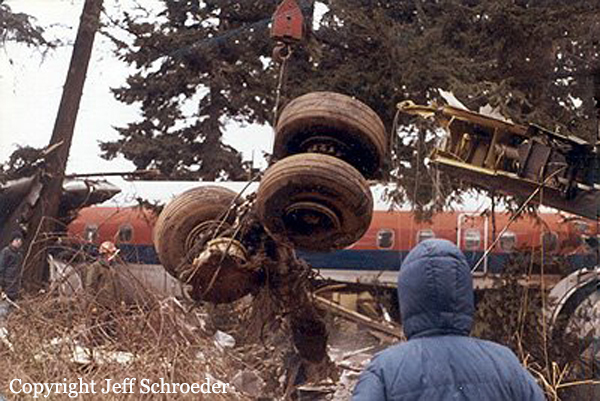Circumstances:
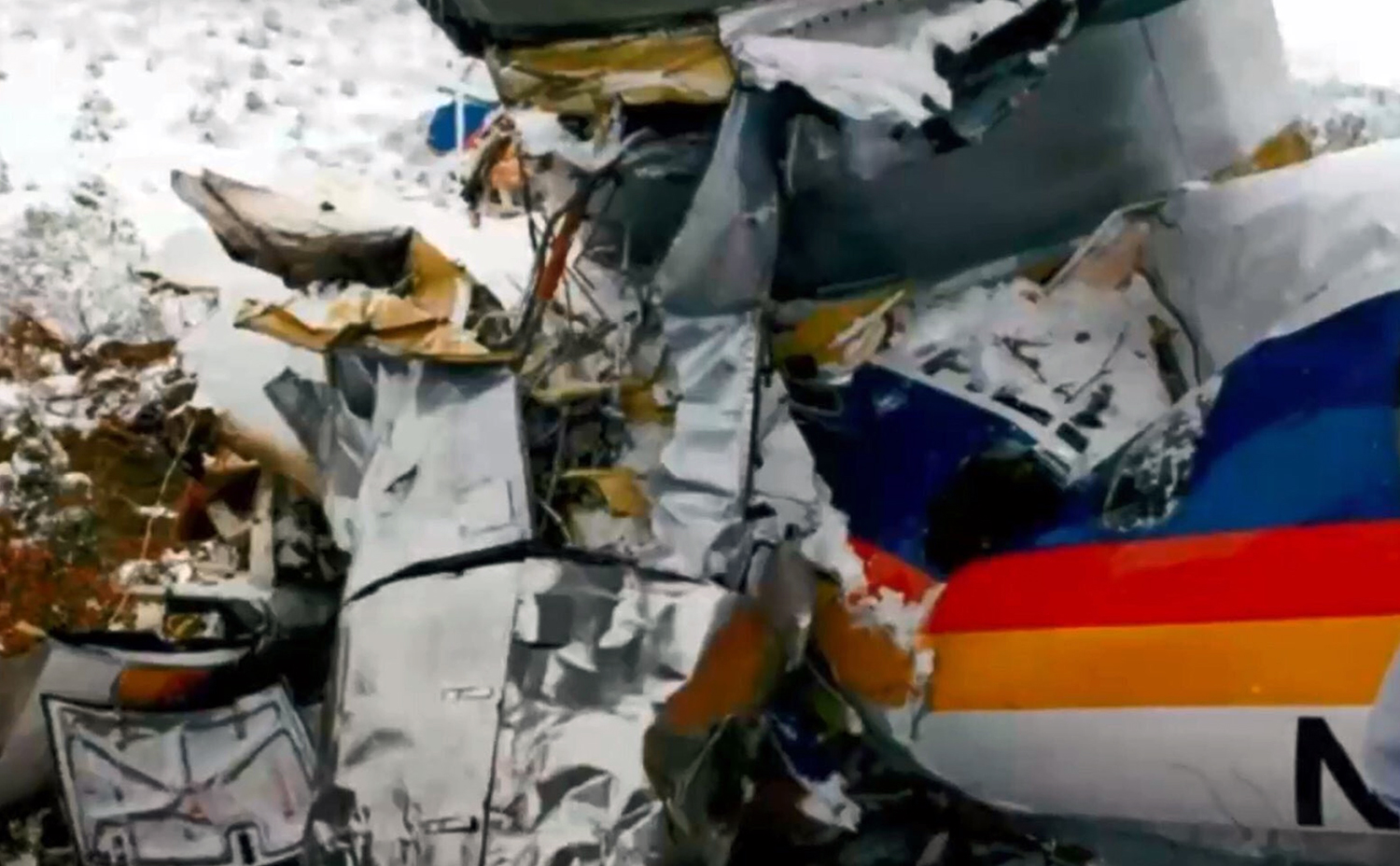
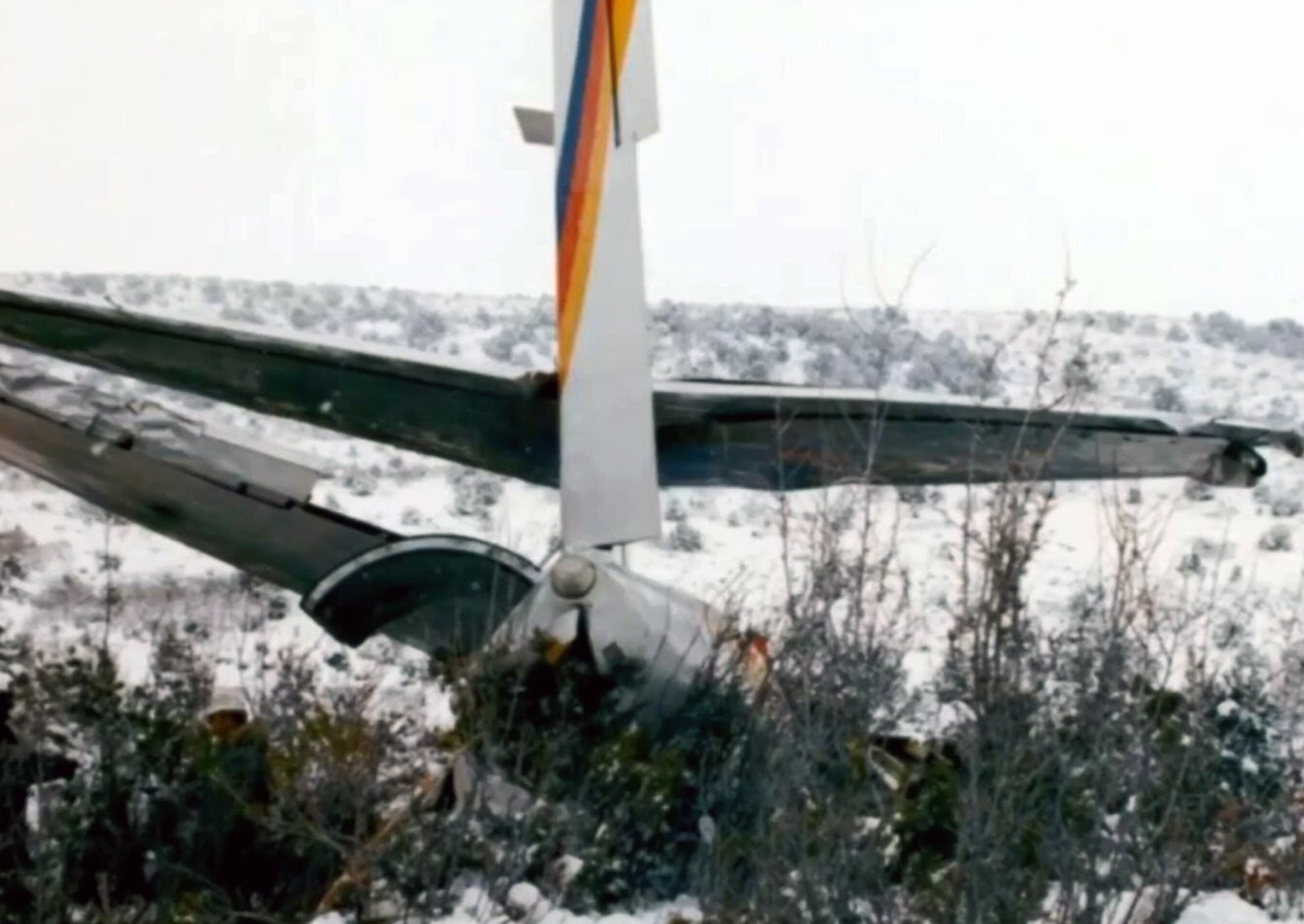
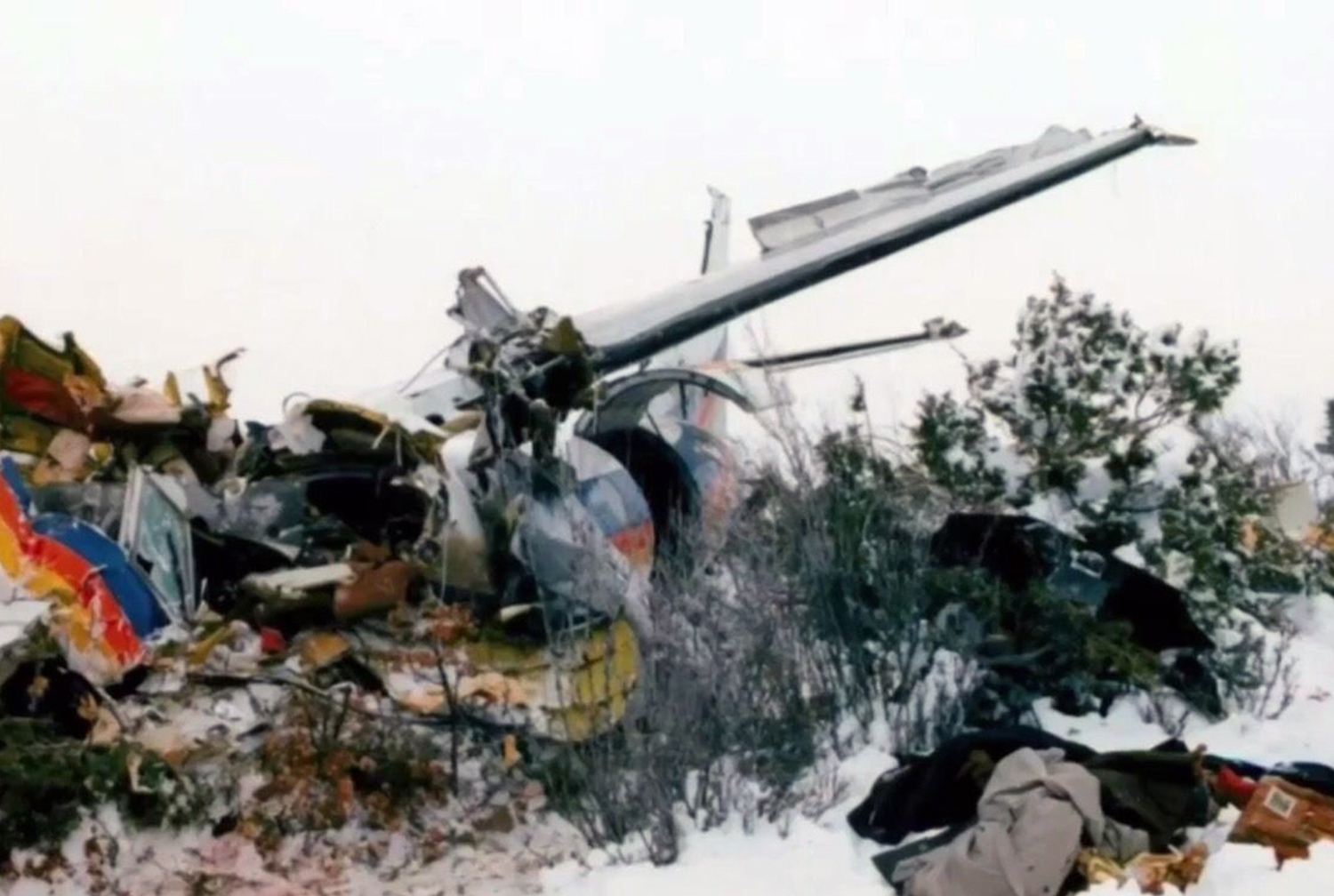
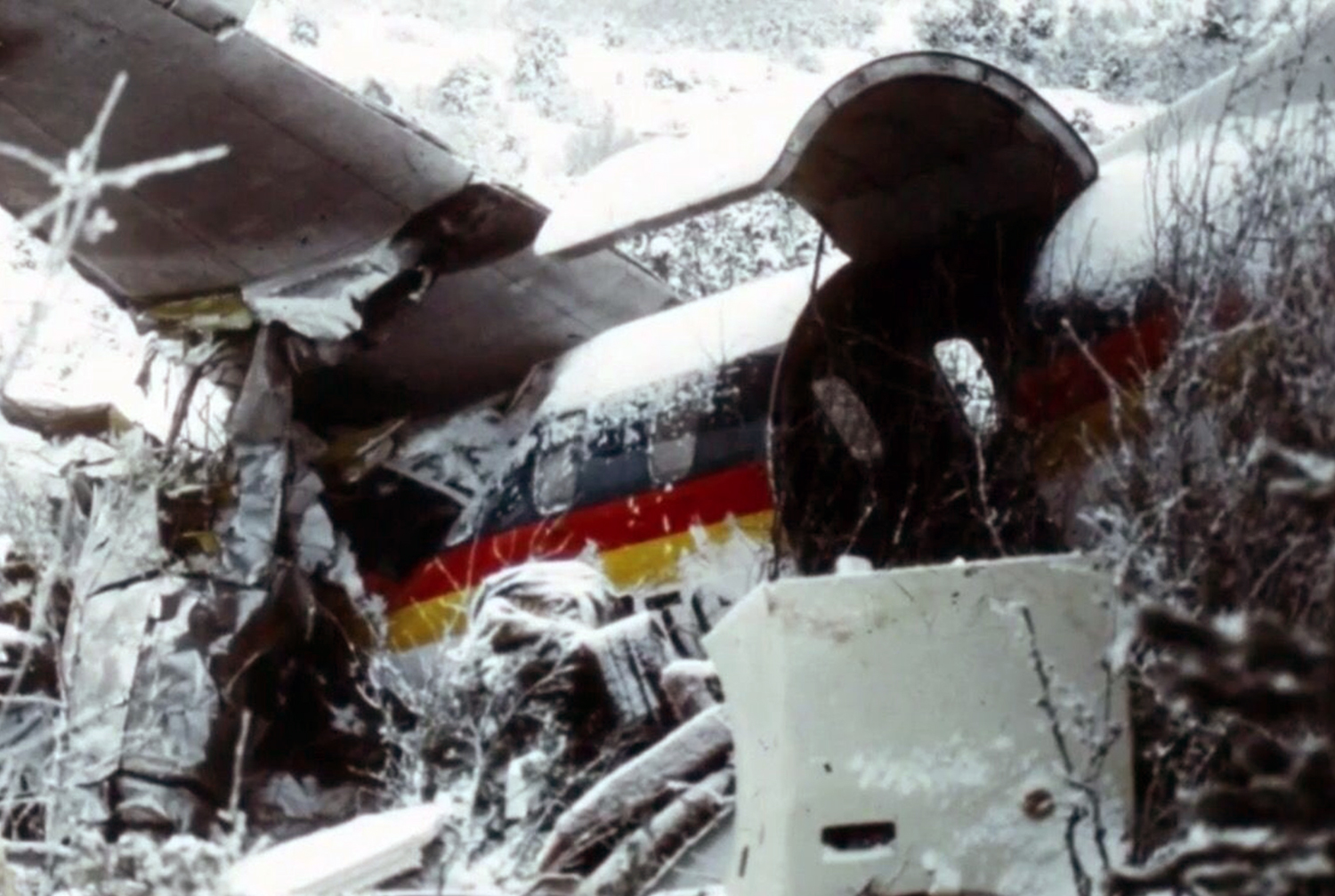
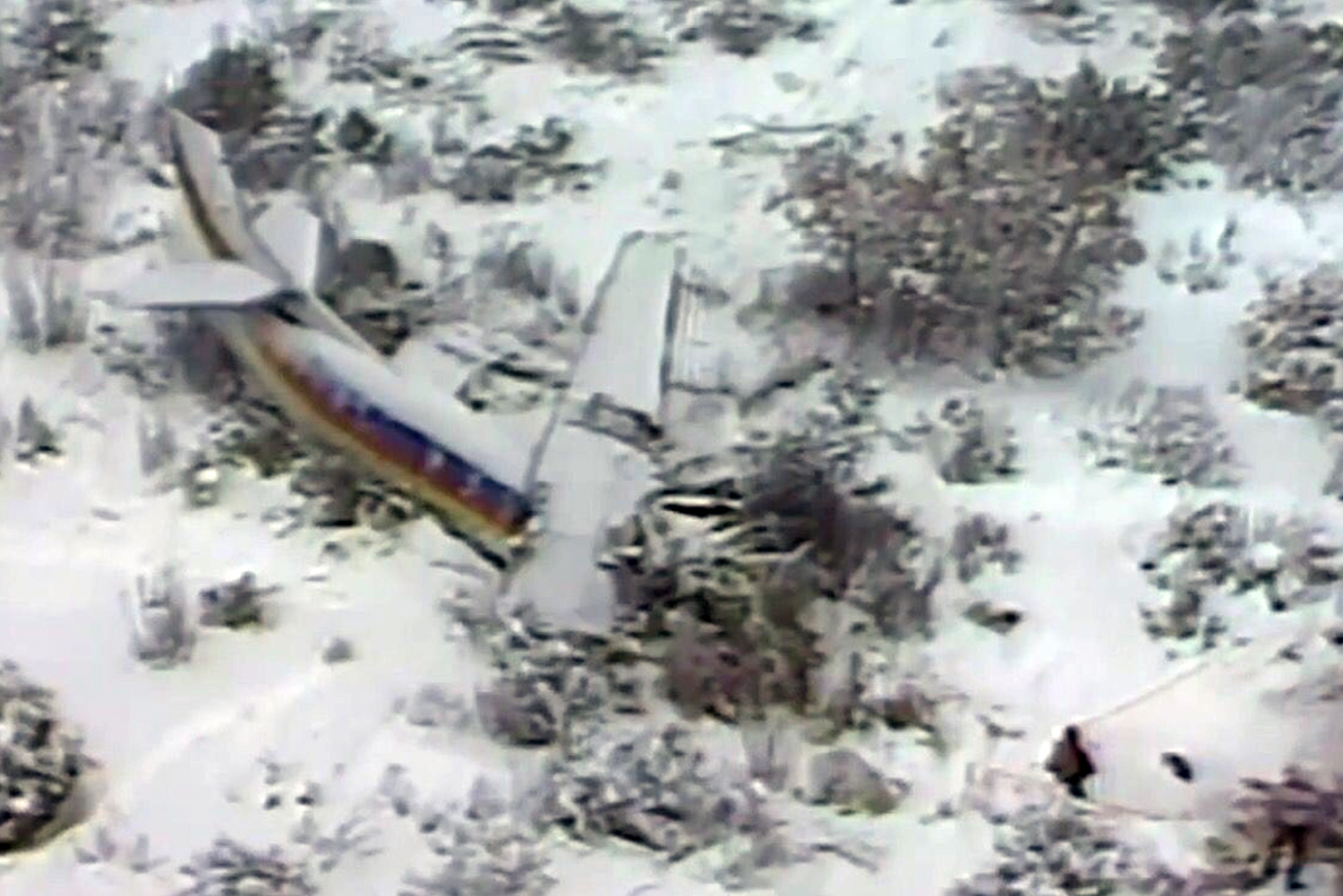
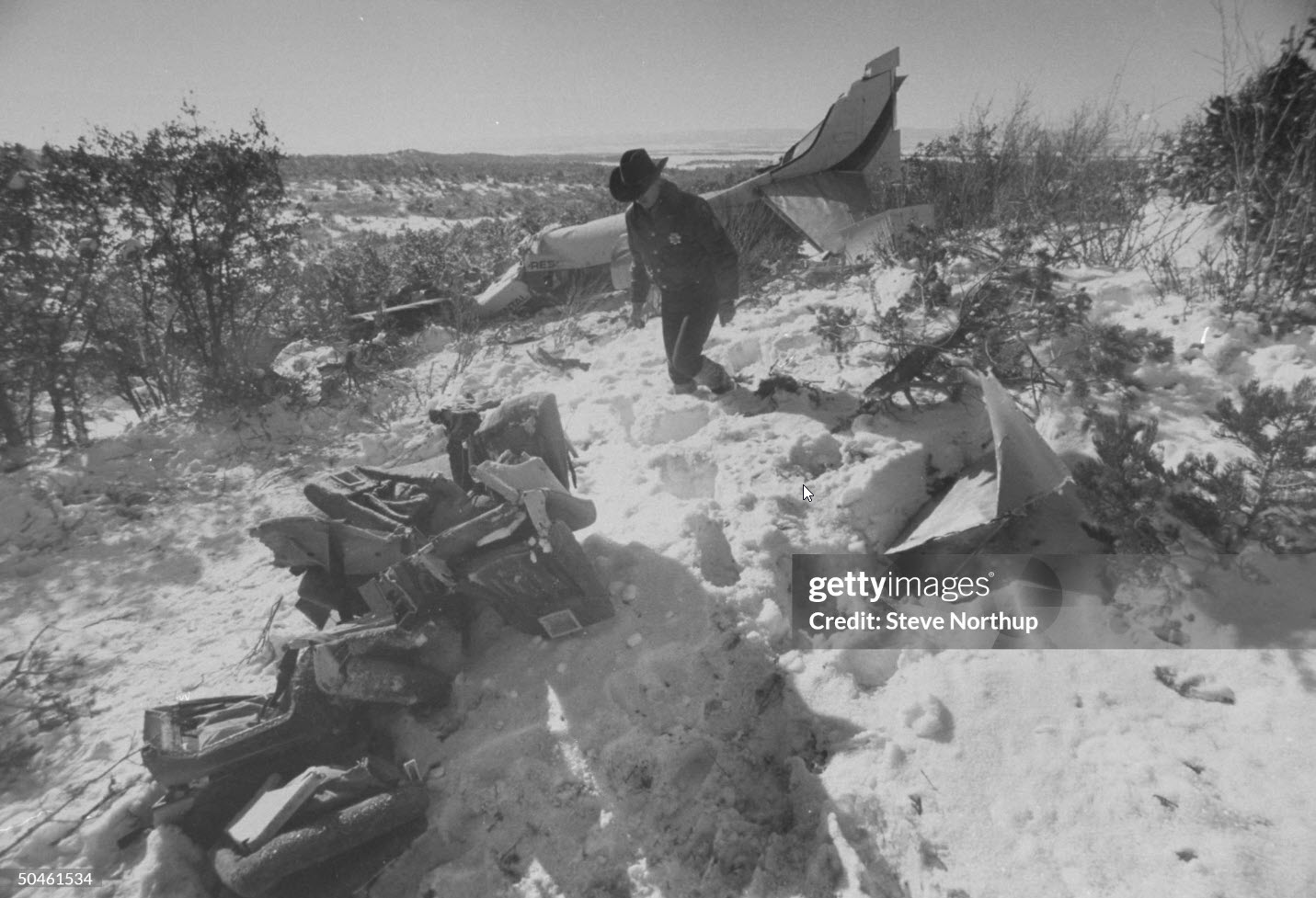
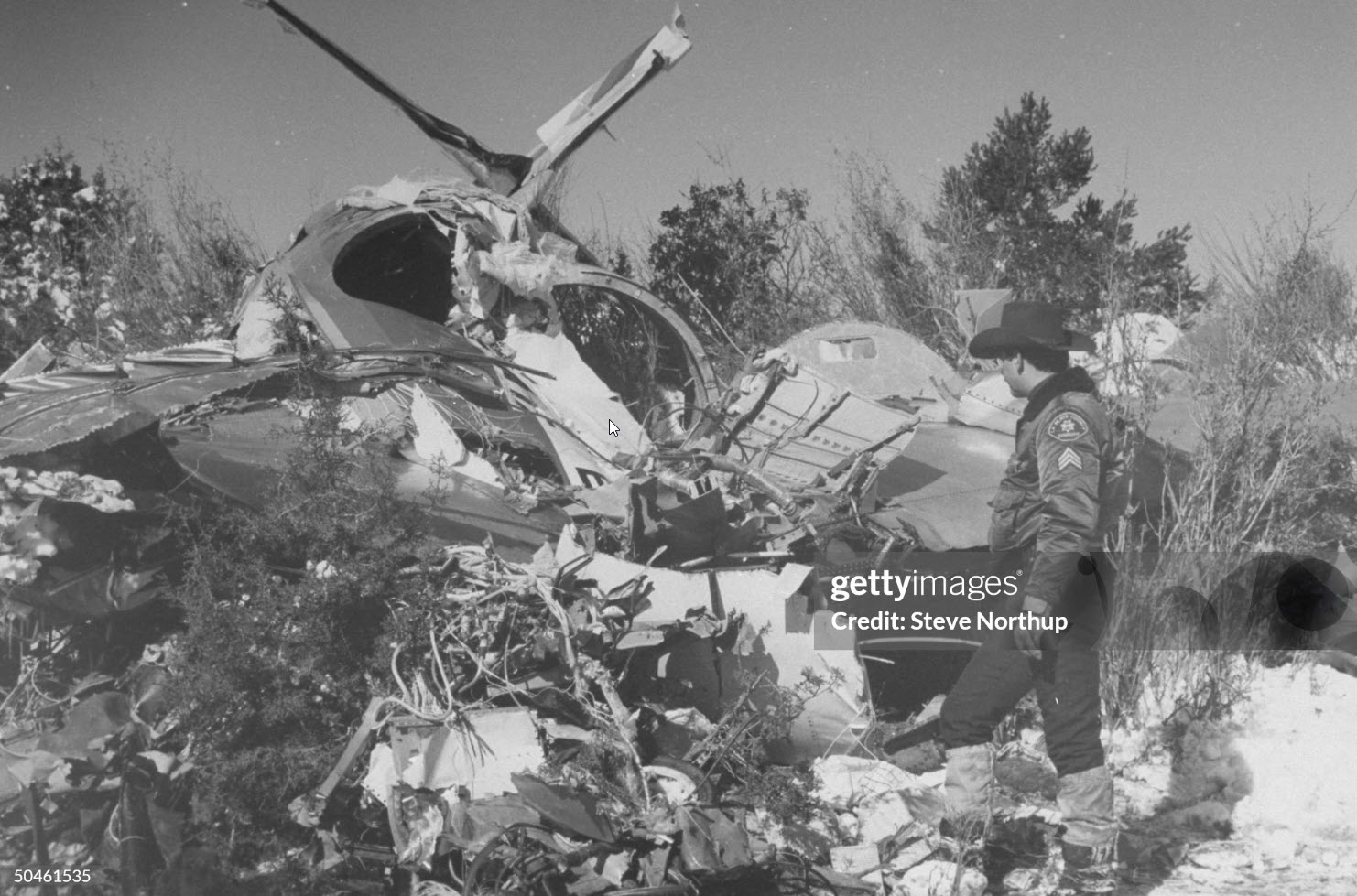
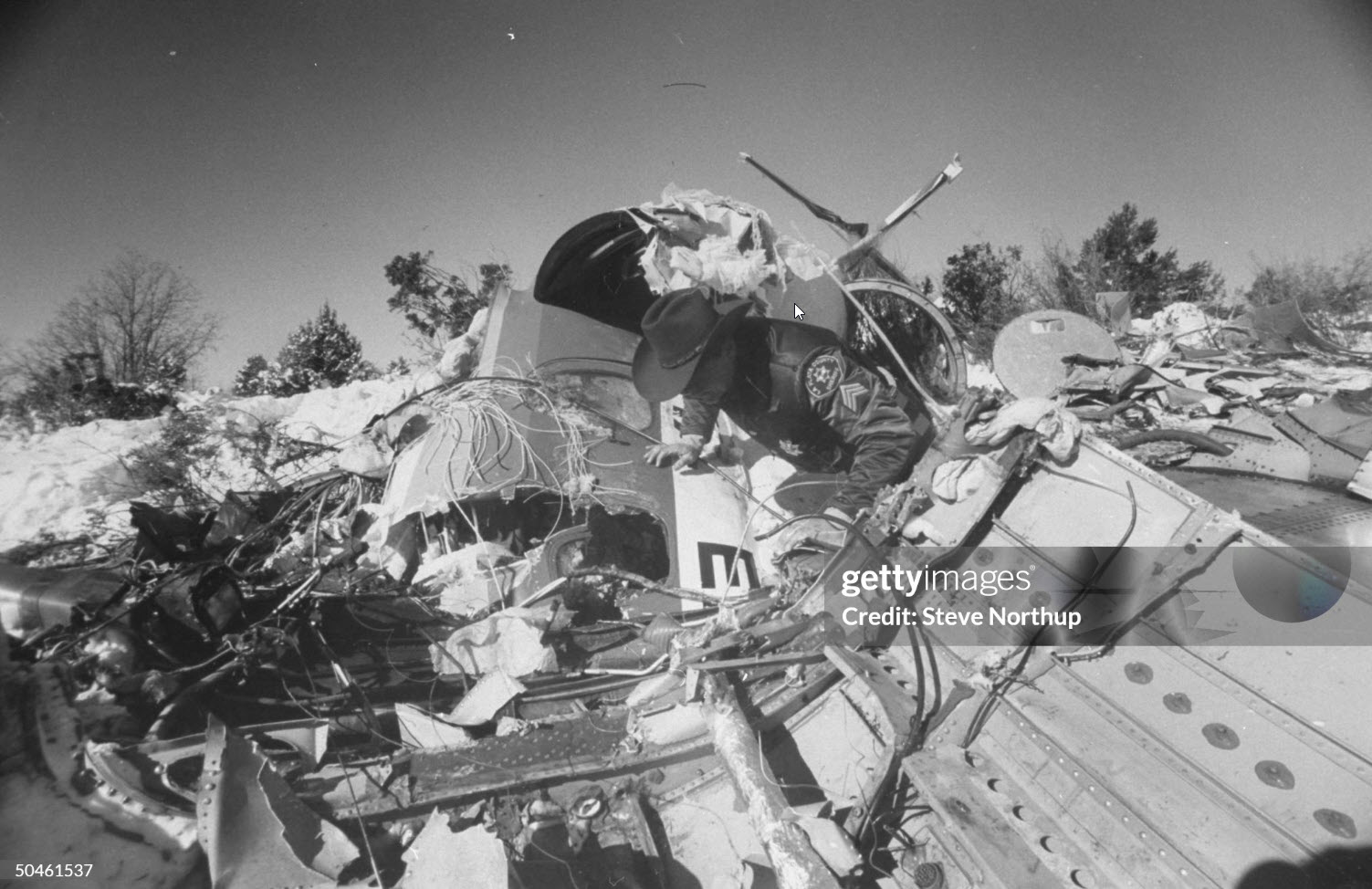
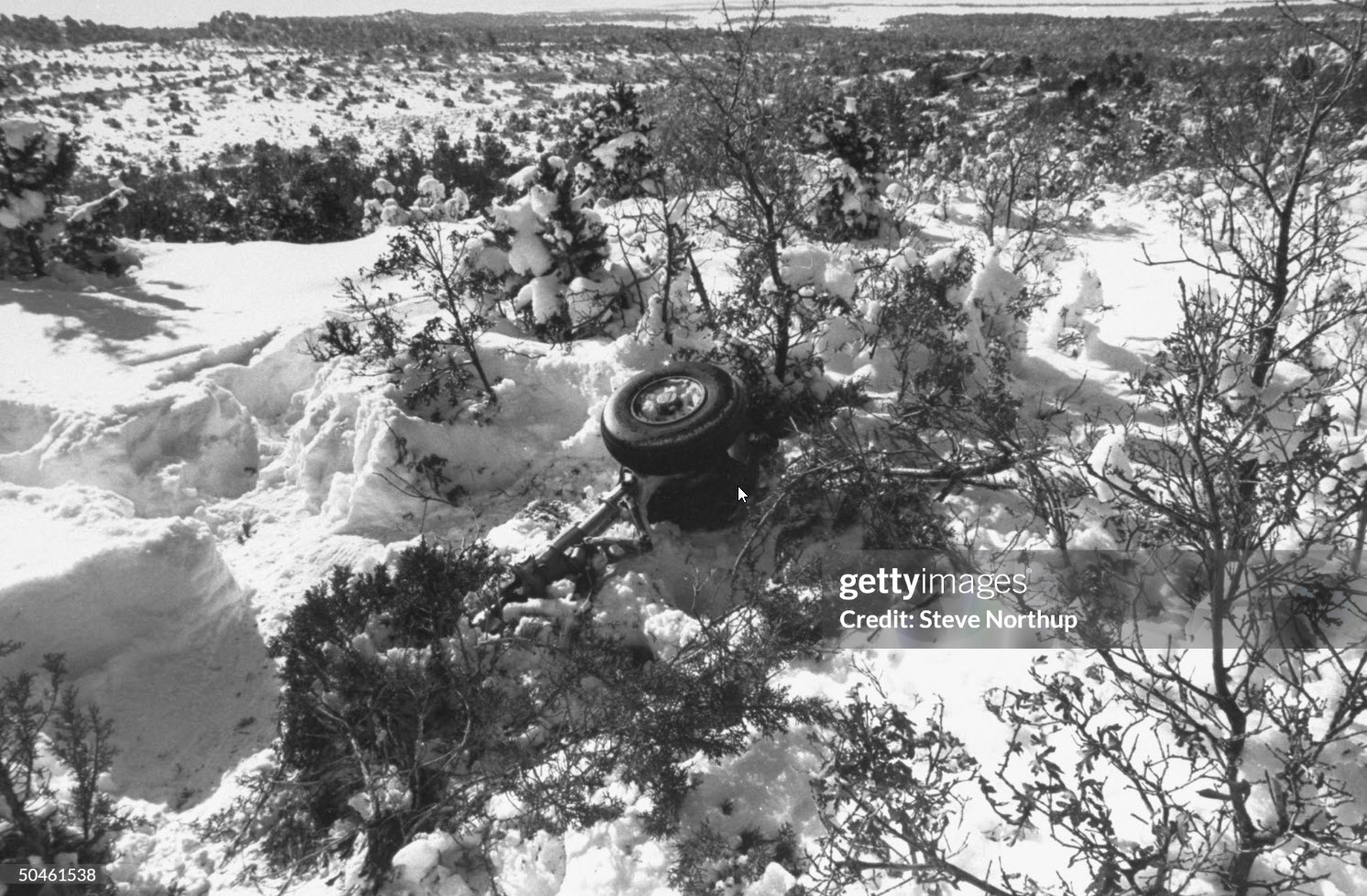
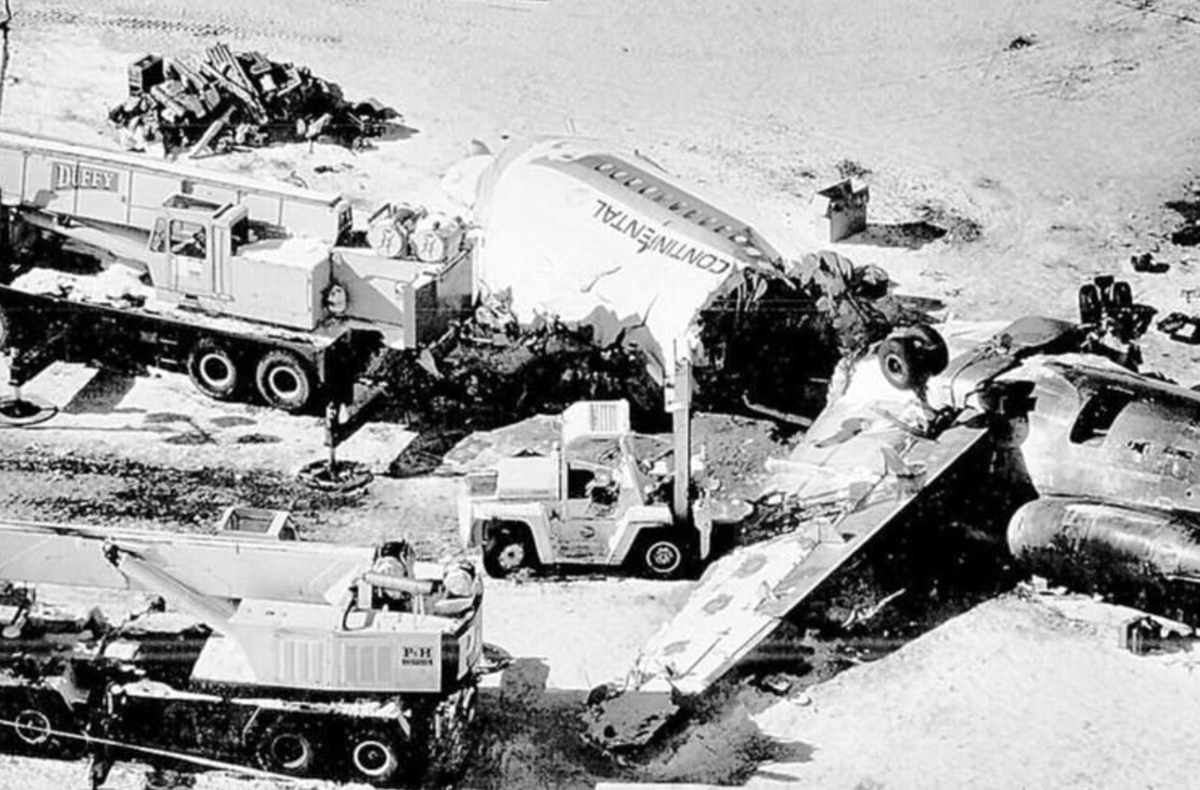
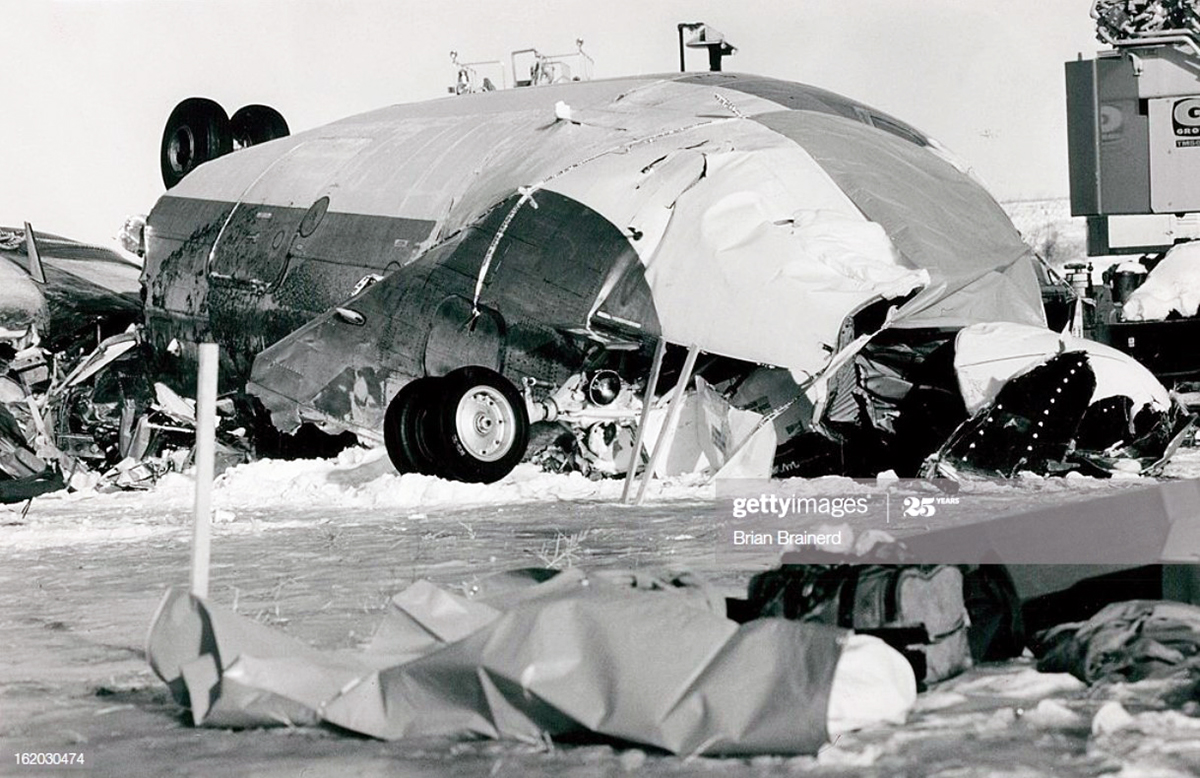
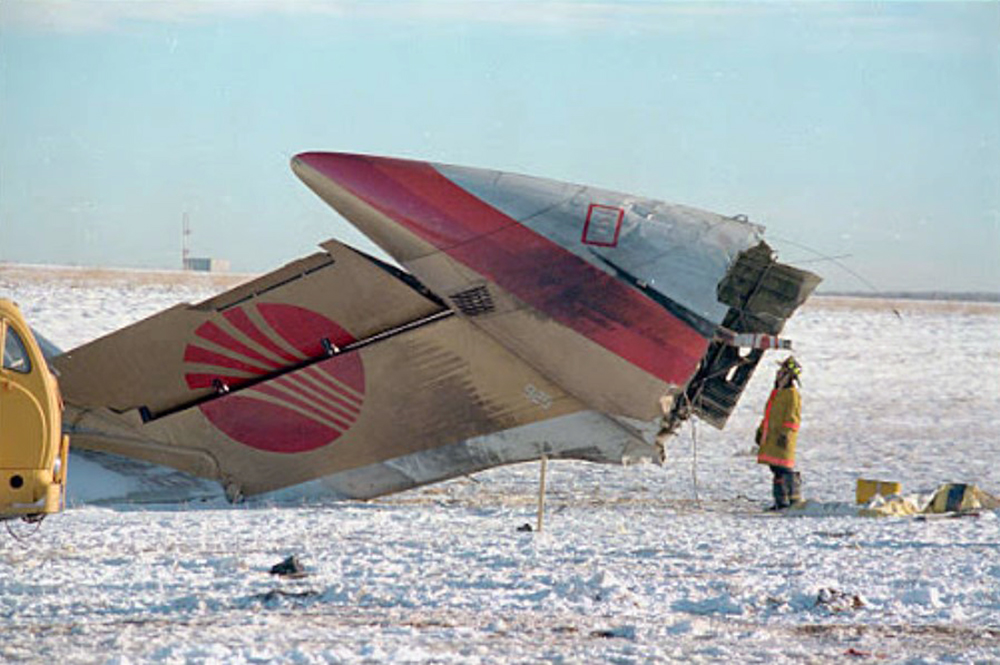
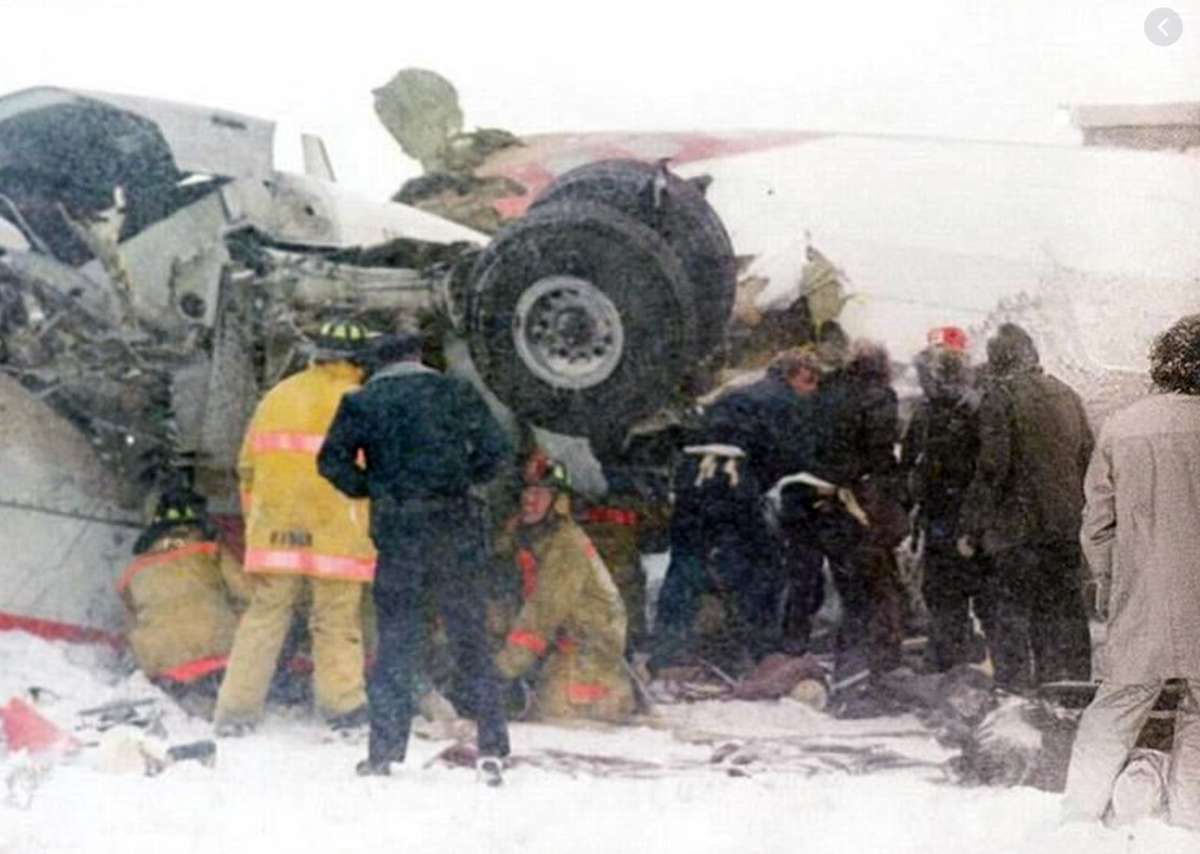
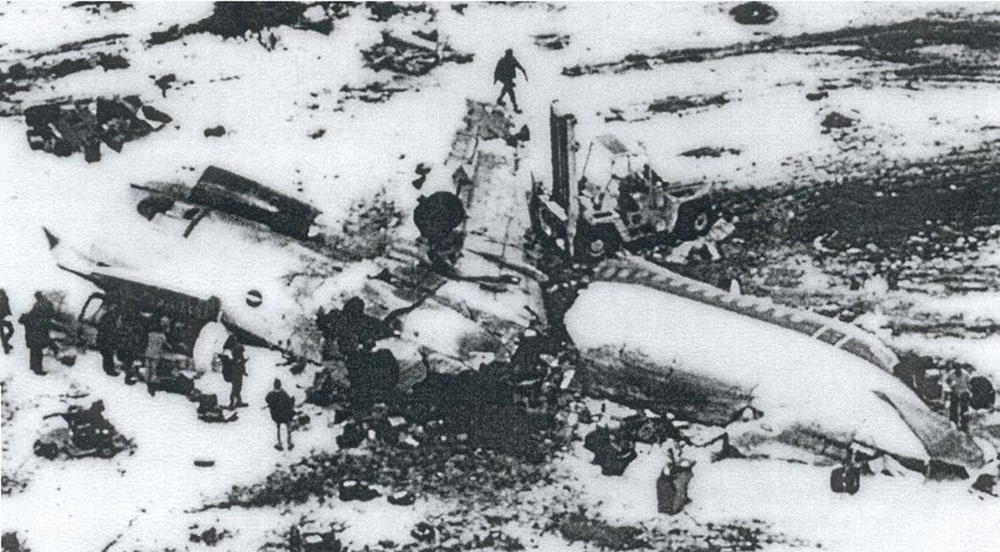
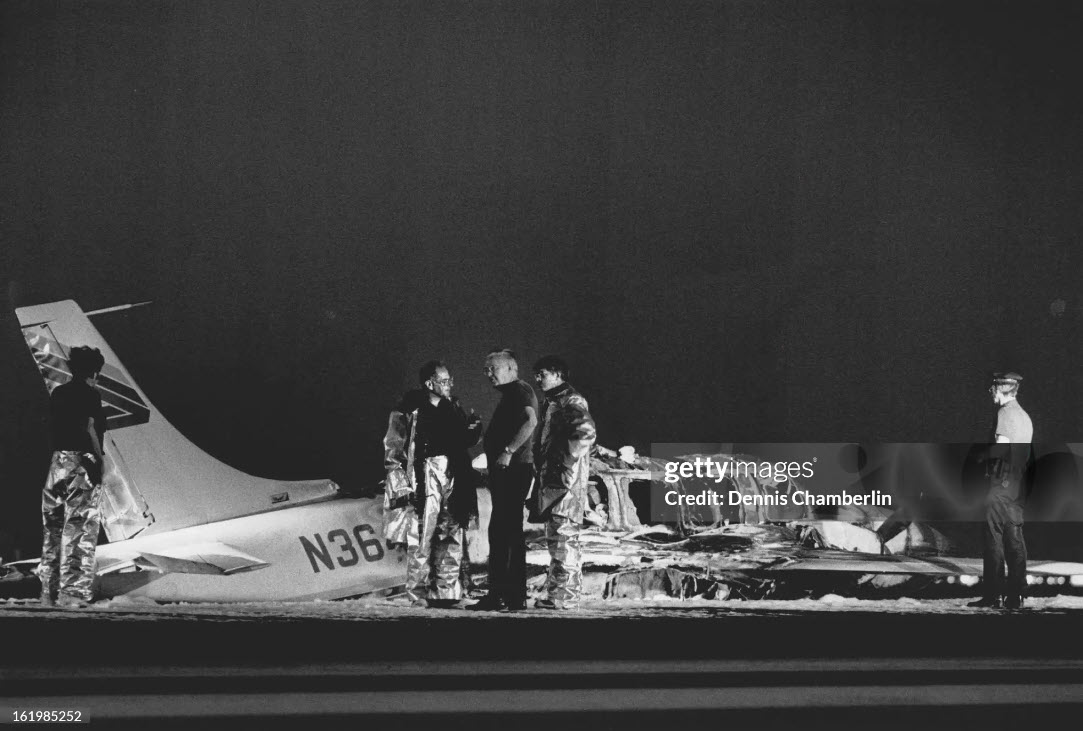
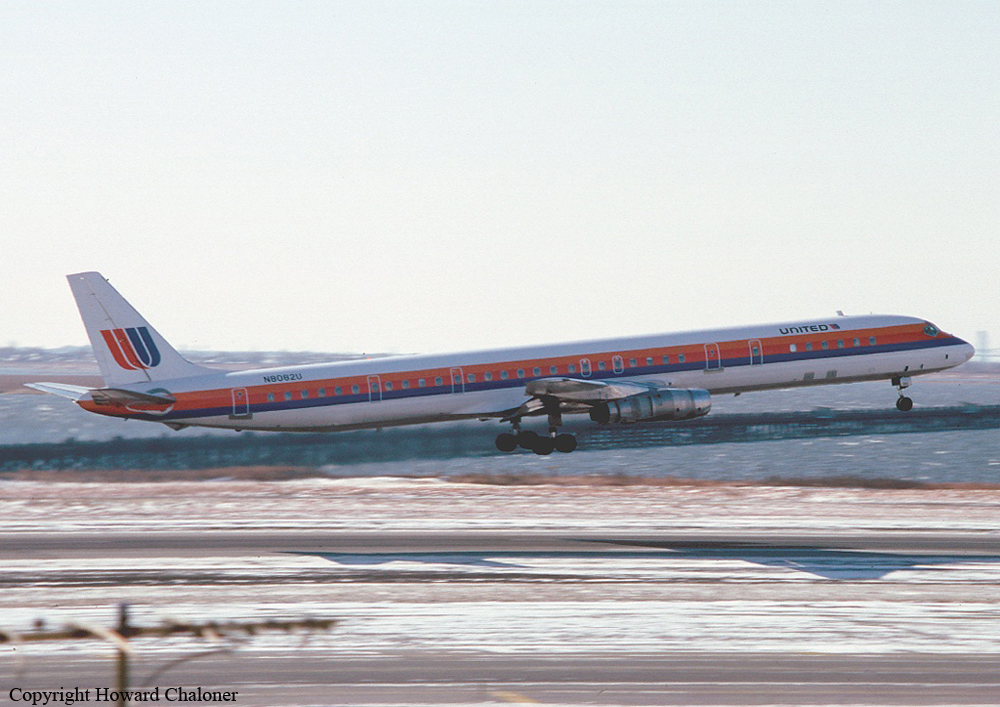
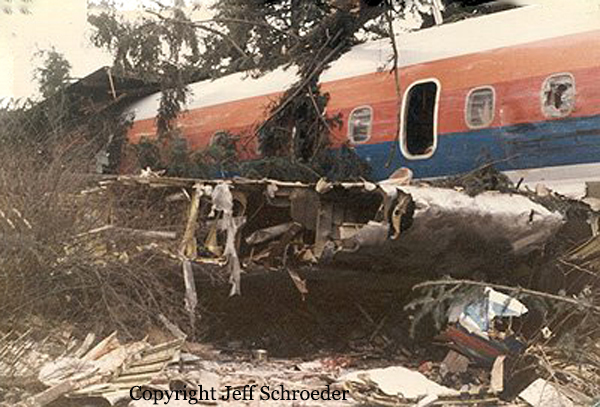
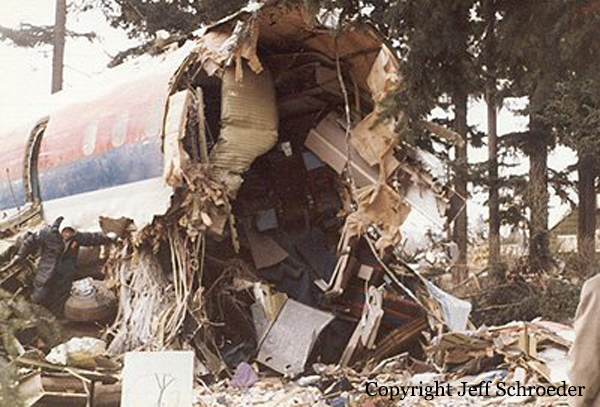
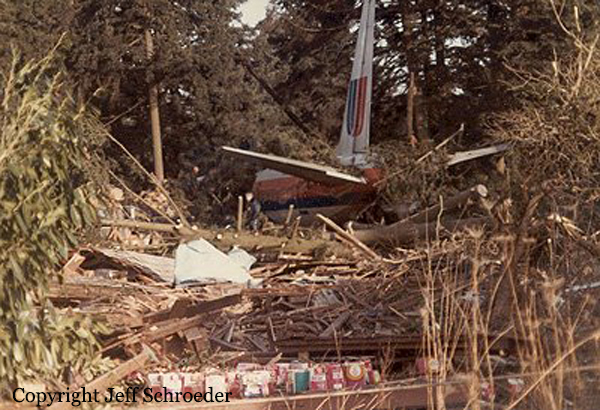
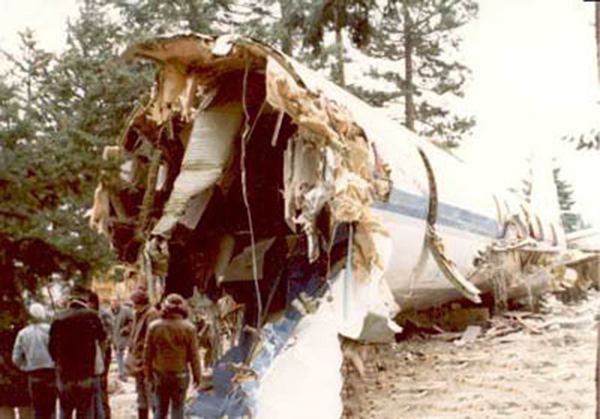
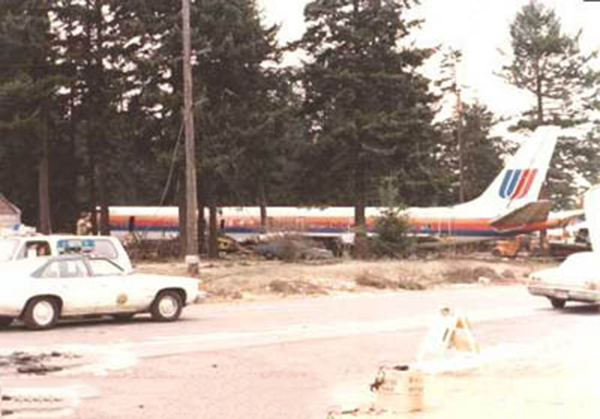
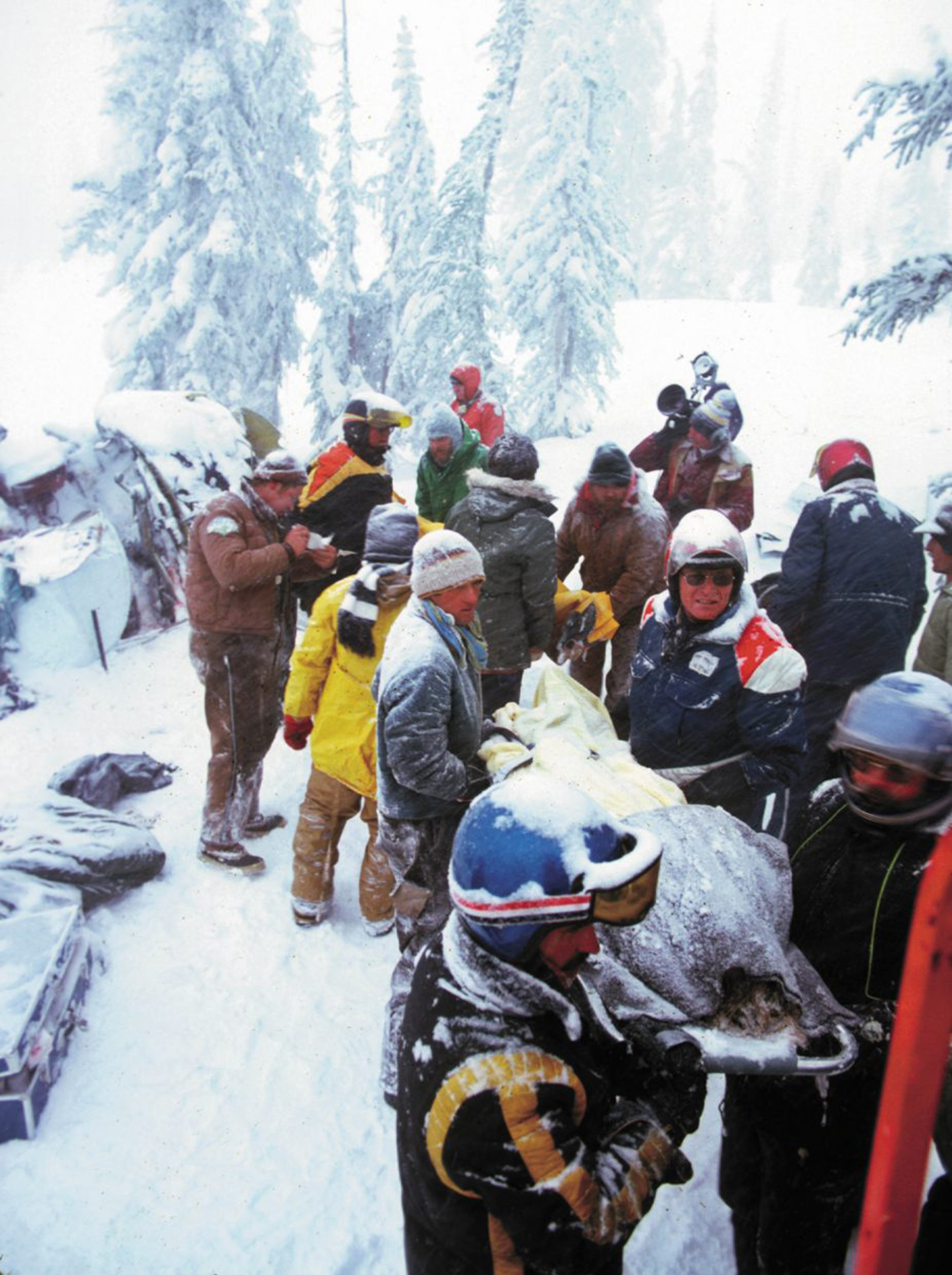
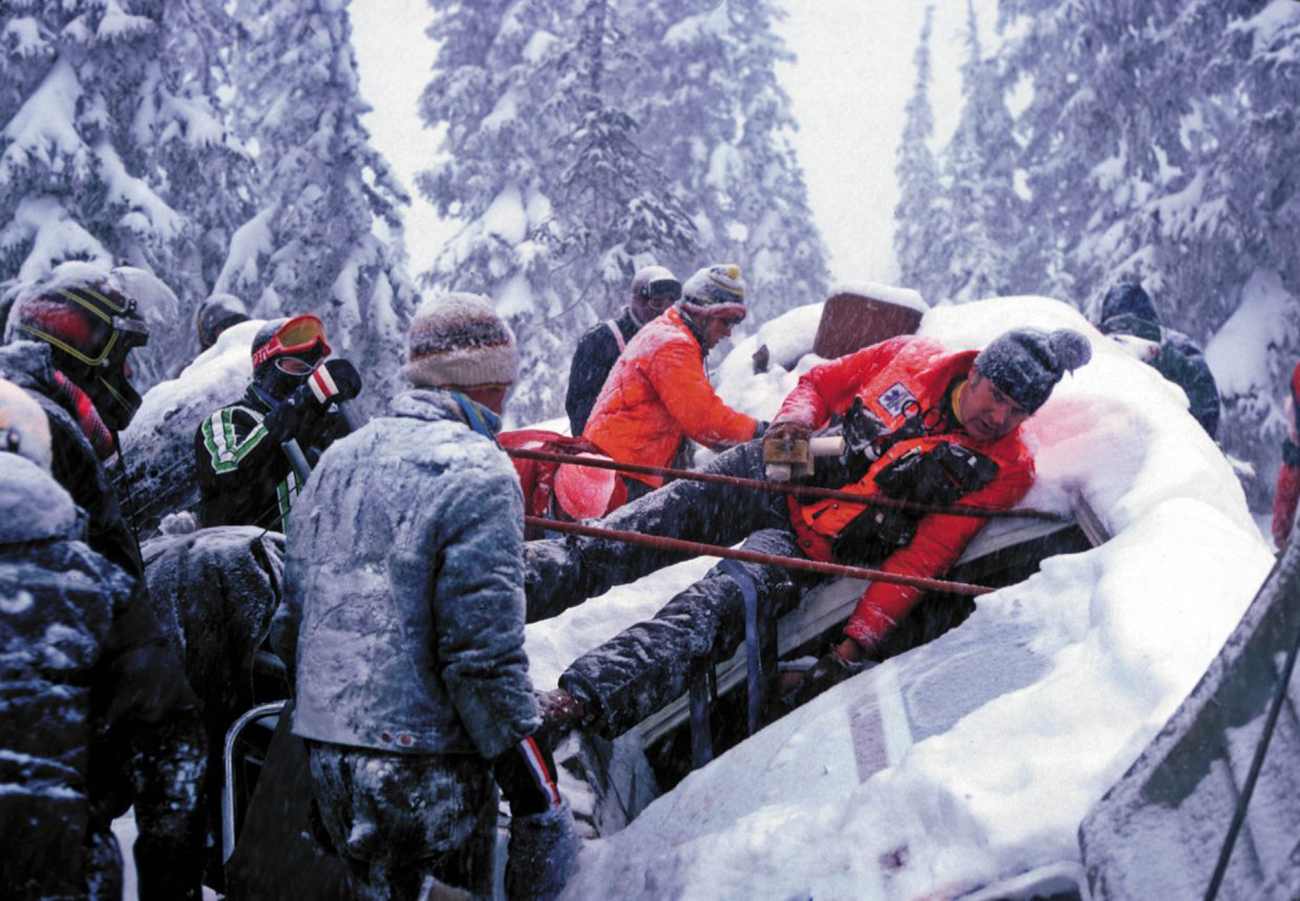
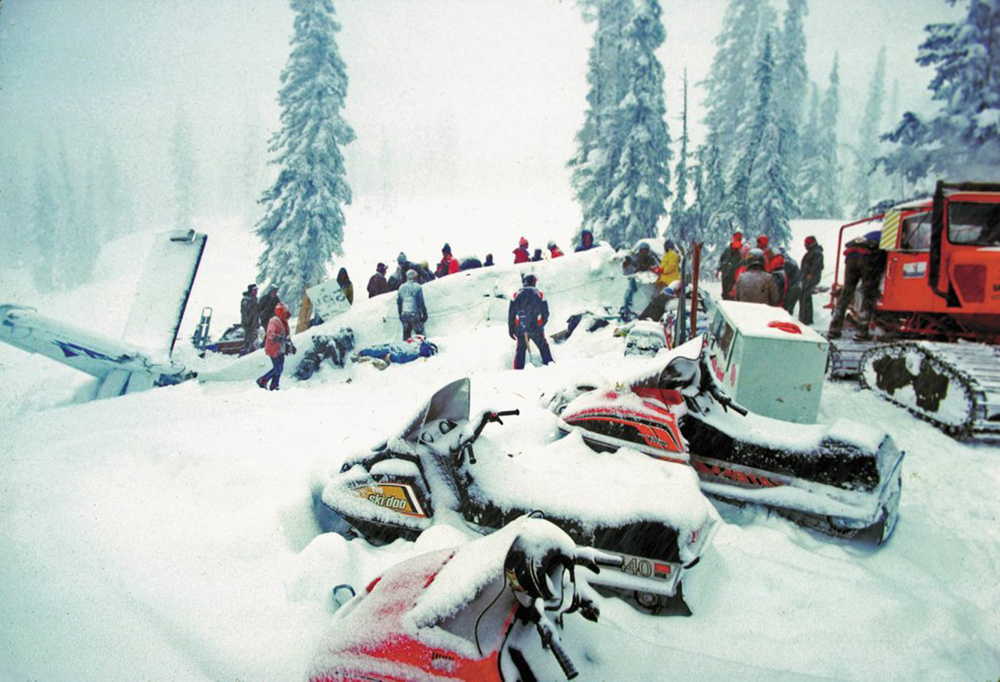
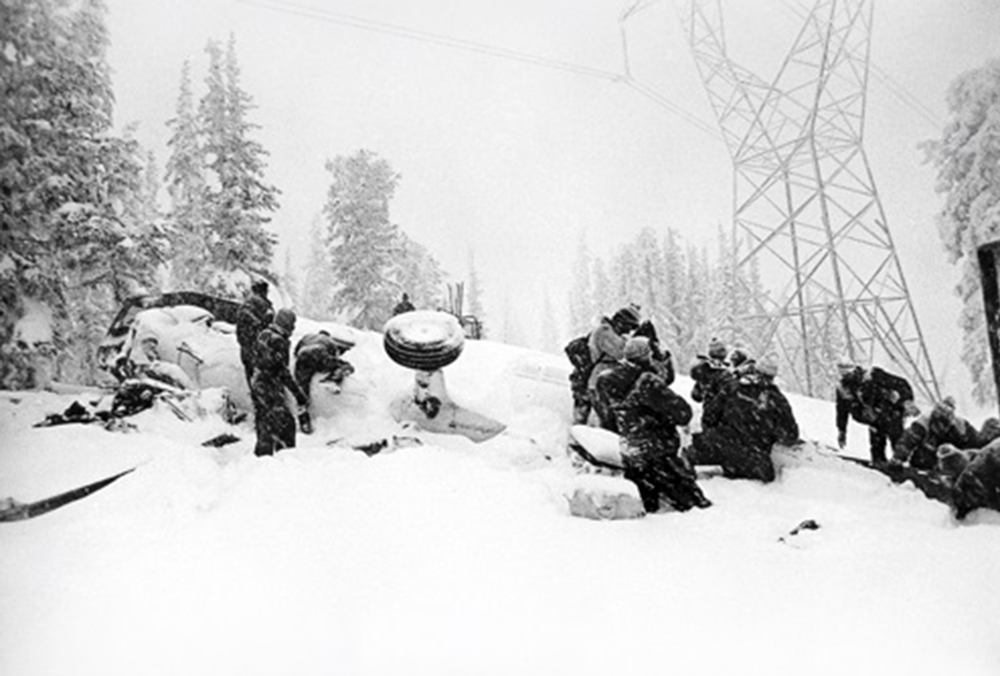
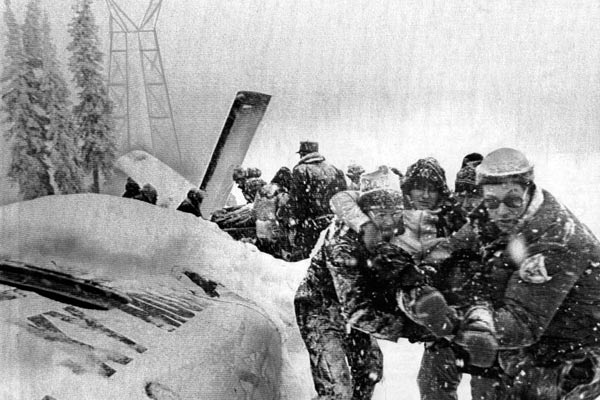
United Airlines Flight 173, departed New York-JFK on a scheduled flight to Portland International Airport (PDX), with an en route stop at Denver (DEN). The DC-8-61 took off from Denver about 14:47. The planned time en route was 2 hrs 26 min. The planned arrival time at Portland was 17:13. There was 46,700 lb of fuel on board the aircraft when it departed the gate at Denver. This fuel included the Federal Aviation Regulation requirement for fuel to destination plus 45 min and the company contingency fuel of about 20 min. At 17:05, Flight 173 called Portland Approach and advised that its altitude was 10,000 ft and its airspeed was being reduced. Portland responded and told the flight to maintain its heading for a visual approach to runway 28. Flight 173 acknowledged the approach instructions and stated, "...we have the field in sight." At 17:07, Portland Approach instructed the flight to descend and maintain 8,000 ft. Flight 173 acknowledged the instructions and advised that it was "leaving ten." At 17:09, Flight 173 received and acknowledged a clearance to continue its descent to 6,000 ft. When the DC-8 was descending through about 8,000 ft, the first officer, who was flying the aircraft, requested the wing flaps be extended to 15 degrees, then asked that the landing gear be lowered. As the landing gear extended, an unusual sound was heard and the aircraft yawed. At 17:12, Portland Approach requested, "United one seven three heavy, contact the tower, one one eight point seven." The flight responded, "negative, we'll stay with you. We'll stay at five. We'll maintain about a hundred and seventy knots. We got a gear problem. We'll let you know." Portland Approach replied, "United one seventy-three heavy roger, maintain five thousand. Turn left heading two zero zero." The flight acknowledged the instructions. At 17:14, Portland Approach advised, "United one seventy three heavy, turn left heading, one zero zero and I'll just orbit you out there 'til you get your problem." Flight 173 acknowledged the instructions. For the next 23 min, while Portland Approach was vectoring the aircraft in a holding pattern south and east of the airport, the flight crew discussed and accomplished all of the emergency and precautionary actions available to them to assure themselves that all landing gear was locked in the full down position. The second officer checked the visual indicators on top of both wings, which extend above the wing surface when the landing gear is down-and-locked. About 17:38, Flight 173 contacted the United Airlines Systems Line Maintenance Control Center in San Francisco. The captain explained to company dispatch and maintenance personnel the landing gear problem and what the flight crew had done to assure that the landing gear was fully extended. He said they were planning to land in about twenty minutes. About 17:44, the captain and the first flight attendant discussed passenger preparation, crash landing procedures, and evacuation procedures. At 17:46, the first officer asked the flight engineer, "How much fuel we got...?" The flight engineer responded, "Five thousand." About 17:50, the captain asked the flight engineer to "Give us a current card on weight. Figure about another fifteen minutes." The first officer responded, "Fifteen minutes?" To which the captain replied, "Yeah, give us three or four thousand pounds on top of zero fuel weight." The flight engineer then said, "Not enough. Fifteen minutes is gonna really run us low on fuel here." Some calculations were made and at 17:52 the flight engineer talked to Portland and discussed the aircraft's fuel state, the number of persons on board the aircraft, and the emergency landing precautions at the airport. A fuel check at 17:57 learned that there were 1,000 lb in each tank, totalling 4,000 lb of fuel. From 17:57 until 18:00, the captain and the first officer engaged in a conversation which included discussions of giving the flight attendants ample time to prepare for the emergency, cockpit procedures in the event of an evacuation after landing, whether the brakes would have antiskid protection after landing, and the procedures the captain would be using during the approach and landing. At 18:01, the flight engineer reported that the cabin would be ready in "another two or three minutes." At 18:02, the flight engineer advised, "We got about three on the fuel and that's it." The aircraft was then about 5 nmi south of the airport on a southwest heading. Portland Approach then asked Flight 173 for a status report. The first officer replied, "Yeah, we have indication our gear is abnormal. It'll be our intention, in about five minutes, to land on two eight left. We would like the equipment standing by. Our indications are the gear is down and locked. We've got our people prepared for an evacuation in the event that should become necessary." At 18:03 Portland Approach asked that Flight 173 advise them when the approach would begin. The captain responded, "...They've about finished in the cabin. I'd guess about another three, four, five minutes." At this time the aircraft was about 8 nmi south of the airport on a southwesterly heading. At 18:06, the first flight attendant entered the cockpit and reported that they were ready in the passenger cabin. At this time the aircraft was about 17 nmi south of the airport on a southwesterly heading. The captain then said, "Okay. We're going to go in now. We should be landing in about five minutes." Almost simultaneous with this comment, the first officer said, "I think you just lost number four ..." followed immediately by advice to the flight engineer, "... better get some crossfeeds open there or something." At 18:06:46, the first officer told the captain, "We're going to lose an engine..." At 18:06:49, the first officer again stated, "We're losing an engine." Again the captain asked, "Why?" The first officer responded, "Fuel." The captain replied, "Why?" Between 18:06:52 and 18:07:06, the CVR revealed conflicting and confusing conversation between flight crewmembers as to the aircraft's fuel state. At 18:07:06, the first officer said, "It's flamed out." At 18:07:12, the captain called Portland Approach and requested, "...would like clearance for an approach into two eight left, now." The aircraft was about 19 nmi south southwest of the airport and turning left. This was the first request for an approach clearance from Flight 173 since the landing gear problem began. Portland Approach immediately gave the flight vectors for a visual approach to runway 28L. The flight turned toward the vector heading of 010 degrees. At 18:09:21, the captain advised Portland Approach, "United, seven three is going to turn toward the airport and come on in." After confirming Flight 173's intentions, Portland Approach cleared the flight for the visual approach to runway 28L. At 18:10:17, the captain requested that the flight engineer "reset that circuit breaker momentarily. See if we get gear lights." The flight engineer complied with the request. At 18:10:47, the captain requested the flight's distance from the airport. Portland approach responded, "I'd call it eighteen flying miles." At 18:12:42, the captain made another request for distance. Portland Approach responded, "Twelve flying miles." The flight was then cleared to contact Portland tower. At 18:13:21, the flight engineer stated, "We've lost two engines, guys." At 18:13:25, he stated, "We just lost two engines - one and two." At 1813:38, the captain said, They're all going. We can't make Troutdale." The first officer said, "We can't make anything." At 18:13:46, the captain told the first officer, "Okay. Declare a mayday." At 18:13:50, the first officer called Portland International Airport tower and declared, "Portland tower, United one seventy three heavy, Mayday. We're--the engines are flaming out. We're going down. We're not going to be able to make the airport." This was the last radio transmission from Flight 173. About 18:15, the aircraft crashed into a wooded section of a populated area of suburban Portland about 6 nmi east southeast of the airport. There was no fire. The wreckage path was about 1,554 ft long and about 130 ft wide. Two crew members and eight passengers were killed, 34 other occupants were injured.
Probable cause:
The failure of the captain to monitor properly the aircraft's fuel state and to properly respond to the low fuel state and the crew member's advisories regarding fuel state. This resulted in fuel exhaustion to all engines. His inattention resulted from preoccupation with a landing gear malfunction and preparations for a possible emergency landing. Contributing to the accident was the failure of the other two flight crewmembers either to fully comprehend the criticality of the fuel state or to successfully communicate their concern to the captain. The following findings were reported:
- Except for the failure of the piston rod on the right main landing gear retract cylinder assembly, with the resulting damage to the landing gear position indicating system switch, there was no evidence of a failure or malfunction of the aircraft’s structure, powerplants, flight controls, or systems,
- All of the aircraft’s engines flamed out because of fuel exhaustion about 1815, one hour and 3 minutes after it entered into hold and 3 hrs 27 min after it departed Denver,
- Fuel exhaustion was predictable. The crew failed to equate the fuel remaining with time and distance from the airport,
- No pertinent malfunctions were found during examinations of the fuel quantity measuring system,
- The captain failed to make decisive timely decisions,
- The captain failed to relate time, distance from the airport, and the aircraft’s fuel state as his attention was directed completely toward the diagnosis of the gear problem and preparation of the passengers for an emergency landing. The gear problem had a disorganizing effect on the captain's performances,
- Neither the first officer nor the flight engineer conveyed any concern about fuel exhaustion to the captain until the accident was inevitable.