Crash of a NAMC YS-11A-202 near Borrego Springs
Date & Time:
Mar 5, 1974 at 1110 LT
Registration:
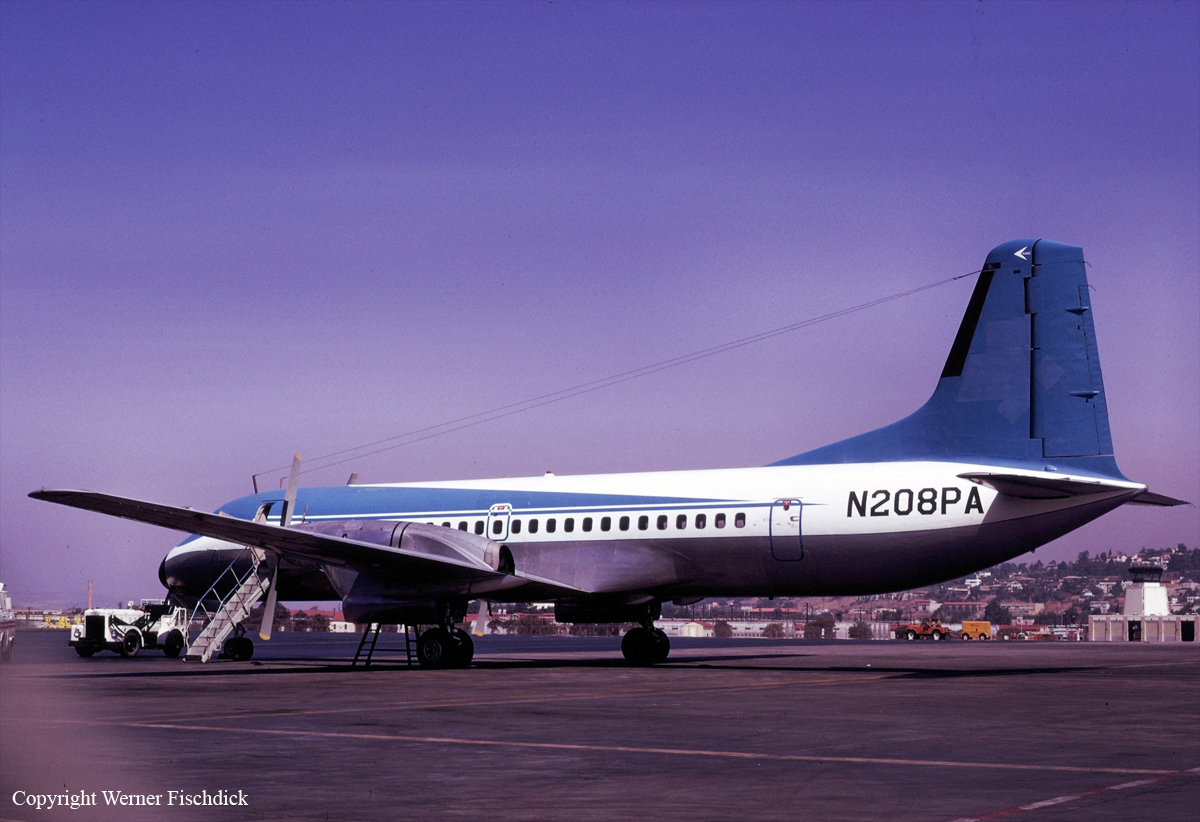
N208PA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
San Diego - San Diego
MSN:
2082
YOM:
1968
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
797.00
Circumstances:
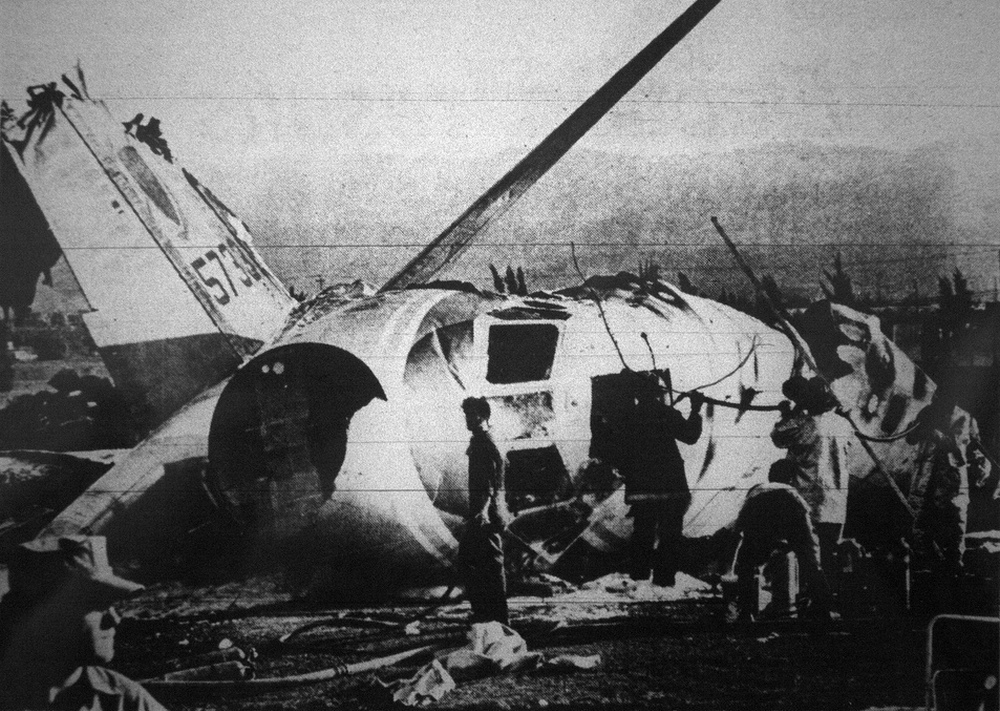
The crew (four pilots) departed San Diego Airport on a training mission. En route, the crew simulated stall conditions when both engines failed to respond. Shortly later, both engines caught fire and the crew decided to attempt an emergency landing. The aircraft belly landed about 8,8 miles east of Borrego Springs and came to rest in flames in a desert area. While all four crew members escaped uninjured, the aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
Double engine failure in flight due to inadequate maintenance and inspection and failure of the propeller system. The following factors were reported:
- Improper operation of powerplant,
- Inadequate supervision of flight,
- Excessive temperature,
- Failure of both engines,
- Fire on both engines,
- Hi stop hub connecting switch inoperative.
- Improper operation of powerplant,
- Inadequate supervision of flight,
- Excessive temperature,
- Failure of both engines,
- Fire on both engines,
- Hi stop hub connecting switch inoperative.
Final Report: