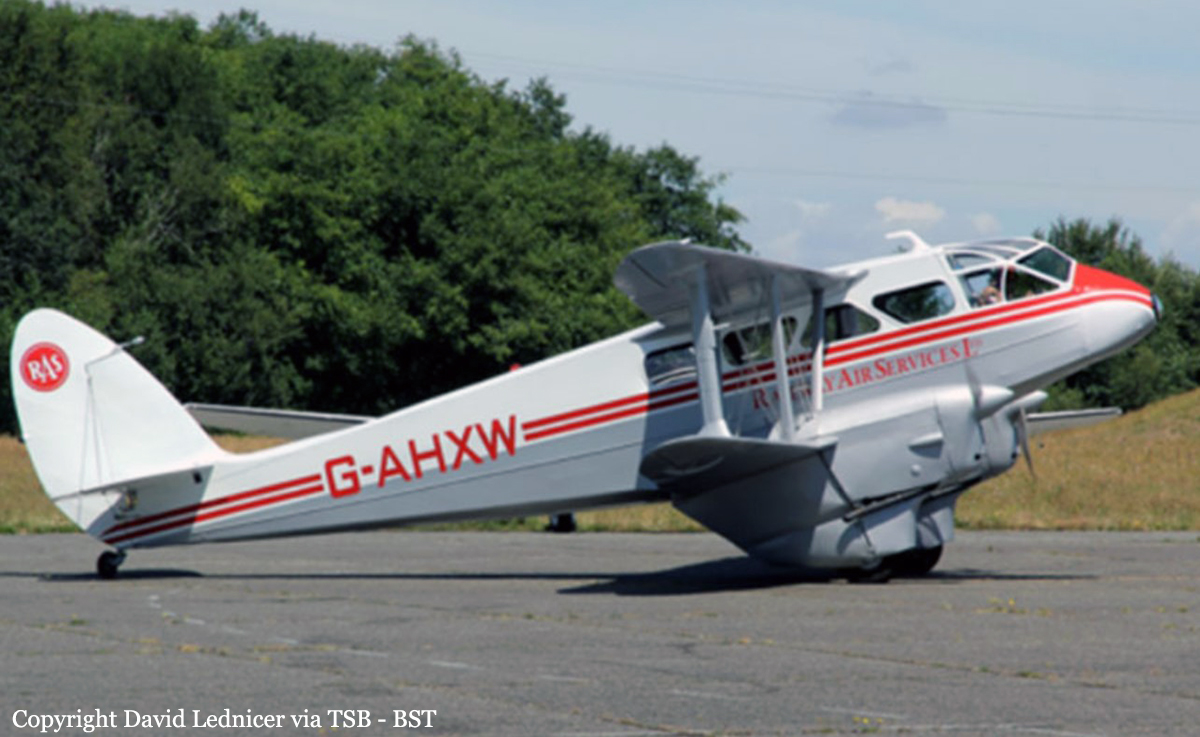
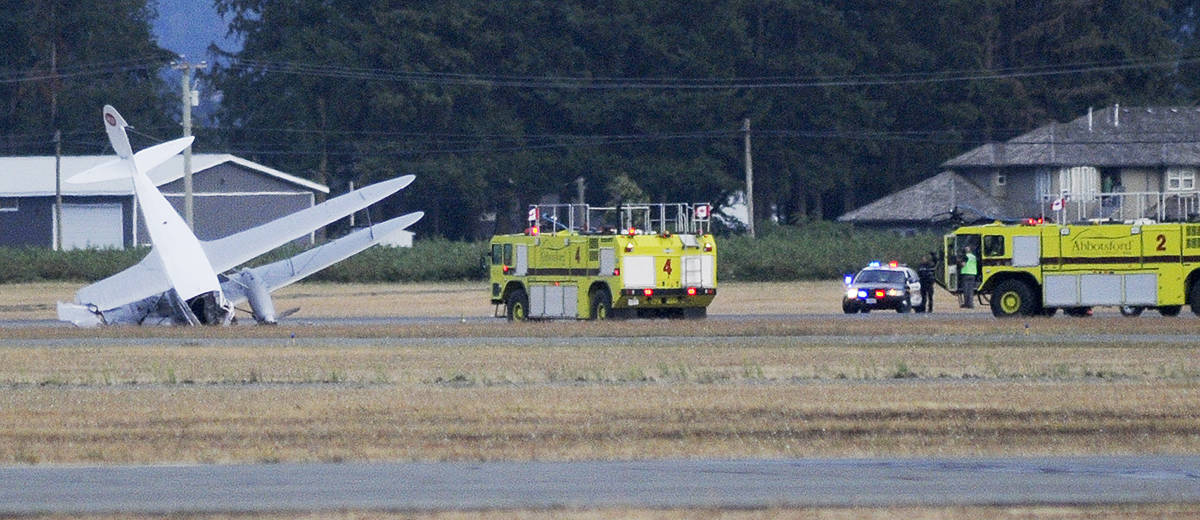
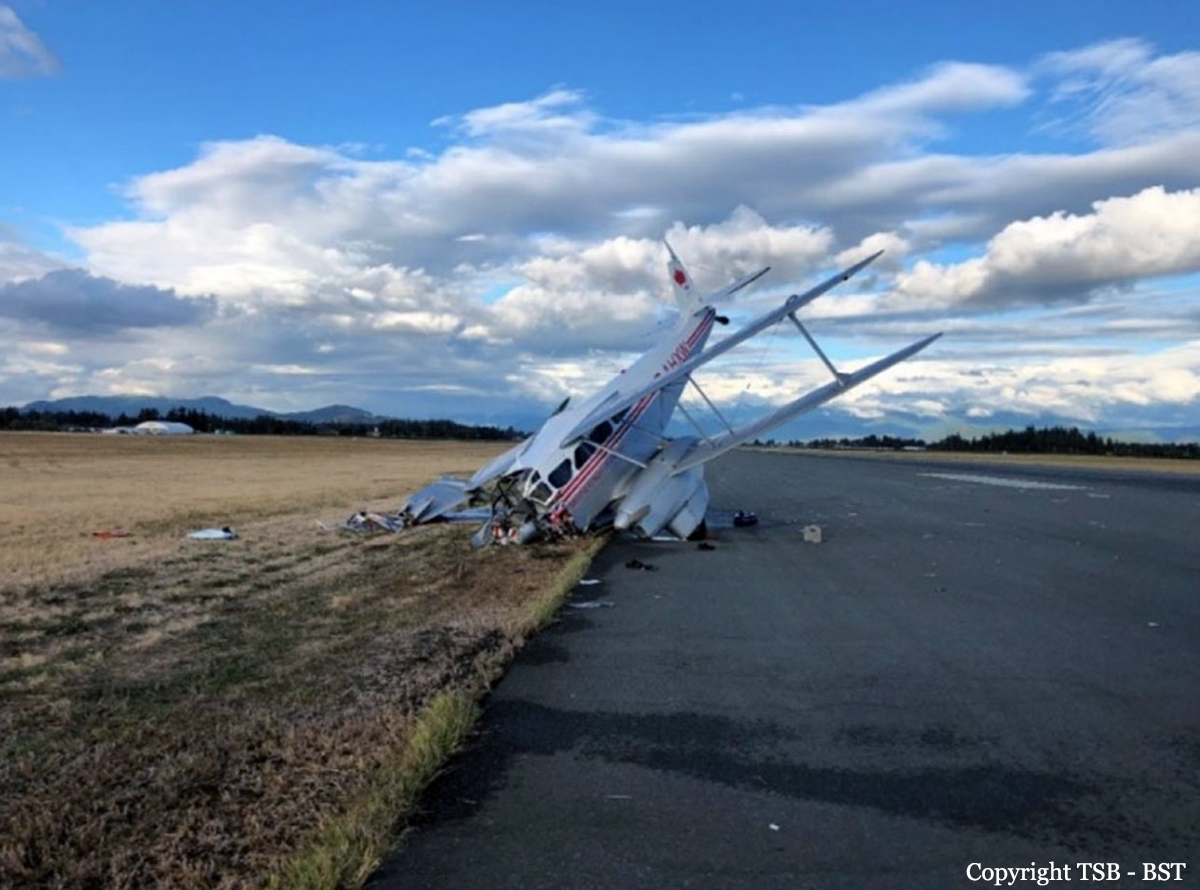
Crash of a De Havilland DH.89A Dragon Rapide 4 in Abbotsford
Date & Time:
Aug 11, 2018 at 1731 LT
Registration:
N683DH
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Abbotsford - Abbotsford
MSN:
6782
YOM:
1944
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
20.00
Circumstances:
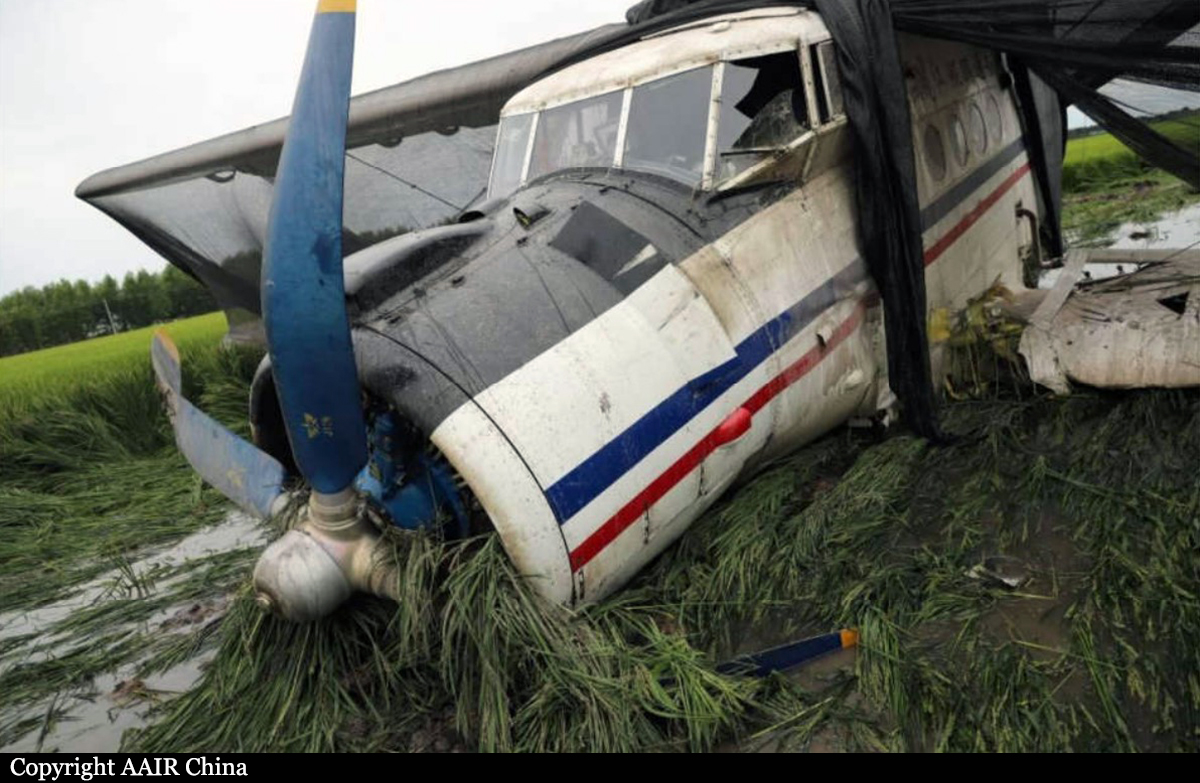
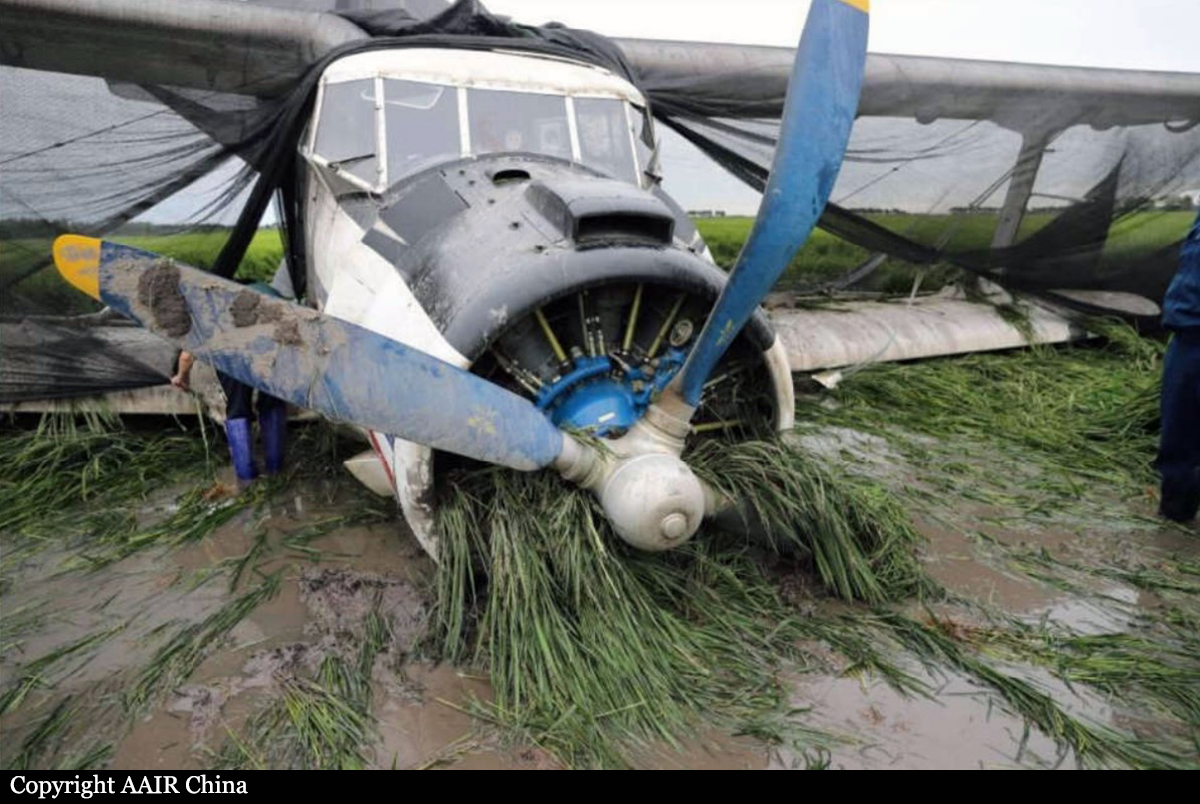
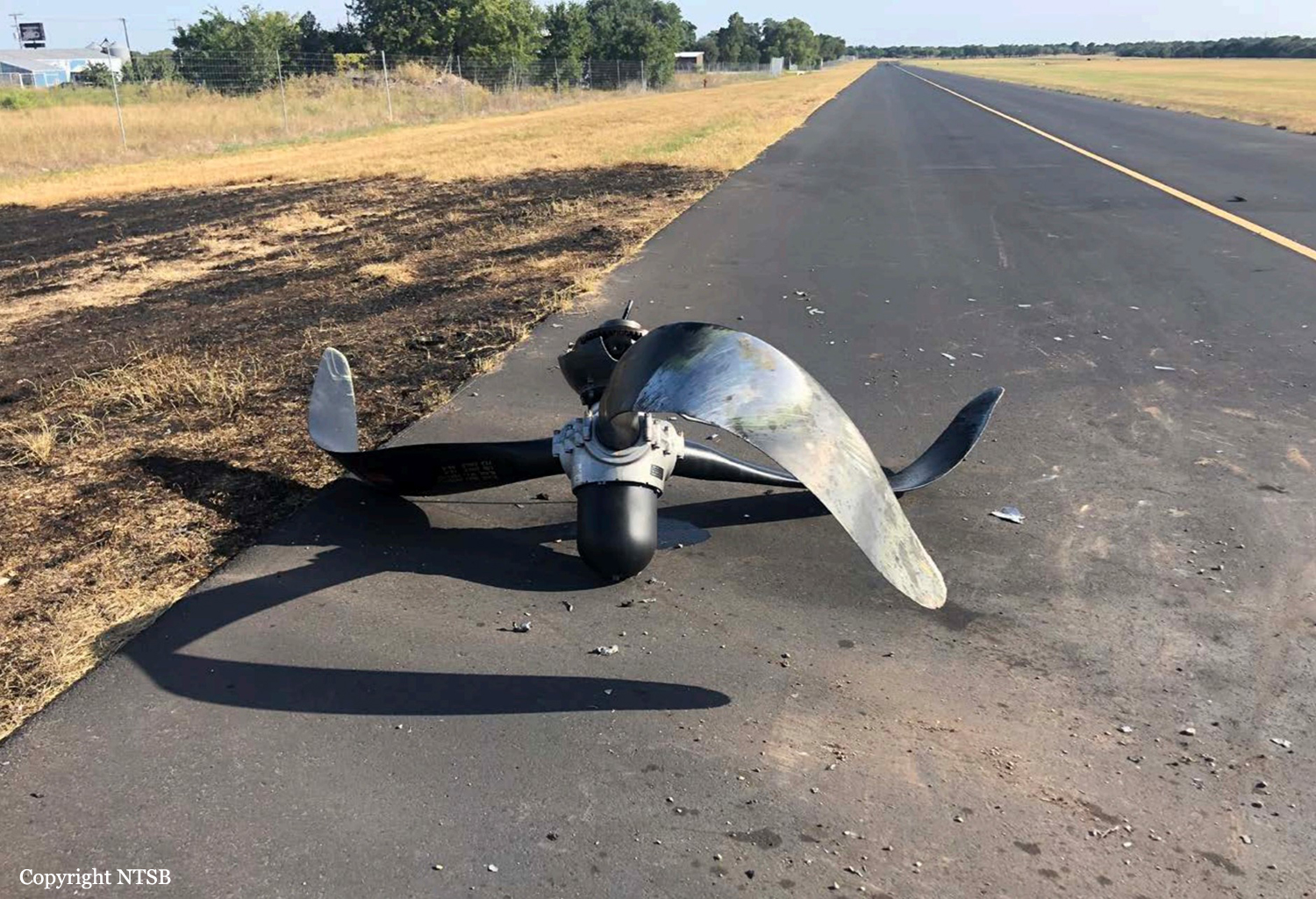
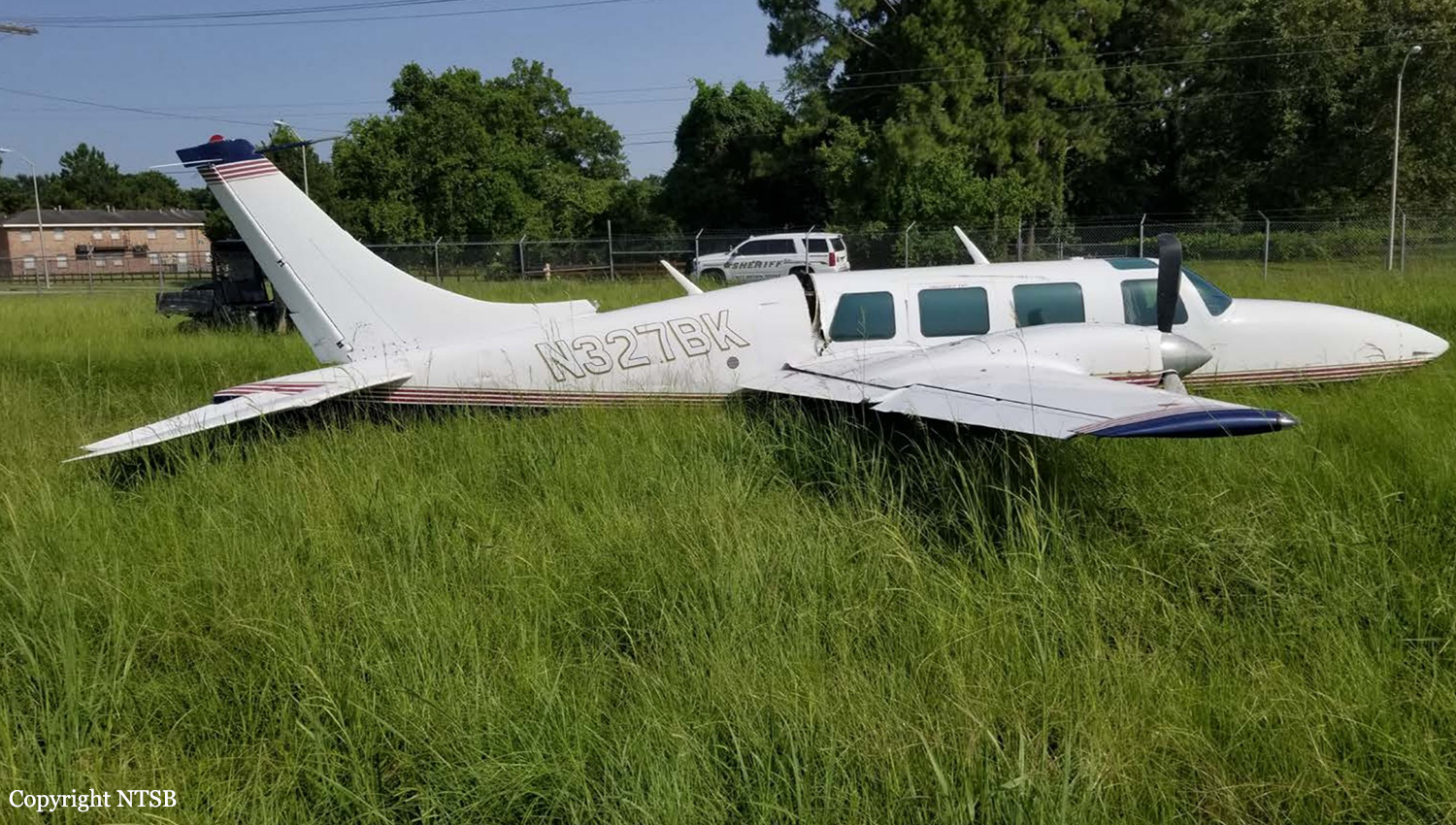
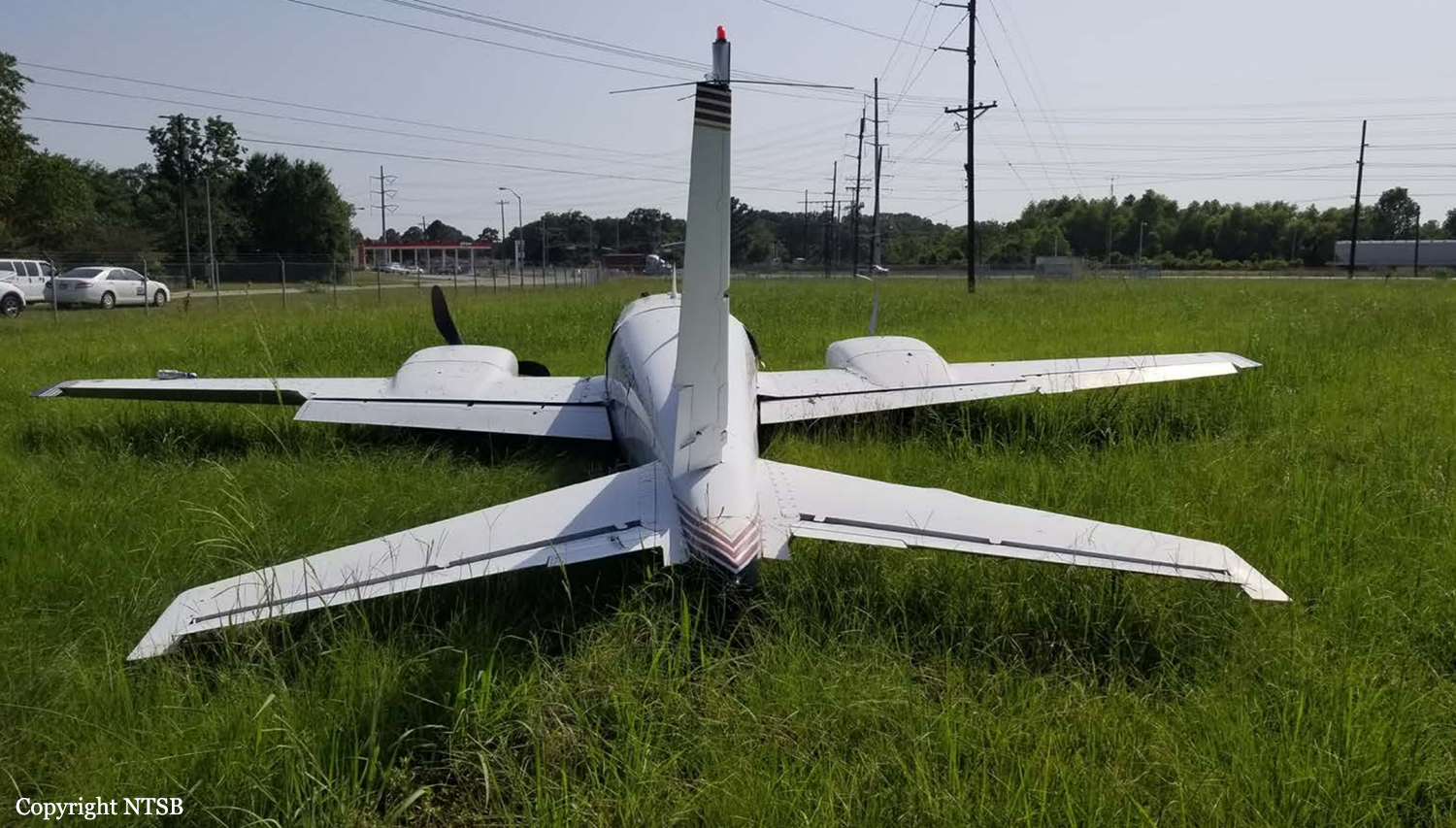
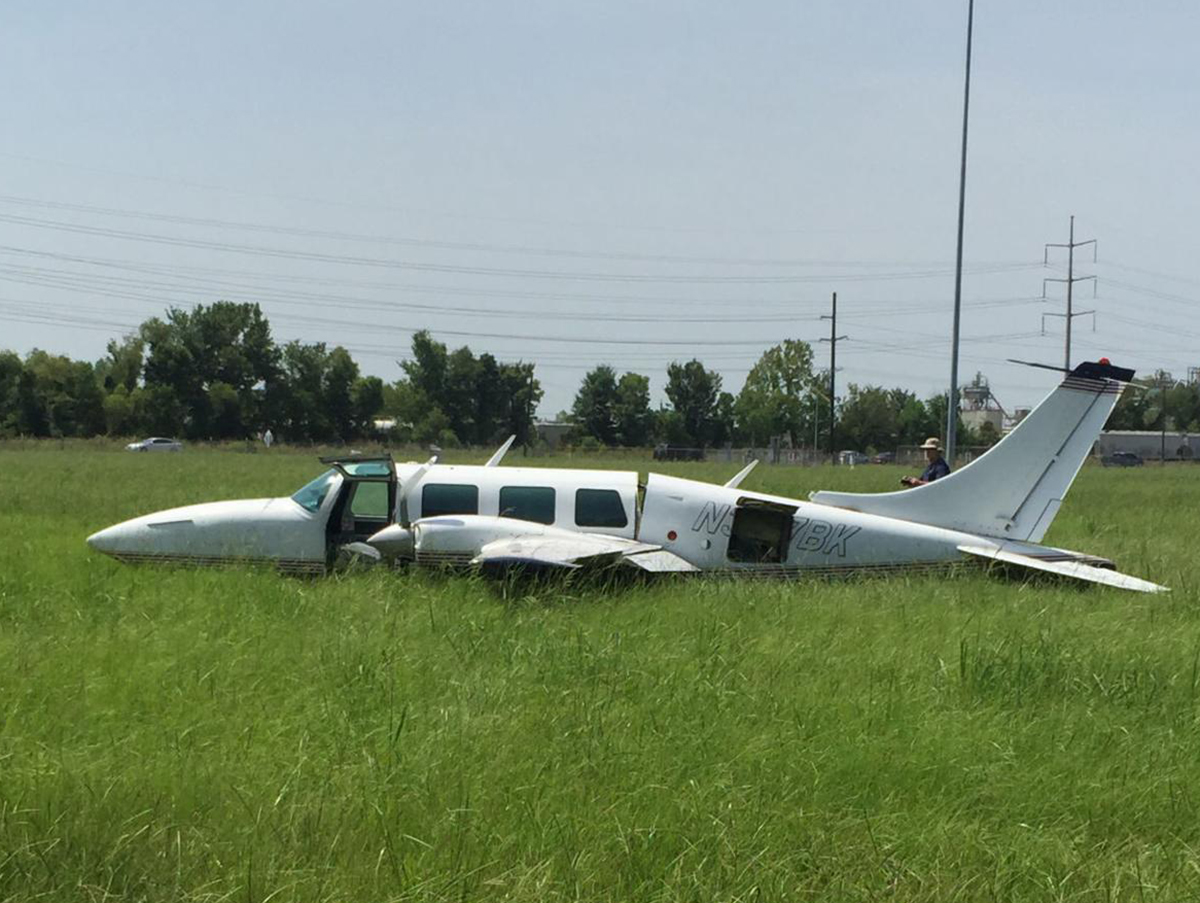
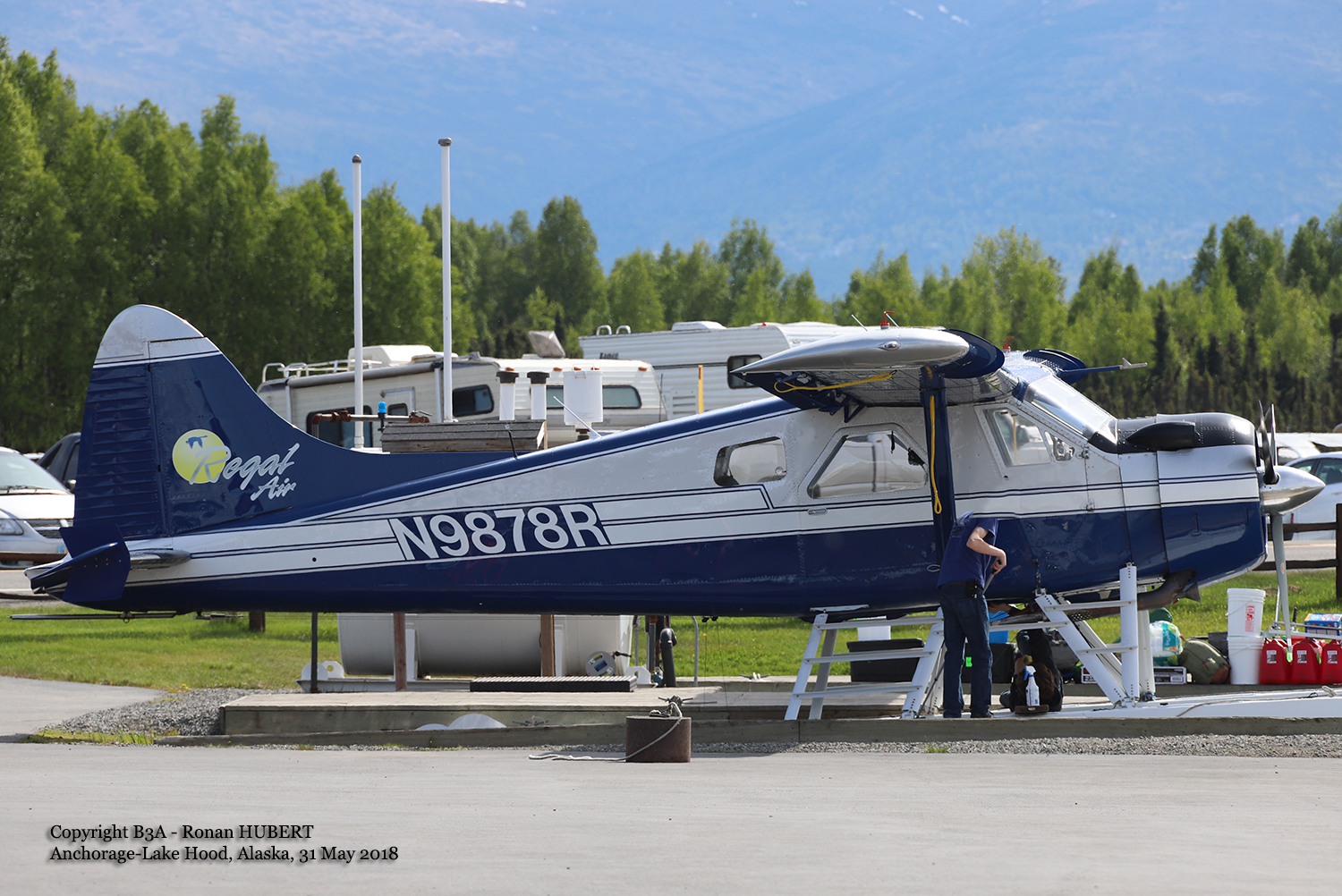
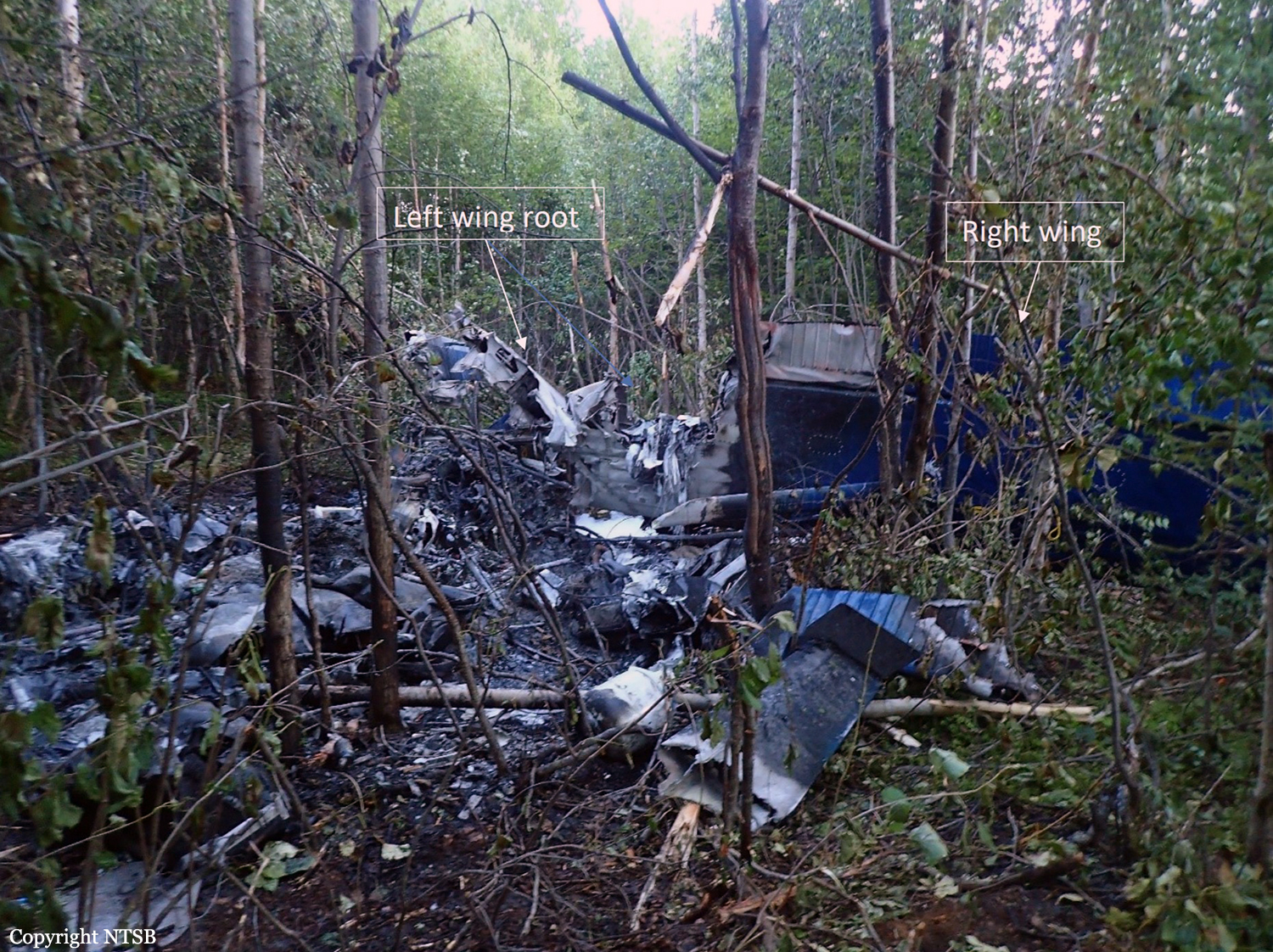
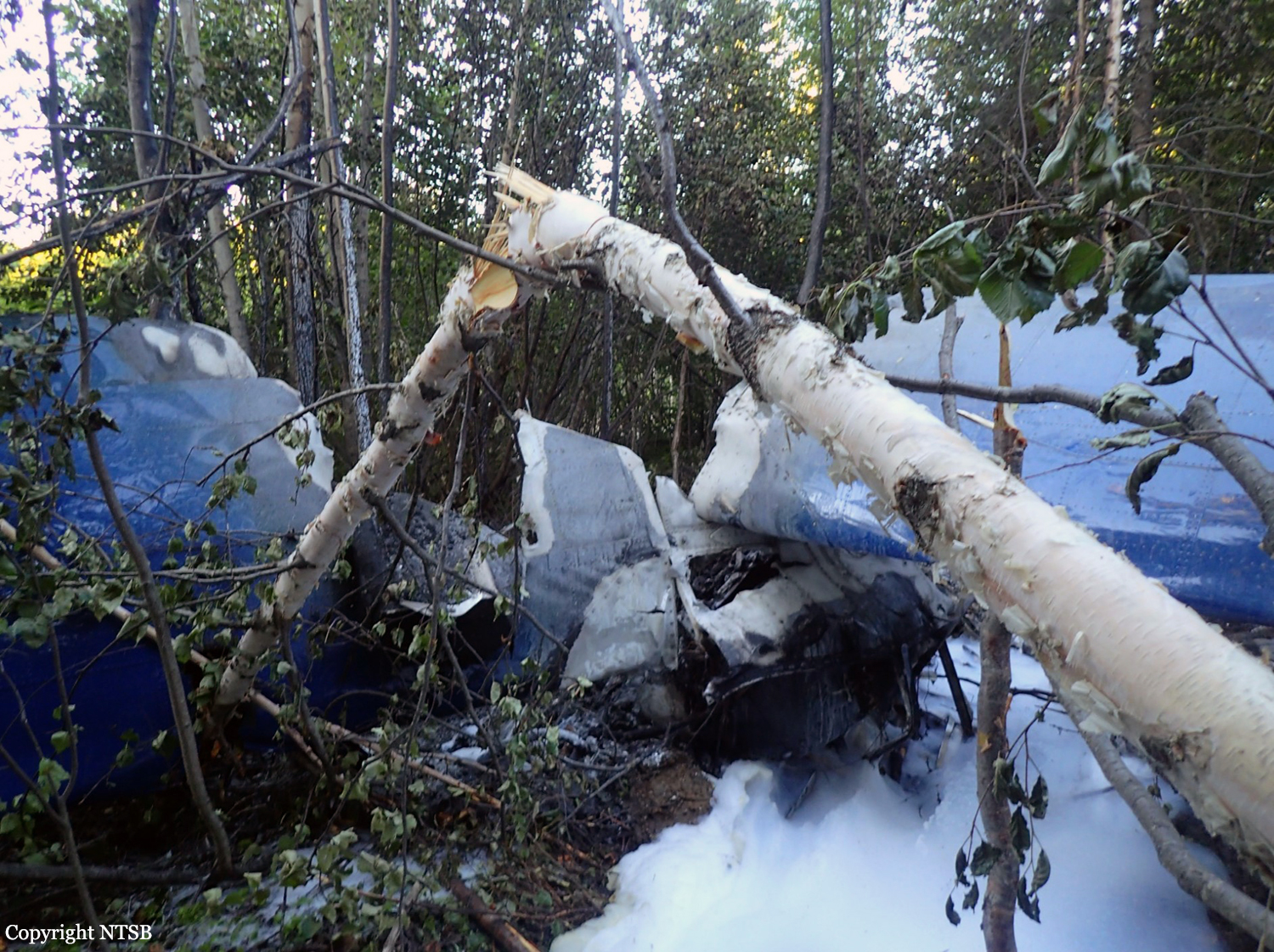
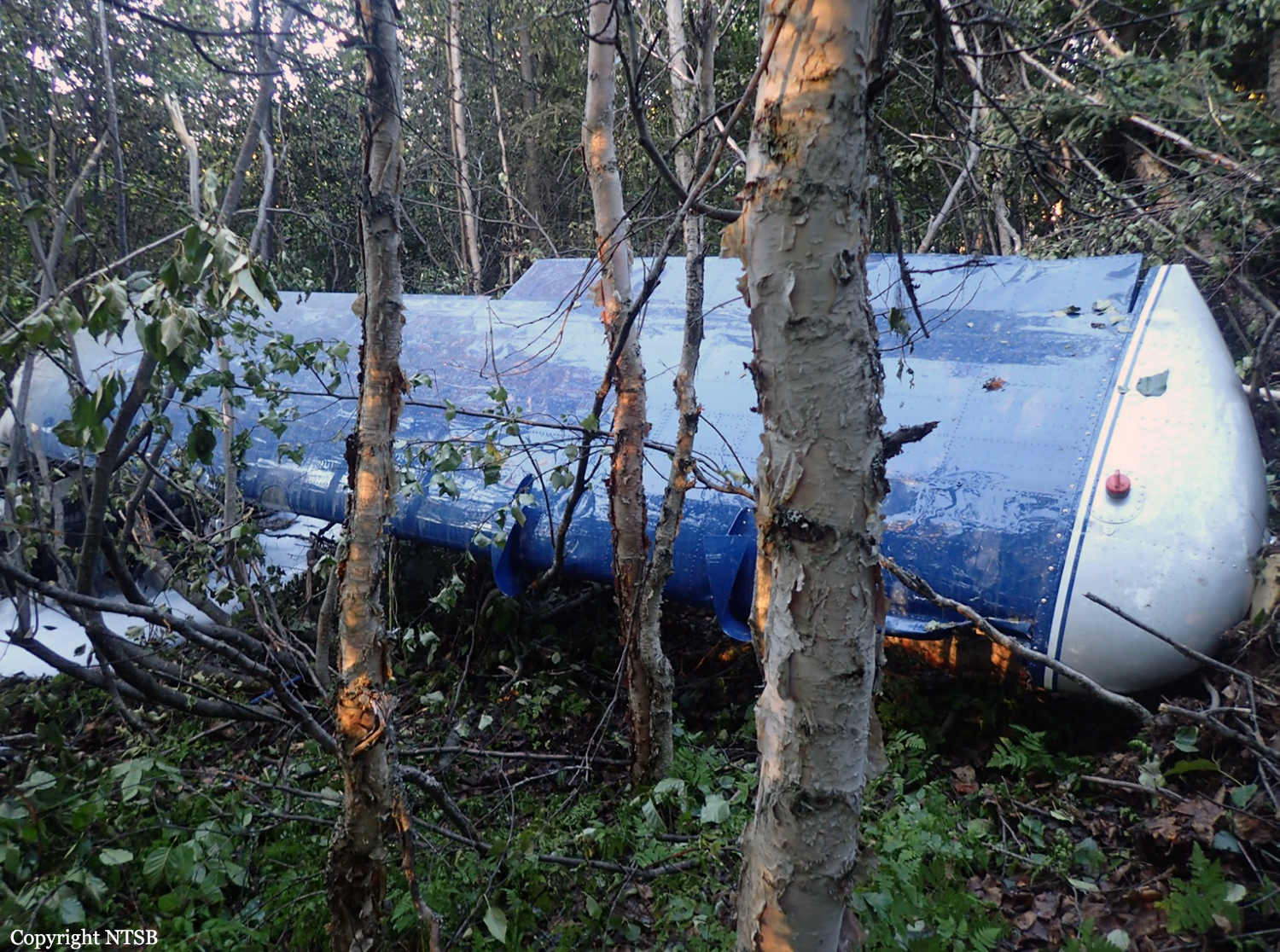
The vintage de Havilland DH-89A MKIV Dragon Rapide biplane (U.S. registration N683DH, serial number 6782) operated by Historic Flight Foundation was part of the static aircraft display at the Abbotsford International Airshow at Abbotsford Airport (CYXX), British Columbia. Following the conclusion of the airshow that day, the aircraft was being used to provide air rides. At approximately 1731 on 11 August 2018, the aircraft began its takeoff from Runway 25 with the pilot and 4 passengers on board for a local flight to the southeast. During the takeoff, the aircraft encountered strong, gusting crosswinds. It climbed to about 30 feet above ground level before descending suddenly and impacting the runway, coming to rest on its nose immediately off the right edge of the runway. Within 2 minutes, 2 aircraft rescue firefighting trucks arrived on the scene along with an operations/command vehicle. About 10 minutes later, 2 St. John Ambulances arrived. A representative of the HFF was escorted to the scene to ensure all electronics on the aircraft were turned off. Shortly thereafter, 2 BC Ambulance Service ground ambulances arrived, followed by 2 City of Abbotsford fire trucks. Two BC Ambulance Service air ambulances arrived after that. The fire trucks stabilized the aircraft, and the first responders who arrived with the fire truck finished evacuating the occupants. The pilot and 1 passenger received serious injuries; the other 3 passengers received minor injuries. All of the aircraft occupants were taken to the hospital. The aircraft was substantially damaged. There was a fuel spill, but no fire. The emergency locator transmitter activated.
Final Report: