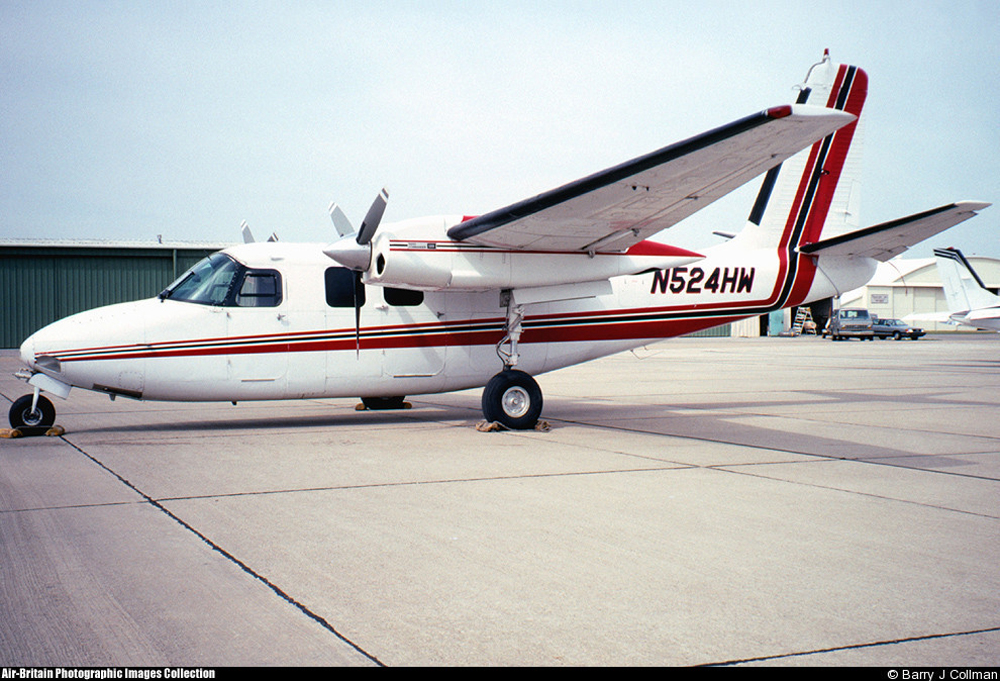
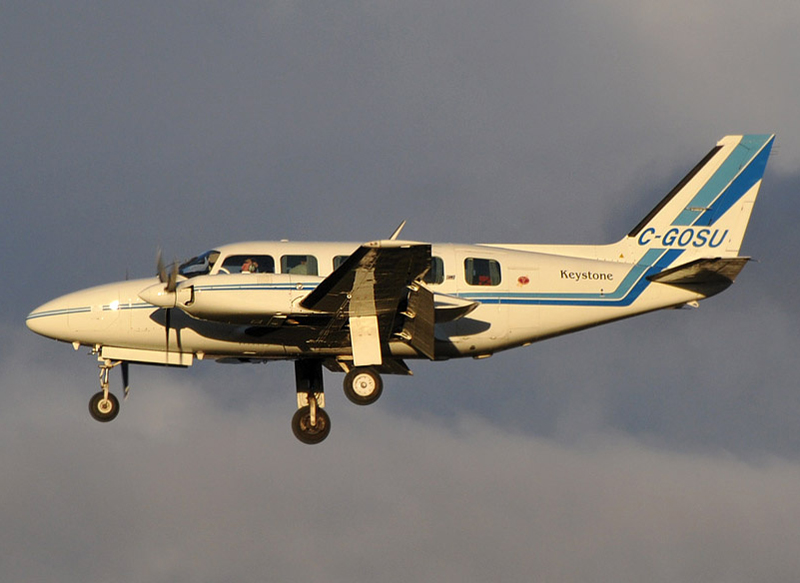
Crash of a Piper PA-31-325 Navajo C/R in Welshpool: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 18, 2012 at 1117 LT
Registration:
G-BWHF
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Welshpool - Welshpool
MSN:
31-7612076
YOM:
1976
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Captain / Total hours on type:
375.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
2177
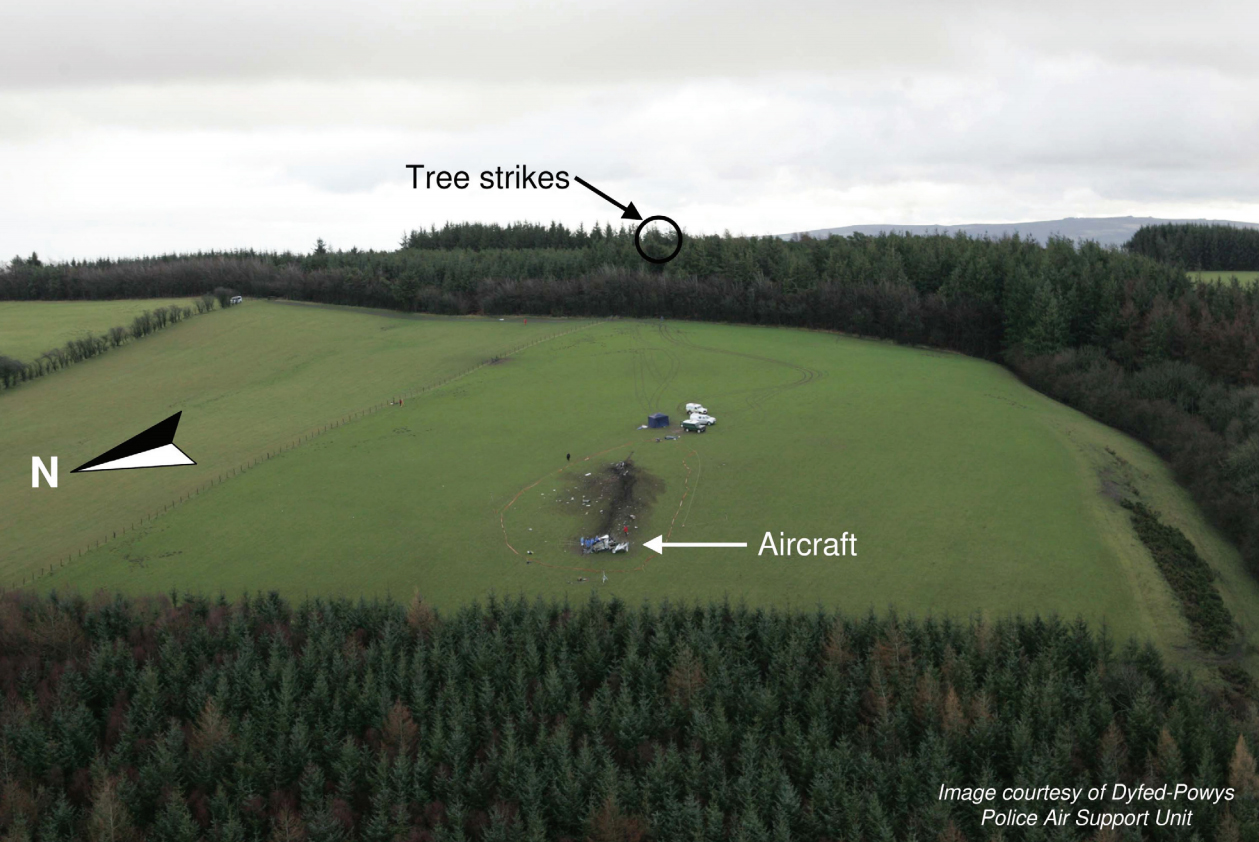
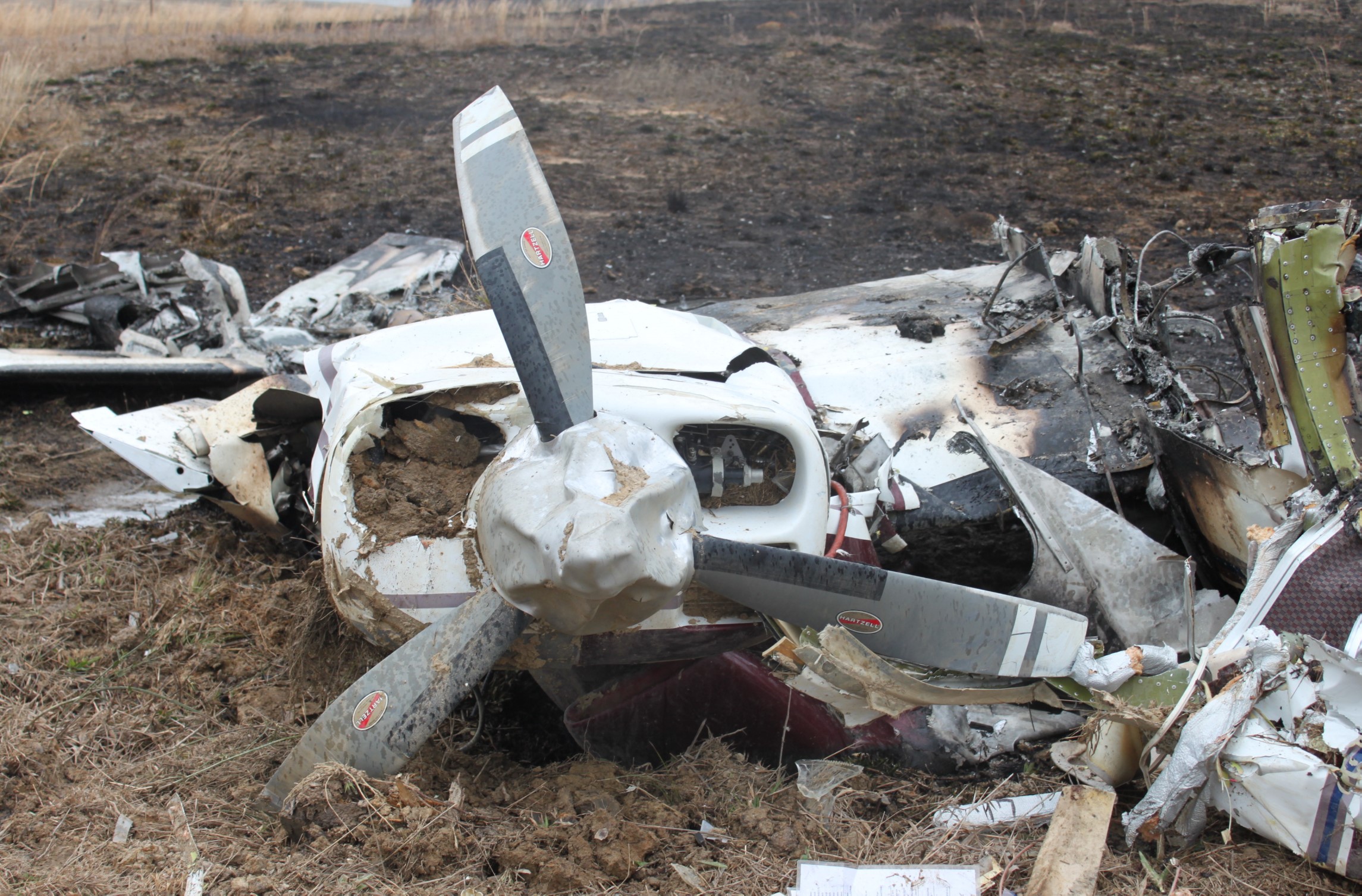
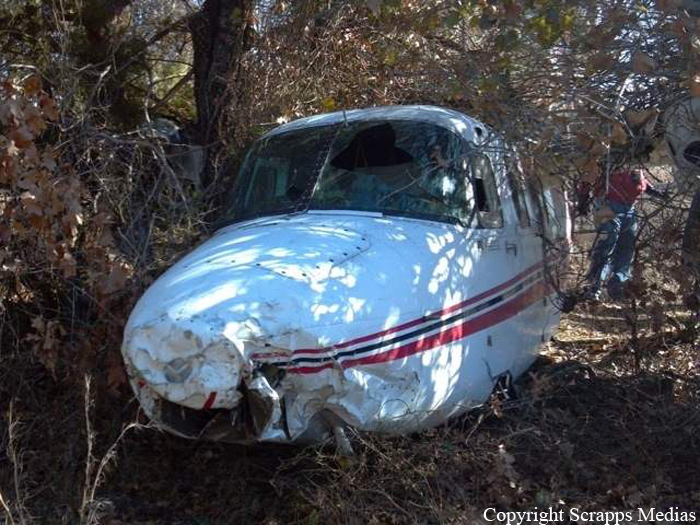
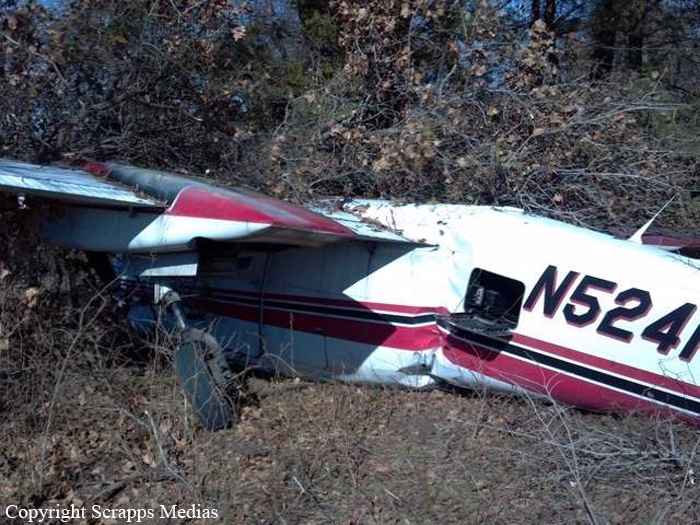
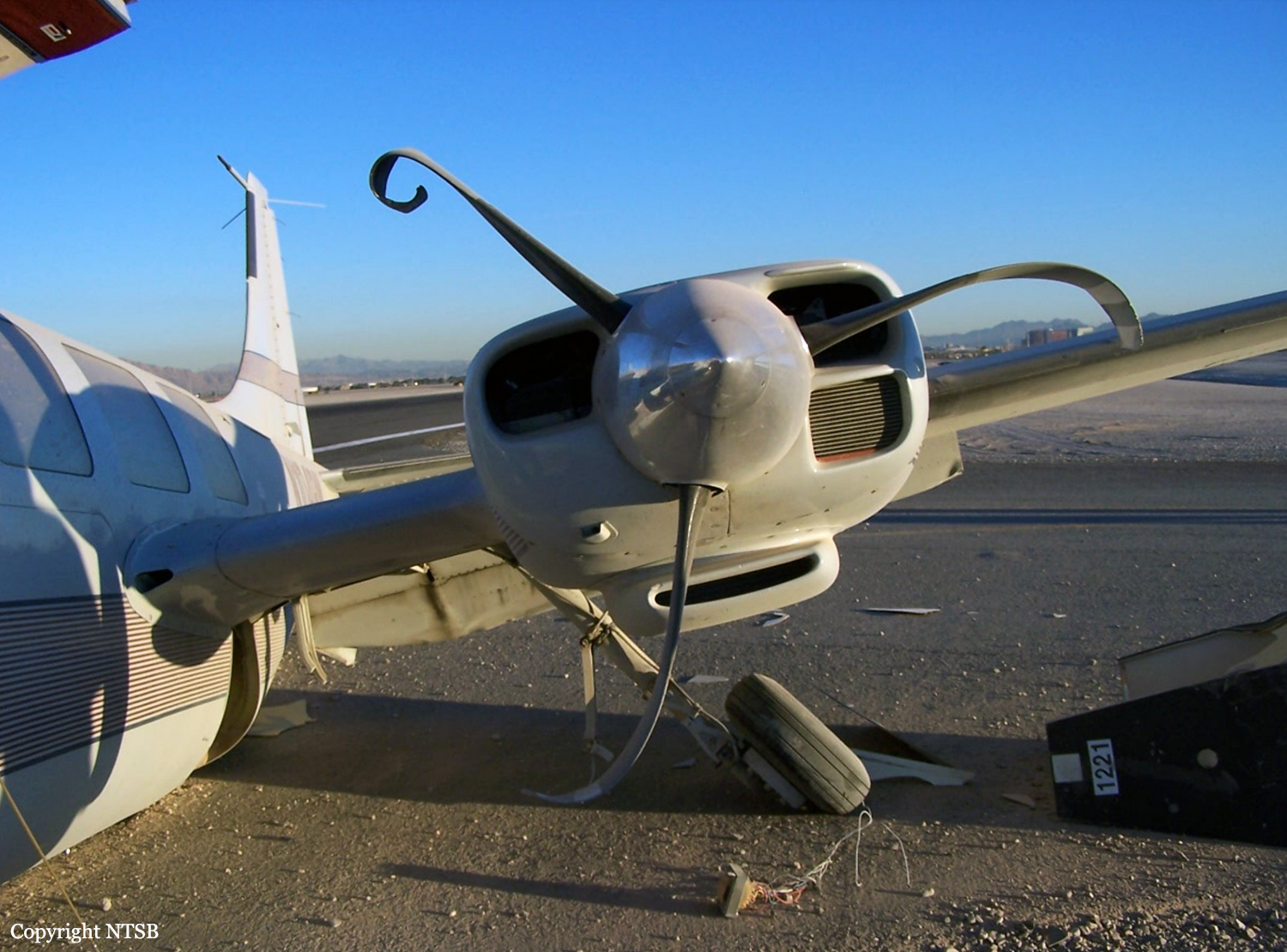
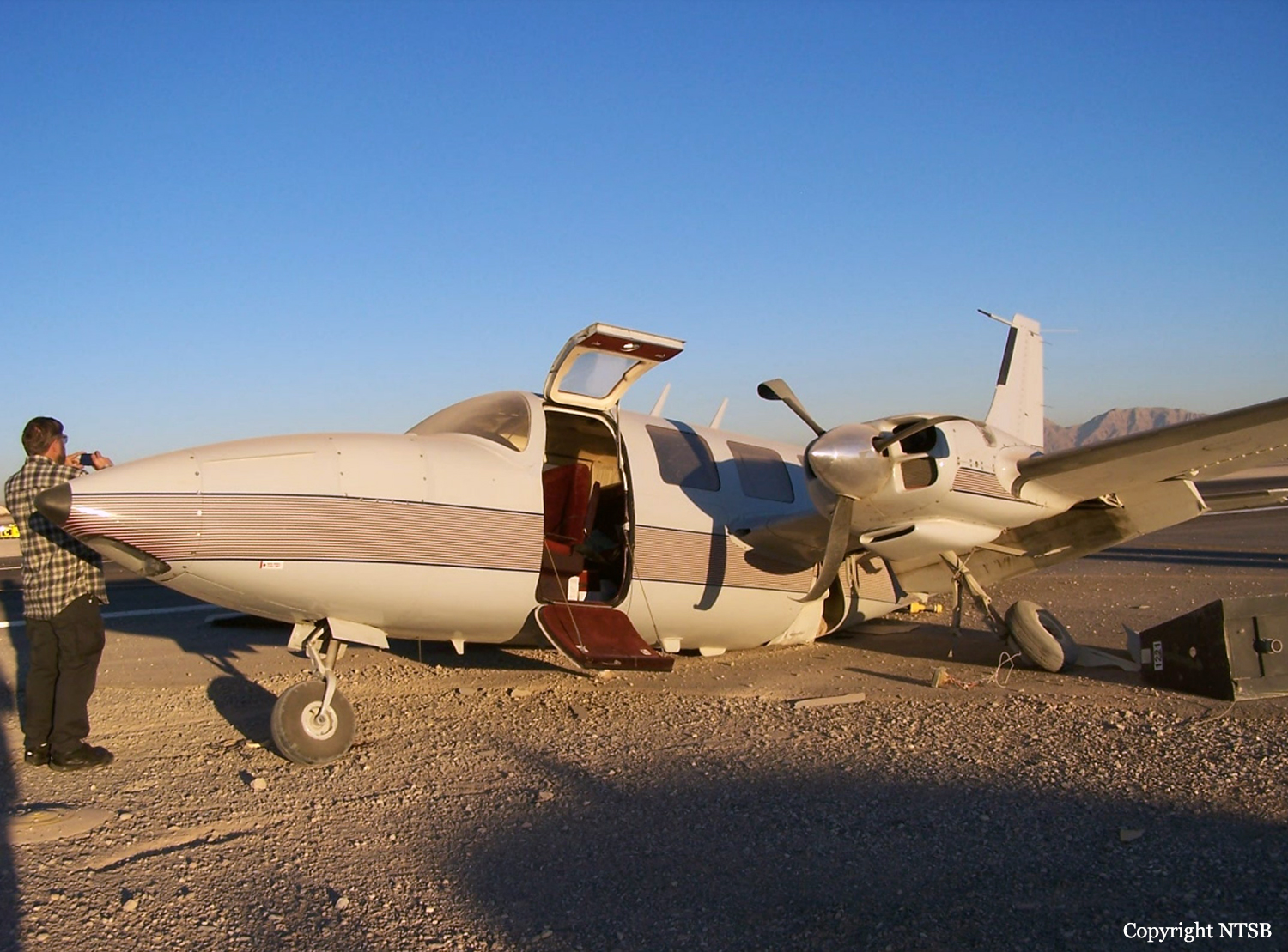
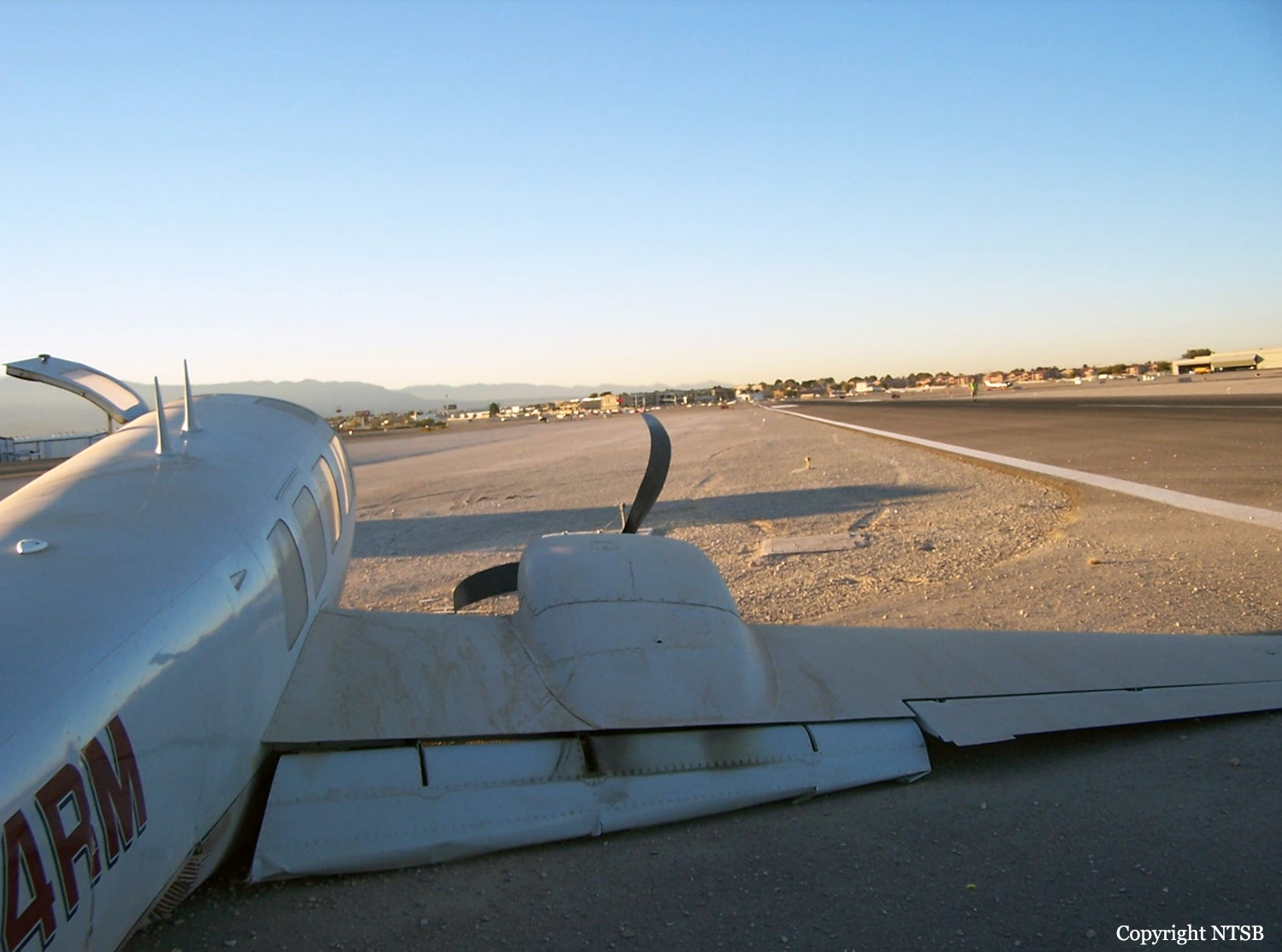
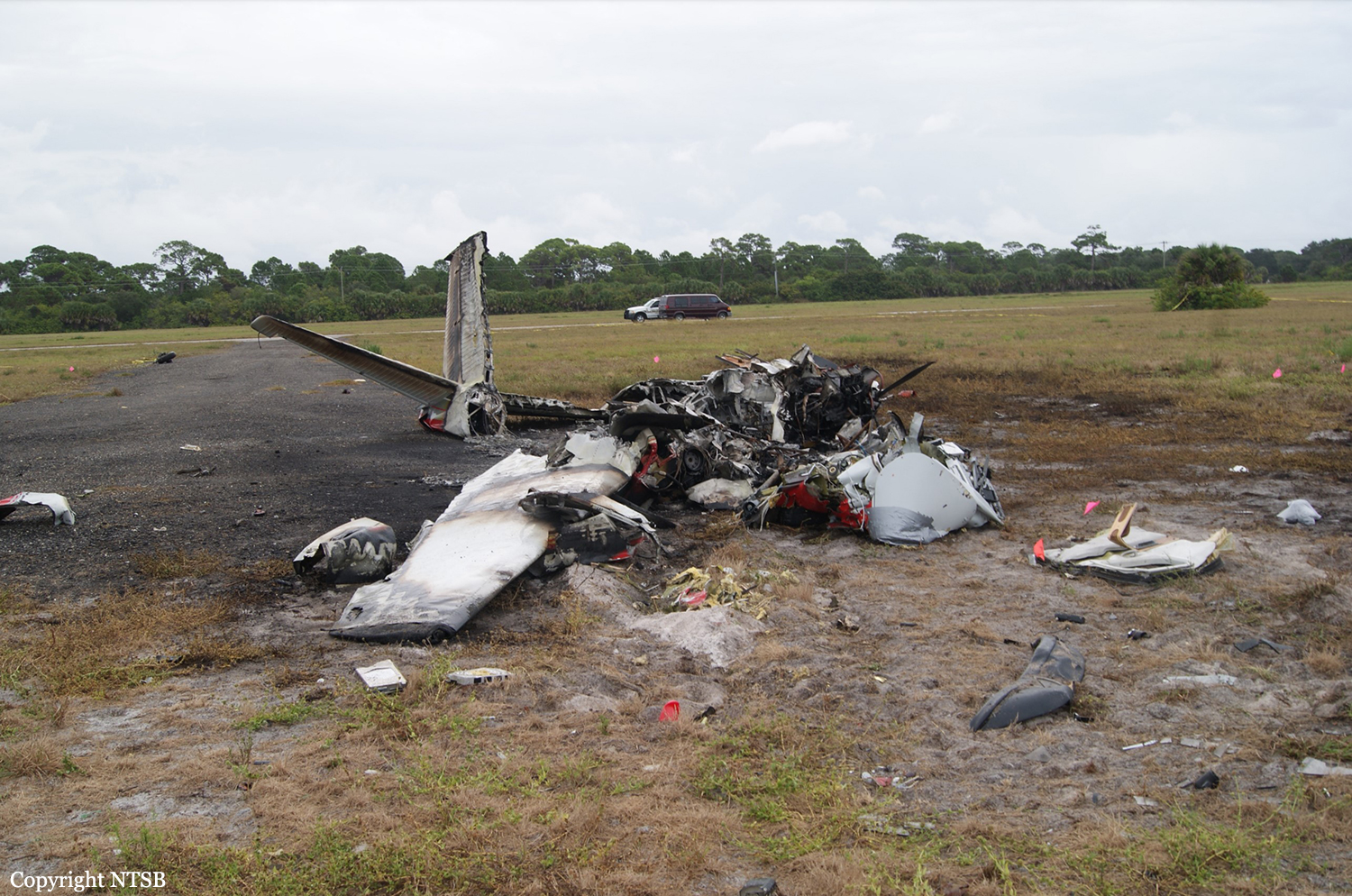
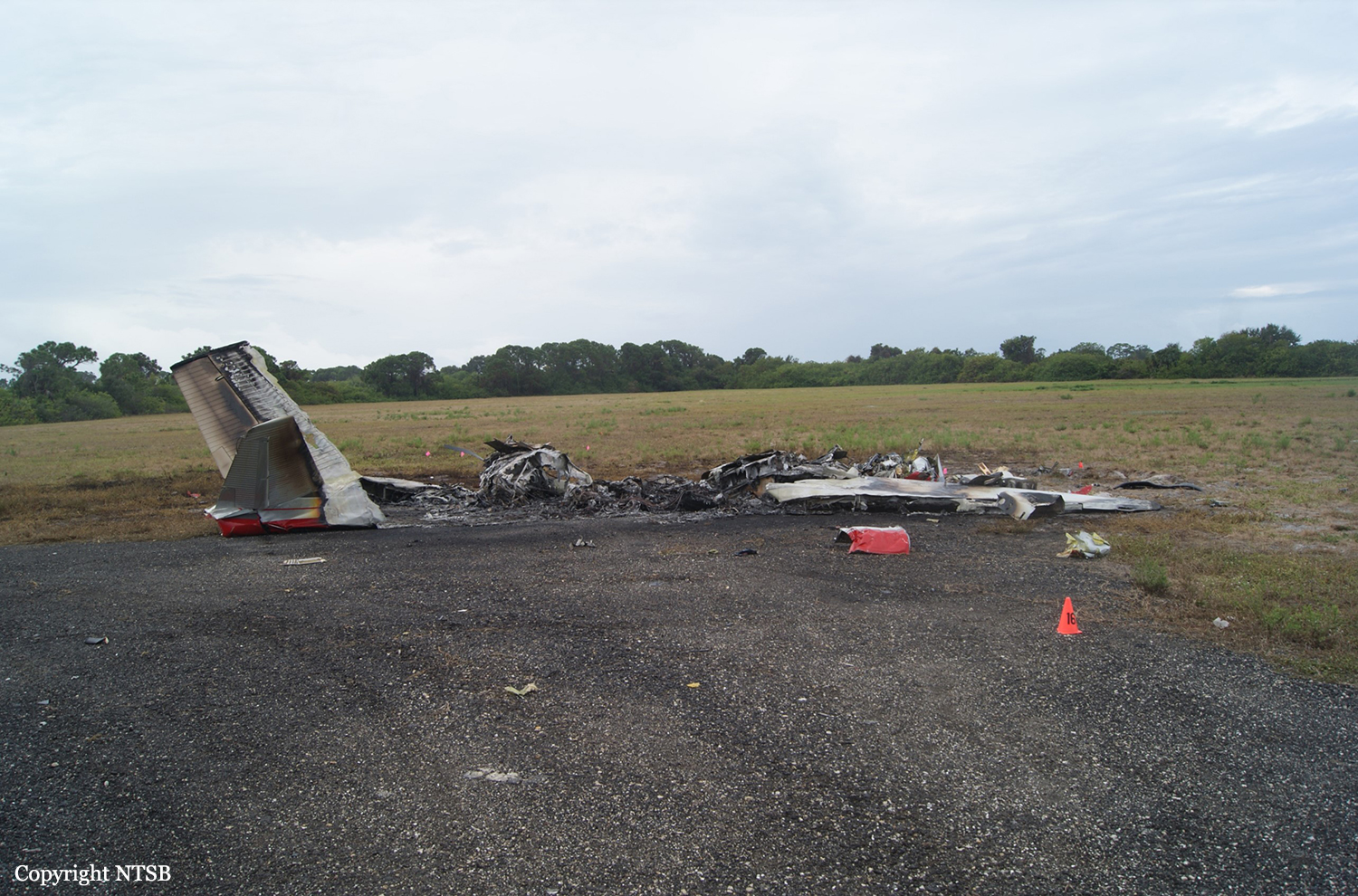
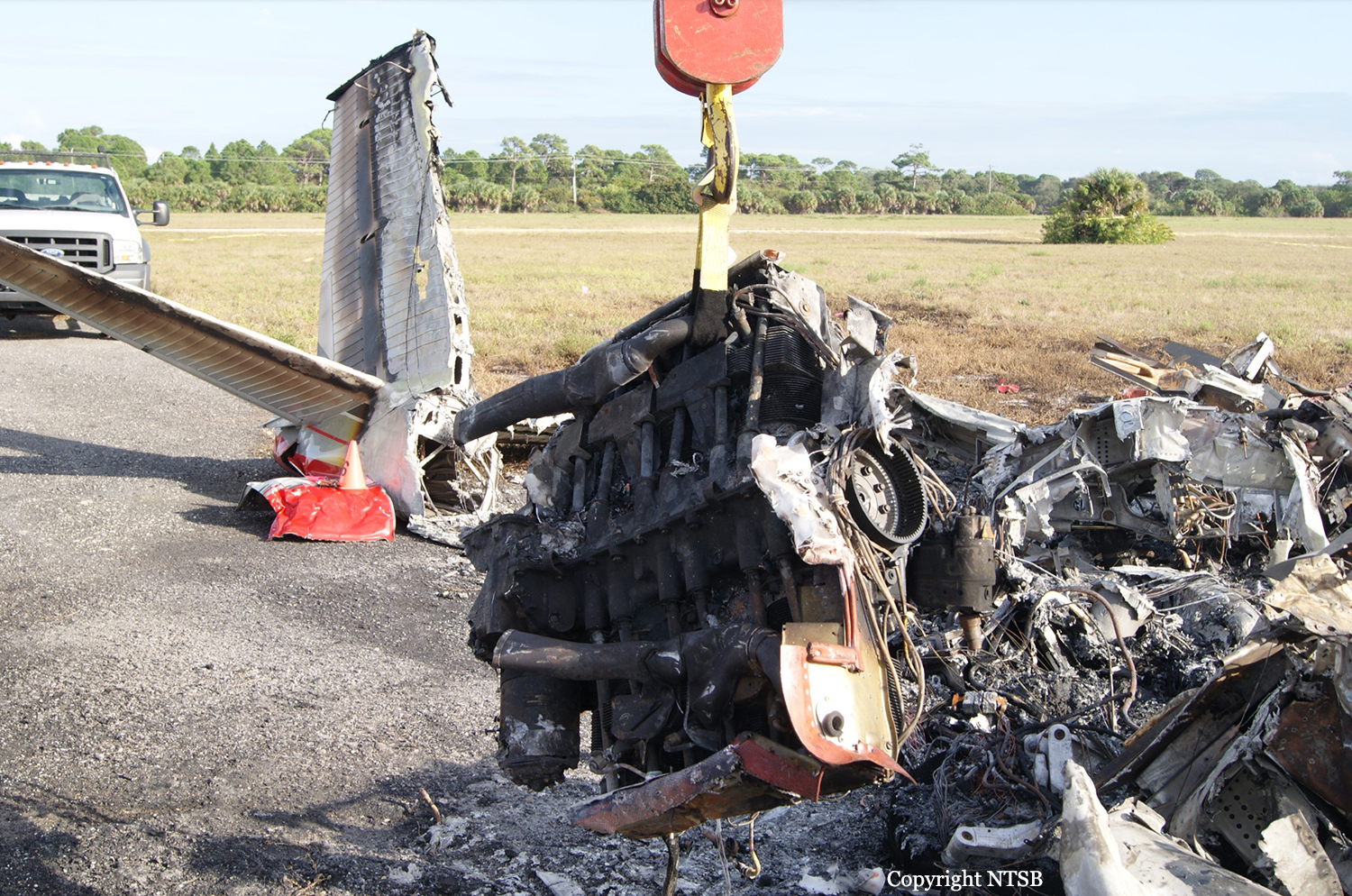
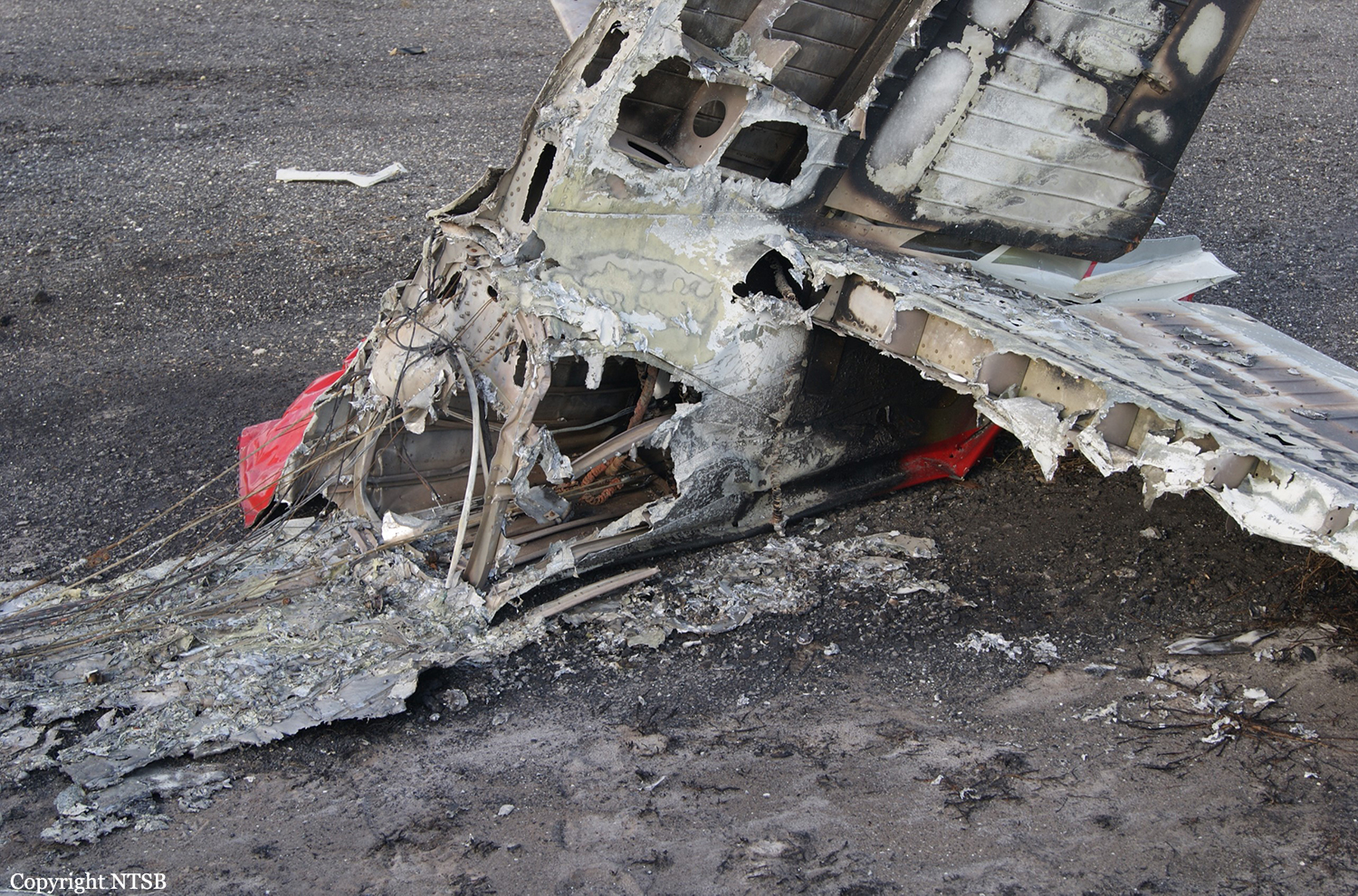
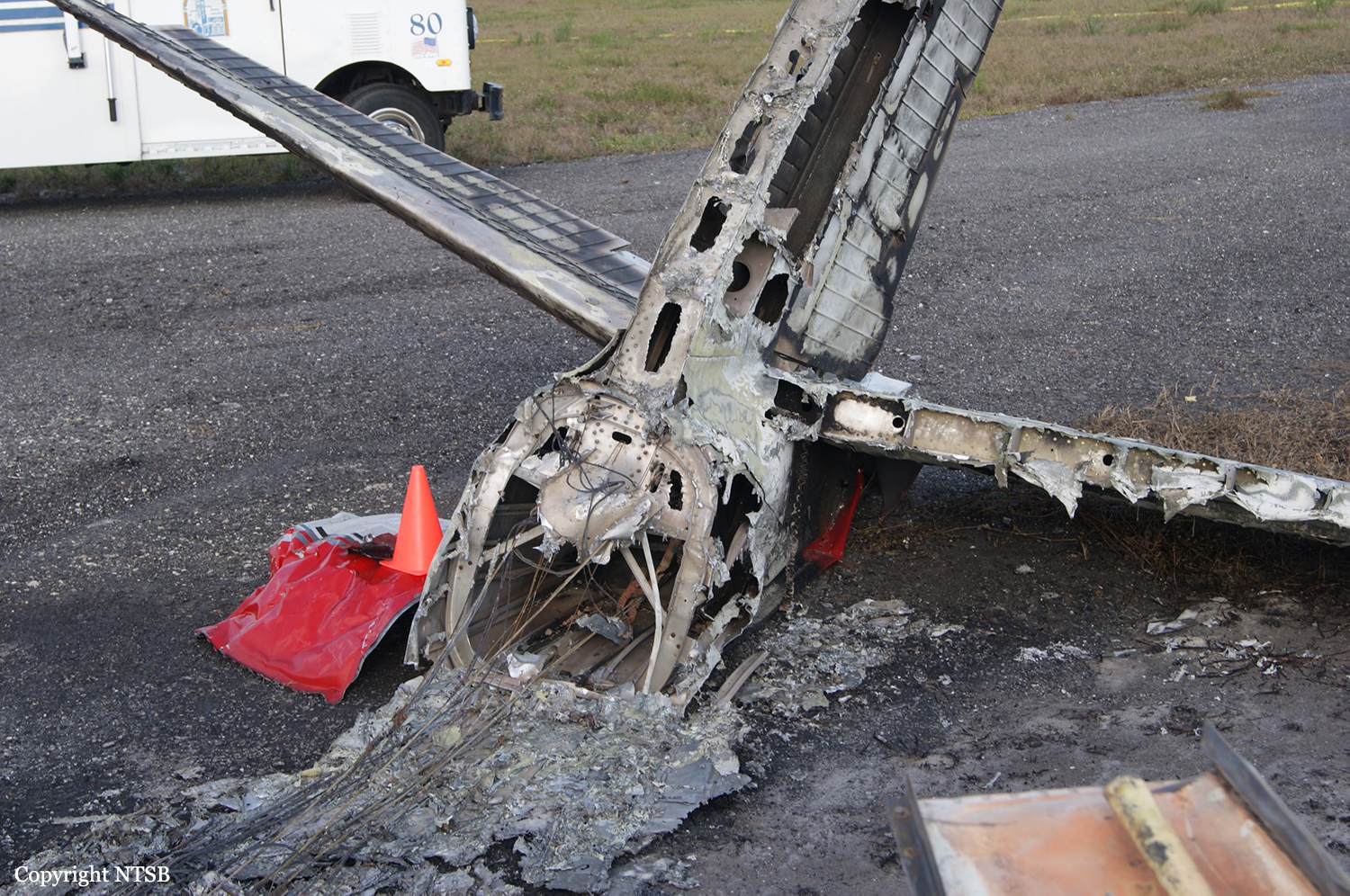
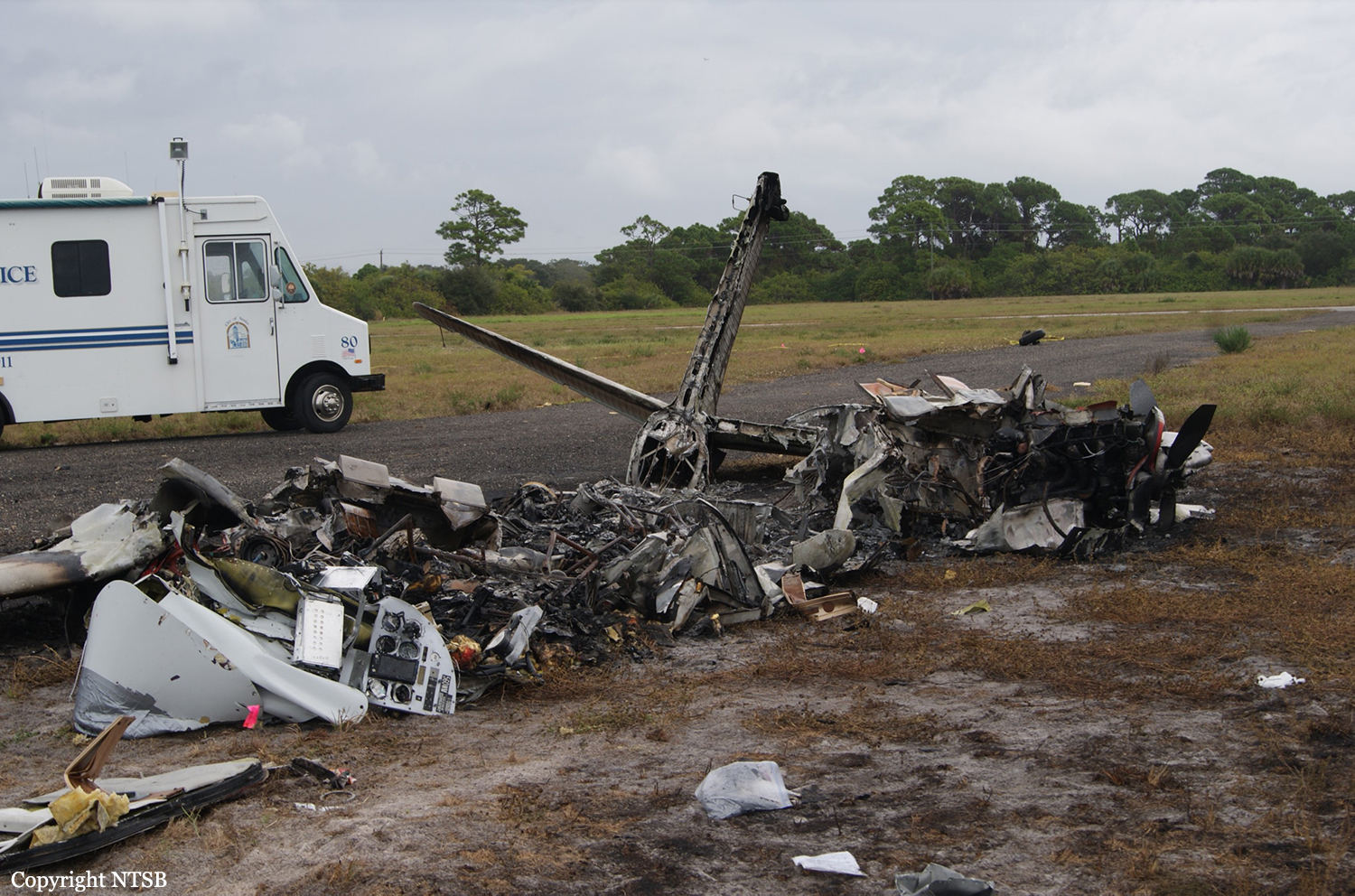
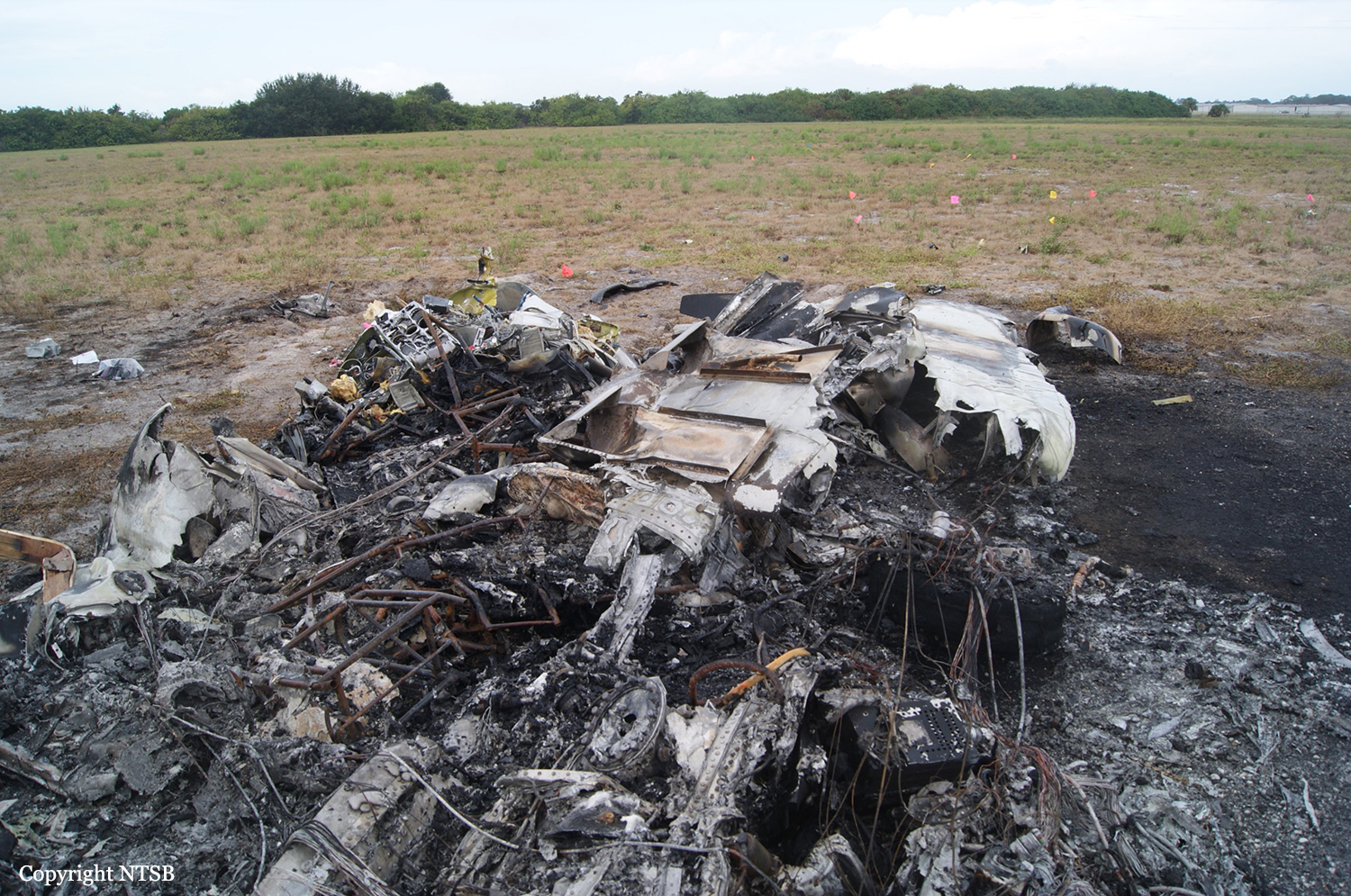
Circumstances:
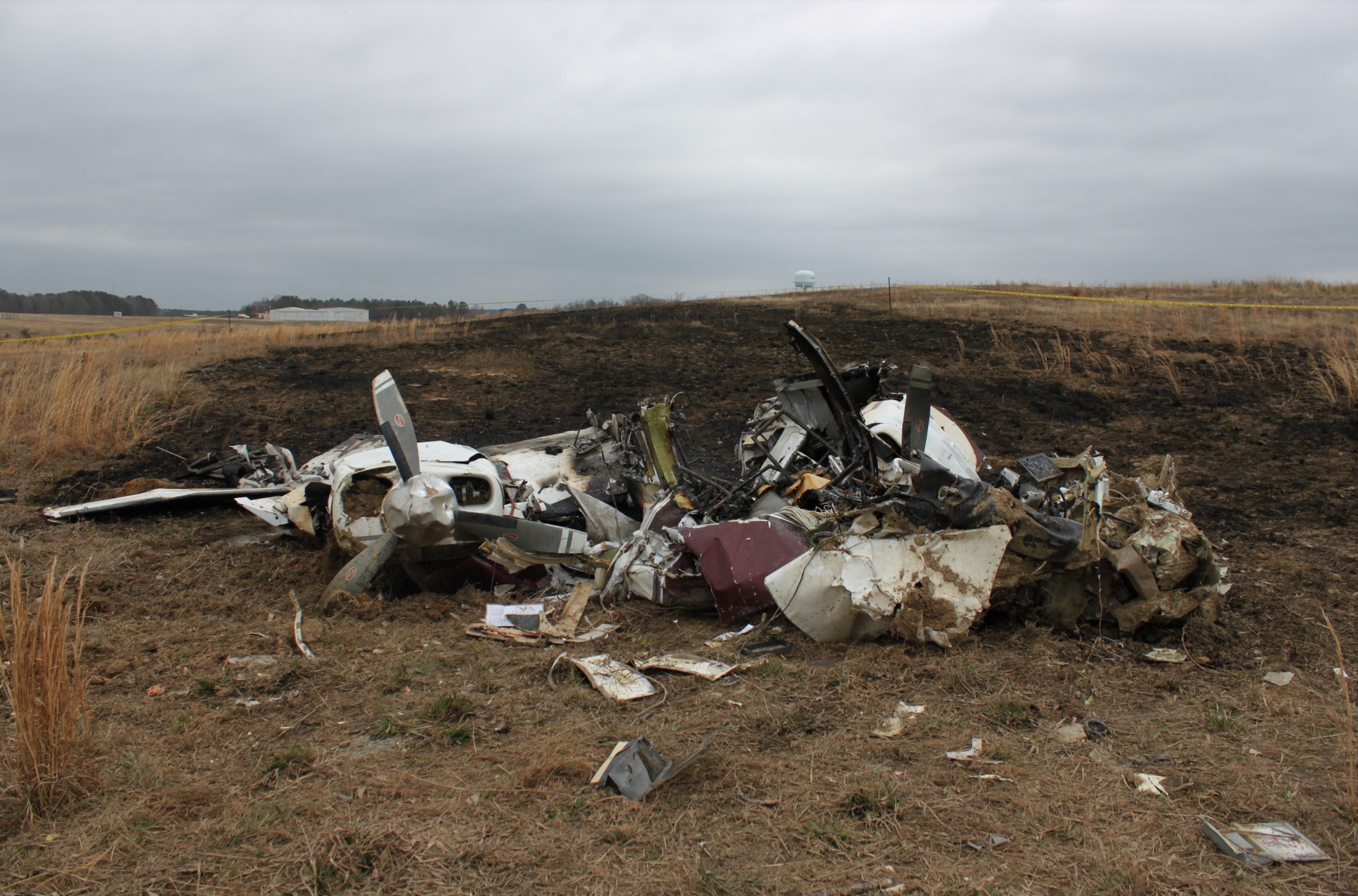
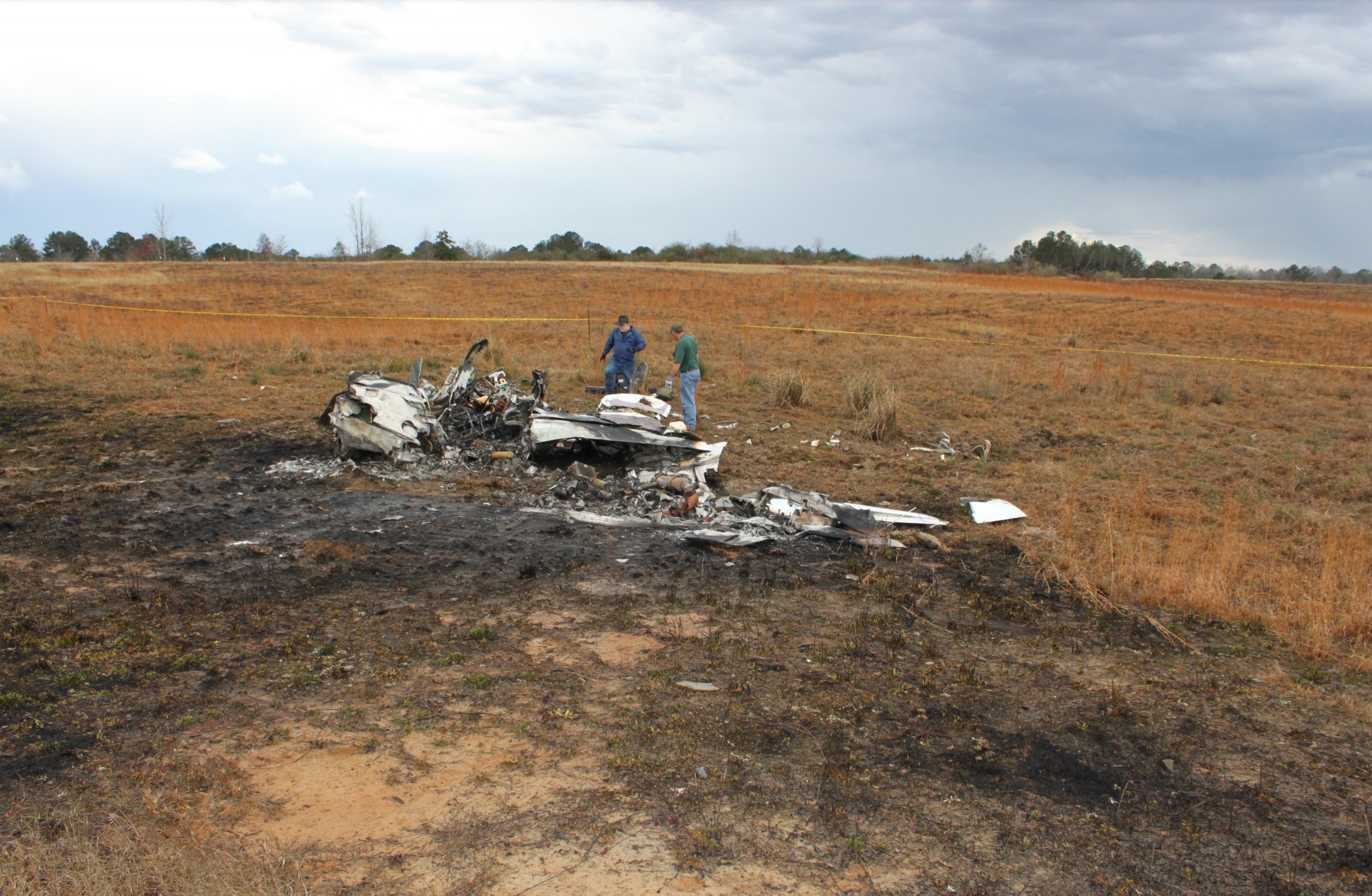
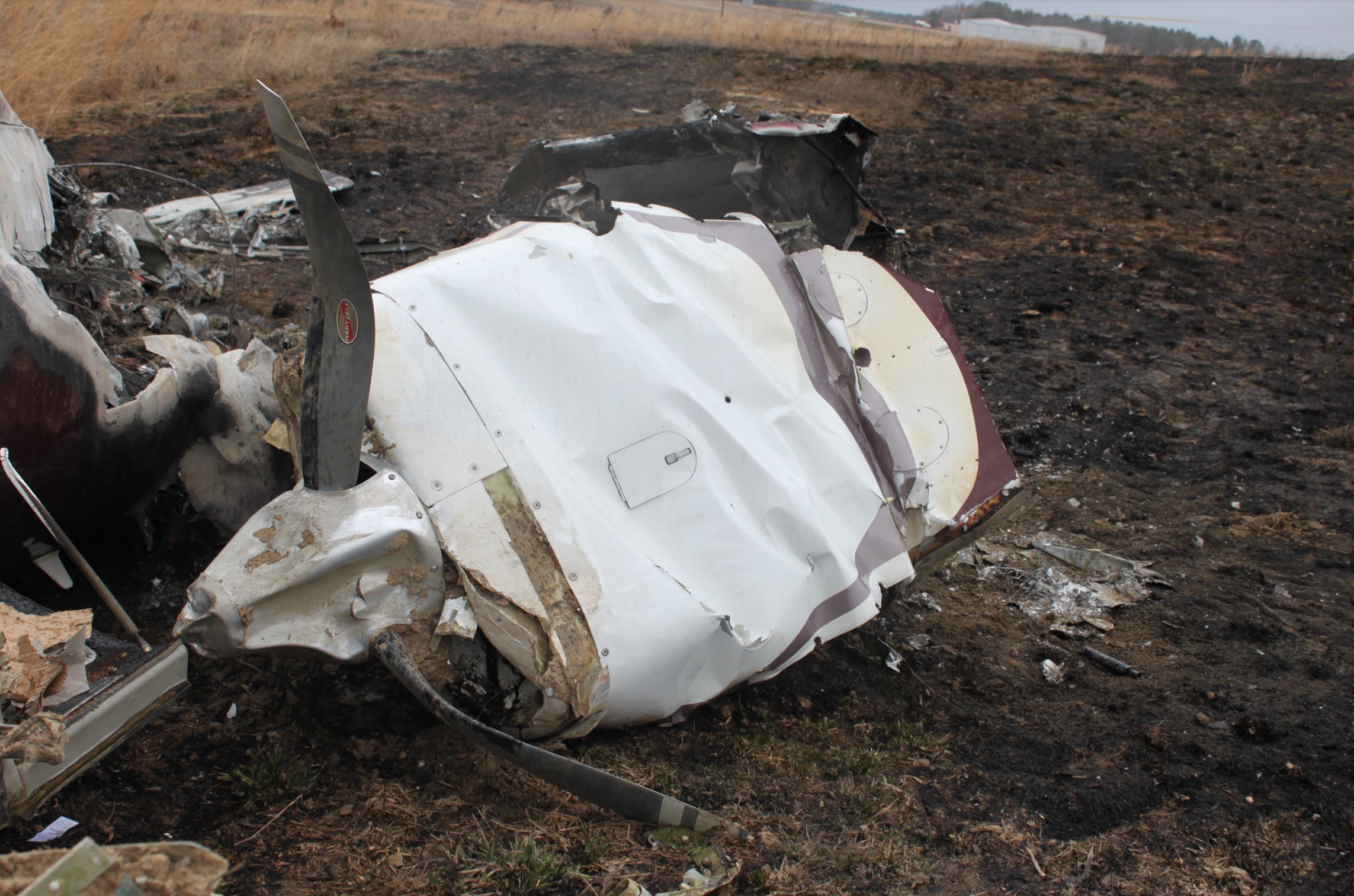
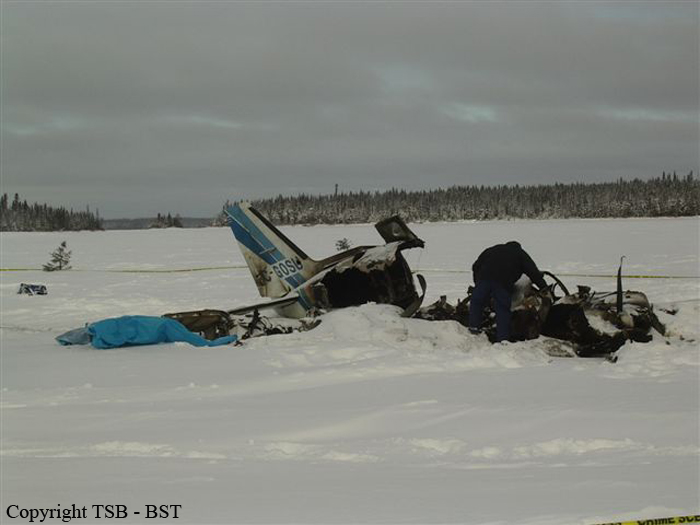
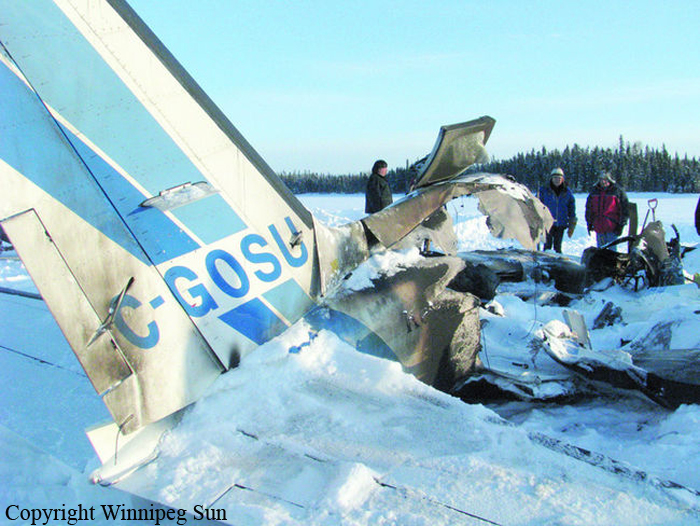
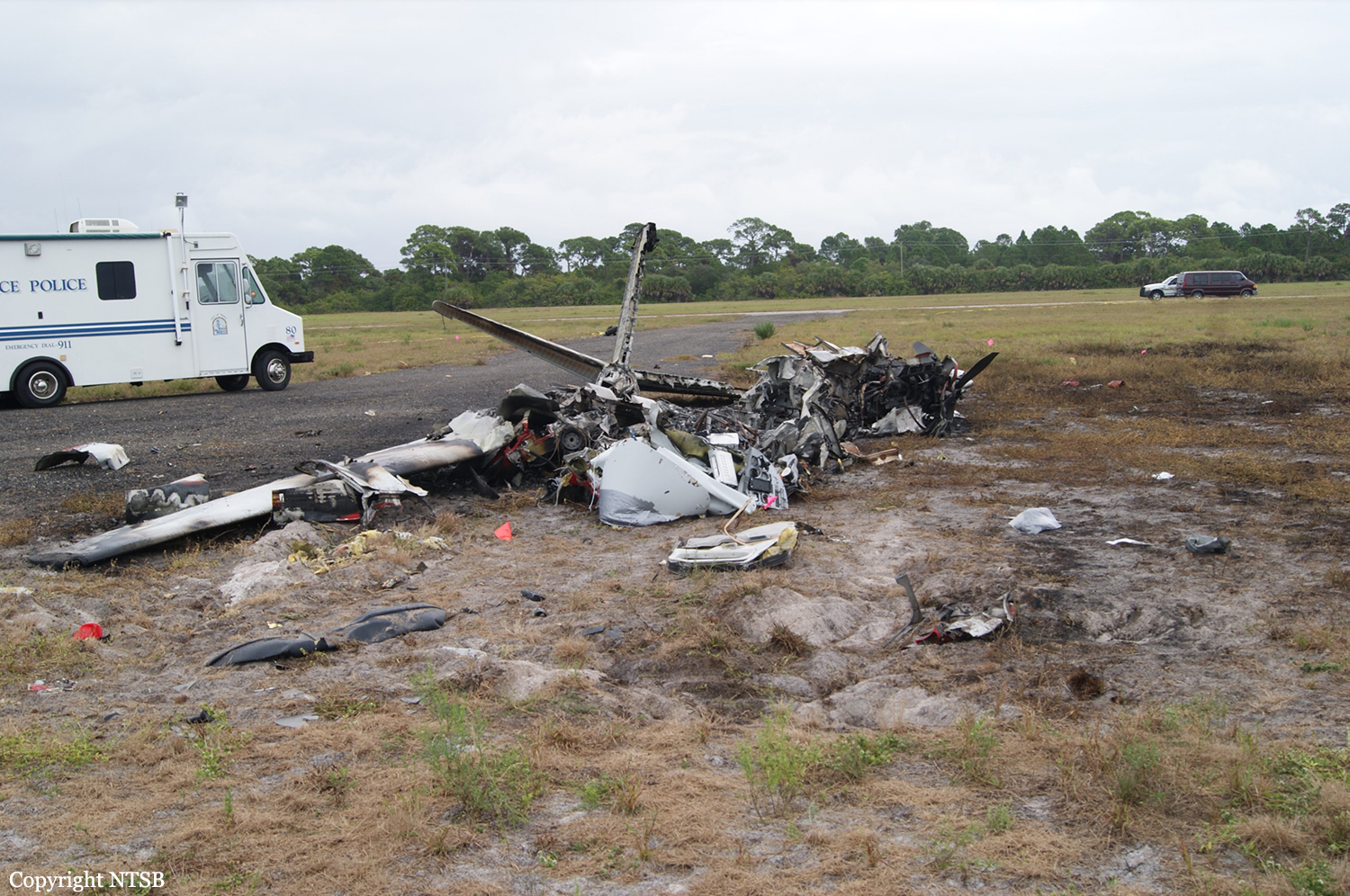
The commander had retired from flying Commercial Air Transport operations with an airline in August 2011. He had recently renewed his single pilot Instrument Rating and Multi Engine Piston (Land) planes rating and his intention was to continue flying part-time. He had been invited to fly G‑BWHF, which was privately operated for business purposes, but his last flight in this aircraft was on 10 November 1998. Accordingly, he planned to conduct a re-familiarisation flight. The commander was accompanied by another pilot who was not a flight instructor but had recent experience of flying the aircraft and was familiar with the aerodrome. A webcam recorded the pilots towing the aircraft to the refuelling point, refuelling it and carrying out pre‑flight preparations. There were no witnesses to any briefings which may have taken place. The commander first started the right engine, which initially ran roughly and backfired before running smoothly. The left engine started normally. The second pilot took his place in the front right seat. The aircraft taxied to the holding point of Runway 22, and was heard by witnesses to be running normally. A witness who lived adjacent to the airfield but could not see the aircraft heard the power and propeller checks being carried out, three or four times instead of once per engine as was usual. The engines were heard to increase power and the witness observed the aircraft accelerate along the runway and takeoff at 1105 hrs. It climbed straight ahead and through a small patch of thin stratus cloud, the base of which the witness estimated was approximately 1,000 ft aal. The aircraft remained visible as it passed through the cloud and continued climbing. The witness turned away from the aircraft to continue working but stated that apart from the unusual number of run-up checks, the aircraft appeared and sounded normal. The pilot of a Robinson R22 helicopter which departed Welshpool at 1015 hrs described weather to the south of the aerodrome as drizzle with patches of broken stratus at 600-700 ft aal. He was able to climb the helicopter between the patches of stratus until, at 1,500 ft, he was above the tops of the cloud. Visibility below the cloud was approximately 5-6 km but, above the cloud, it was in excess of 10 km. He noted that the top of Long Mountain was in cloud and his passenger took a photograph of the Long Mountain area The R22 returned to the airfield and joined left hand downwind for Runway 22. As it did so, its pilot heard a transmission from the pilot of the PA-31 stating that he was rejoining for circuits. The R22 pilot transmitted his position in order to alert the PA-31, then continued around the circuit and called final before making his approach to the runway, landing at about 1115 hrs. After passing overhead Welshpool, it made a descending left circuit, becoming established on a left hand, downwind leg for Runway 22. A witness approximately 3.5 nm northeast of the accident site saw the aircraft coming towards him with both propellers turning. It made a turn to the left with the engines apparently at a high power setting and, as it passed over Long Mountain, commenced a descent. He could not recall whether he could still hear the engines as the aircraft descended. He then lost sight of it behind the rising ground of Long Mountain. A search was initiated when the aircraft failed to return to Welshpool. Its wreckage was located in an open field on the west slope of Long Mountain. There were no witnesses to the actual impact with the trees or surface of the field but the sound was heard by a witness in the wood who stated that the engines were audible immediately prior to impact. The accident, which was not survivable, occurred at 1117 hrs. Both pilots were fatally injured.
Probable cause:
The aircraft struck the tops of the trees located on the upper slope of Long Mountain, while descending for a visual approach to land on Runway 22 at Welshpool Airport. The trees were probably not visible to the pilots because of cloud covering the upper slopes.
Final Report: