Circumstances:
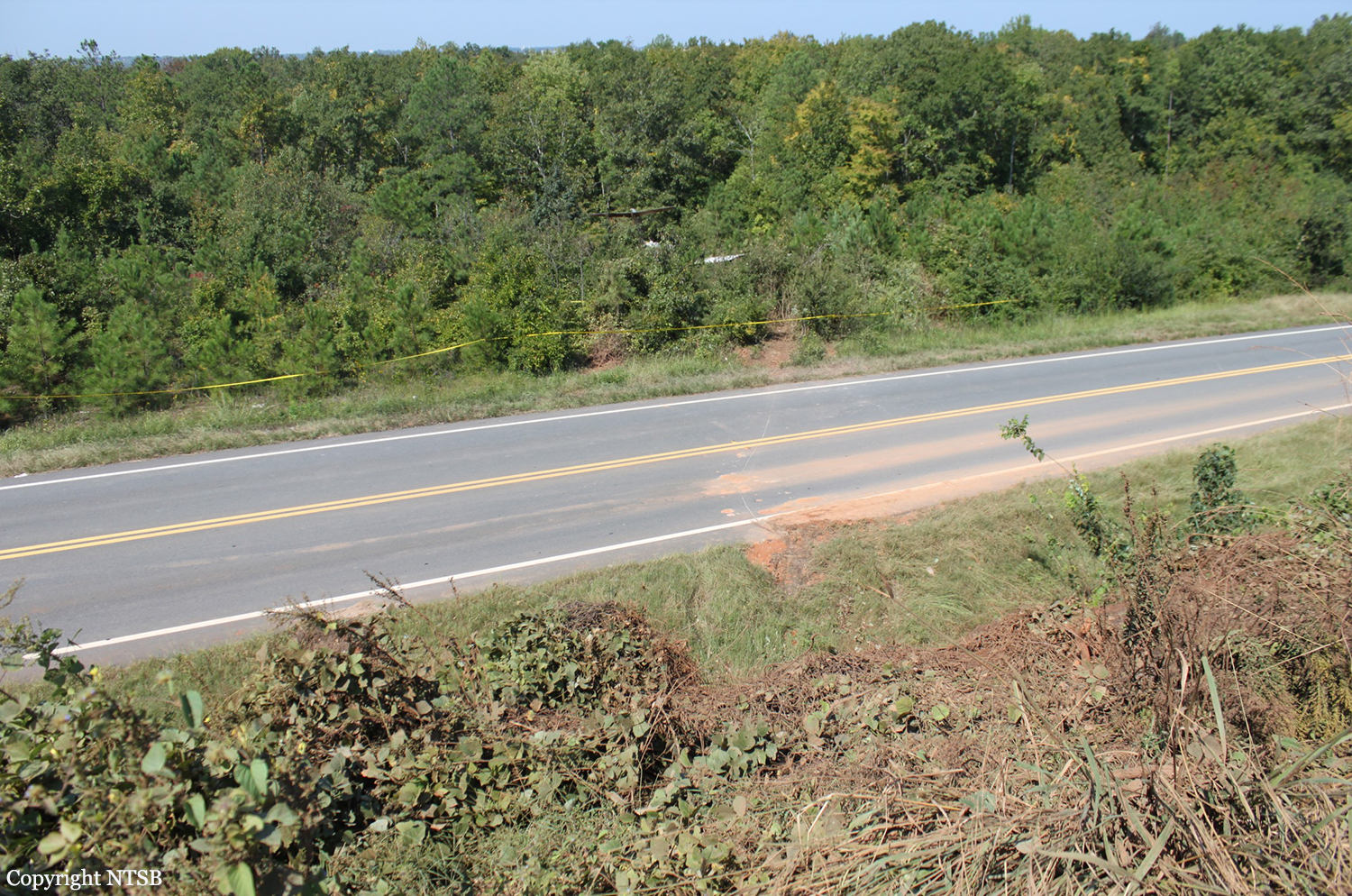
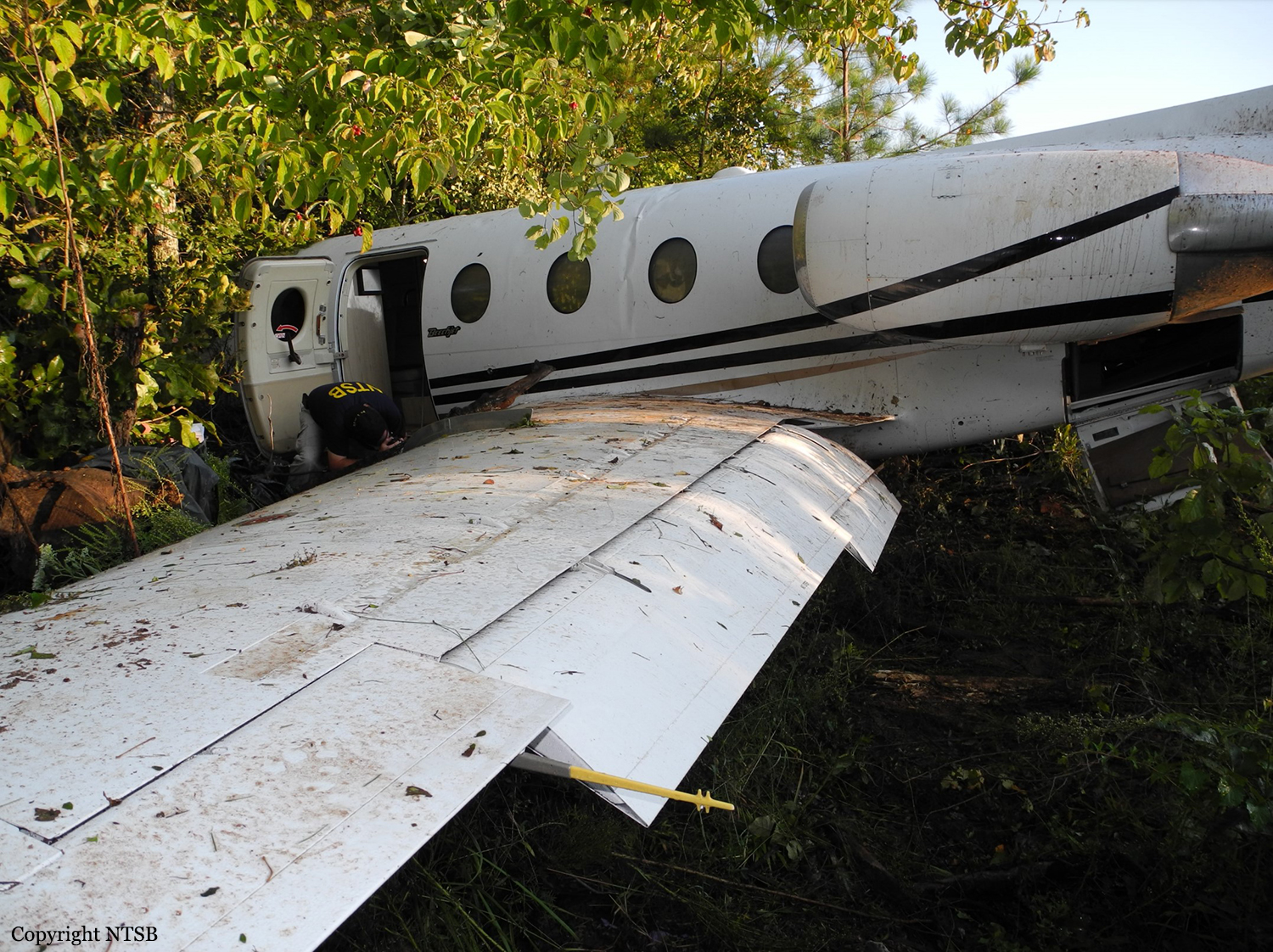
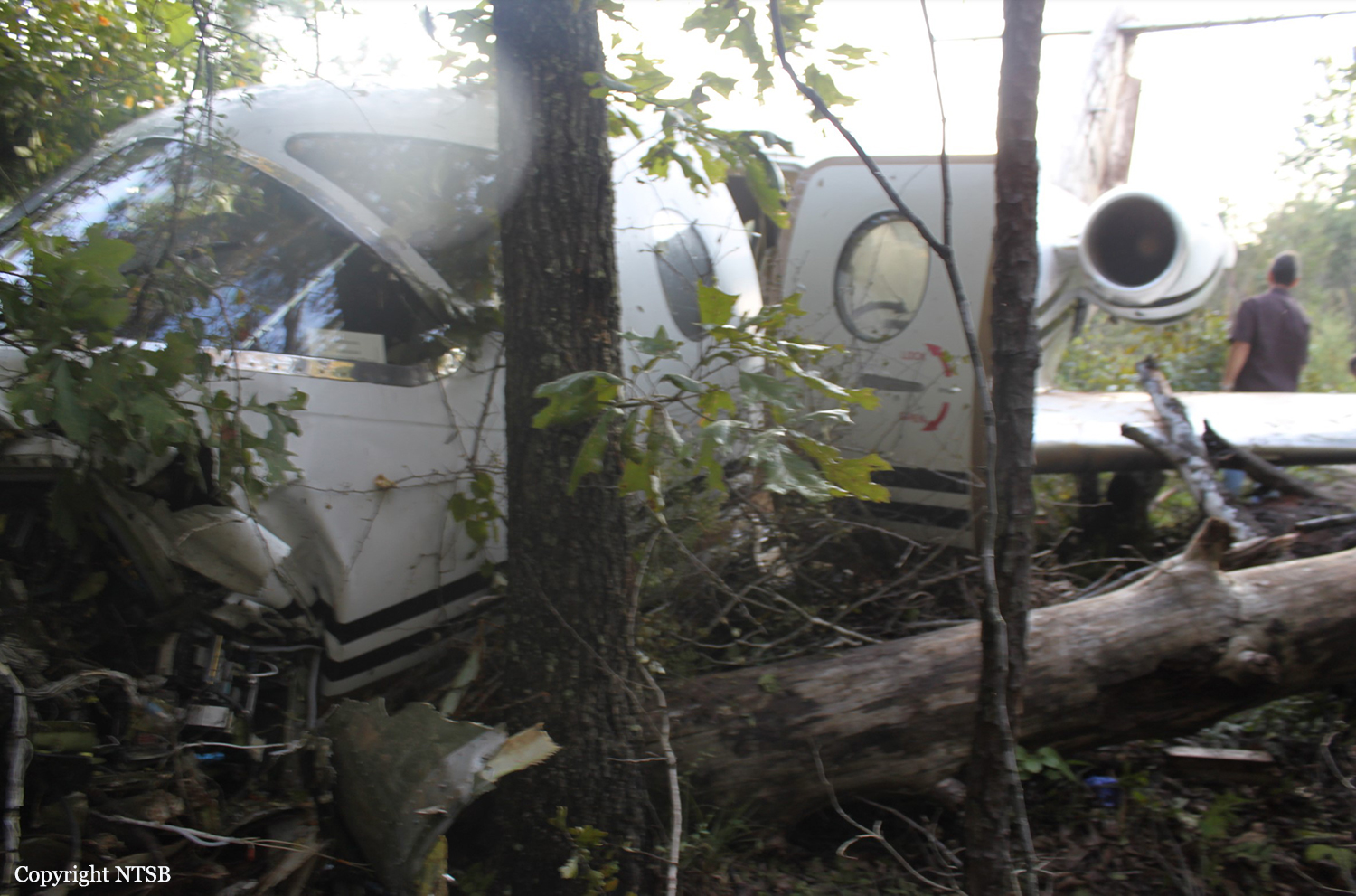
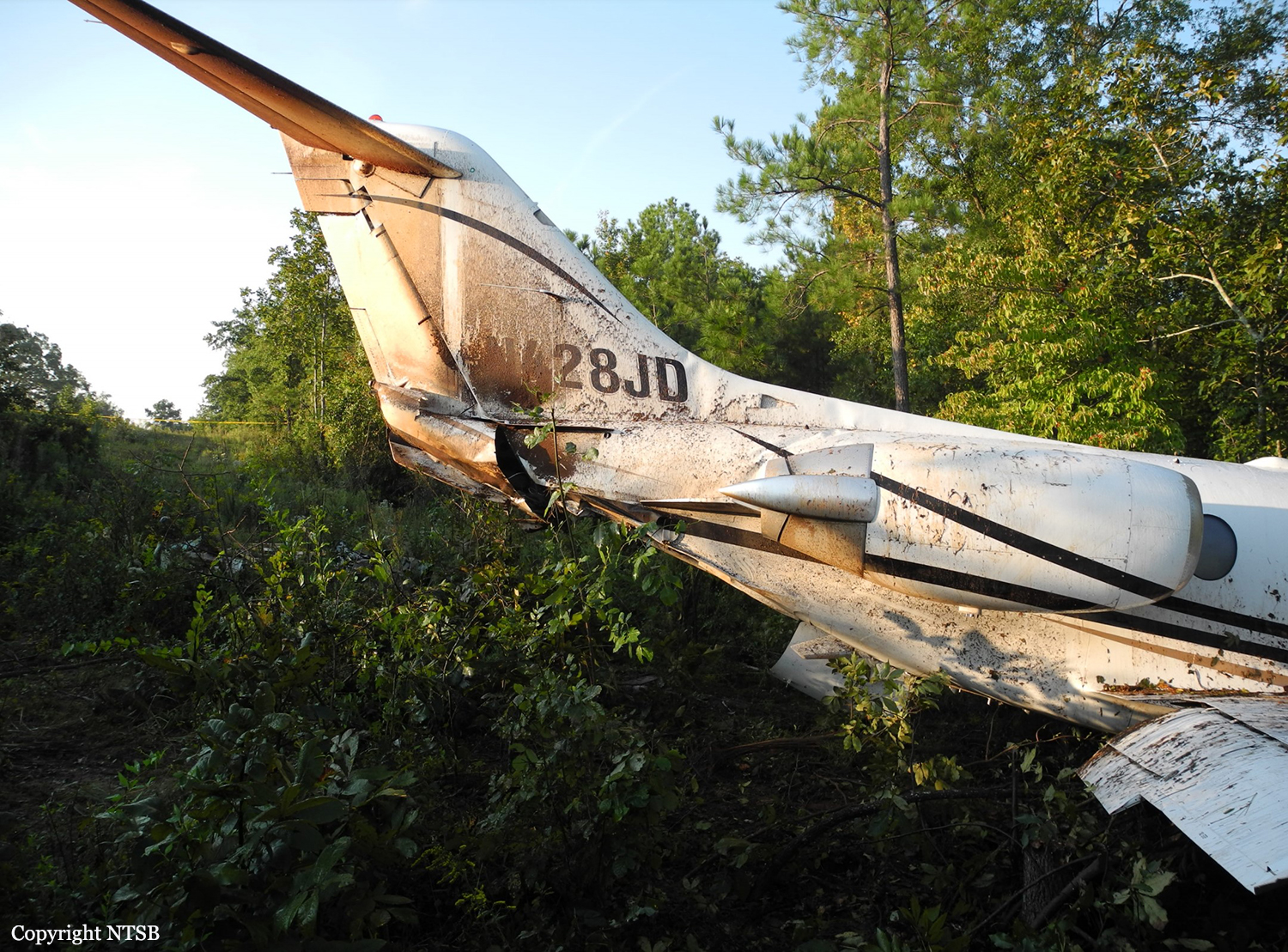
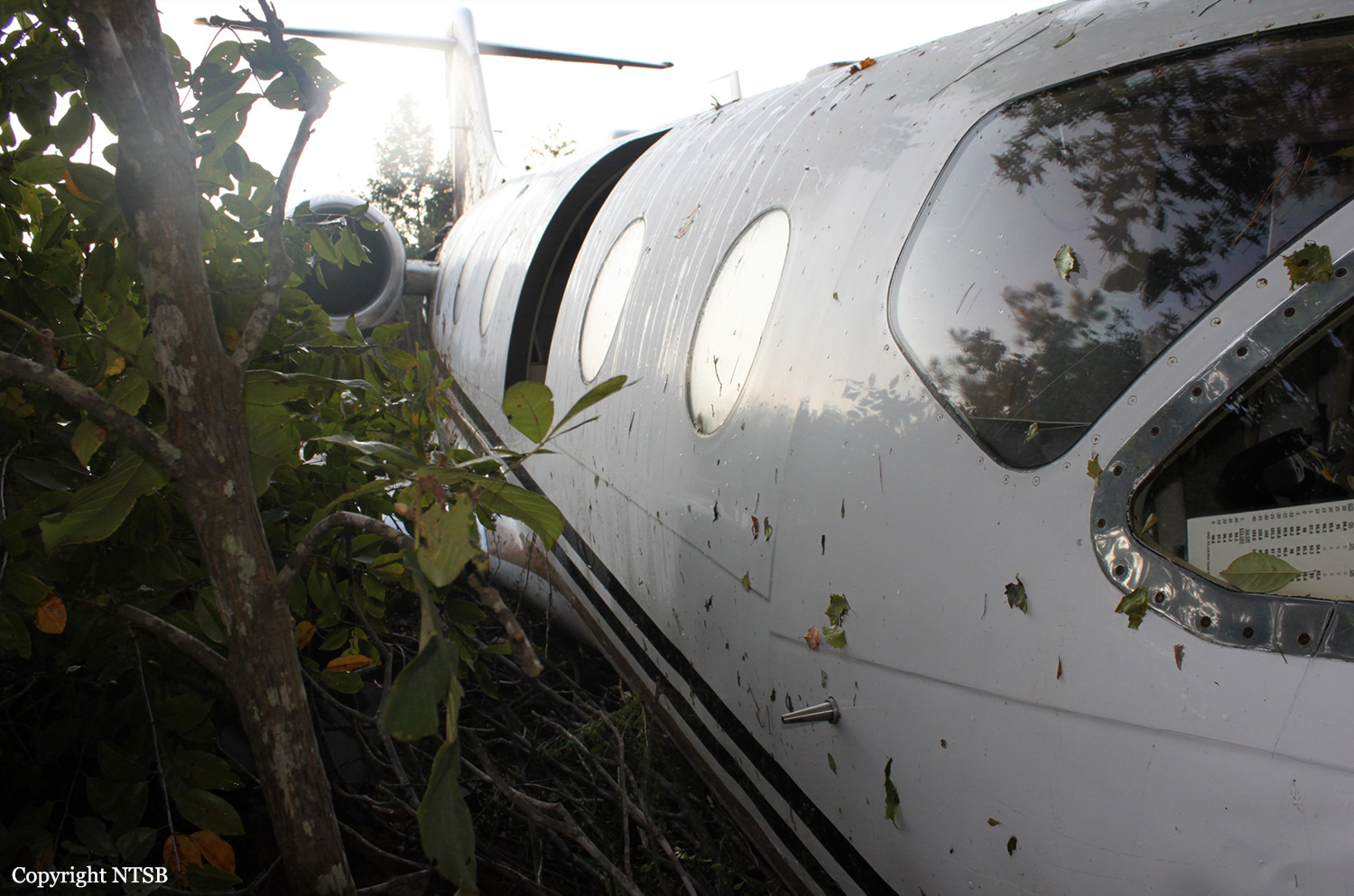
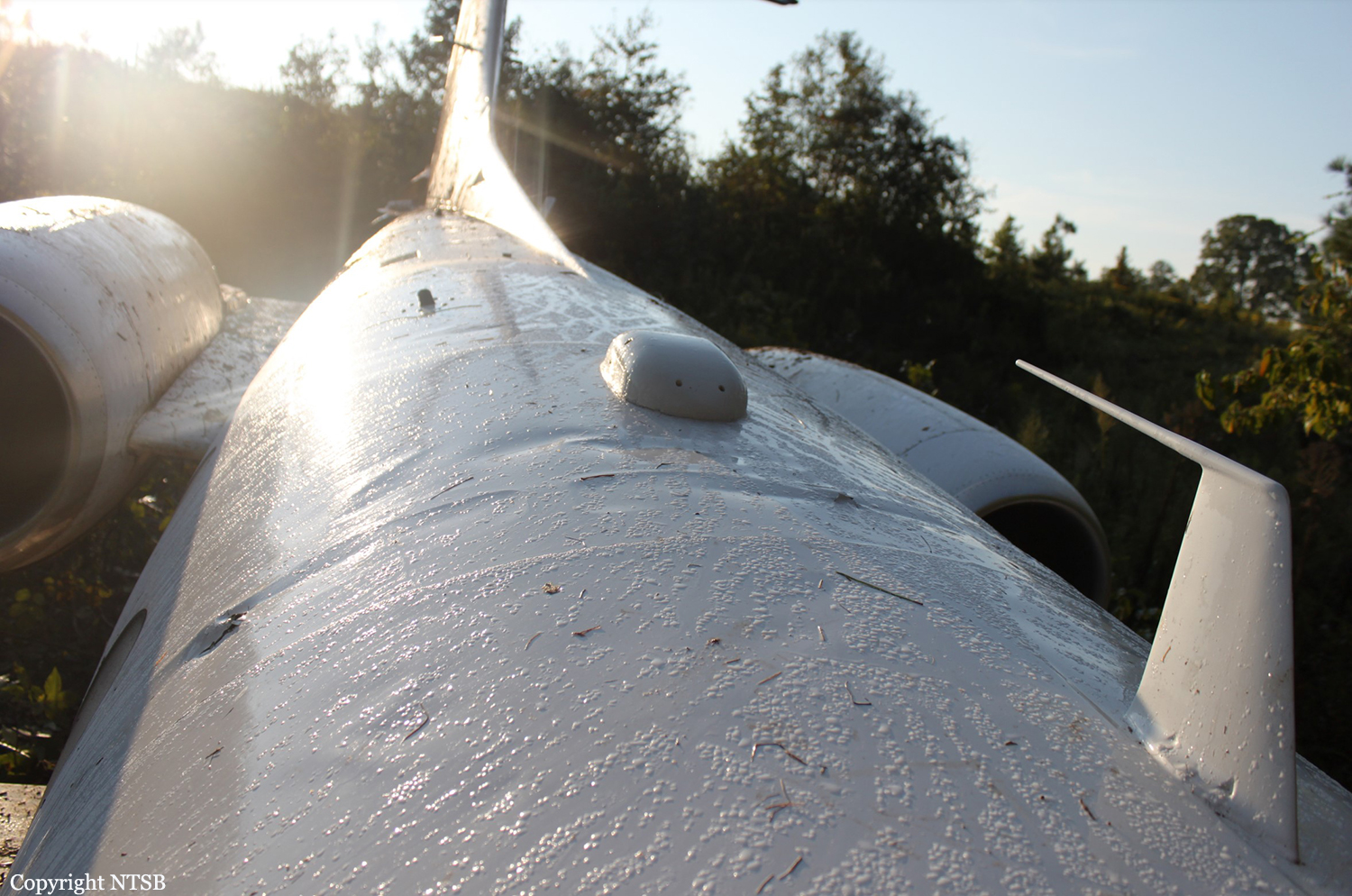
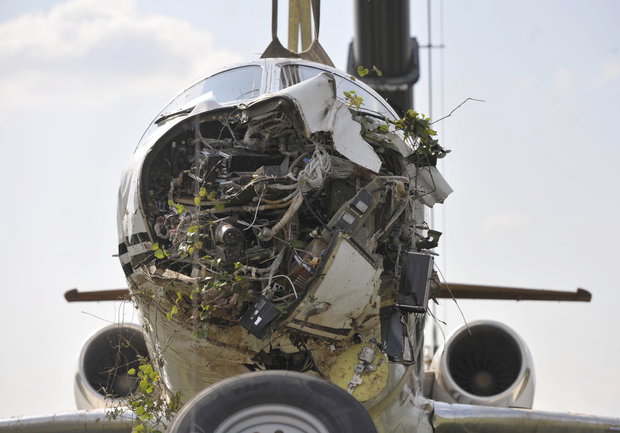
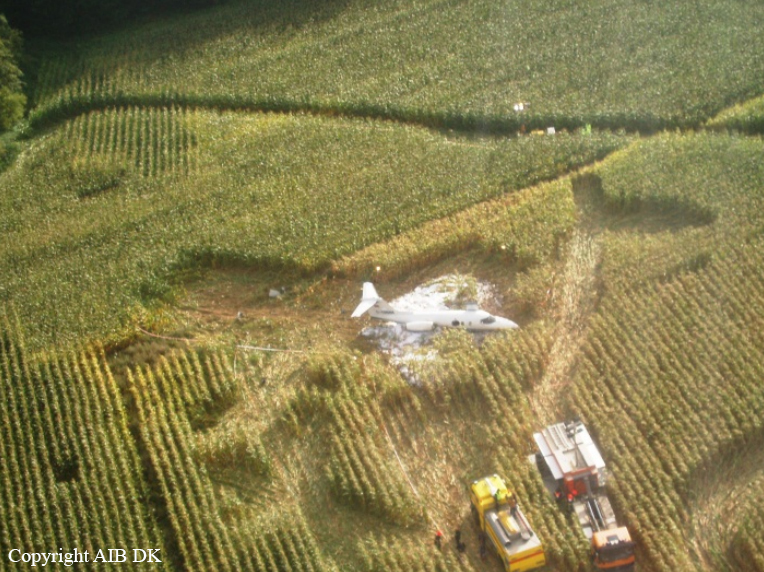
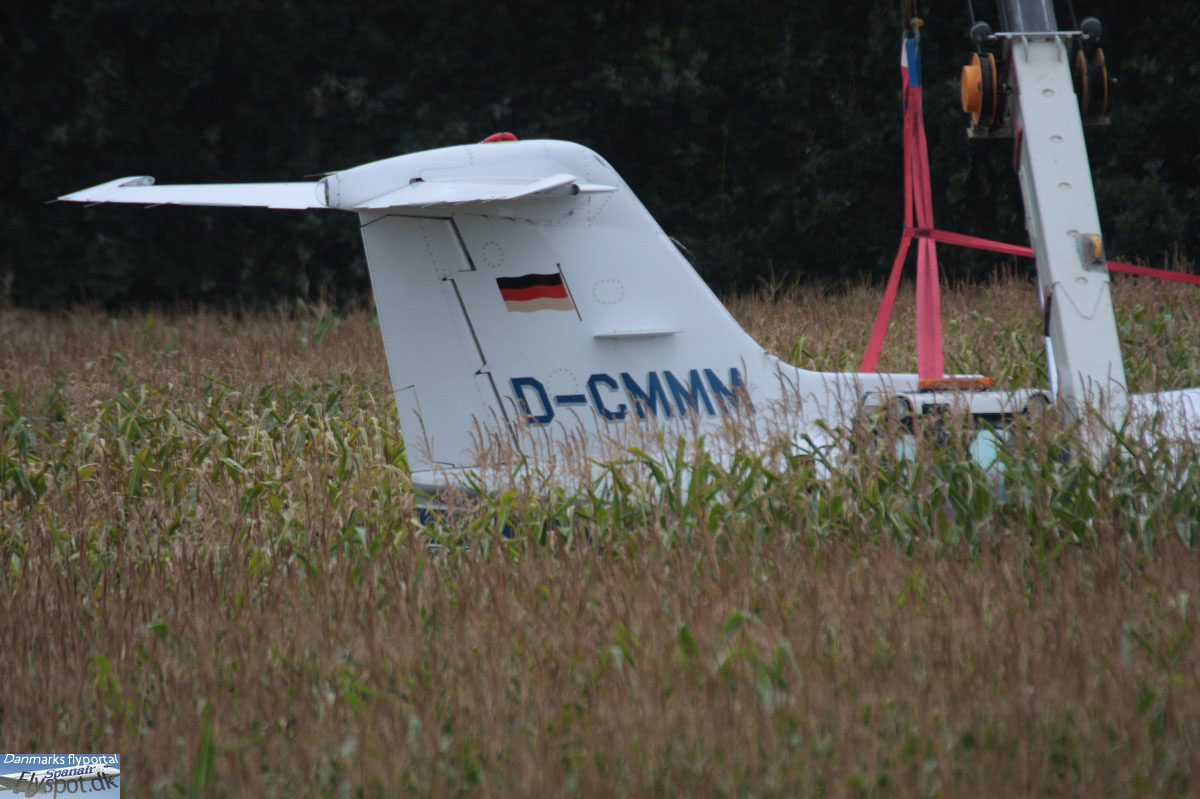
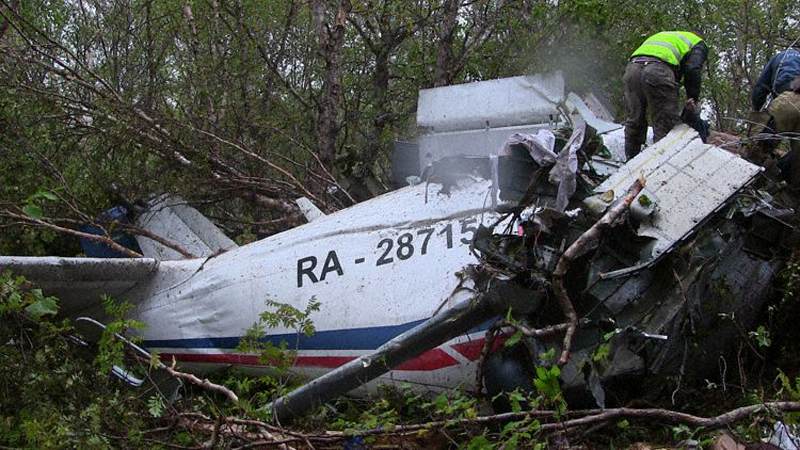
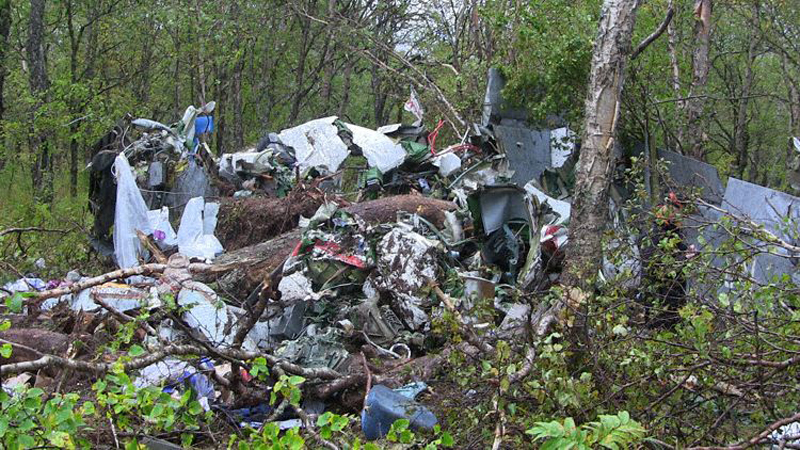
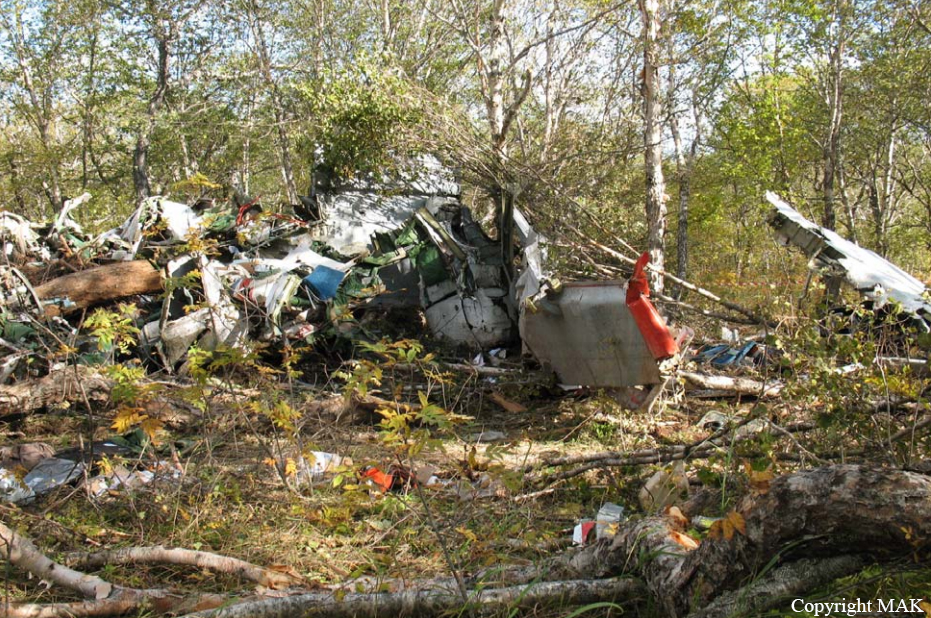
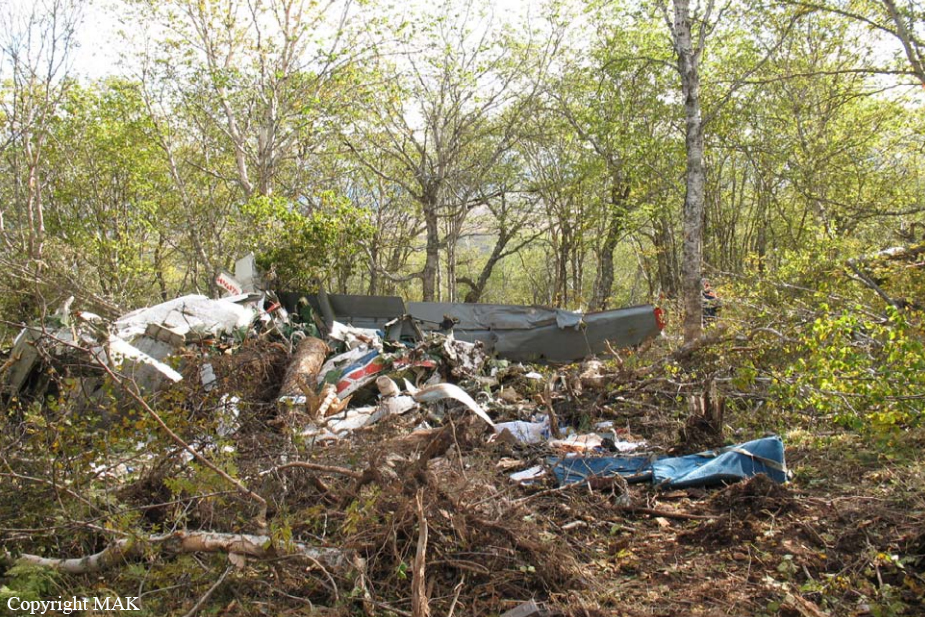
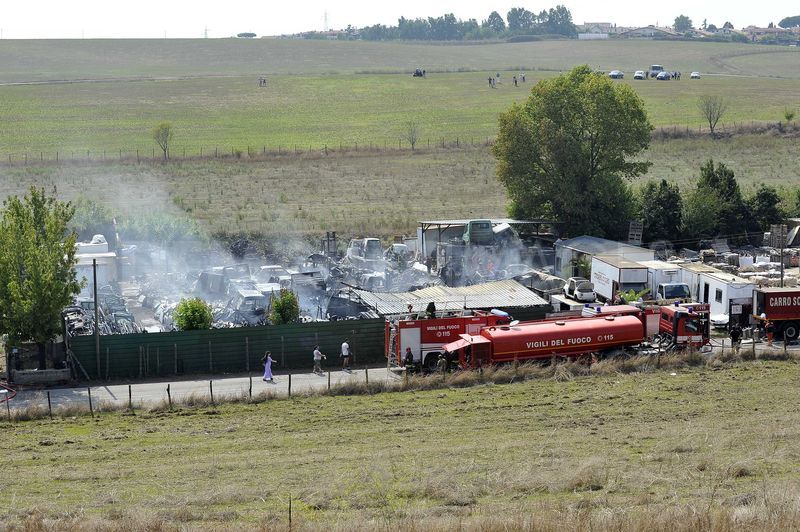
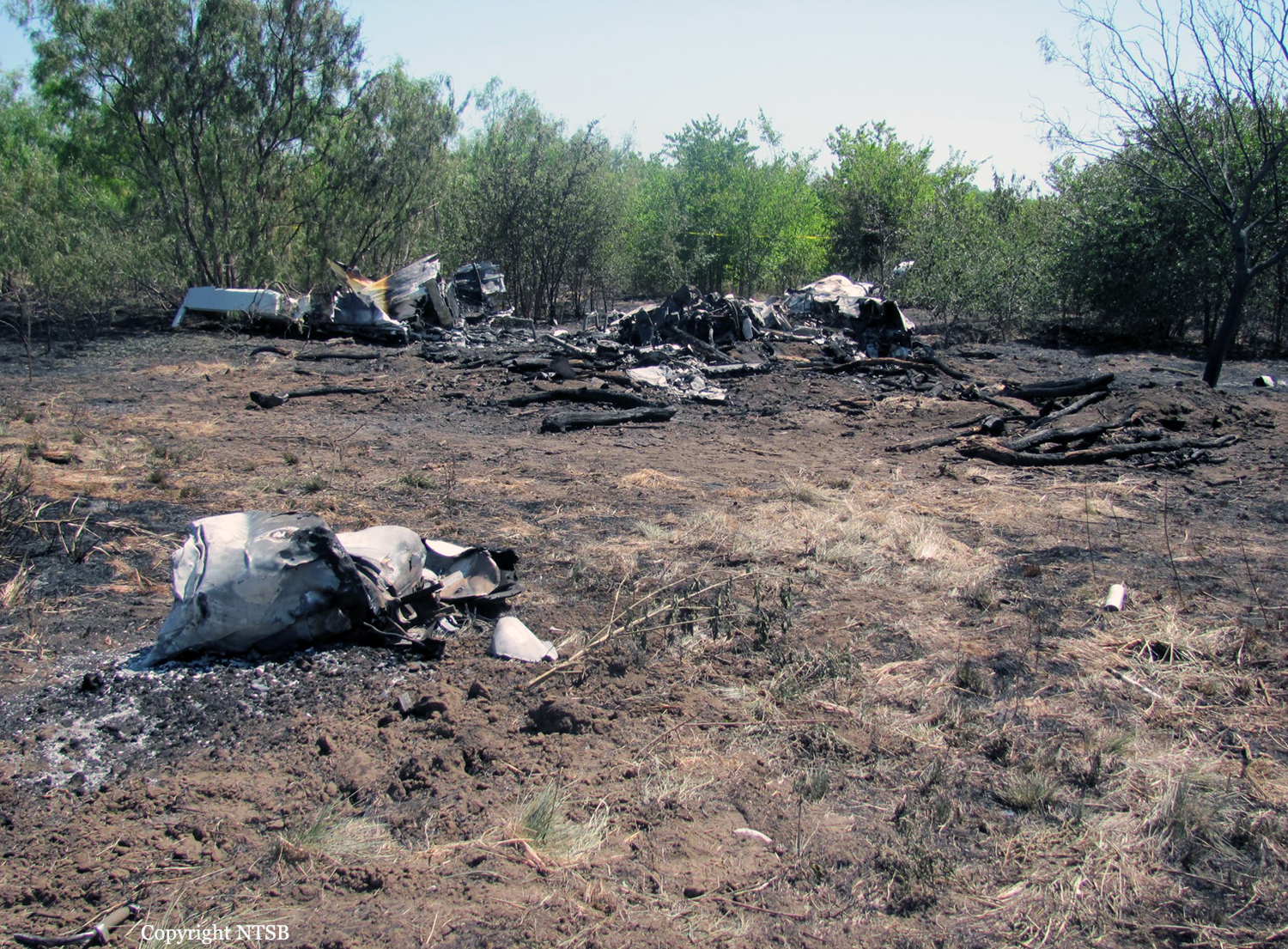
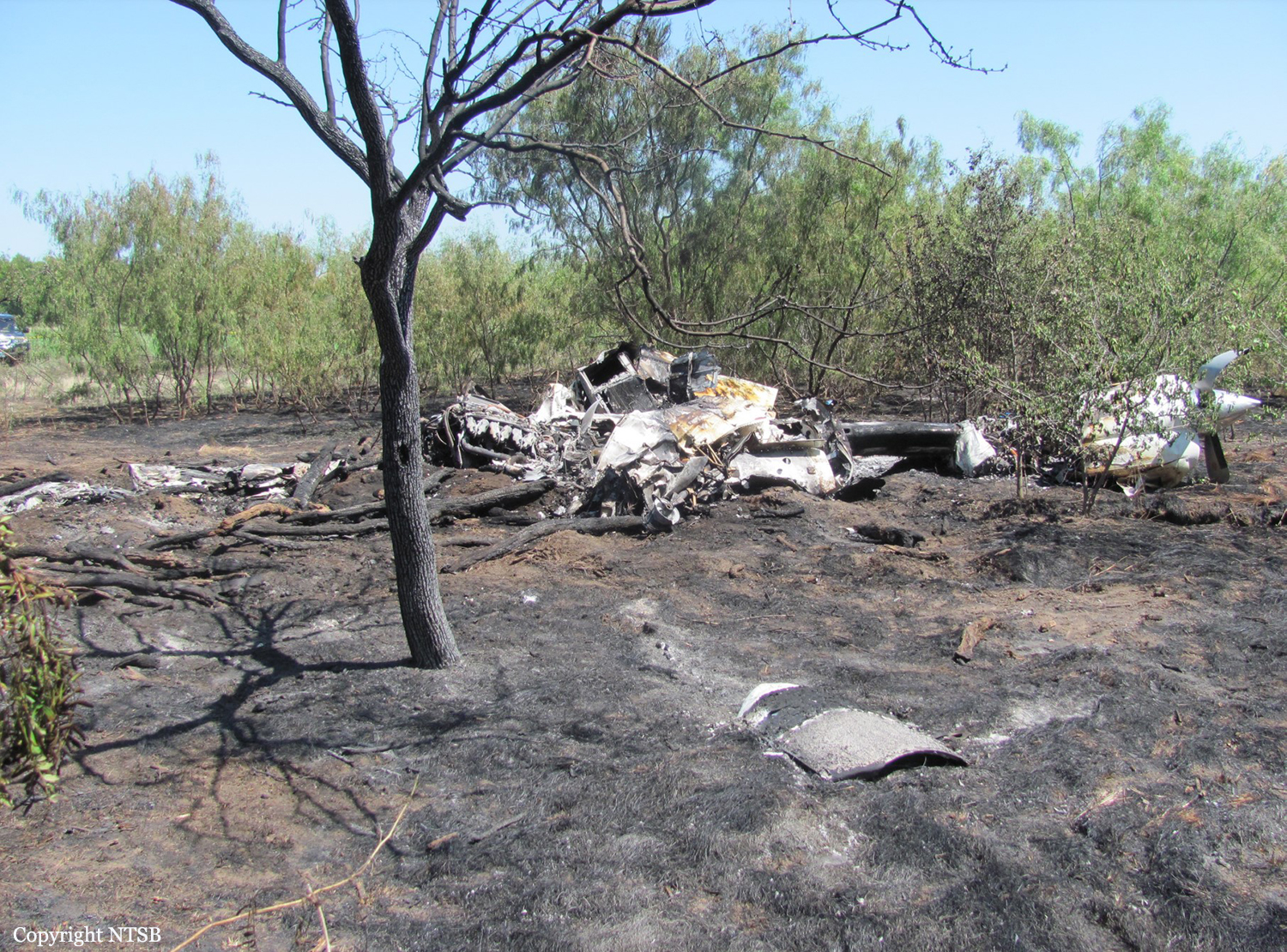
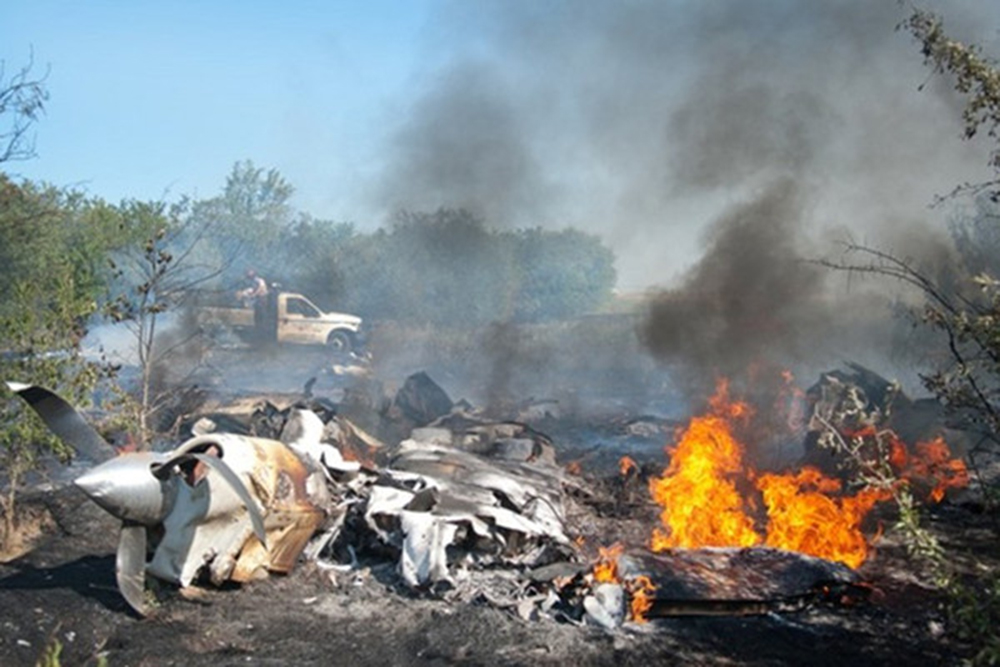
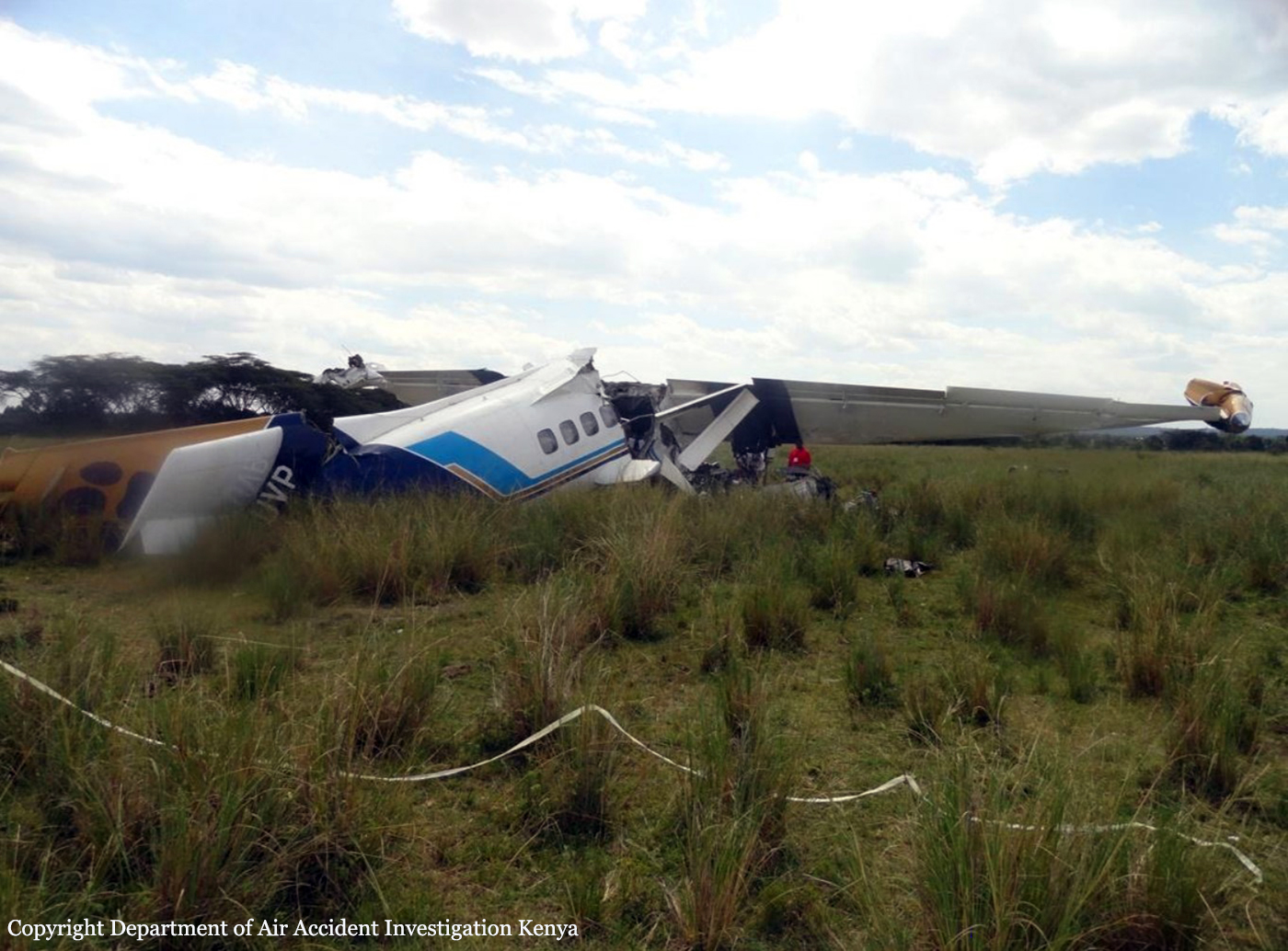
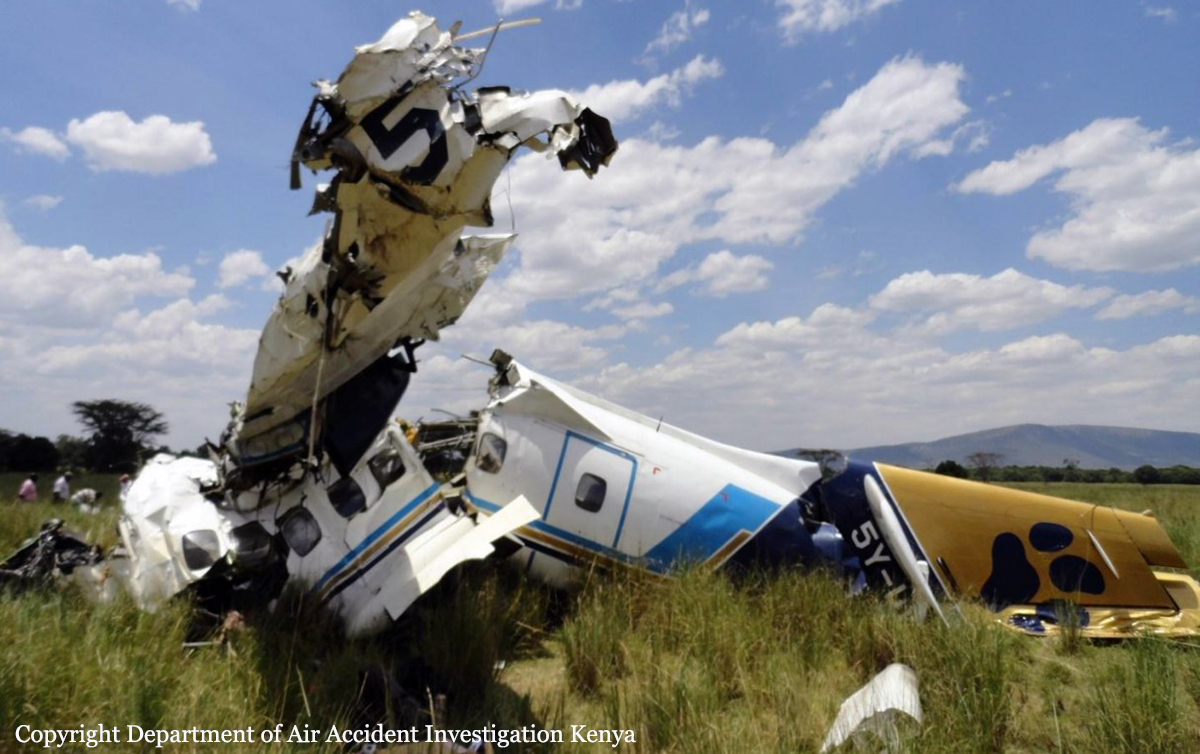
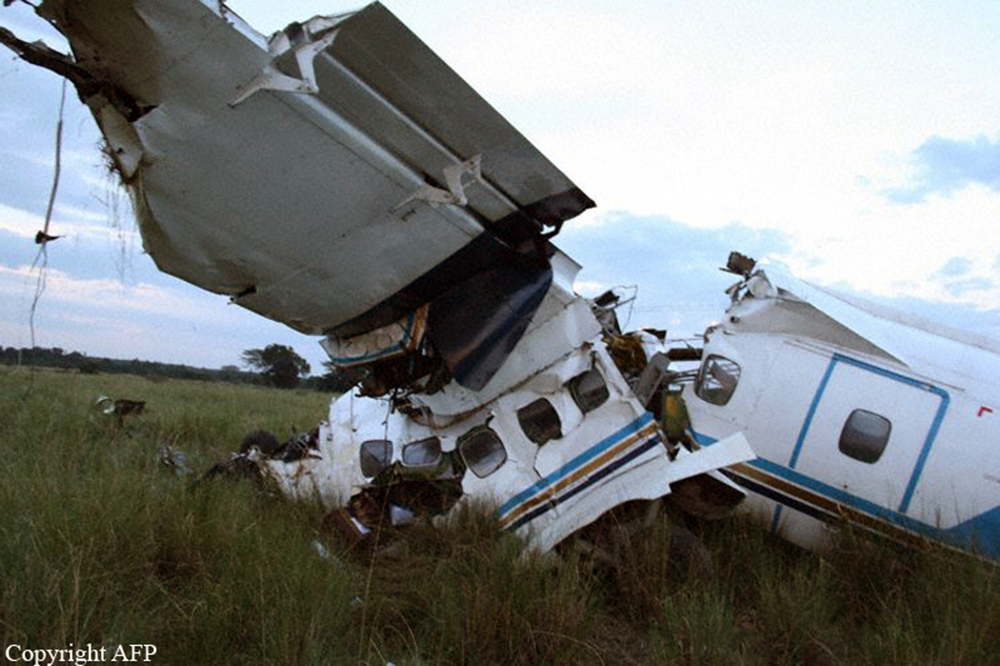
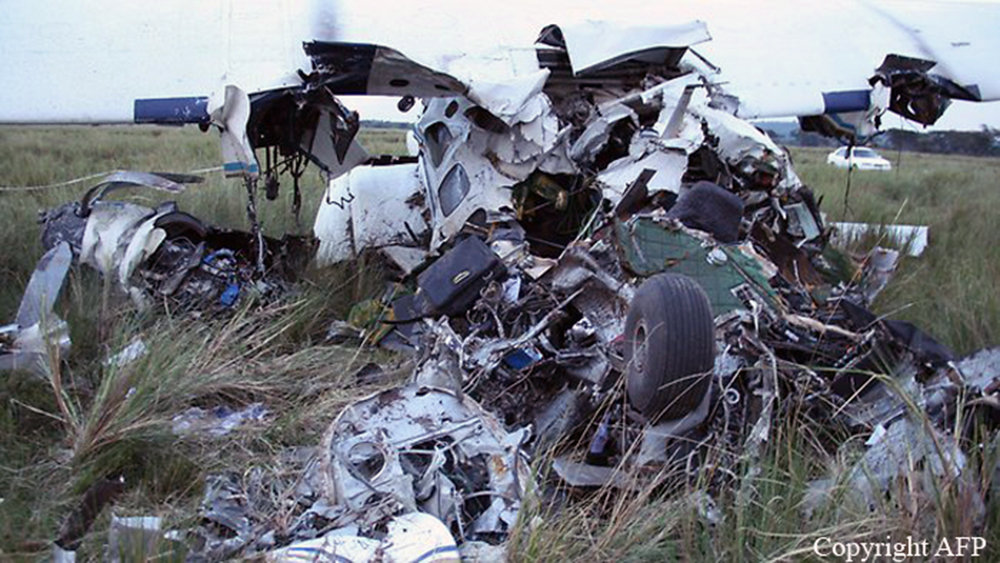
The aircraft was substantially damaged when it overran runway 28 during landing at Macon Downtown Airport (MAC), Macon, Georgia. The airplane departed from Charleston Air Force Base/International Airport (CHS), Charleston, South Carolina, about 0930. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed and an instrument flight rules (IFR) flight plan was filed. Both Airline Transport Pilots (ATP) and one passenger sustained minor injuries. The airplane was owned by Dewberry, LLC and operated by The Aviation Department. The corporate flight was conducted under the provisions of Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 91. According to an interview with the pilots, they arrived at DeKalb-Peachtree Airport (PDK), Atlanta, Georgia, which was their home base airport, about 0400, and then drove about 4 1/2 hours to CHS for the 0930 flight. The flight departed on time, the airspeed index bug was set on the co-pilot's airspeed for a decision takeoff speed (V1) of about 102 knots and a single engine climb speed (V2) on the pilot's side of 115 knots. The flight climbed to 16,000 feet prior to beginning the descent into MAC. When the flight was about 11 miles from the airport the flight crew visually acquired the airport and cancelled their IFR clearance with the Macon Radar Approach controller and proceeded to the airport visually. The second-in-command activated the runway lights utilizing the common traffic advisory frequency for the airport. Both crew members reported that about 3 seconds following activation of the lights and the precision approach path indicator (PAPI) lights, the PAPI lights turned off and would not reactivate. During the approach, the calculated reference speed (Vref) was 108 knots and was set on both pilots' airspeed indicator utilizing the index bug that moved around the outside face of the airspeed instrument. The landing was within the first 1,000 feet of the runway and during the landing roll out the airplane began to "hydroplane" since there was visible standing water on the runway and the water was "funneling into the middle." Maximum reverse thrust, braking, and ground spoilers were deployed; however, both pilots reported a "pulsation" in the brake system. The airplane departed the end of the runway into the grass, went down an embankment, across a road, and into trees. They further added that the airplane "hit hard" at the bottom of the embankment. They also reported that there were no mechanical malfunctions with the airplane prior to the landing. According to an eyewitness statement, a few minutes prior to the airplane landing, the airport experienced a rain shower with a "heavy downpour." The witness reported observing the airplane on approach, heard the engine thrust reverse, and then observed the airplane "engulfed in a large ball of water vapor." However, he did not observe the airplane as it departed the end of the runway. Another witness was located in a hangar on the west side of the airport and heard the airplane, looked outside and then saw the airplane with the reverse thrusters deployed. He watched it depart the end of the runway and travel into the nearby woods.
Probable cause:
The pilot’s failure to maintain proper airspeed, which resulted in the airplane touching down too fast on the wet runway with inadequate runway remaining to stop and a subsequent runway overrun. Contributing to the landing overrun were the flight crew members’ failure to correctly use the appropriate performance chart to calculate the runway required to stop on a contaminated runway and their general lack of proper crew resource management.