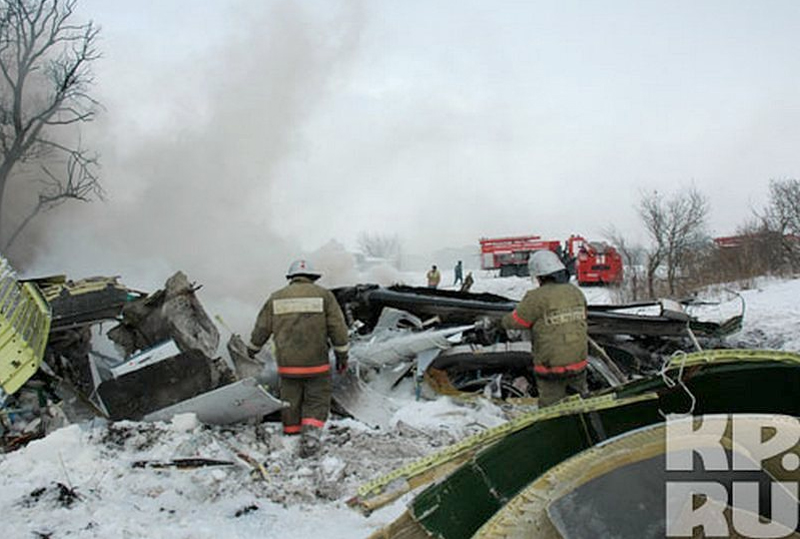
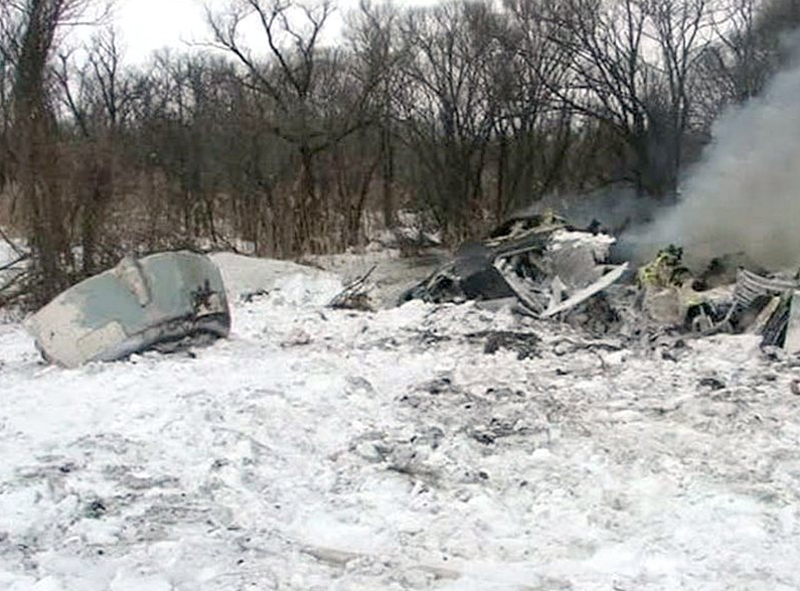
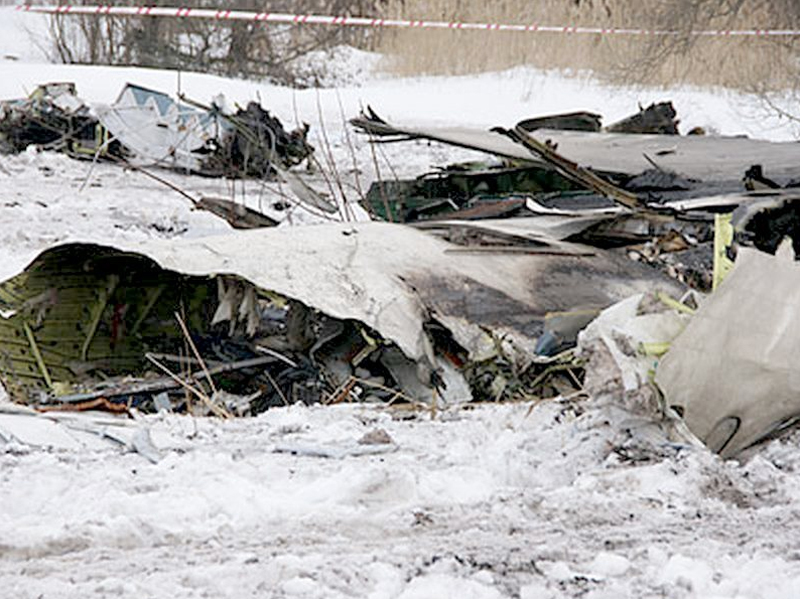
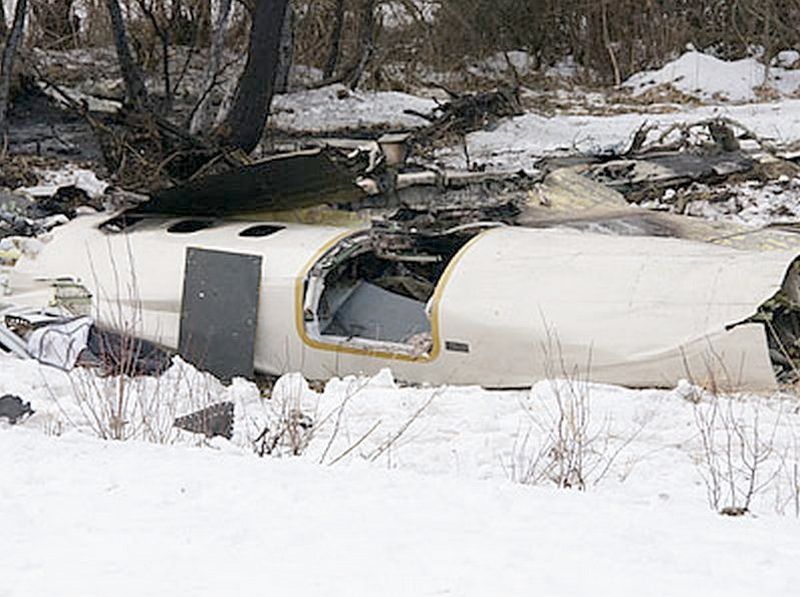
Crash of an Antonov AN-148-100E in Garbuzovo: 6 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 5, 2011 at 1040 LT
Registration:
61708
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Voronezh - Voronezh
MSN:
41-03
YOM:
2010
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
6
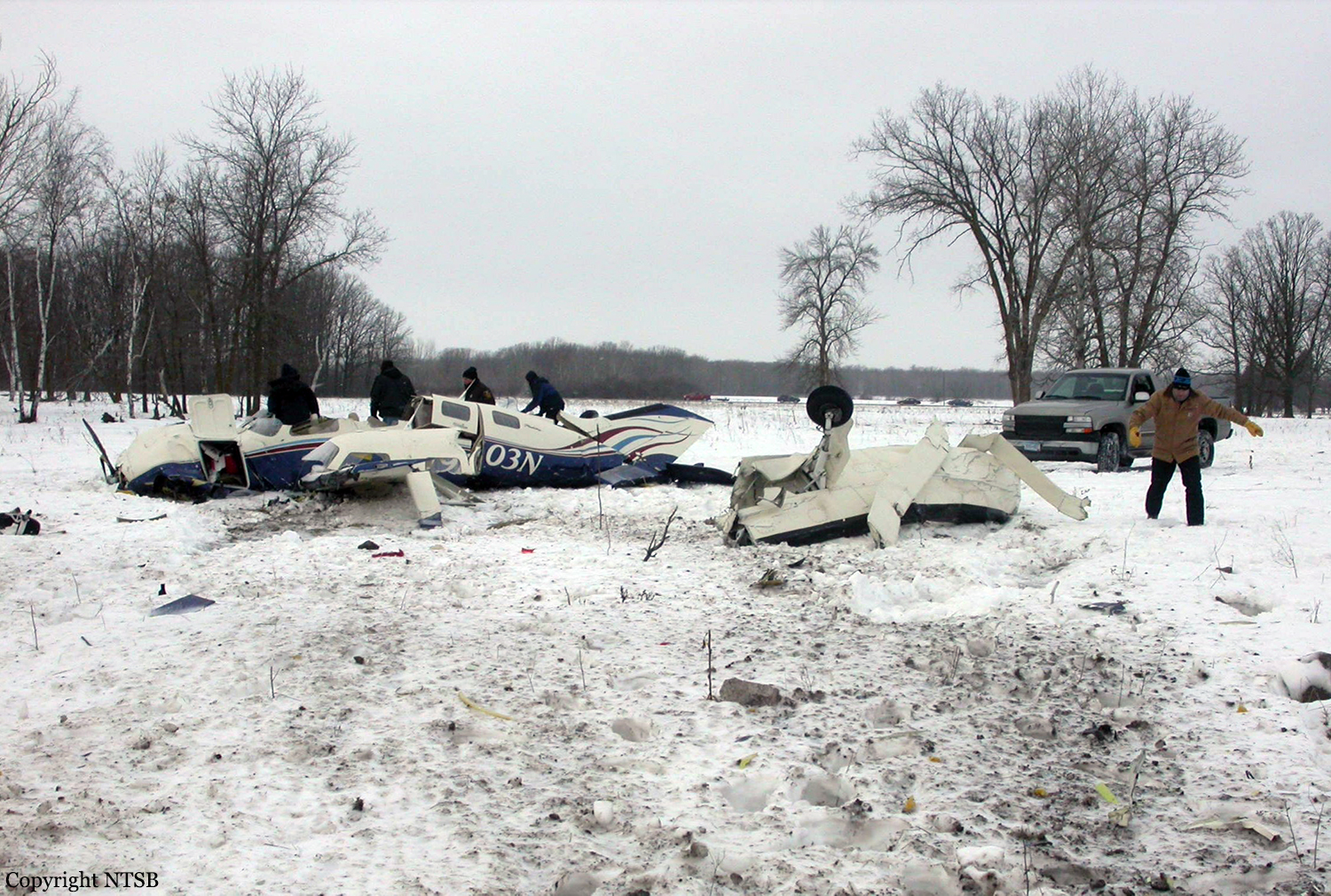
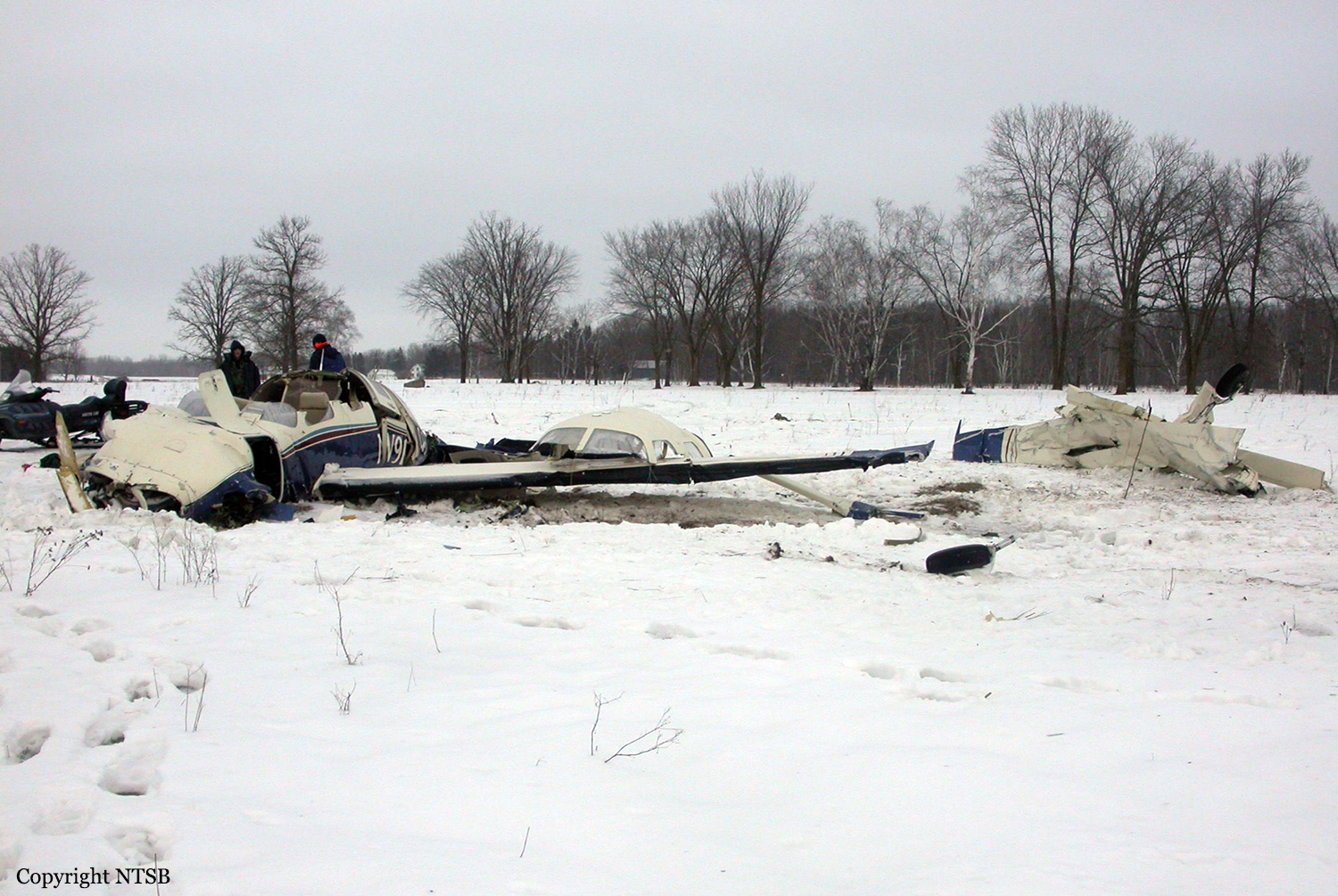
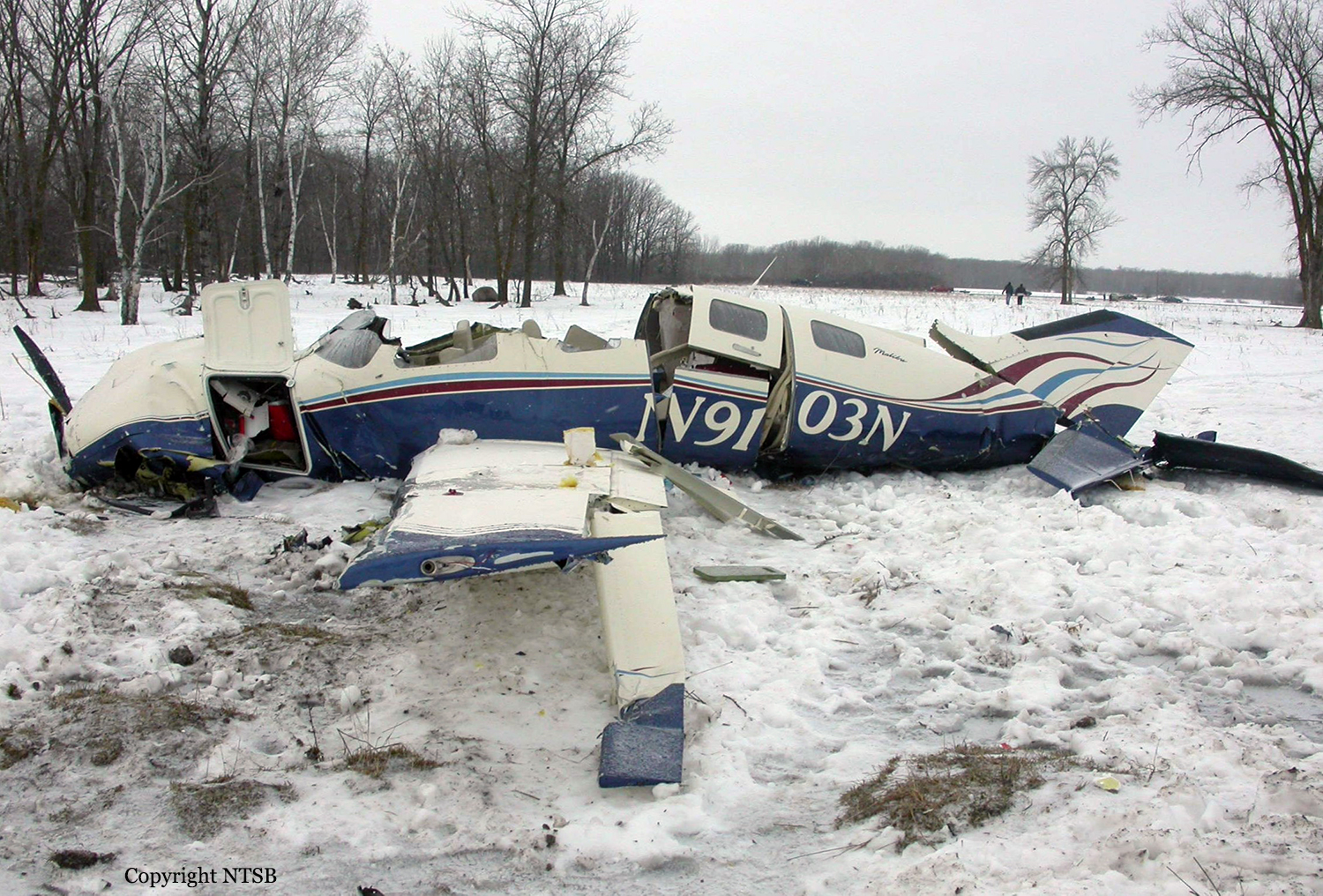
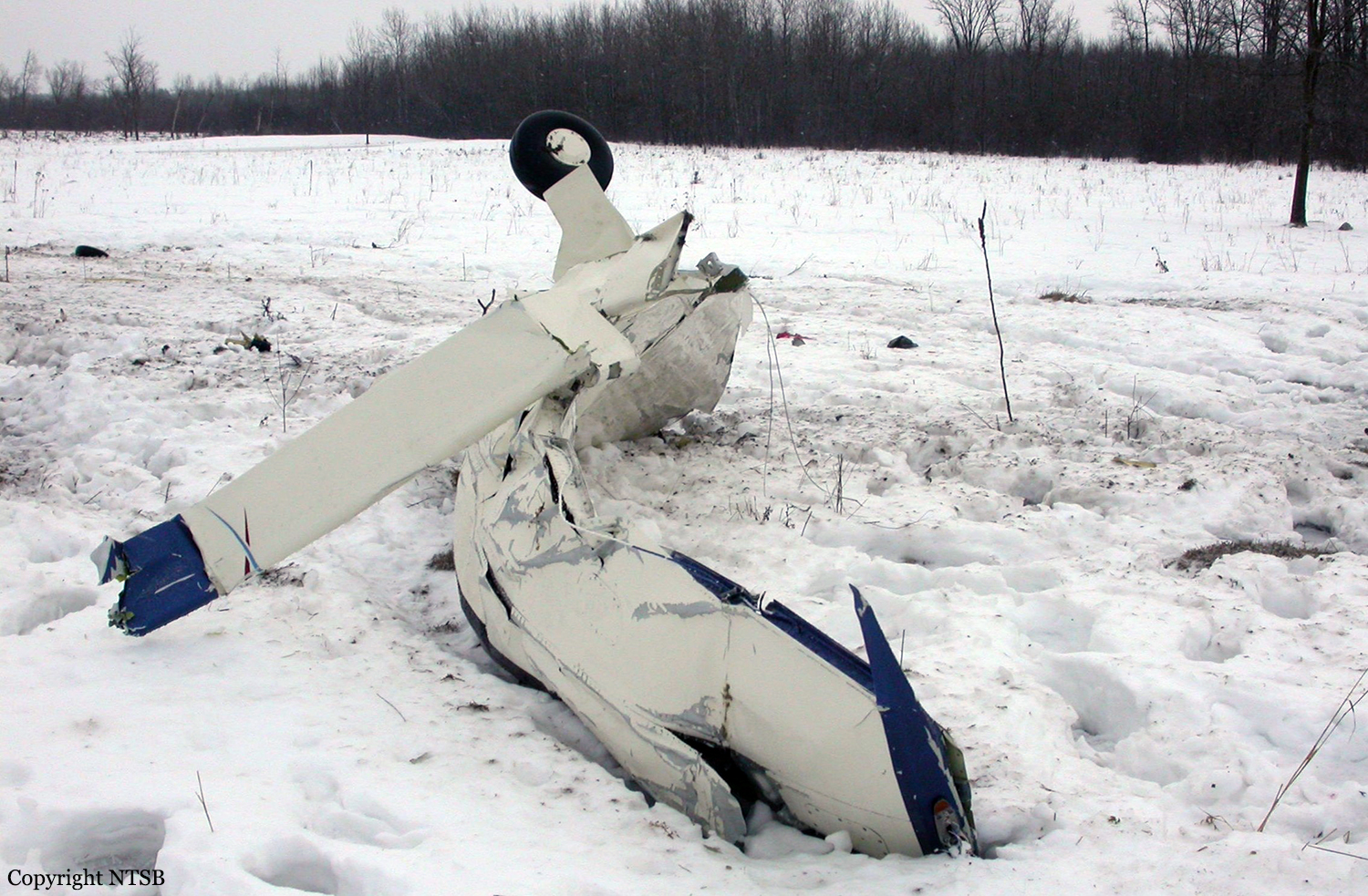
Circumstances:
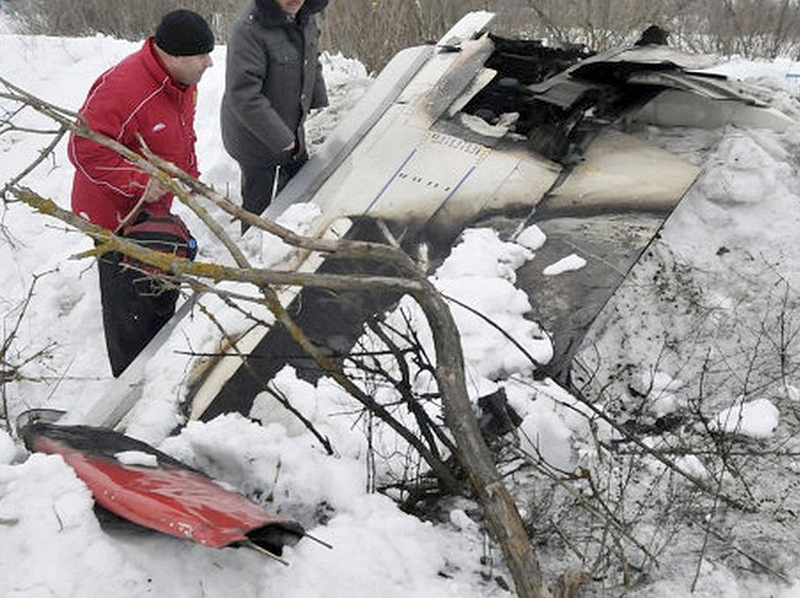
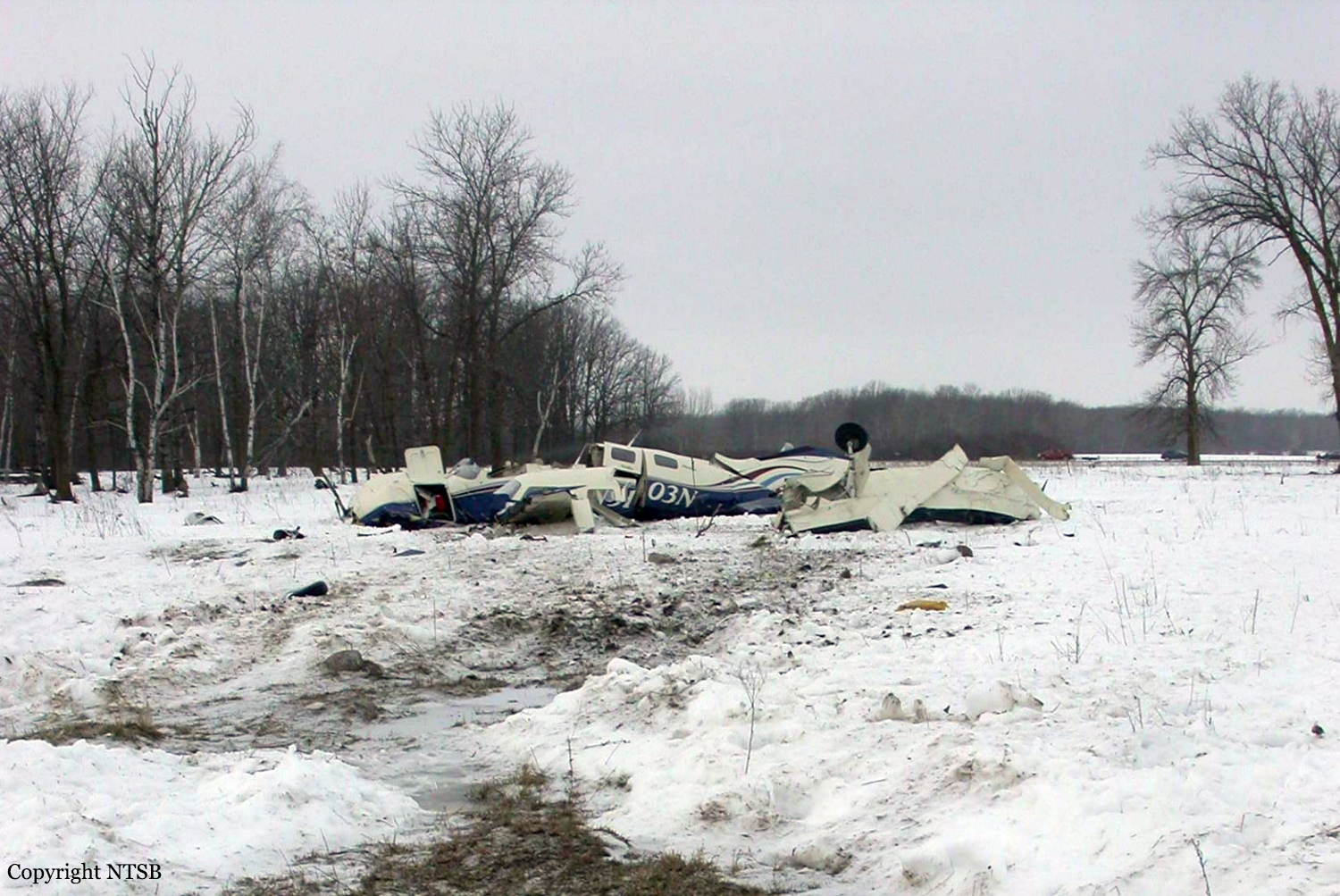
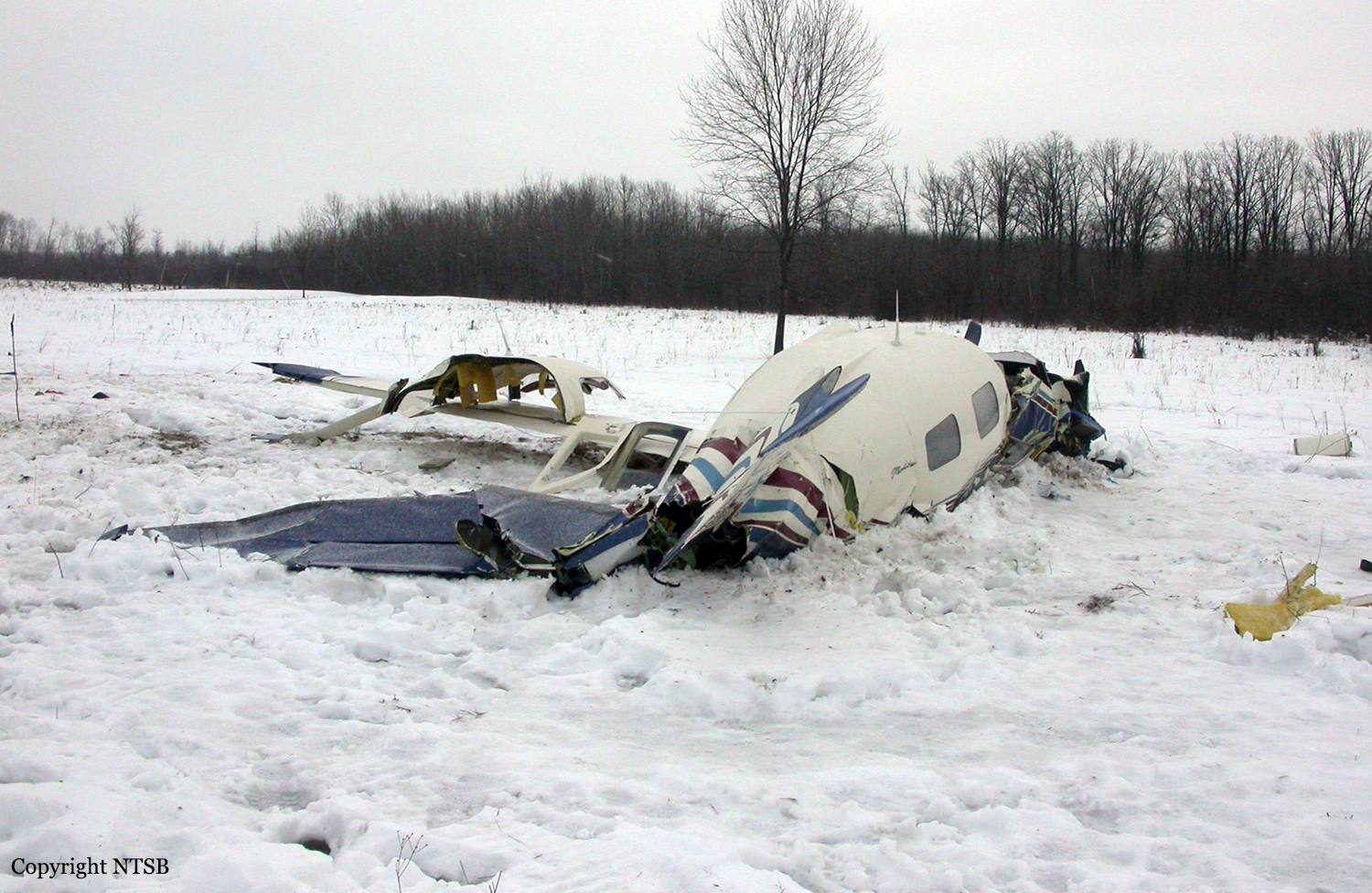
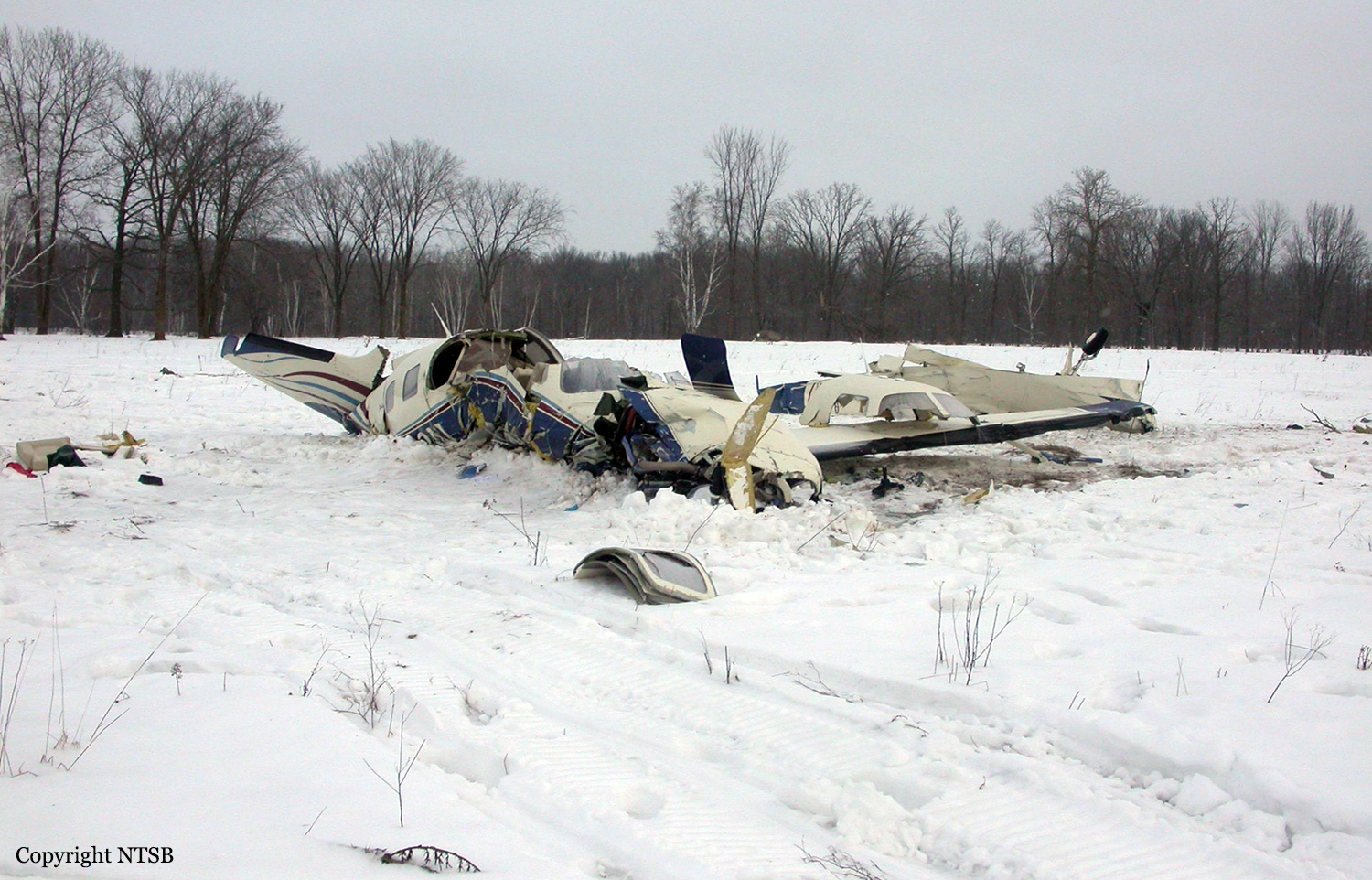
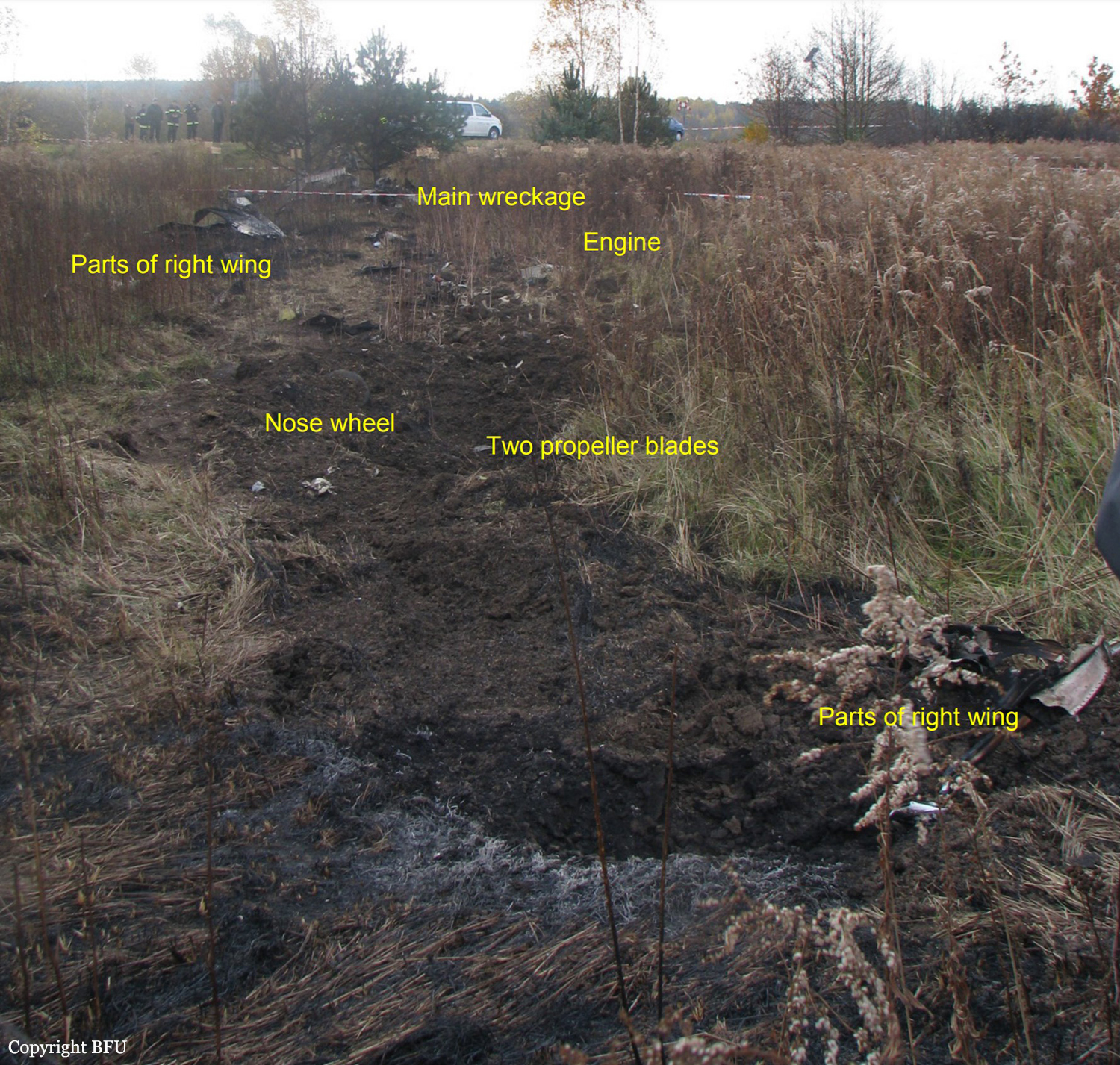
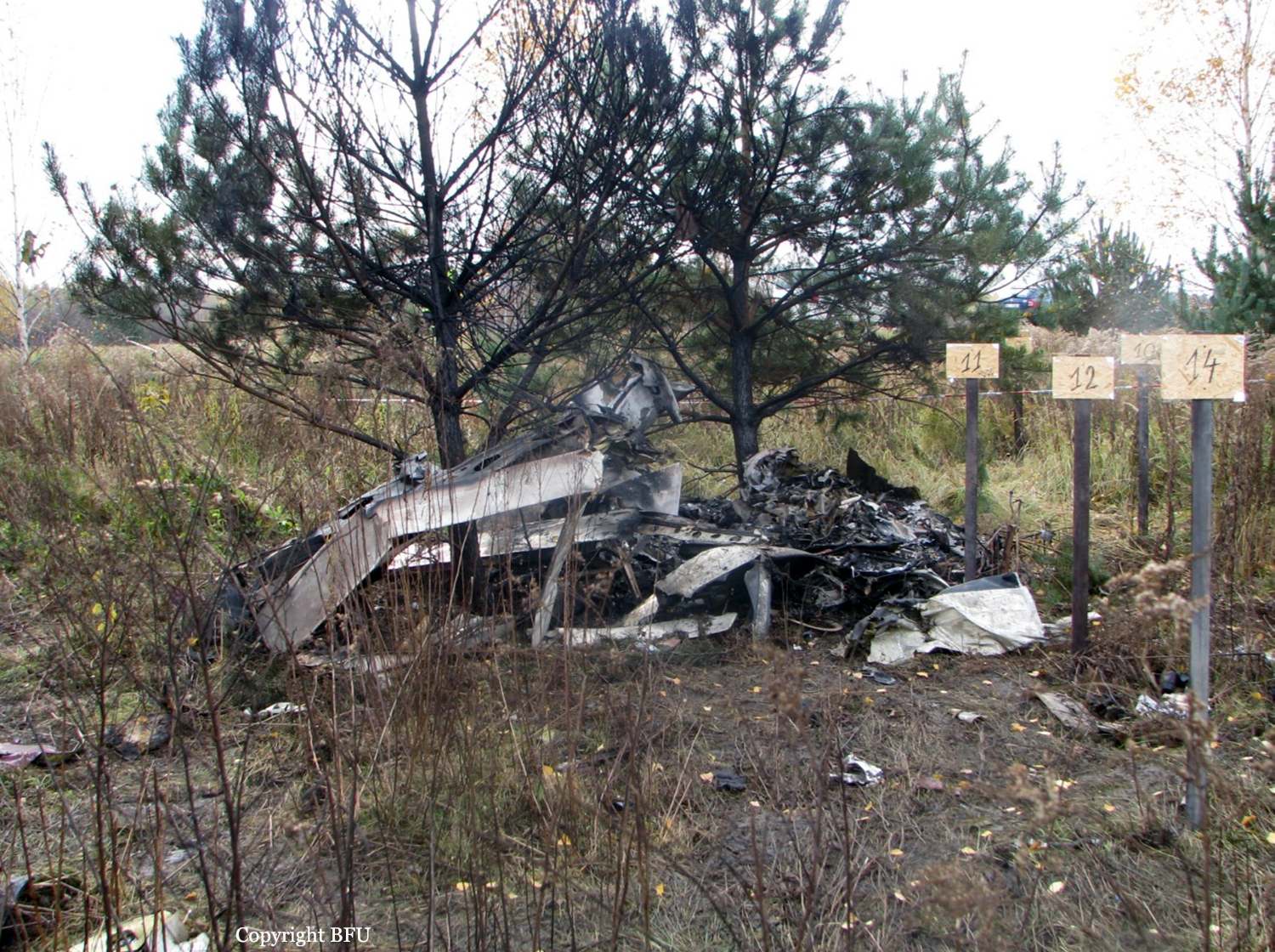
The aircraft departed Voronezh-Pridacha Airport in the morning to conduct a test flight with six crew on board, two pilots from the manufacturer, two engineers and two pilots from the Myanmar Air Force to whom the aircraft should be delivered. In flight, the crew decided to perform an emergency descent. During this manoeuvre, the aircraft reached an excessive speed and lost part of its tail, stabilizers and elevators. It entered an uncontrolled descent and crashed in a snow covered field located near Garbuzovo, bursting into flames. The aircraft was totally destroyed and all six occupants were killed. Tail parts, stabilizers and elevators were later found about 3 km from the point of impact. The airplane was operated by the Voronezh Aircraft Production Association. (VASO - Voronezhskoye Aktsionernoye Samoletostroitelnoe Obshestvo). First accident involving an Antonov AN-148.
Probable cause:
The cause of the accident was the inadvertently permitted the aircraft to accelerate 110 km/h above the design limit speed during an emergency descent. This led to low-frequency vibrations on the aircraft in all axes, an increase of alternating accelerations exceeding the margin of safety. The result was the break up of the aircraft in the air, followed by its collision with the earth.
The main factors contributing to the accident were:
- Untimely and inadequate actions of the crew to control the emergency decent,
- Lack of proper coordination among the members of the crew,
- Deviations from recommendations in the flight manual in executing the emergency descent,
- Misleading indications on basic instruments when outside characteristic operating conditions.
The main factors contributing to the accident were:
- Untimely and inadequate actions of the crew to control the emergency decent,
- Lack of proper coordination among the members of the crew,
- Deviations from recommendations in the flight manual in executing the emergency descent,
- Misleading indications on basic instruments when outside characteristic operating conditions.