Date & Time:
Jan 3, 1992 at 0546 LT
Type of aircraft:
Beechcraft 1900C
Registration:
N55000
Flight Phase:
Landing (descent or approach)
Flight Type:
Scheduled Revenue Flight
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Plattsburgh – Saranac Lake – Albany
MSN:
UC-135
YOM:
1990
Flight number:
US4821
Country:
United States of America
Region:
North America
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
1
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
1
Other fatalities:
0
Total fatalities:
2
Captain / Total hours on type:
3700
Aircraft flight hours:
1675
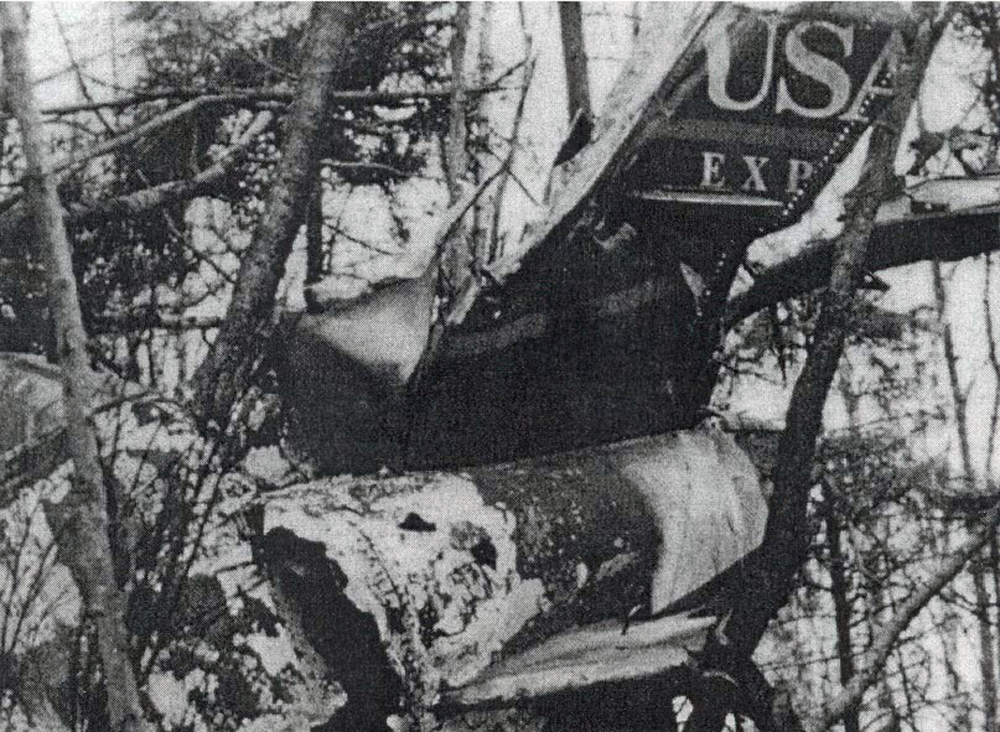
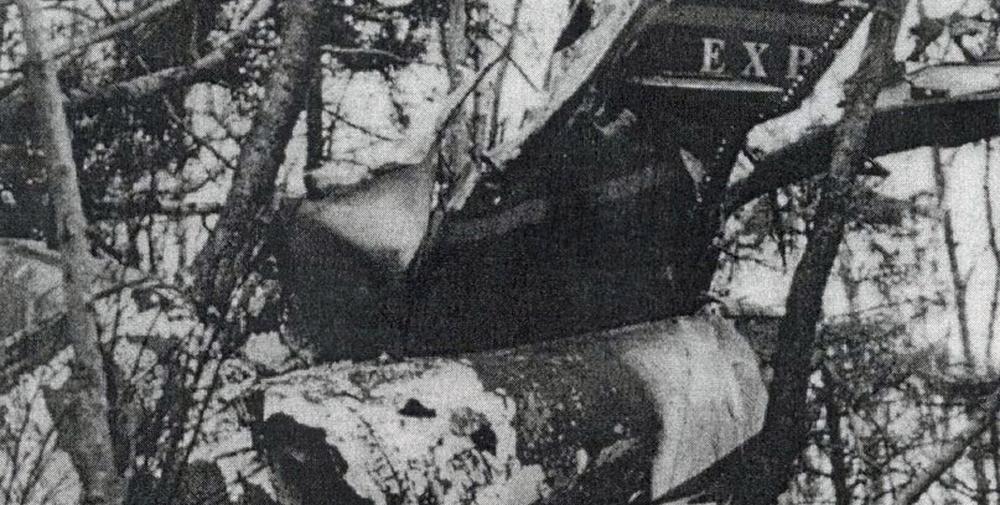
Circumstances:
On IFR arrival, flight 4821 was cleared to intersection 17 northeast of airport at 6,000 feet, then for ILS runway 23 approach. Radar service was terminated 6.5 east of intersection. Radar data showed that flight crossed and then bracketed localizer. Flight intercepted glide slope from below about 7 miles outside of outer marker and thence deviated above glide slope. About 2 miles outside of marker, flight was at a full fly down deflection when it entered a descent varying from 1,200 to 2,000 fpm. Aircraft struck wooded mountain top 2.0 miles inside of outer marker (3.9 miles from runway) at elevation of 2,280 feet. Minimum altitude at marker was 3,600 feet. Glide slope elevation at point of impact was approximately 2,900 feet. Evidence was found of inadequate electrical ground path between radome and fuselage which, when combined with existing weather conditions, may have produced electrostatic discharge (precipitation static). Although post-accident tests were not conclusive, the safety board believes that the glide slope indications might have been unreliable due to precipitation static interference. Two occupants survived while two others (one pilot and one passenger) were killed.
Probable cause:
Failure of the captain to establish a stabilized approach, his inadequate cross-check of instruments, his descent below specified minimum altitude at the final approach fix, and failure of the copilot to monitor the approach. Factors related to the accident were: weather conditions and possible precipitation static interference, caused by inadequate grounding between the radome and fuselage that could have resulted in unreliable glide slope indications.
Final Report:
N55000.pdf92.16 KB