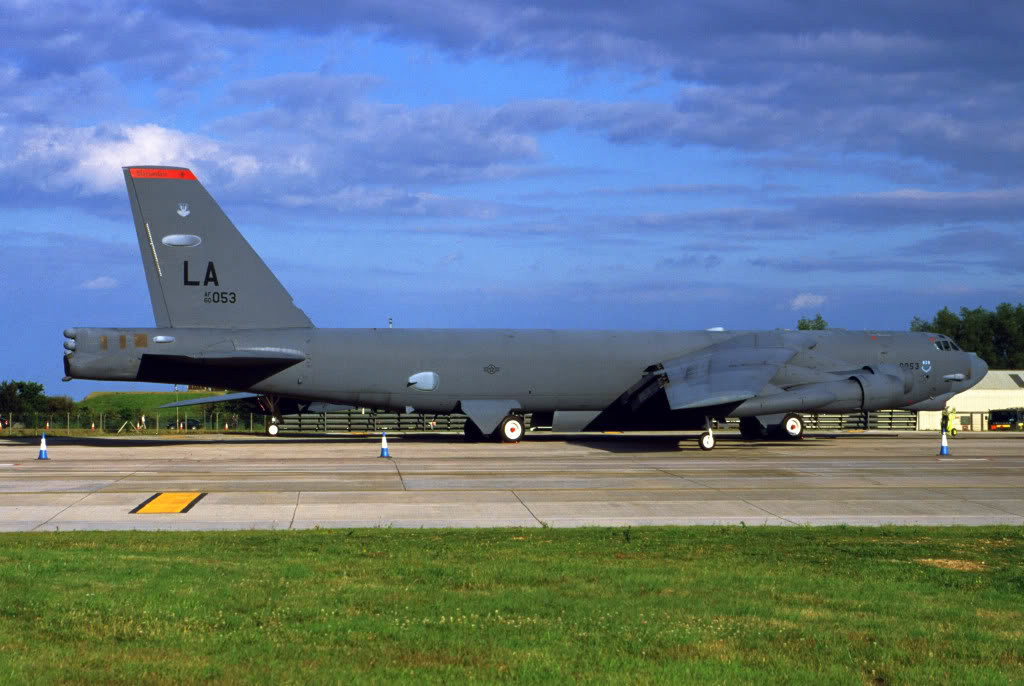
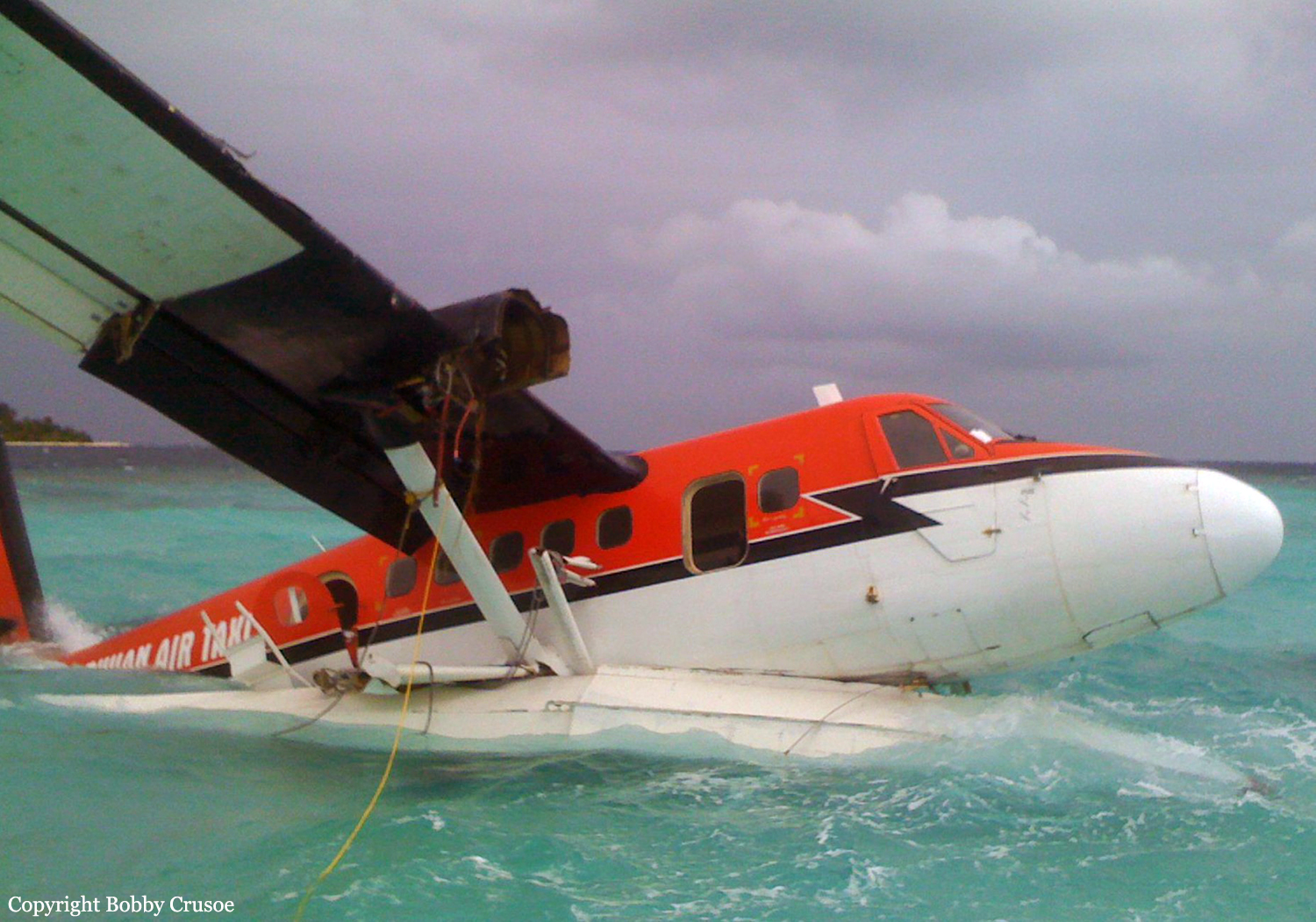
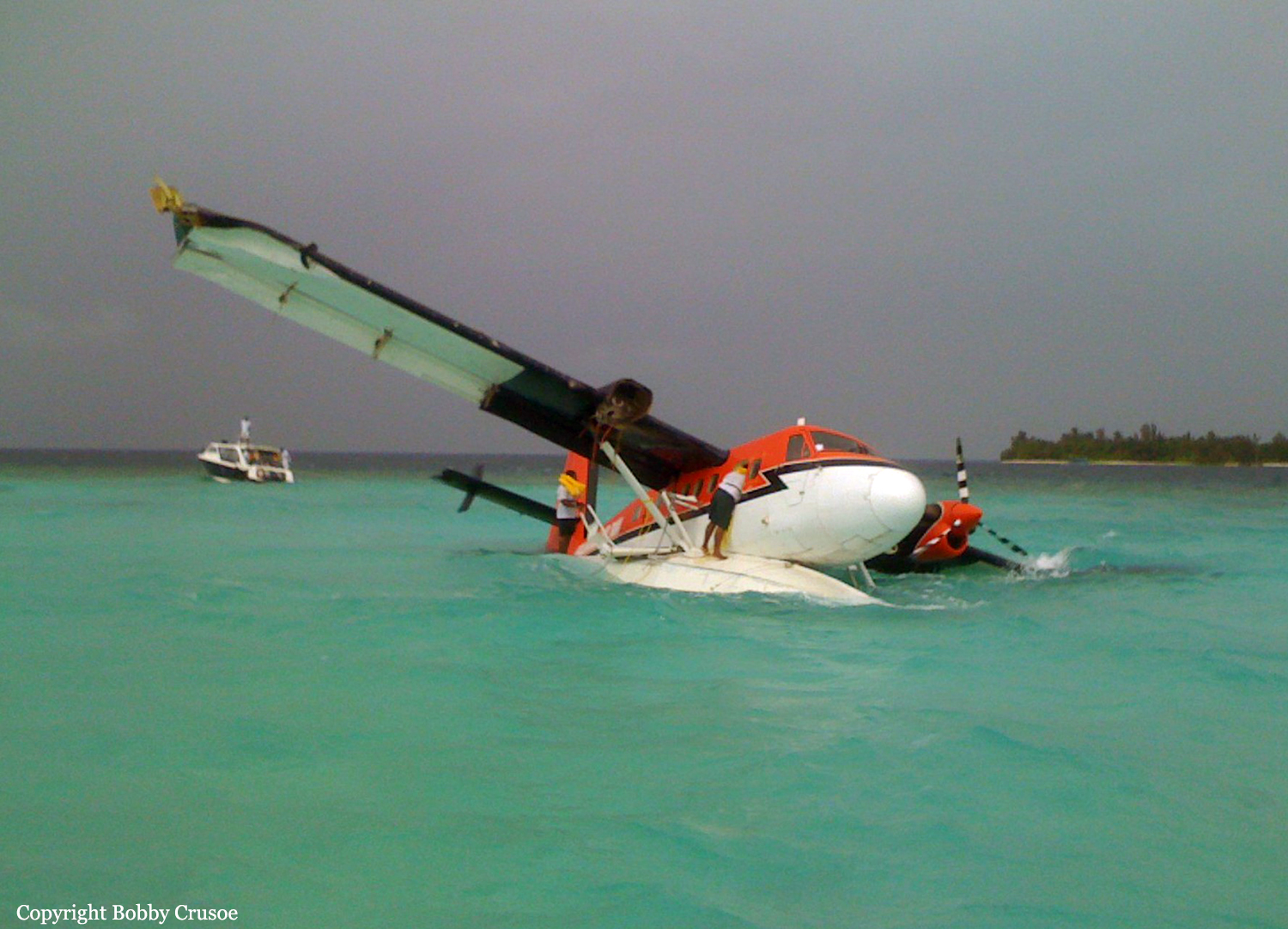
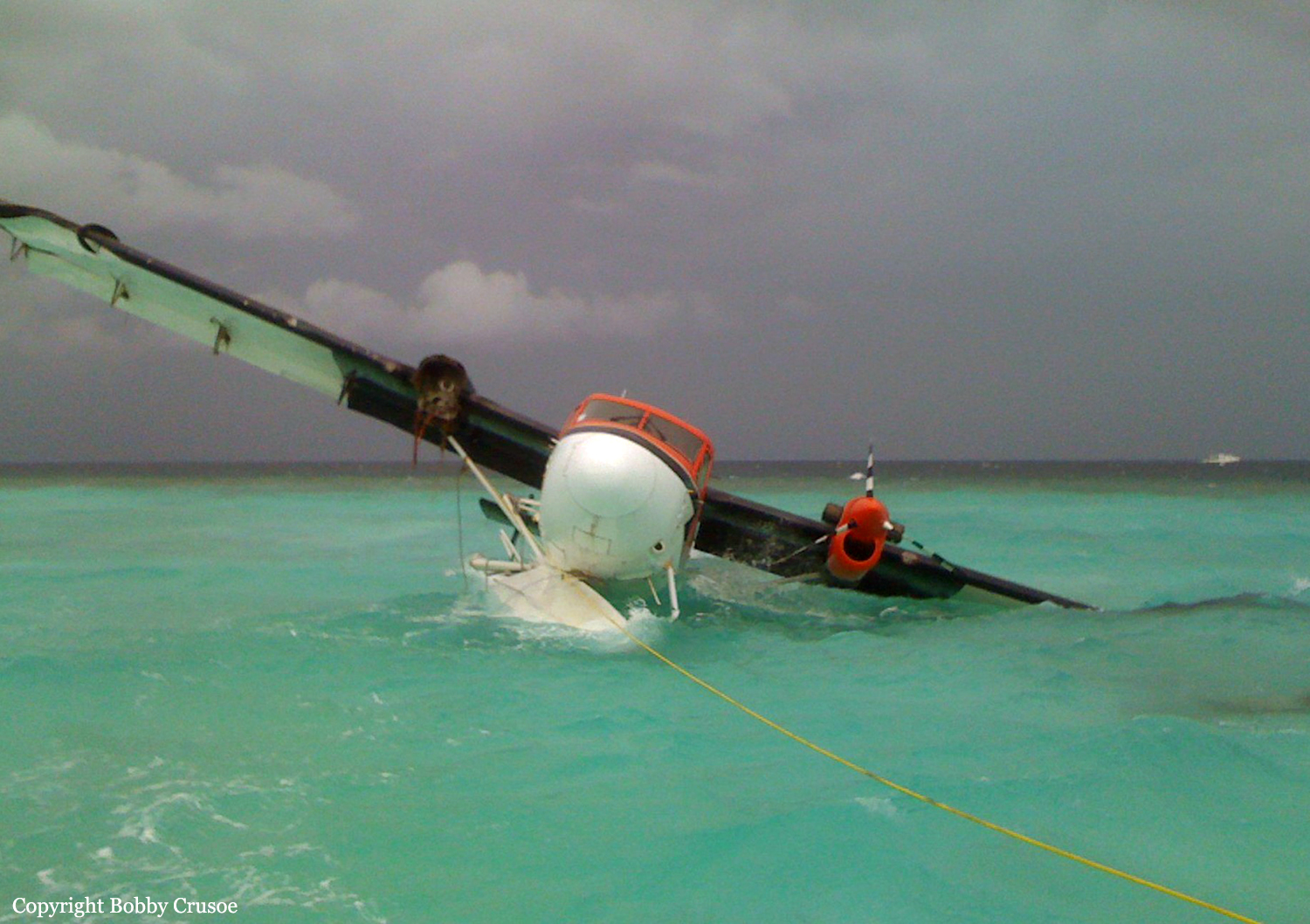
Crash of a Boeing B-52H-155-BW Stratofortress off Guam Island: 6 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 21, 2008 at 0945 LT
Registration:
60-0053
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Andersen AFB - Andersen AFB
MSN:
464418
YOM:
1960
Flight number:
Raider 21
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
6
Circumstances:
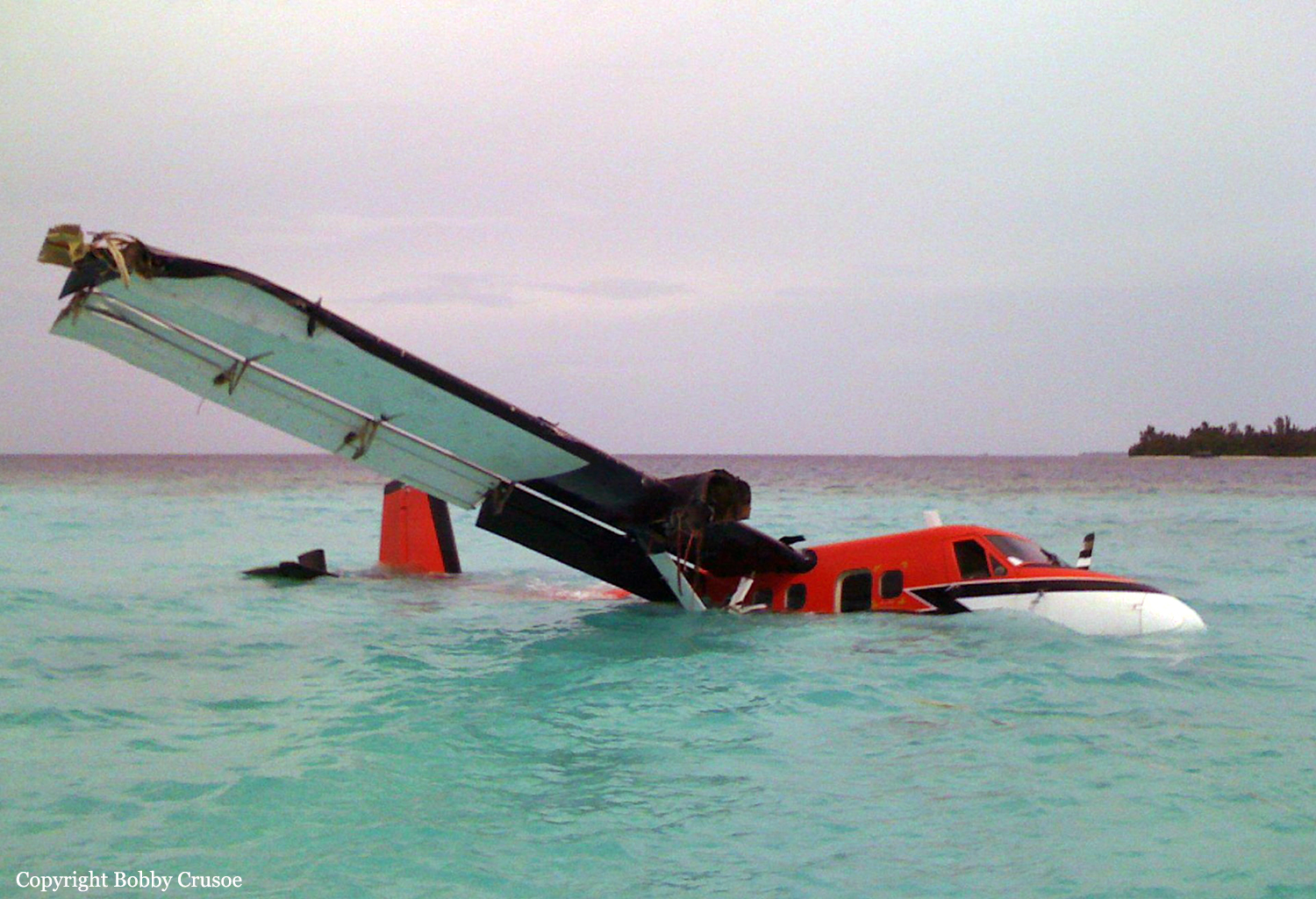
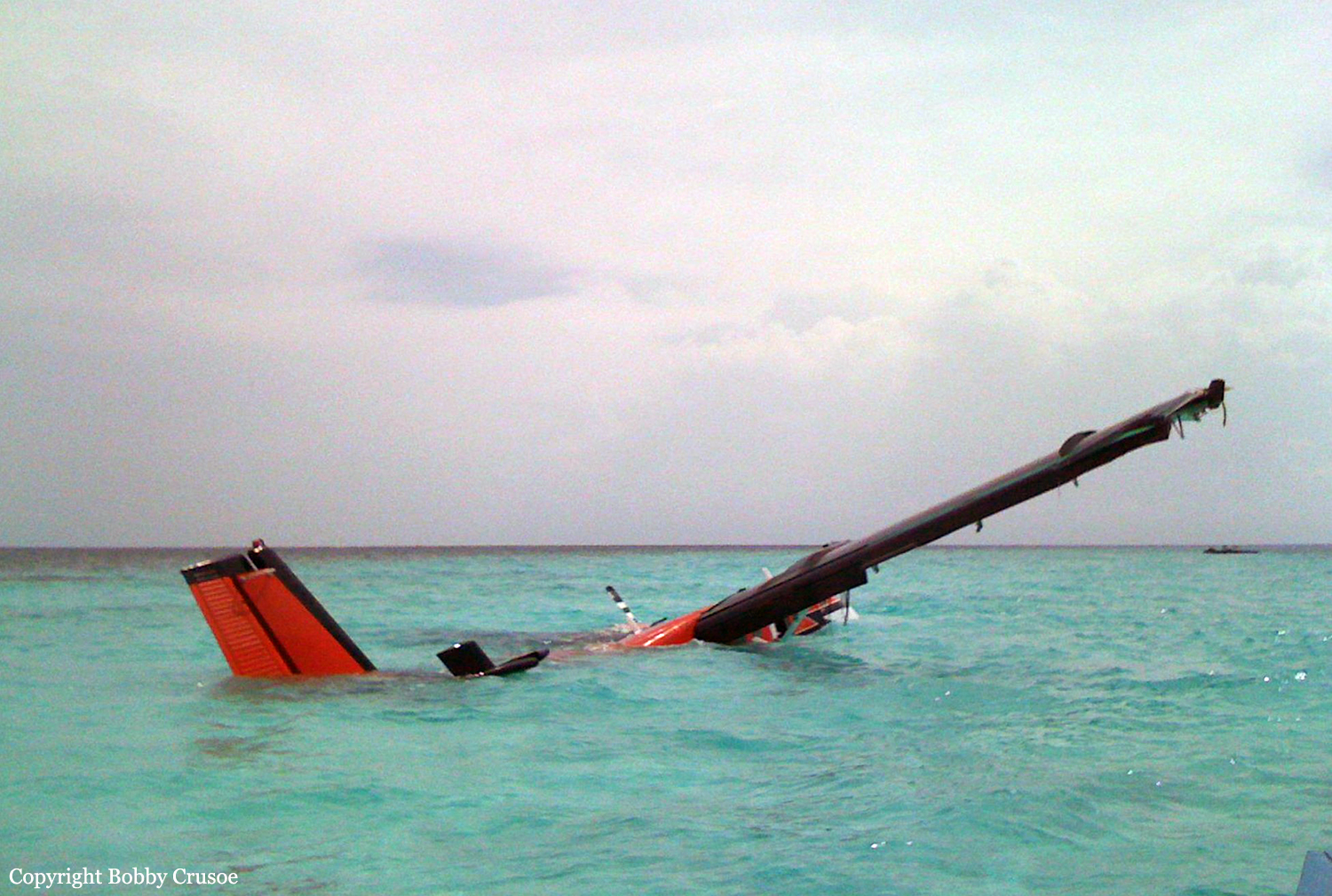
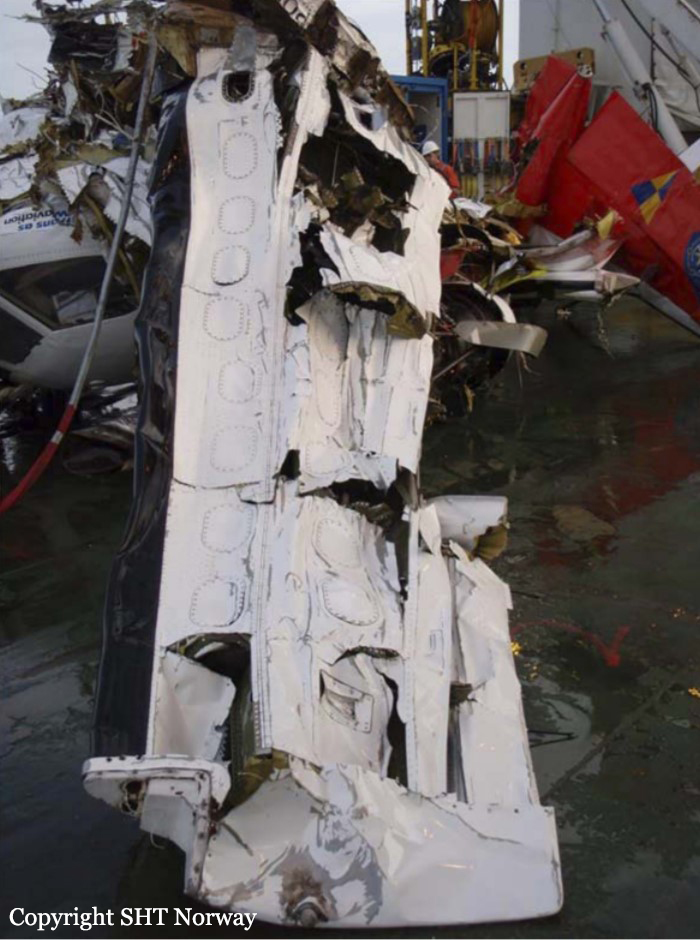
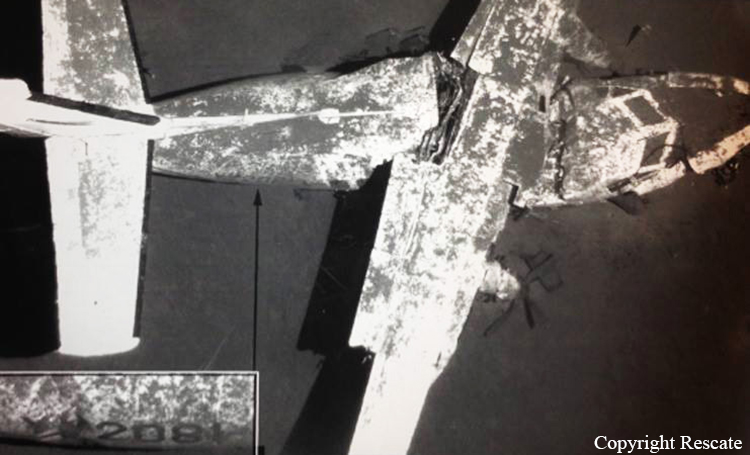
The aircraft departed Andersen AFB on a flight around the Guam Island under call sign 'Raider 21' with 6 crew members on board, taking part to the Guam Liberation Day celebrations. About 15 minutes into the flight, while descending from 14,000 to 1,000 feet, the aircraft became uncontrollable and crashed in the sea about 50 km north of Guam Island. The aircraft disintegrated on impact and only few debris were found. All six crew members were killed.
Crew:
Maj Chris Cooper, pilot,
Cpt Michael Dodson, copilot,
1st Lt Robert Gerren, electronic warfare officer,
1st Lt Joshua Shepherd, navigator,
Maj Brent Williams, radar navigator,
Col George Martin, flight surgeon.
Crew:
Maj Chris Cooper, pilot,
Cpt Michael Dodson, copilot,
1st Lt Robert Gerren, electronic warfare officer,
1st Lt Joshua Shepherd, navigator,
Maj Brent Williams, radar navigator,
Col George Martin, flight surgeon.
Probable cause:
Malfunctioning parts and late recognition of spiraling problems likely led to the fatal crash of a B-52H Stratofortress in July, an Air Force accident investigation board concluded in a report issued Feb. 13. The problem parts, investigators decided, were the bomber’s rear stabilizers — the large horizontal fins at the jet’s tail that help angle the B-52H up or down. Although the inquiry could not determine what led to the stabilizer problem, the board said it believed the stabilizers malfunctioned while the bomber was in a fast descent from 14,000 feet to 1,000 feet. “Even an experienced aircrew could have found it difficult to recognize, assess and recover from the very rapidly developing situation involving the rear stabilizer trim,” board president Brig. Gen. Mark Barrett concluded. The bomber did not carry a flight data recorder, so the investigation team pieced together events leading up to the crash from air traffic control radar information and from parts recovered from the ocean floor by remote-controlled Navy submarines. One recovered part was a component called a jackscrew that helps control the stabilizers. The jackscrew revealed the stabilizer trim was set at 4.5 to 5 degrees nose down, but parts that could have helped determine why the stabilizers were pointed down were not recovered. Based on flight simulations, the investigative team determined the flight was normal until the jet turned left and began to descend about 33 miles west of Guam. As the 48-year-old bomber dove toward the Pacific at a speed of more than 240 mph, the stabilizers suddenly unhinged, putting the jet into a dive with the nose pointed down 30 degrees and more. One of the pilots likely tried to level the stabilizers manually using a control wheel in the cockpit that moves the stabilizer 1 degree every two to three seconds, the report said. However, because the plane was already low, there wasn’t enough time to level the stabilizers. At least three crew members tried to bail out seconds before the plane hit the water, but the plane’s speed, altitude and angle already were past the point where they could survive the ejection.