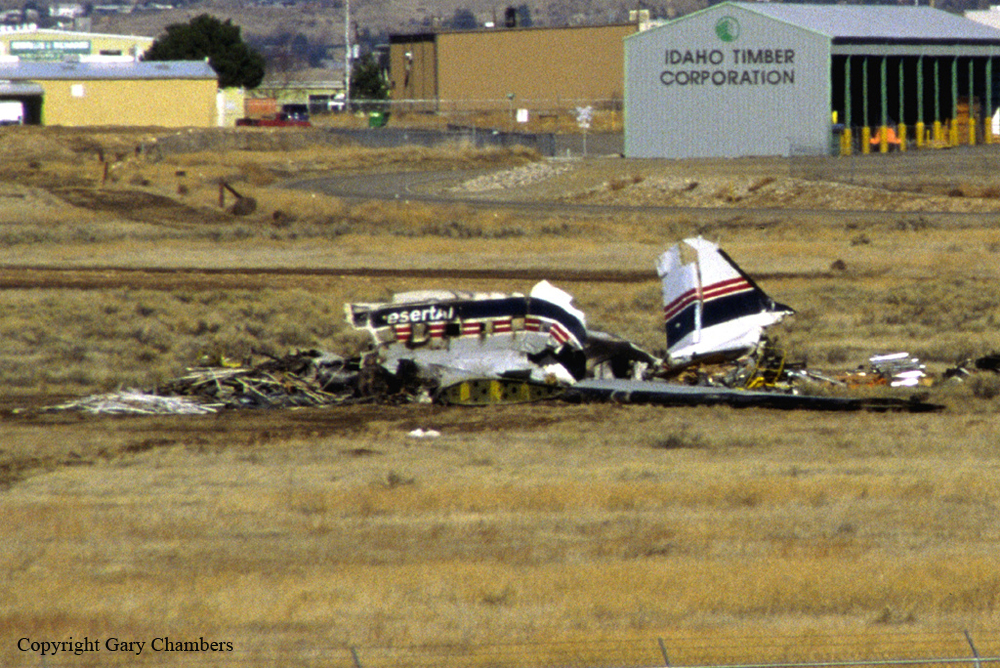
Crash of a Cessna 441 Conquest II in Lakeland
Date & Time:
Jan 2, 1997 at 1121 LT
Registration:
N441MS
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Lakeland - Lakeland
MSN:
441-0056
YOM:
1978
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
533.00
Aircraft flight hours:
4697
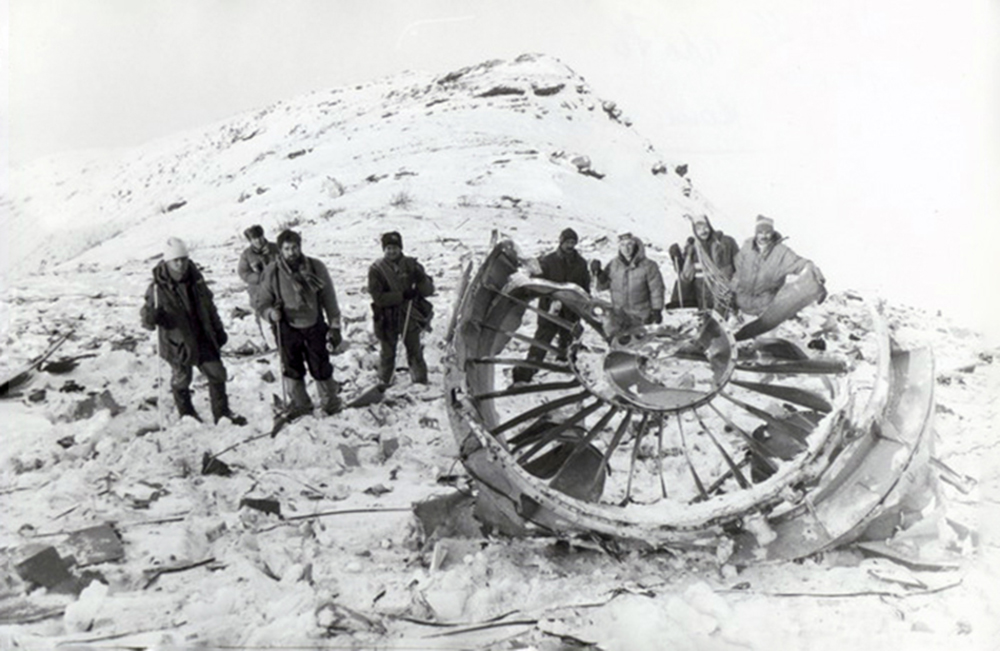
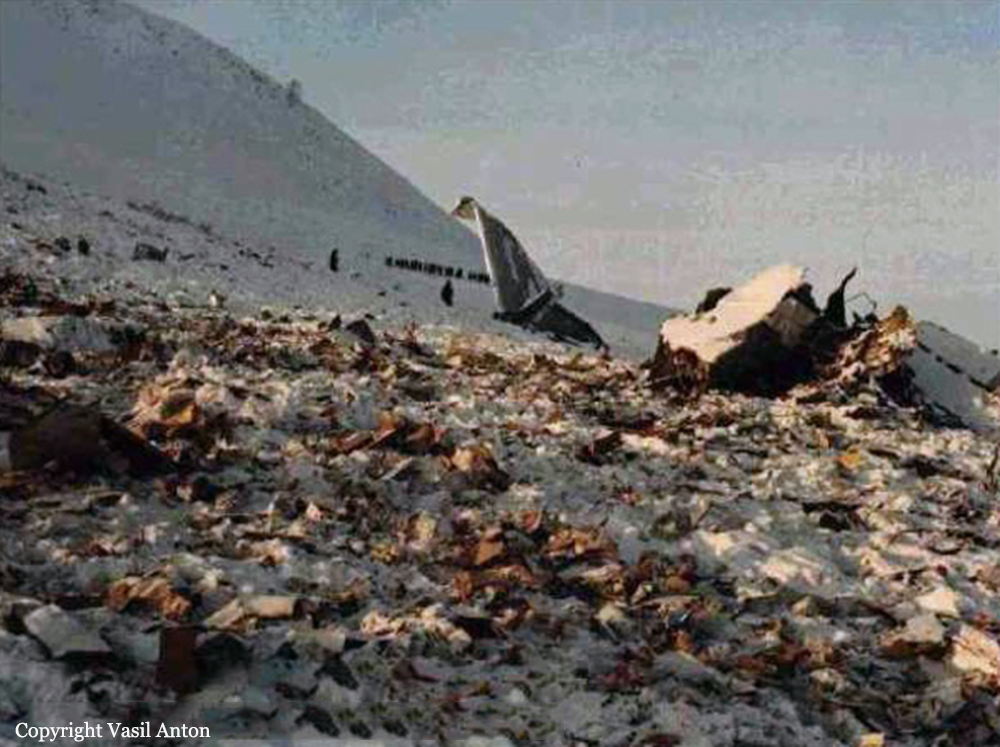
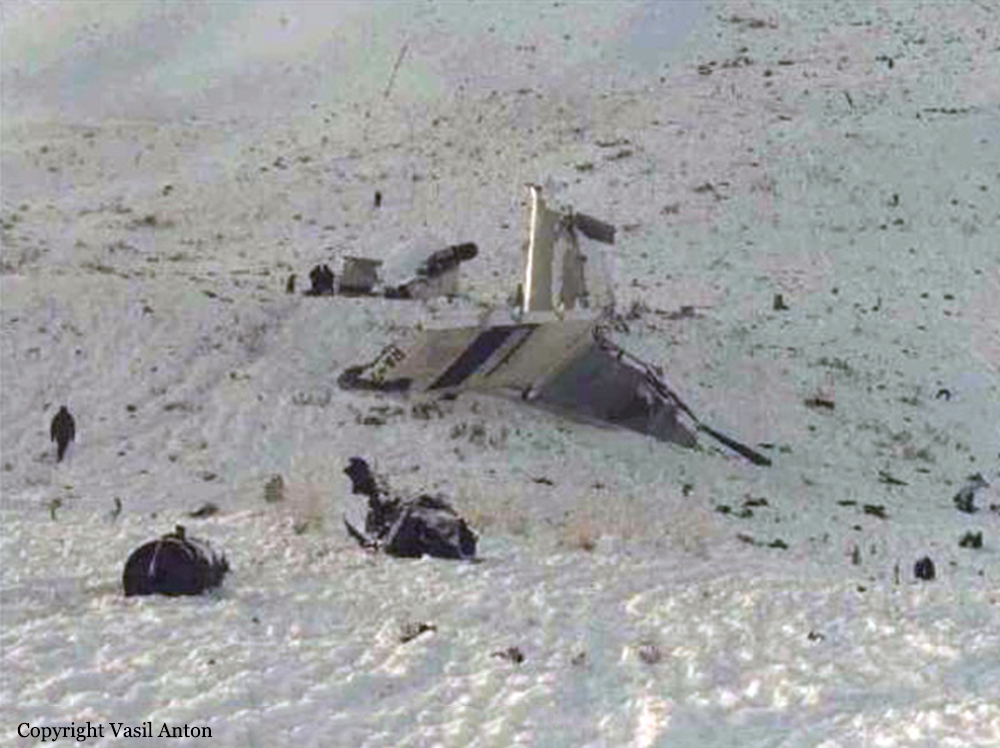
Circumstances:
During the takeoff roll the pilot stated the right engine had an over torque condition and he was unable to control the aircraft. The aircraft went off the runway to the left and crashed coming to rest upright. A post crash fire erupted and destroyed the aircraft. The mechanic rated passenger stated he was observing the right engine gauges during this maintenance test flight and did not observe any over torque indications. When he looked up from the instruments at about the time the aircraft should lift off, the aircraft was drifting to the left. The pilot, who was looking at the engine instruments, looked up, saw the aircraft was about to drift off the runway, and retarded both power levers. The passenger/mechanic (who was also a pilot) reported that the pilot placed the propellers in reverse. Six thousand feet of runway remained at the abort point. The aircraft pitched up and then crashed on the left wing and nose. Cessna Service Newsletter SLN99-15 and AlliedSignal Operating Information Letter OI 331-17 report an abnormality that may affect the model engine in which an uncommanded engine fuel flow increase or fluctuation may occur, resulting in an unexpected high torque and asymmetric thrust. The condition is associated with an open torque motor circuit within the engine fuel control. A system malfunction resulting in engine acceleration to maximum power would produce an overtorque of about 2,288 foot-pounds (ft-lb). This power output is restricted by a fuel flow stop in the engine fuel control. Normal takeoff power is 1,669 ft-lbs; therefore, one engine accelerating to the stop limit while one engine continued to operate normally would cause a torque differential of 619 ft-lbs. The total loss of power in one engine during takeoff while one engine continued to operate normally would result in a torque differential of 1,669 ft-lbs. The Cessna 441 Flight Manual states that at 91 knots indicated airspeed, the airplane is controllable with one engine inoperative (that is, with a torque differential between engines of up to 1,669 ft-lbs). However, if an electronic engine control failure occurs on one engine and the other engine is retarded to idle, the fuel flow to the failed engine will not be reduced, and a torque differential of about 2,288 ft-lbs will occur, at which point the airplane is uncontrollable by the pilot.
Probable cause:
Failure of the electronic engine control, which caused an overtorque condition in the right engine that made directional control of the airplane not possible by the pilot when the power to the left engine was retarded to idle during the takeoff roll.
Final Report: