Country
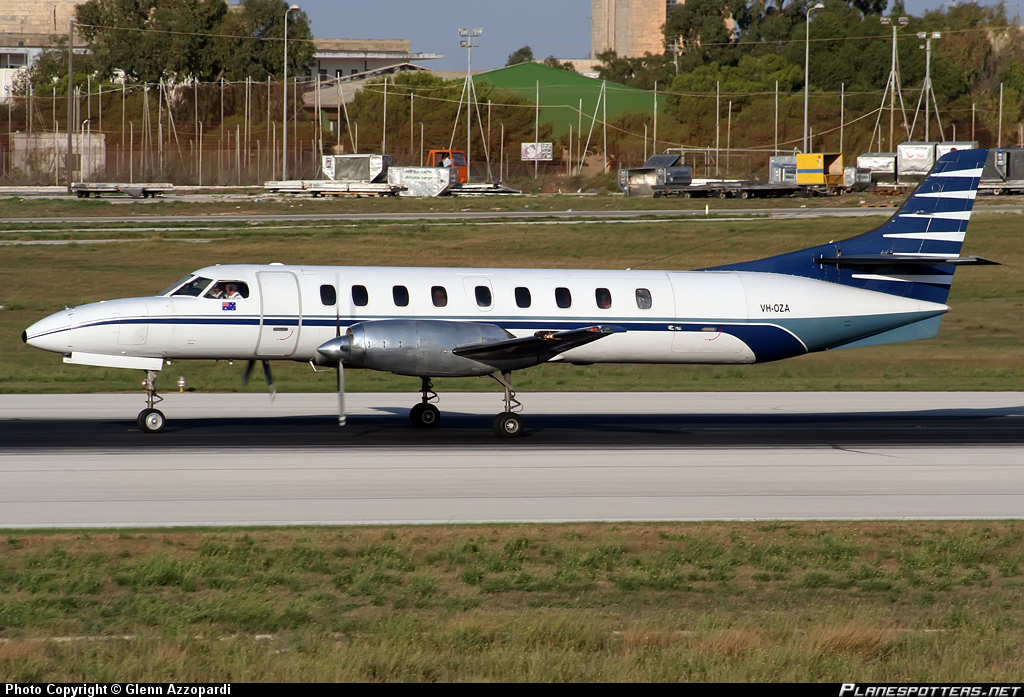
Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III off Sydney: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 9, 2008 at 2327 LT
Registration:
VH-OZA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Sydney – Brisbane
MSN:
AC-600
YOM:
1984
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
175.00
Aircraft flight hours:
32339
Aircraft flight cycles:
46710
Circumstances:
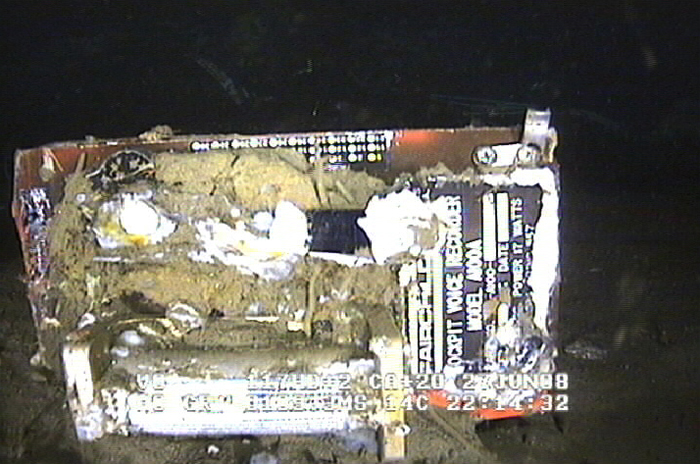
On 9 April 2008, at 2325 Eastern Standard Time, a Fairchild Industries Inc. SA227-AC (Metro III) aircraft, registered VH-OZA, departed Sydney Airport, New South Wales on a freight charter flight to Brisbane, Queensland with one pilot on board. The aircraft was subsequently observed on radar to be turning right, contrary to air traffic control instructions to turn left to an easterly heading. The pilot reported that he had a ‘slight technical fault’ and no other transmissions were heard from the pilot. Recorded radar data showed the aircraft turning right and then left, followed by a descent and climb, a second right turn and a second descent before radar returns were lost when the aircraft was at an altitude of 3,740 ft above mean sea level and descending at over 10,000 ft/min. Air traffic control initiated search actions and search vessels later recovered a small amount of aircraft wreckage floating in the ocean, south of the last recorded radar position. The pilot was presumed to be fatally injured and the aircraft was destroyed. Both of the aircraft’s on-board flight recorders were subsequently recovered from the ocean floor. They contained data from a number of previous flights, but not for the accident flight. There was no evidence of a midair breakup of the aircraft.
Probable cause:
Contributing Safety Factors:
- It was very likely that the aircraft’s alternating current electrical power system was not energised at any time during the flight.
- It was very likely that the aircraft became airborne without a functioning primary attitude reference or autopilot that, combined with the added workload of managing the ‘slight technical fault’, led to pilot spatial disorientation and subsequent loss of control.
Other Safety Factors:
- The pilot’s Metro III endorsement training was not conducted in accordance with the operator’s approved training and checking manual, with the result that the pilot’s competence and ultimately, safety of the operation could not be assured. [Significant safety issue].
- The chief pilot was performing the duties and responsibilities of several key positions in the operator’s organisational structure, increasing the risk of omissions in the operator’s training and checking requirements.
- The conduct of the flight single-pilot increased the risk of errors of omission, such as not turning on or noticing the failure of aircraft items and systems, or complying with directions.
- It was very likely that the aircraft’s alternating current electrical power system was not energised at any time during the flight.
- It was very likely that the aircraft became airborne without a functioning primary attitude reference or autopilot that, combined with the added workload of managing the ‘slight technical fault’, led to pilot spatial disorientation and subsequent loss of control.
Other Safety Factors:
- The pilot’s Metro III endorsement training was not conducted in accordance with the operator’s approved training and checking manual, with the result that the pilot’s competence and ultimately, safety of the operation could not be assured. [Significant safety issue].
- The chief pilot was performing the duties and responsibilities of several key positions in the operator’s organisational structure, increasing the risk of omissions in the operator’s training and checking requirements.
- The conduct of the flight single-pilot increased the risk of errors of omission, such as not turning on or noticing the failure of aircraft items and systems, or complying with directions.
Final Report:


Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III in Buenos Aires
Date & Time:
Dec 15, 2006 at 1820 LT
Registration:
LV-WRA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Buenos Aires - Buenos Aires
MSN:
AC-429
YOM:
1981
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
1556.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
1232
Aircraft flight hours:
34587
Circumstances:
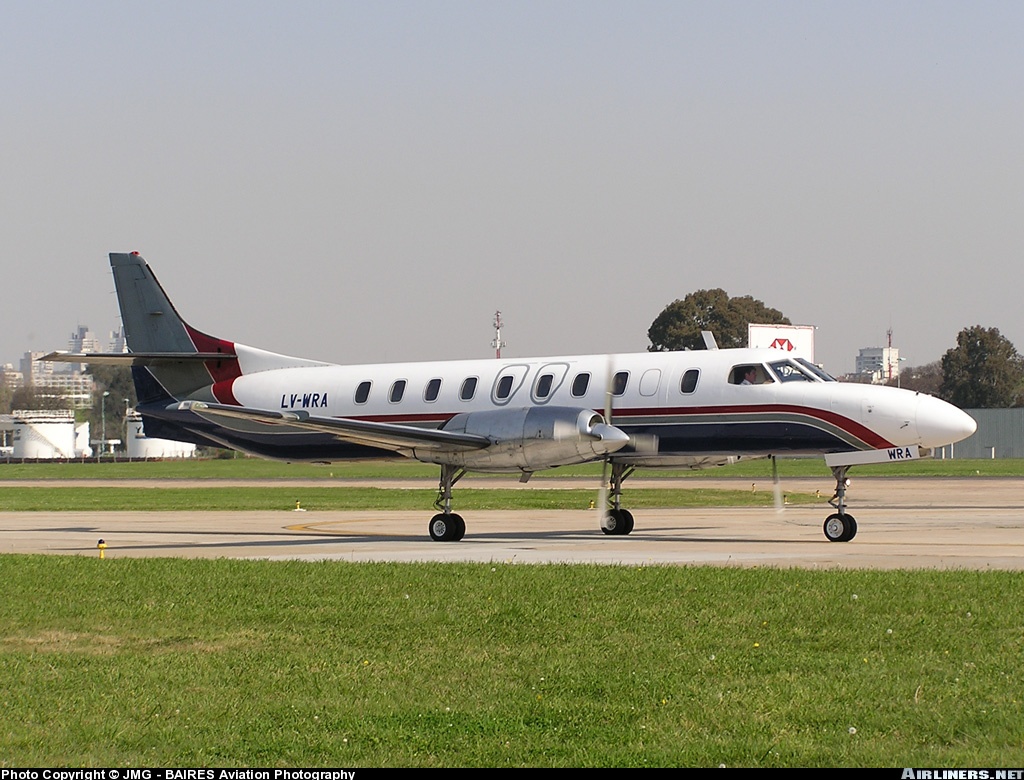
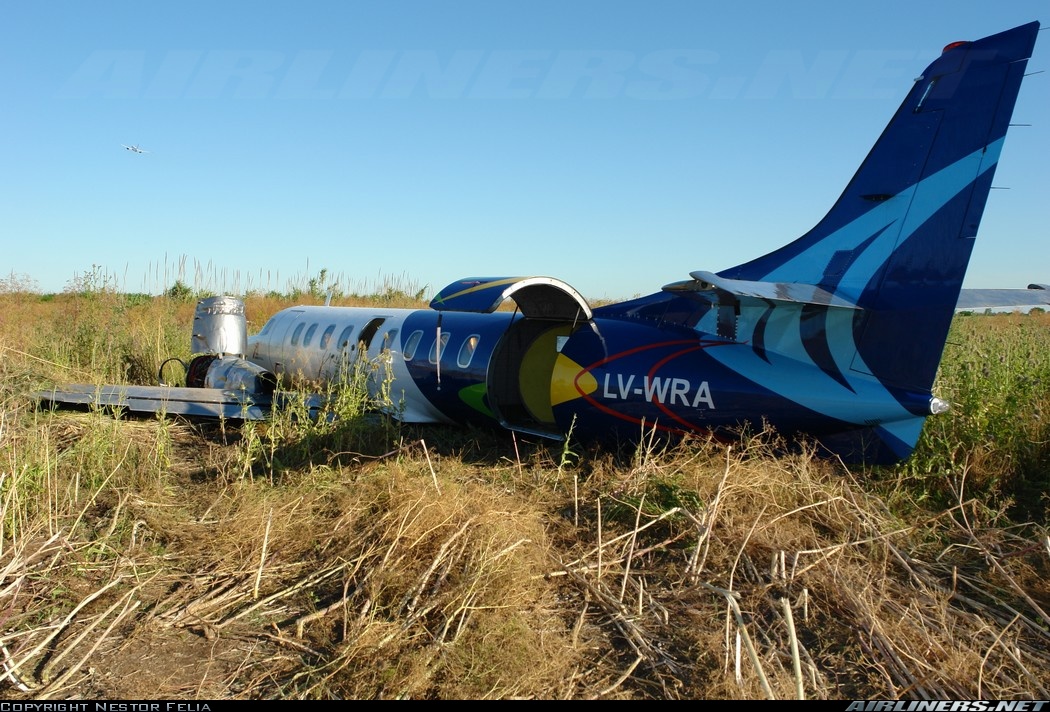
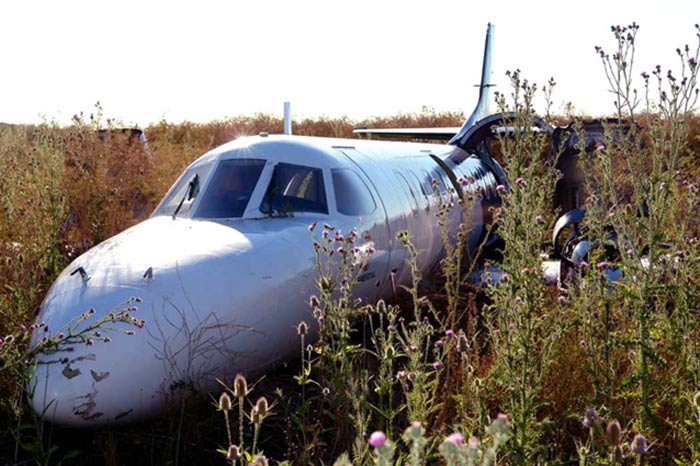
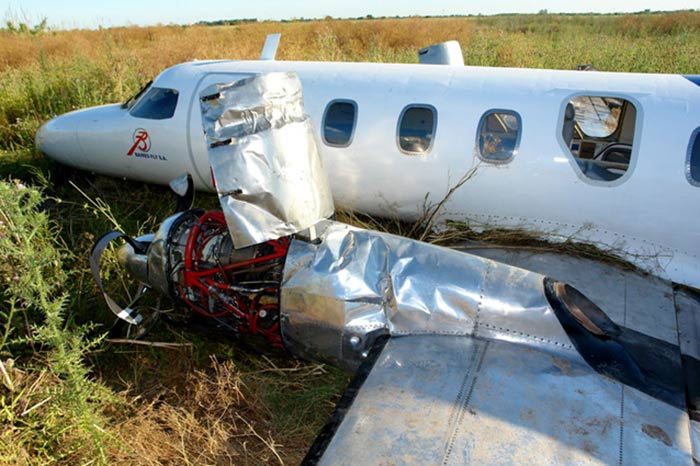
The crew was performing a positioning flight from Buenos Aires-Ezeiza-Ministro Pistarini Airport to Buenos Aires-Aeroparque-Jorge Newbury Airport. Before departure, the captain switched off the Stall Alarm System for unknown reasons. Shortly after takeoff from runway 17, the climb gradient was small and landing gear were retracted at a very low altitude. The left wing stalled and struck the runway surface. Out of control, the aircraft impacted ground, slid for few dozen metres, overran the runway and came to rest in a field. Both pilots were uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Loss of control shortly after rotation due to the premature retraction of the landing gear and a takeoff completed with a low climb gradient in the second segment.
Final Report:




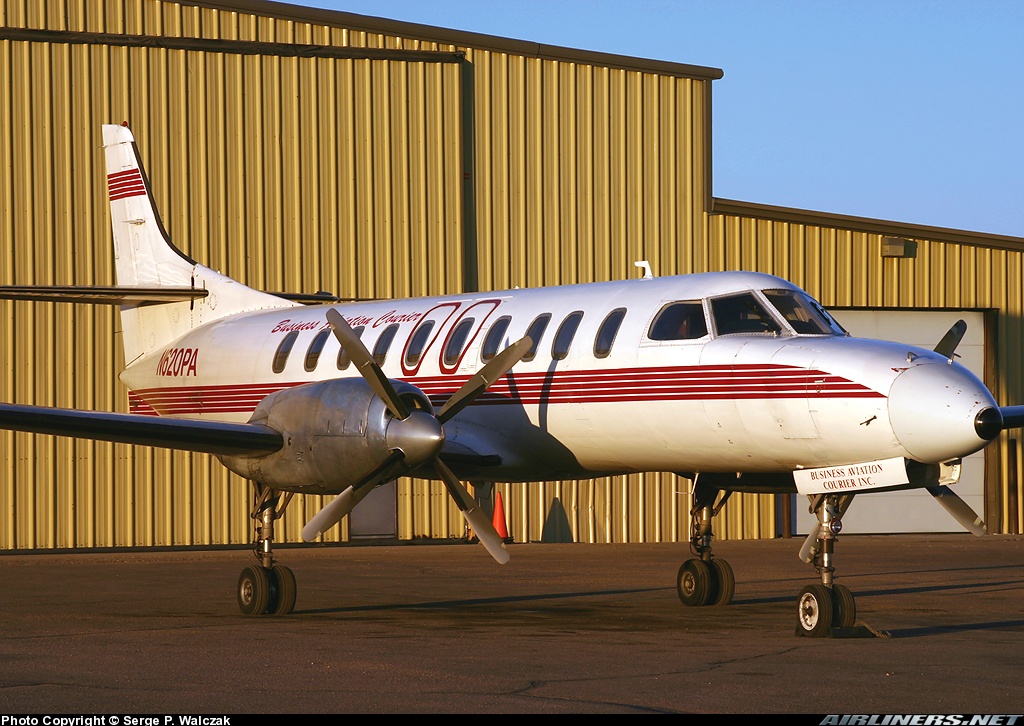
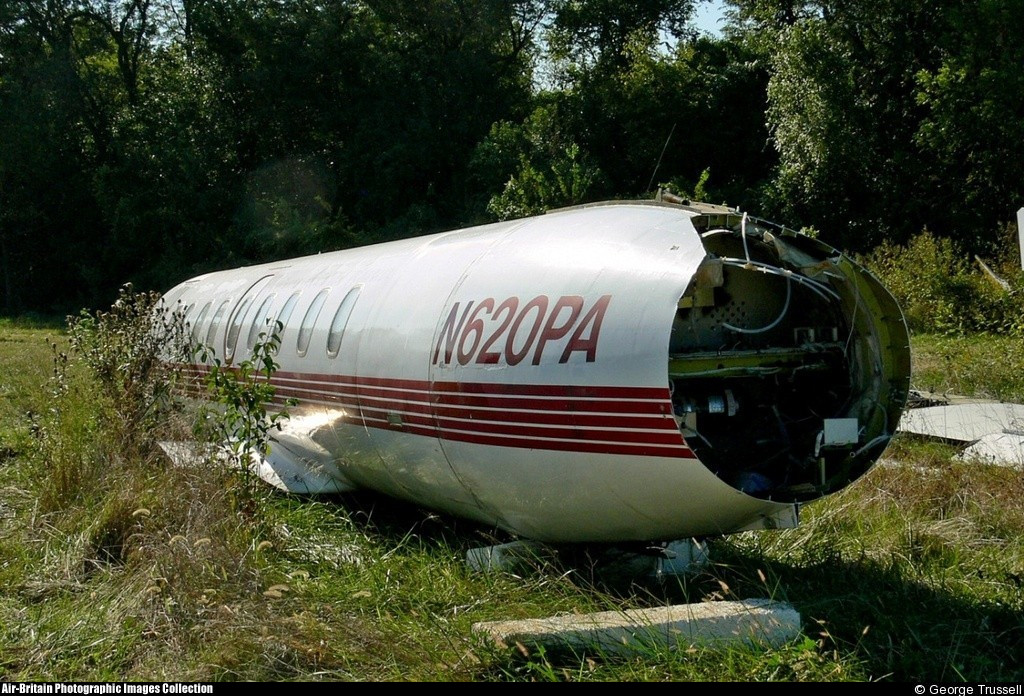
Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III in Grain Valley
Date & Time:
Aug 17, 2006 at 1551 LT
Registration:
N620PA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Tuscaloosa - Grain Valley
MSN:
AC-533
YOM:
1982
Flight number:
PKW321
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
188.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
165
Aircraft flight hours:
22504
Circumstances:
The airplane impacted a fence and terrain on short final during a visual approach to runway 27. The airplane was operated as a cargo airplane with two flight crewmembers by a commercial operator certificated under 14 CFR Part 135. The flightcrew worked approximately 18.75 hours within a 24-hour period leading up to the accident performing flights listed by the operator as either 14 CFR Part 91 or 14 CFR Part 135, all of which were in the conduct of company business. Of this total, 5.9 hours involved flying conducted under 14 CFR Part 135. The flight to the accident airport was for the purposes of picking up repair parts for another company airplane that received minor damage in which the flight crew was previously piloting in the 24- hour period. They were then going to fly back to the operator's home base on the same day, which would have had an estimated flying time of 2:45 hours. The captain said he was tired and that he and the first officer had not slept at any of the stops made during the period. The captain said that the company likes for the airplanes to return to their home base. The captain said that the company prefers an option for pilots to stay overnight if tired and he has stayed overnight on previous trips but only due to maintenance related reasons. The Aeronautical Information Manual states that acute fatigue affects timing and perceptional field performance.
Probable cause:
The pilot not maintaining clearance from the fence. Contributing factors were the pilot's fatigue and the fence.
Final Report:


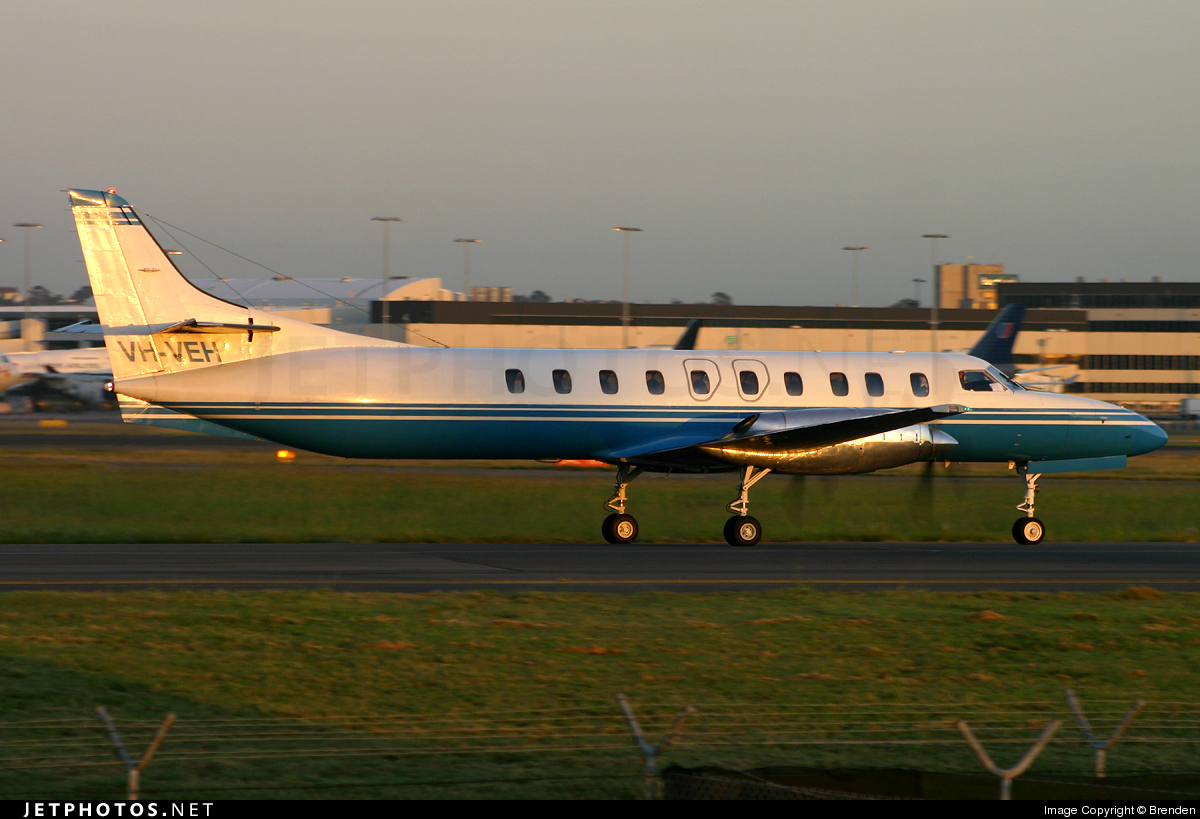
Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III in Canberra
Date & Time:
Jul 1, 2006
Registration:
VH-VEH
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
AC-663B
YOM:
1986
Crew on board:
0
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
By night, the twin engine aircraft landed hard at Canberra Airport. There were no injuries but the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
ATSB did not conduct any investigations on this event.

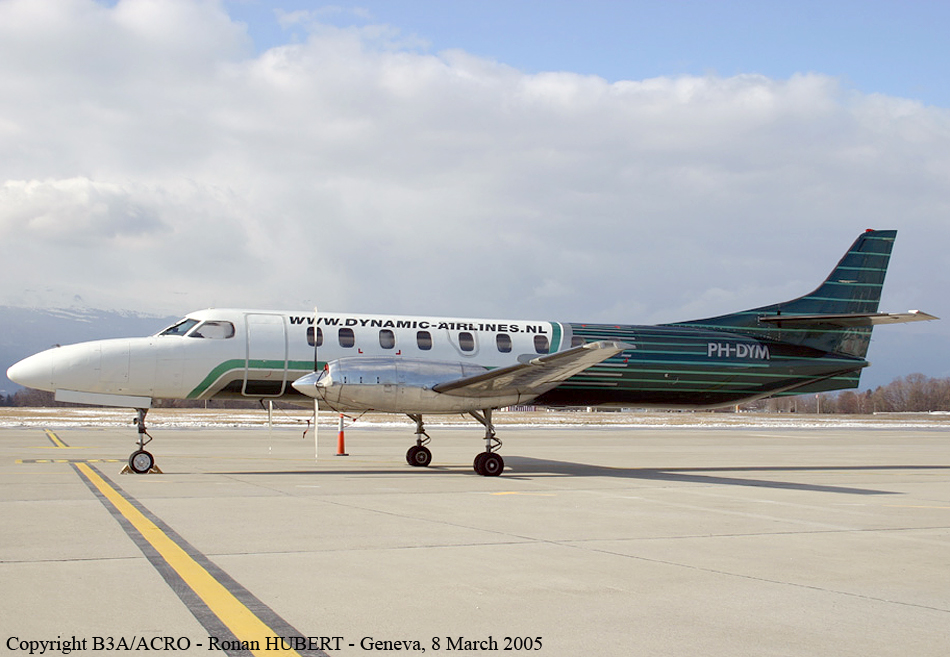
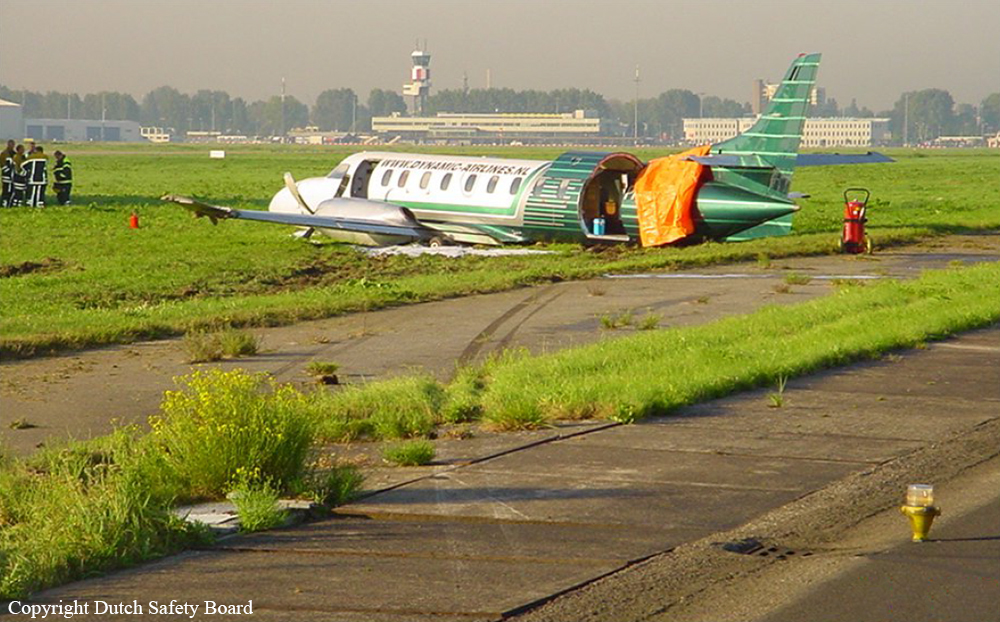
Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III in Rotterdam
Date & Time:
Sep 19, 2005 at 0730 LT
Registration:
PH-DYM
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Rotterdam – Birmingham
MSN:
AC-523
YOM:
1982
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
17
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
On 19 September 2005, the type F-Swearingen SA227-AC aircraft with registration PH-DYM was scheduled to make a charter flight from Rotterdam Airport to Birmingham Airport. Seventeen passengers and two cockpit crew members were on board. The planned departure time was 07.30 hours. The aircraft taxied to the beginning of runway 24 and lined up for take-off. During line-up, the speed levers for the engines were moved from taxi position to flight position. The nose wheel steering fault indicator lit up and the first officer, who was steering the aircraft, responded by saying that he had no nose wheel steering. The captain informed the first officer that he had forgotten to press the switch on the throttles, which activates the nose wheel steering system. The first officer then confirmed that he had nose wheel steering. With the engines in the low RPM range (taxi position, up to 70% of maximum RPM), the pilot can steer the aircraft using the rudder pedals while taxing. When the engines are operated in the high RPM selection (flight position, between 70% and 100% of the maximum RPM), the switch on the throttles, which activates the nose wheel steering system, must be pressed in during the first part of the take-off roll in order to be able to operate the nose wheel with the rudder pedal. At a speed around 50 knots, the switch which activates the nose wheel steering system is released. The aerodynamic forces of on the rudder are then sufficient to take over the steering from the nose wheel. Once take-off clearance was given by air traffic control, the first officer engaged power and started the take-off roll. He stated that once the nose wheel operating switch had been released, the aircraft almost immediately began moving towards the left hand side of the runway. He tried to use the brakes and the directional rudder, to return the aircraft to the centre of the runway. The aircraft had a speed of between 50 and 60 knots at that point. The crew rejected the take-off but could not prevent the aircraft ending up alongside the runway, on the left hand side. The captain stated that various forces influence the directional control of an aircraft during the take-off, such as wind, propeller wash, increasing air speed, etc. These forces necessitate steering corrections during the take-off. Only when the nose wheel steering system was disengaged the captain realized something was wrong. The grass area alongside the runway is lower than the runway and the ground was soft. The left landing gear sank in the soft ground first and, as a result, the aircraft decelerated heavily and the left landing gear broke off almost immediately. The tip of the left wing struck the ground. This caused a ground loop effect and turned the aircraft further left. As a consequence the right landing gear and the nose gear also broke off. Once the aircraft had come to a standstill, the captain switched off all onboard systems and cut off the fuel supply to the engines. Simultaneously, the first officer was given the task of evacuating the passengers. The passengers were calm and left the aircraft without problems via the left hand door at the front of the aircraft. A moment later, the airport fire service arrived at the location of the accident. One of the passengers was taken to hospital for a check-up; he was able to leave hospital the same morning. There was severe damage despite the relatively slow speed at which the aircraft left the runway.
Probable cause:
This accident was caused by an hydraulic leakage in the nose wheel steering system. The tyre tracks on the runway implied that the steering problem had occurred from the beginning of the take-off. The crew intervened as soon as after the nose wheel switch had been released and the nose wheel steering fault came on but were unable to prevent the aircraft leaving the runway.
Final Report:







