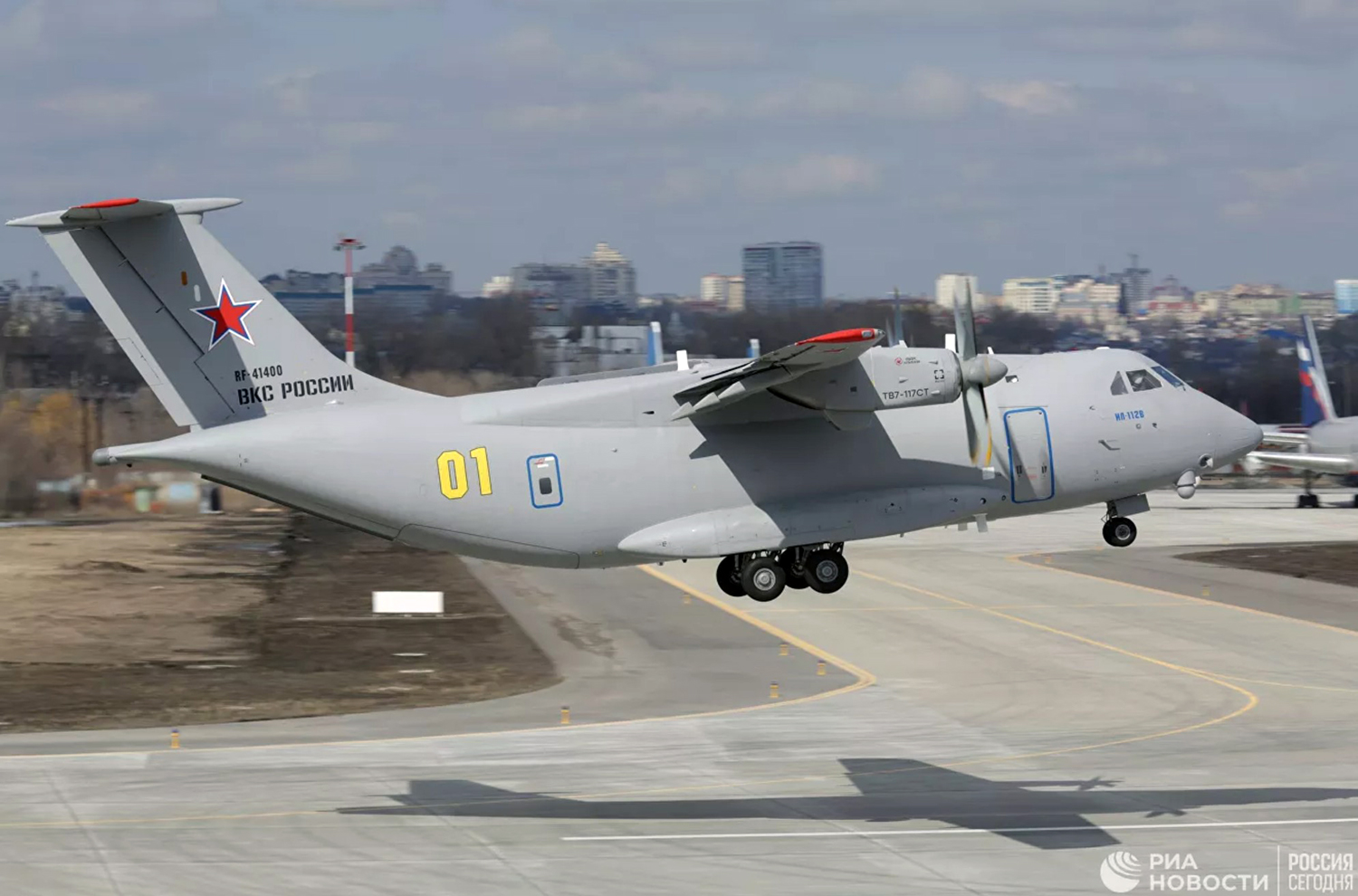
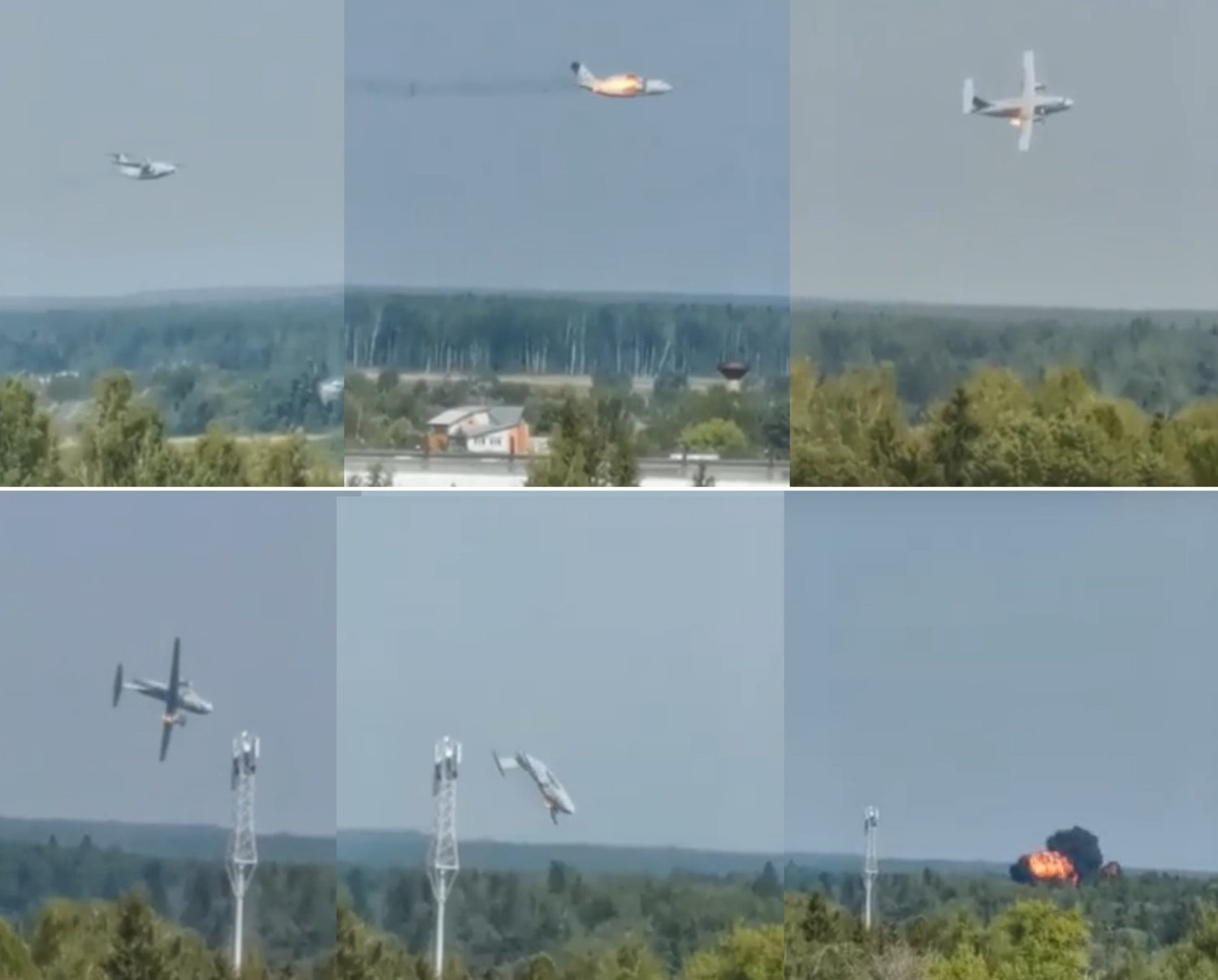
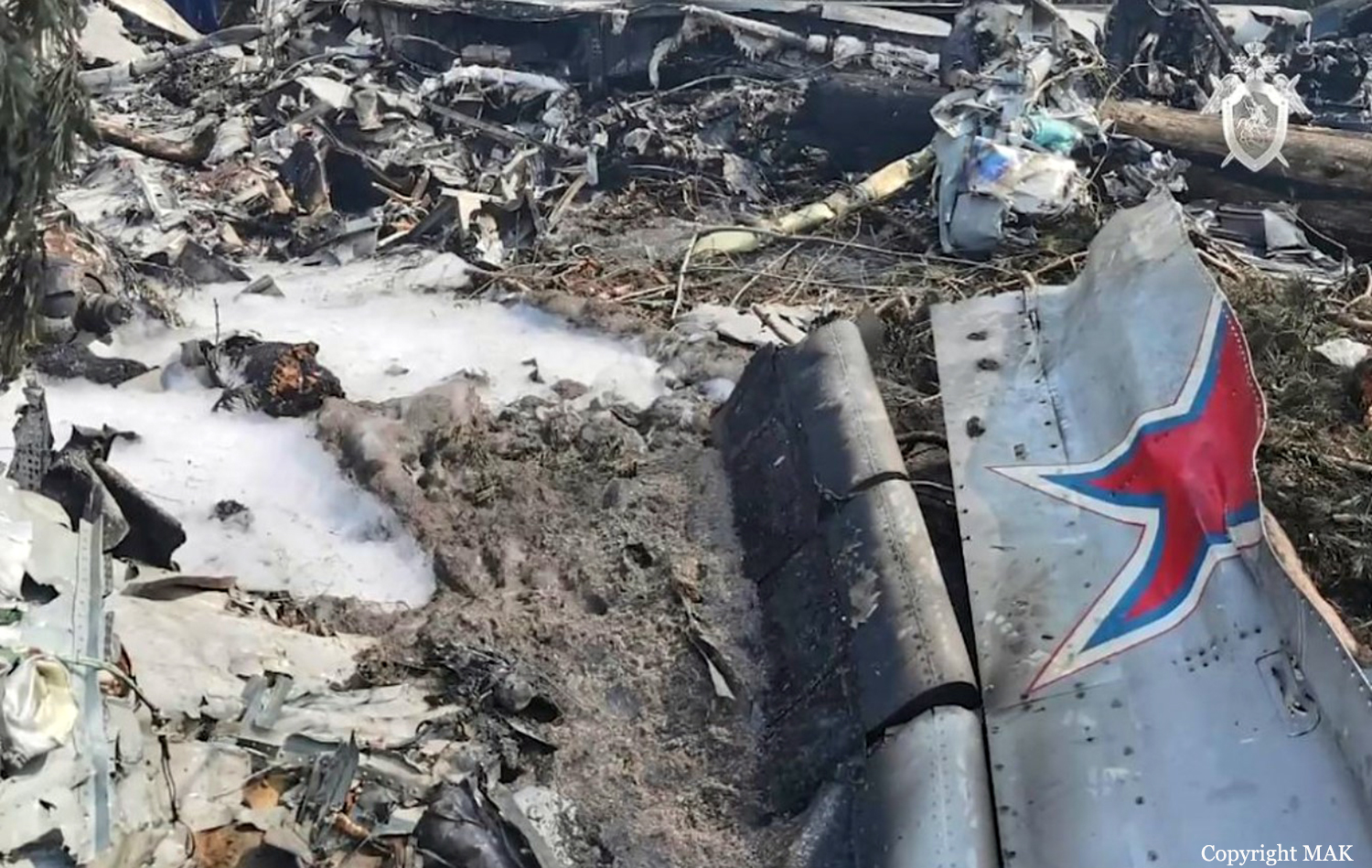
Crash of an Ilyushin II-112V in Kubinka: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 17, 2021 at 1118 LT
Registration:
RF-41400
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kubinka - Kubinka
MSN:
01-01
YOM:
2008
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
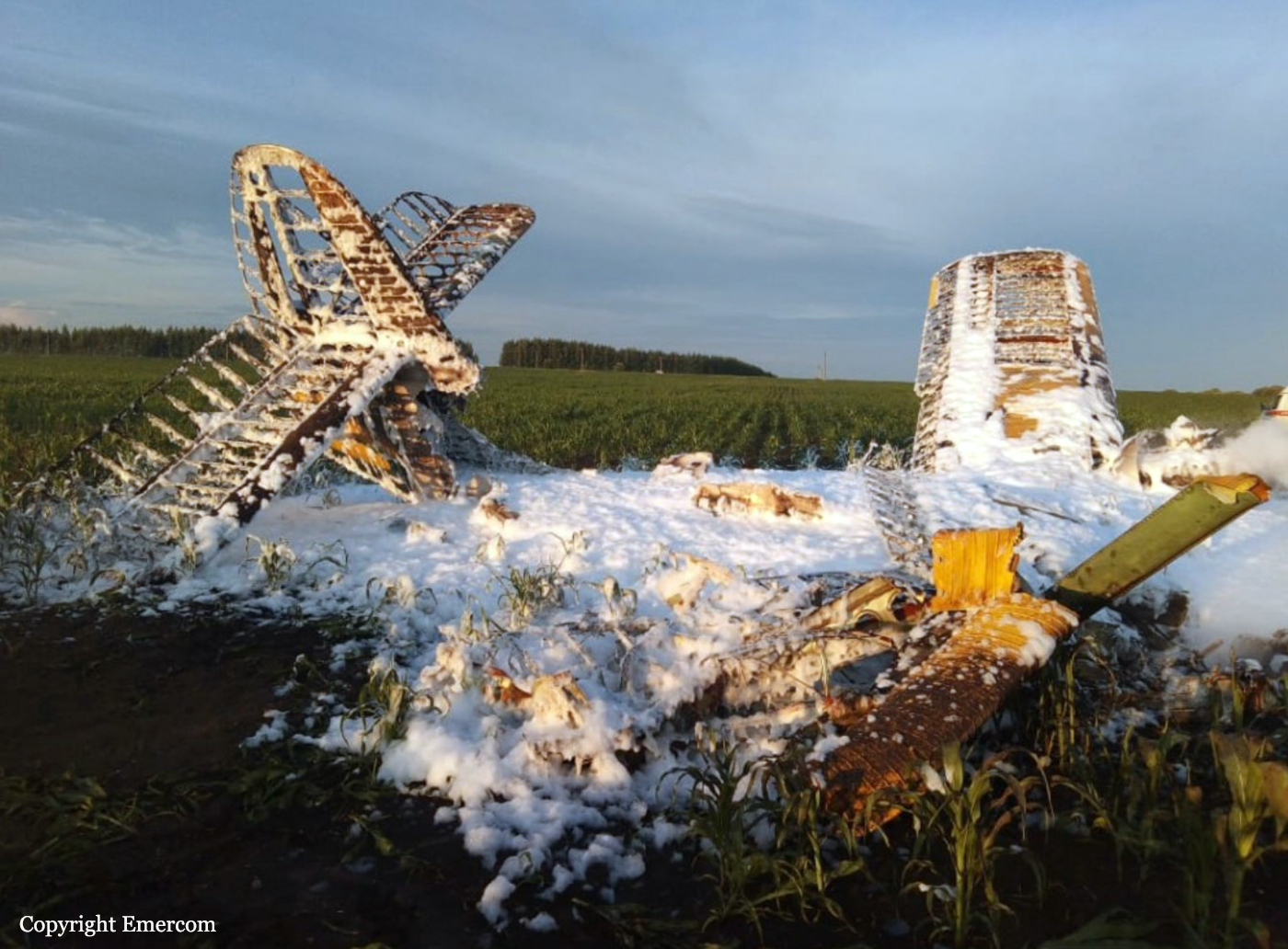
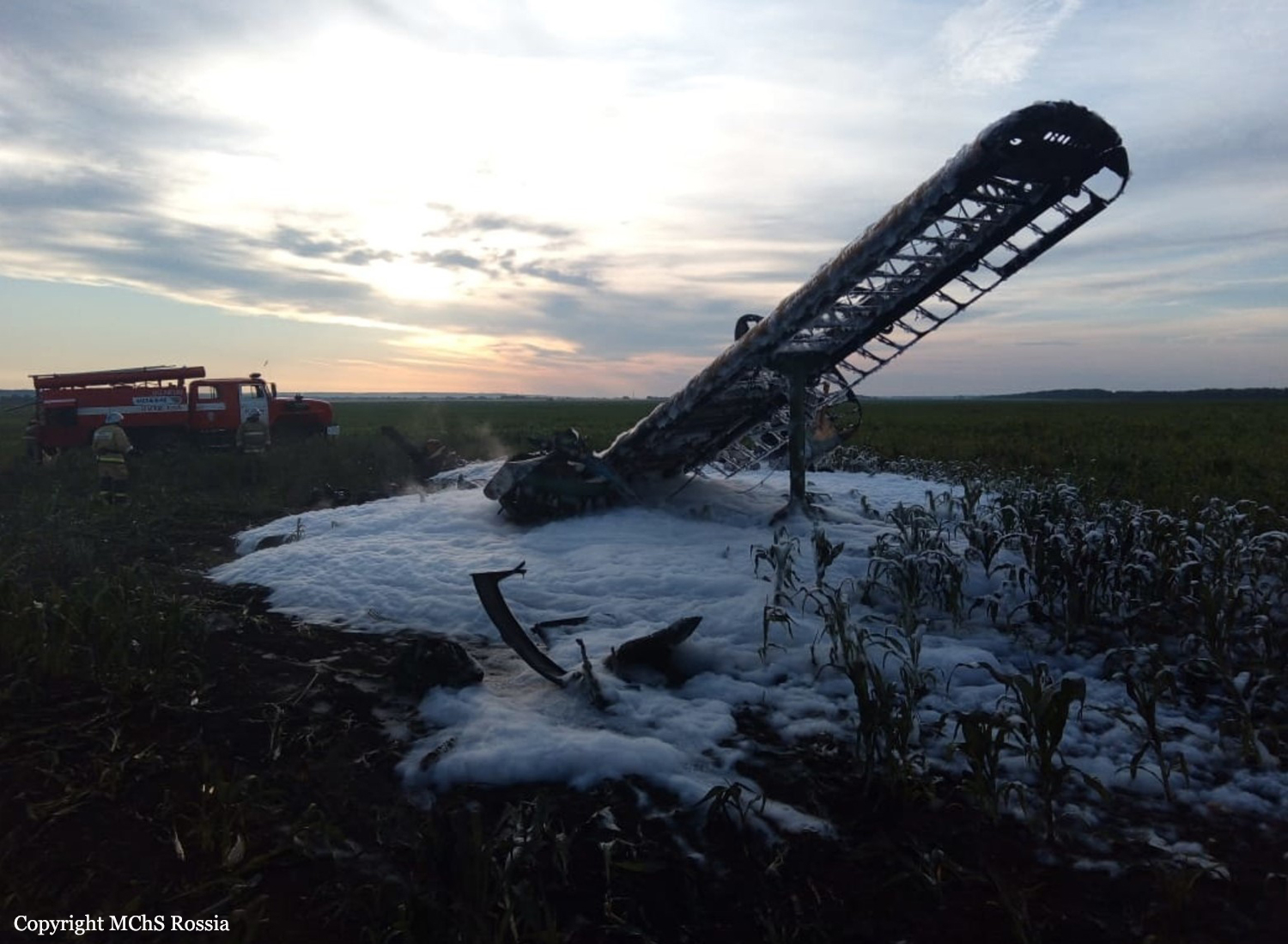
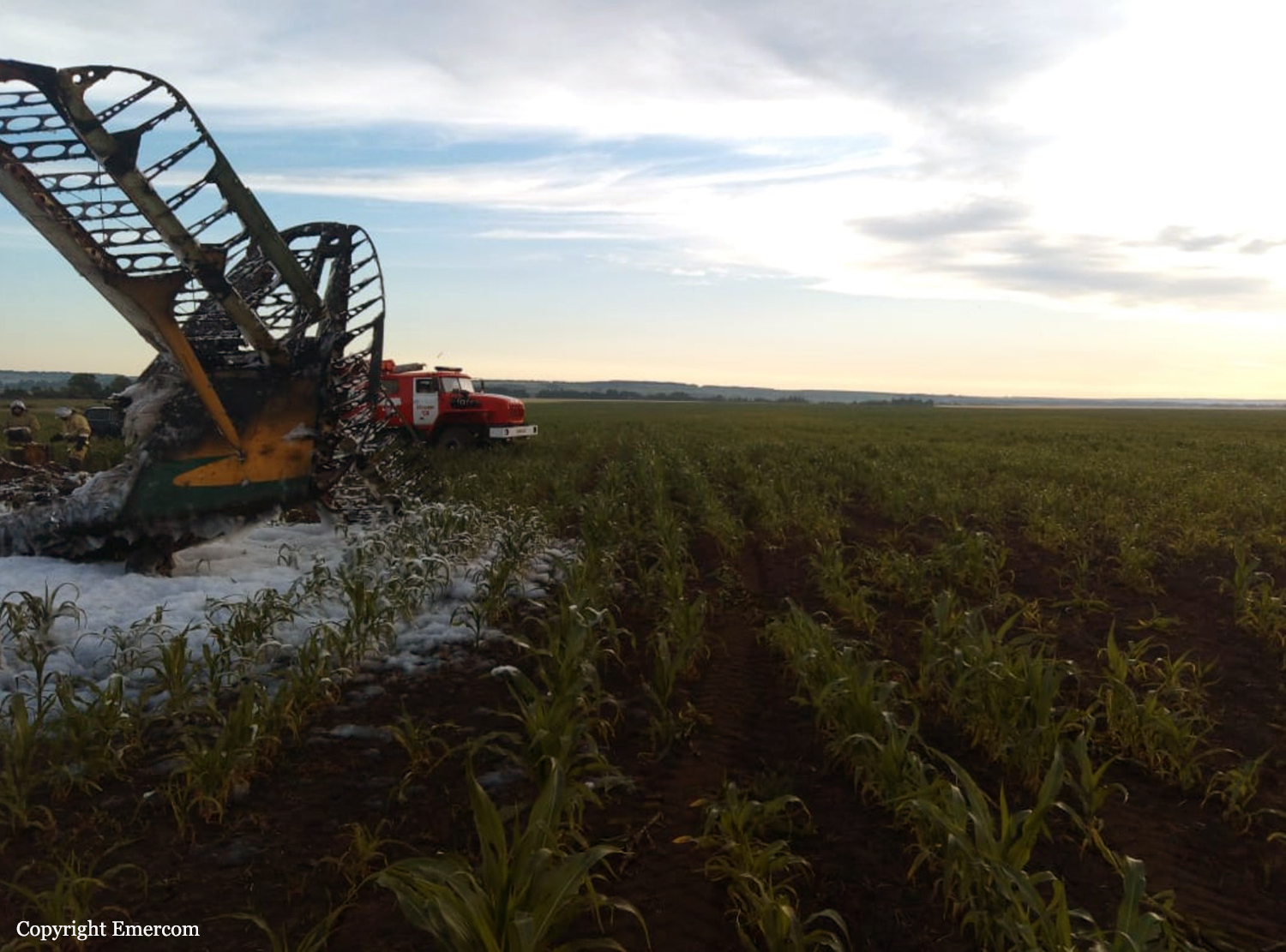
Circumstances:
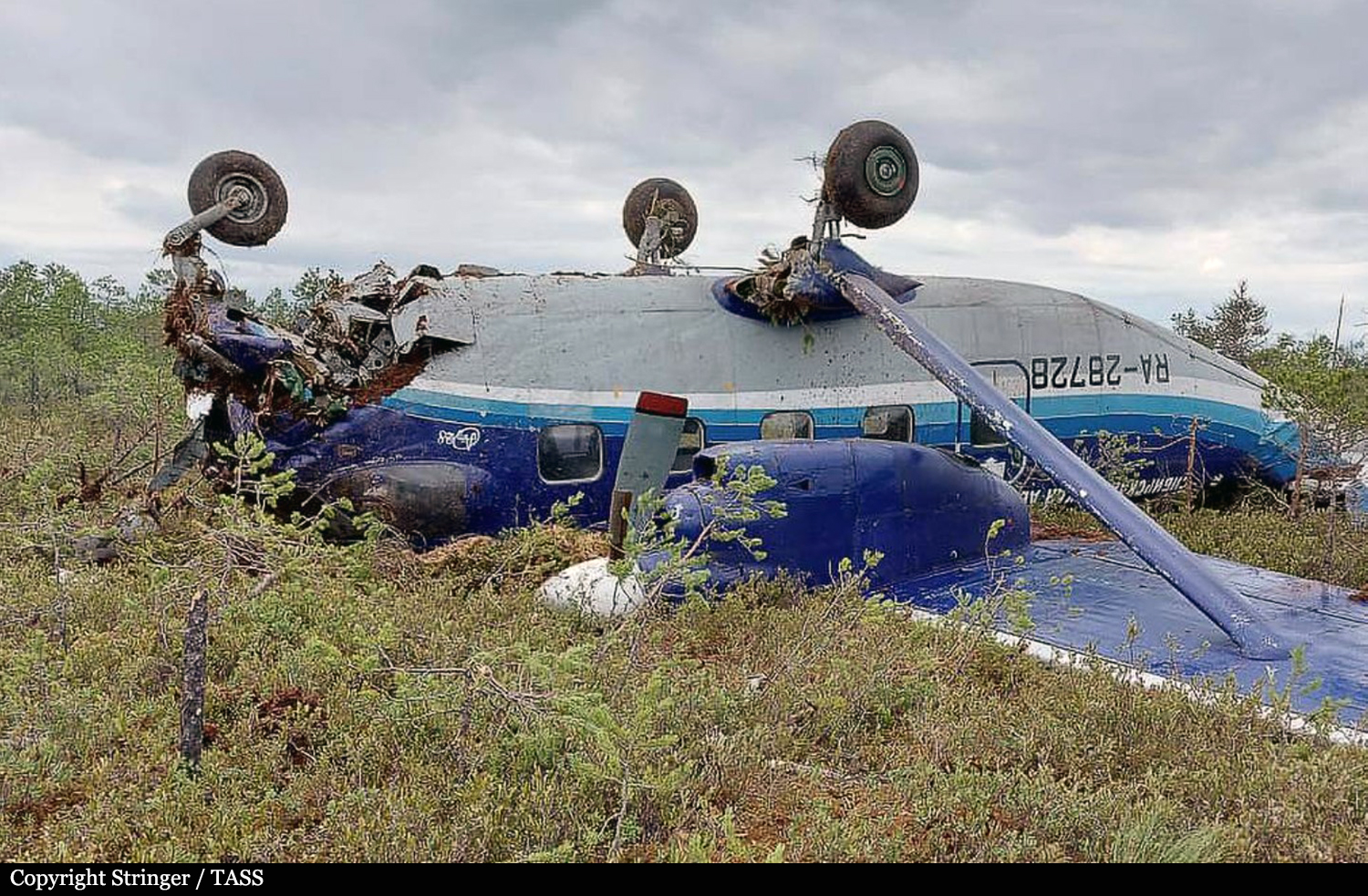
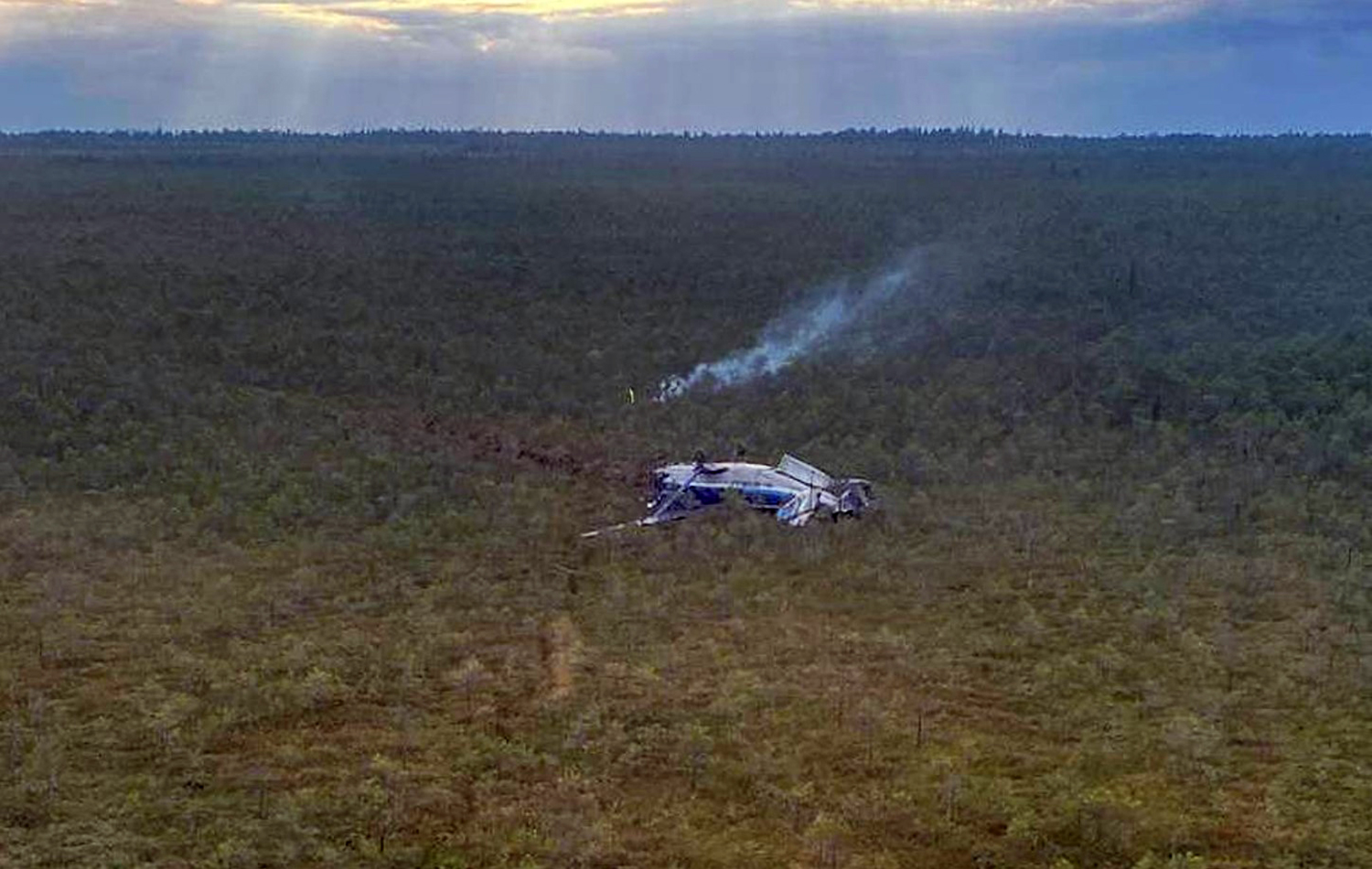
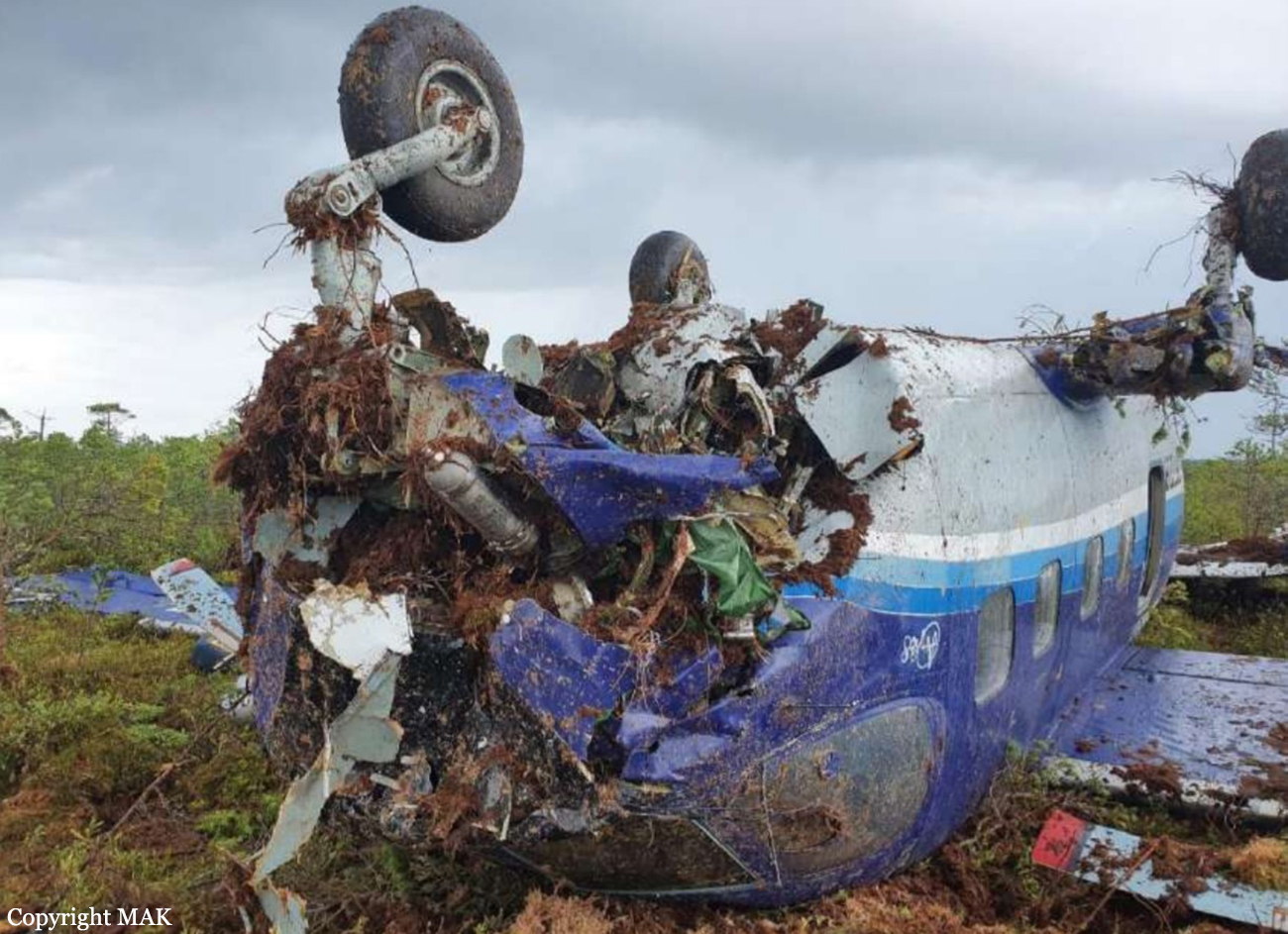
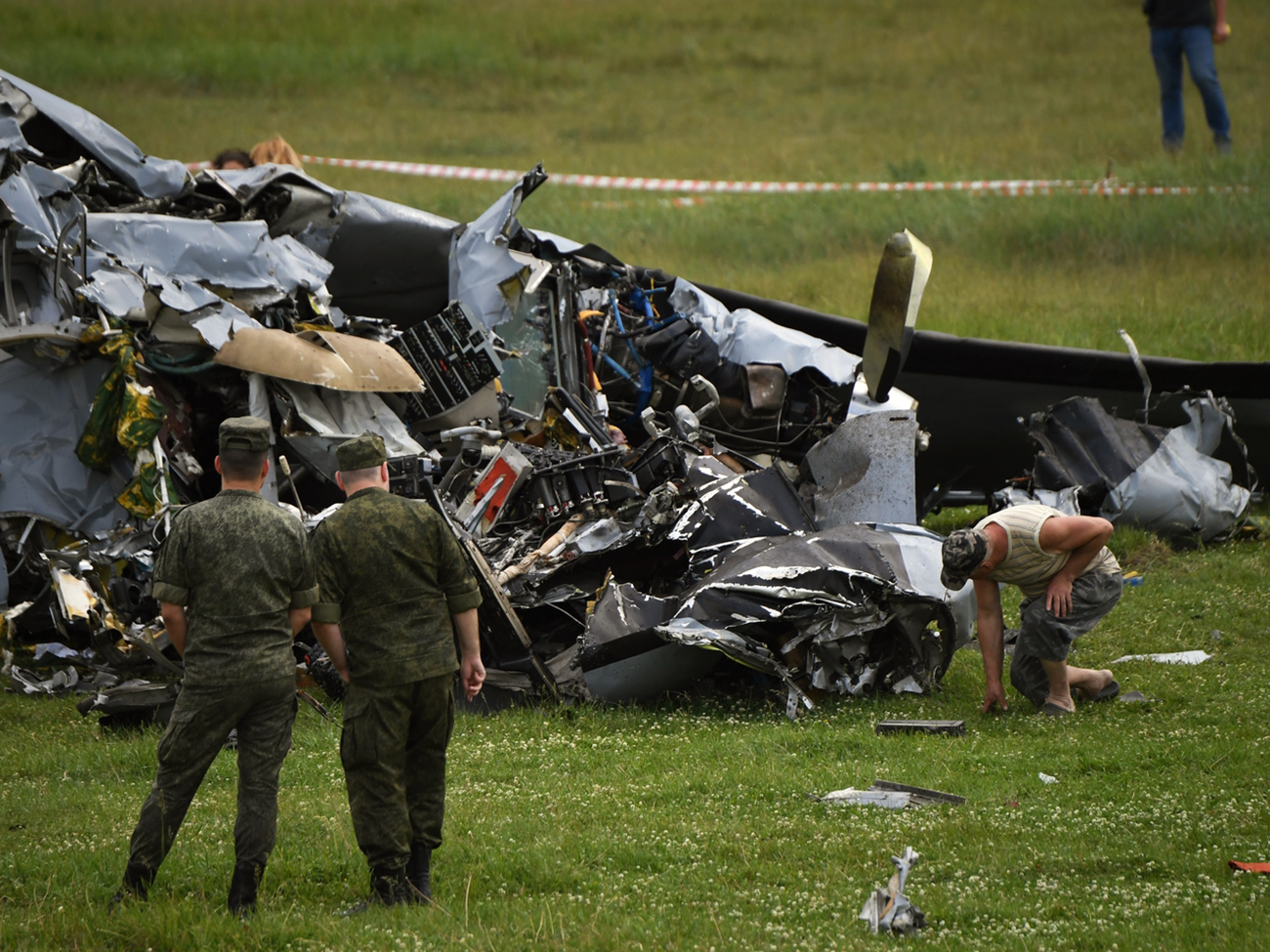
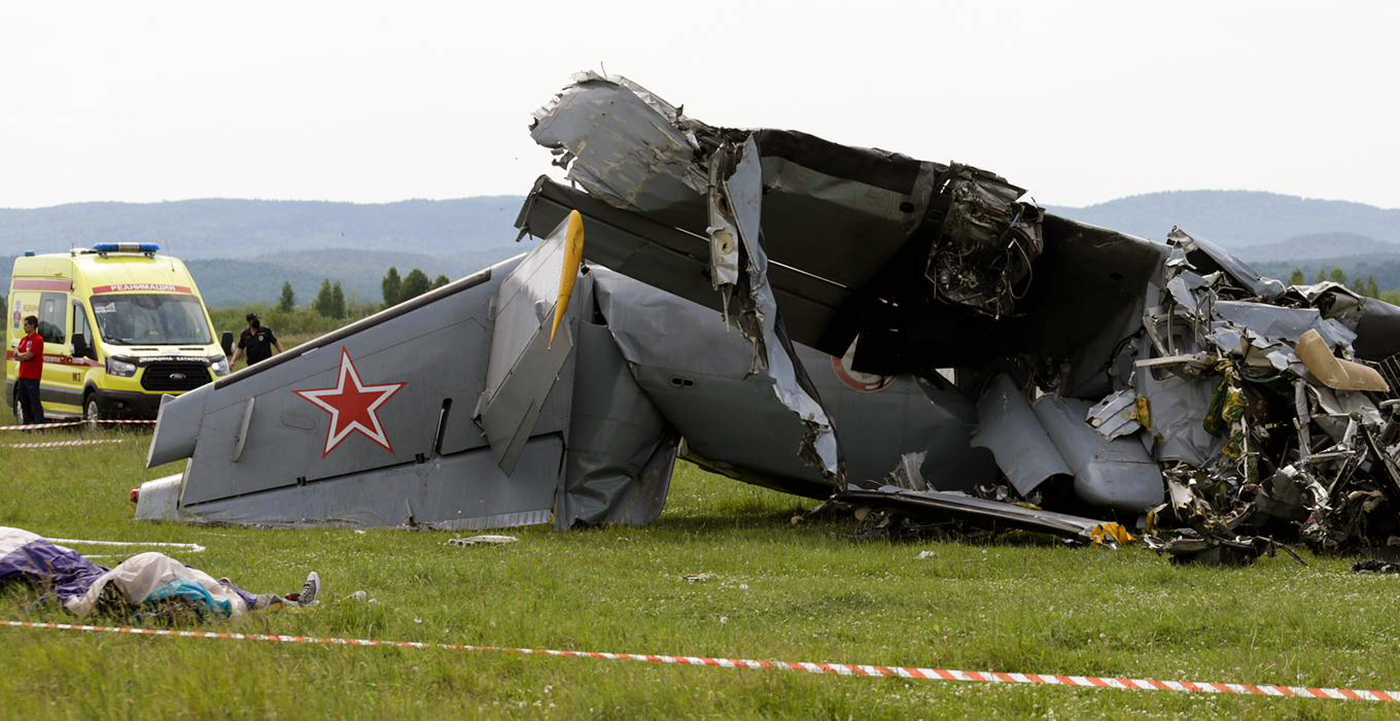
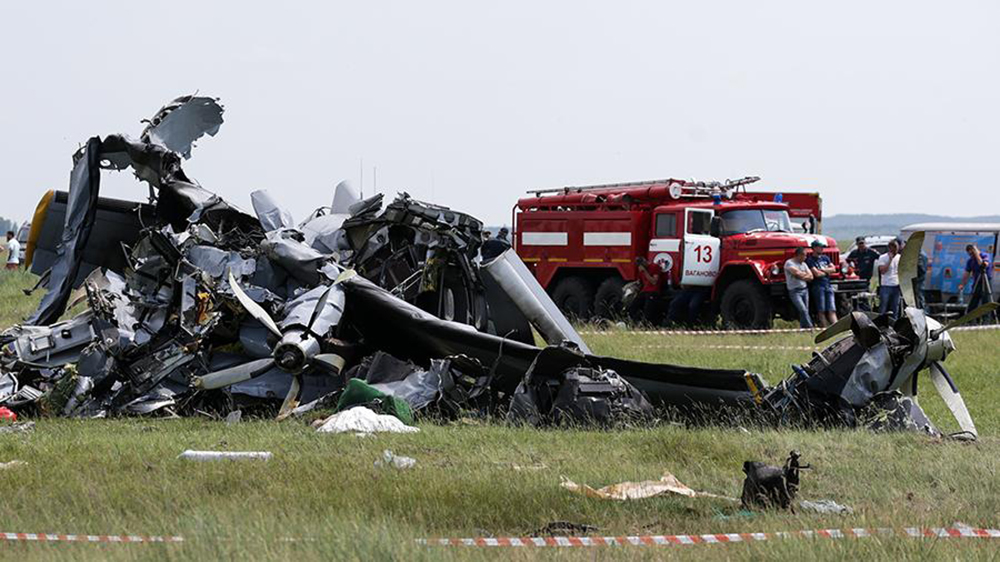
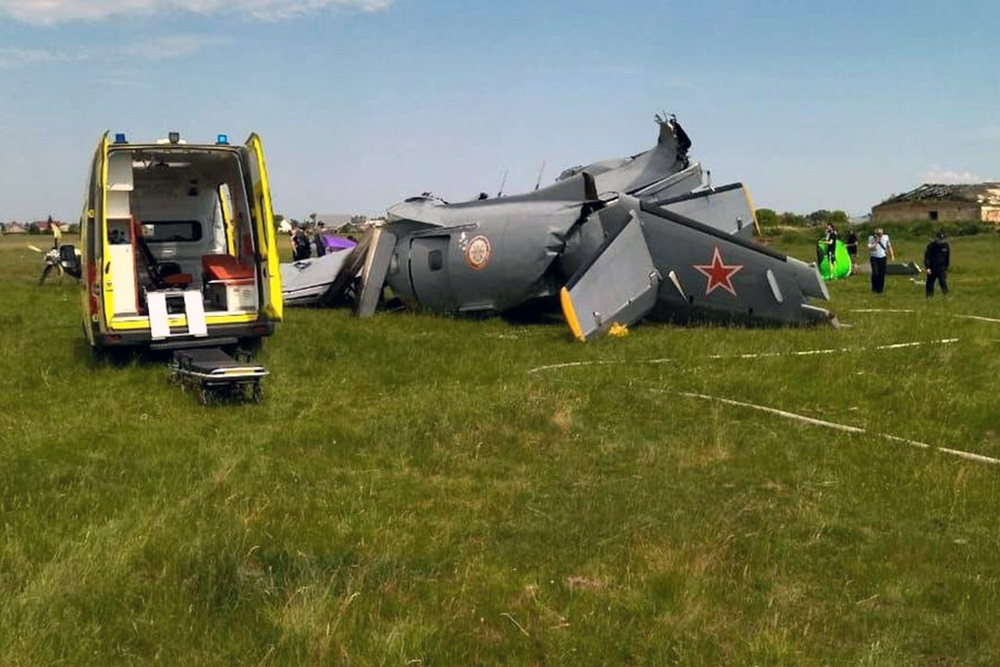
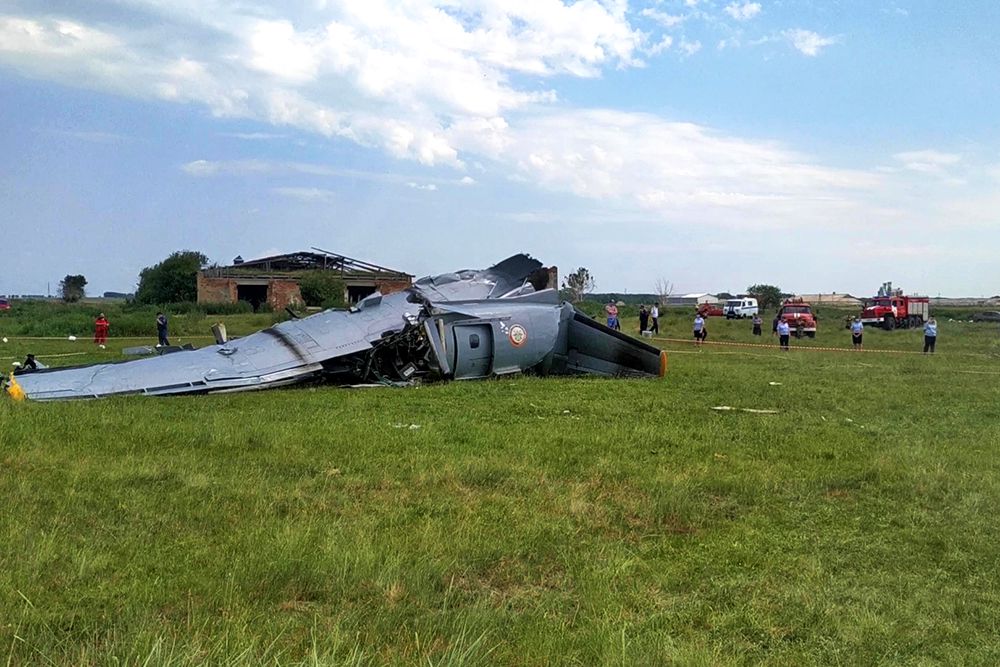
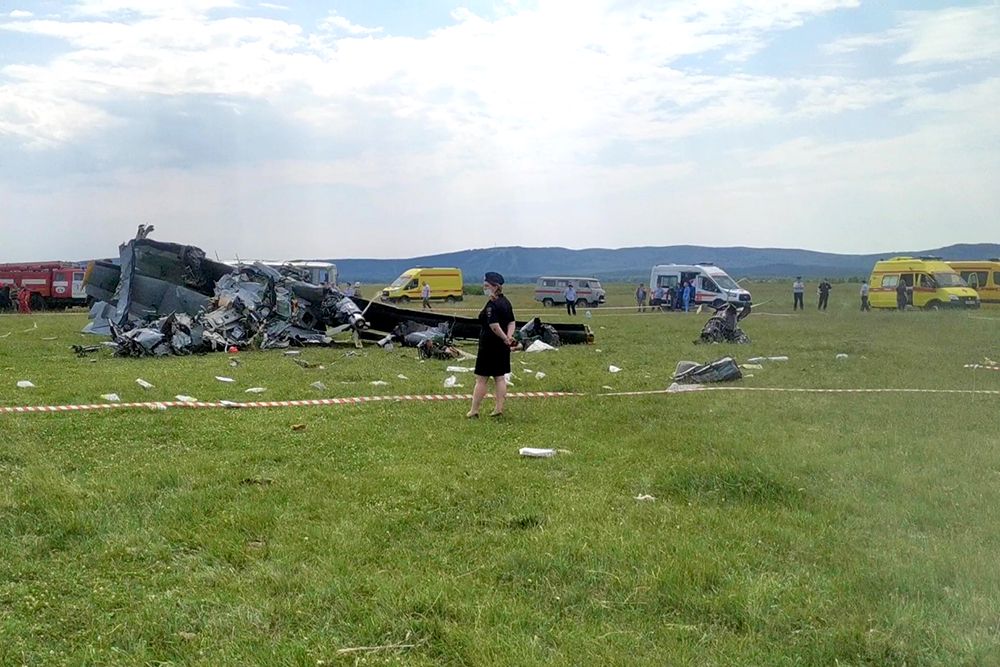
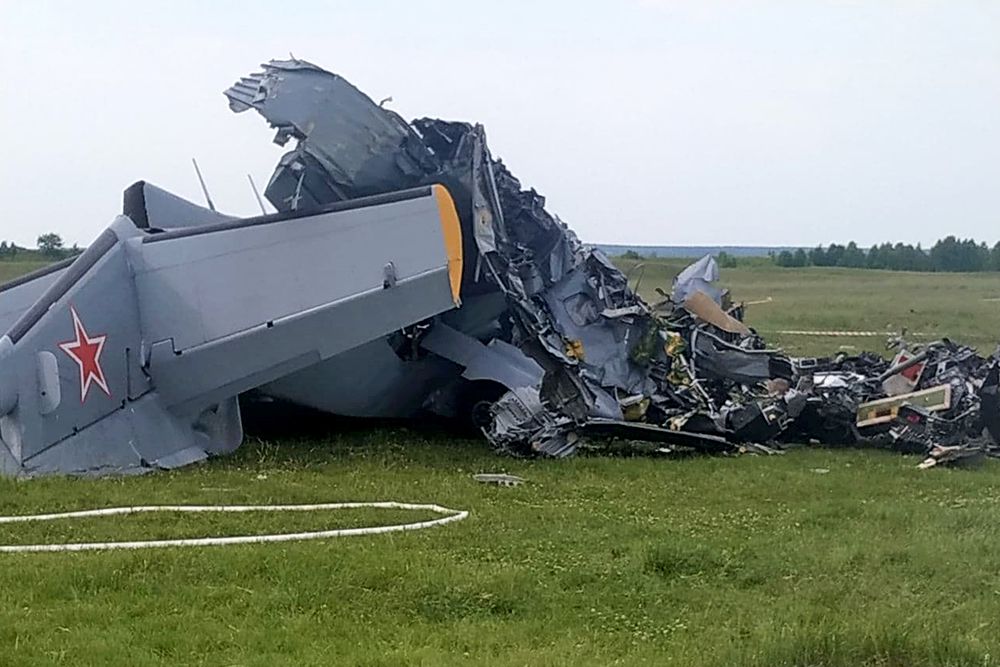
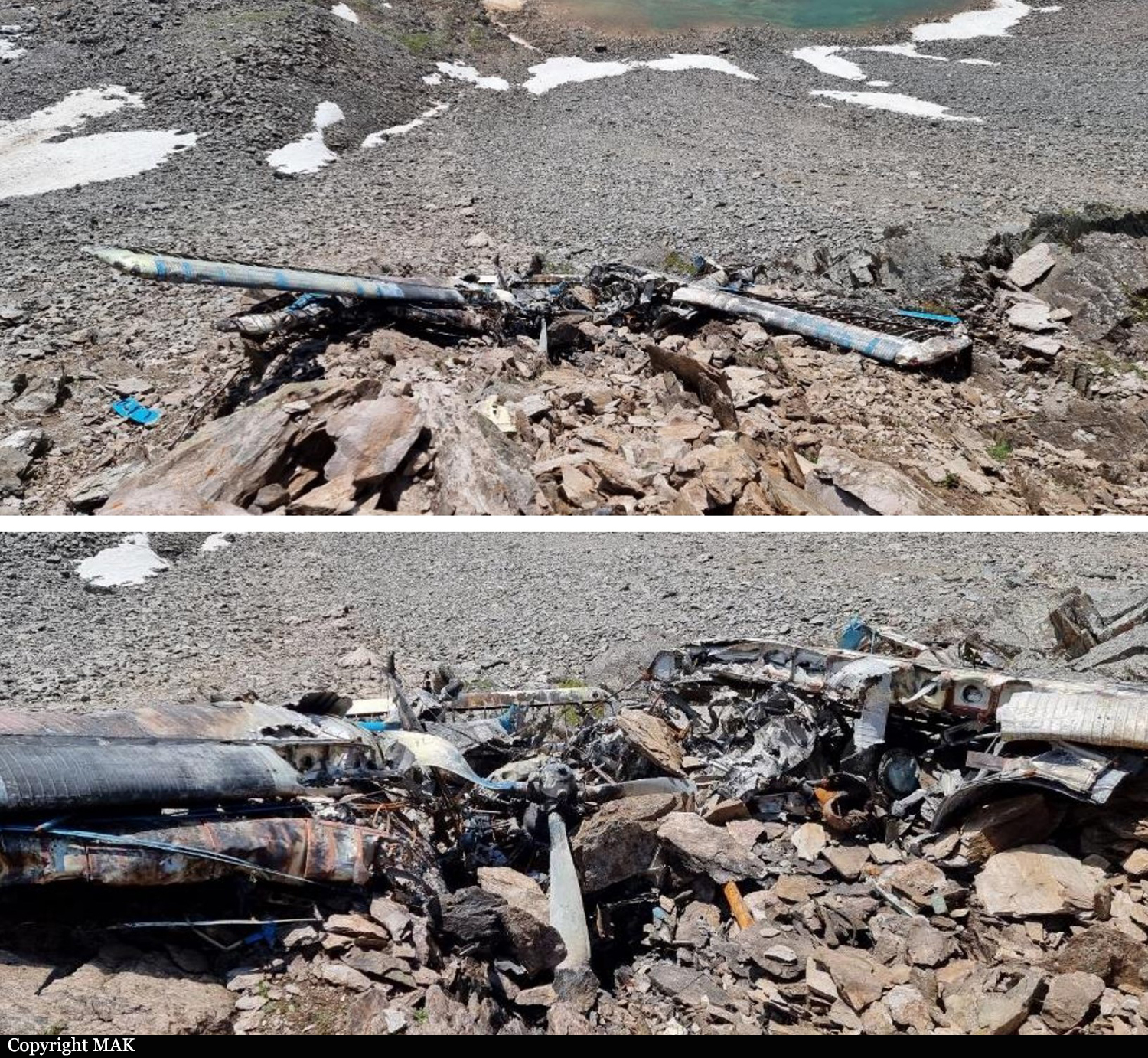
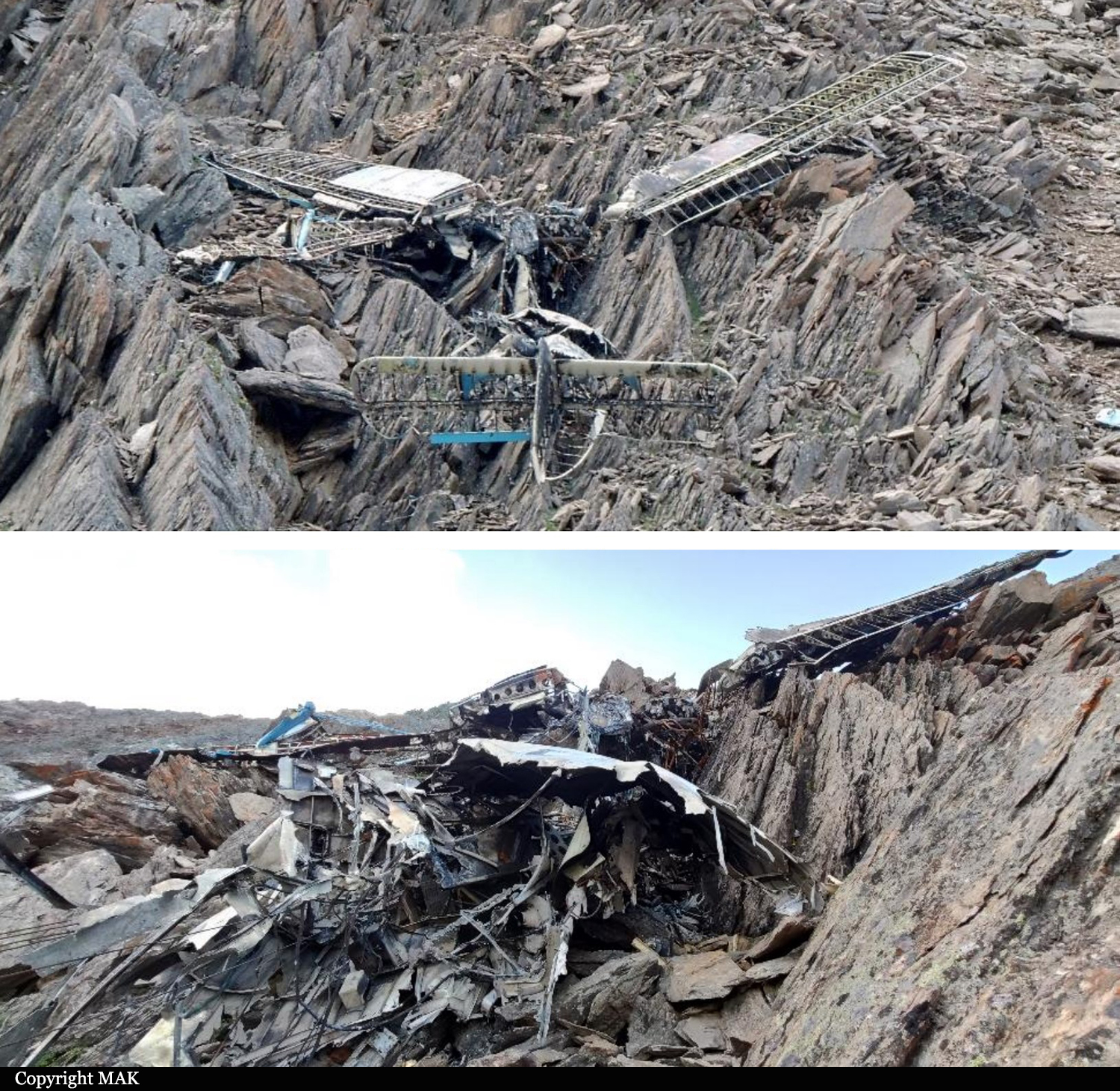
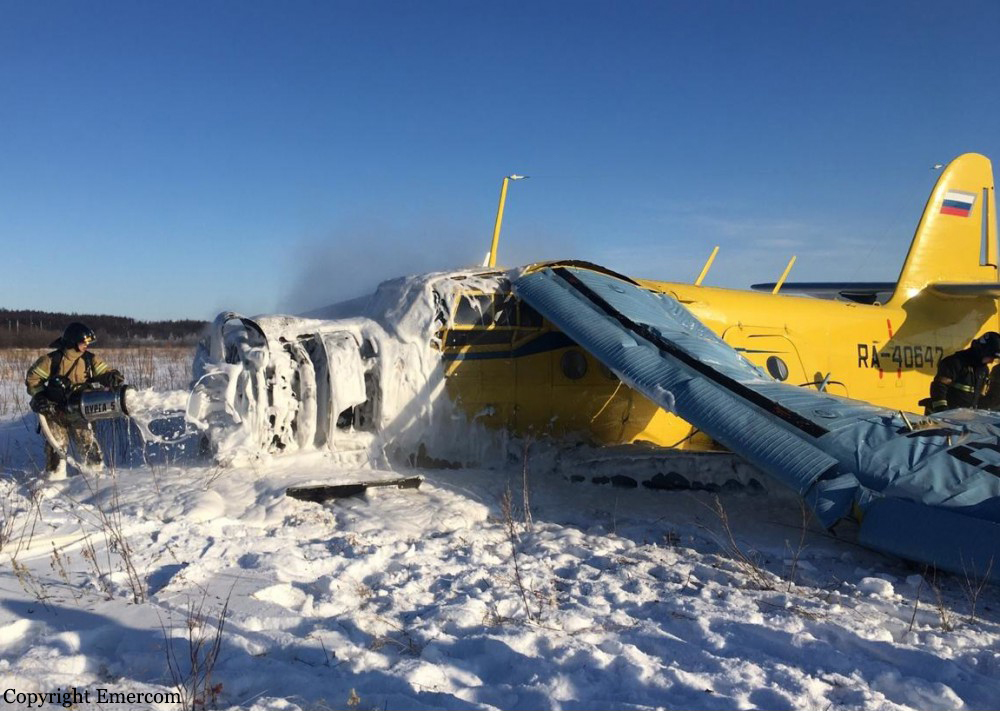
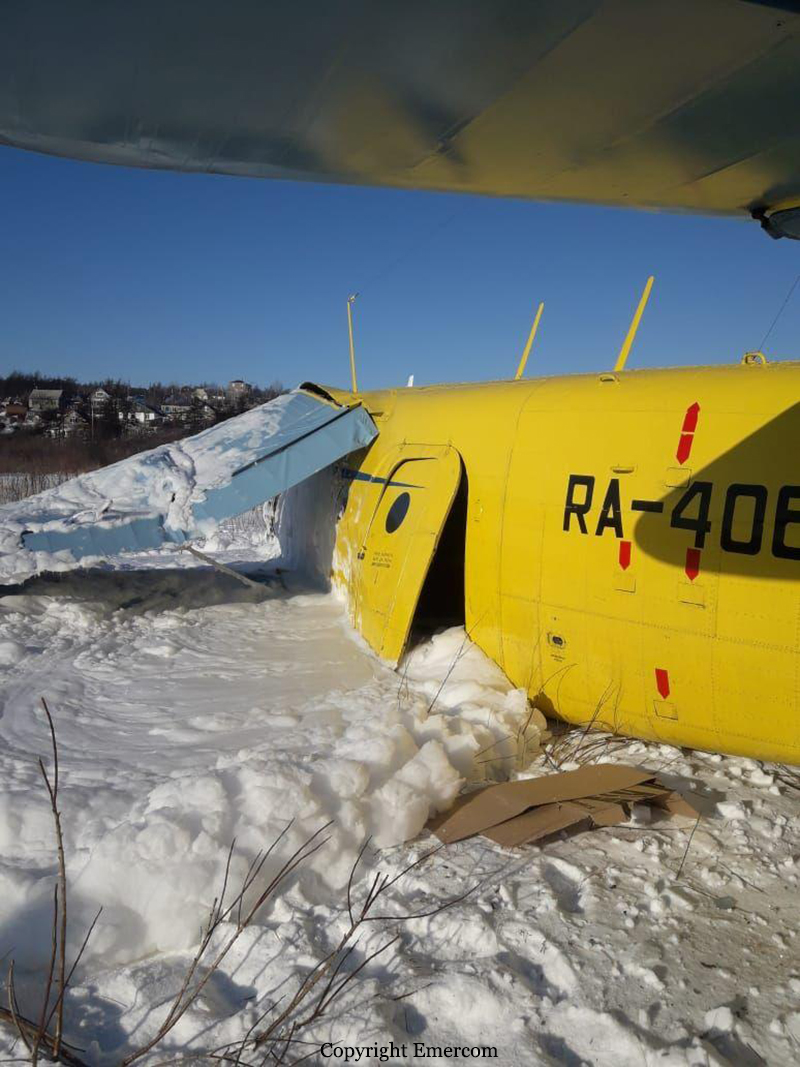
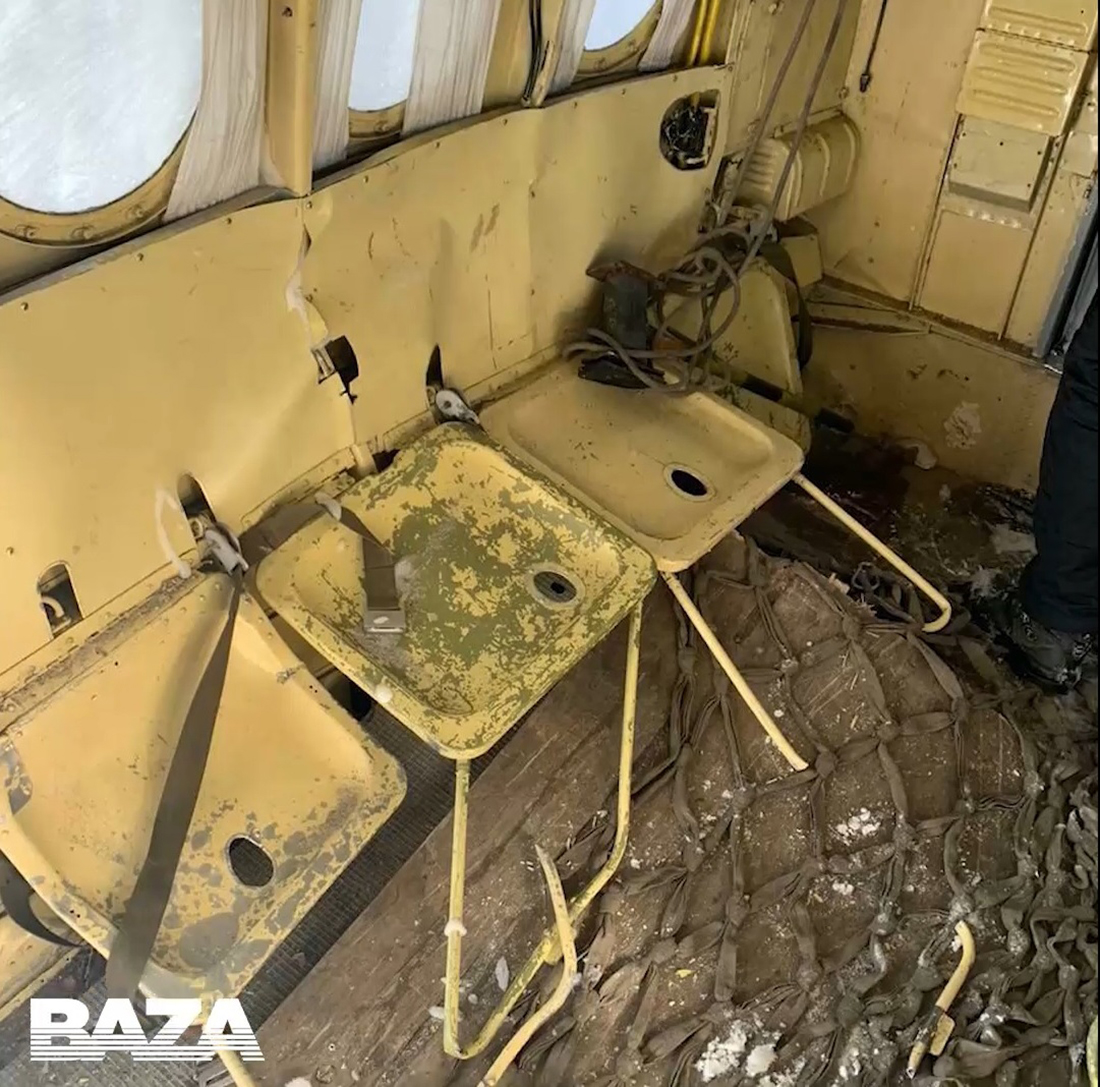
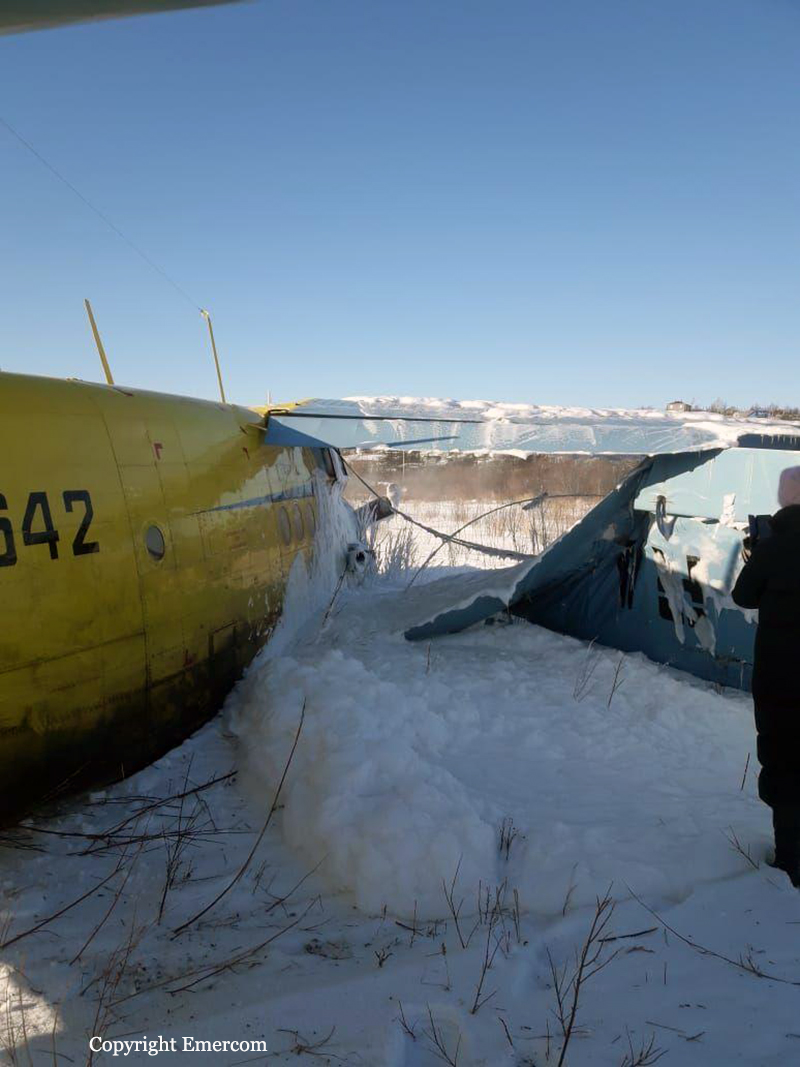
On August 13, the aircraft (first prototype of this new model) departed the aviation plant at Voronezh Airport on a flight to Moscow-Zhukovsky, preparing for a demonstration flight at the 7th Military Technical Forum. On August 17, the crew departed Zhukovsky for a test flight to Kubinka Airport where the aircraft landed at 1109LT. Four minutes after takeoff at 1114LT, while flying at low altitude in a flat attitude, the right engine caught fire. 35 seconds later, while the crew elected to reach the airport, the aircraft rolled to the right, got inverted and crashed in a wooded area located 2,5 km short of runway 22. The aircraft was totally destroyed and all three crew members were killed. This first exemple was dedicated to the Russian Aerospace Forces (Vozdushno-kosmicheskiye sily) and was also registered 01 yellow.
Crew:
Nikolay Dmitrievich Kuimov, test pilot,
Dmitry Komarov, test pilot,
Nikolai Khludeyev, flight engineer.
Crew:
Nikolay Dmitrievich Kuimov, test pilot,
Dmitry Komarov, test pilot,
Nikolai Khludeyev, flight engineer.