Circumstances:
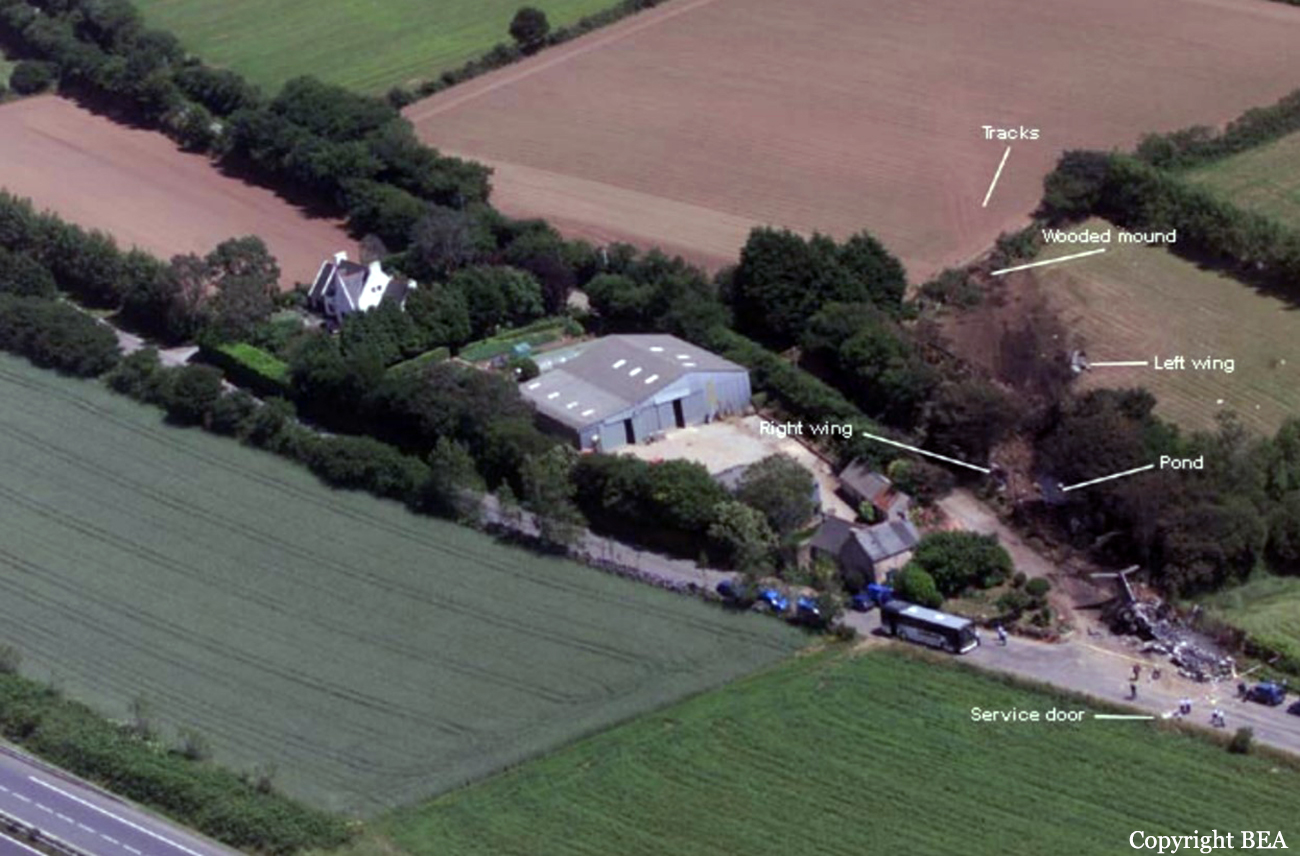
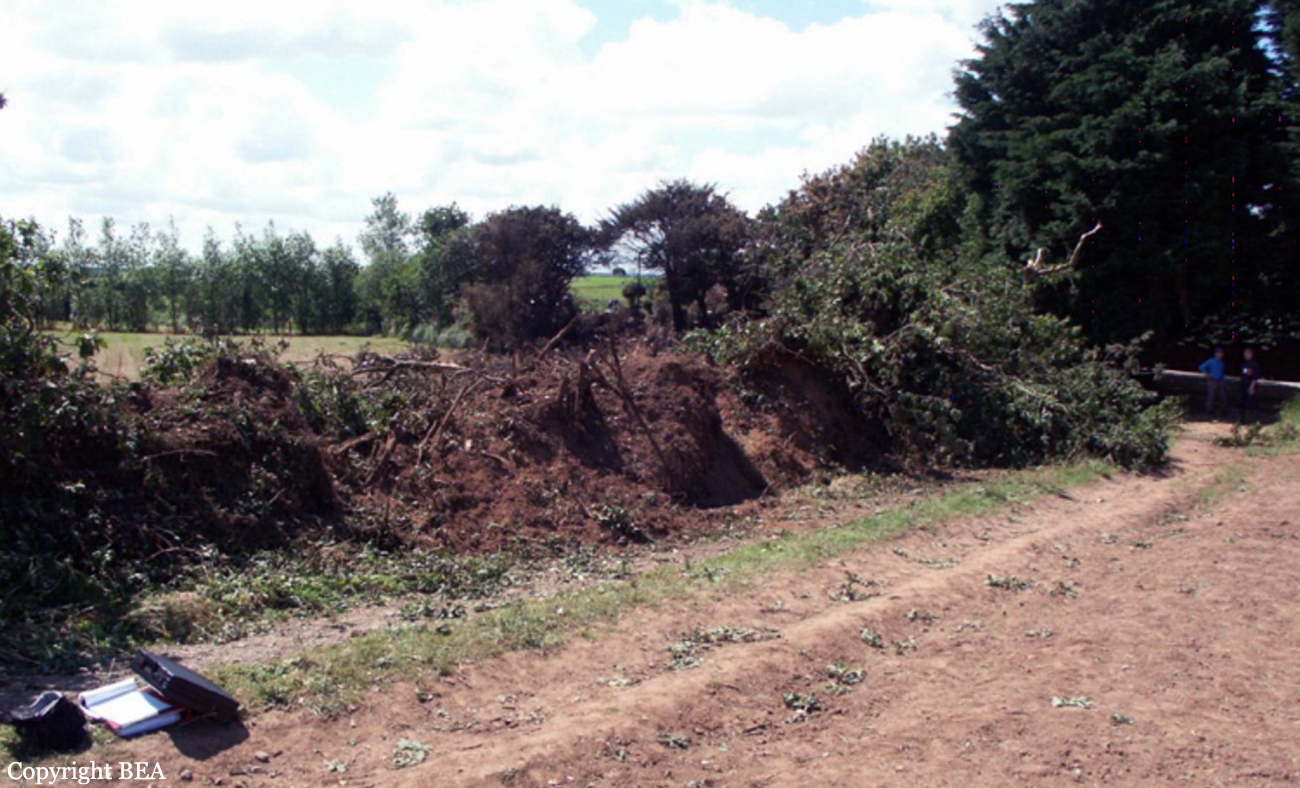
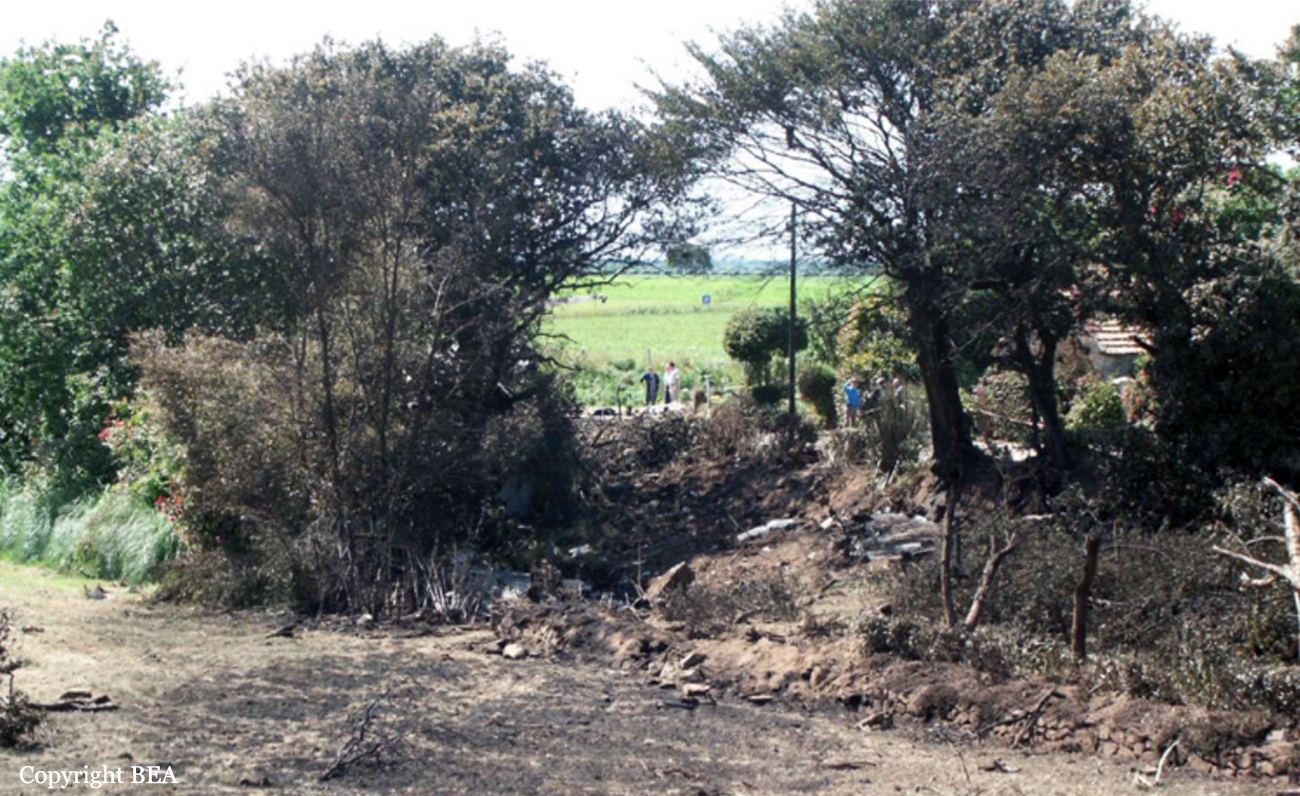
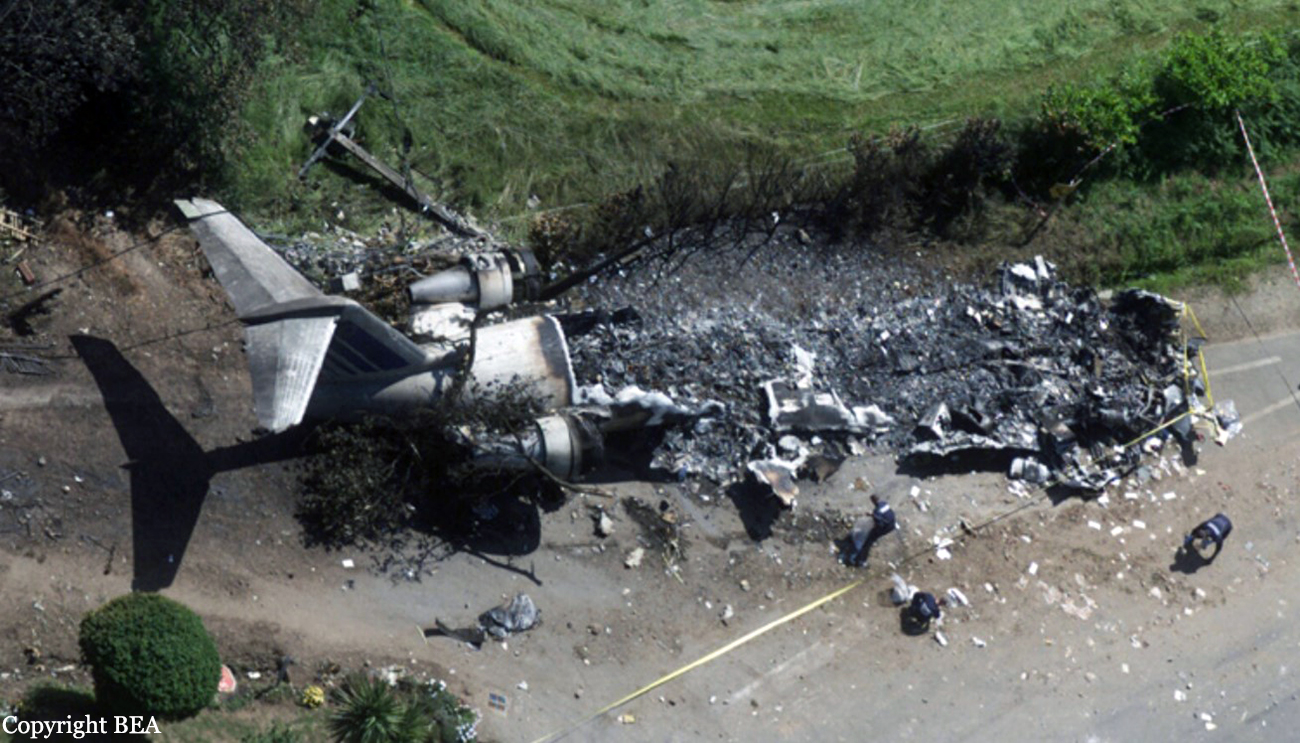
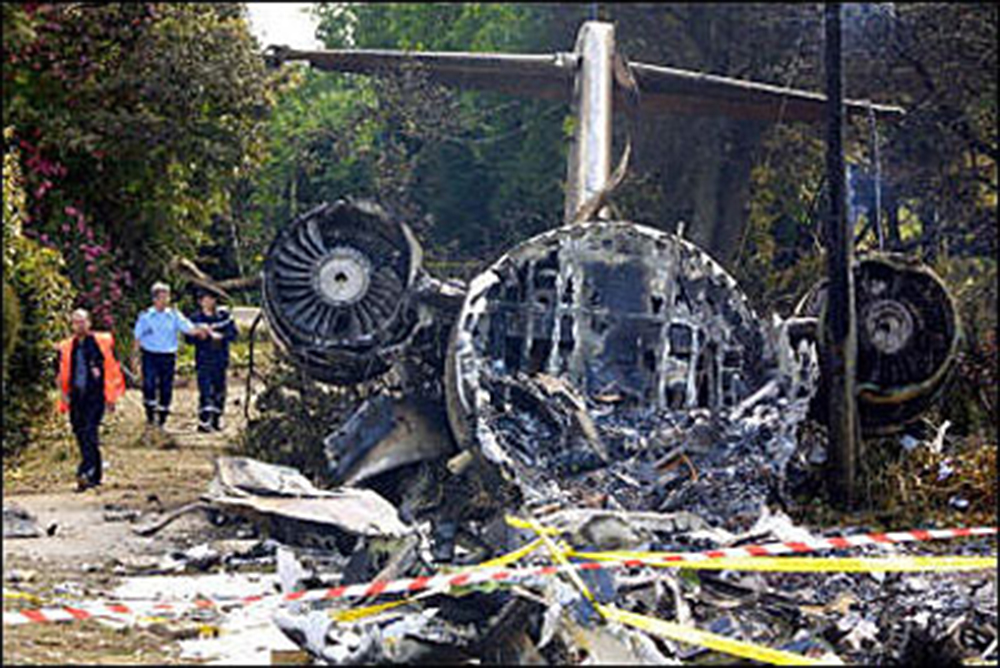
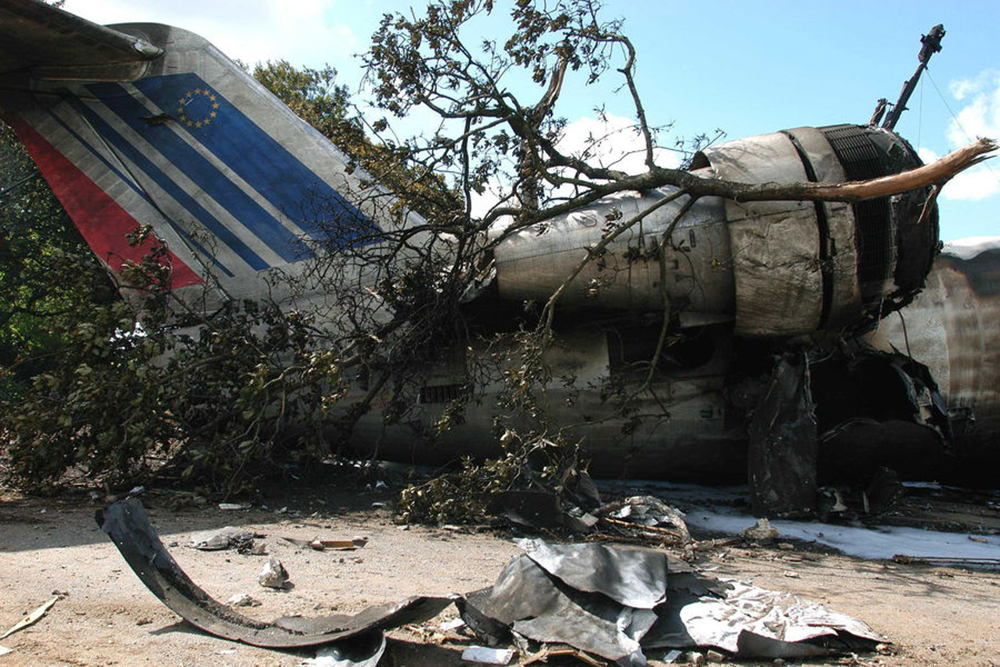
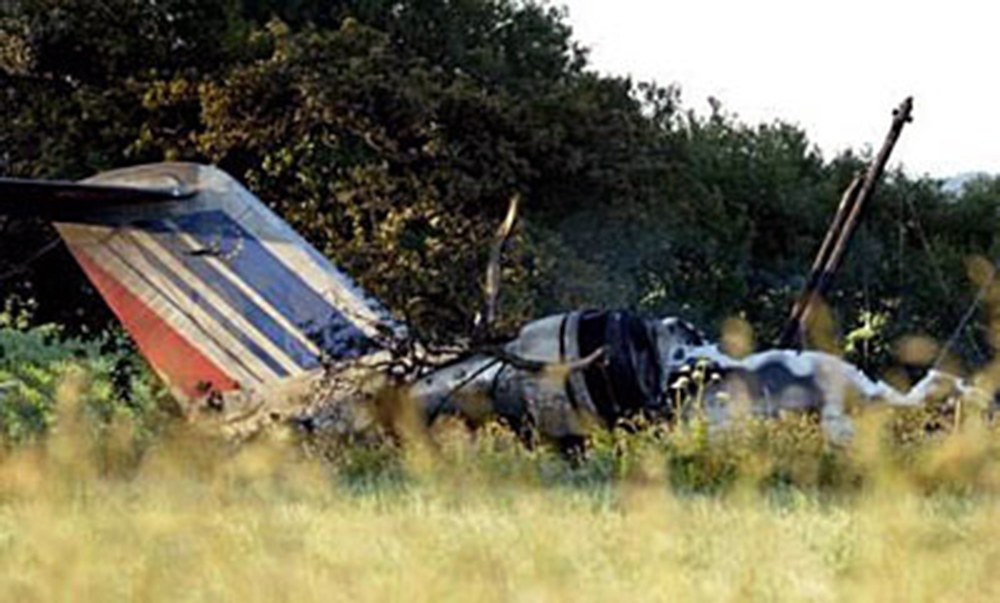
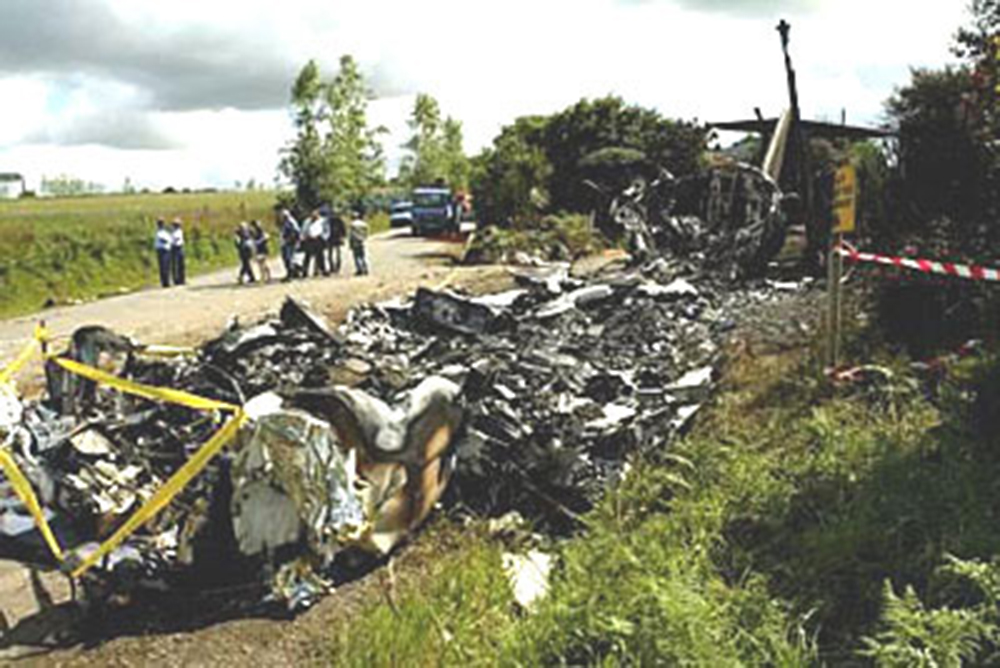
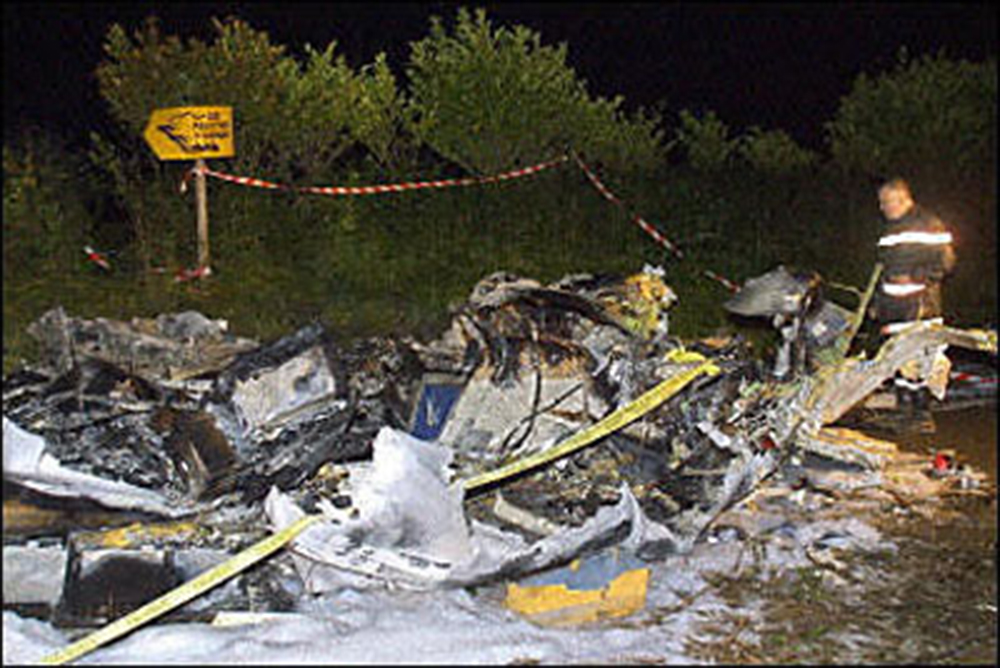
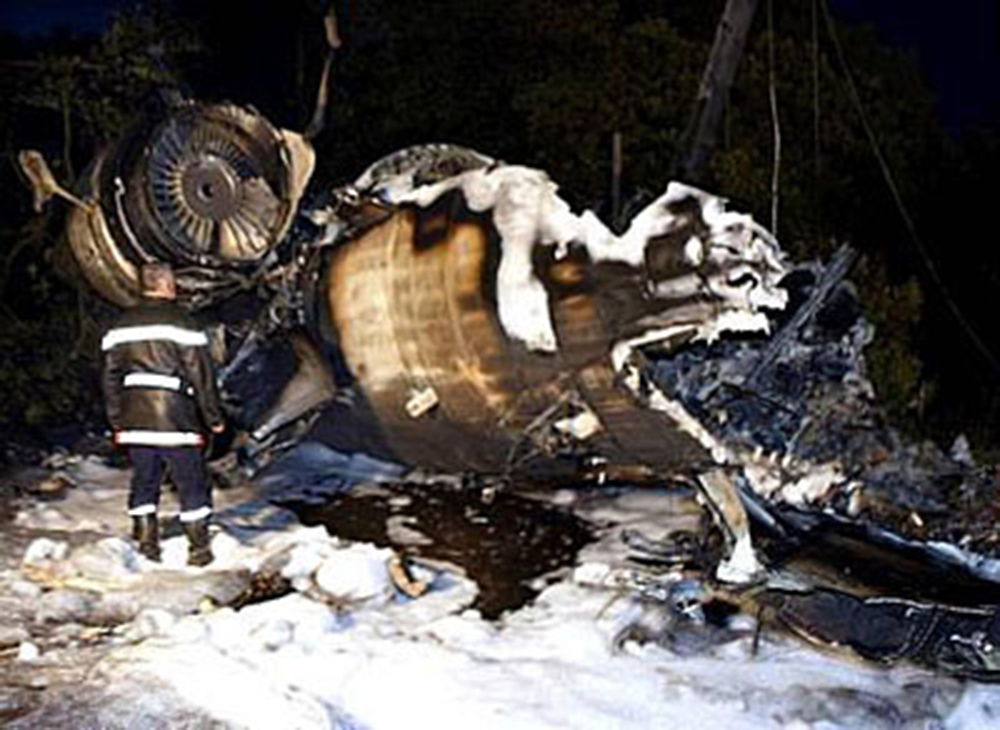
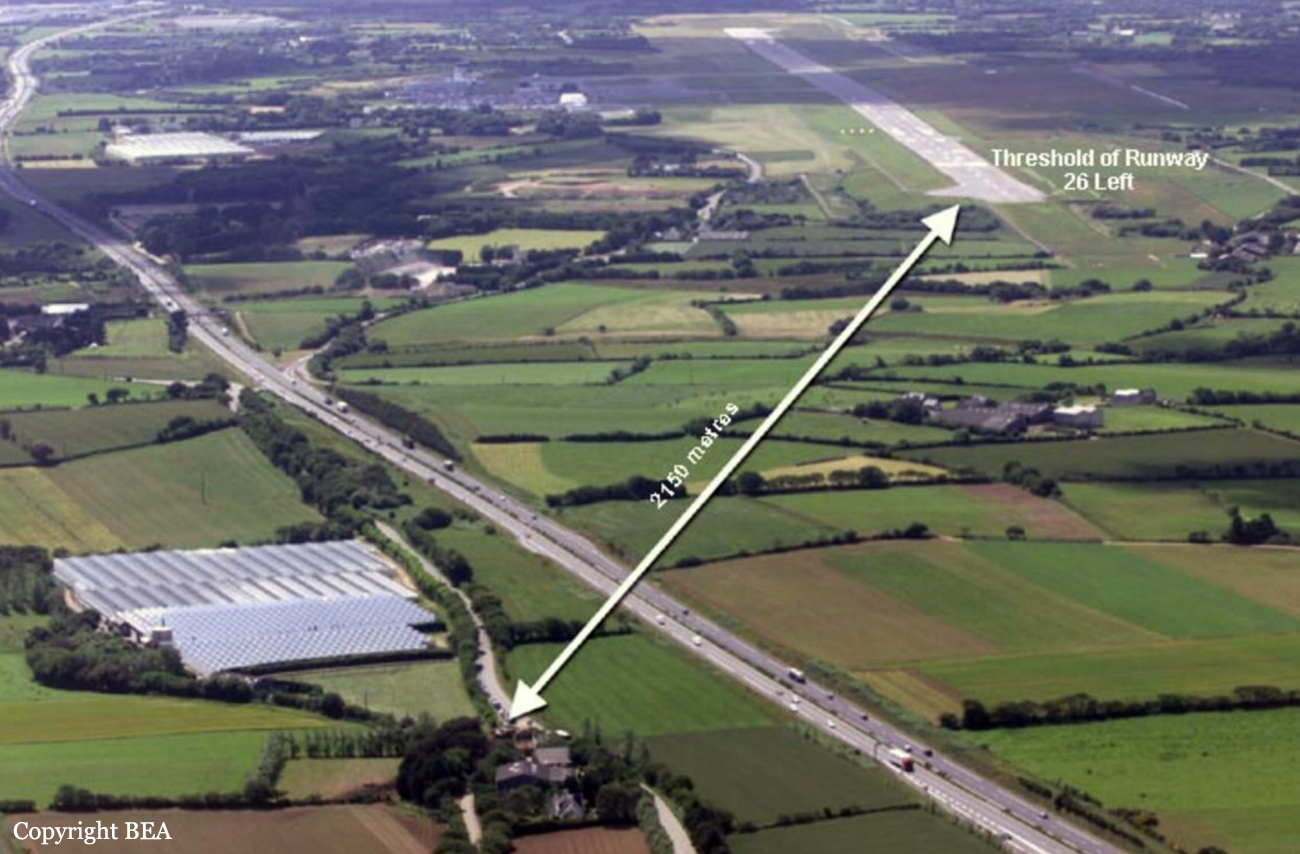
On Sunday 22 June 2003, the CRJ-100 registered F-GRJS was operating as scheduled flight AF 5672 between Nantes Atlantique and Brest-Guipavas aerodromes (France) under an IFR flight plan. The flight represented the last leg of a Brest – Nantes – Strasbourg – Nantes – Brest rotation. The aeroplane was operated by Brit Air on behalf of Air France. The Captain was pilot flying (PF). The crew also included another pilot (the co-pilot), and one cabin crew. The aeroplane took off at 21 h 16 (2) with twenty-one passengers. The flight was approximately fifty minutes late, due to a delay in the first flight of the day that had affected the subsequent flights. During the flight, with the authorisation of the control centre, the crew passed northeast of the planned track in order to avoid cumulonimbus formations. At Brest Guipavas, the 21 h 00 ATIS indicated visibility of eight hundred meters with some fog and a cloud base at two hundred feet with the presence of cumulonimbus. The runway in use was 26 Left with an ILS approach. Runway use was temporarily restricted to Cat I due to presence of works. At 21 h 36 min 27 s, the flight (radio call sign BZ 672 EC) was cleared by the enroute controller to descend to Flight Level 150 then, at 21 h 39 min 10 s, to Flight Level 70. At 21 h 39 min 23 s, the crew announced that they were descending to Flight Level 70 towards BODIL, the initial approach fix, avoiding storms. At 21 h 39 min 31 s, the Brest approach controller transmitted "Descend four thousand feet QNH one thousand and eight, number two on approach, plan a holding pattern at Golf Uniform". At 21 h 44 min 21 s, the controller cleared descent to three thousand feet and added "and perform a holding pattern". The aeroplane was approximately 20 NM DME from BG. At 21 h 47 min 40 s, that is, approximately one-and-a-half-minutes before the planned start of the hold, the controller cleared descent to two thousand feet QNH. At 21 h 48 min 01 s, the controller announced "Echo Charlie, preceding aeroplane has landed, continue the approach, report at Outer Marker". Four seconds later, at 9.4 NM DME, the autopilot "Heading" and "Vertical Speed" modes became active and the aeroplane adopted a heading of 257°. The Brest ILS frequency was displayed on the VOR 1 and the VOR navigation source was selected. At 21 h 48 min 21 s, the controller called back "Are you ready for the approach?". The crew confirmed and the controller asked "Report at Outer Marker". The Copilot read this back. At the Captain’s request, the Co-pilot extended the flaps to 20° then the landing gear. The aeroplane stabilized at two thousand feet QNH on autopilot, still in Heading mode, at about 7 NM DME. Simultaneously, the wind, which had started to veer northwest during the descent, caused the aeroplane to drift towards the left. The flight crew did not notice this drift. At 21 h 49 min, the co-pilot extended the flaps to 30° then to 45° and the crew performed the pre-landing checklist. At 21 h 49 min 35 s, the controller cleared the landing for runway 26 Left and indicated a cloud base of less than one hundred feet. At 21 h 49 min 40 s, the aeroplane, in level flight, passed under then above the glide slope. At 21 h 50 min, the aeroplane passed the GU beacon, slightly to the left, with a track deviating to the left in relation to the localizer centreline. At that moment, the wind calculated by the Flight Management System (FMS) was 300° / 20 kt. A short time later, the aeroplane began its descent. The aeroplane continued to drift to the left of the localizer centreline. At 21 h 50 min 45 s the aeroplane again passed through the glide slope, and the Captain said "Approach selected, LOC and Glide"; the Co-pilot confirmed. The autopilot "heading" and "vertical speed" modes remained active. The aeroplane thereafter remained below the glide slope for the remainder of the flight. Between 21 h 50 min 58 s and 21 h 51 min 02 s, the GPWS announced, successively, "Five hundred", "Glide slope" then "Sink rate". At 21 h 51 min 01 s, the aeroplane began a turn to the right. By this time, the aeroplane was 4.68 points to the left of the localizer centreline. At 21 h 51 min 04 s, the Captain disengaged the autopilot. At 21 h 51 min 05 s, the GPWS announced "Three hundred". Between 21 h 51 min 07 s and 21 h 51 min 14 s, seven "Glide slope" alarms sounded. During this time, the Co-pilot said "come right" on two occasions and the aeroplane attitude changed from - 5° to 0°. At 21 h 51 min 15 s, the GPWS announced "One hundred". At 21 h 51 min 16 s, with the aeroplane at 529 feet QNH and 93 feet on the radio altimeter, the Co-pilot said "I’ve got nothing in front", then the Captain said "Go around". Simultaneously, the engine thrust increased significantly. The aeroplane attitude returned to - 5 in four seconds. At 21 h 51 min 19 s, the Co-pilot said "Go around". At 21 h 51 min 20 s, the GPWS announced "Sink rate" then "Pull up". The Co-pilot said "Go around" again at 21 h 51 min 22. The first sounds of the impact were recorded by the CVR at 21 h 51 min 22 s, and the recording stopped at 21 h 51 min 24. s. The aeroplane, which touched the ground without any great force, rolled, struck several obstacles and ended up 450 meters left of the extended runway centreline, 2,150 meters from the runway threshold. The Captain was killed. The rest of the crew and the passengers managed to evacuate the aeroplane, which was destroyed by fire.