Circumstances:
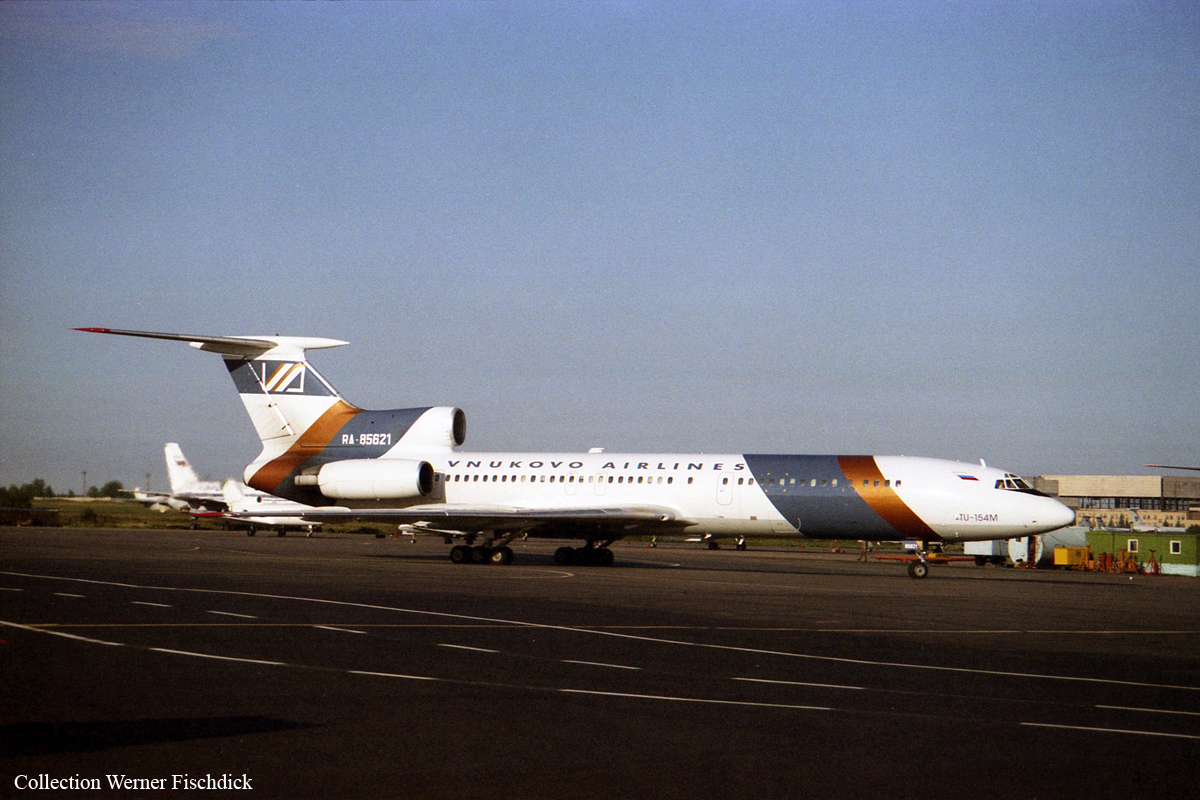
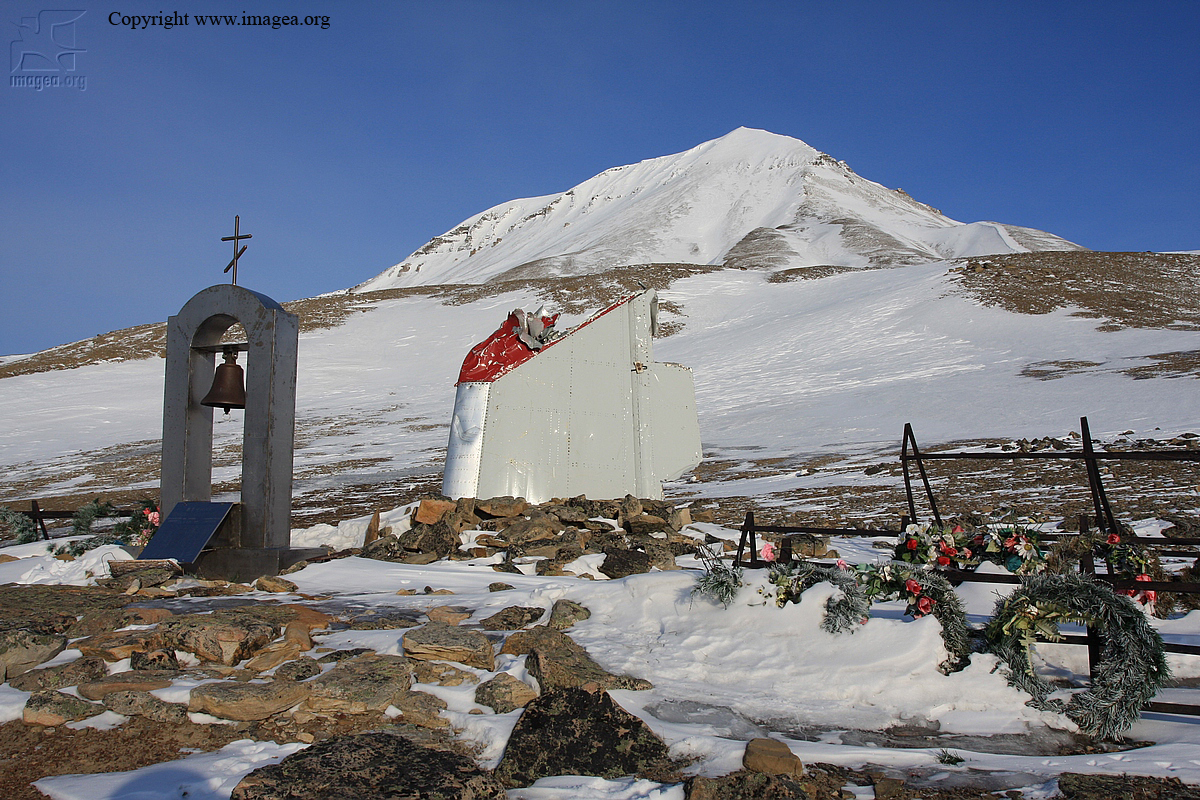
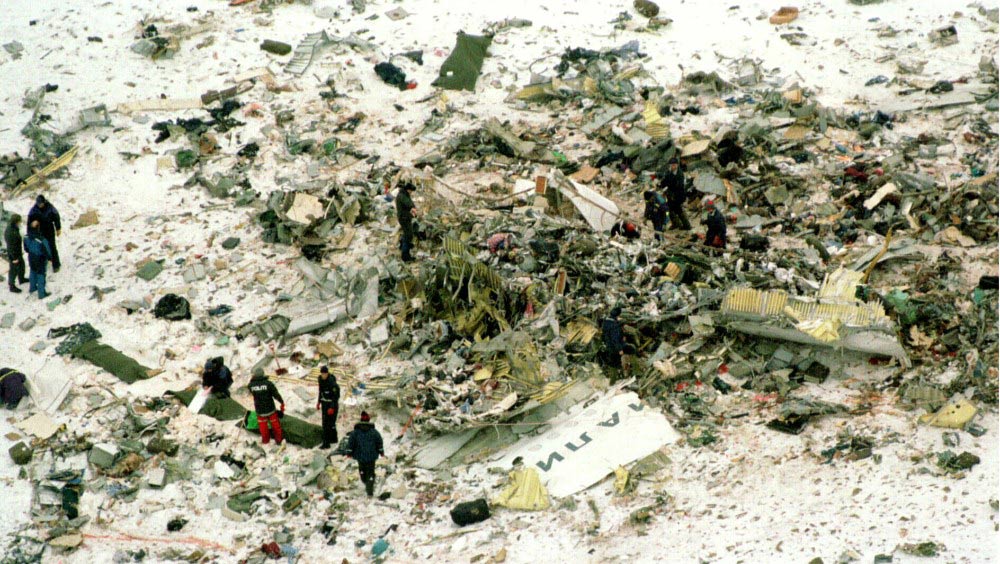
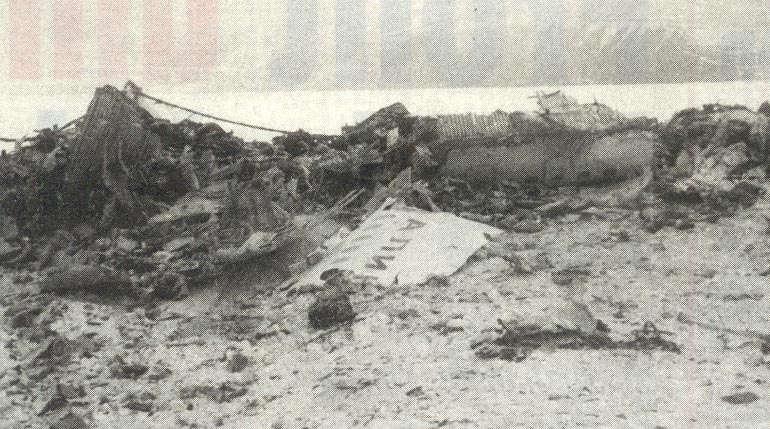
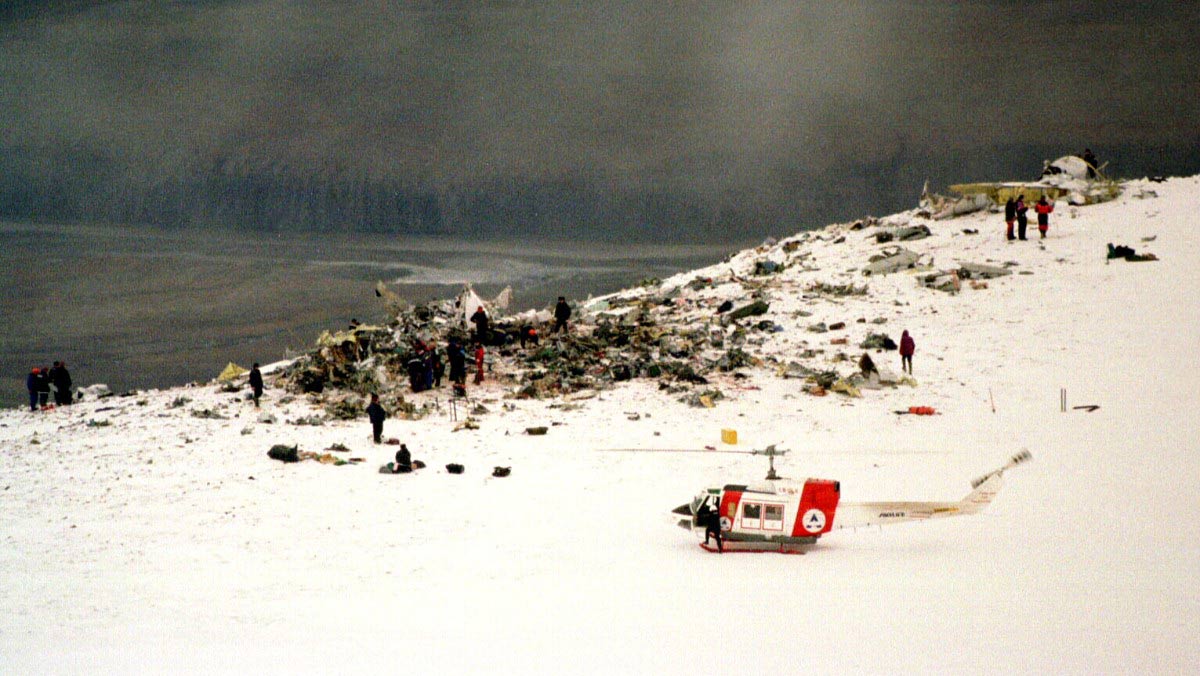
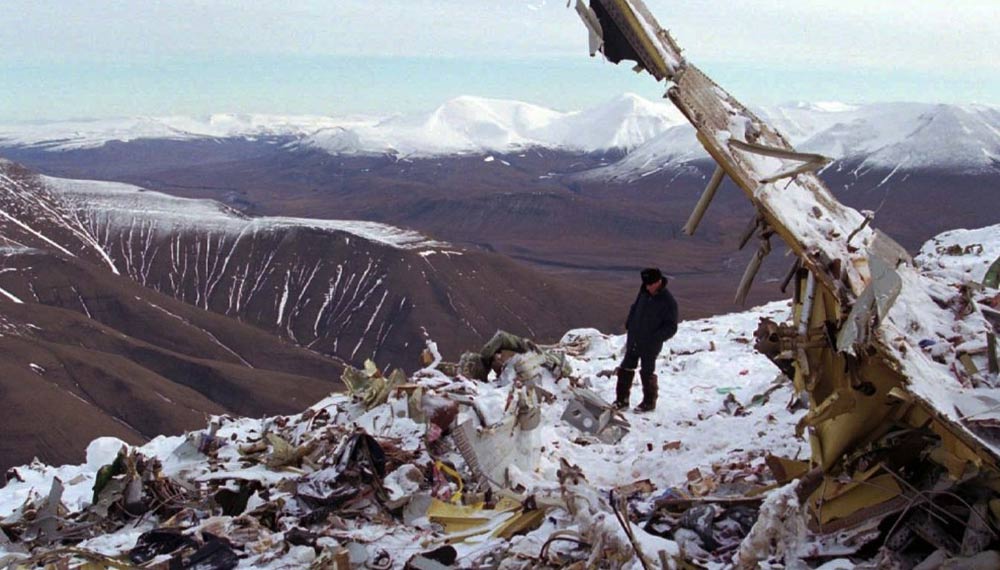
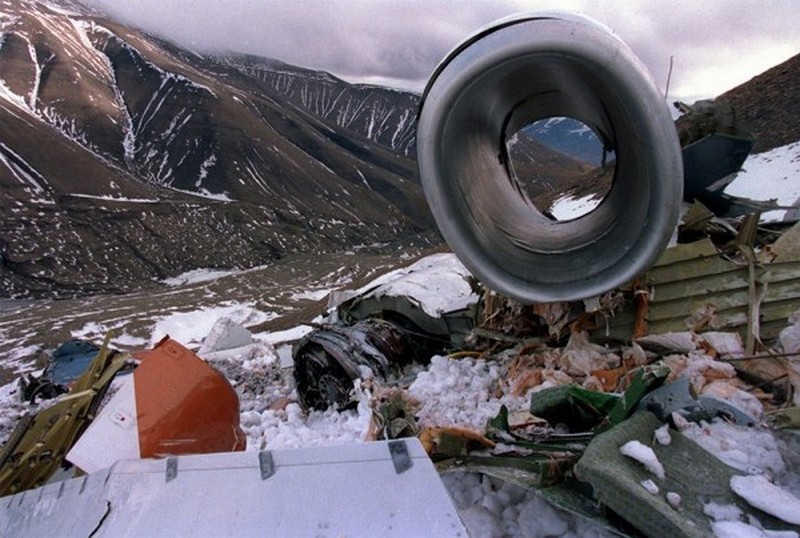
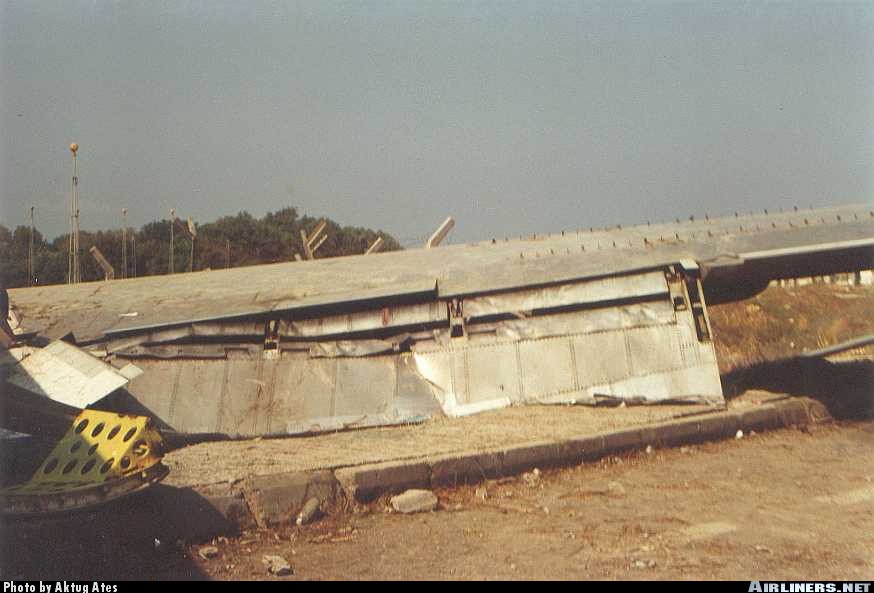
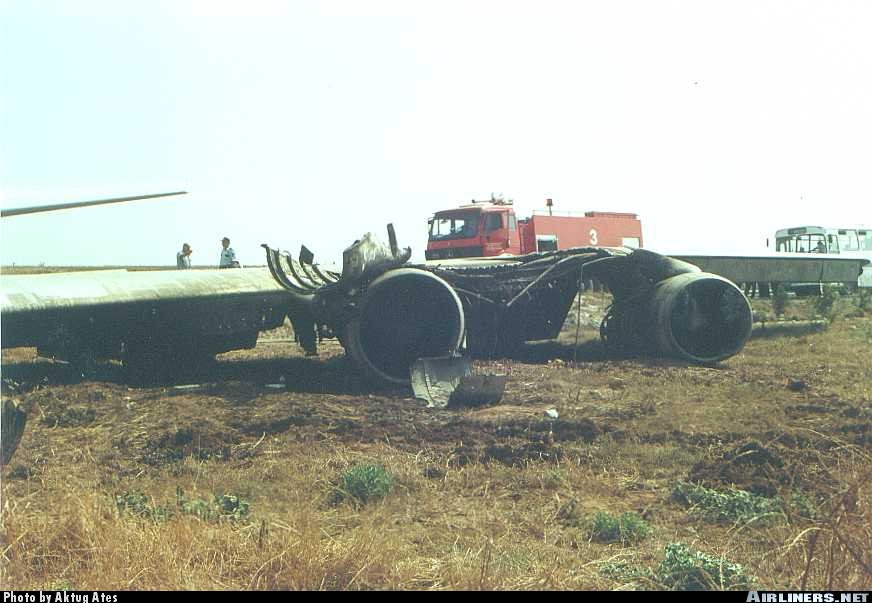
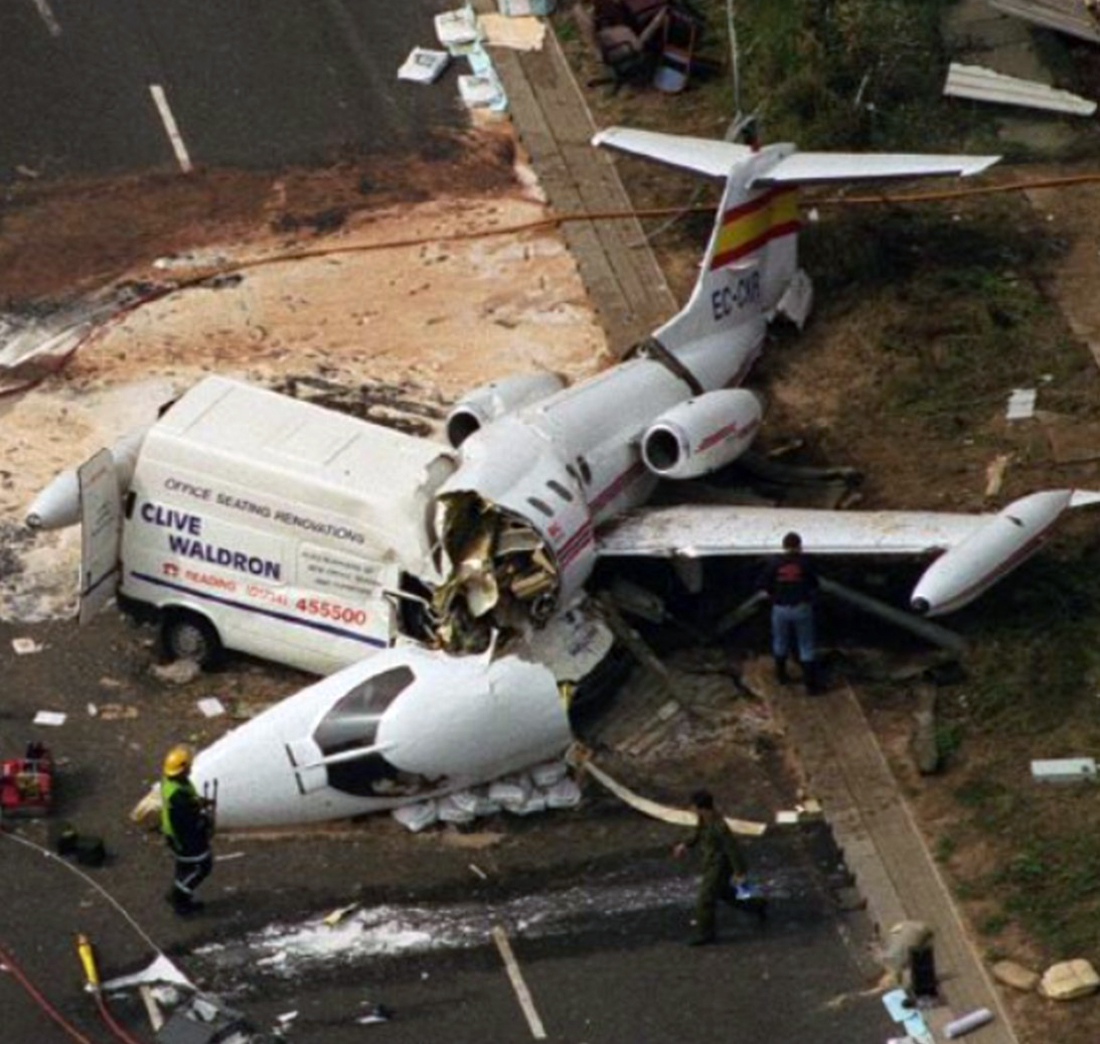
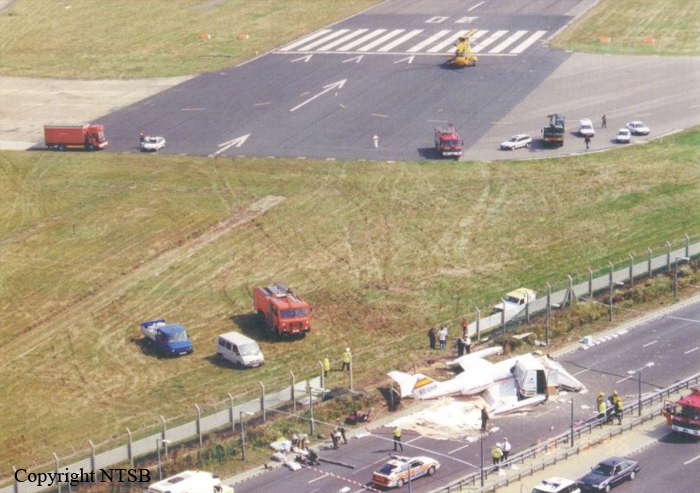
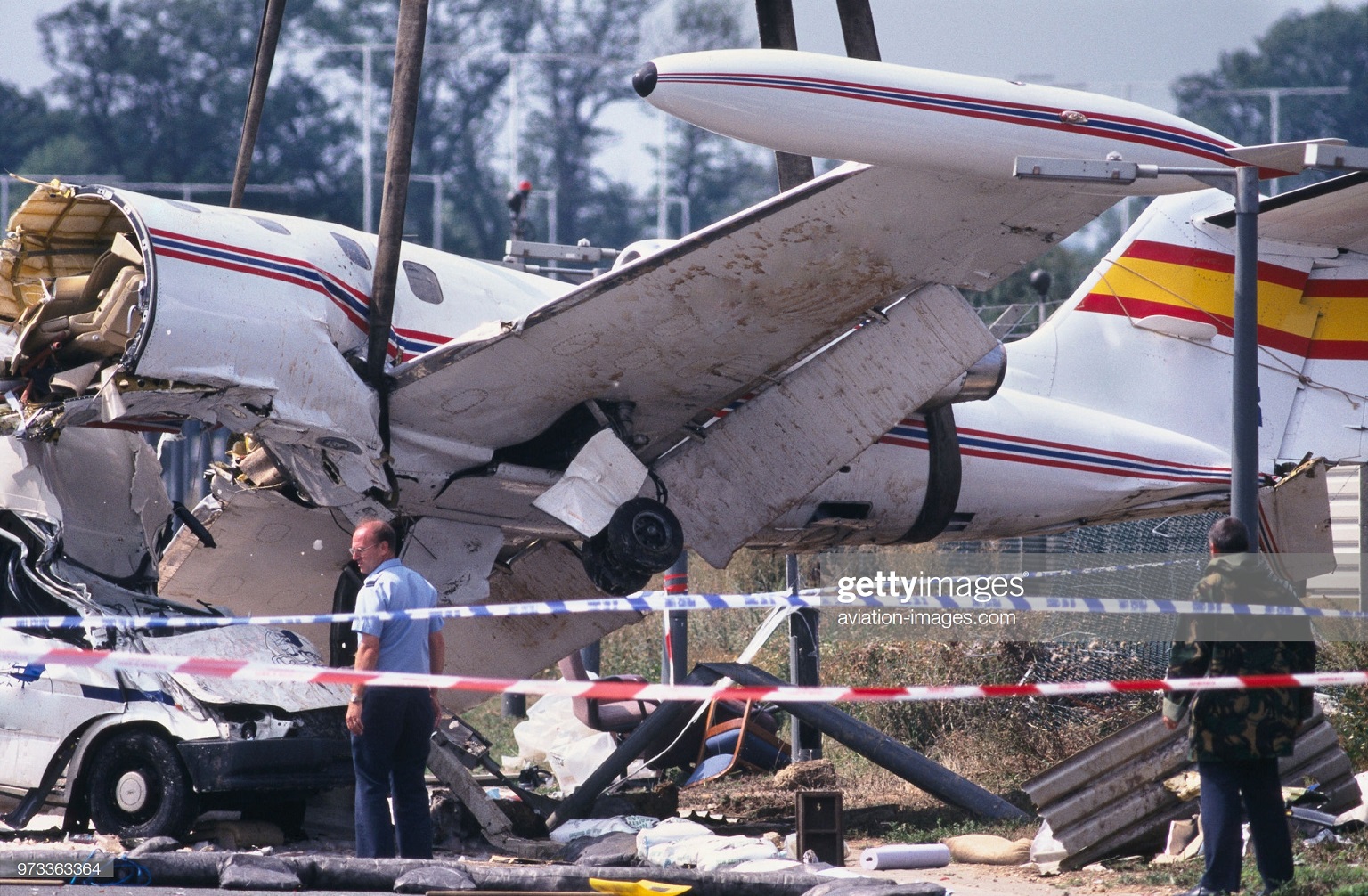
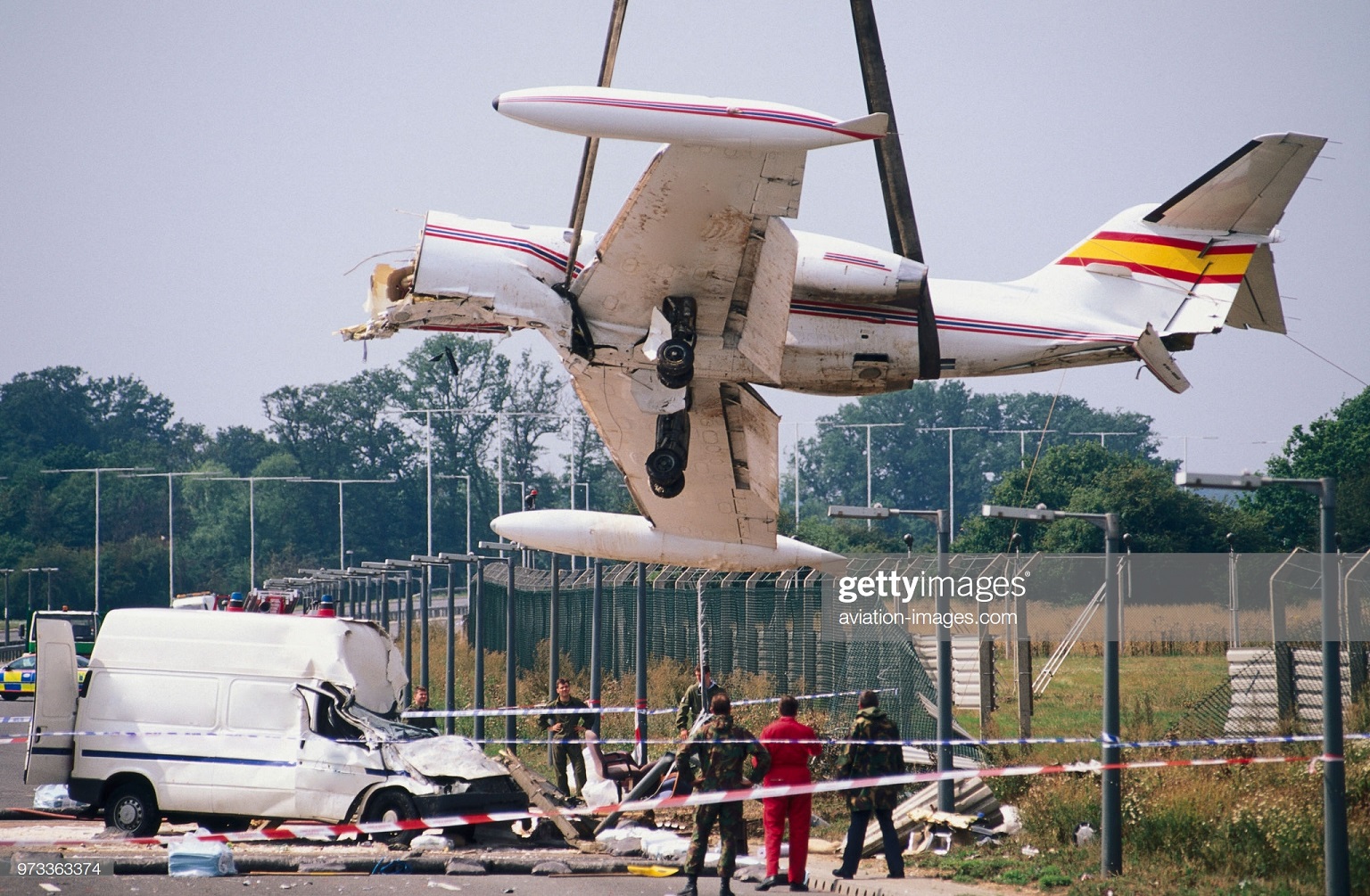
Vnukovo Airlines flight VKO2801 departed Moscow-Vnukovo Airport at 04:44 UTC bound for Longyearbyen Airport on the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard. It was a chartered flight with workers and their families to coal mining towns on Svalbard. The flight was uneventful until the start of the descent. Before radio contact with Longyear Information, the crew went through the detailed landing procedure for runway 10. At 09:56, the crew were cleared to start the descent. A little later, the crew received additional information consisting of runway in use 28, wind 230 degrees at 16 knots, visibility more than 10 km, rain showers, clouds: few at 1500 feet, scattered at 2000 feet and broken at 4000 feet, temperature +5°C, dewpoint -0°C and QNH 1005 hPa. (Later changed to 1006 hPa). The crew tried to request runway 10 for landing twice, but the request was not understood as such by Longyear Information due to language difficulties. When the flight was overhead the ADV beacon, at 10:15 hrs, the crew reported their position to Longyear Information and entered the base turn with a bank angle of 22 degrees. At 10:16 hrs, the aircraft came out of this turn on magnetic heading 160 degrees. During the right turn to the base turn, a malfunction occurred in the electric trimming mechanism, which was corrected by the crew. At 10:17, the crew started the turn to bring the aircraft out on the magnetic inbound course 300 degrees, as prescribed by the approach chart. The distance from the airport at this moment was 14 NM (25.9 km), as prescribed by the approach chart, but the lateral deviation from the outbound magnetic course 155 degrees from ADV was 2 NM (3.7 km) to the left. At 10:18, after the radio altimeter aural warning had been activated twice, the co-pilot took the controls and, after 6 seconds, turned the autopilot pitch channel off by 'overriding' it. From then on until the impact, the flight continued in autopilot mode in the roll channel, and in manual mode in the pitch channel. The aircraft passed through the localizer centerline and when the turn had been completed, the aircraft rolled out on a magnetic heading of 290 degrees. At this time, there was a discussion within the crew as to whether or not the final turn had been made at the correct time. The discussion led to the roll out of the turn to final approach and a corrective turn to the right to magnetic heading 306 degrees. At this point, the aircraft was 14.7 NM (27.4 km) from the airport, 2.8 km to the right of the approach centerline, maintaining an altitude of 5000 feet (1520 m ) and the crew increased the flap setting to 28 degrees. The airspeed was reduced to approx. 330 km/hr (180 kts). Instead of intercepting the centerline, the crew continued the flight on the right side, more or less paralleling the localizer course with minor heading changes. At 10:20 the flight made a corrective turn, resulting in a track close to 300 degrees. At this point, the lateral deviation from the approach centerline was 3.7 km to the right. During this corrective turn, the aircraft started descending. At 10:21, the crew made yet another corrective turn to the right. At 10:22:05, the aircraft started turning towards the left. The distance to the airport was 8 NM (14.8 km). On this part of the final approach, the aircraft apparently entered an area of strong turbulence created by the proximity to the mountains. The GPWS then activated 9 seconds before impact. The crew reacted to this by applying power and initiating a pitch-up. At 10:22:23, 7.7 NM (14.2 km) from the airport at an altitude of 2975 feet (907 m), the aircraft collided with the top of the mountain Operafjellet 3.7 km to the right of the approach centerline. All 141 occupants were killed, most of them employees of a local carbon mine and their family members.
Probable cause:
The following findings were reported:
1) There is no Russian procedure for offset localizer approaches modifying the required rule to set the landing course on the HSI.
2) The course selected on both HSIs was 283° even though the approach course is 300°. This setting does not affect the indication of the CDI. However, the CDI was pointing to 283° on the dial, which is 17° to the left of the approach course, giving a visual impression of wind drift to the left and therefore giving a possible reason for a heading correction to the right.
3) The navigator in a stressed and overloaded working situation most probably followed the rule setting the landing course 283° on the GPS in OBS mode instead of the approach course 300°.
4) The crew was not fully aware of the status of an AFIS officer in comparison with the authority of a Russian air traffic controller with the result that the crew accepted safety information from the AFIS officer as orders.
5) The crew had limited knowledge of the English language with the consequence that they had problems communicating their intentions to the AFIS officer.
6) The navigator was overloaded with tasks leaving little time for rechecking his work, thereby setting the scene for making mistakes.
7) The pilots did not monitor the work of the navigator sufficiently.
8) Leaving the communication with AFIS to the navigator during the approach was not according to the normative documents.
9) Due to the workload of the navigator, the decision of the co-pilot to transfer the responsibility of controlling the aircraft laterally to him, was inappropriate.
10) The crew resource management of the PIC was not satisfactory.
11) When the crew had made the decision to carry out the approach to runway 28, a new approach briefing was not accomplished.
12) The crew made the proper correction for the wind drift, but did not try to intercept the outbound track from ADV with the consequence that they overshot the approach centerline turning inbound.
13) Seemingly confusing indications on the HSIs in the base turn caused the crew to become uncertain of the aircraft position in relation to the LLZ 28 centerline. In this situation, the crew showed a lack of situational awareness.
14) The two pilots did not have the approach chart in front of them at all times during the approach making it difficult for them to maintain situational awareness.
15) The crew did not know of the possibility to check the position of the aircraft in relation to the localizer centerline by the VDF service available.
16) On final approach the crew probably put too much emphasis on the indications displayed on the GPS.
17) The crew started descent in a mountainous area without firm and positive control of the lateral navigation demonstrated by the disagreement within the crew as to whether to correct to the left or right.
18) In spite of the uncertainty within the crew as to whether they were approaching correctly or not, they continued instead of abandoning the approach and climbing to a safe altitude to solve the problem.