Country
Operator Image
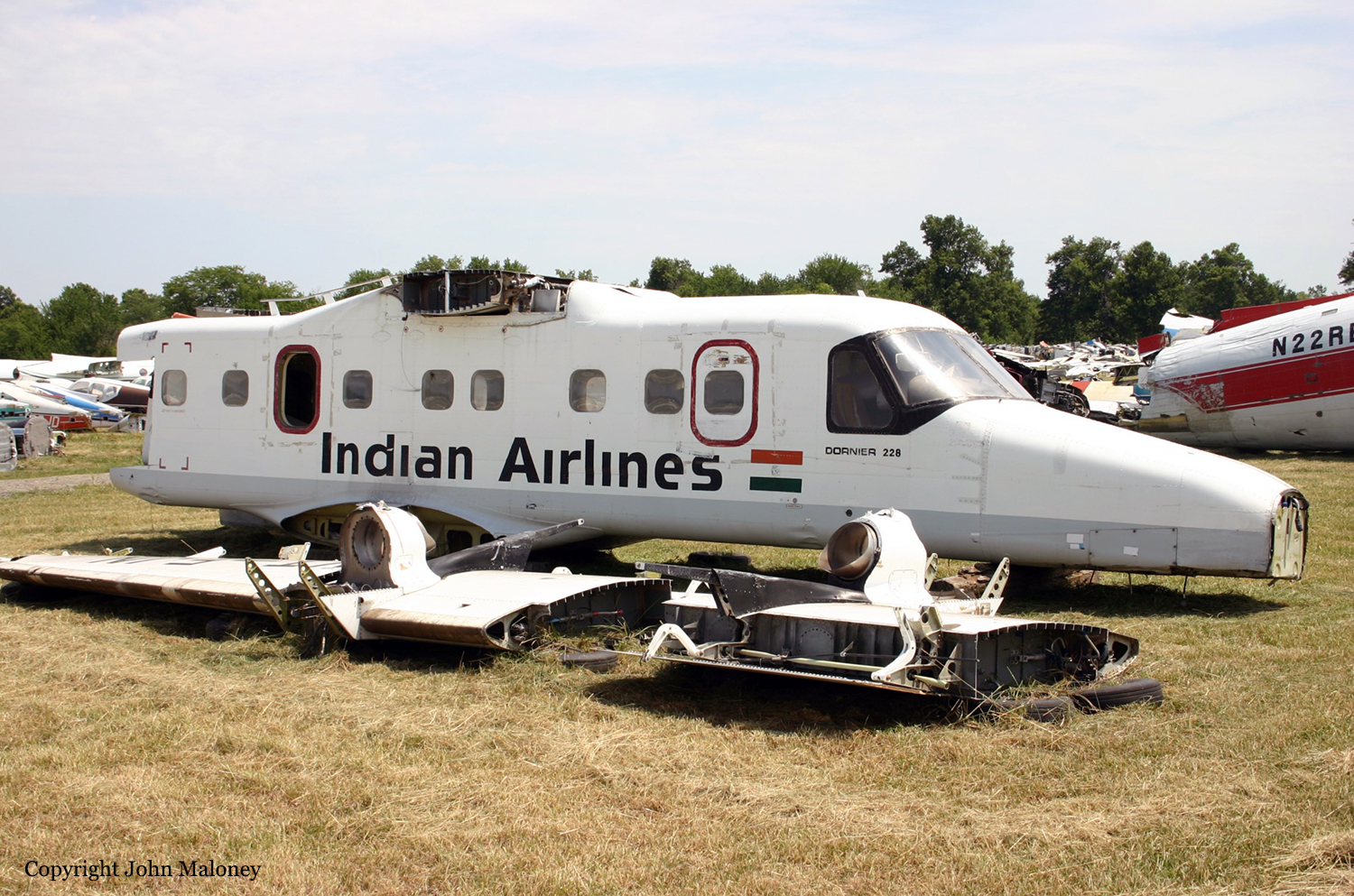
Crash of a Dornier DO228-201 in Jaipur
Date & Time:
Jun 9, 2002
Registration:
VT-EJN
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Jaipur - Jaipur
MSN:
8060
YOM:
1986
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
The crew was completing a local training flight at Jaipur-Sanganer Airport. After touchdown, the twin engine aircraft skidded on runway, veered off runway and came to rest. Both pilots escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.

Ground accident of an Airbus A300B2-101 in New Delhi
Date & Time:
Mar 8, 2002 at 0315 LT
Registration:
VT-EFW
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
111
YOM:
1980
Crew on board:
5
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
A group of five technicians/engineers of the company was preparing the aircraft to be transferred to a hangar for maintenance. After engine startup, the power was reduced to idle after someone inadvertently pulled out the circuit breaker. The aircraft jumped the chocks and started to roll. Since the engine's power was in idle, the brakes and the nosewheel steering system were inoperative. The crew elected to reduce power on the left engine but mistakenly increased the power on the right engine by 90%. This caused the aircraft to rotate 80° when control was lost. The airplane rolled through a perimeter wall, causing the nose gear to collapse. All five occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.

Crash of a Boeing 737-2A8 in New Delhi
Date & Time:
Dec 2, 1995 at 1253 LT
Registration:
VT-ECS
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Bombay – Jaipur – New Delhi
MSN:
20963
YOM:
1974
Flight number:
IC492
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
102
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
Following a wrong approach configuration, the aircraft landed too far down the runway, about 600 metres from the runway end. Unable to stop within the remaining distance, the aircraft overran, struck a concrete wall (45 cm high) and came to rest 450 metres further. All 108 occupants were evacuated safely and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of the combination of the following factors:
- The injudicious and imprudent decision of the Pilot-in-Command to hastily complete the flight in the inadequate time available before the notified closure of Delhi airport for a VVIP flight,
- The dangerously unstabilised approach made by the Pilot-in-Command, primarily due to his failure to decelerate the aircraft in time,
- The failure of the First Officer to call out significant deviations from the stipulated approach parameters,
- The failure of the Pilot-in-Command to carry out a missed approach in spite of his approach being grossly unstabilised,
- The inadvertent omission of the Pilot-in-Command to arm the speed brake before landing,
- Touch-down of the aircraft at excessive speed and too far down the runway,
- Failure of the First Officer and Pilot-in-Command to monitor the automatic deployment of the speed brake, and failure of the Pilot-in-Command to deploy it manually,
- Impact of the aircraft with an 18-inch high cement-concrete cable duct in the kutcha ground beyond the over-run area,
- The pilot disregard of procedures, regulations and instructions.
- The injudicious and imprudent decision of the Pilot-in-Command to hastily complete the flight in the inadequate time available before the notified closure of Delhi airport for a VVIP flight,
- The dangerously unstabilised approach made by the Pilot-in-Command, primarily due to his failure to decelerate the aircraft in time,
- The failure of the First Officer to call out significant deviations from the stipulated approach parameters,
- The failure of the Pilot-in-Command to carry out a missed approach in spite of his approach being grossly unstabilised,
- The inadvertent omission of the Pilot-in-Command to arm the speed brake before landing,
- Touch-down of the aircraft at excessive speed and too far down the runway,
- Failure of the First Officer and Pilot-in-Command to monitor the automatic deployment of the speed brake, and failure of the Pilot-in-Command to deploy it manually,
- Impact of the aircraft with an 18-inch high cement-concrete cable duct in the kutcha ground beyond the over-run area,
- The pilot disregard of procedures, regulations and instructions.
Final Report:
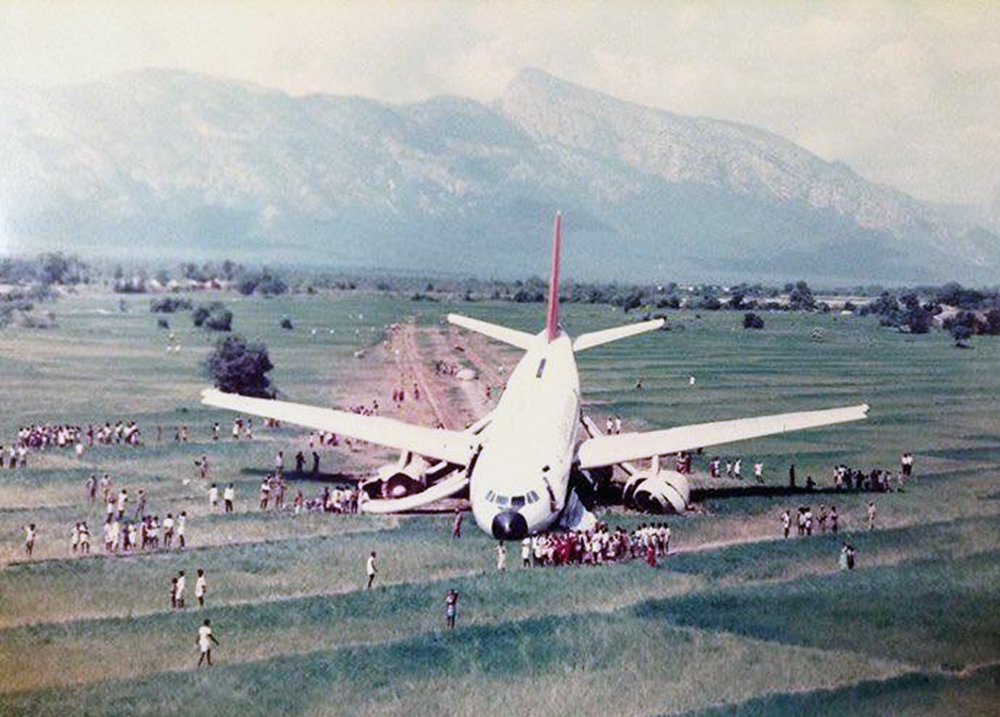
Crash of an Airbus A300B2-101 near Tirupati
Date & Time:
Nov 15, 1993 at 0925 LT
Registration:
VT-EDV
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Madras - Hyderabad
MSN:
034
YOM:
1976
Flight number:
IC440
Crew on board:
12
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
250
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
Indian Airlines Airbus A-300 aircraft VT-EDV was operating scheduled flight IC-440 (Madras - Hyderabad sector) on 15.11.1993. There were a total of 262 persons were on board the aircraft including 247+3 passengers and 12 crew members. The aircraft could not land at Hyderabad due to low visibility and carried out a missed approach. After the missed approach, the aircraft reported "Flap Problem" and was holding overhead at Hyderabad during which the flight crew enquired visibility at nearby Air Force airfields which was also low. The aircraft then diverted to Madras. Due to flaps problem, the crew had to maintain low speed and low altitude as a result of which it experienced fuel shortage and sought permission from Madras control for landing at Tirupati. However, the aircraft could not reach even Tirupati airport and executed forced landing in an open paddy field about 14 nautical miles from Tirupati airport. The aircraft dragged on the soft paddy field before coming to final stop. There was no fire. Passenger evacuation was carried out by means of escape slides. All the persons on board escaped unhurt except four who received minor injuries.
Probable cause:
The probable cause of accident has been attributed to:
- The ill-conceived decision of the aircraft's Commander to divert to Madras, without ensuring that adequate fuel was available for reaching there, when he was faced with a flap-jam and poor
visibility at Hyderabad.
- The failure of the aircraft's Commander and his Flight Crew to monitor fuel consumption correctly, and the failure of the Commander to revise his decision accordingly, until it became impossible to reach any airfield.
- A forced landing due to the eventual shortage of fuel.
- The ill-conceived decision of the aircraft's Commander to divert to Madras, without ensuring that adequate fuel was available for reaching there, when he was faced with a flap-jam and poor
visibility at Hyderabad.
- The failure of the aircraft's Commander and his Flight Crew to monitor fuel consumption correctly, and the failure of the Commander to revise his decision accordingly, until it became impossible to reach any airfield.
- A forced landing due to the eventual shortage of fuel.
Final Report:
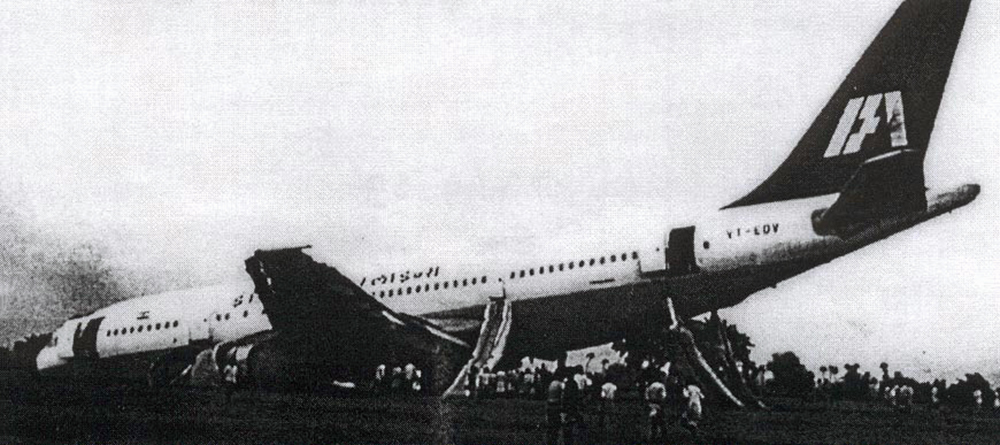



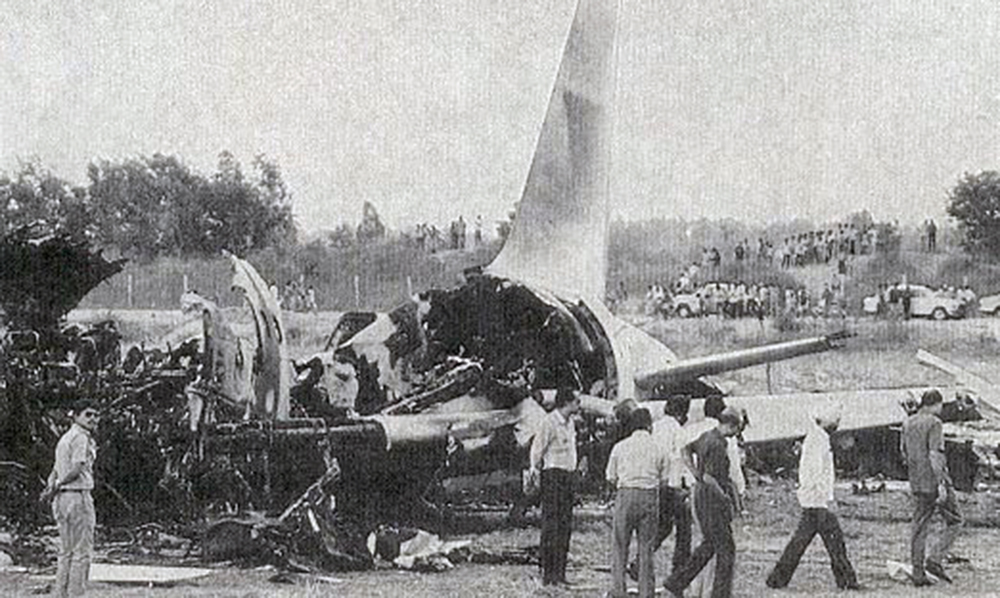
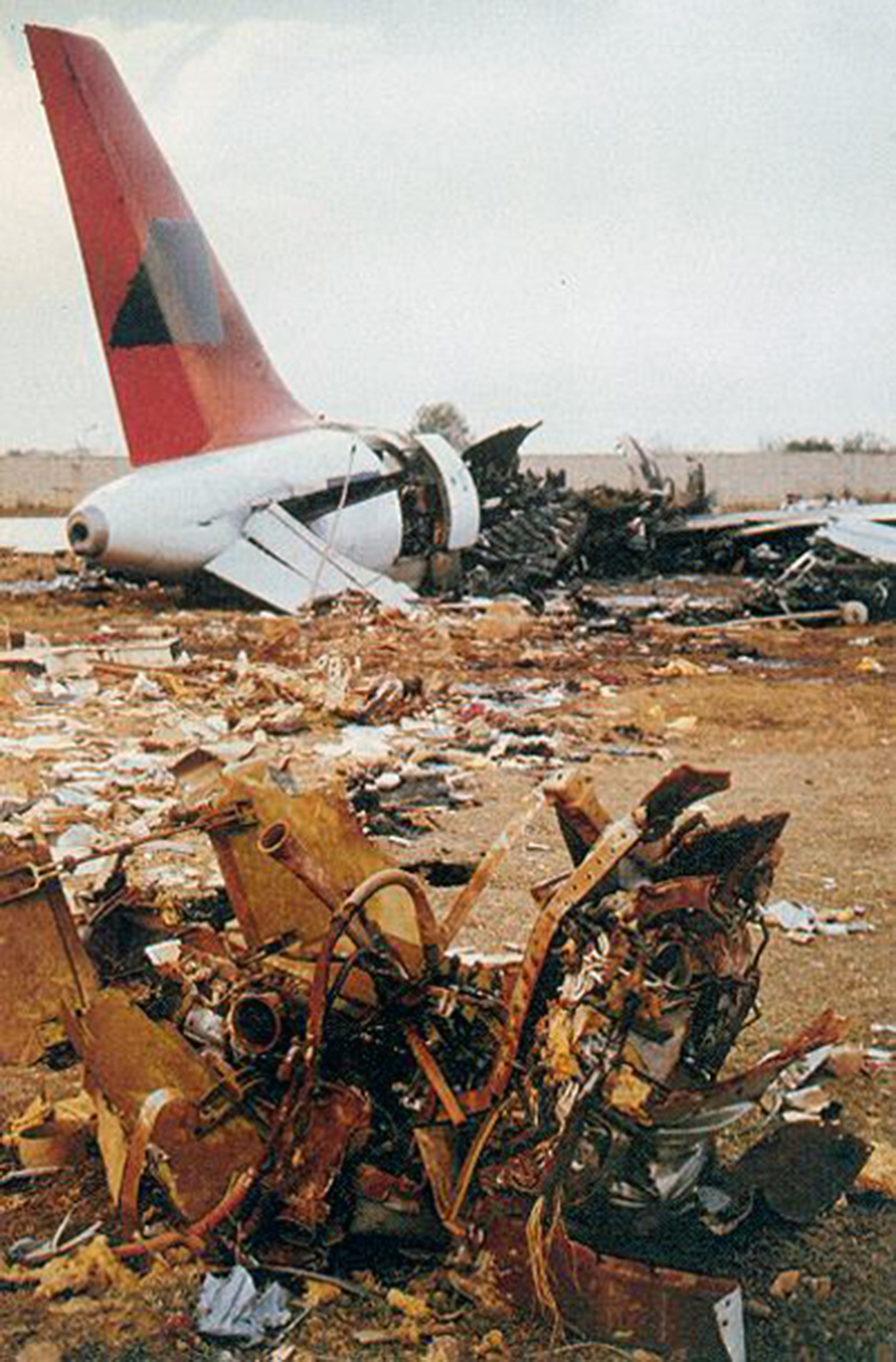
Crash of a Boeing 737-2A8 in Aurangabad: 55 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 26, 1993 at 1306 LT
Registration:
VT-ECQ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
New Delhi – Jaipur – Udaipur – Aurangabad – Bombay
MSN:
20961
YOM:
1974
Flight number:
IC491
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
112
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
55
Captain / Total hours on type:
1720.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
921
Aircraft flight hours:
43886
Circumstances:
Indian Airlines Boeing 737 aircraft VT-ECQ was operating scheduled flight IC491 from Delhi to Jaipur, Udaipur, Aurangabad and Bombay. The flight from Delhi to Aurangabad was uneventful. The aircraft took-off from Aurangabad with 118 persons on board. Aircraft lifted up almost at the end of runway and impacted heavily with a lorry carrying pressed cotton bales running from North to South on a highway at a distance of about 410 feet from the end of runway. The aircraft left main landing gear, left engine bottom cowling and thrust reverser impacted the left side of the truck at a height of nearly seven feet from the level of the road. Thereafter the aircraft hit the high tension electric wires nearly 3 kms North-East of the runway and hit the ground. In all 55 persons received fatal injuries. The aircraft was destroyed due to post impact fire.
Probable cause:
The probable cause of accident has been attributed to :
- Pilots' error in initiating late rotation and following wrong rotation technique, and
- Failure of the NAA to regulate the mobile traffic on the Beed road during the flight hours.
- Pilots' error in initiating late rotation and following wrong rotation technique, and
- Failure of the NAA to regulate the mobile traffic on the Beed road during the flight hours.
Final Report:
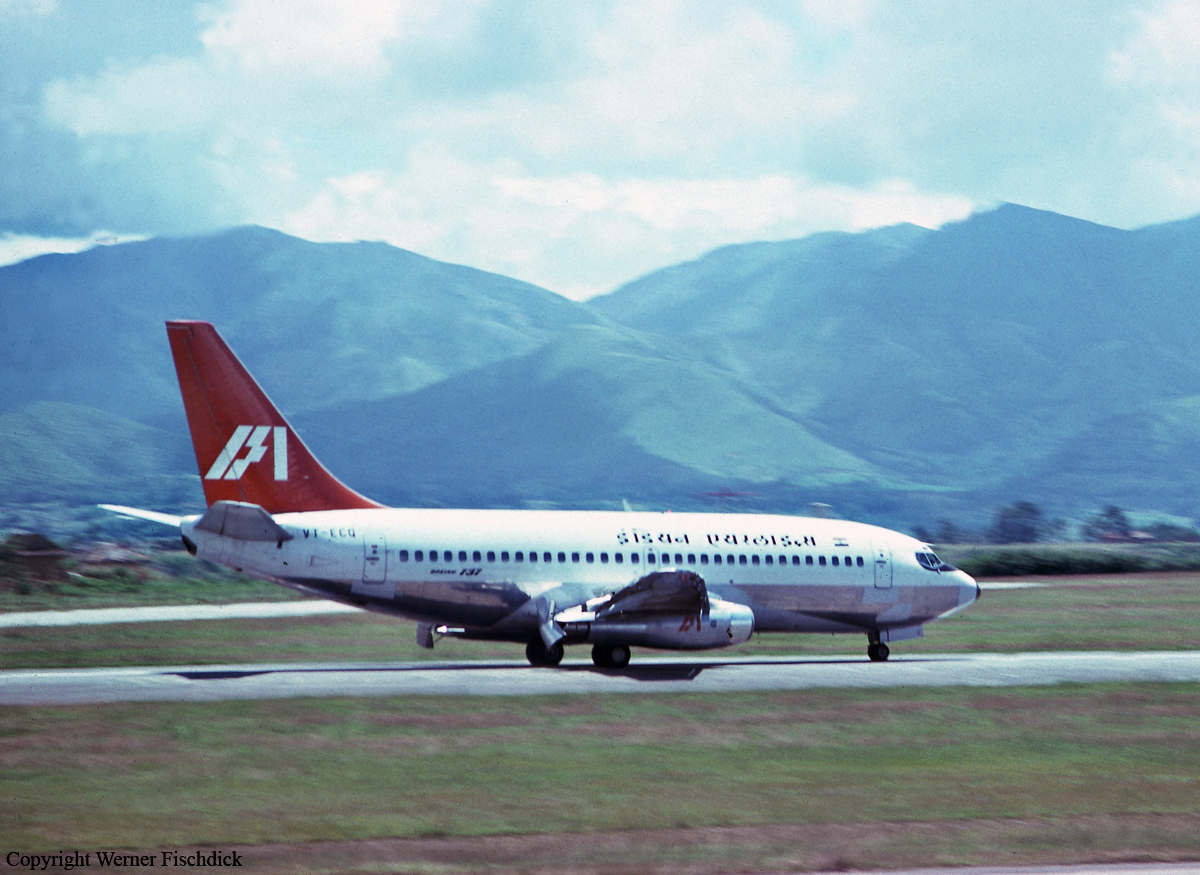
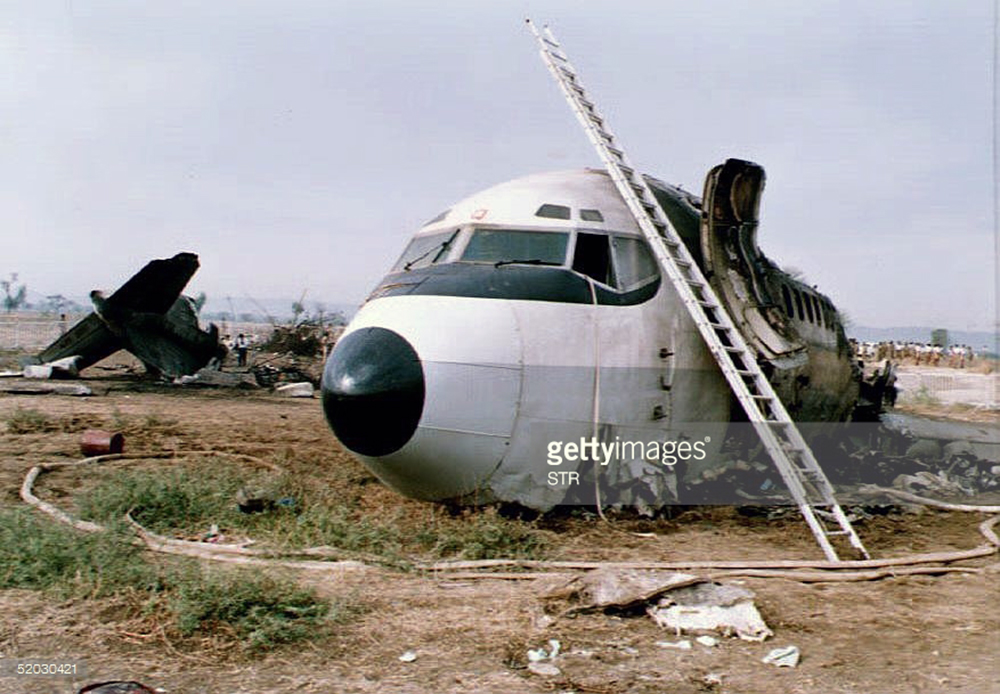
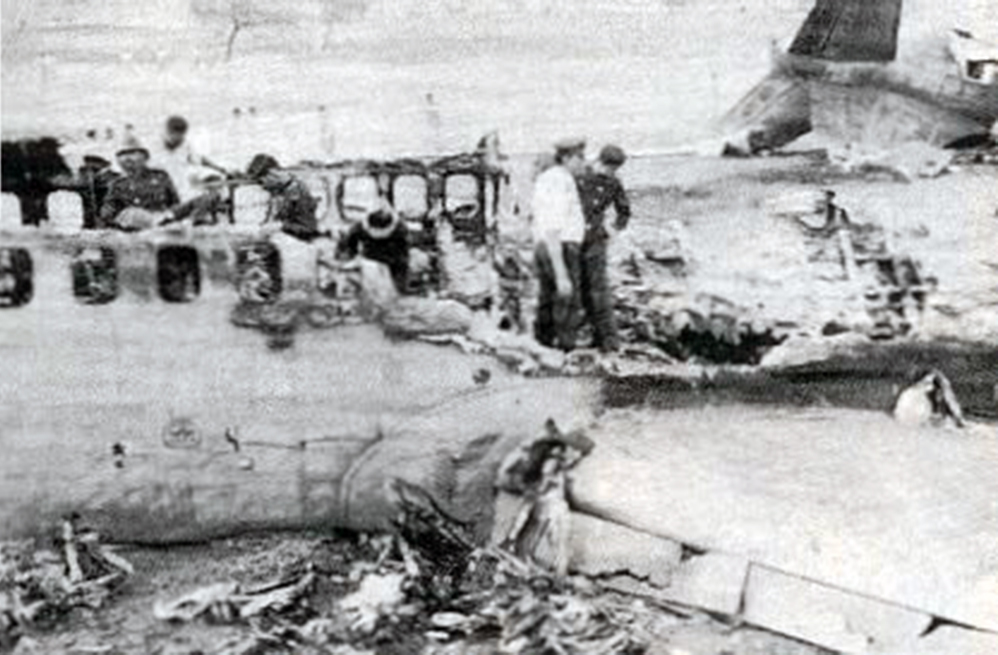
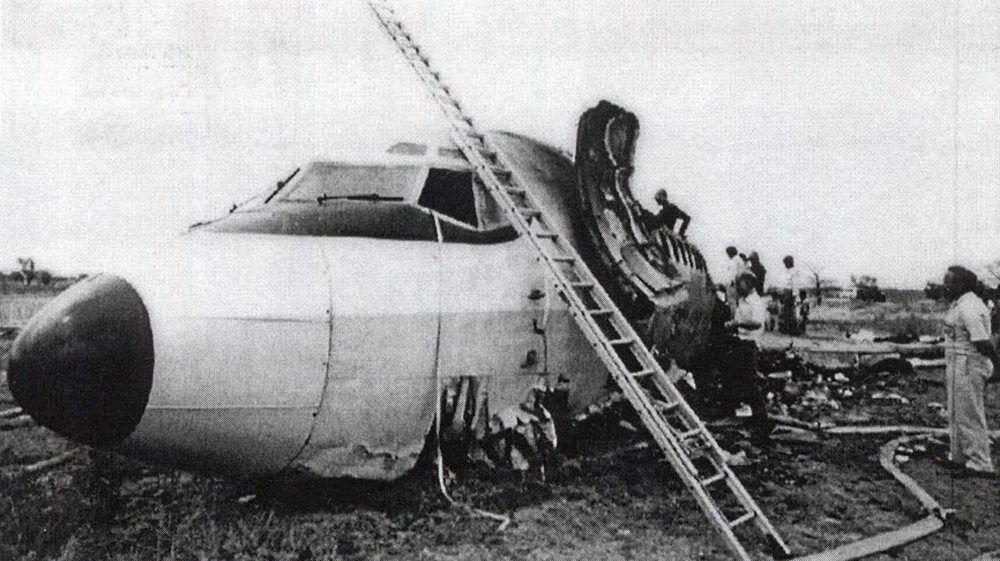




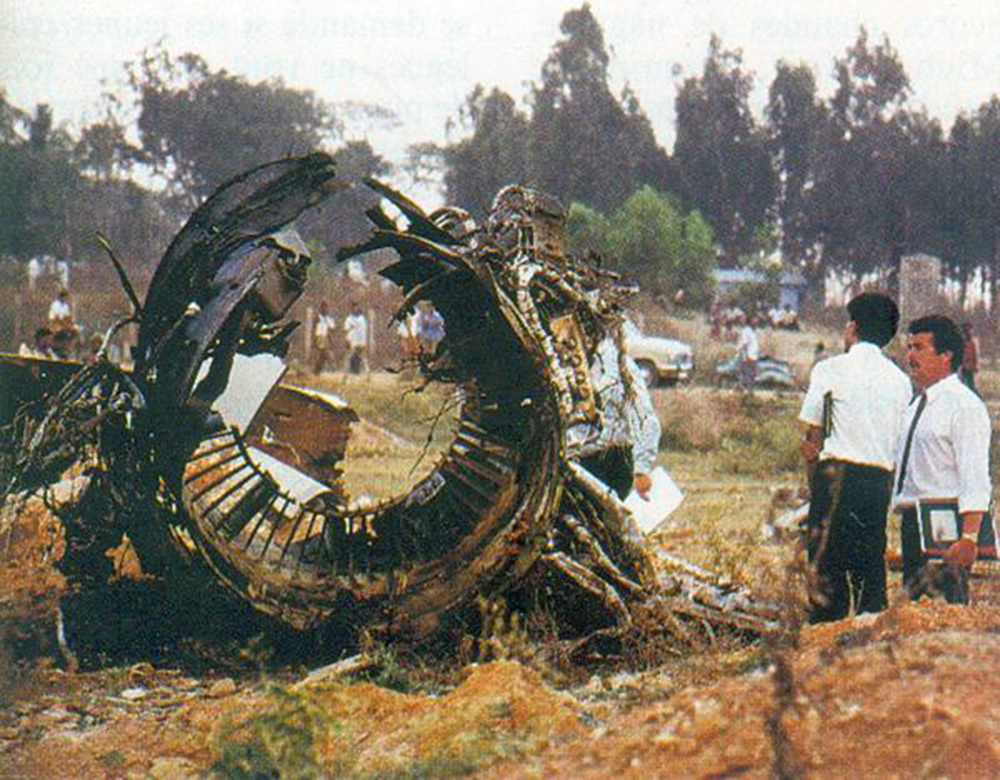
Crash of a Tupolev TU-154B-2 in New Delhi
Date & Time:
Jan 9, 1993 at 0408 LT
Registration:
85533
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Hyderabad - New Delhi
MSN:
82A533
YOM:
1982
Flight number:
IC840
Crew on board:
13
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
152
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
On 9th January, 1993 TU-154 aircraft No. 85533 wet leased by Indian Airlines from Uzbekistan Airways was operating flight IC-840 from Hyderabad to Delhi. The aircraft was being flown by Uzbeki operating crew and there were 165 persons on board including the crew. The aircraft touched down slightly outside the right edge of the runway, collided with some fixed installations on the ground, got airborne once again and finally touched down on kutcha ground on the right side of the runway. At this stage the right wing and the tail of the aircraft broke away and it came to rest in an inverted position. During the process, the aircraft caught fire and was destroyed. Most occupants of the aircraft escaped unhurt. Six persons suffered either limb fracture or other serious injuries while 45 persons suffered injuries of a minor nature.
Probable cause:
The probable cause of accident has been attributed to :
- The failure of the Pilot-in-Command to divert to Ahmedabad when he was informed that the RVR on runway 28 was below the minima applicable to his flight.
- The switching on of landing lights, on the instruction of the second Captain, at a height of only about ten metres, resulting in the loss of all visual references due to the blinding effect of
light reflections from fog.
- The failure of captain to carry out a missed approach when visual reference to the runway was lost.
- The failure of the Pilot-in-Command to divert to Ahmedabad when he was informed that the RVR on runway 28 was below the minima applicable to his flight.
- The switching on of landing lights, on the instruction of the second Captain, at a height of only about ten metres, resulting in the loss of all visual references due to the blinding effect of
light reflections from fog.
- The failure of captain to carry out a missed approach when visual reference to the runway was lost.
Final Report:
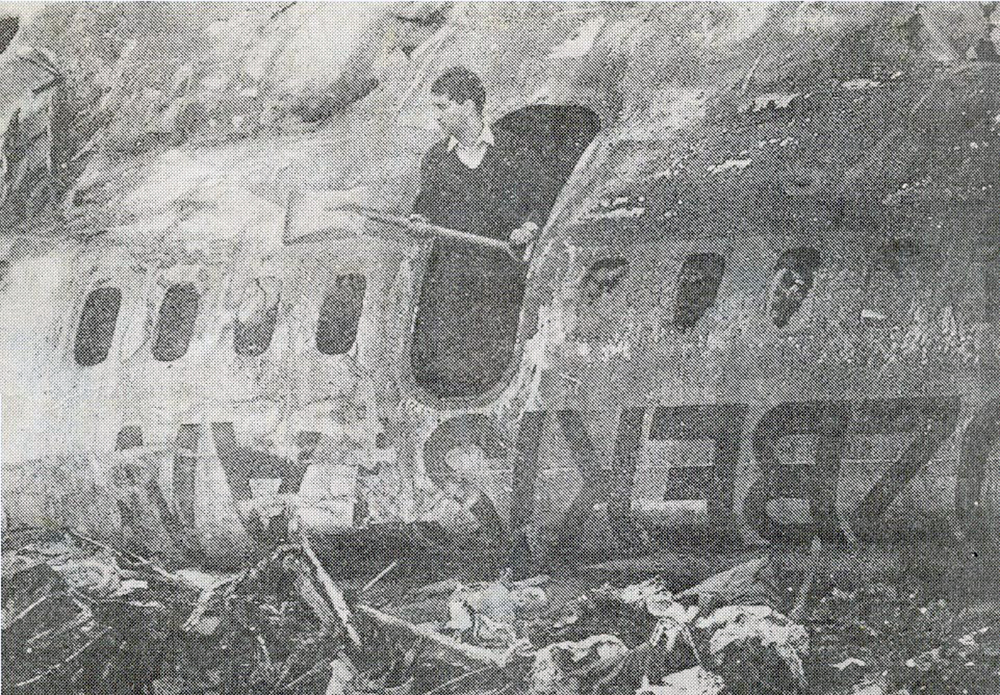
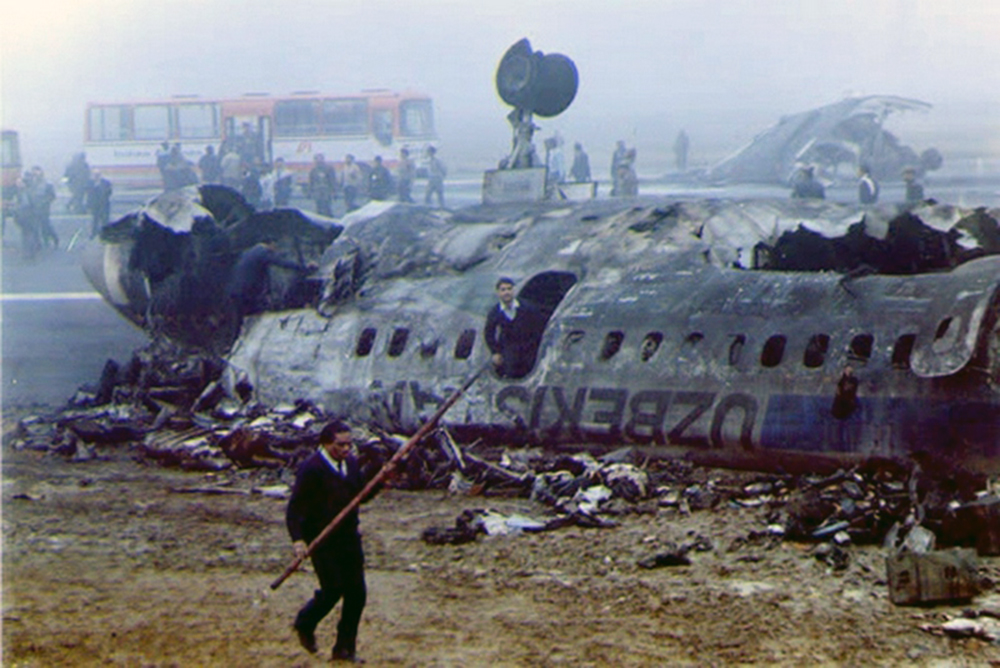

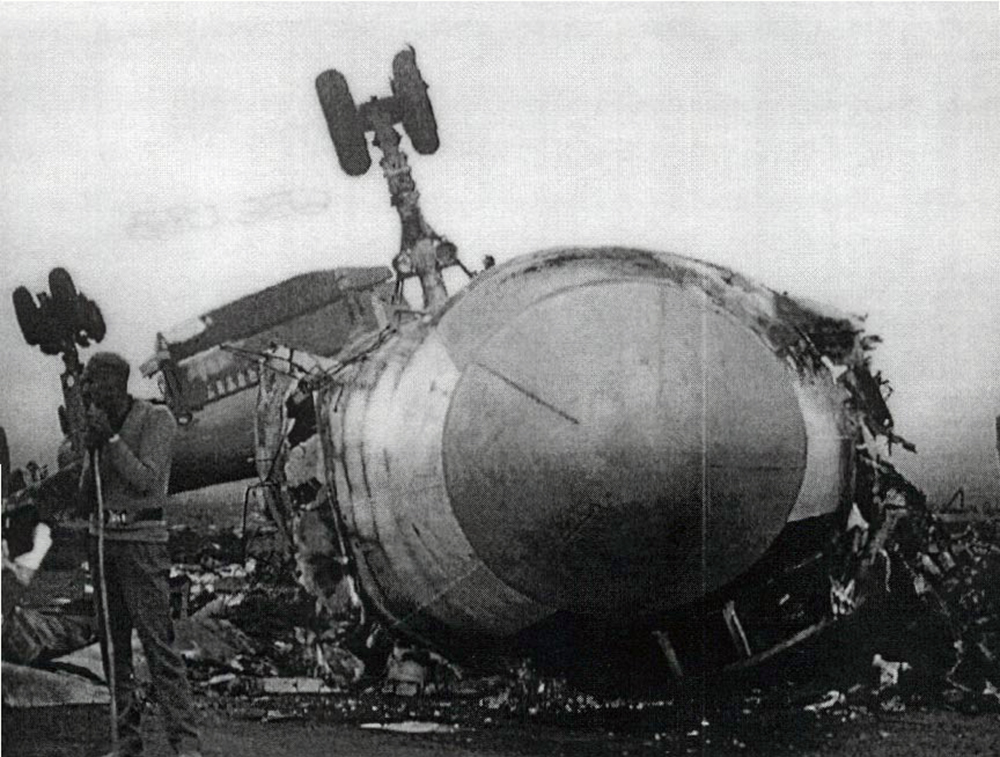

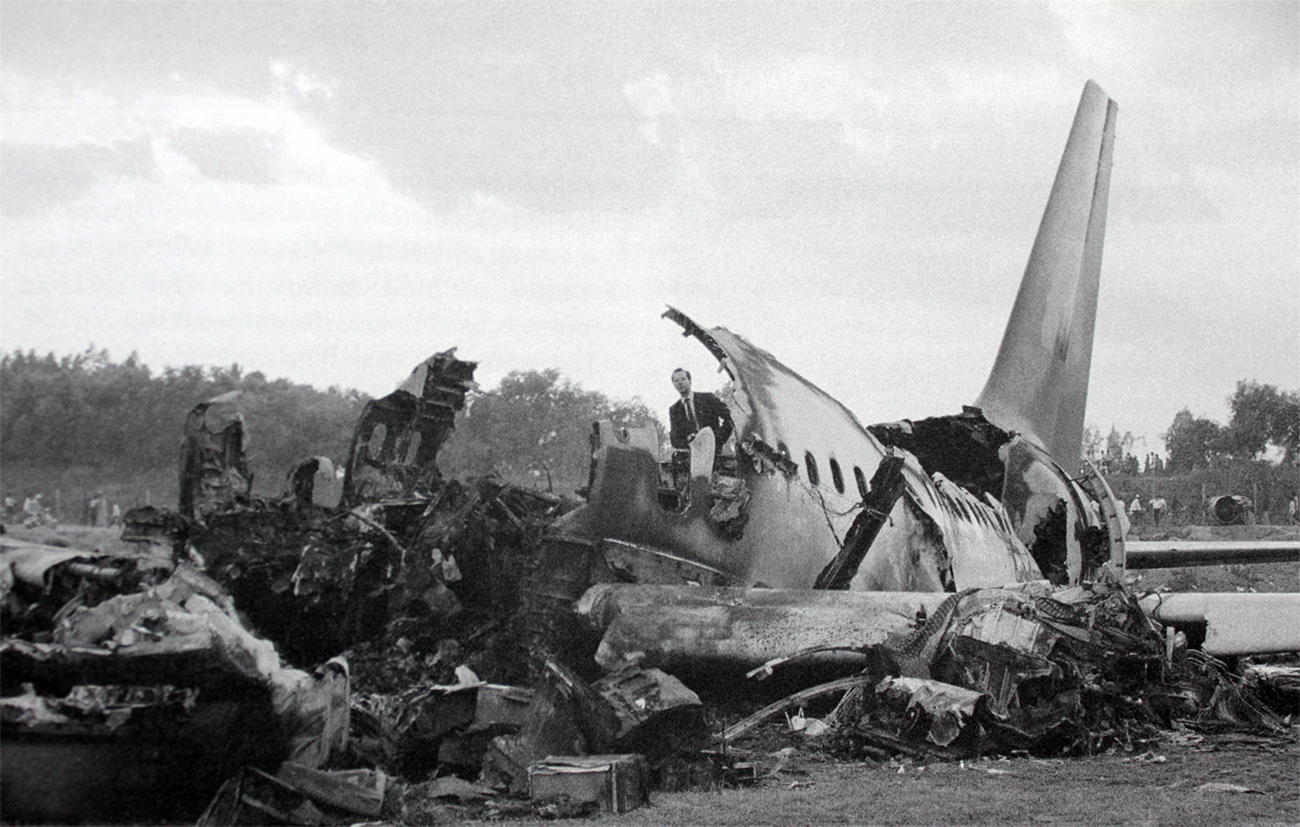
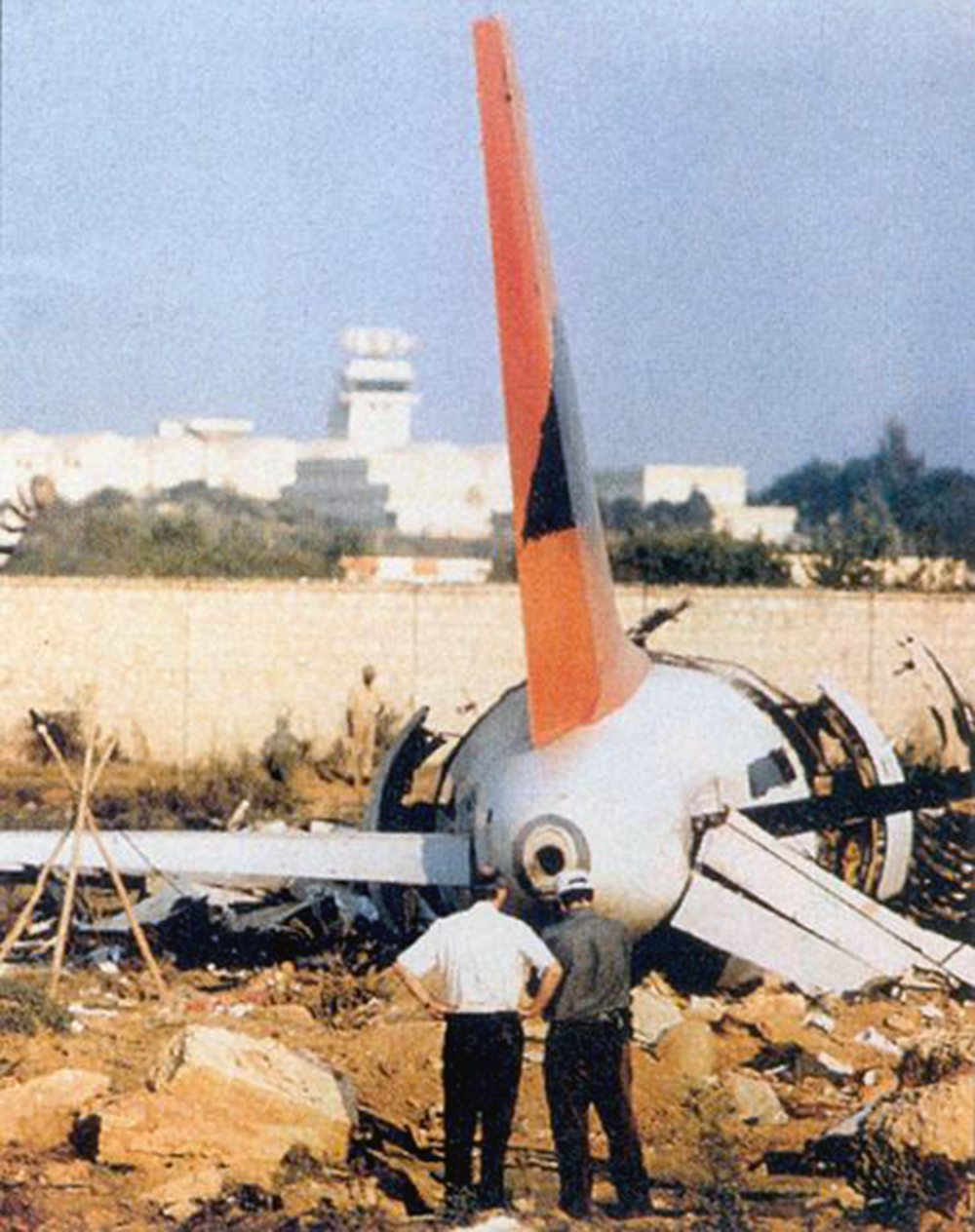
Crash of a Boeing 737-2A8 near Imphal: 69 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 16, 1991 at 1246 LT
Registration:
VT-EFL
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Calcutta - Imphal
MSN:
21497
YOM:
1977
Flight number:
IC257
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
63
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
69
Circumstances:
The aircraft departed Calcutta-Dum Dum Airport at 1154 on a regular schedule service to Imphal, Manipur. On descent, the crew encountered poor weather conditions and the visibility was low. After being cleared to descend to 10,000 feet, the crew obtain the permission to make a direct outbound course in view of an ILS approach to runway 04. While completing a turn to join the approach path, the crew failed to realize his altitude was insufficient when the GPWS alarm sounded in the cockpit during 6,3 seconds. The aircraft struck the slope of Mt Thangjing located 39 km southwest of runway 04 threshold and disintegrated on impact. All 69 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The accident occurred by reason of a grave error on the part of the Pilot-in-Command in not adhering to the operational flight plan and ILS let down chart and not realizing that his early descent to 10,000 feet and turning right for outbound leg without reporting overhead VOR would result in loss of time reference and as such misplace him in the hilly terrain. The Pilot-in-Command's action may have been influenced by his extreme familiarity with the terrain.
Final Report:

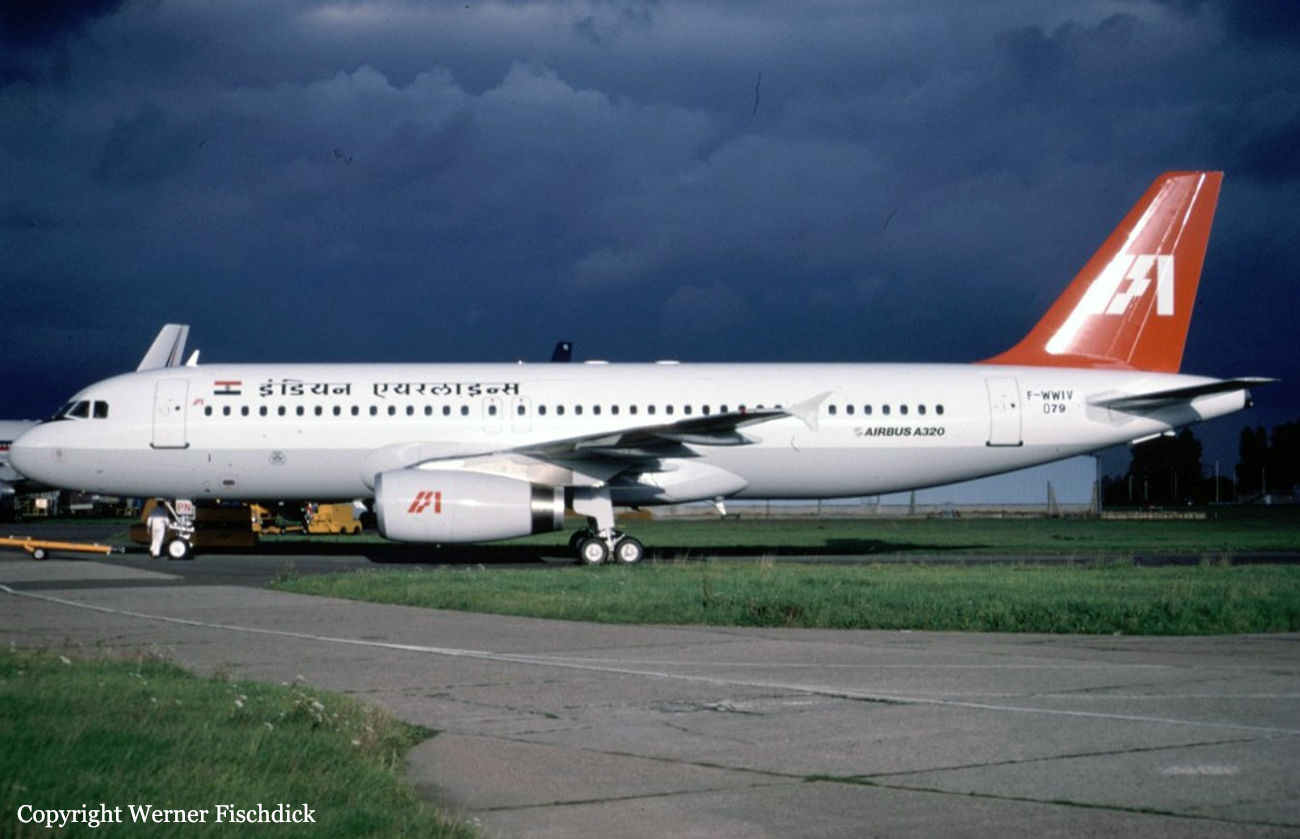
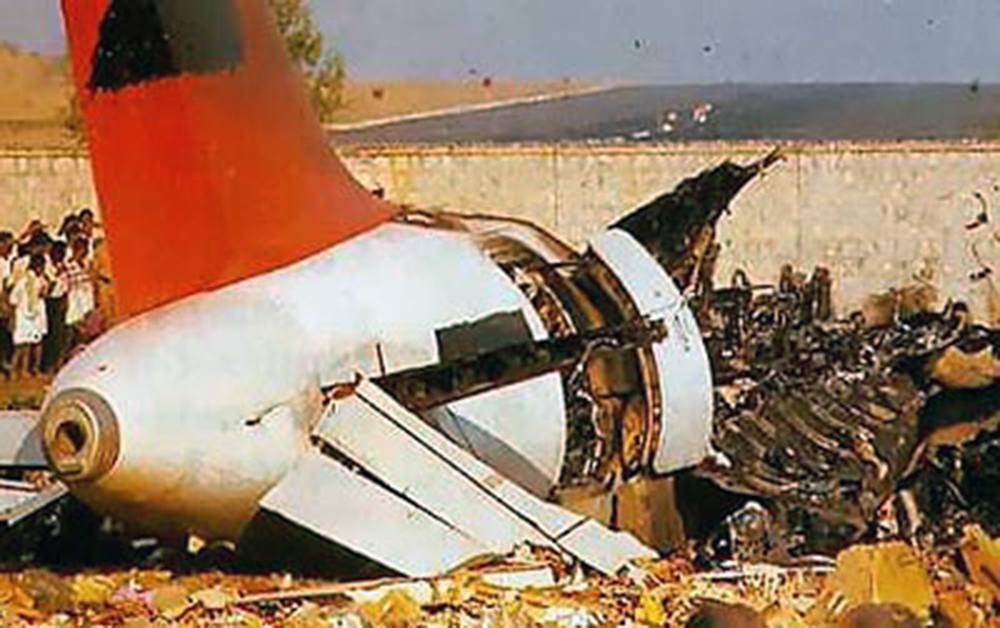
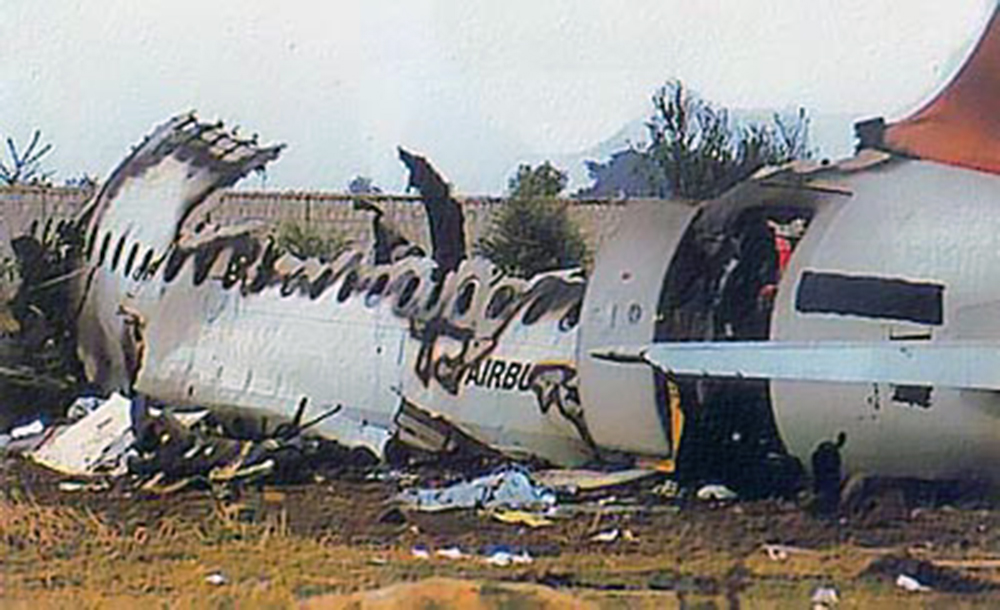
Crash of an Airbus A320-231 in Bangalore: 92 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 14, 1990 at 1303 LT
Registration:
VT-EPN
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Bombay - Bangalore
MSN:
79
YOM:
1989
Flight number:
IC605
Crew on board:
7
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
139
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
92
Captain / Total hours on type:
212.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
68
Aircraft flight hours:
370
Aircraft flight cycles:
302
Circumstances:
Indian Airlines Flight 605 took off from Mumbai, India, at 11:58 for a domestic flight to Bangalore. At 12:25 Bangalore approach was contacted and prevailing weather was passed on to the crew (wind variable 5 knots, visibility 10 km, clouds 2 octa 2,000 feet, temperature 27° C, QNH 1018). At 12:44 the aircraft was cleared to descend to FL110. Reaching FL110, vectors were given for a visual runway 09 approach. On final approach, the aircraft descended well below the normal approach profile and kept descending until it struck the boundaries of the Karnataka Golf Club (2,300 feet short of the runway and 200 feet right of the extended centerline. The aircraft rolled for 80 feet and lifted off again for about 230 feet and came down again on the 17th green of the golf course. The landing gear wheels dug into the ground and the aircraft impacted a 12 feet high embankment, causing the gears and engines to be sheared off. The aircraft continued over the embankment and came to rest in a grassy, marshy and rocky area.
Probable cause:
Failure of the pilots to realize the gravity of the situation and respond immediately towards proper action of moving the throttles, even after the radio altitude call-outs of "Four hundred", "Three hundred" and "Two hundred" feet, in spite of knowing that the plane was in idle/open descent mode. However, identification of the cause for the engagement of idle/open descent mode in short final approach during the crucial period of the flight is not possible.
Final Report:









