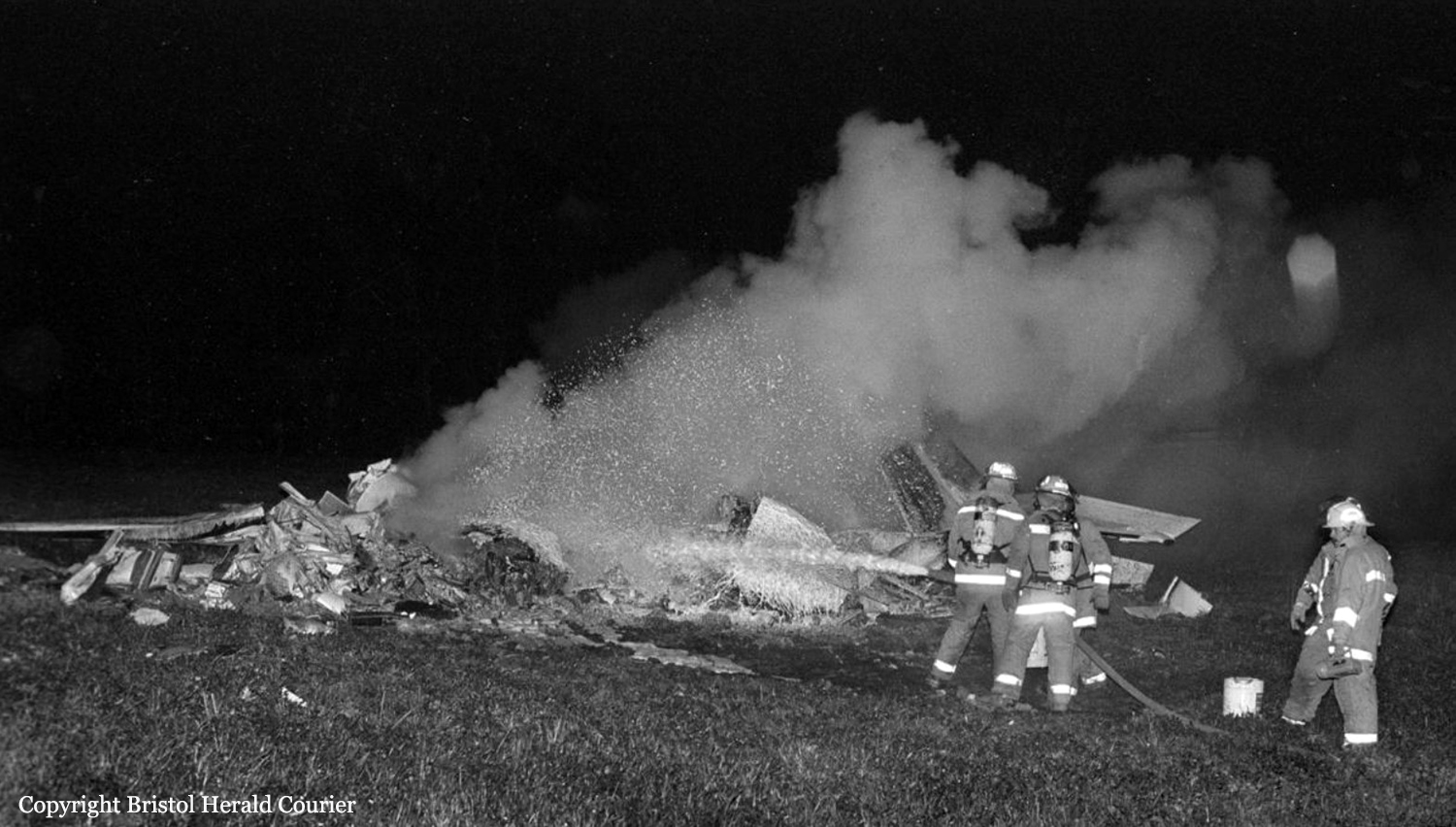
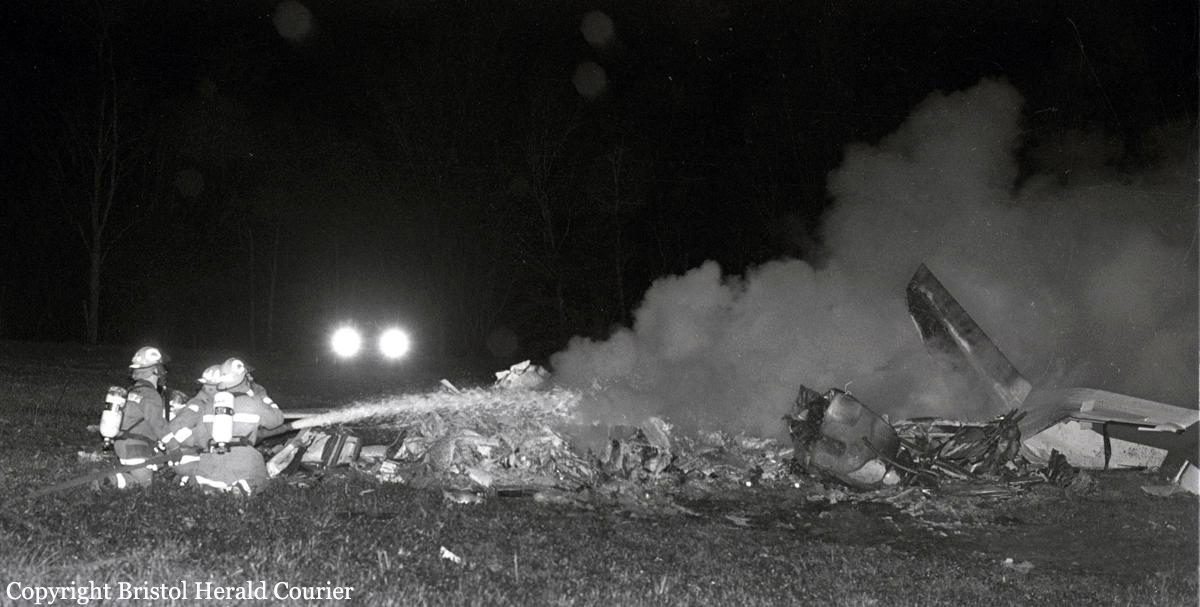
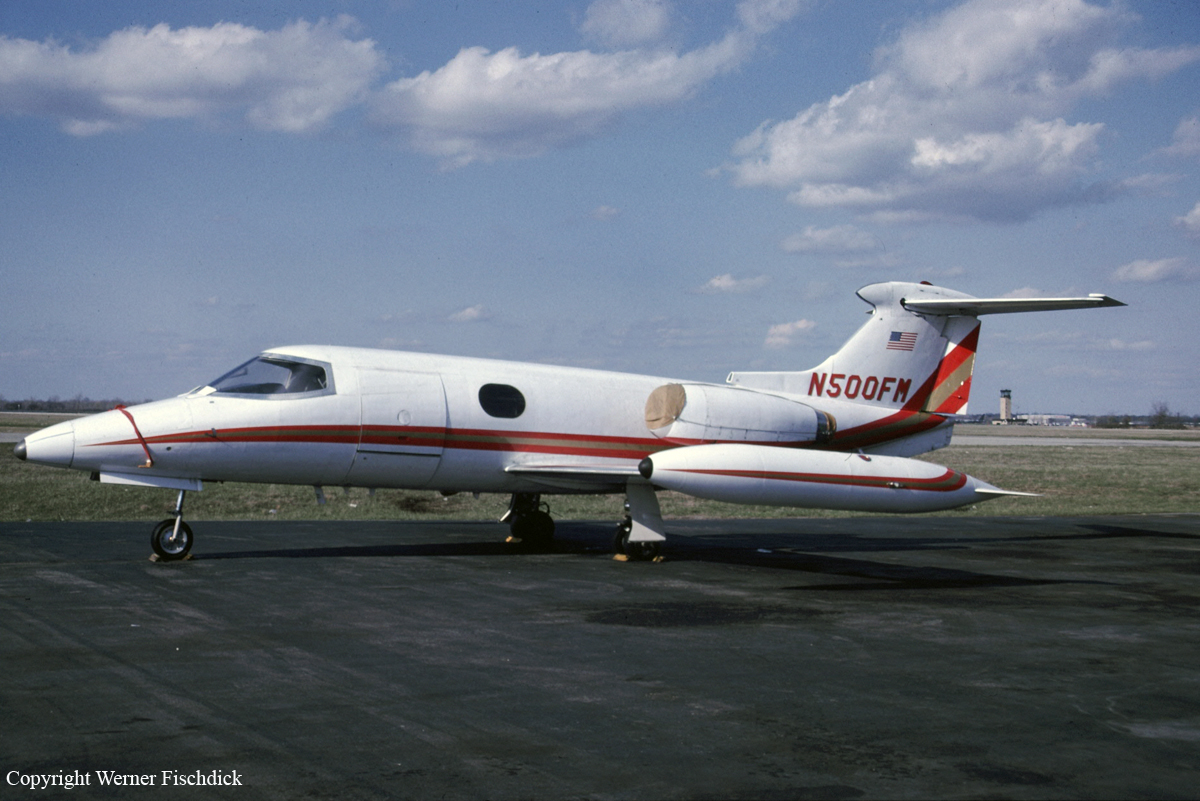
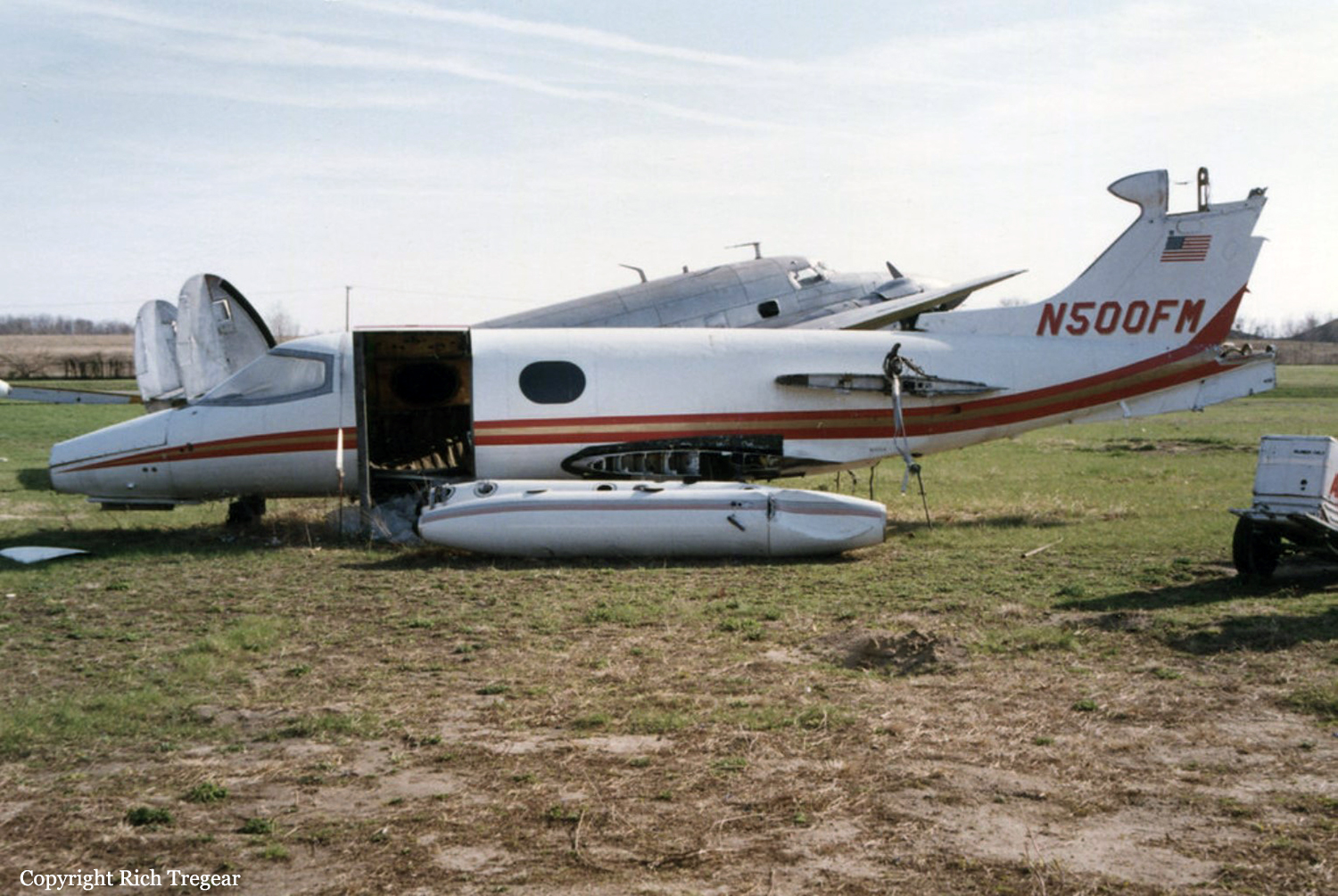
Crash of a Beechcraft C-45 Expeditor in Blountville
Date & Time:
Feb 2, 1996 at 1830 LT
Registration:
N204AA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Madison - Charlotte
MSN:
AF-79
YOM:
1954
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
350.00
Aircraft flight hours:
16972
Circumstances:
The pilot reported that as he overflew the Tri-City airport, Tennessee at 9,000 feet, the right engine power slowly decreased. The airplane was in the clouds with an outside air temperature of about zero degrees Celsius. Right engine manifold heat was applied for a few seconds, with no noticeable difference in engine performance. The right magnetos were also checked with no obvious malfunctions noted. A descent for landing was initiated to the Tri-City airport and manifold heat was applied and removed several times, with no appreciable effect. On short final approach, when the landing gear was extended, the right main gear did not indicate down. There was insufficient time to perform the emergency gear extension procedure. A go-around was initiated, during which the pilot discovered that the left manifold heat control was now stuck in the 'ON' position. The pilot stated that with less than full power available on the left engine, and the right propeller unfeathered, the airplane could be climbed to about 200 feet. He flew the airplane until terrain clearance was no longer possible, then landed in a field, gear up. The airplane slid into trees and was substantially damaged.
Probable cause:
The pilot's improper use of carburetor heat which resulted in a continuing loss of engine power, and the right landing gear's failure to extend during a single engine approach. A factor was the
insufficient time available to extend the landing gear via the emergency extension procedure.
insufficient time available to extend the landing gear via the emergency extension procedure.
Final Report: