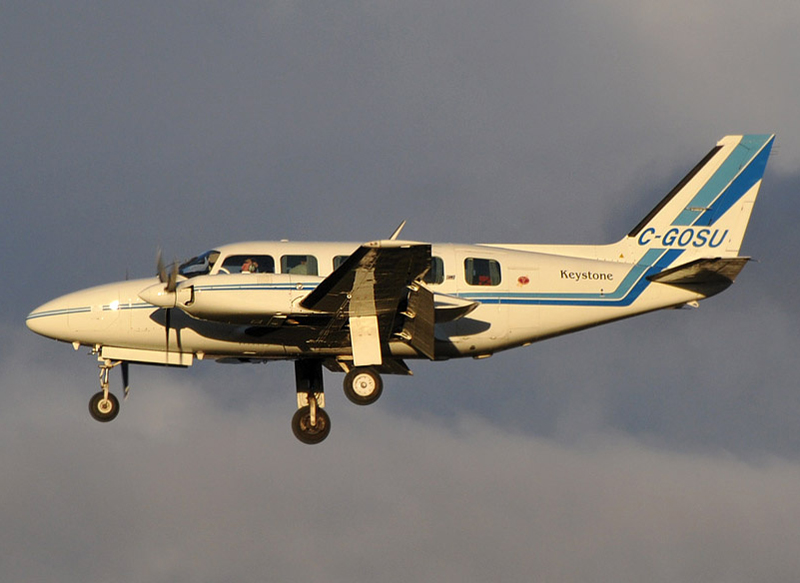
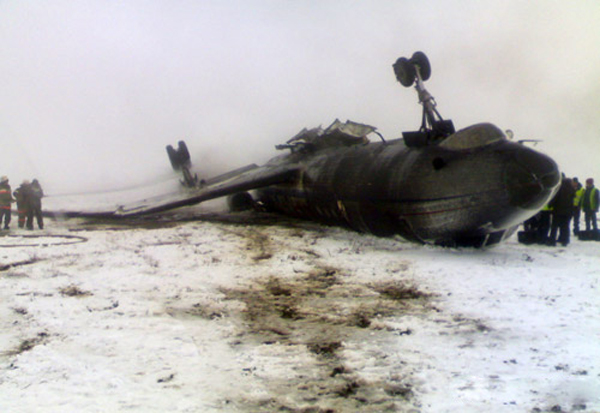
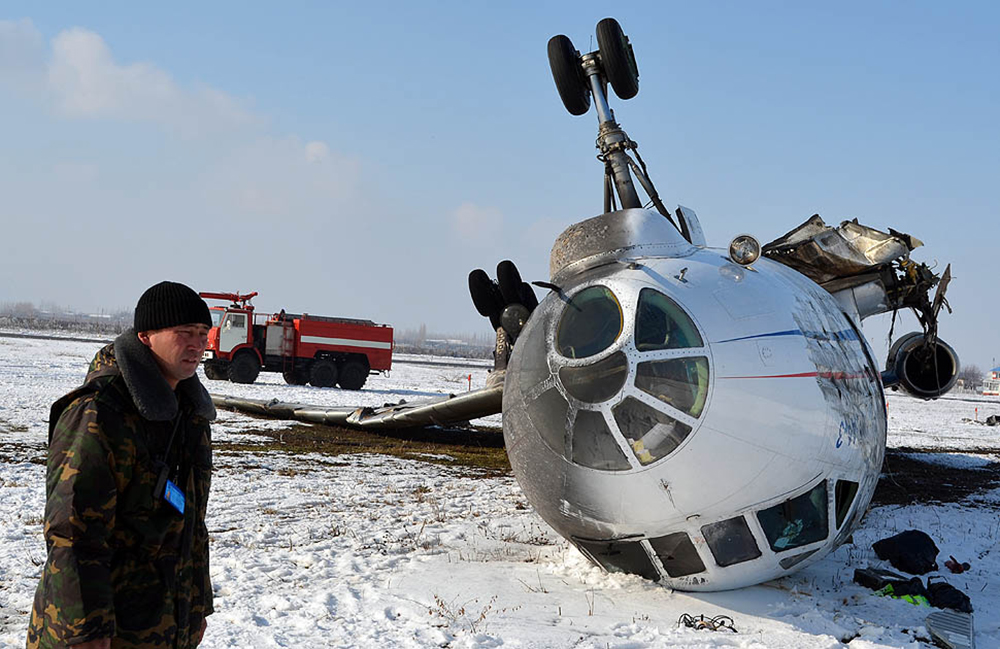
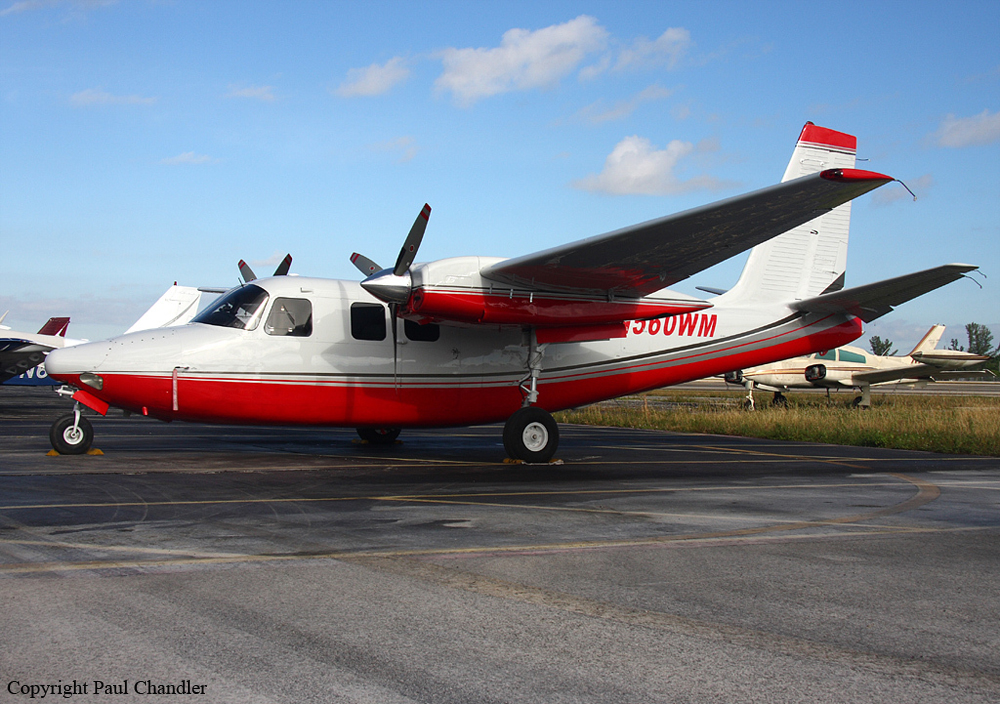
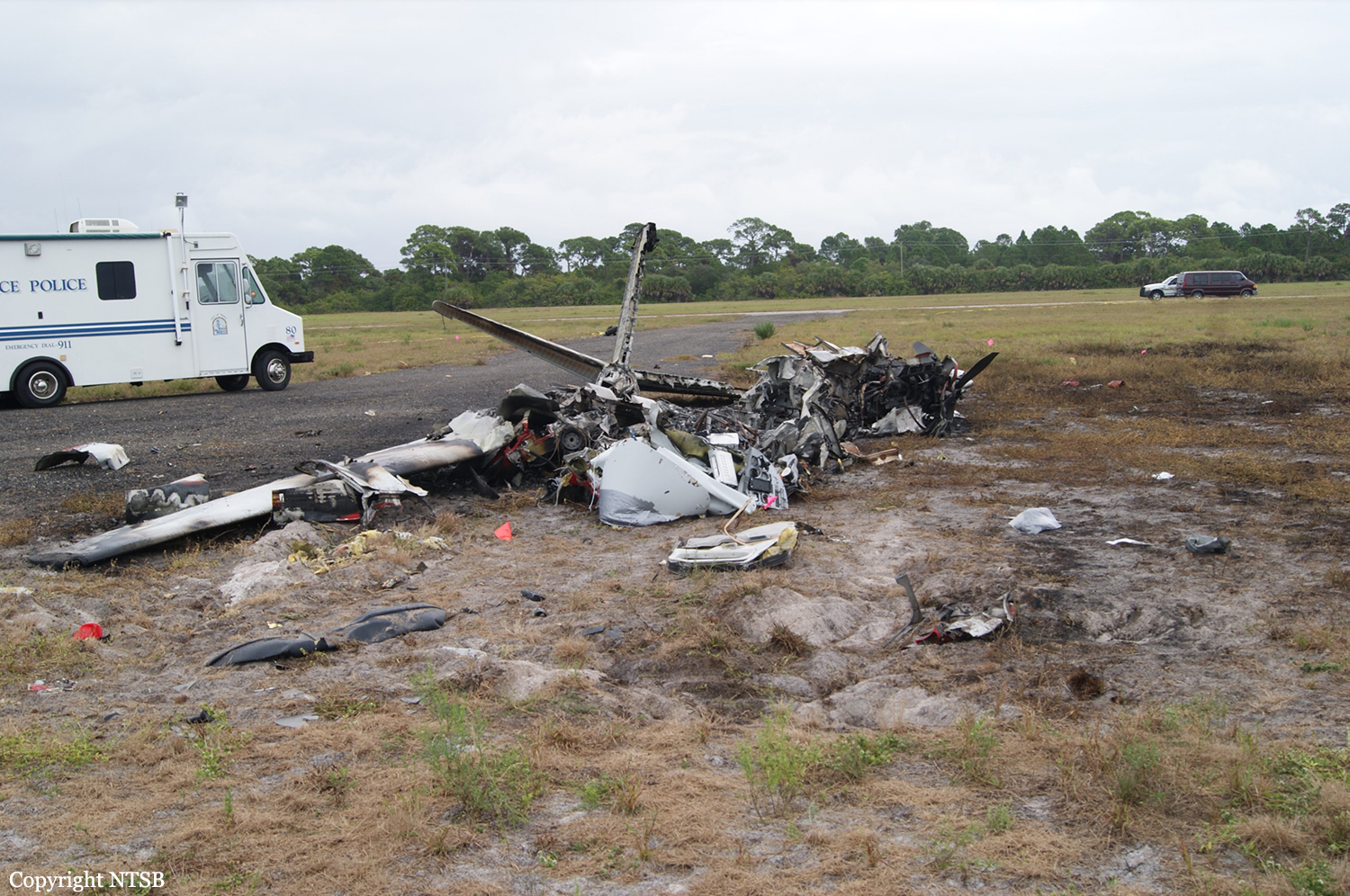
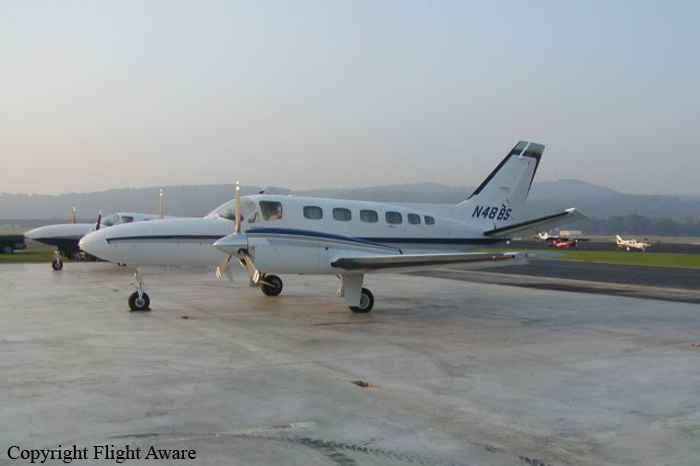
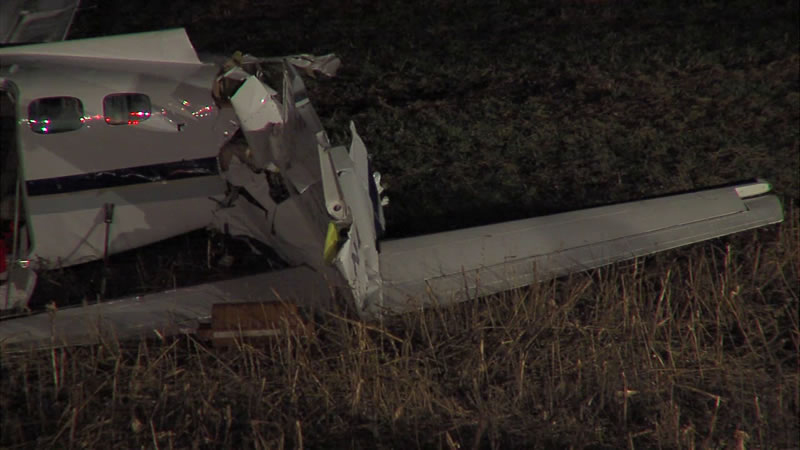
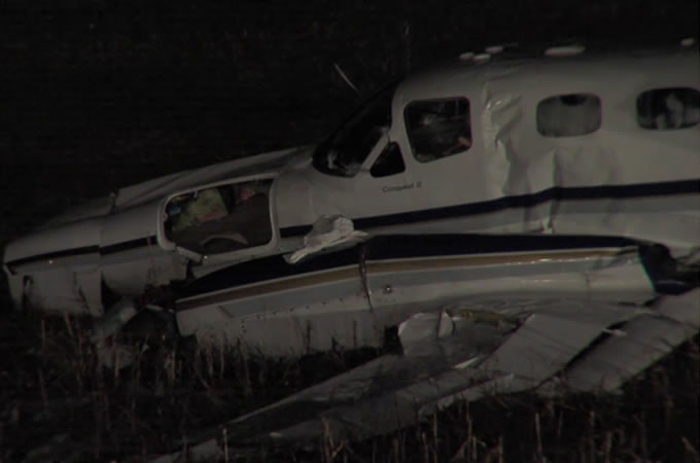
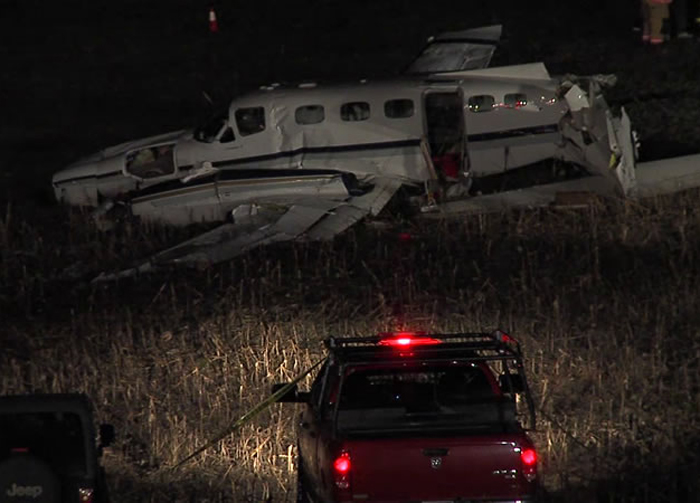
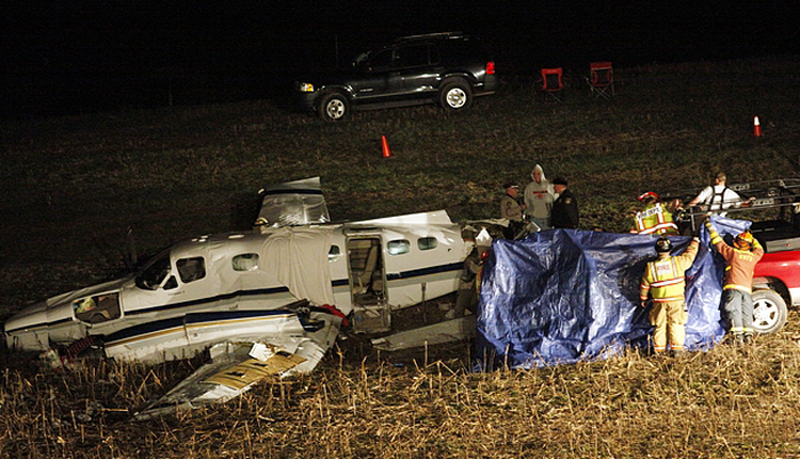
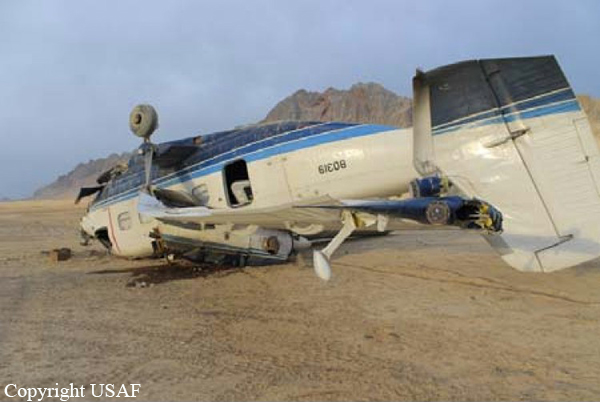
Crash of a Piper PA-31-350 Navajo Chieftain in North Spirit Lake: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 10, 2012 at 0957 LT
Registration:
C-GOSU
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Winnipeg - North Spirit Lake
MSN:
31-7752148
YOM:
1977
Flight number:
KEE213
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Captain / Total hours on type:
95.00
Circumstances:
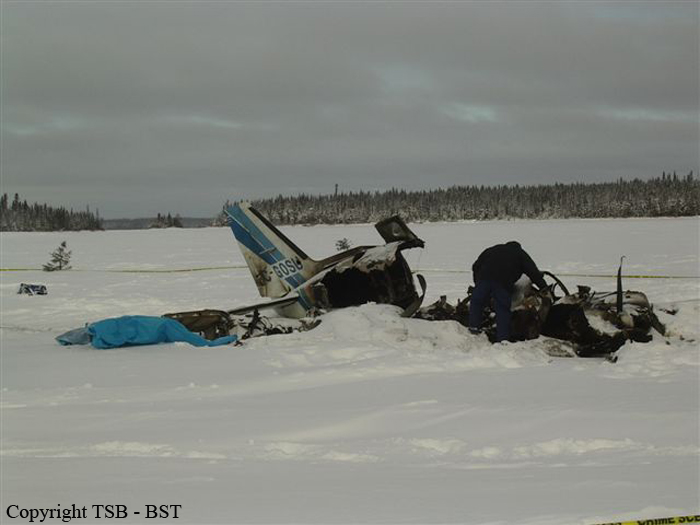
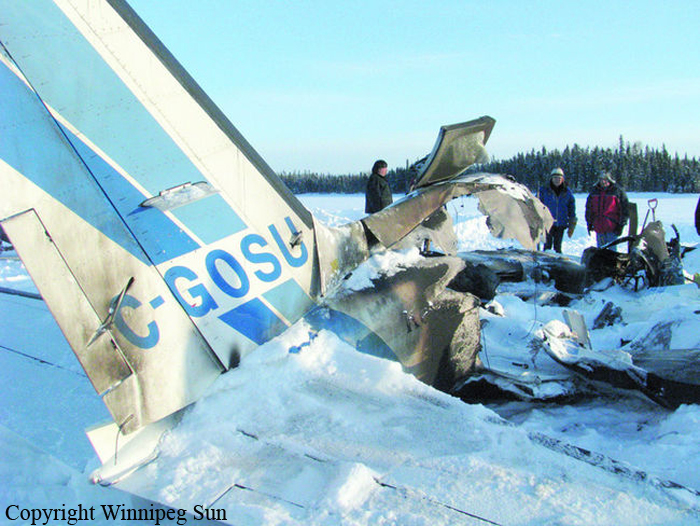
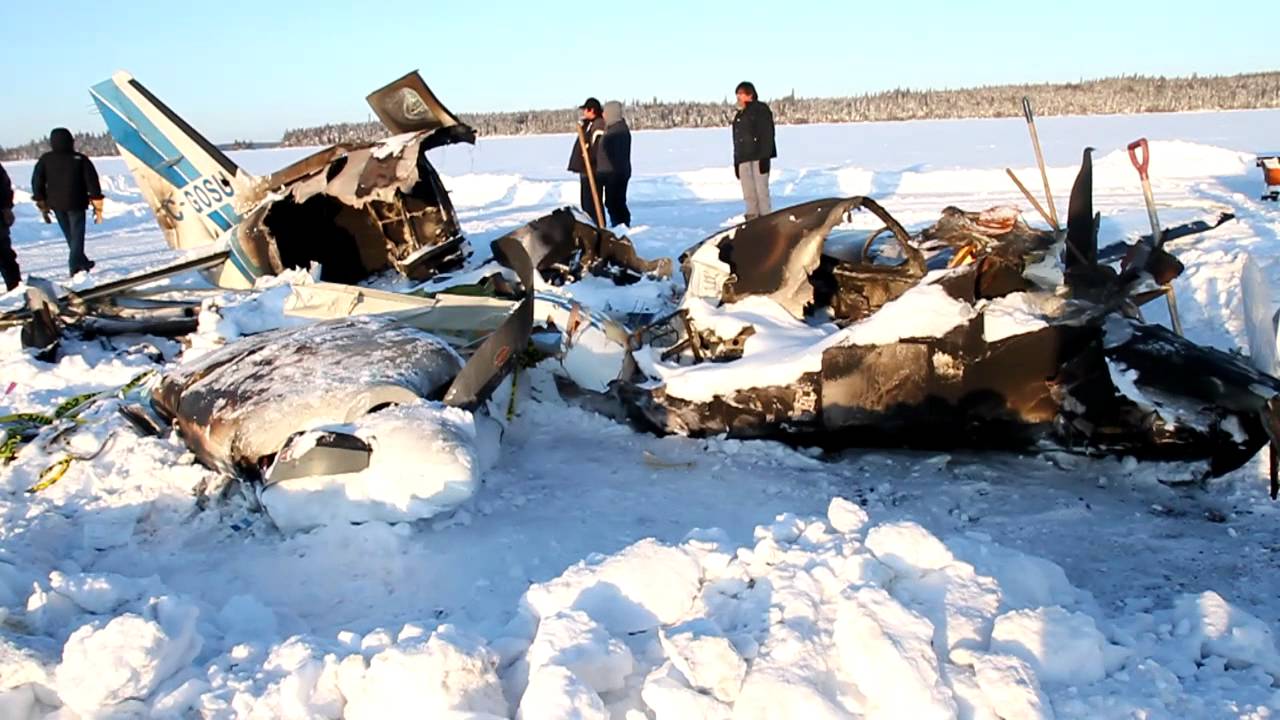
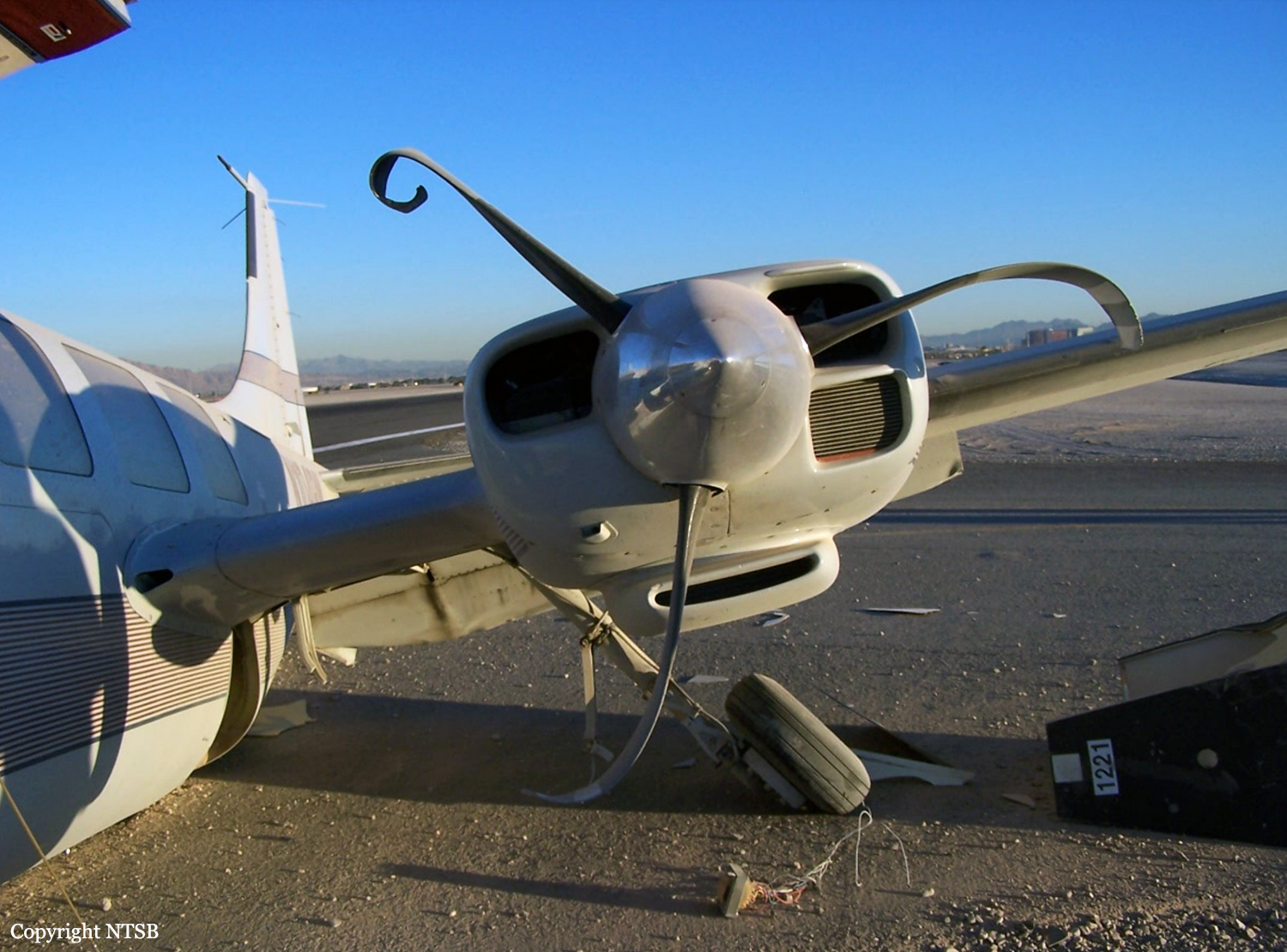
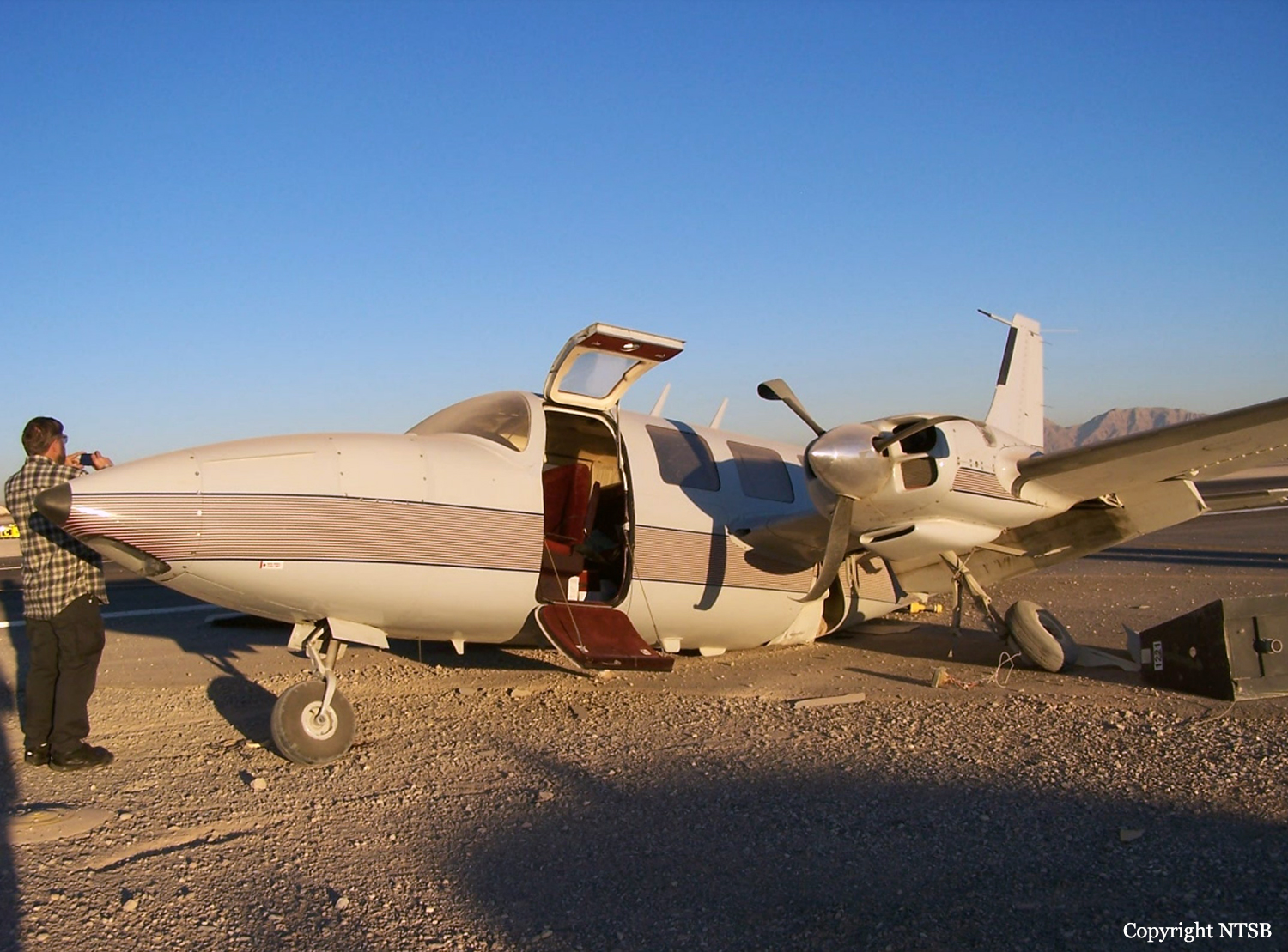
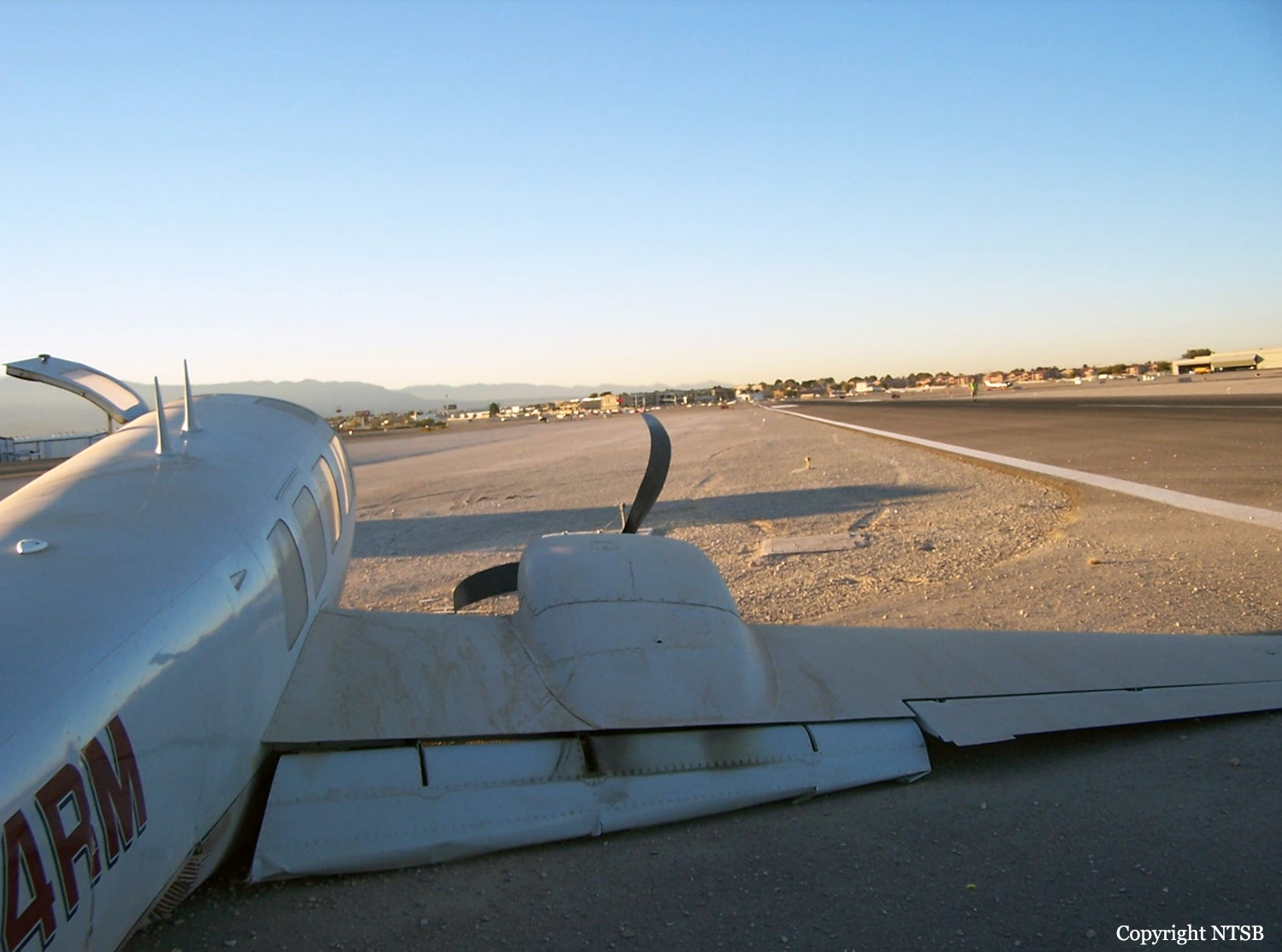
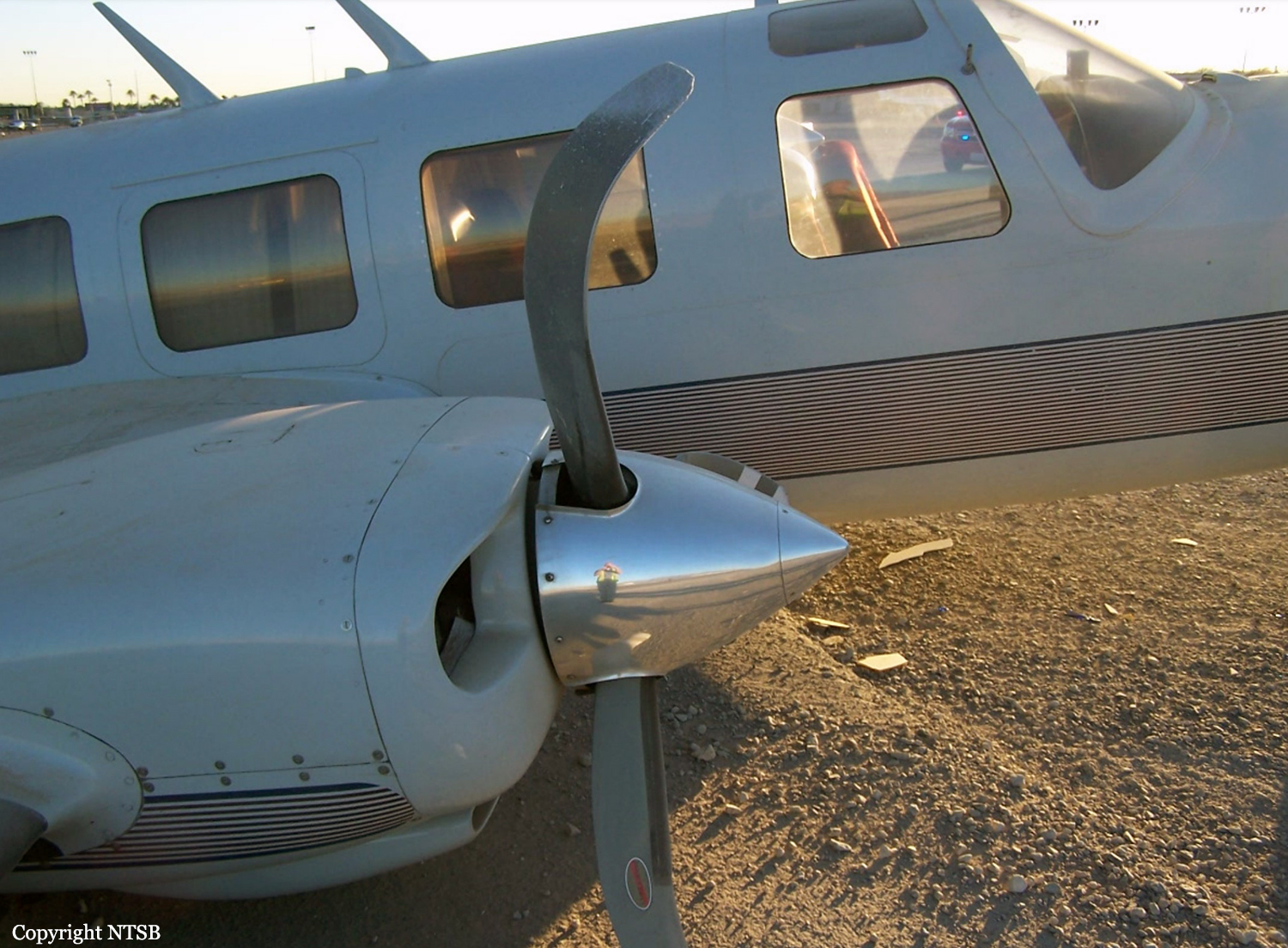
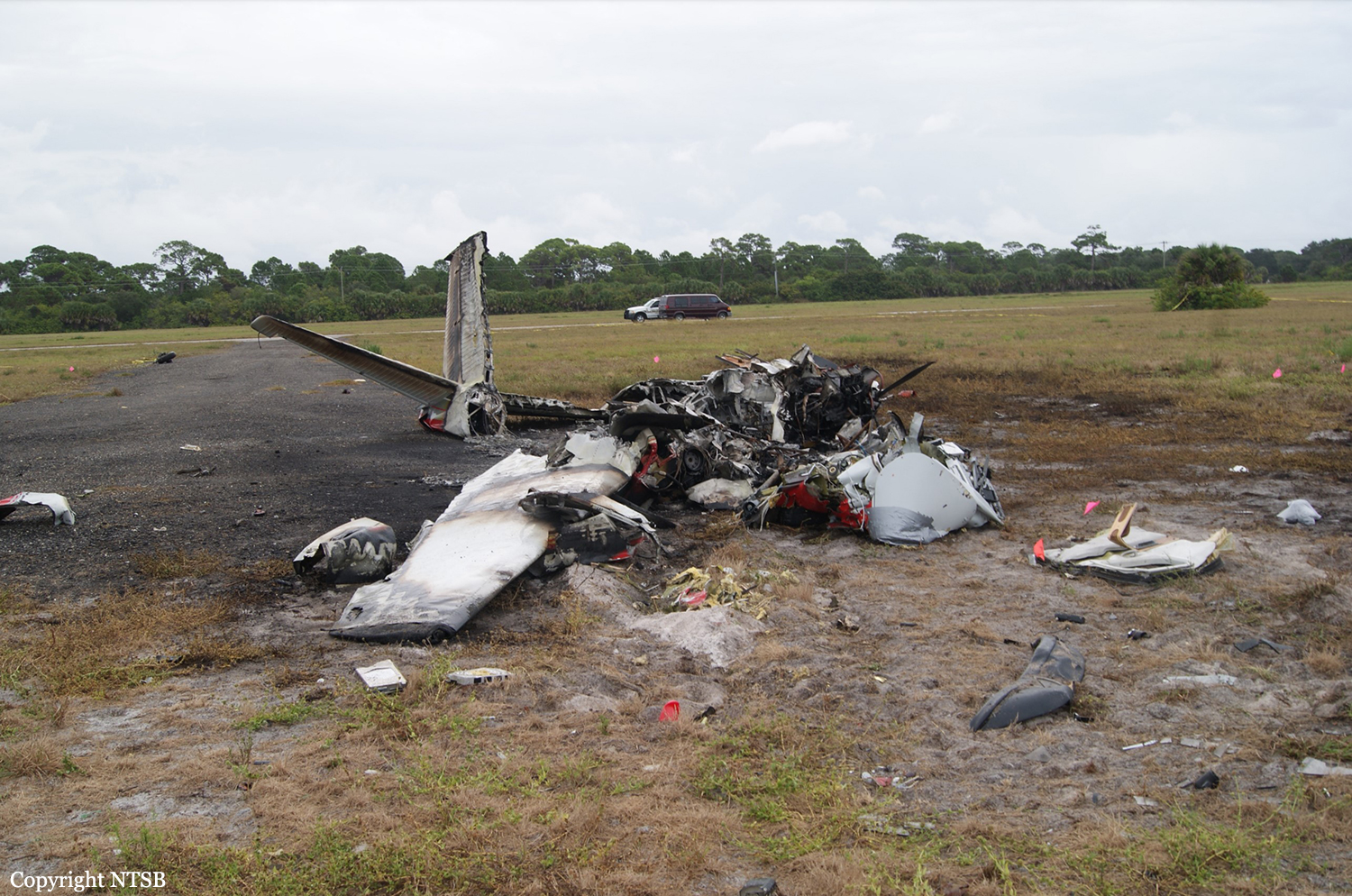
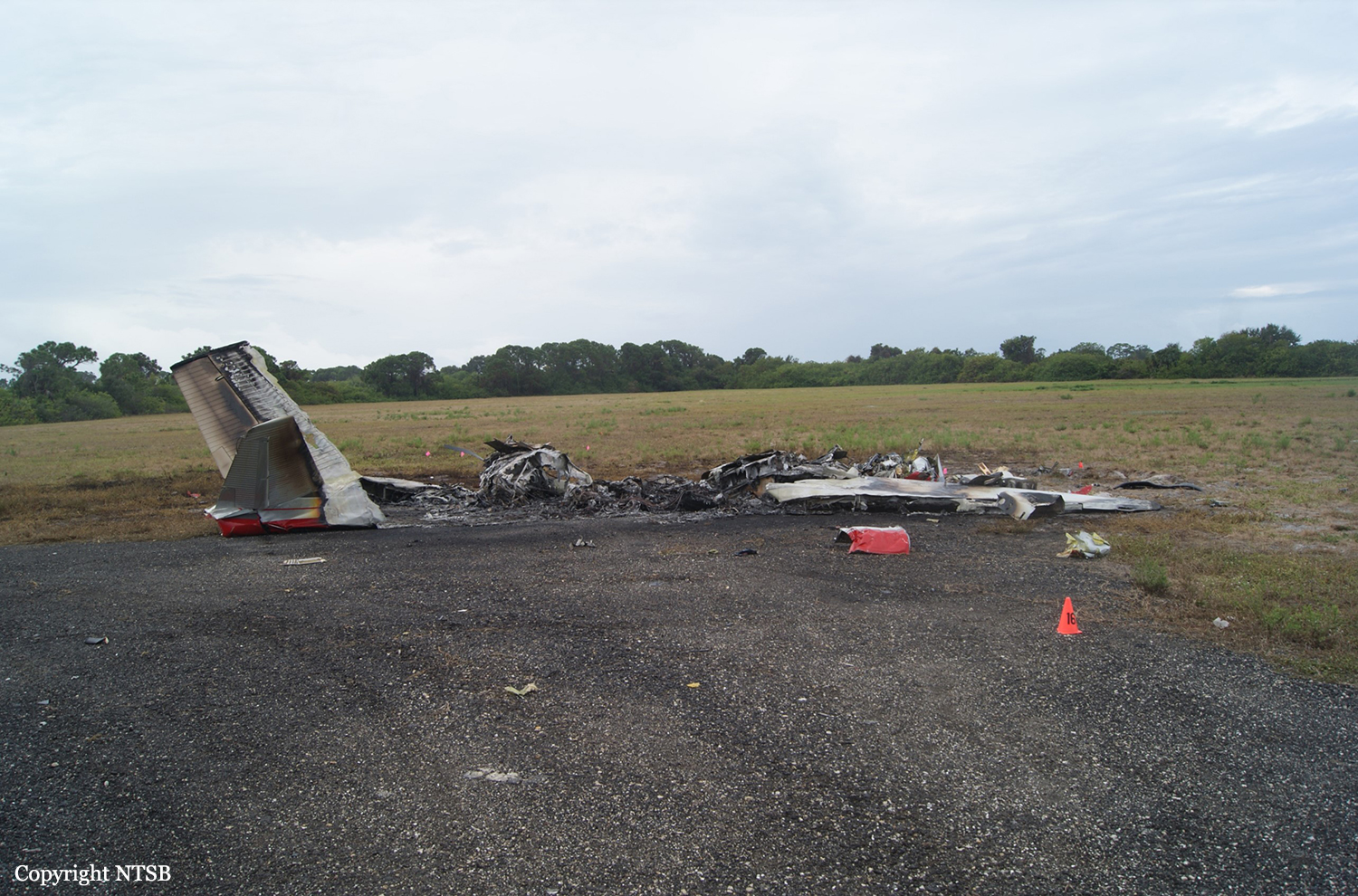
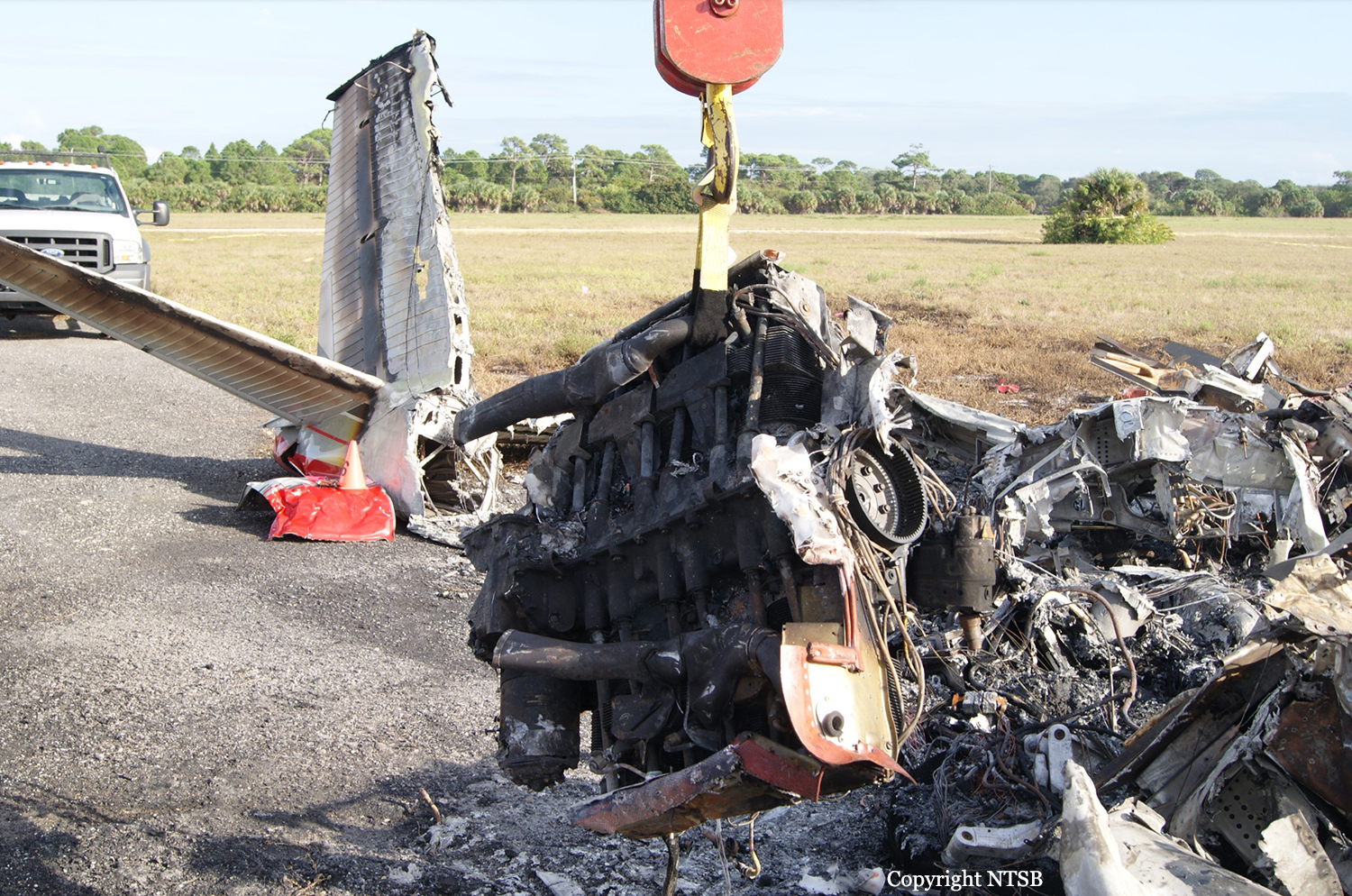
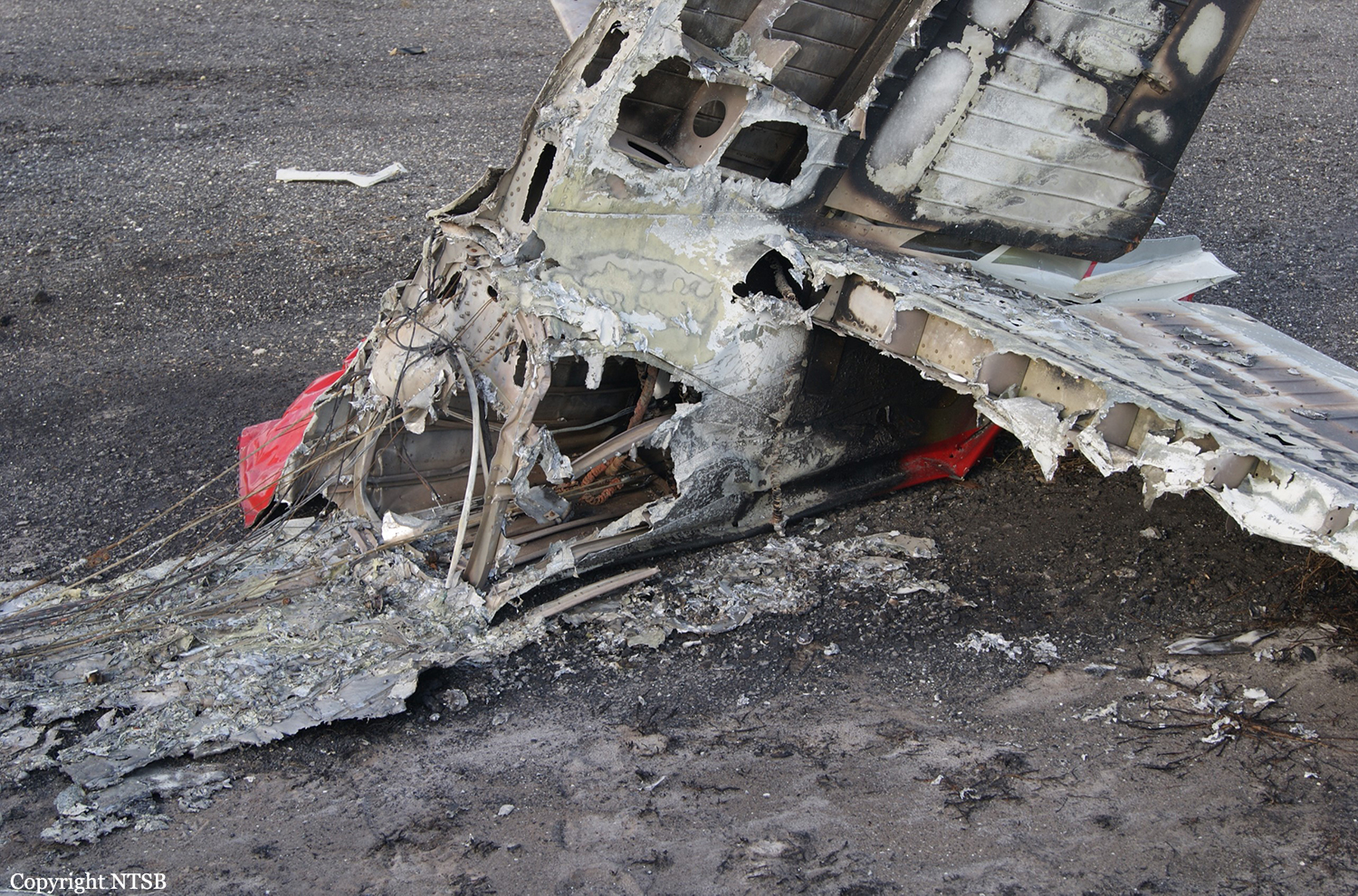
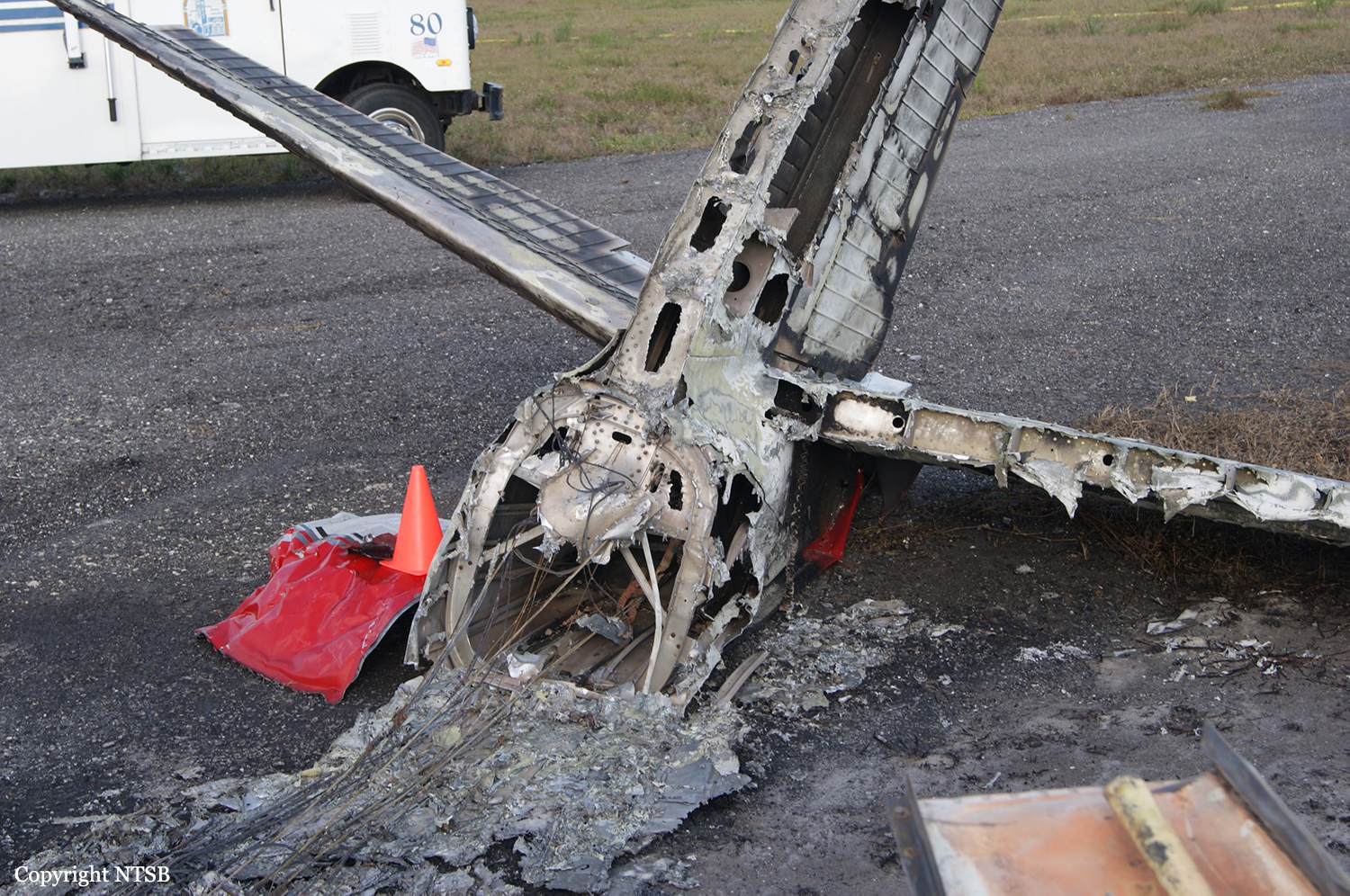
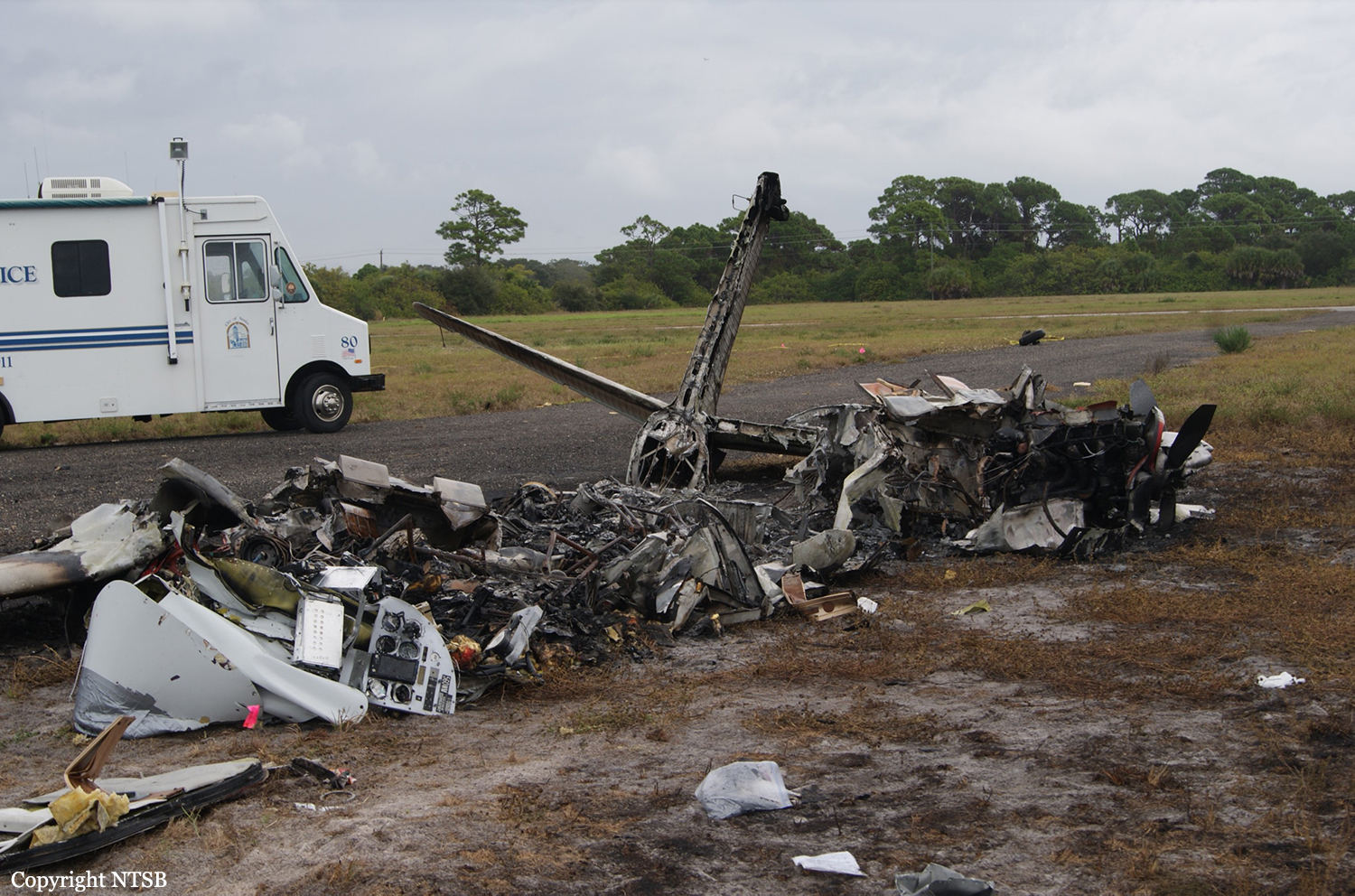
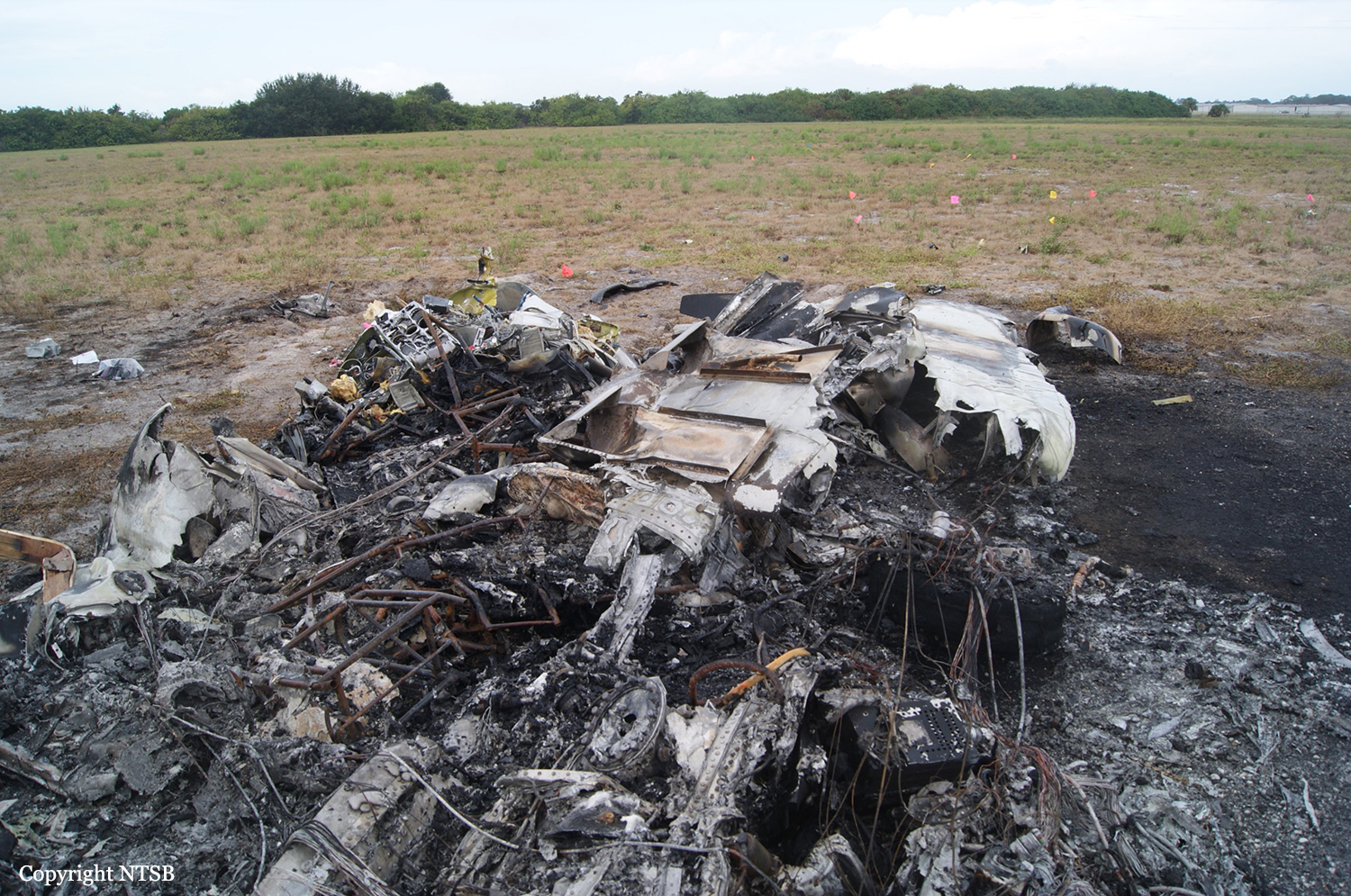
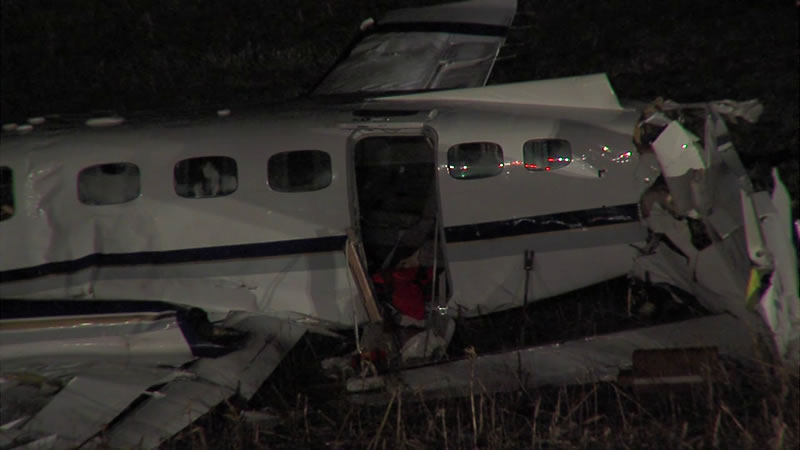
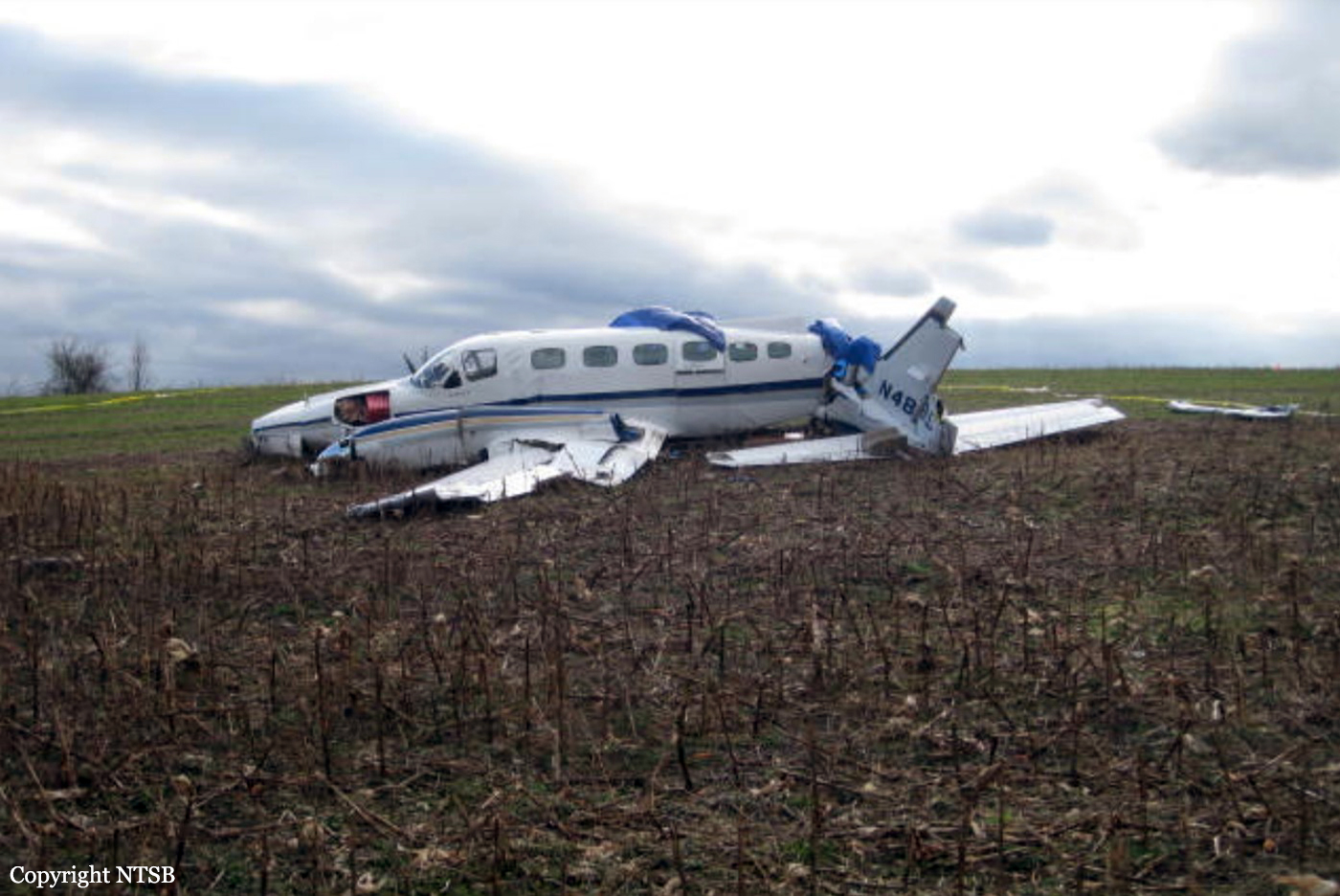
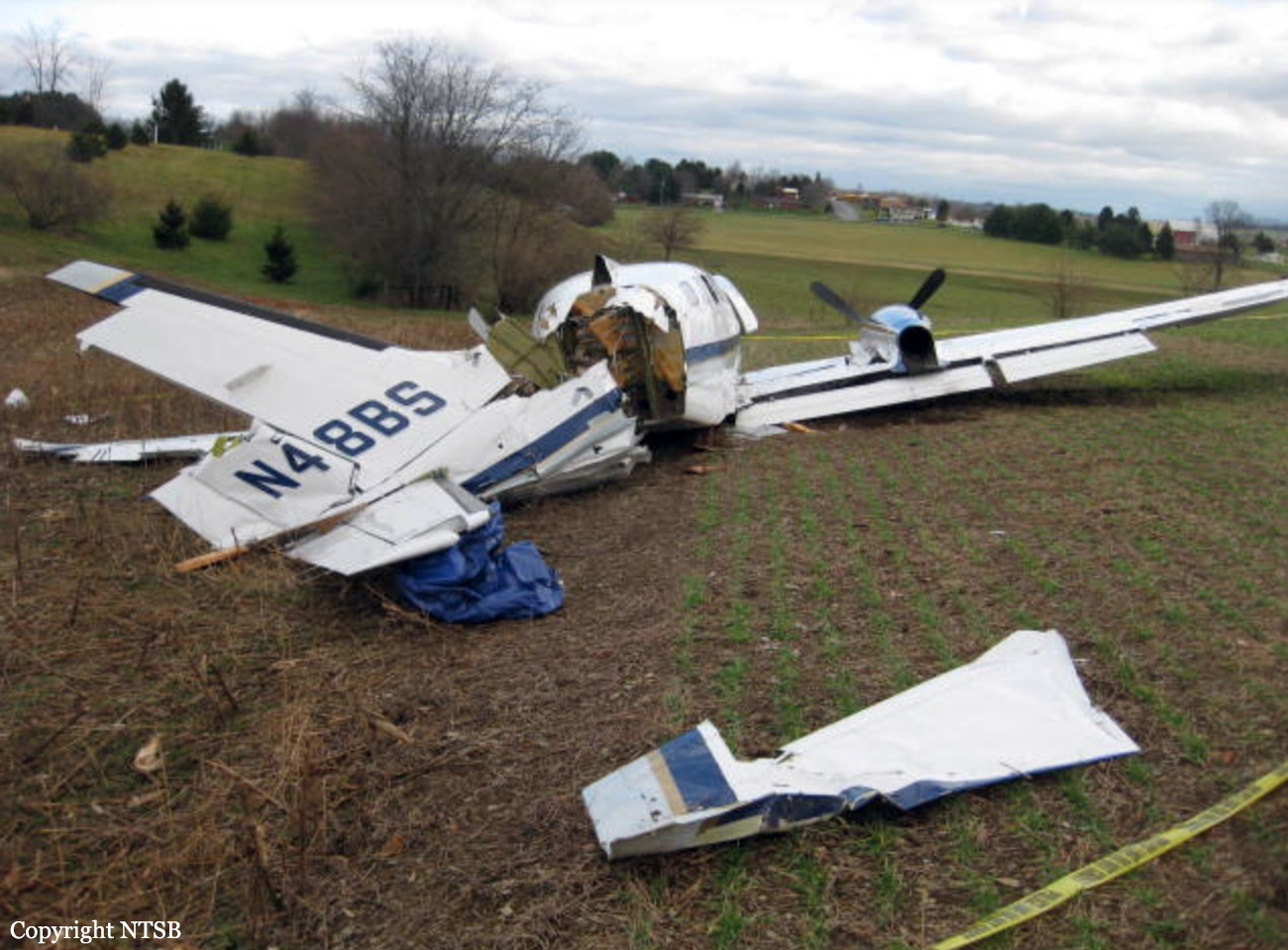
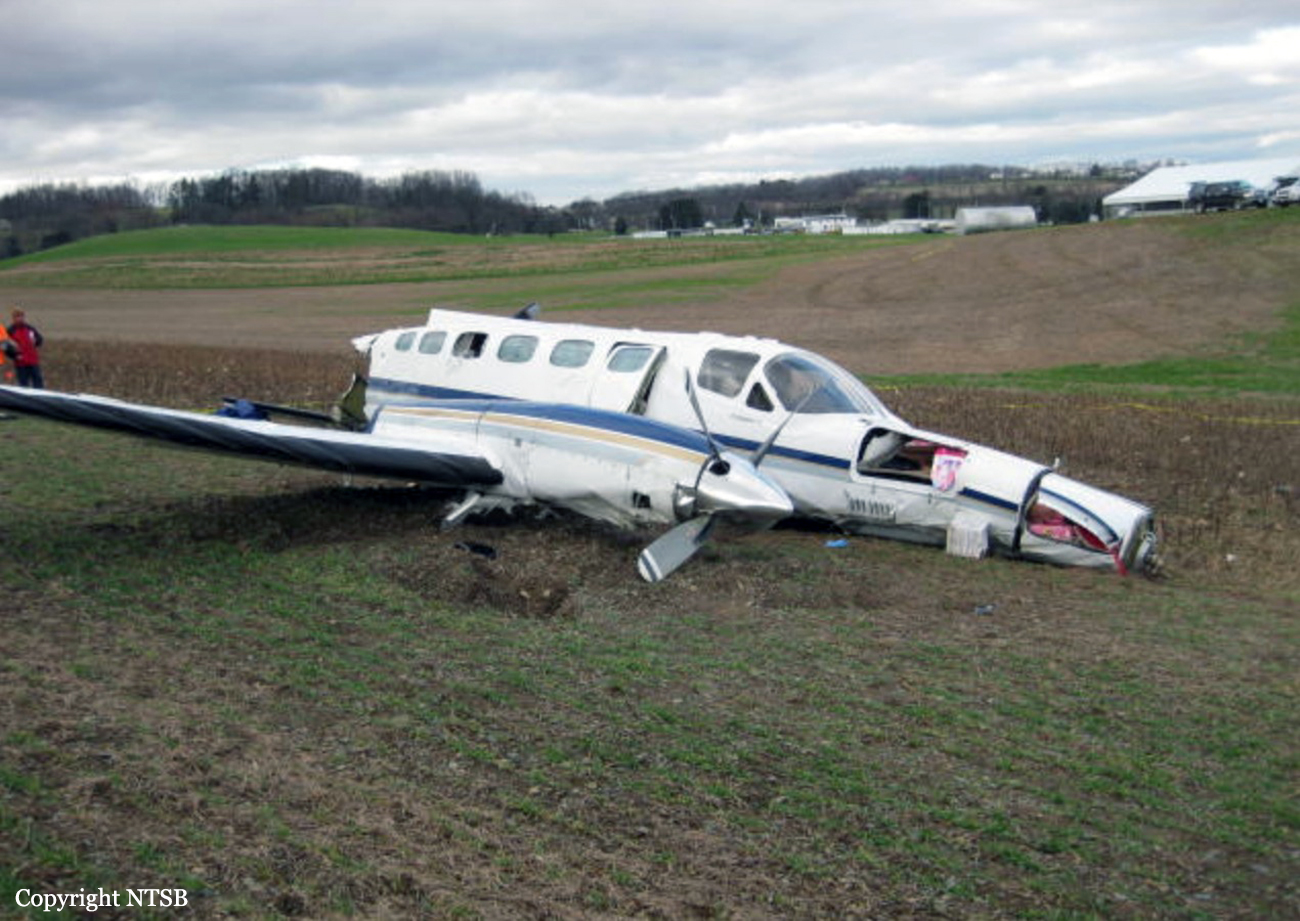
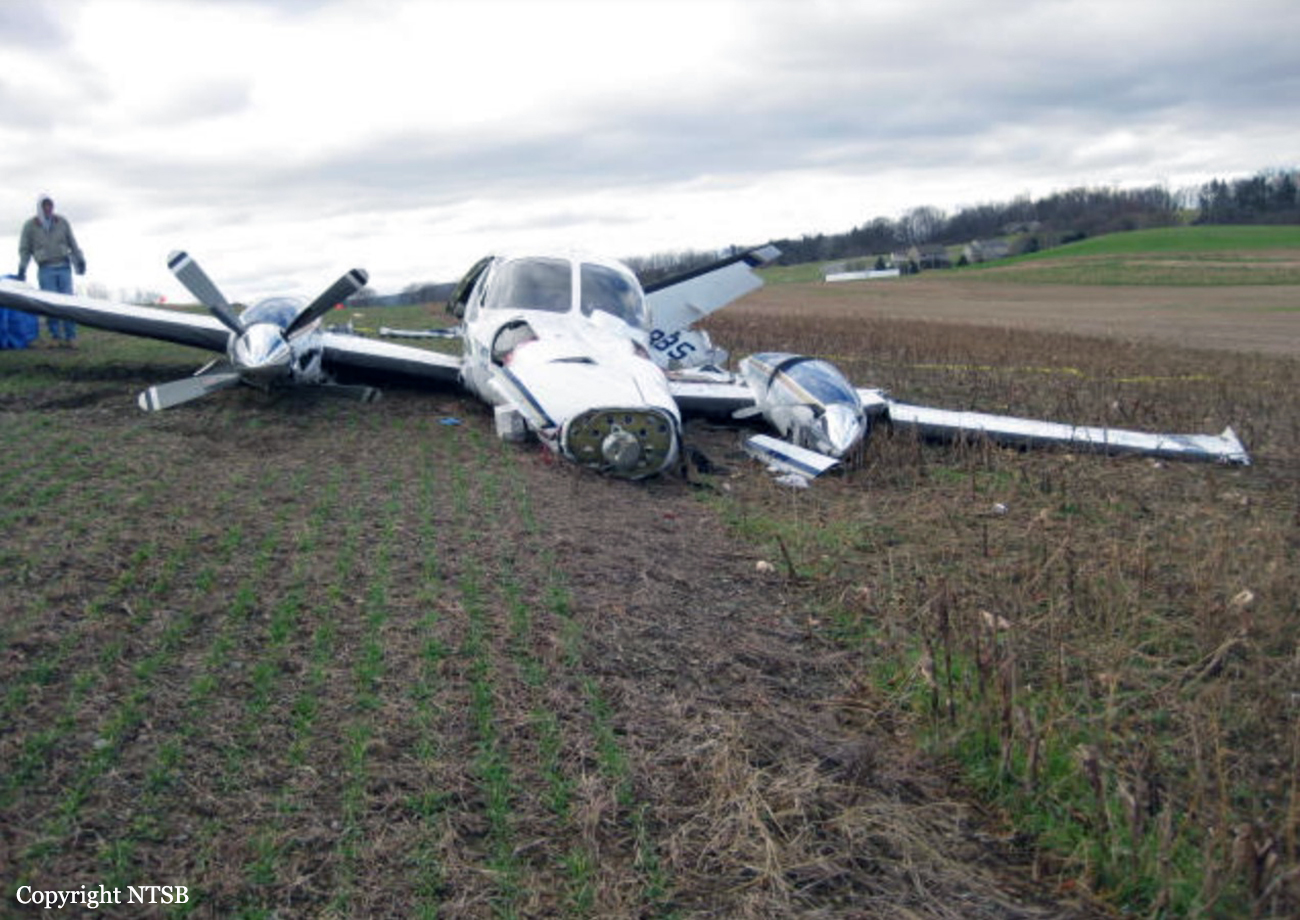
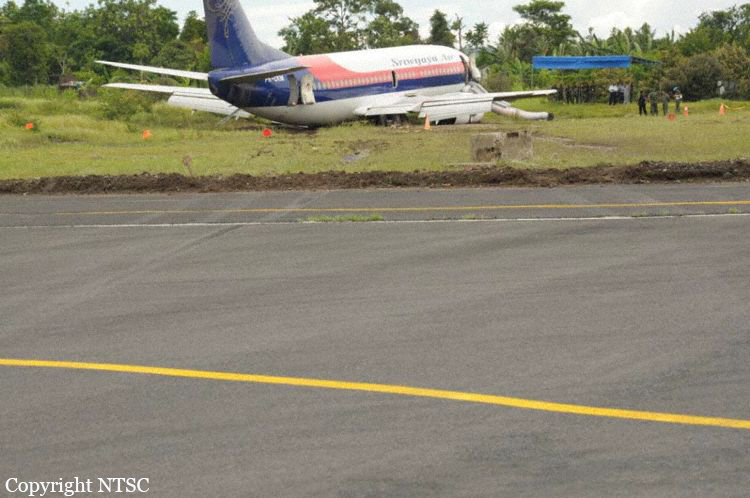
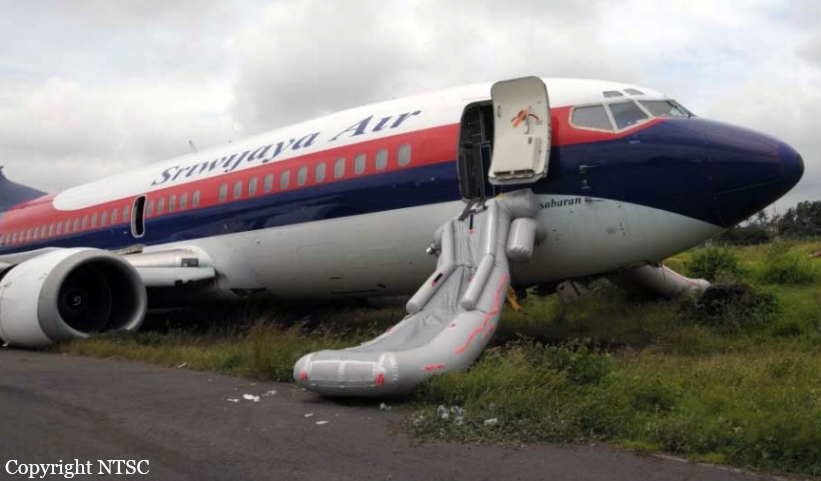
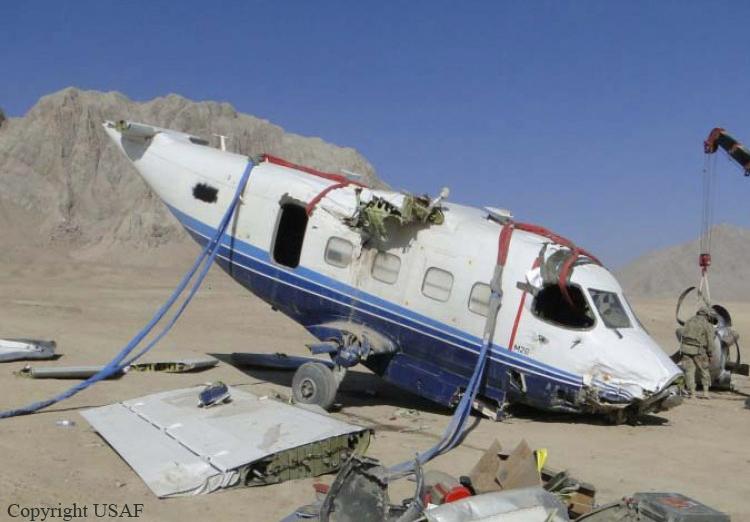
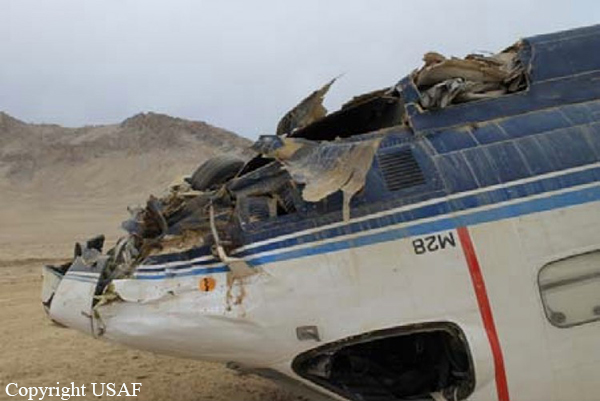
The Piper PA31-350 Navajo Chieftain (registration C-GOSU, serial number 31-7752148), operating as Keystone Air Service Limited Flight 213, departed Winnipeg/James Armstrong Richardson International Airport, Manitoba, enroute to North Spirit Lake, Ontario, with 1 pilot and 4 passengers on board. At 0957 Central Standard Time, on approach to Runway 13 at North Spirit Lake, the aircraft struck the frozen lake surface 1.1 nautical miles from the threshold of Runway 13. The pilot and 3 passengers sustained fatal injuries. One passenger sustained serious injuries. The aircraft was destroyed by impact forces and a post-impact fire. After a short period of operation, the emergency locator transmitter stopped transmitting when the antenna wire was consumed by the fire.
Probable cause:
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
1. The pilot's decision to conduct an approach to an aerodrome not serviced by an instrument flight rules approach in adverse weather conditions was likely the result of the pilot's inexperience, and may have been influenced by the pilot's desire to successfully complete the flight.
2. The pilot's decision to descend into cloud and continue in icing conditions was likely the result of inadequate awareness of the Piper PA31-350 aircraft's performance in icing conditions and of its de-icing capabilities.
3. While waiting for the runway to be cleared of snow, the aircraft held near North Spirit Lake (CKQ3) in icing conditions. The resulting ice accumulation on the aircraft's critical surfaces would have led to an increase in the aircraft's aerodynamic drag and stall speed, causing the aircraft to stall during final approach at an altitude from which recovery was not possible.
Findings as to risk:
1. Terminology contained in aircraft flight manuals and regulatory material regarding “known icing conditions,” “light to moderate icing conditions,” “flight in,” and “flight into” is inconsistent, and this inconsistency increases the risk of confusion as to the aircraft’s certification and capability in icing conditions.
2. If confusion and uncertainty exist as to the aircraft’s certification and capability in icing conditions, then there is increased risk that flights will dispatch into icing conditions that exceed the capability of the aircraft.
3. The lack of procedures and tools to assist pilots in the decision to self-dispatch leaves them at increased risk of dispatching into conditions beyond the capability of the aircraft.
4. When management involvement in the dispatch process results in pilots feeling pressure to complete flights in challenging conditions, there is increased risk that pilots may attempt flights beyond their competence.
5. Under current regulations, Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs) 703 and 704 operators are not required to provide training in crew resource management / pilot decision-making or threat- and error-management. A breakdown in crew resource management / pilot decision-making may result in an increased risk when pilots are faced with adverse weather conditions.
6. Descending below the area minimum altitude while in instrument meteorological conditions without a published approach procedure increases the risk of collision with terrain.
7. If onboard flight recorders are not available to an investigation, this unavailability may preclude the identification and communication of safety deficiencies to advance transportation safety.
1. The pilot's decision to conduct an approach to an aerodrome not serviced by an instrument flight rules approach in adverse weather conditions was likely the result of the pilot's inexperience, and may have been influenced by the pilot's desire to successfully complete the flight.
2. The pilot's decision to descend into cloud and continue in icing conditions was likely the result of inadequate awareness of the Piper PA31-350 aircraft's performance in icing conditions and of its de-icing capabilities.
3. While waiting for the runway to be cleared of snow, the aircraft held near North Spirit Lake (CKQ3) in icing conditions. The resulting ice accumulation on the aircraft's critical surfaces would have led to an increase in the aircraft's aerodynamic drag and stall speed, causing the aircraft to stall during final approach at an altitude from which recovery was not possible.
Findings as to risk:
1. Terminology contained in aircraft flight manuals and regulatory material regarding “known icing conditions,” “light to moderate icing conditions,” “flight in,” and “flight into” is inconsistent, and this inconsistency increases the risk of confusion as to the aircraft’s certification and capability in icing conditions.
2. If confusion and uncertainty exist as to the aircraft’s certification and capability in icing conditions, then there is increased risk that flights will dispatch into icing conditions that exceed the capability of the aircraft.
3. The lack of procedures and tools to assist pilots in the decision to self-dispatch leaves them at increased risk of dispatching into conditions beyond the capability of the aircraft.
4. When management involvement in the dispatch process results in pilots feeling pressure to complete flights in challenging conditions, there is increased risk that pilots may attempt flights beyond their competence.
5. Under current regulations, Canadian Aviation Regulations (CARs) 703 and 704 operators are not required to provide training in crew resource management / pilot decision-making or threat- and error-management. A breakdown in crew resource management / pilot decision-making may result in an increased risk when pilots are faced with adverse weather conditions.
6. Descending below the area minimum altitude while in instrument meteorological conditions without a published approach procedure increases the risk of collision with terrain.
7. If onboard flight recorders are not available to an investigation, this unavailability may preclude the identification and communication of safety deficiencies to advance transportation safety.
Final Report: