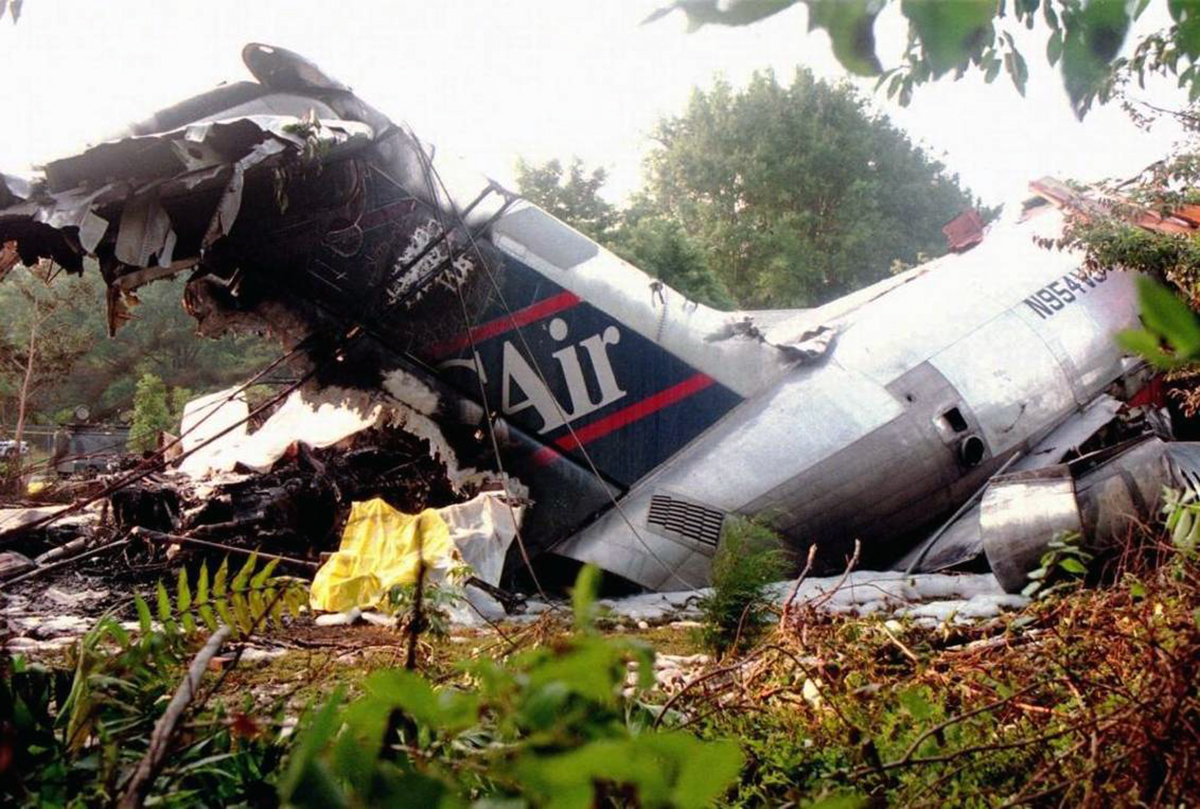
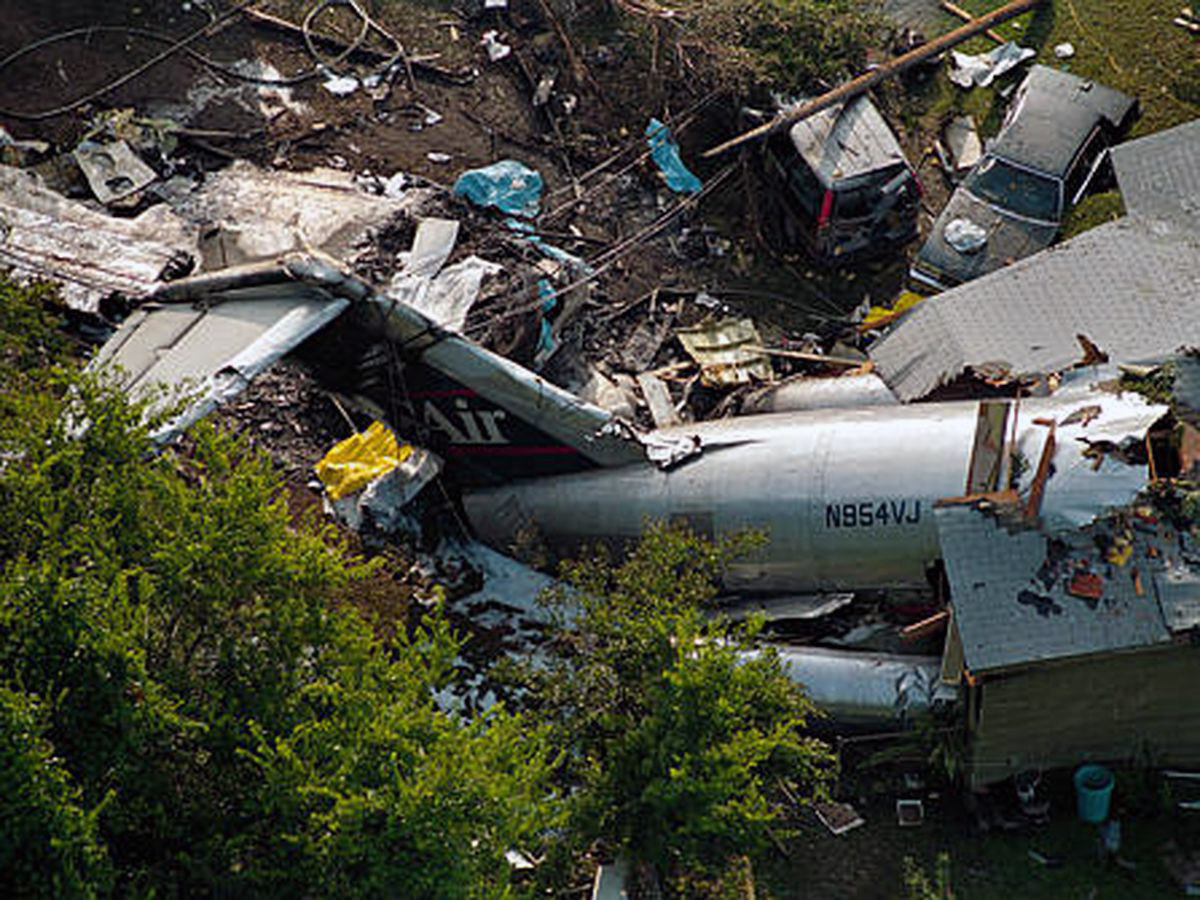
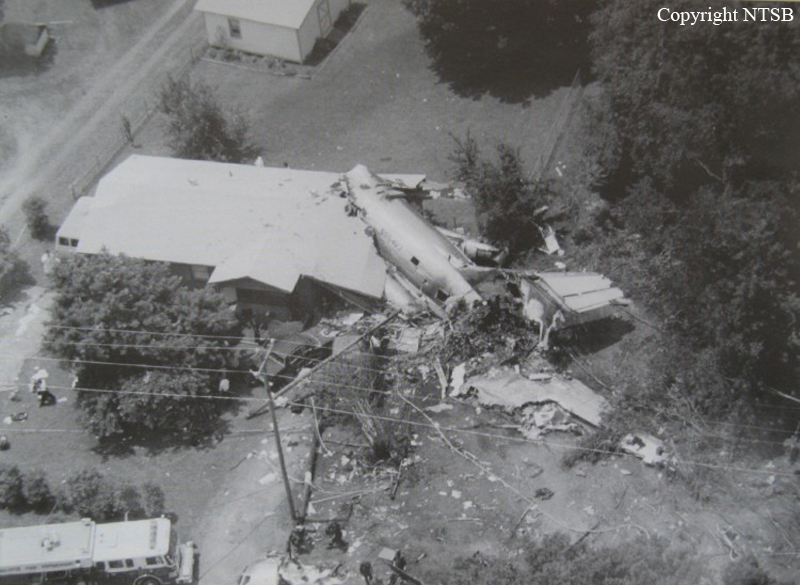
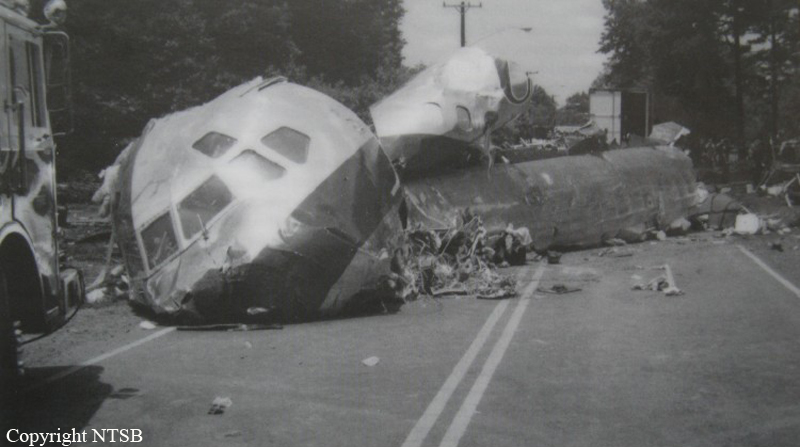
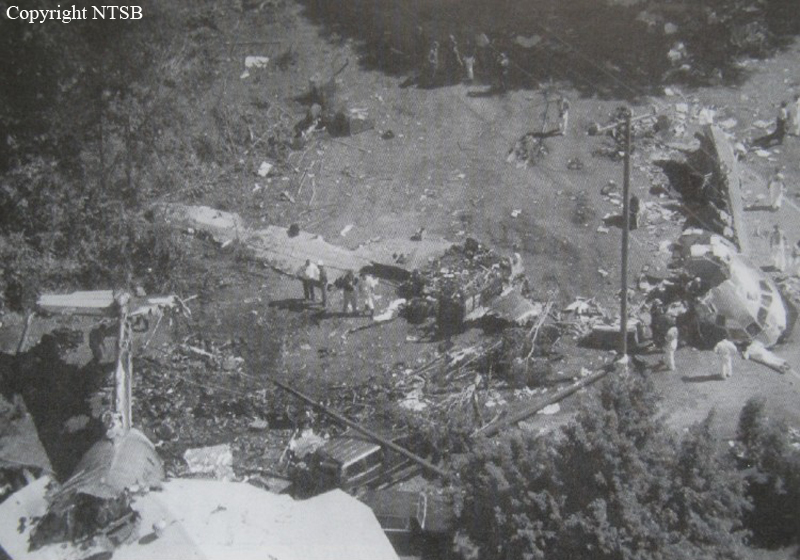
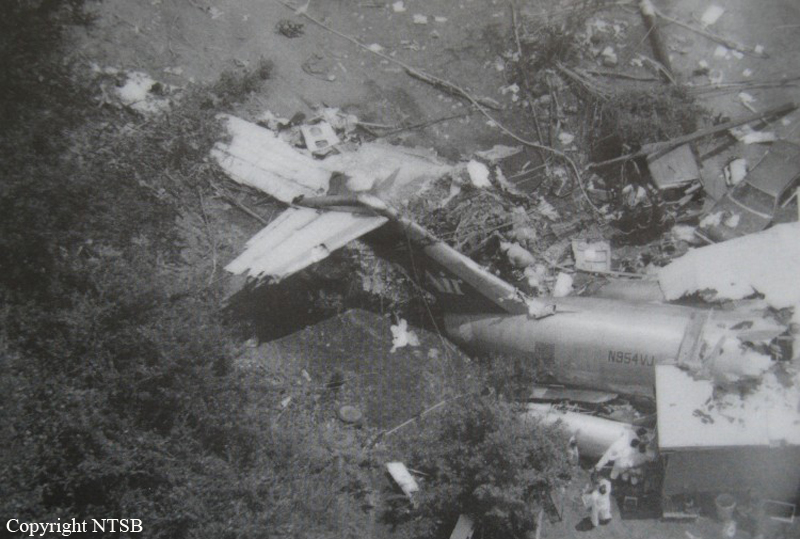
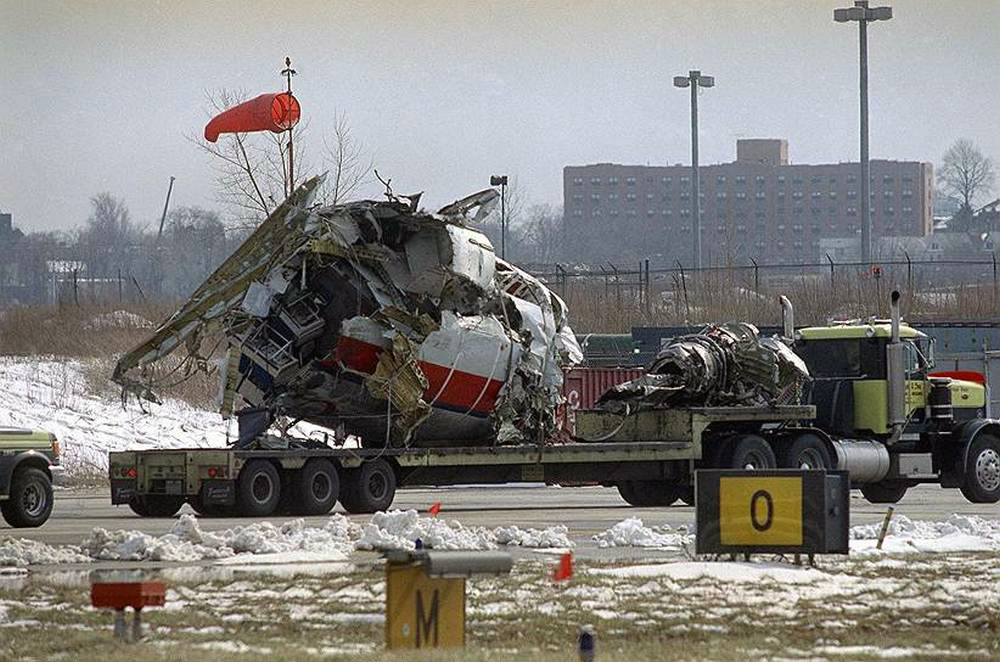
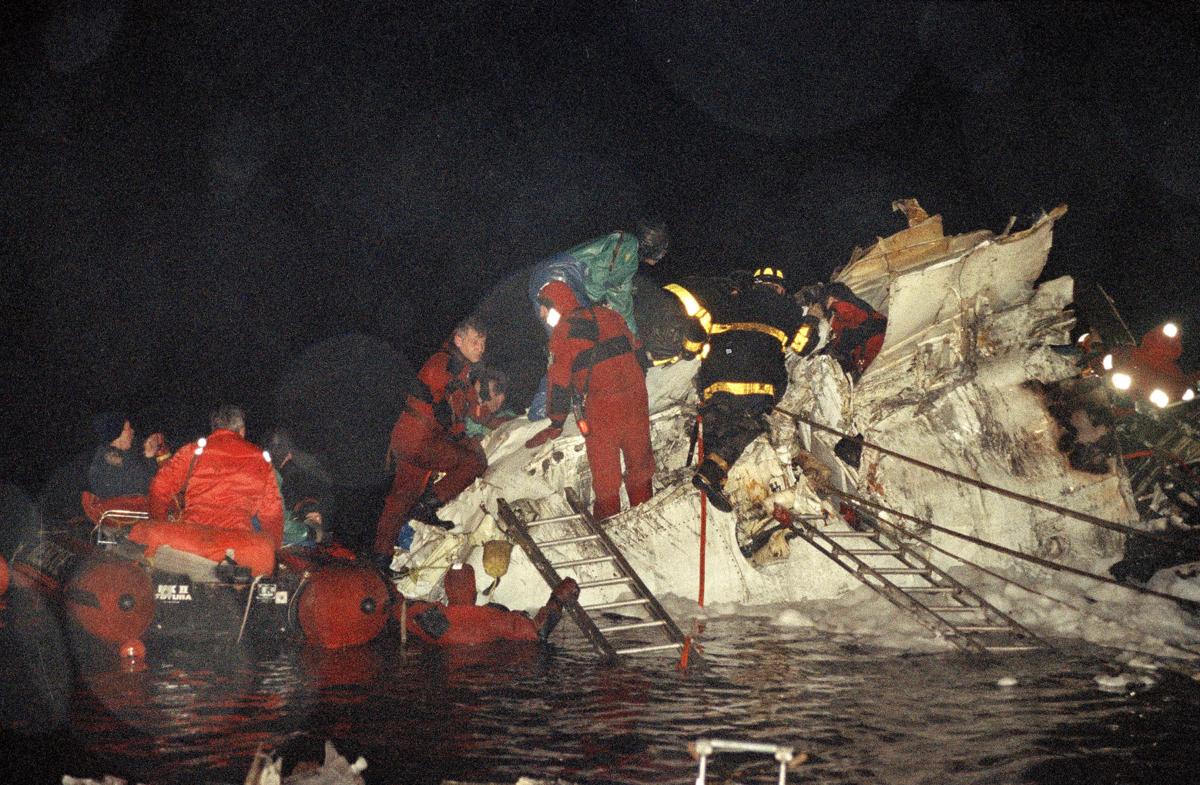
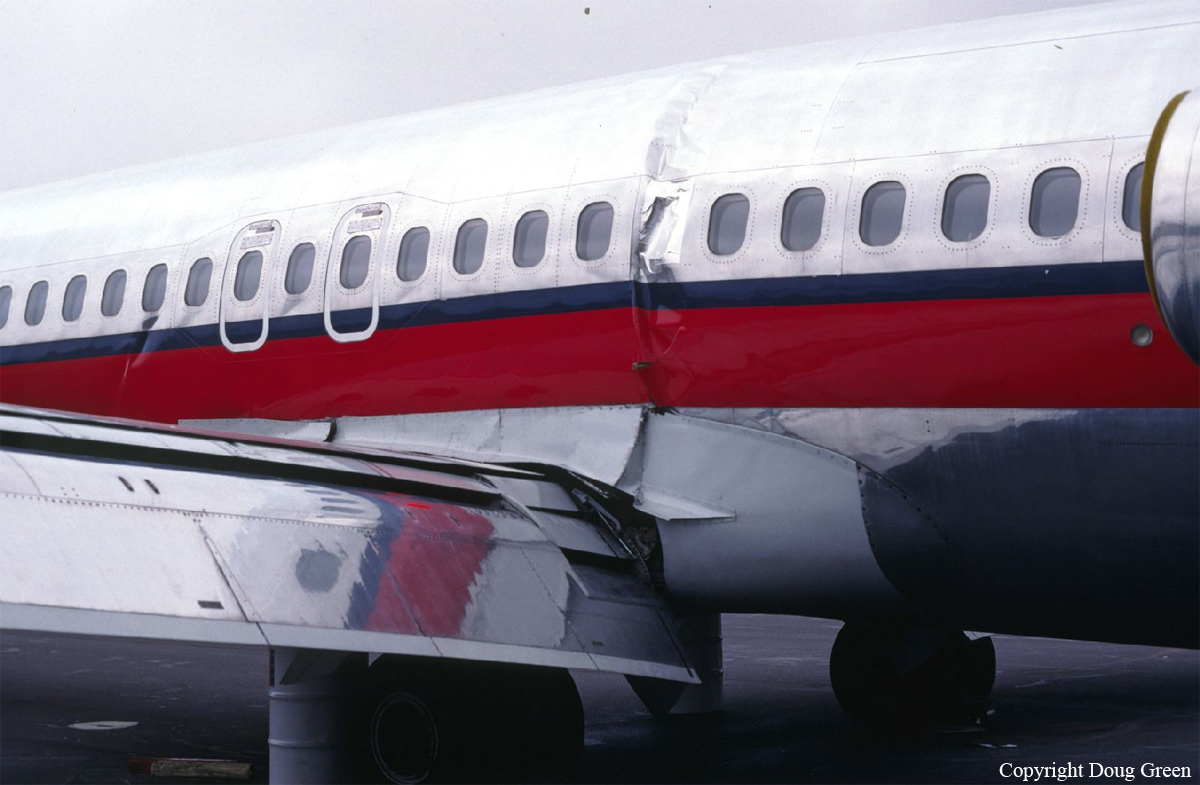
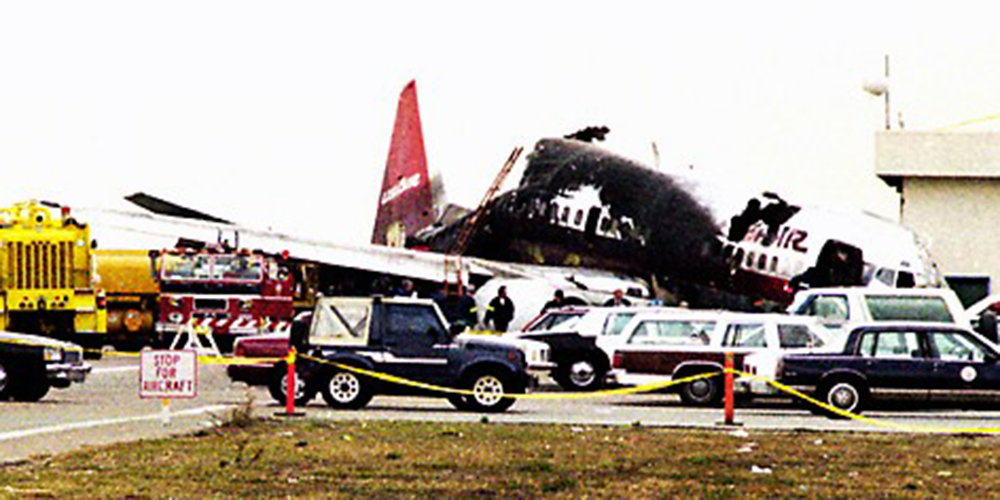
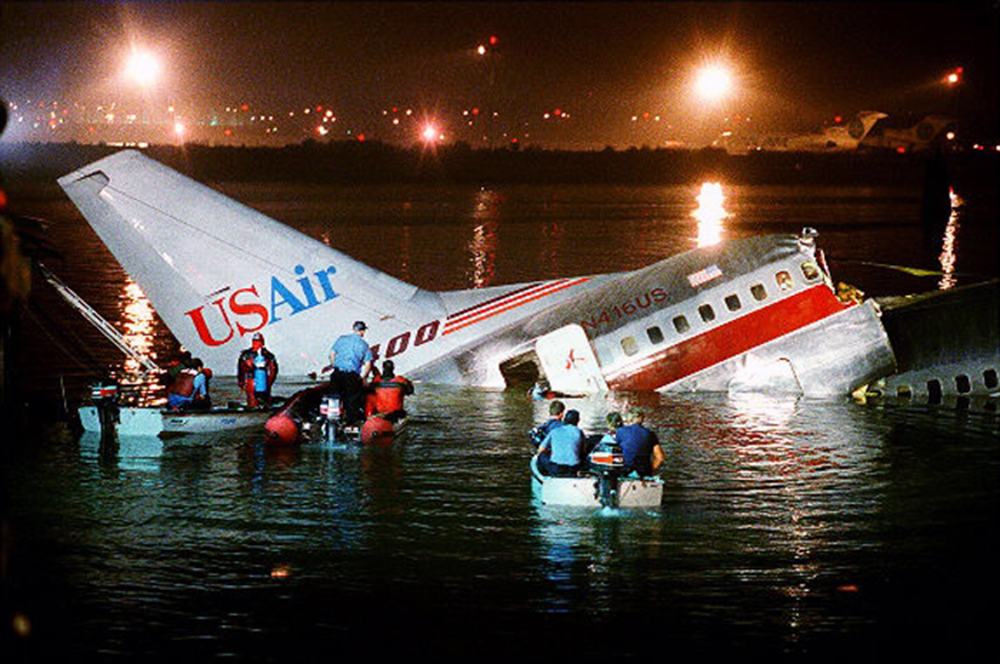
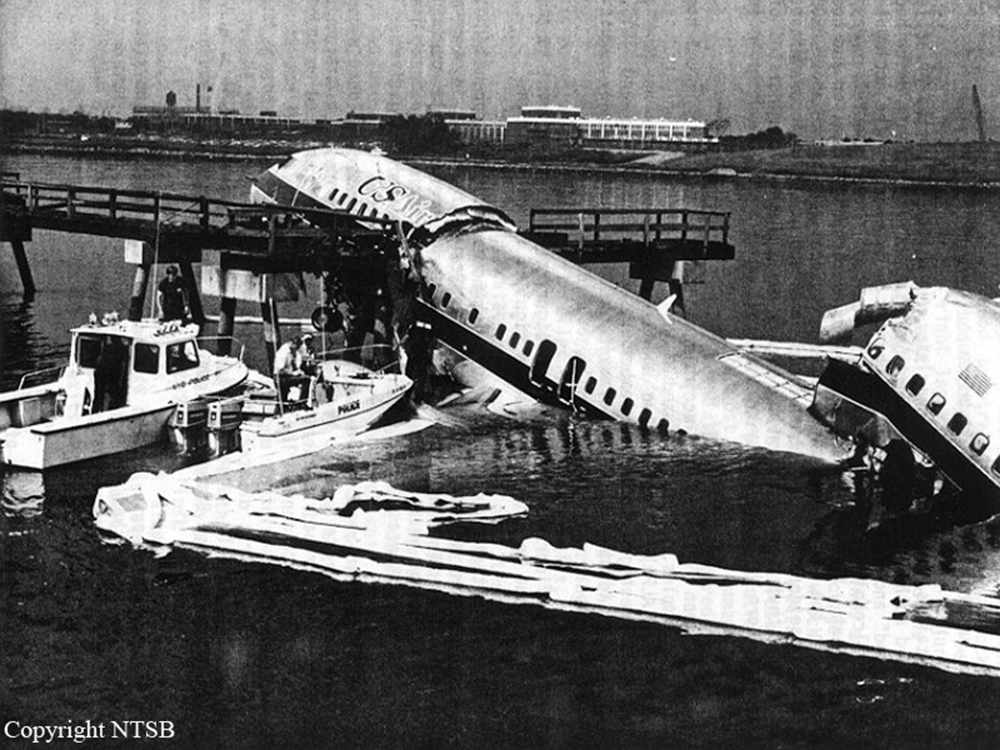
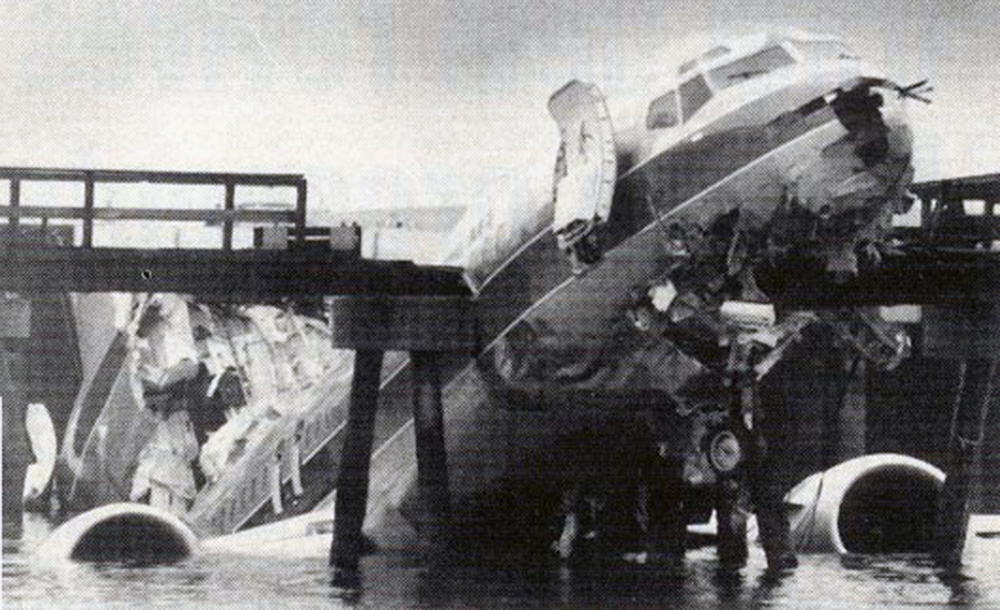
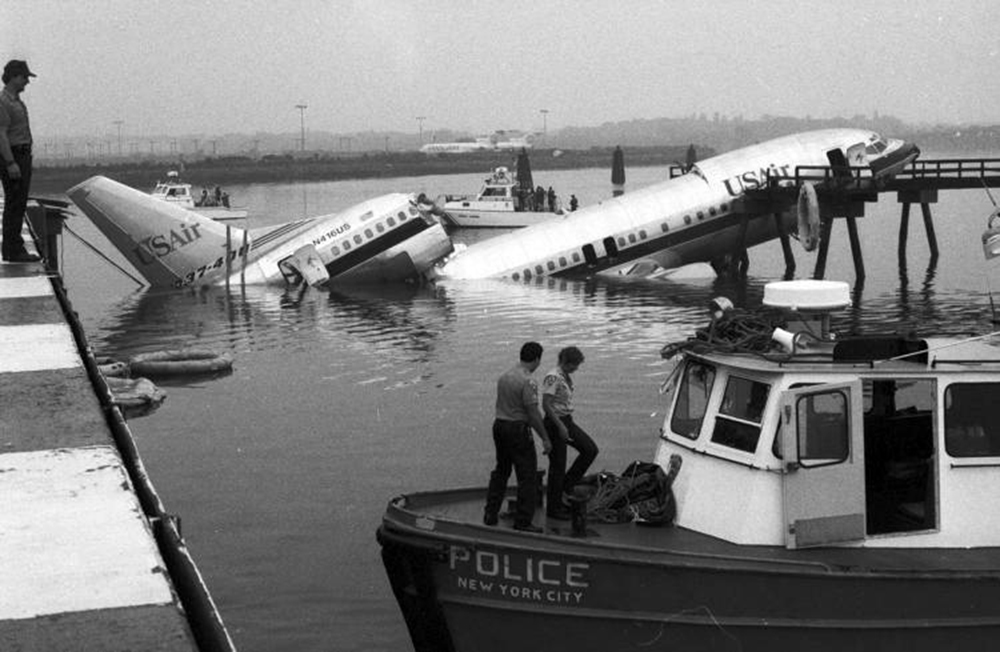
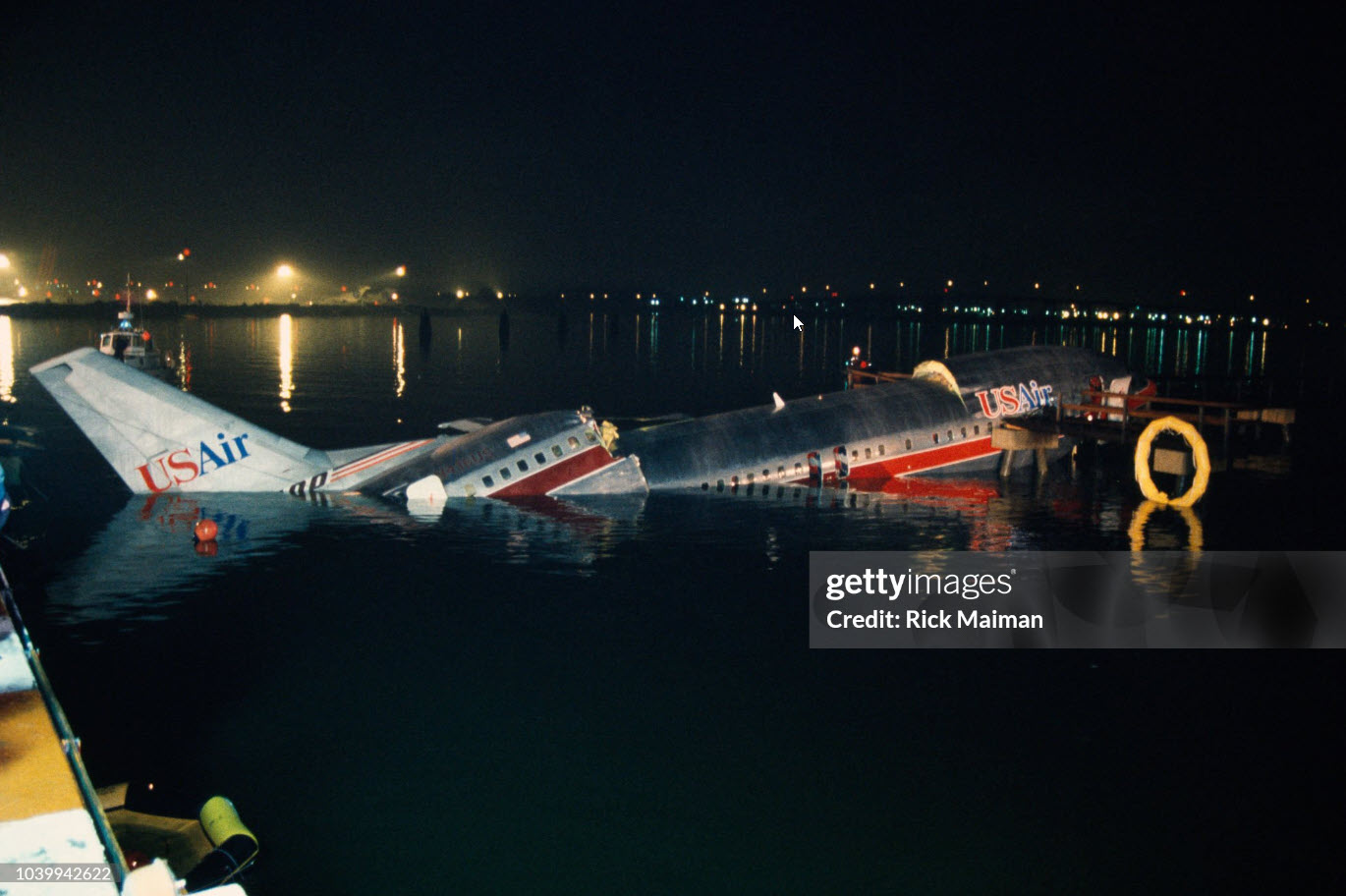
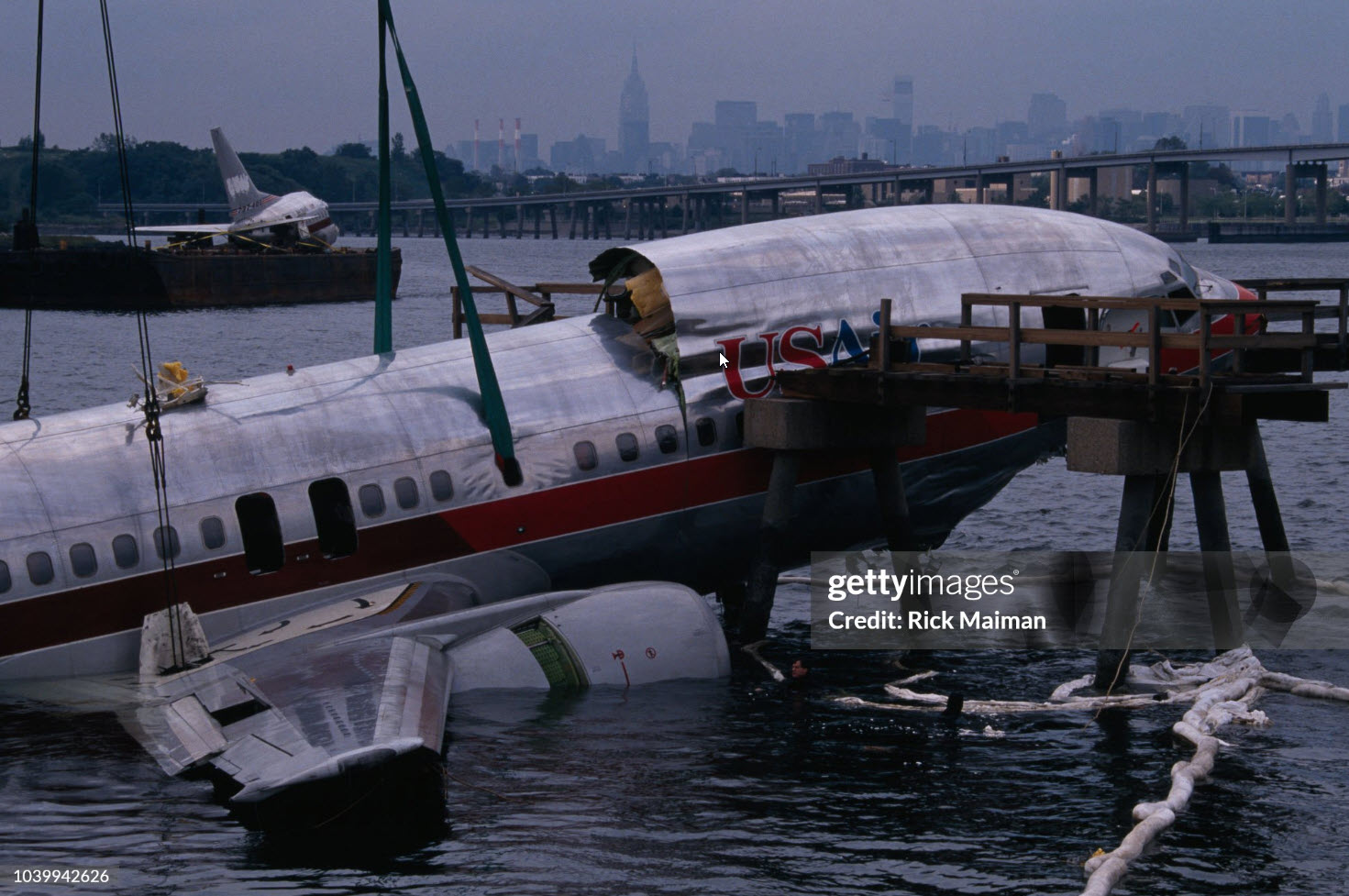
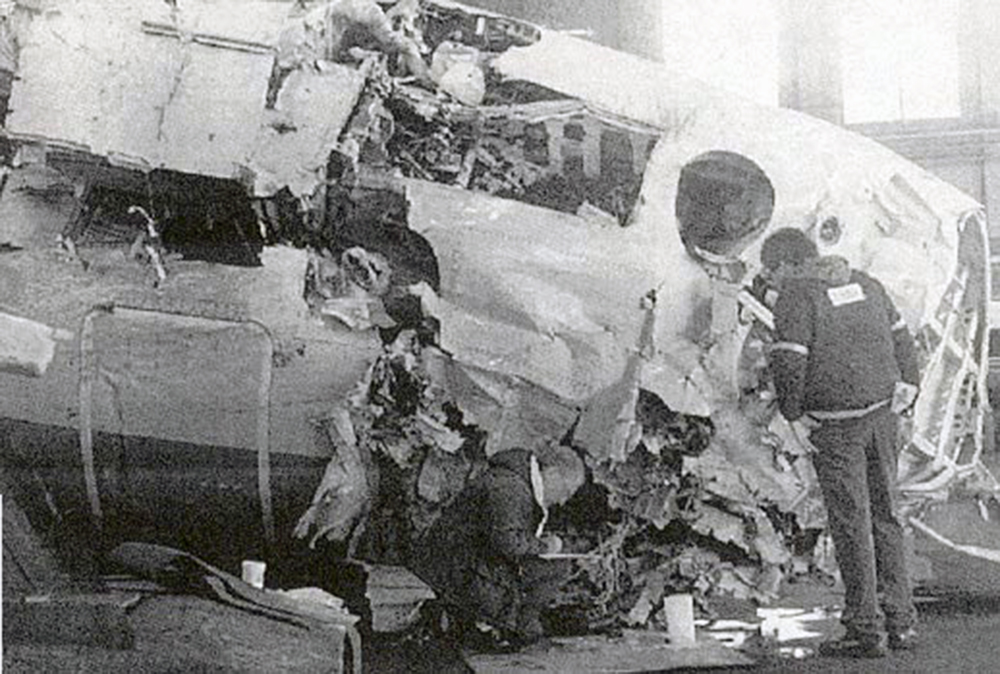
Crash of a Douglas DC-9-31 in Charlotte: 37 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 2, 1994 at 1843 LT
Registration:
N954VJ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Columbia - Charlotte
MSN:
47590
YOM:
1973
Flight number:
US1016
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
52
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
37
Captain / Total hours on type:
1970.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
3180
Aircraft flight hours:
53917
Aircraft flight cycles:
63147
Circumstances:
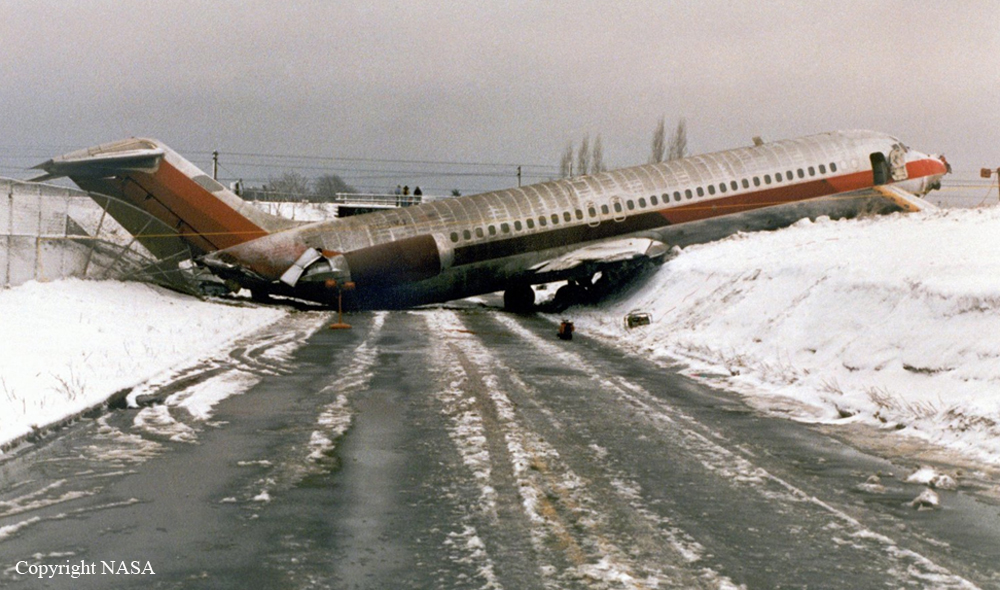
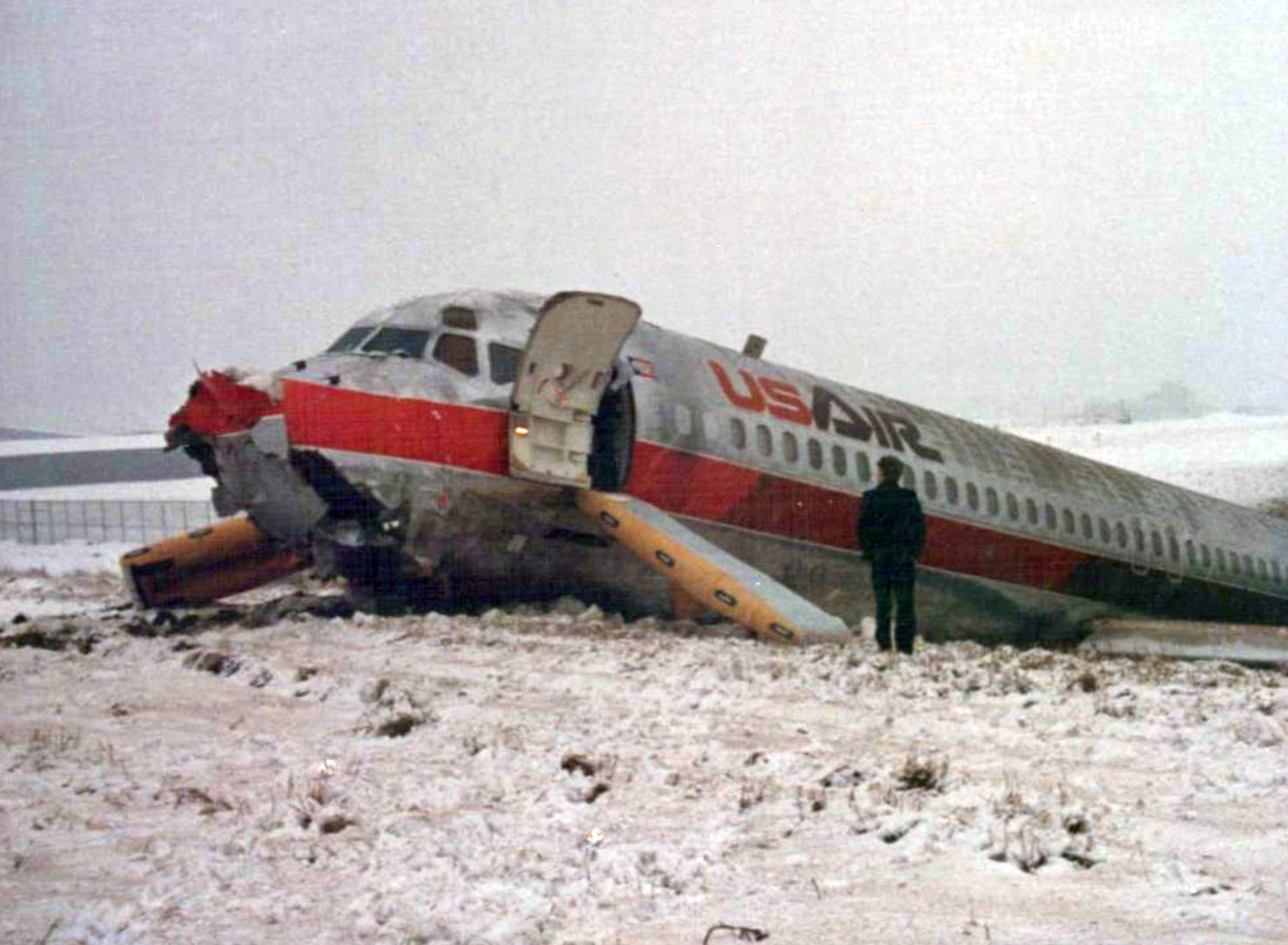
USAir Flight 1016 was a domestic flight from Columbia (CAE) to Charlotte (CLT). The DC-9 departed the gate on schedule at 18:10. The first officer was performing the duties of the flying pilot. The weather information provided to the flightcrew from USAir dispatch indicated that the conditions at Charlotte were similar to those encountered when the crew had departed there approximately one hour earlier. The only noted exception was the report of scattered thunderstorms in the area. Flight 1016 was airborne at 18:23 for the planned 35 minute flight. At 18:27, the captain of flight 1016 made initial contact with the Charlotte Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) controller and advised that the flight was at 12,000 feet mean sea level (msl). The controller replied "USAir ten sixteen ... expect runway one eight right." Shortly afterward the controller issued a clearance to the flightcrew to descend to 10,000 feet. At 18:29, the first officer commented "there's more rain than I thought there was ... it's startin ...pretty good a minute ago ... now it's held up." On their airborne weather radar the crew observed two cells, one located south and the second located east of the airport. The captain said "looks like that's [rain] setting just off the edge of the airport." One minute later, the captain contacted the controller and said "We're showing uh little buildup here it uh looks like it's sitting on the radial, we'd like to go about five degrees to the left to the ..." The controller replied "How far ahead are you looking ten sixteen?" The captain responded "About fifteen miles." The controller then replied "I'm going to turn you before you get there I'm going to turn you at about five miles northbound." The captain acknowledged the transmission, and, at 18:33, the controller directed the crew to turn the aircraft to a heading of three six zero. One minute later the flightcrew was issued a clearance to descend to 6,000 feet, and shortly thereafter contacted the Final Radar West controller. At 18:35 the Final Radar West controller transmitted "USAir ten sixteen ... maintain four thousand runway one eight right.'' The captain acknowledged the radio transmission and then stated to the first officer "approach brief." The first officer responded "visual back up ILS." Following the first officer's response, the controller issued a clearance to flight 1016 to "...turn ten degrees right descend and maintain two thousand three hundred vectors visual approach runway one eight right.'' At 18:36, the Final Radar West controller radioed flight 1016 and said "I'll tell you what USAir ten sixteen they got some rain just south of the field might be a little bit coming off north just expect the ILS now amend your altitude maintain three thousand." At 18:37, the controller instructed flight 1016 to ''turn right heading zero niner zero." At 18:38, the controller said "USAir ten sixteen turn right heading one seven zero four from SOPHE [the outer marker for runway 18R ILS] ... cross SOPHE at or above three thousand cleared ILS one eight right approach." As they were maneuvering the airplane from the base leg of the visual approach to final, both crew members had visual contact with the airport. The captain then contacted Charlotte Tower. The controller said "USAir ten sixteen ... runway one eight right cleared to land following an F-K one hundred short final, previous arrival reported a smooth ride all the way down the final." The pilot of the Fokker 100 in front also reported a "smooth ride". About 18:36, a special weather observation was recorded, which included: ... measured [cloud] ceiling 4,500 feet broken, visibility 6 miles, thunderstorm, light rain shower, haze, the temperature was 88 degrees Fahrenheit, the dewpoint was 67 degrees Fahrenheit, the wind was from 110 degrees at 16 knots .... This information was not broadcast until 1843; thus, the crew of flight 1016 did not receive the new ATIS. At 18:40, the Tower controller said "USAir ten sixteen the wind is showing one zero zero at one nine." This was followed a short time later by the controller saying "USAir ten sixteen wind now one one zero at two one." Then the Tower controller radioed a wind shear warning "windshear alert northeast boundary wind one nine zero at one three.'' On finals the DC-9 entered an area of rainfall and at 18:41:58, the first officer commented "there's, ooh, ten knots right there." This was followed by the captain saying "OK, you're plus twenty [knots] ... take it around, go to the right." A go around was initiated. The Tower controller noticed Flight 1016 going around "USAir ten sixteen understand you're on the go sir, fly runway heading, climb and maintain three thousand." The first officer initially rotated the airplane to the proper 15 degrees nose-up attitude during the missed approach. However, the thrust was set below the standard go-around EPR limit of 1.93, and the pitch attitude was reduced to 5 degrees nose down before the flightcrew recognized the dangerous situation. When the flaps were in transition from 40 to 15 degrees (about a 12-second cycle), the airplane encountered windshear. Although the DC-9 was equipped with an on-board windshear warning system, it did not activate for unknown reasons. The airplane stalled and impacted the ground at 18:42:35. Investigation revealed that the headwind encountered by flight 1016 during the approach between 18:40:40 and 18:42:00 was between 10 and 20 knots. The initial wind component, a headwind, increased from approximately 30 knots at 18:42:00 to 35 knots at 18:42:15. The maximum calculated headwind occurred at 18:42:17, and was calculated at about 39 knots. The airplane struck the ground after transitioning from a headwind of approximately 35 knots, at 18:42:21, to a tailwind of 26 knots (a change of 61 knots), over a 14 second period.
Probable cause:
The board determines that the probable cause of the accident was:
- The flight crew's decision to continue an approach into severe convective activity that was conducive to a microburst,
- The flight crew's failure to recognize a windshear situation in a timely manner,
- The flight crew's failure to establish and maintain the proper airplane attitude and thrust setting necessary to escape the windshear,
- The lack of real-time adverse weather and windshear hazard information dissemination from air traffic control, all of which led to an encounter with and failure to escape from a microburst-induced windshear that was produced by a rapidly developing thunderstorm located at the approach end of runway 18R.
The following contributing factors were reported:
- The lack of air traffic control procedures that would have required the controller to display and issue ASR-9 radar weather information to the pilots of flight 1016,
- The Charlotte tower supervisor's failure to properly advise and ensure that all controllers were aware of and reporting the reduction in visibility and the RVR value information, and the low level windshear alerts that had occurred in multiple quadrants,
- The inadequate remedial actions by USAir to ensure adherence to standard operating procedures,
- The inadequate software logic in the airplane's windshear warning system that did not provide an alert upon entry into the windshear.
- The flight crew's decision to continue an approach into severe convective activity that was conducive to a microburst,
- The flight crew's failure to recognize a windshear situation in a timely manner,
- The flight crew's failure to establish and maintain the proper airplane attitude and thrust setting necessary to escape the windshear,
- The lack of real-time adverse weather and windshear hazard information dissemination from air traffic control, all of which led to an encounter with and failure to escape from a microburst-induced windshear that was produced by a rapidly developing thunderstorm located at the approach end of runway 18R.
The following contributing factors were reported:
- The lack of air traffic control procedures that would have required the controller to display and issue ASR-9 radar weather information to the pilots of flight 1016,
- The Charlotte tower supervisor's failure to properly advise and ensure that all controllers were aware of and reporting the reduction in visibility and the RVR value information, and the low level windshear alerts that had occurred in multiple quadrants,
- The inadequate remedial actions by USAir to ensure adherence to standard operating procedures,
- The inadequate software logic in the airplane's windshear warning system that did not provide an alert upon entry into the windshear.
Final Report: