Country
Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C in Seattle
Date & Time:
Aug 13, 1997 at 1913 LT
Registration:
N3172A
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Portland - Seattle
MSN:
UB-47
YOM:
1985
Flight number:
AMF262
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
106.00
Aircraft flight hours:
23892
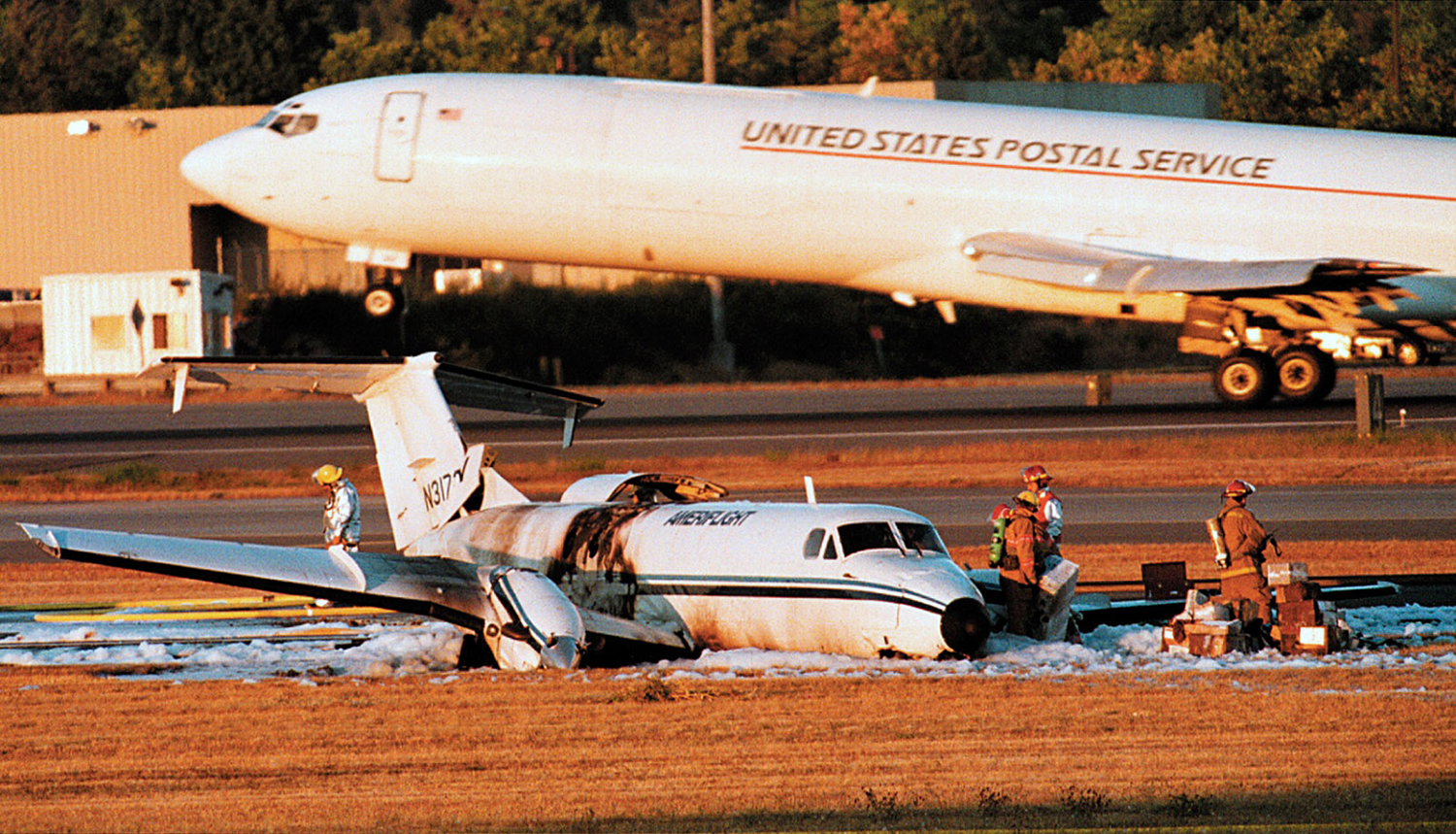
Circumstances:
The Beech 1900C cargo aircraft was loaded with more than 4,962 pounds of cargo during an approximate 20 minute period. No scale was available at the aircraft, forcing loaders to rely on tallying either waybill weights or estimates of total cargo weight and center of gravity (CG) during the brief loading period. Additionally, a strike had shut down a major cargo competitor at the time with substantial cargo overflow to the operator. Post-crash examination determined the cargo load was 656 pounds greater than that documented on the pilot's load manifest, and the CG was between 6.8 and 11.3 inches aft of the aft limit. The airplane behaved normally, according to the pilot, until he initiated full flaps for landing approaching the threshold of runway 34L at the Seattle-Tacoma International airport. At this time, the aircraft's airspeed began to decay rapidly and a high sink rate developed as the aircraft entered into a stall/mush condition. The aircraft then landed hard, overloading the nose and left-main landing gear which collapsed. A post-impact fuel system leak during the ground slide led to a post-crash fire.
Probable cause:
A stall/mush condition resulting from an aft center of gravity which was inaccurately provided to the pilot-in-command by contractual cargo-loading personnel. Additional causes were overloading of the aircraft's landing gear and fuel leakage resulting in a post-crash fire. Factors contributing to the accident were the pilot's improper lowering of flaps in an aft CG situation and the inadequate company procedures for cargo loading.
Final Report:

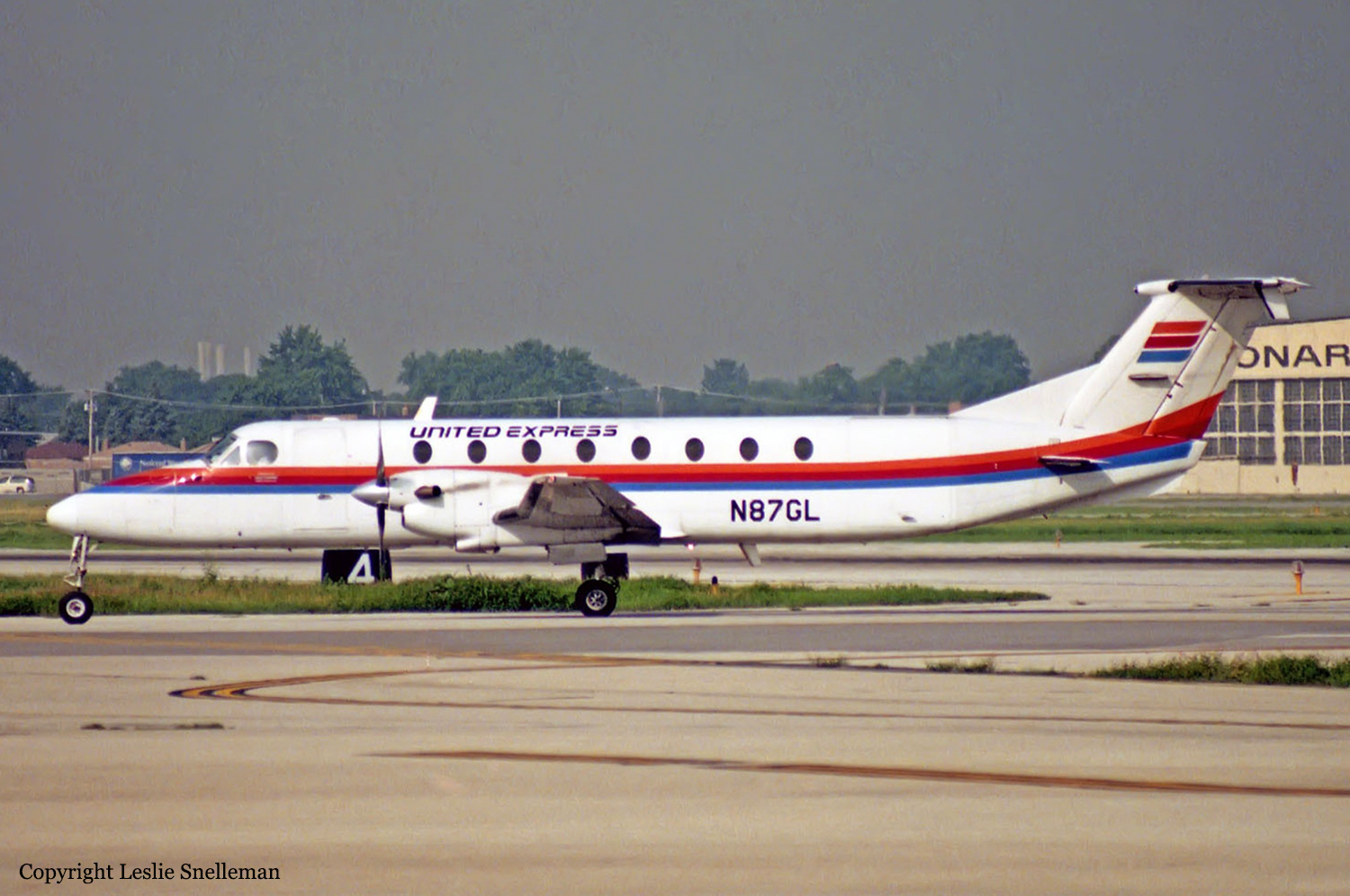
Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C-1 in Quincy: 12 killed
Date & Time:
Nov 19, 1996 at 1701 LT
Registration:
N87GL
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Chicago – Burlington – Quincy
MSN:
UC-087
YOM:
1989
Flight number:
UA5925
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
10
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
12
Captain / Total hours on type:
700.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
800
Aircraft flight hours:
18446
Aircraft flight cycles:
26797
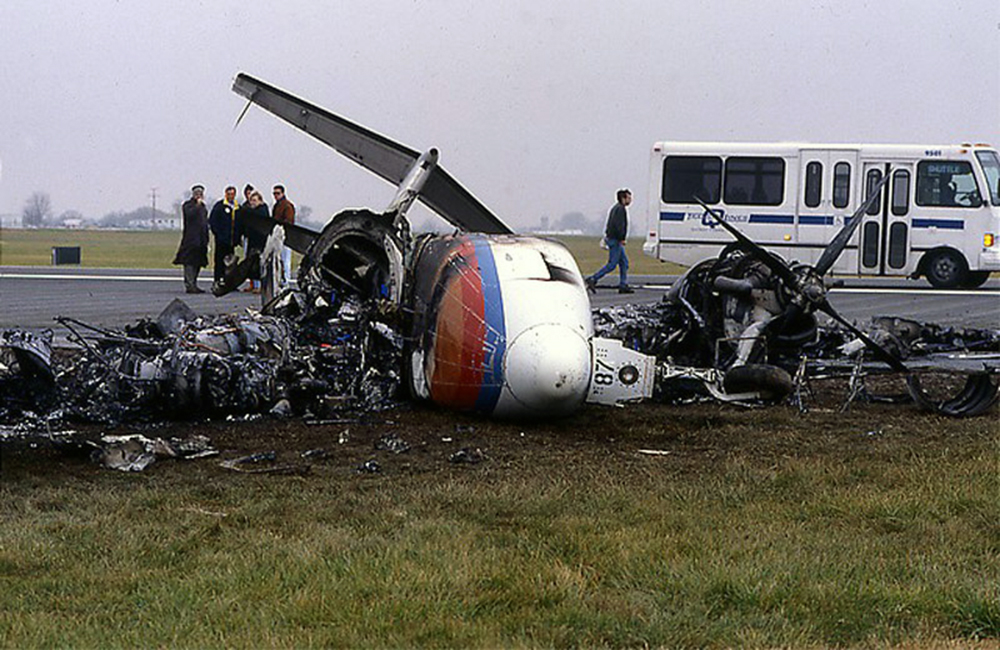
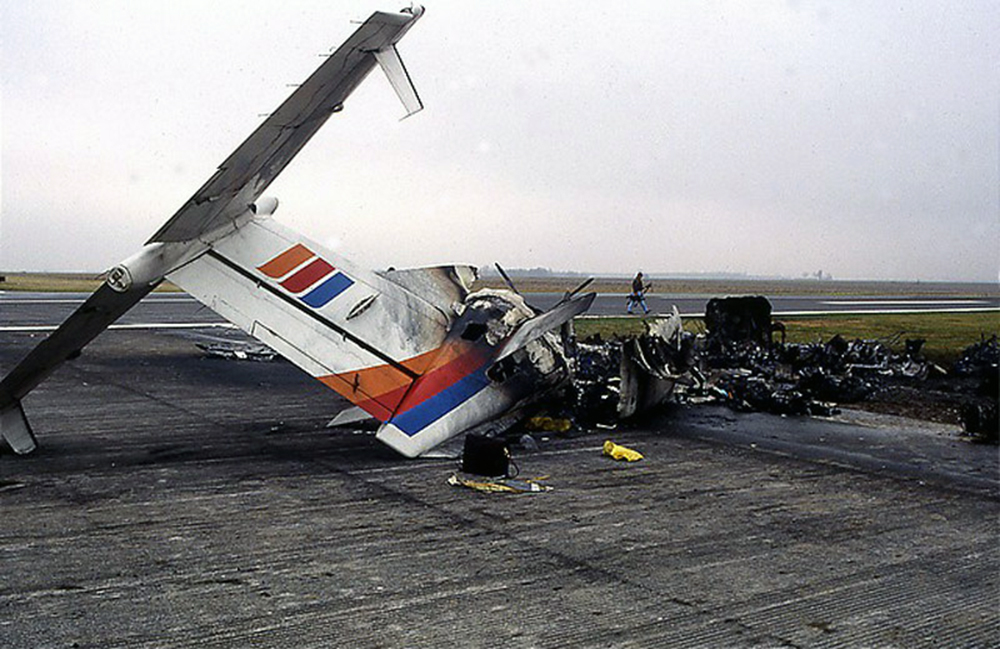
Circumstances:
The Beechcraft 1900C, N87GL, was in its landing roll on runway 13, and the Beechcraft A90, N1127D, was in its takeoff roll on runway 04. The collision occurred at the intersection of the two runways. The flight crew of the Beechcraft 1900C had made appropriate efforts to coordinate the approach and landing through radio communications and visual monitoring; however they mistook a Cherokee pilot's transmission (that he was holding for departure on runway 04) as a response from the Beechcraft A90 to their request for the Beechcraft A90's intentions, and therefore mistakenly believed that the Beechcraft A90 was not planning to take off until after the Beechcraft 1900C had cleared the runway. The failure of the Beechcraft A90 pilot to announce over the common traffic advisory frequency his intention to take off created a potential for collision between the two airplanes.
Probable cause:
The failure of the pilots in the King Air A90 to effectively monitor the common traffic advisory frequency or to properly scan for traffic, resulting in their commencing a takeoff roll when the Beechcraft 1900C (United Express flight 5925) was landing on an intersecting runway. Contributing to the cause of the accident was the Cherokee pilot's interrupted radio transmission, which led to the Beechcraft 1900C pilot's misunderstanding of the transmission as an indication from the King Air that it would not take off until after flight 5925 had cleared the runway. Contributing to the severity of the accident and the loss of life were the lack of adequate aircraft rescue and firefighting services and the failure of the air stair door on the Beechcraft 1900C to be opened.
Final Report:
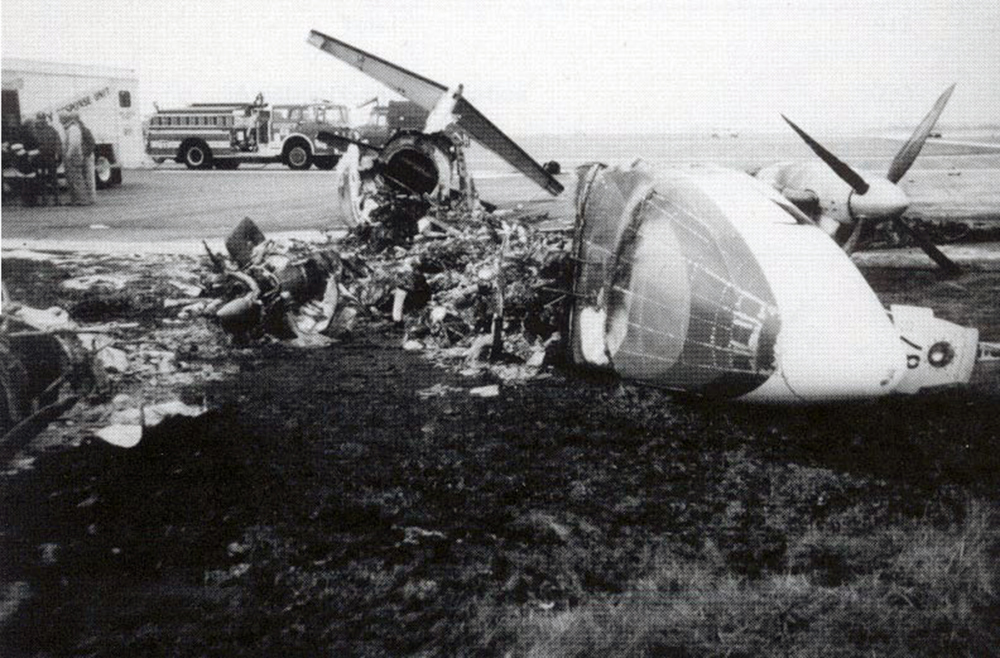




Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C in Saranac Lake: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 3, 1992 at 0546 LT
Registration:
N55000
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Plattsburgh – Saranac Lake – Albany
MSN:
UC-135
YOM:
1990
Flight number:
US4821
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Captain / Total hours on type:
3700.00
Aircraft flight hours:
1675
Circumstances:
On IFR arrival, flight 4821 was cleared to intersection 17 northeast of airport at 6,000 feet, then for ILS runway 23 approach. Radar service was terminated 6.5 east of intersection. Radar data showed that flight crossed and then bracketed localizer. Flight intercepted glide slope from below about 7 miles outside of outer marker and thence deviated above glide slope. About 2 miles outside of marker, flight was at a full fly down deflection when it entered a descent varying from 1,200 to 2,000 fpm. Aircraft struck wooded mountain top 2.0 miles inside of outer marker (3.9 miles from runway) at elevation of 2,280 feet. Minimum altitude at marker was 3,600 feet. Glide slope elevation at point of impact was approximately 2,900 feet. Evidence was found of inadequate electrical ground path between radome and fuselage which, when combined with existing weather conditions, may have produced electrostatic discharge (precipitation static). Although post-accident tests were not conclusive, the safety board believes that the glide slope indications might have been unreliable due to precipitation static interference. Two occupants survived while two others (one pilot and one passenger) were killed.
Probable cause:
Failure of the captain to establish a stabilized approach, his inadequate cross-check of instruments, his descent below specified minimum altitude at the final approach fix, and failure of the copilot to monitor the approach. Factors related to the accident were: weather conditions and possible precipitation static interference, caused by inadequate grounding between the radome and fuselage that could have resulted in unreliable glide slope indications.
Final Report:
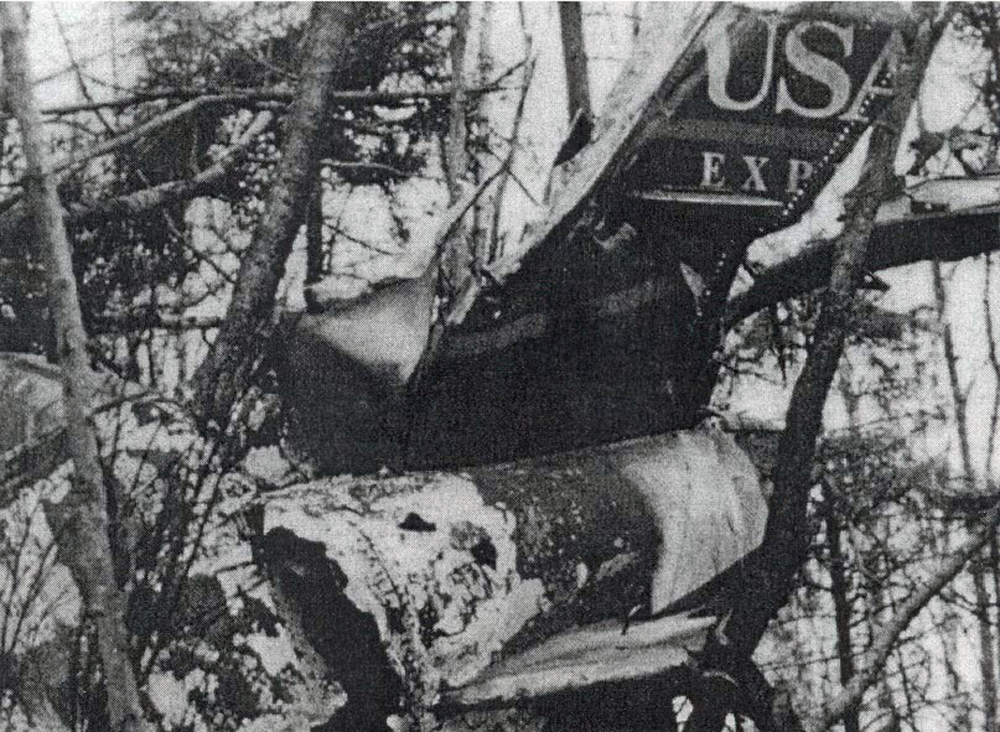

Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C off Block Island: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 28, 1991 at 2146 LT
Registration:
N811BE
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Bridgeport - Bridgeport
MSN:
UB-049
YOM:
1985
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Captain / Total hours on type:
2200.00
Aircraft flight hours:
11265
Circumstances:
The purpose of the flight was to prepare two first officers for a captain upgrade flight. The instructor pilot disabled the student's attitude indicator during flight, and the student had difficulty maintaining airplane control. During a simulated instrument approach, while in the procedure turn, the instructor simulated an engine failure in addition to the attitude indicator failure. The student asked the instructor to take control of the airplane because he became disoriented, however, the instructor refused. The investigation revealed that the instructor would turn his own flight instrument lights to the 'dim' position when the student was flying so that he could not 'peek' at the operable attitude indicator. Examination of the wreckage revealed that the instructor's light rheostat was in the dim position. The accident occurred over the ocean, on a moonless night. Neither the operator, nor the FAA were aware that this instructor was using Block Island for training, or what training methods he was employing.
Probable cause:
The instructor pilot's loss of altitude awareness and possible spatial disorientation, which resulted in the loss of control of the airplane at an altitude too low for recovery; and company management's lack of involvement in and oversight of its beechcraft 1900 flight training program. Contributing to the accident was the instructor pilot's exercise of poor judgment in establishing a flight situation and airplane configuration conducive to spatial disorientation that afforded the pilots little or no margin for error.
Final Report:

Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C-1 in Yuanlin: 18 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 21, 1990 at 0758 LT
Registration:
1905
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Taipei - Chiayi
MSN:
UC-5
YOM:
1988
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
16
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
18
Circumstances:
En route from Taipei to Chiayi, the crew encountered poor weather conditions with heavy rain falls and moderate to severe turbulences. The aircraft entered an uncontrolled descent and crashed in a sugar cane field located in Yuanlin, about 60 km northeast of Chiayi Airport. The aircraft disintegrated on impact and all 18 occupants were killed, among them high ranking officers of the Taiwan Army who were flying to Chiayi to proceed to an inspection of the military installations. At the time of the accident, weather was poor as the typhoon 'Yancy' was passing over Taiwan.
Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C-1 in Manila: 25 killed
Date & Time:
May 18, 1990 at 0623 LT
Registration:
RP-C314
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Manila - Surigao
MSN:
UC-46
YOM:
1988
Flight number:
LFT075
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
19
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
25
Circumstances:
After takeoff from Manila-Ninoy Aquino Airport, while climbing to an altitude of about 400 feet, the crew reported engine problems and elected to return for an emergency landing. Shortly later, the aircraft banked right, lost height and nosed down by an angle of 70° before crashing onto a house located in the district of Paranaque, about one km from the airport. The aircraft and the house were destroyed. All 21 occupants as well as four people on the ground were killed.
Probable cause:
Failure of the right engine during initial climb for undetermined reasons. It was reported that the crew failed to follow emergency procedures which was considered as a contributing factor. When the right engine failed, the aircraft was still in takeoff configuration with flaps and gear down.
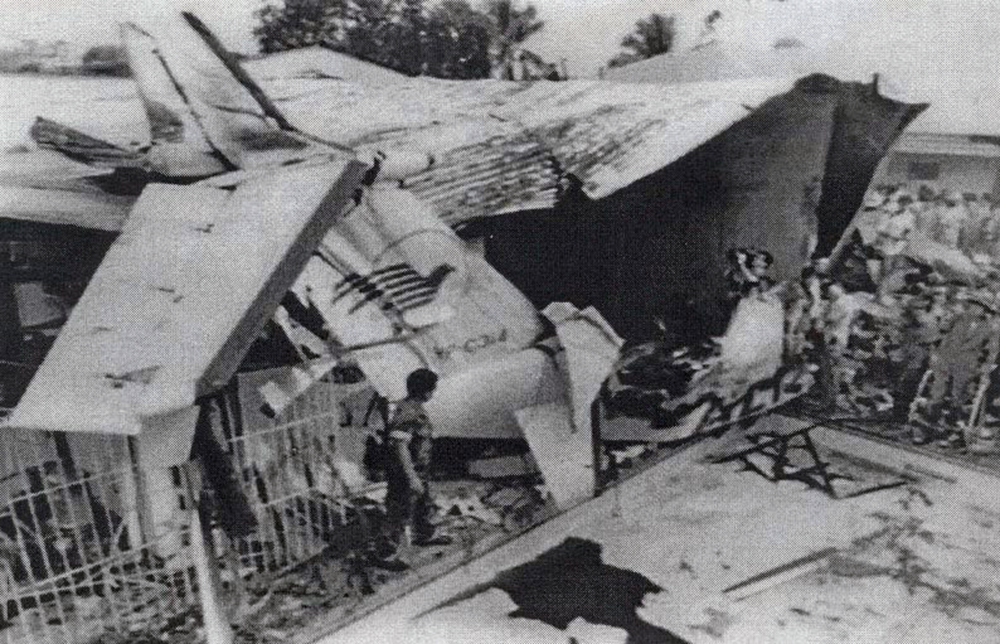


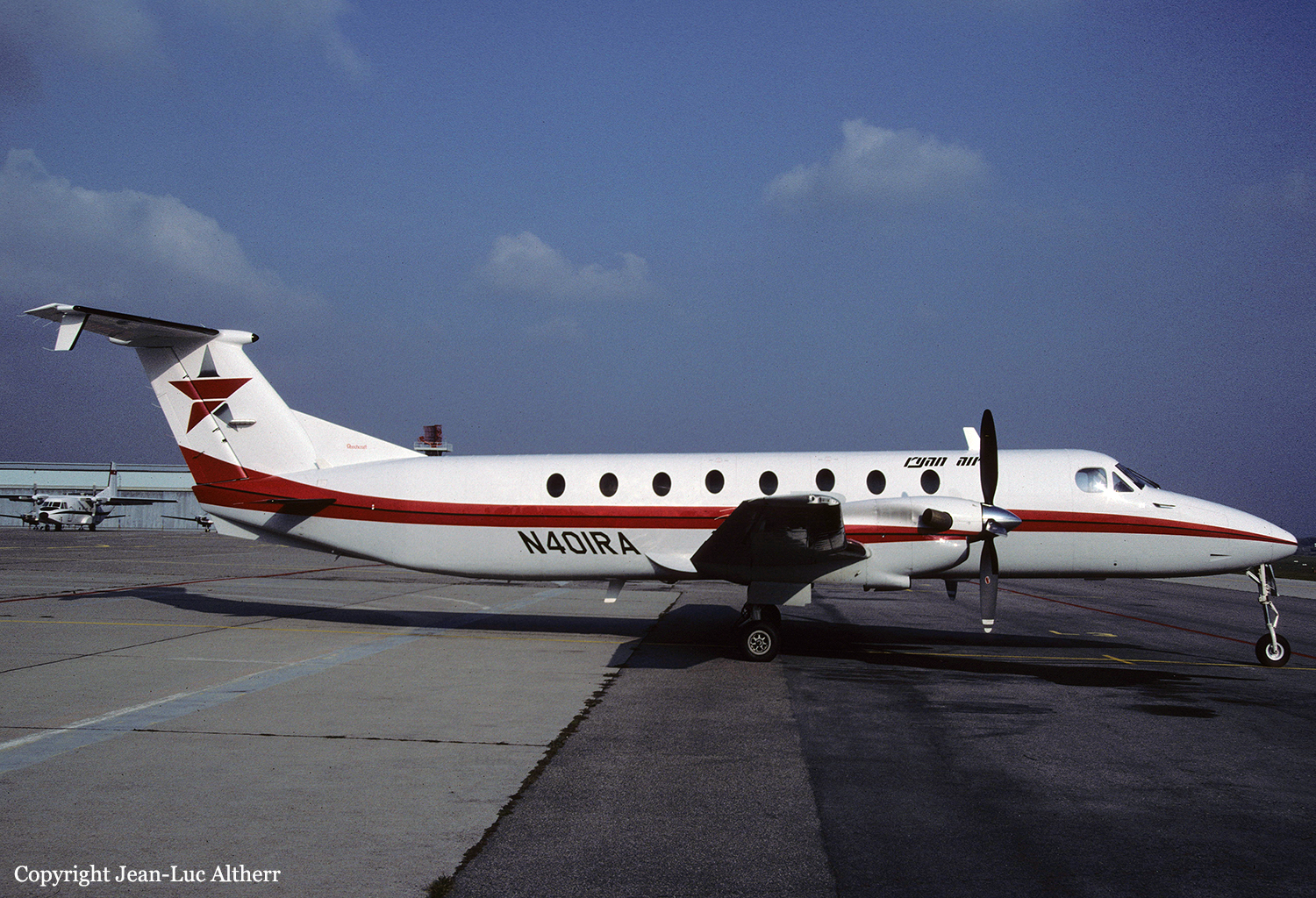
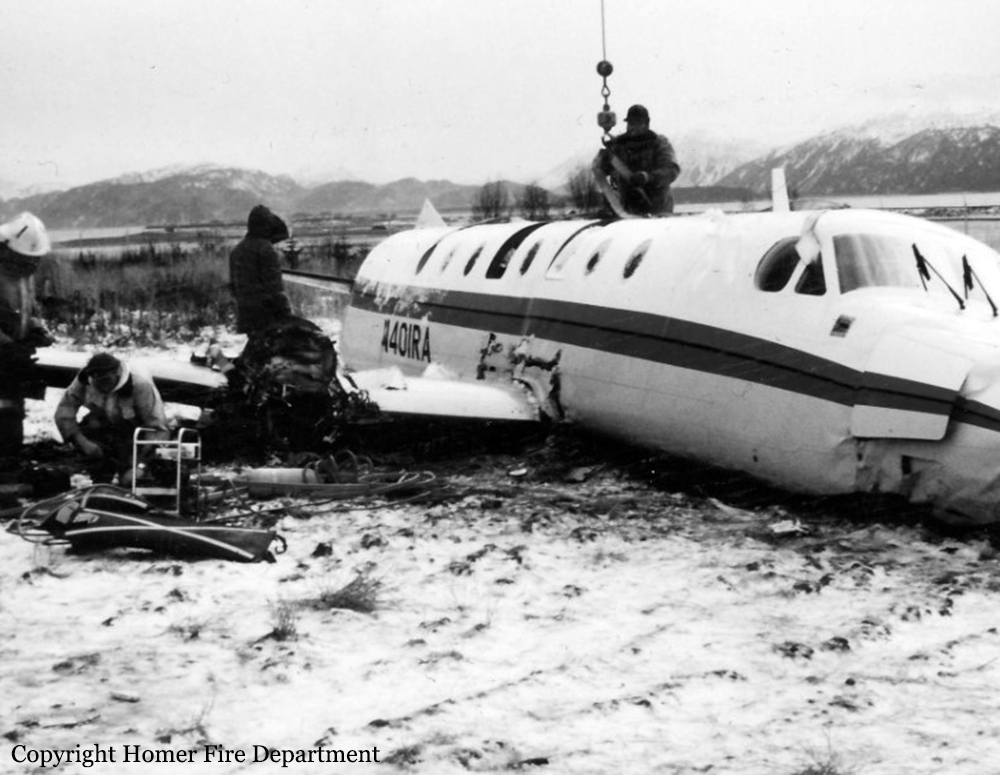
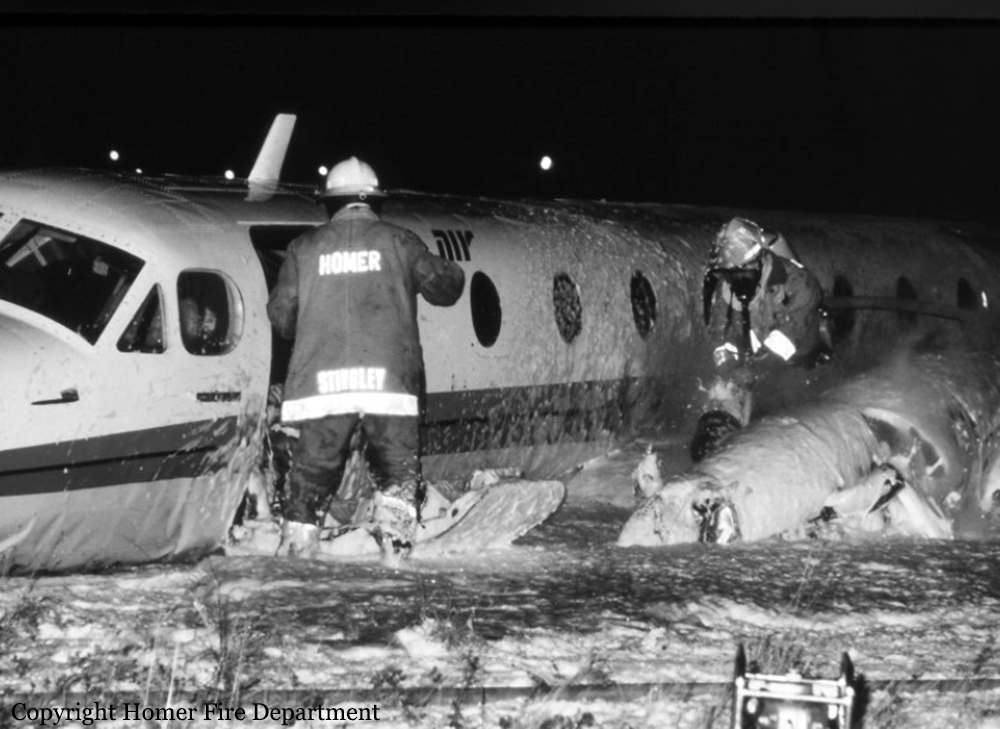
Crash of a Beechcraft 1900C in Homer: 18 killed
Date & Time:
Nov 23, 1987 at 1825 LT
Registration:
N401RA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Kodiak - Homer - Kenai - Anchorage
MSN:
UB-058
YOM:
1986
Flight number:
XY103
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
19
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
18
Captain / Total hours on type:
4420.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
300
Circumstances:
During arrival, the aircraft (Ryan flight 103) crashed short of runway 03. The fuselage stayed intact during impact, but the belly structure was compressed and vertical deceleration forces exceeded the design capability of the seats. Rescue personnel had difficulty shutting off the aircraft's electrical power which delayed removal of the 1st officer (f/o) from the aircraft. An investigation revealed the aircraft was loaded with approximately 600 lbs more cargo than the f/o had requested. The center-of-gravity (cg) was 8 to 11 inches behind the allowable aft limit and the flight crew did not comply with company and FAA procedures in computing the cg. During flight, up to 3/8 inches of ice accumulated on the aircraft's leading edges. There was evidence the crew lost control of the aircraft as the flaps were lowered. The right flap actuator was found in the 7 to 12° position and the stabilizer trim was found at the full nose down position. Flight tests showed there would be no significant difficulty in controlling the aircraft with up to 1.5 inch of ice on the leading edges and that static stability would deteriorate during flap extension with the aft cg configuration. Three passengers survived while 18 other occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The failure of the flight crew to properly supervise the loading of the airplane which resulted in the centre of gravity being displaced to such an aft location that the airplane control was lost when the flaps were lowered for landing.
Final Report: