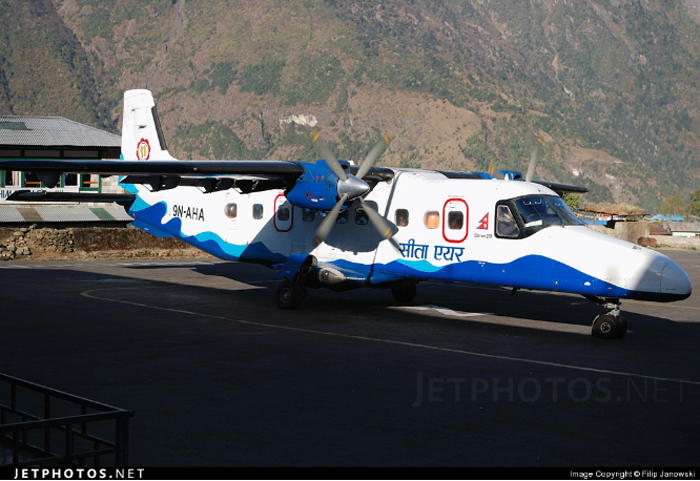
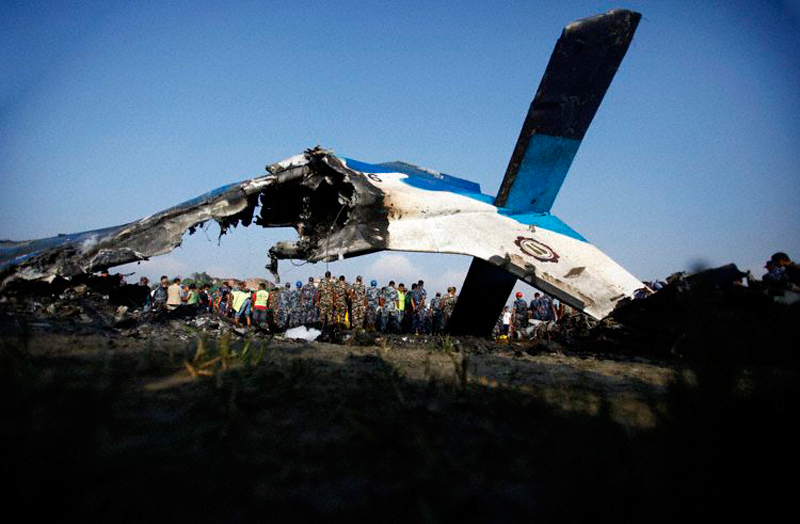
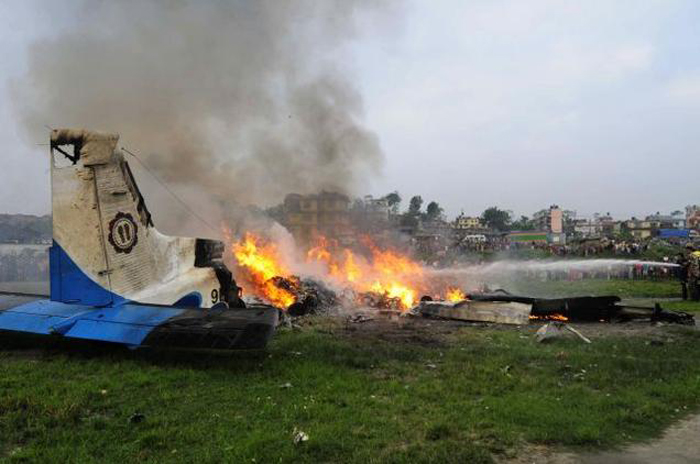
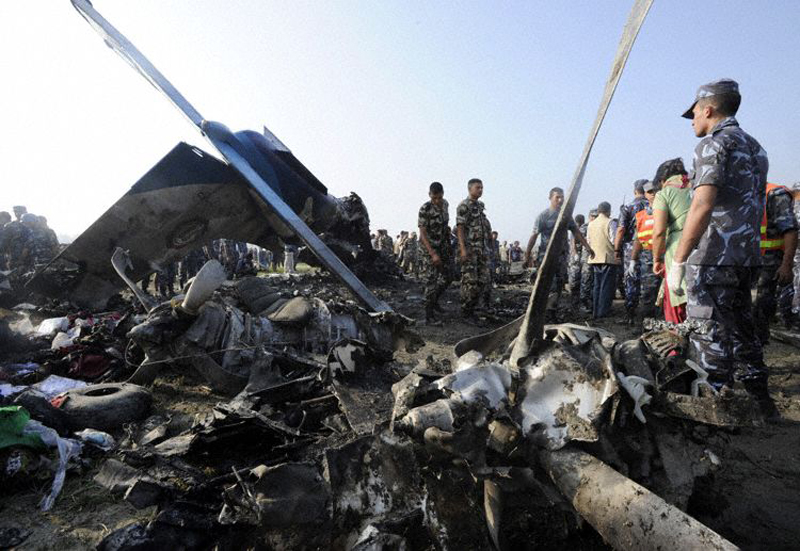
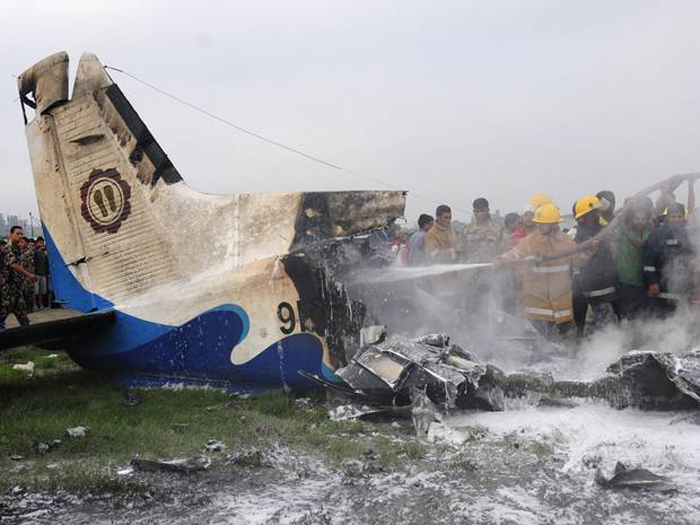
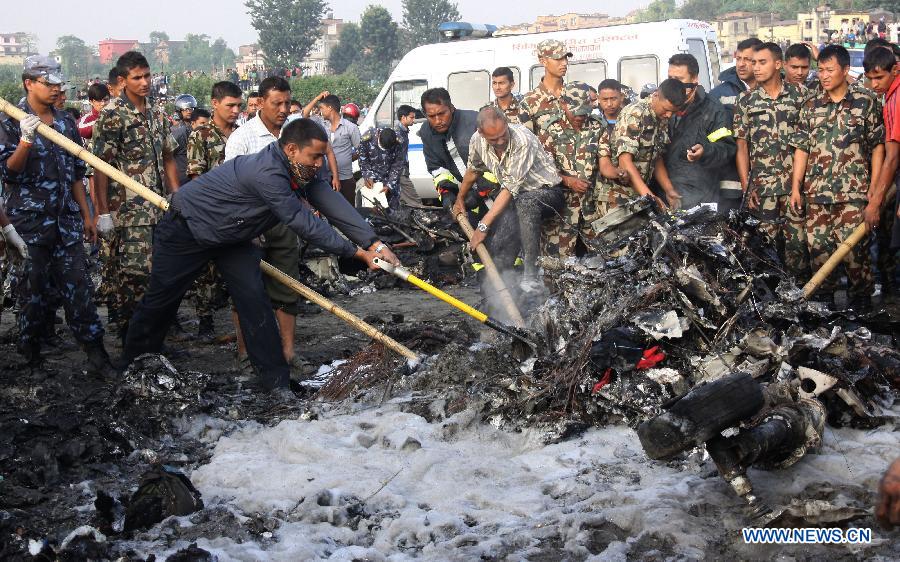
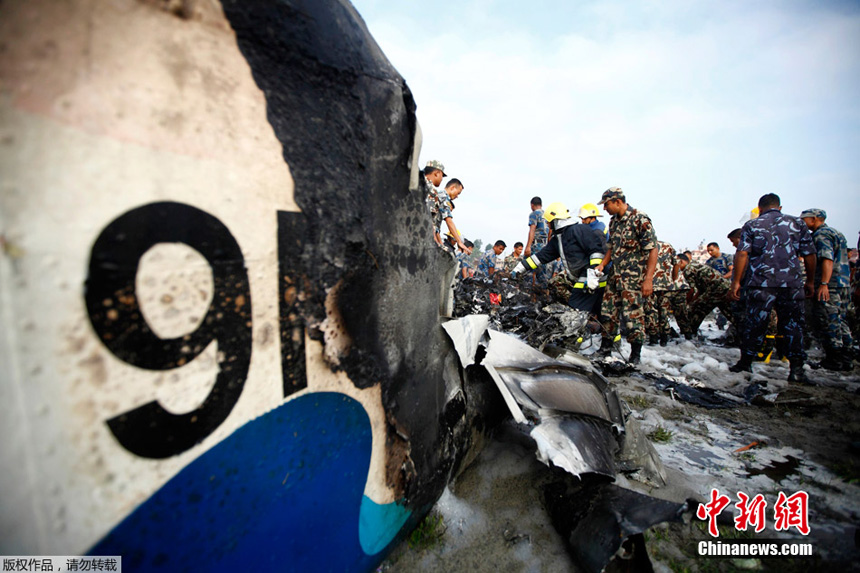
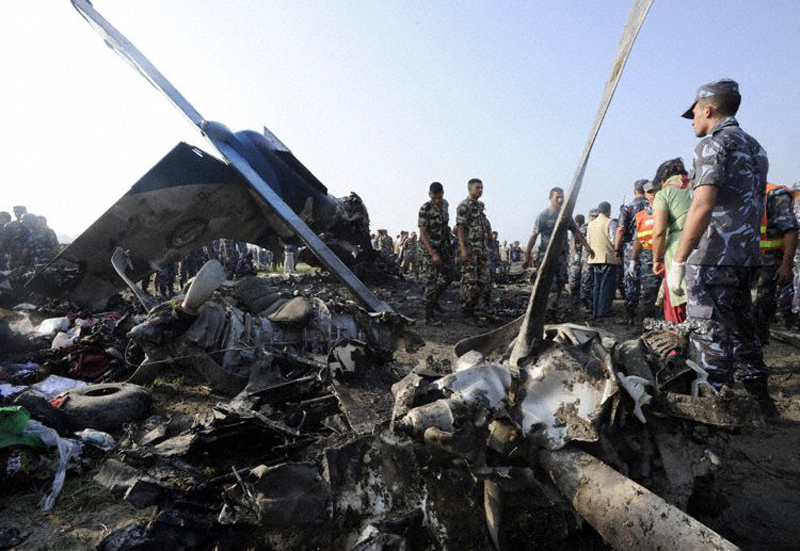
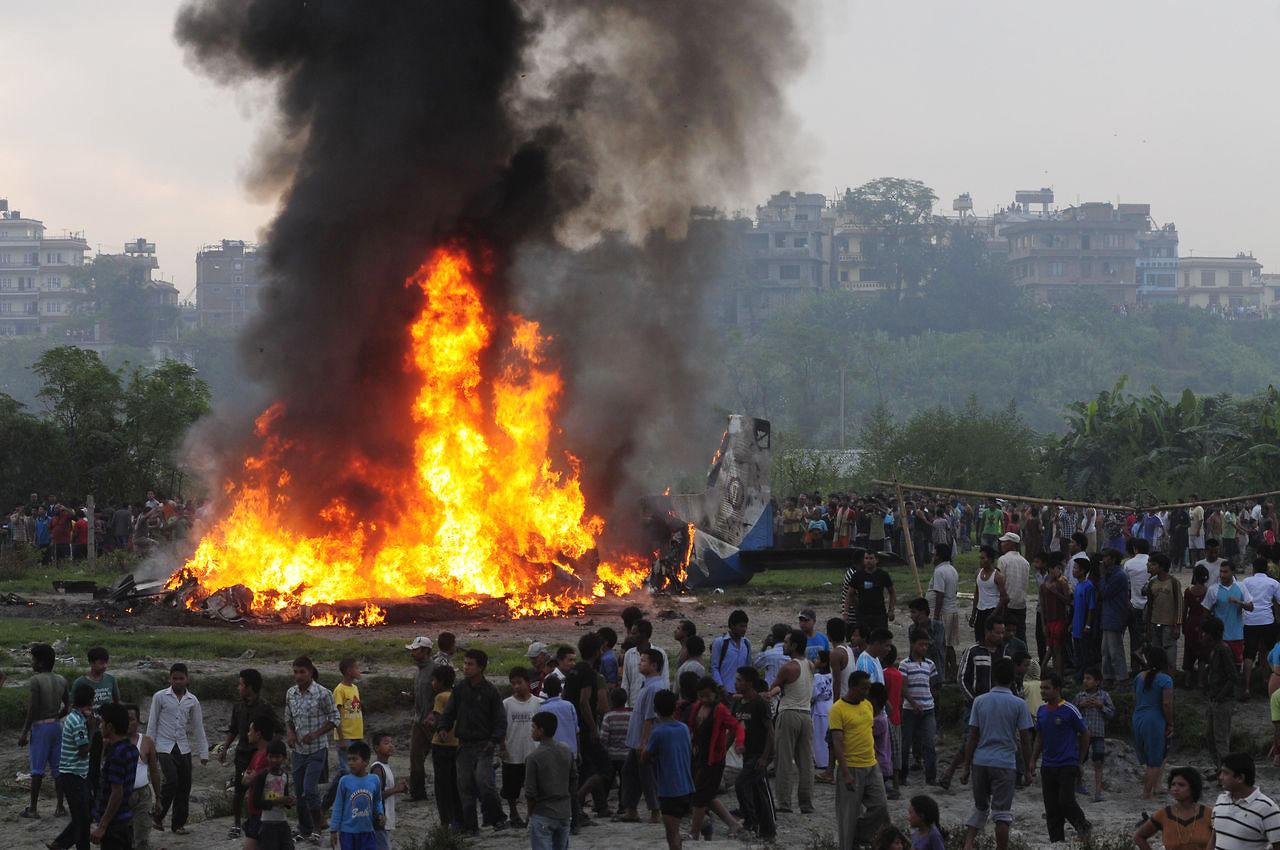
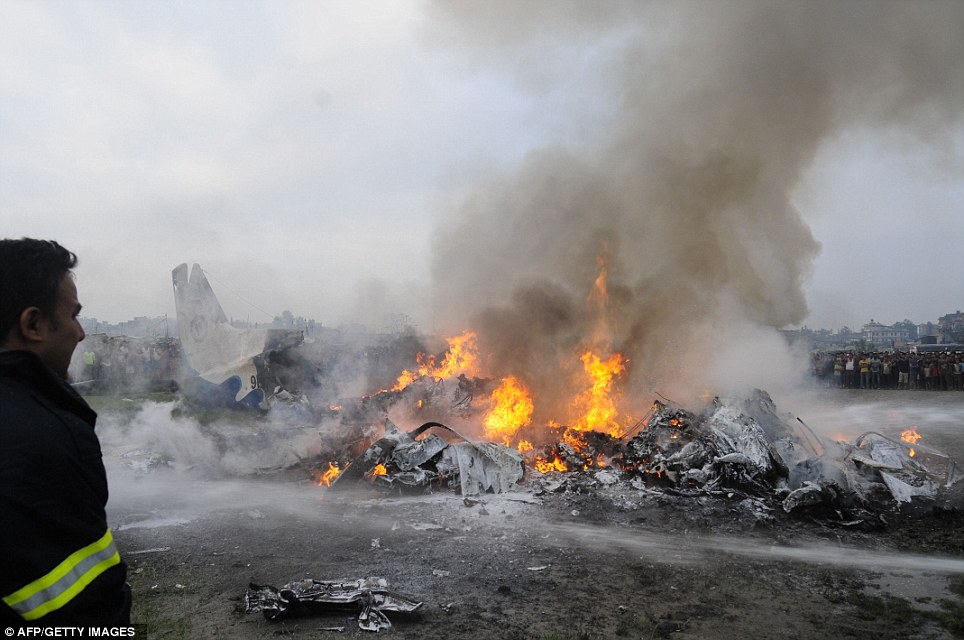
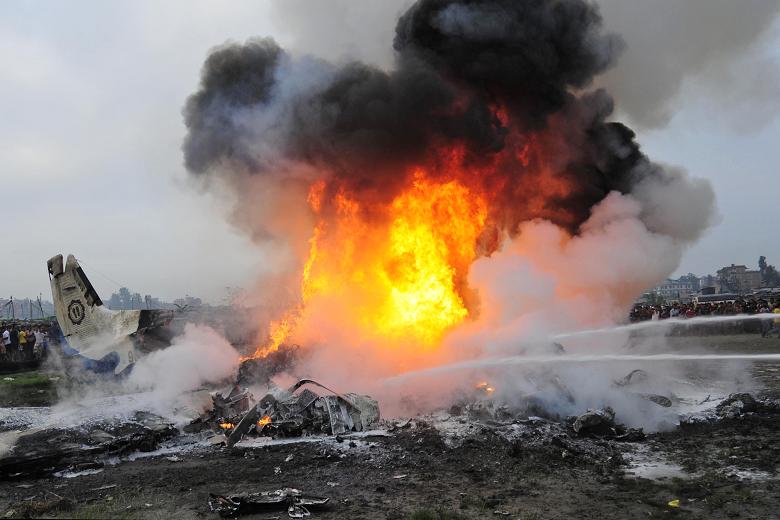
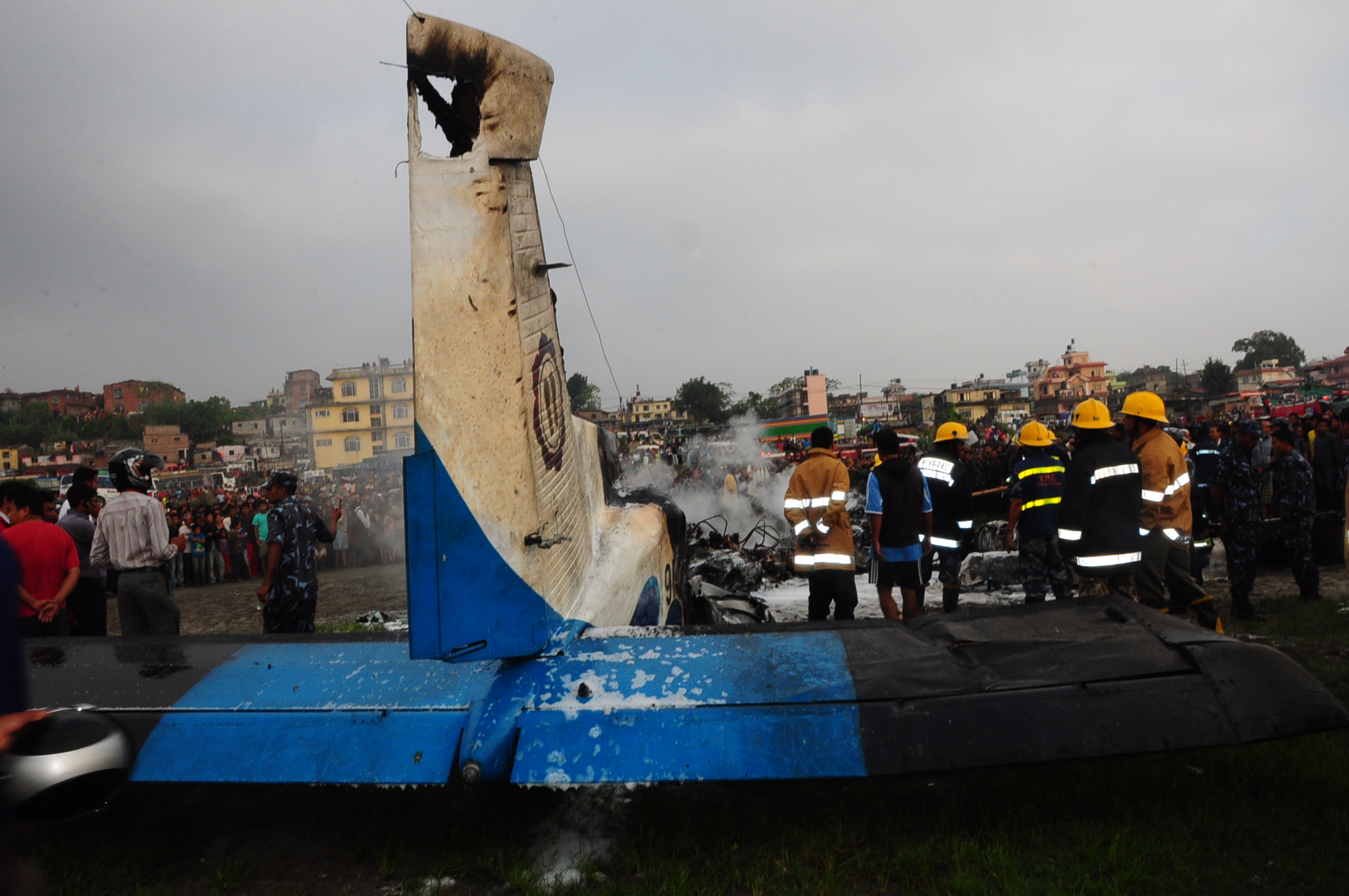
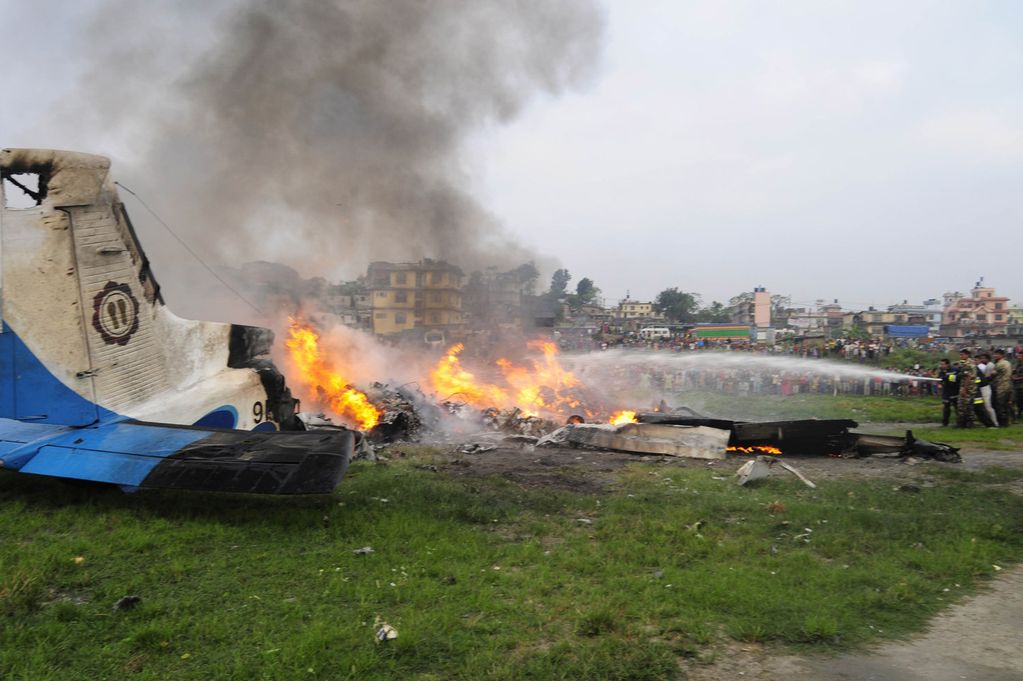
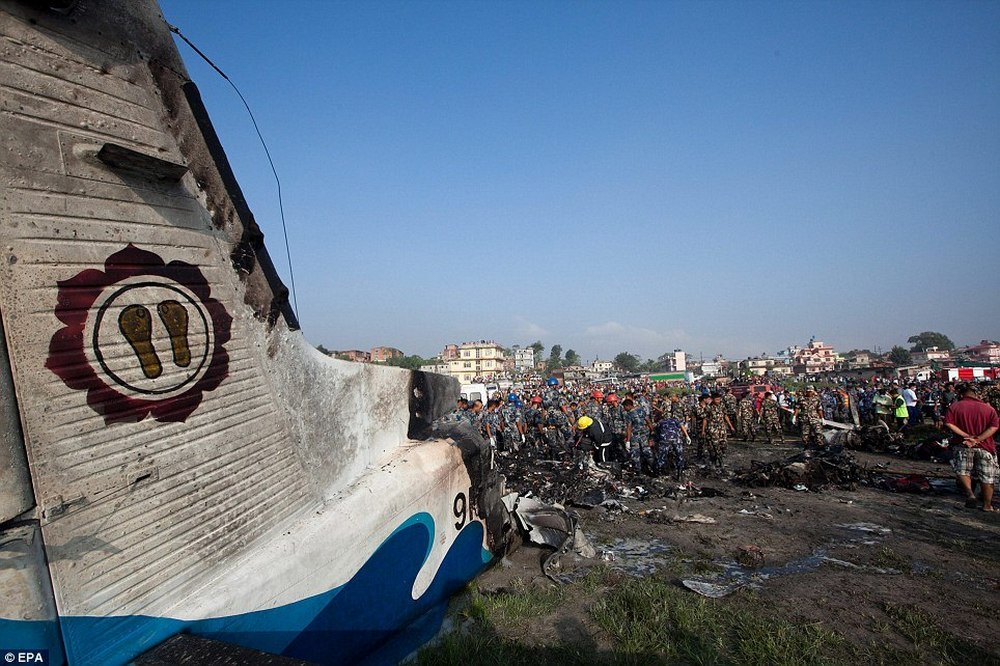
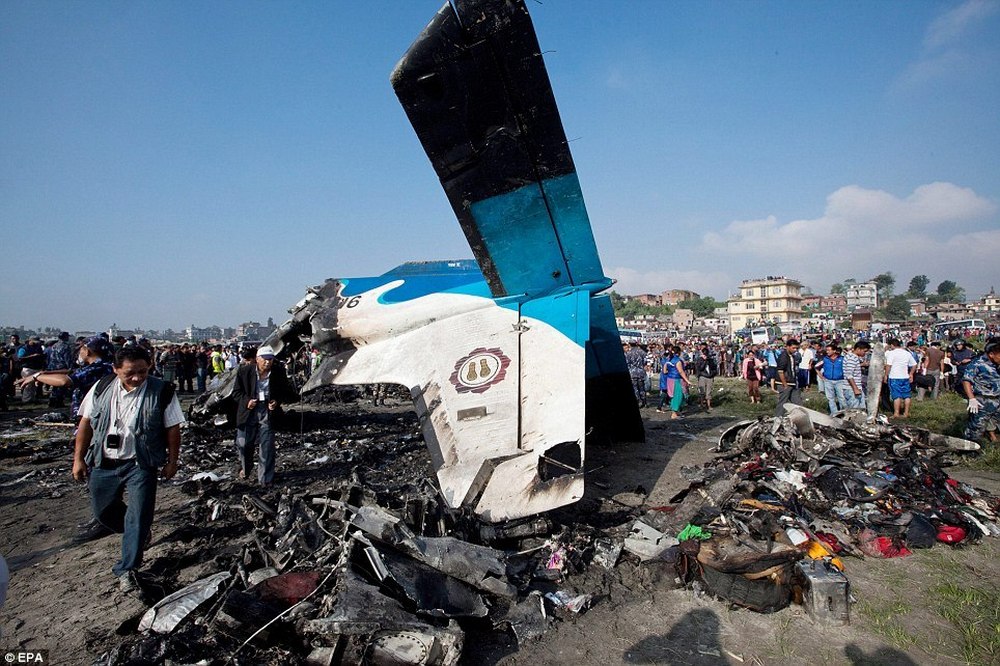
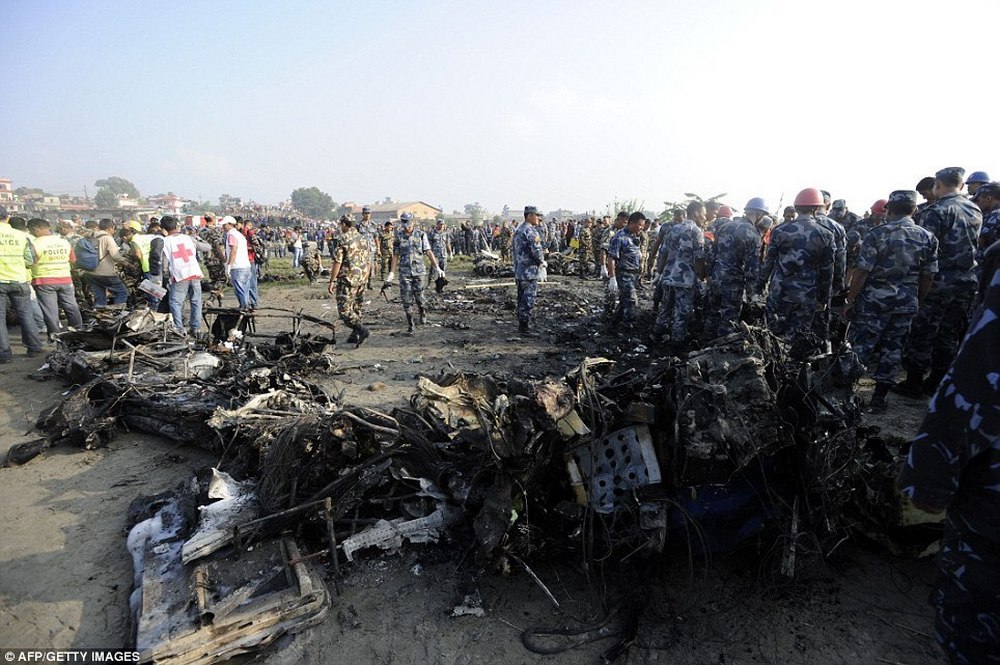
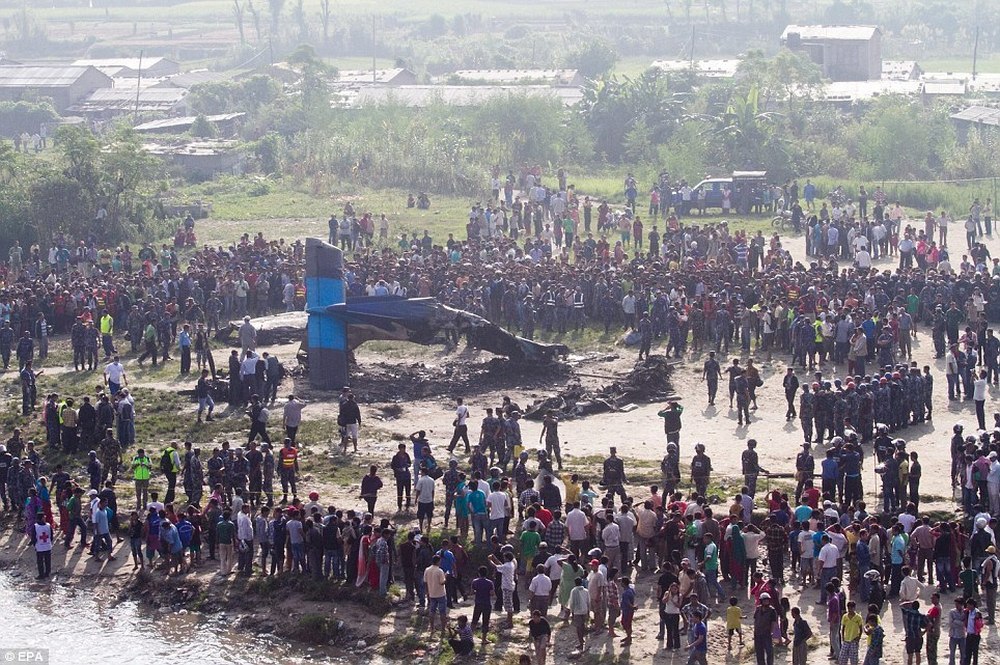
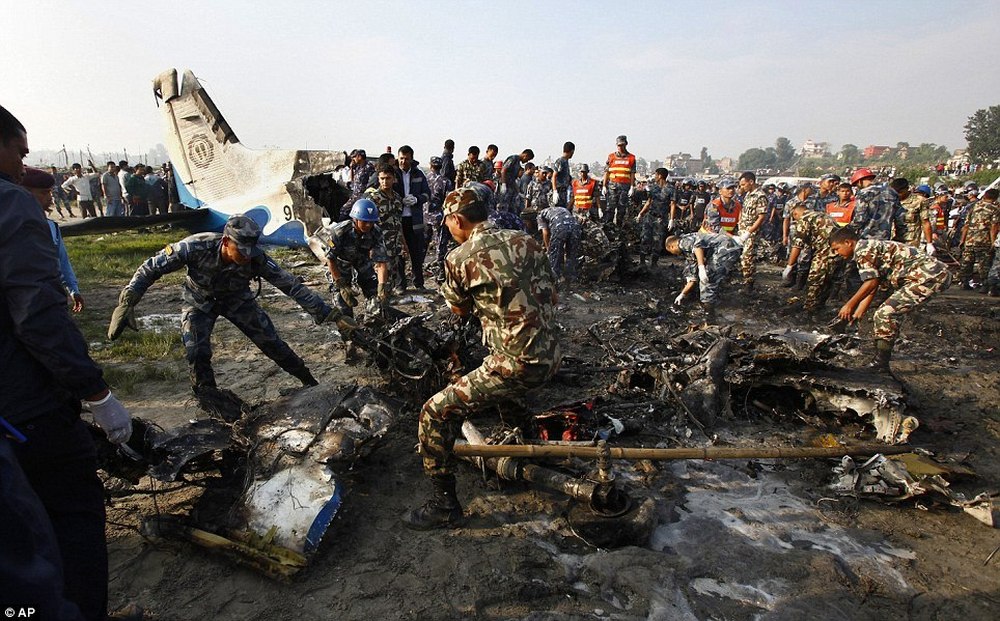
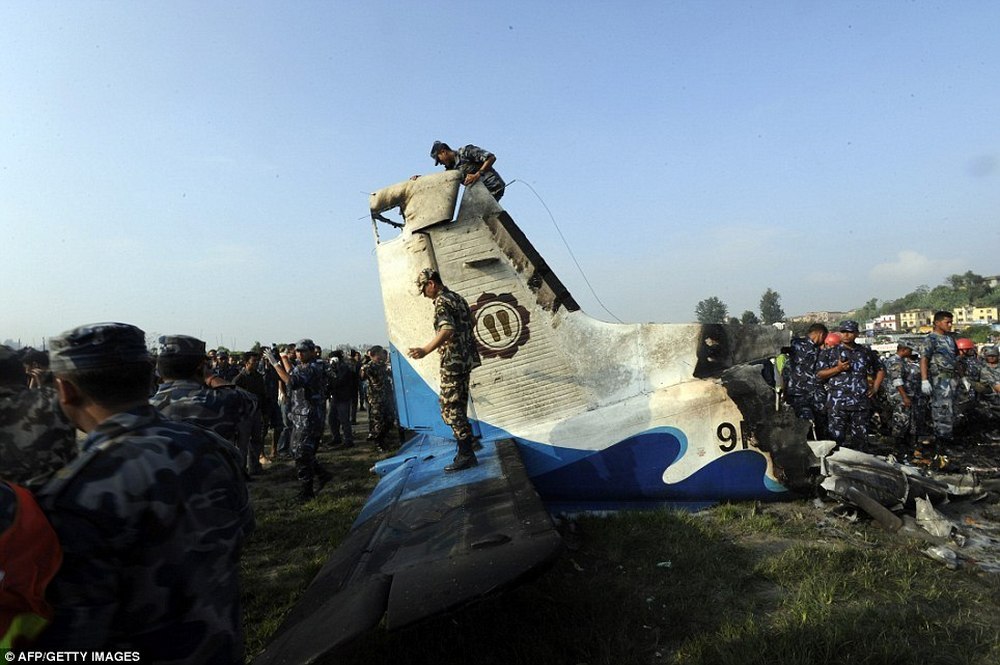
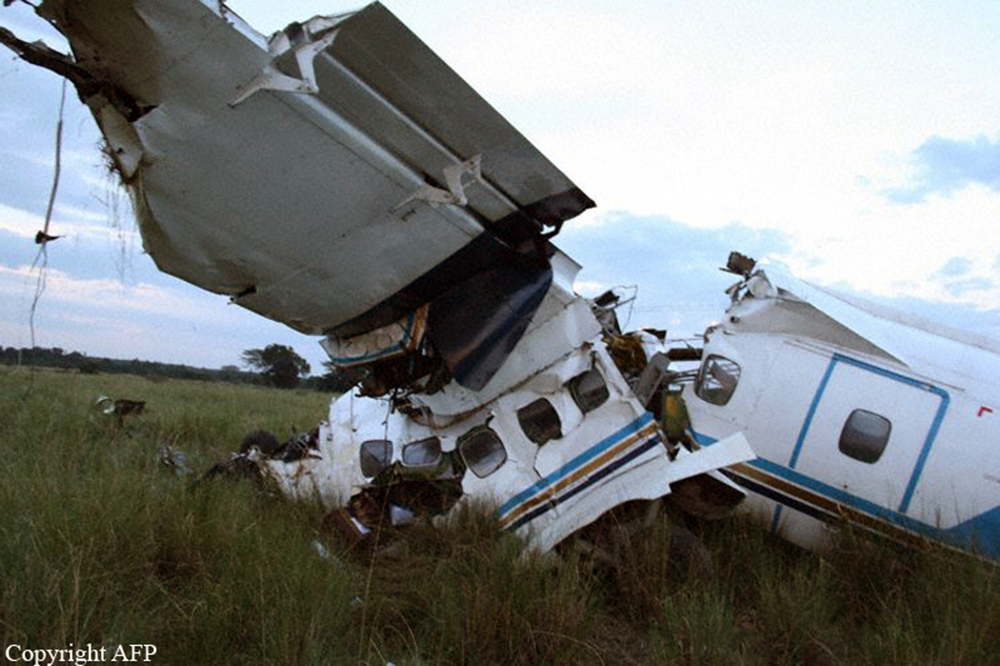
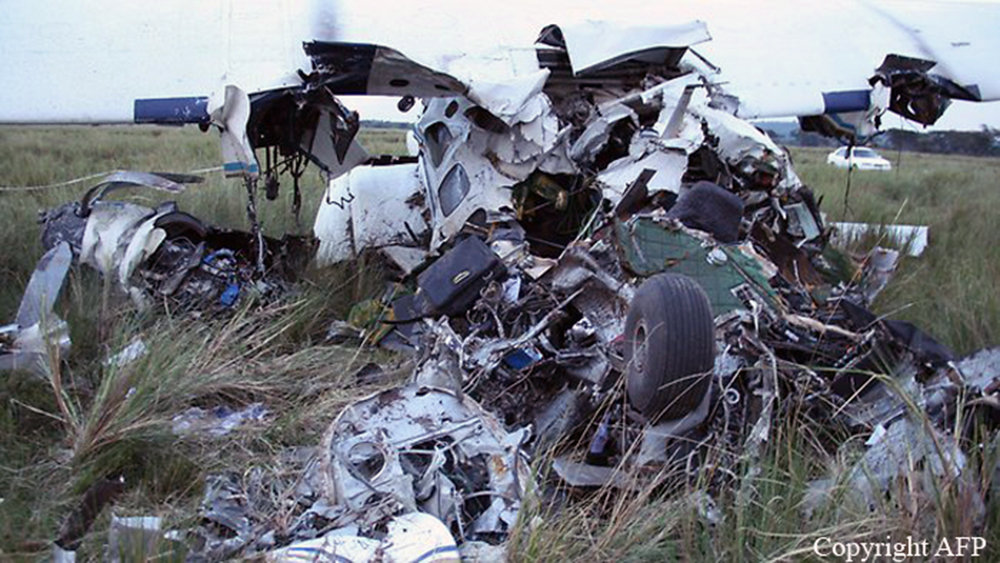
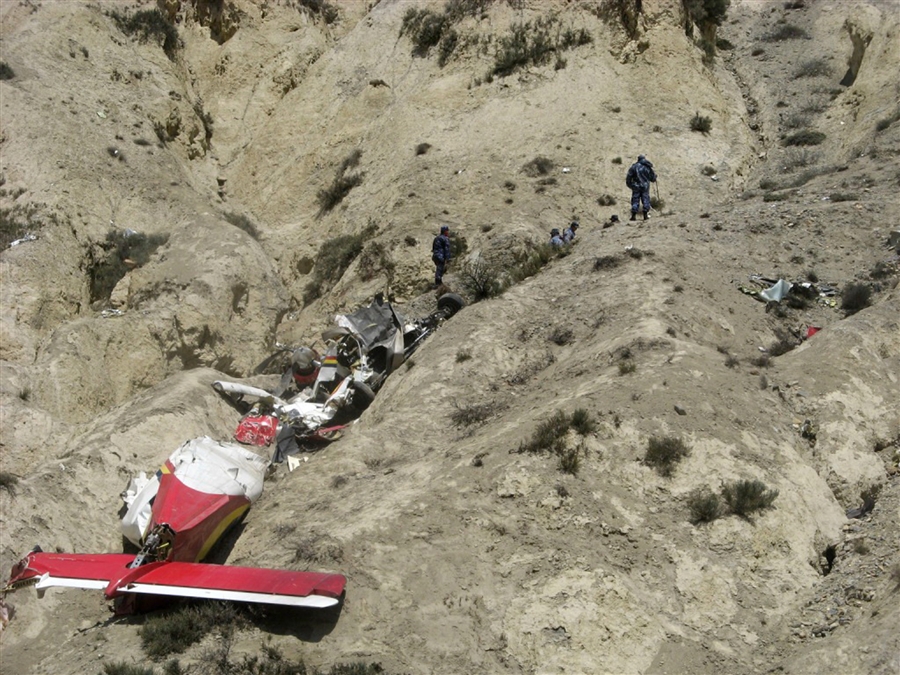
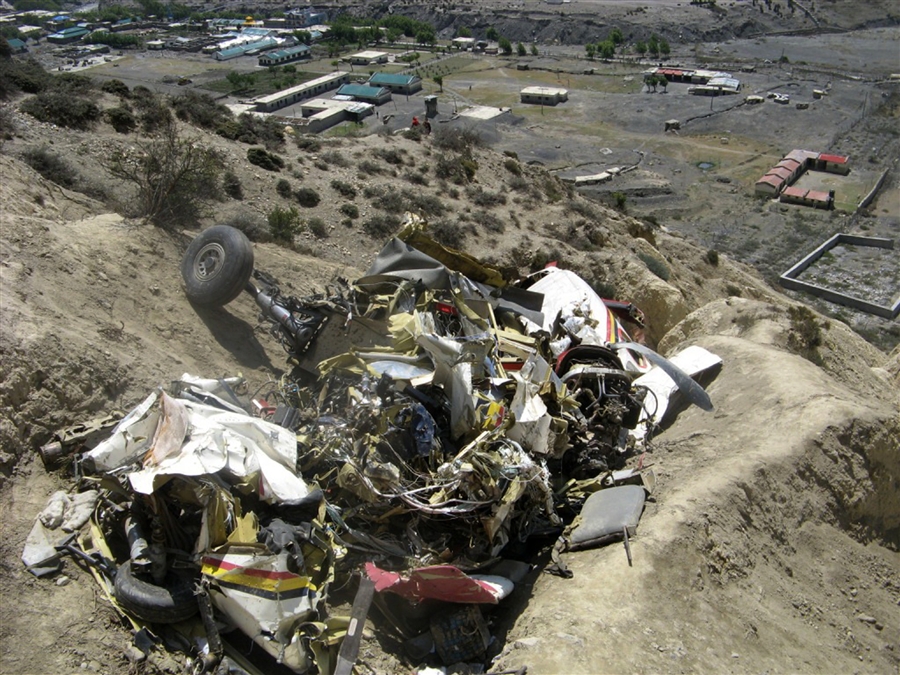
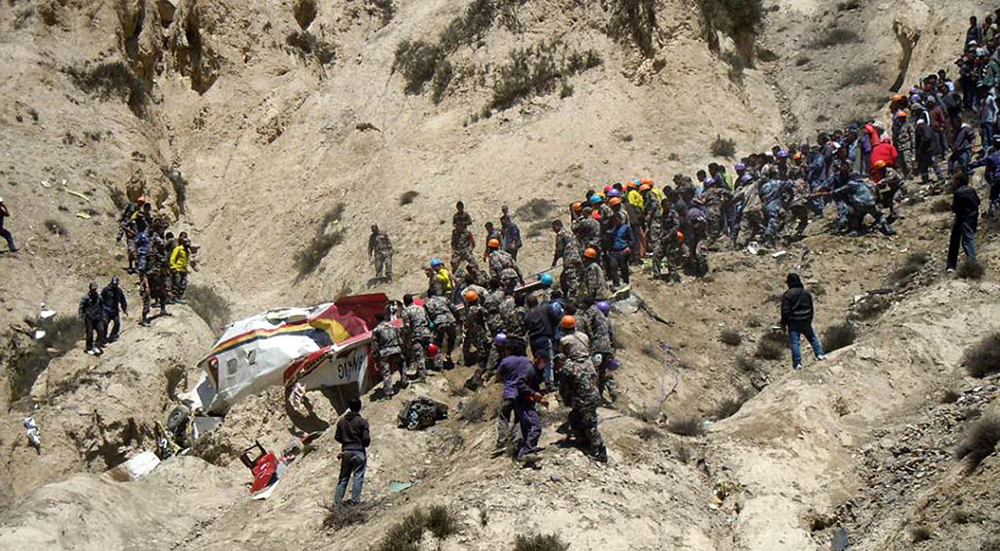
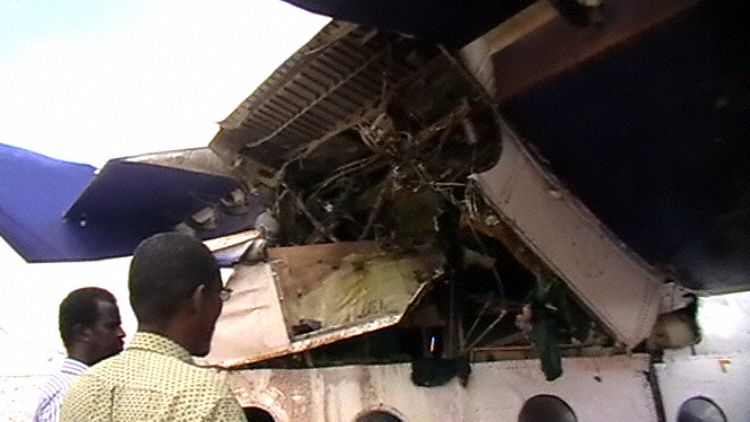
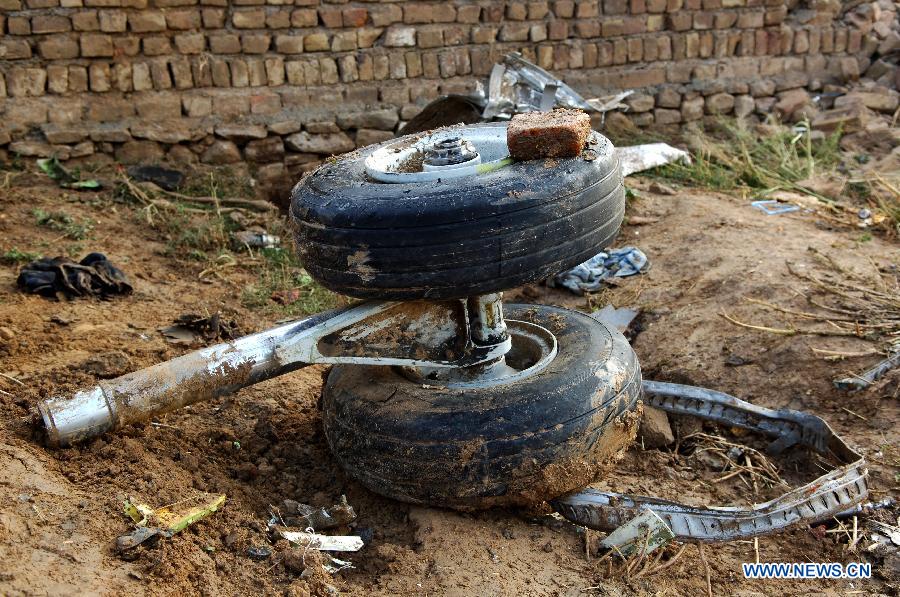
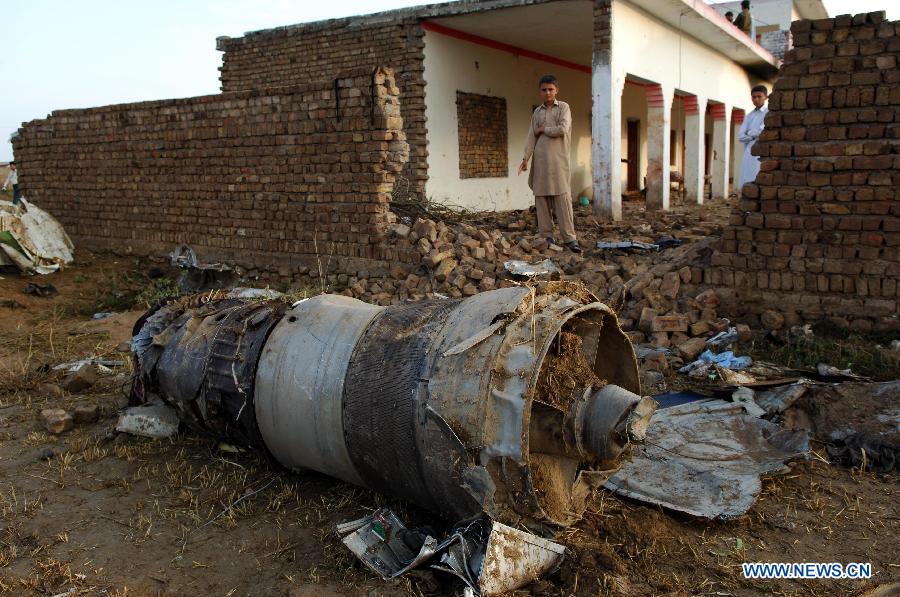
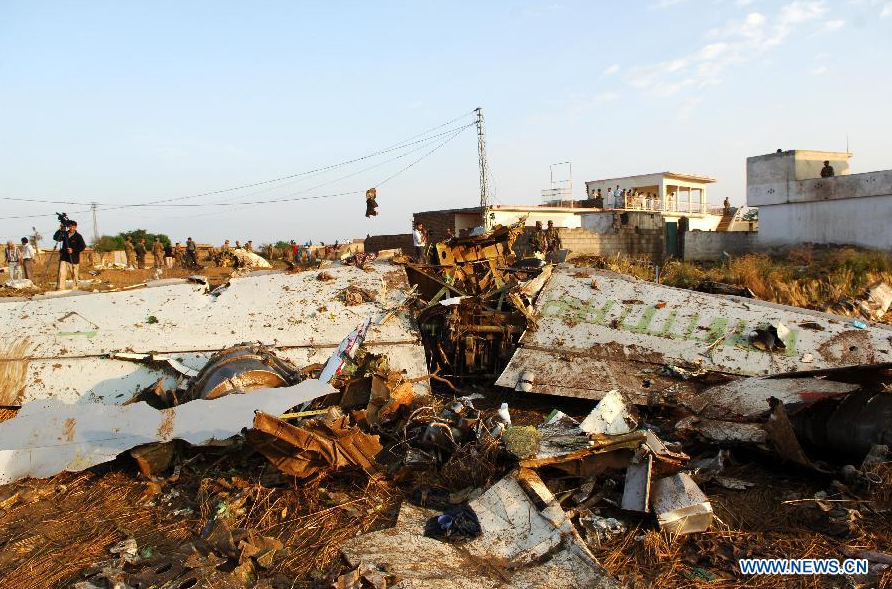
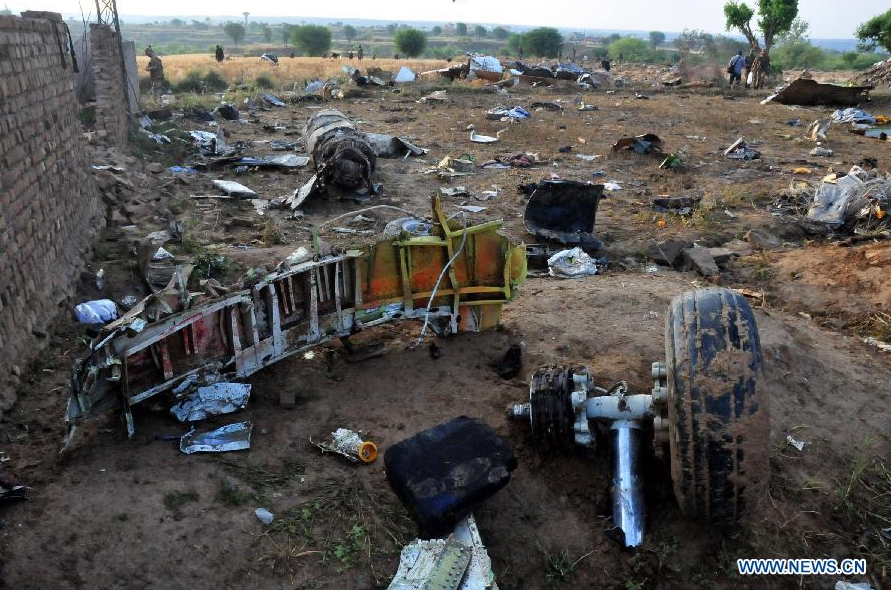
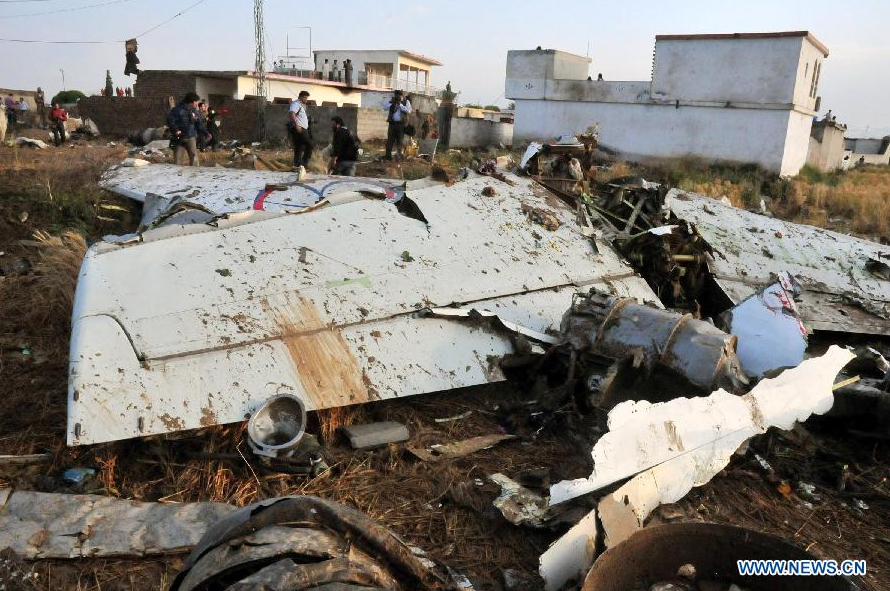
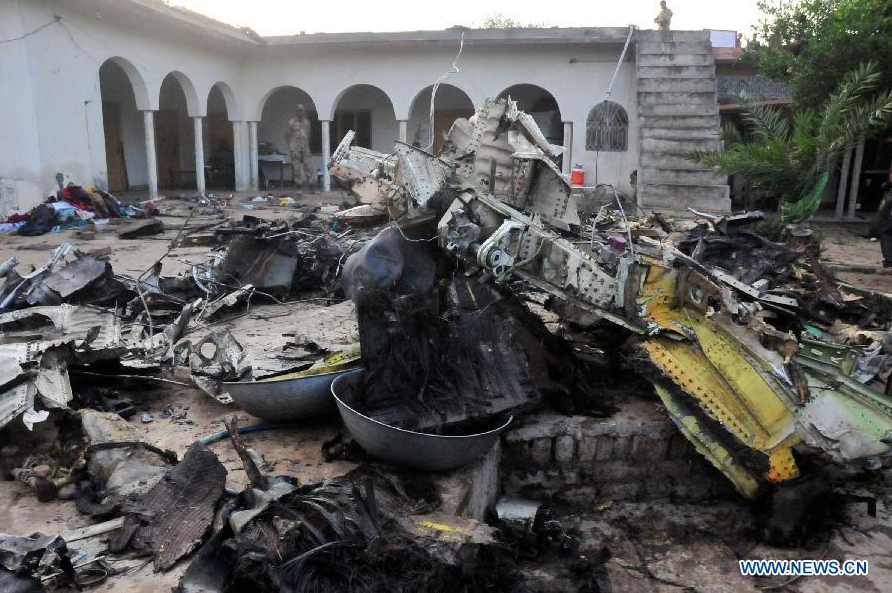
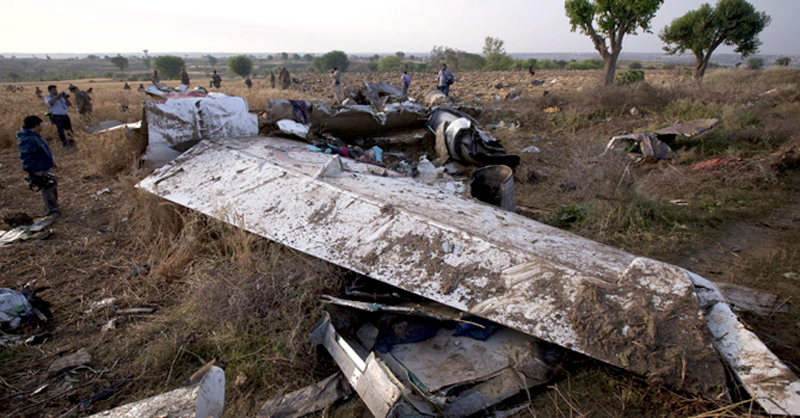
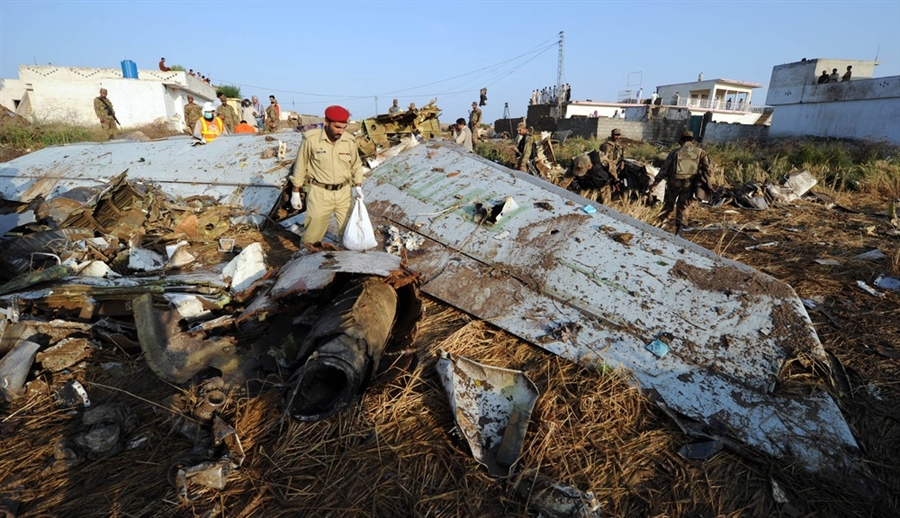
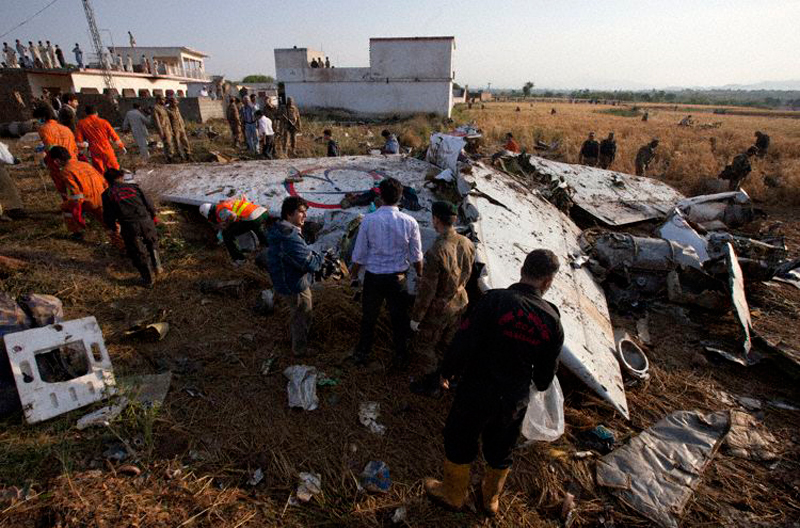
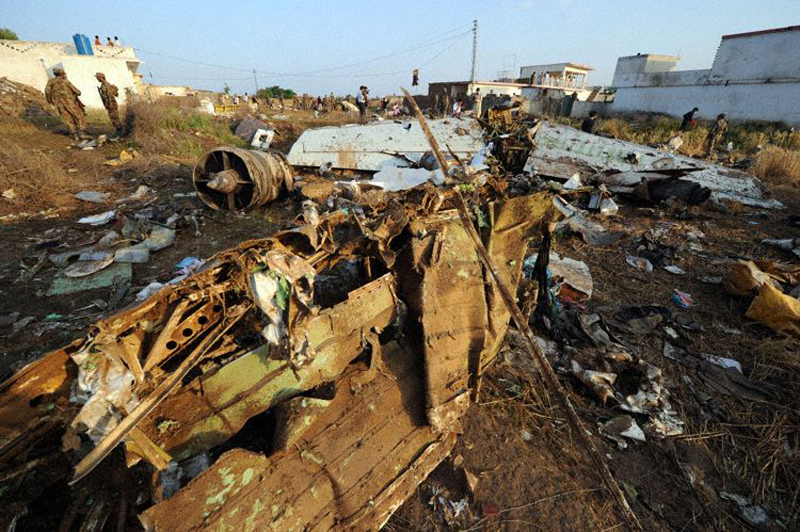
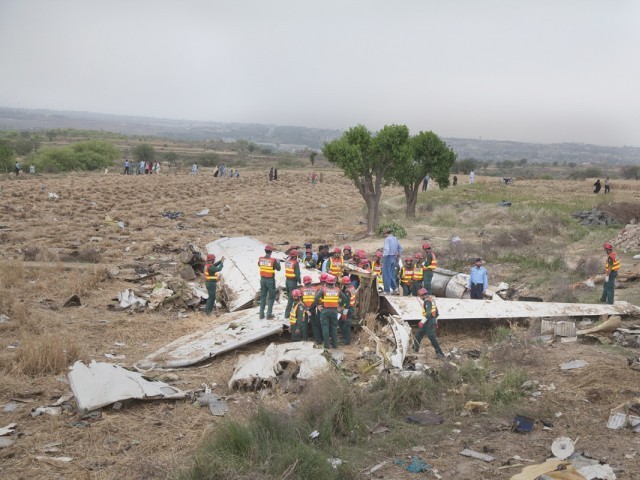
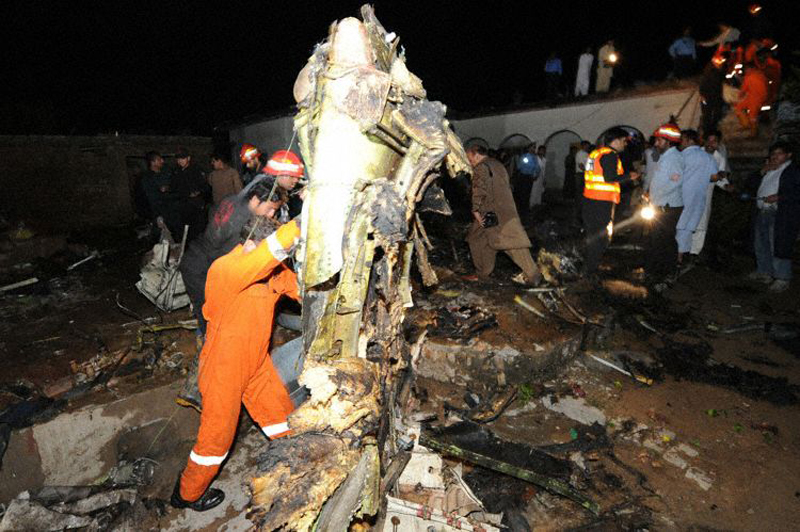
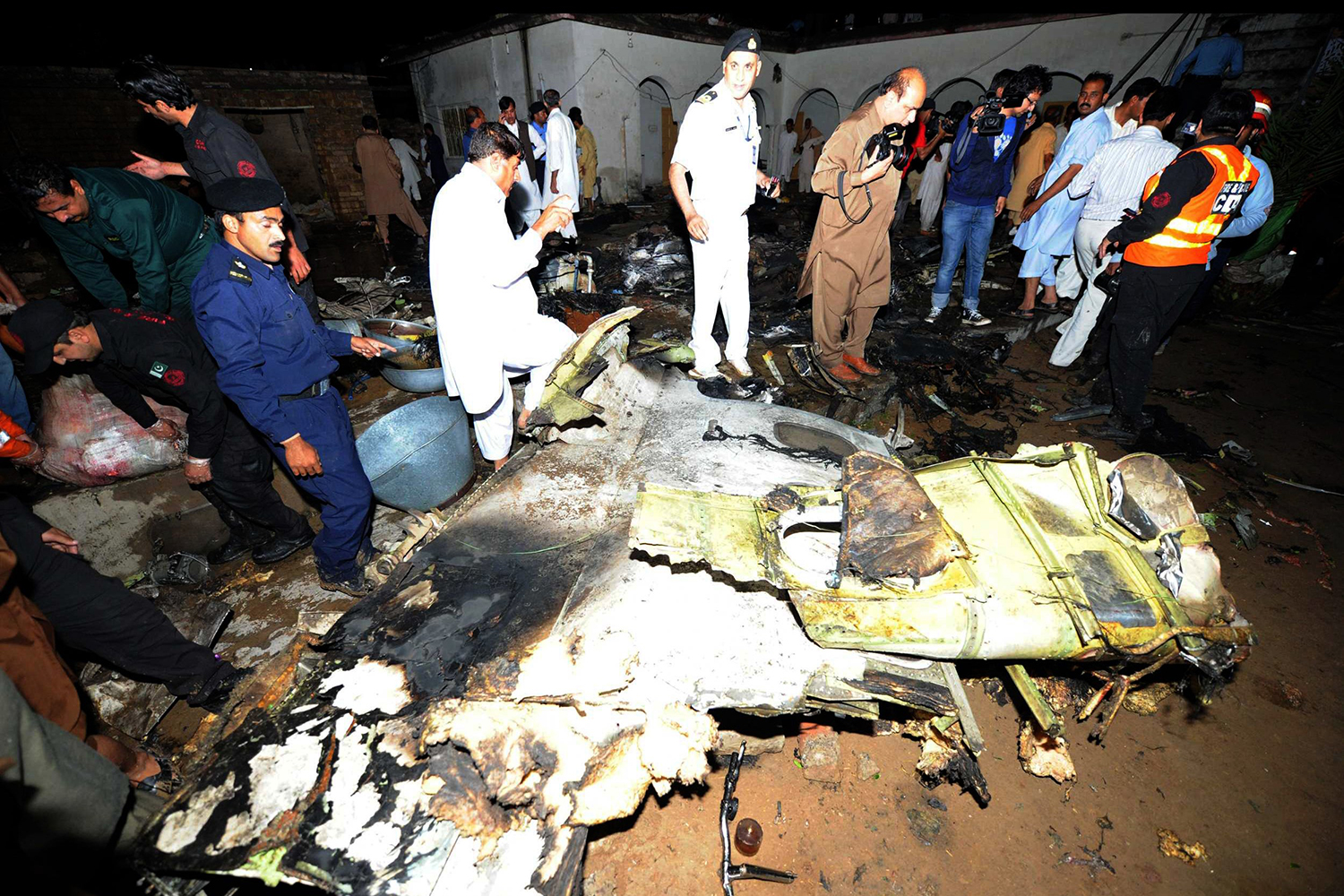
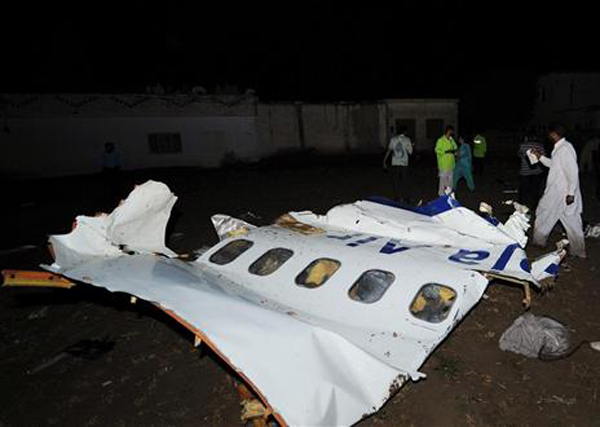
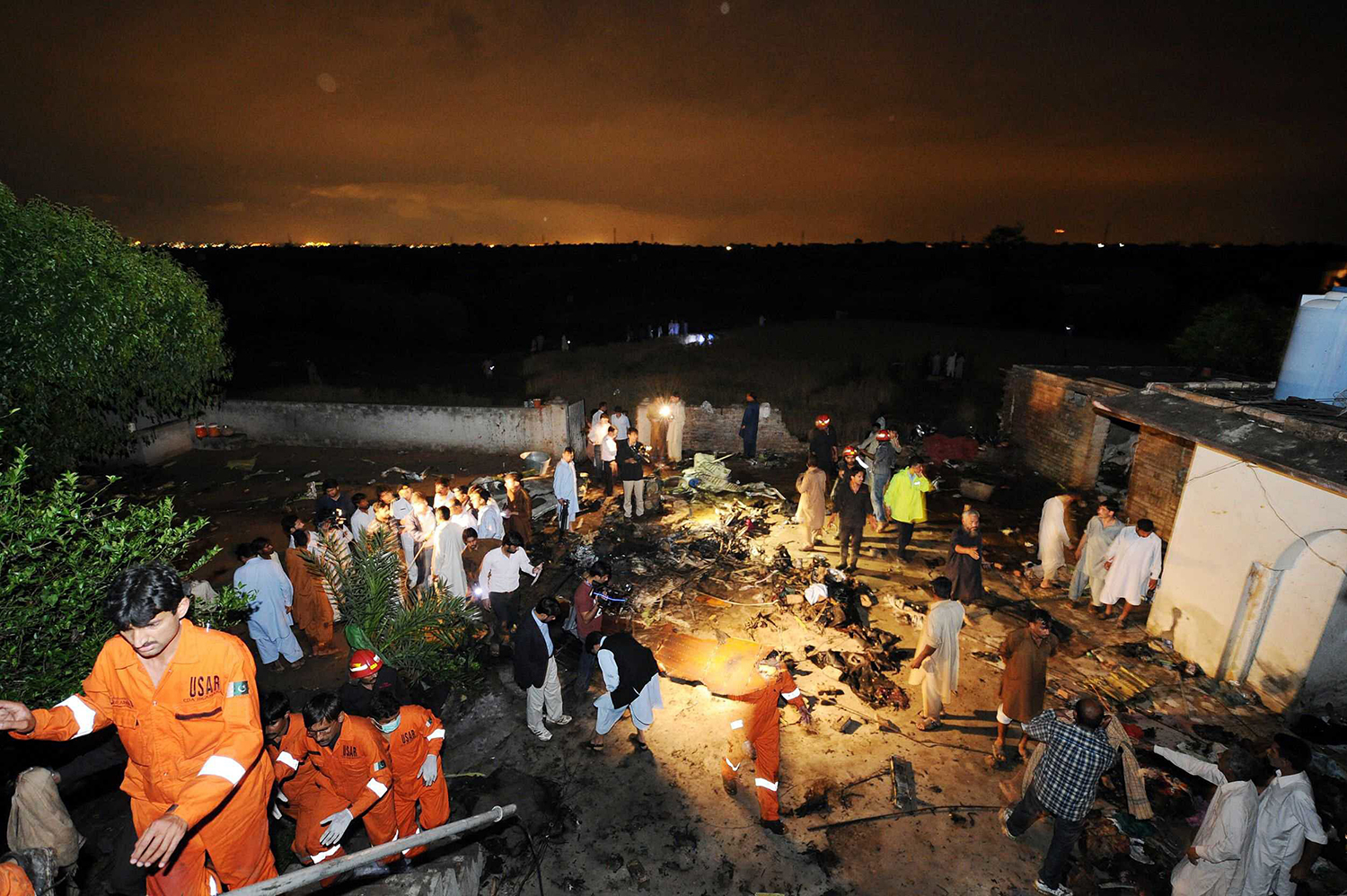
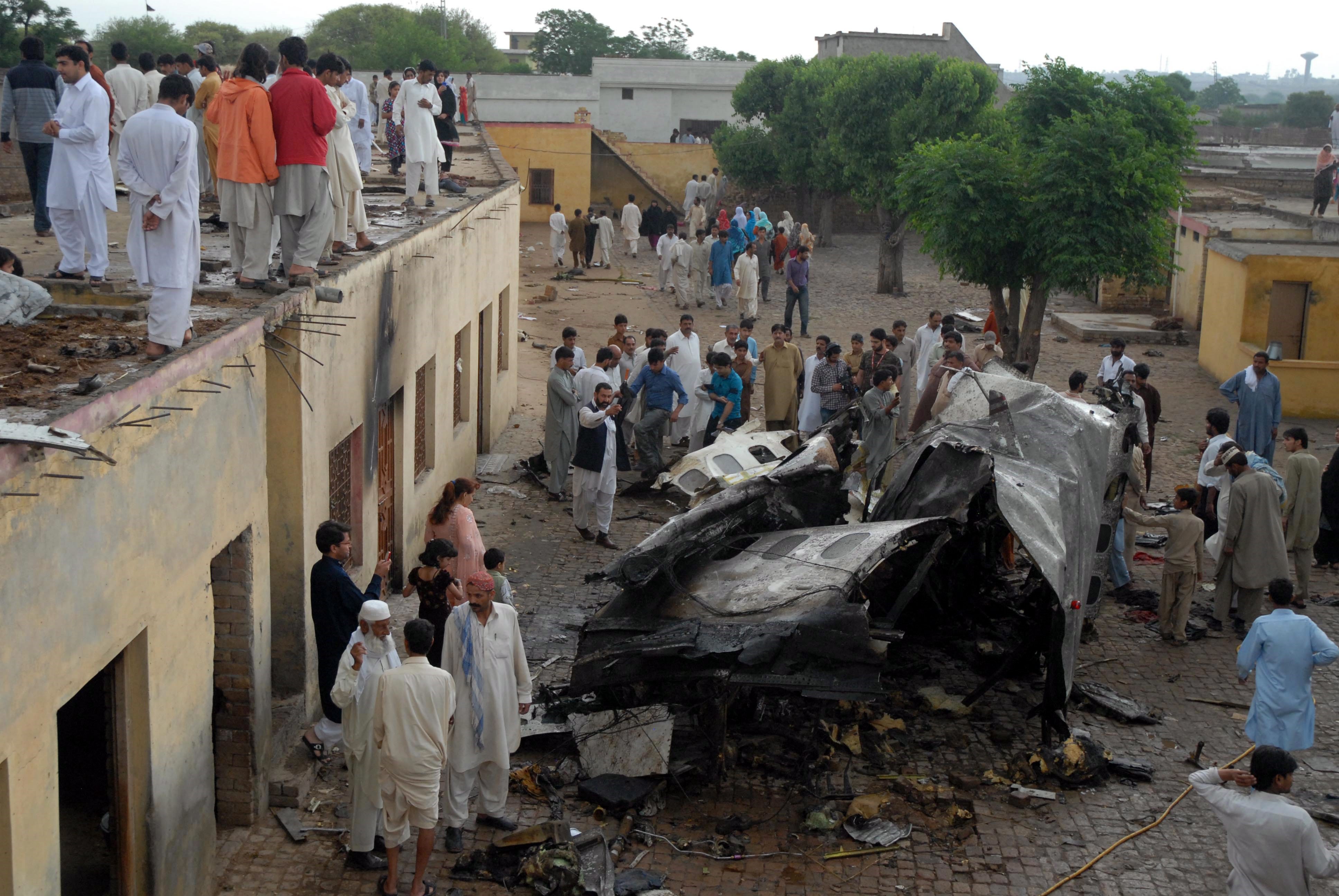
Crash of a Dornier DO228-202 in Kathmandu: 19 killed
Date & Time:
Sep 28, 2012 at 0618 LT
Registration:
9N-AHA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kathmandu - Lukla
MSN:
8123
YOM:
1987
Flight number:
SIT601
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
16
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
19
Captain / Total hours on type:
7112.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
519
Circumstances:
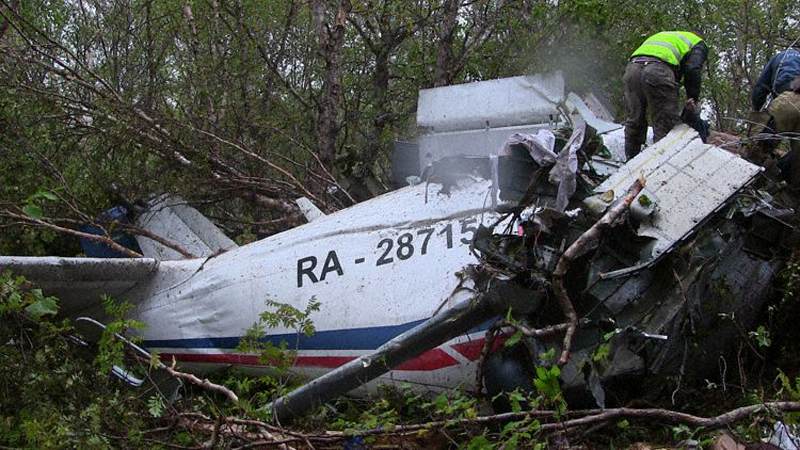
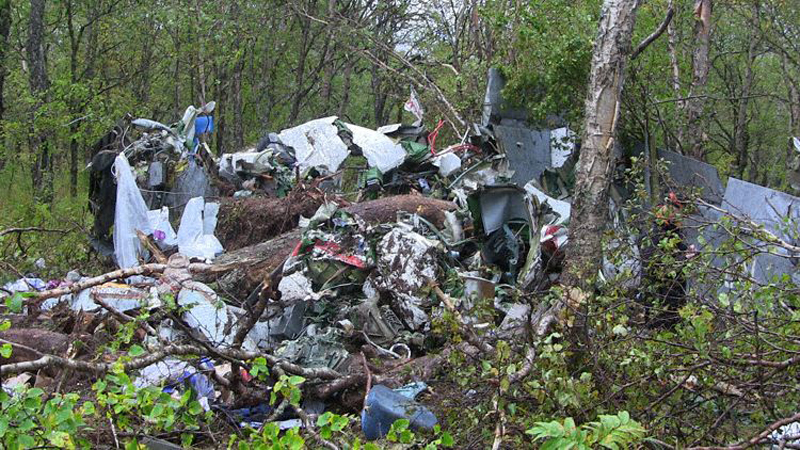
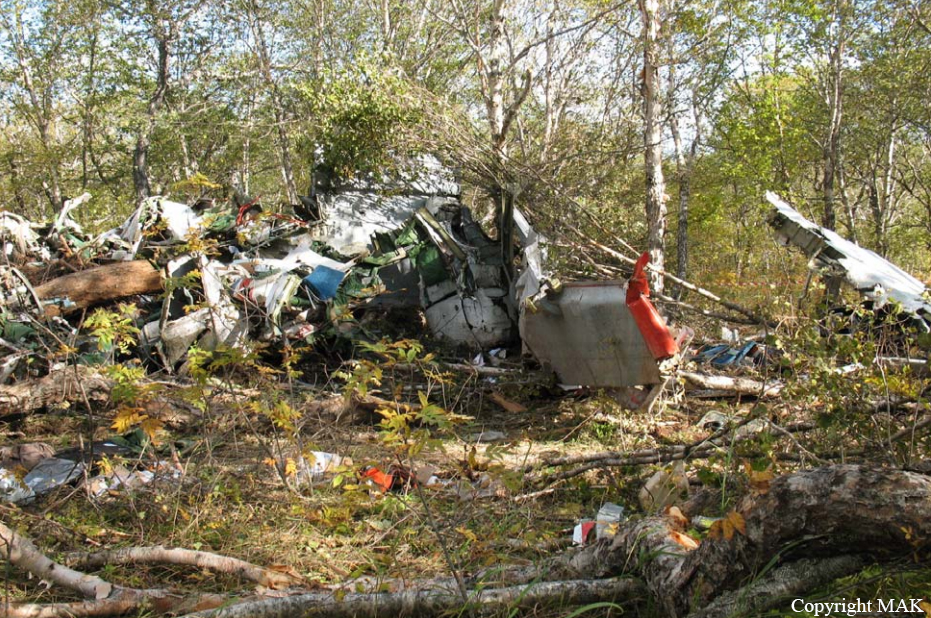
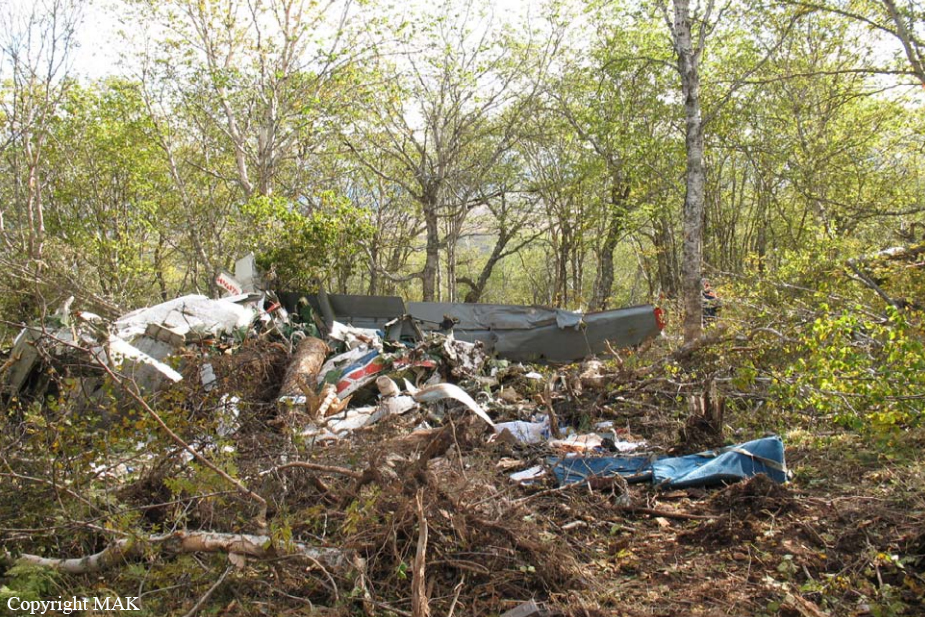
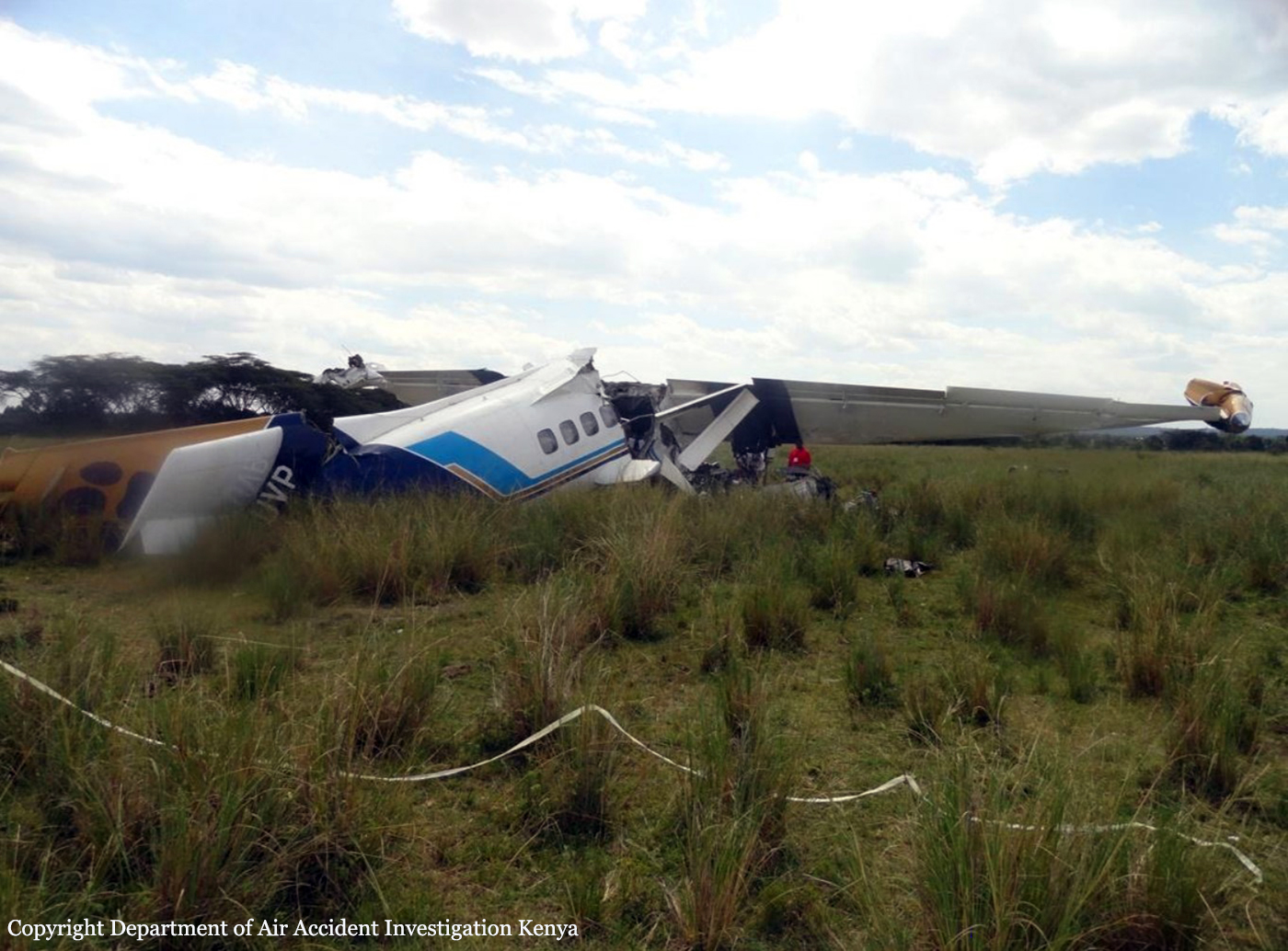
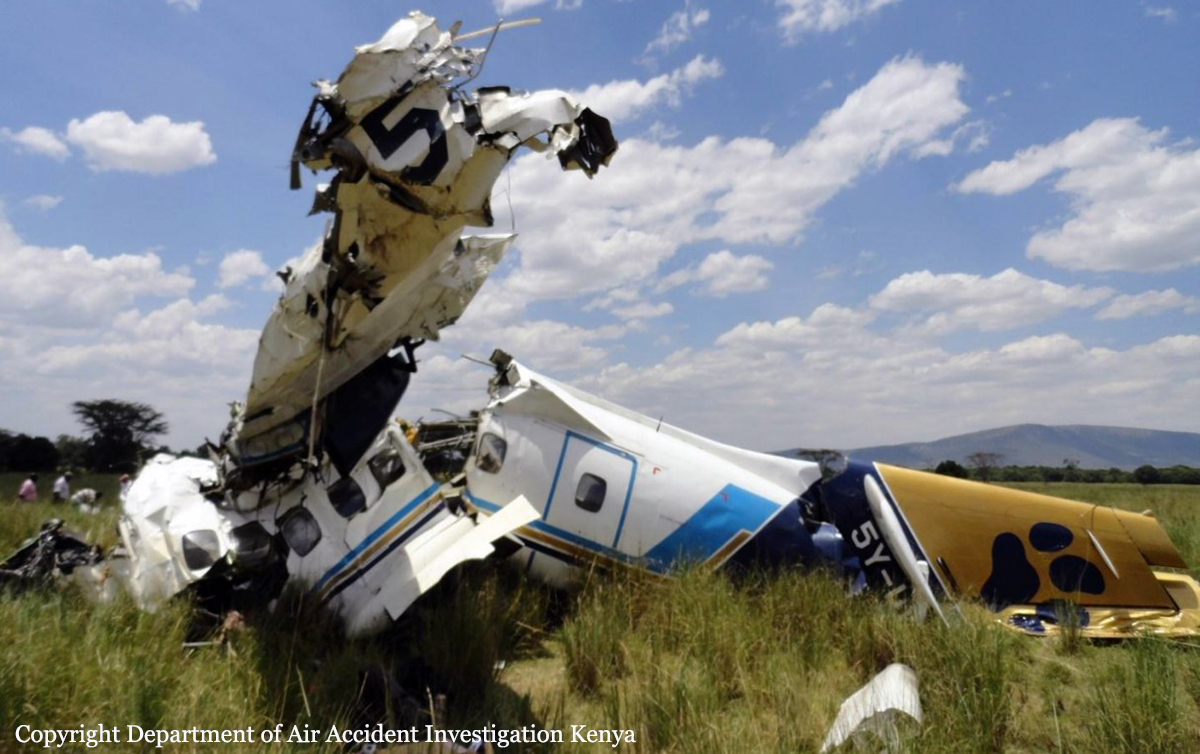
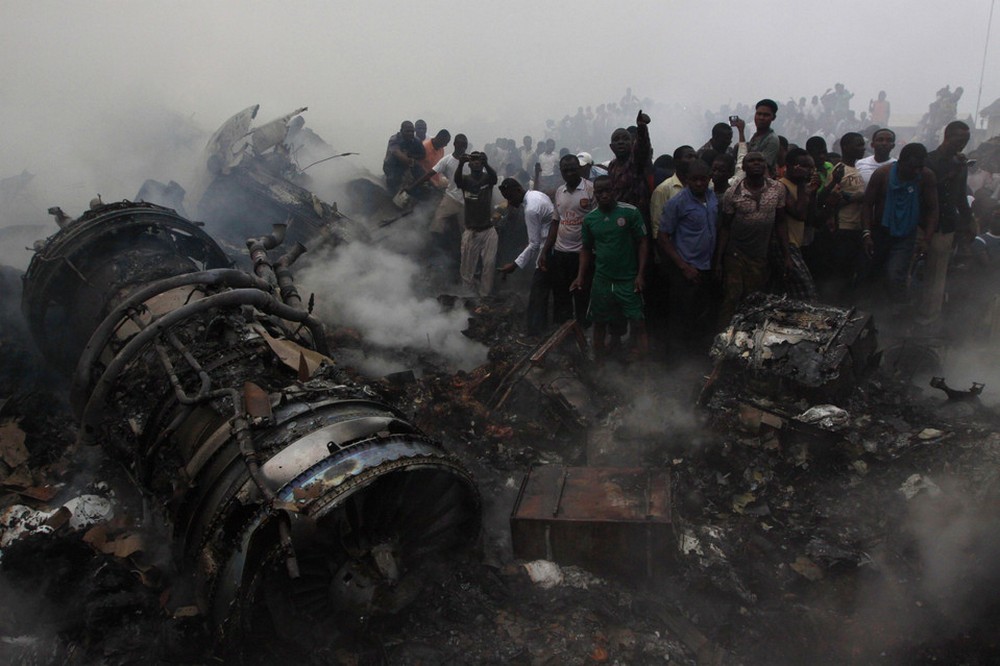
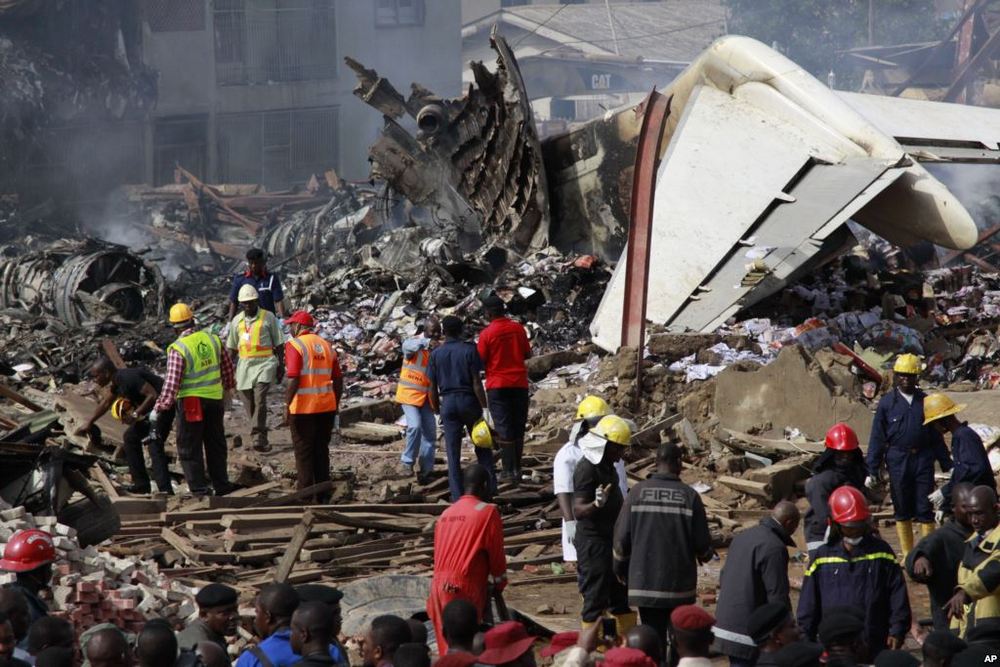
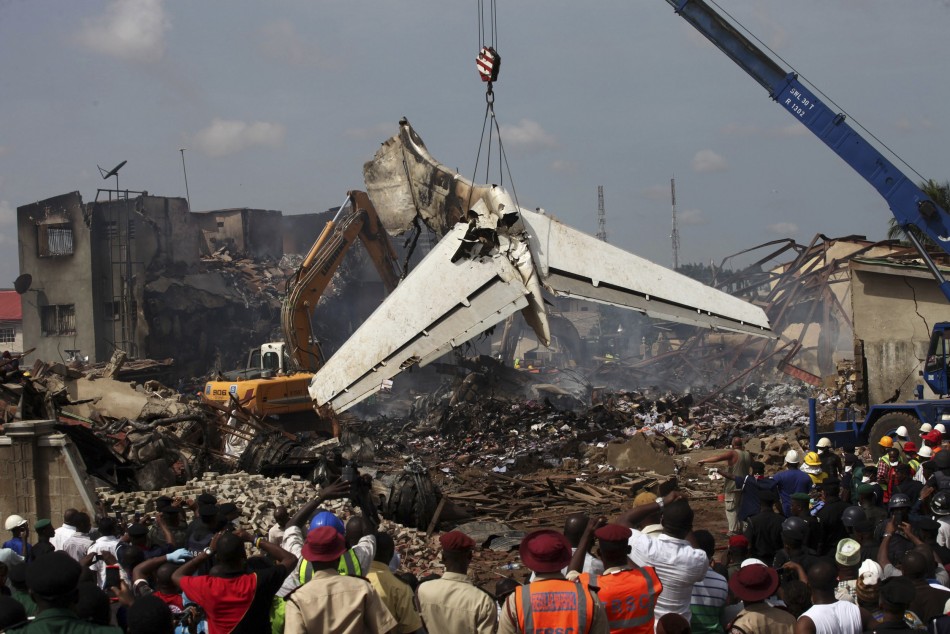
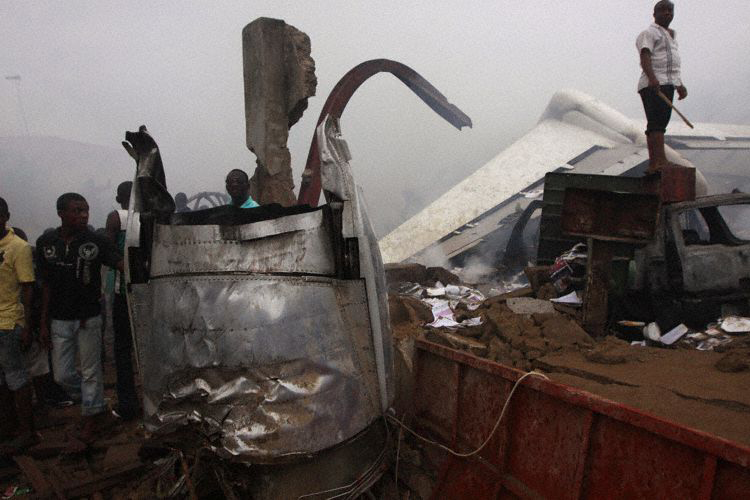
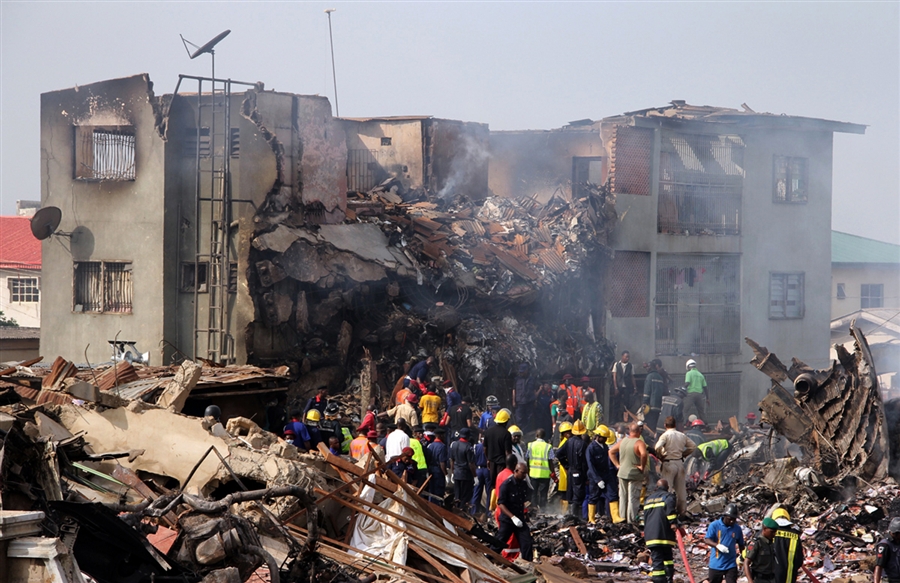
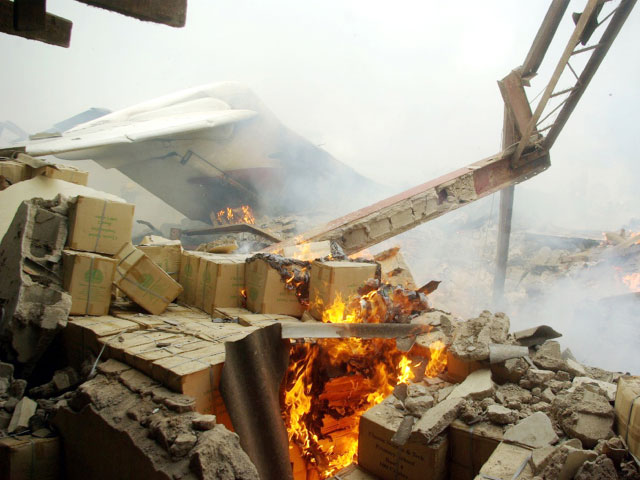
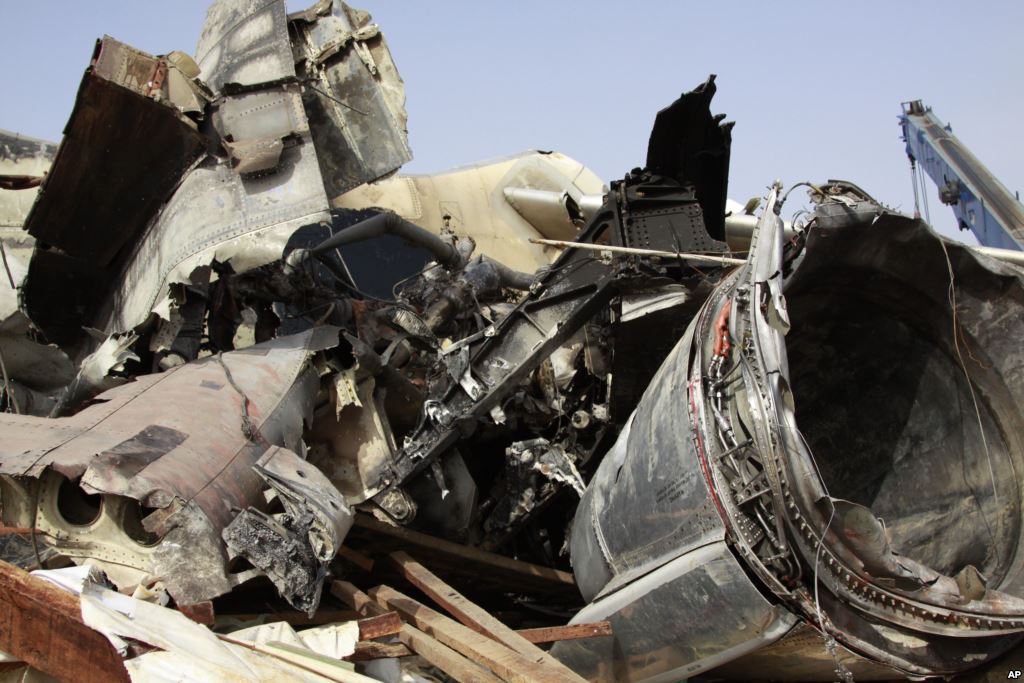
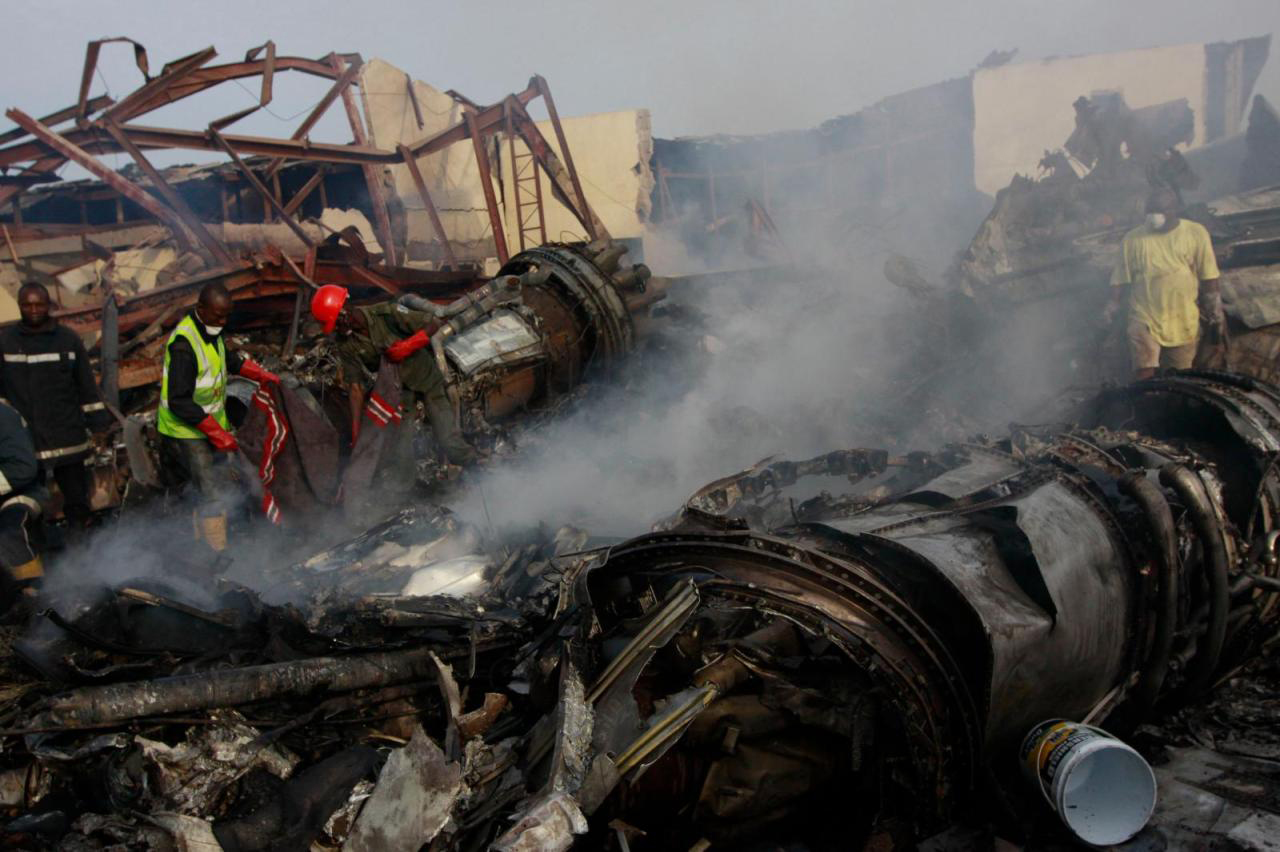
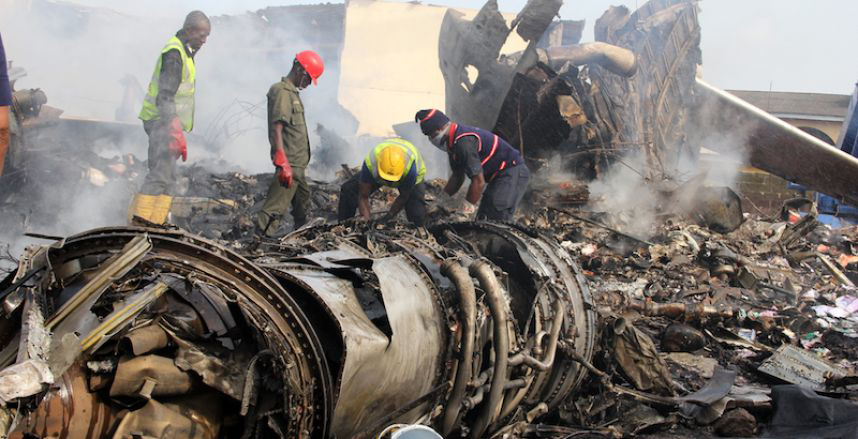
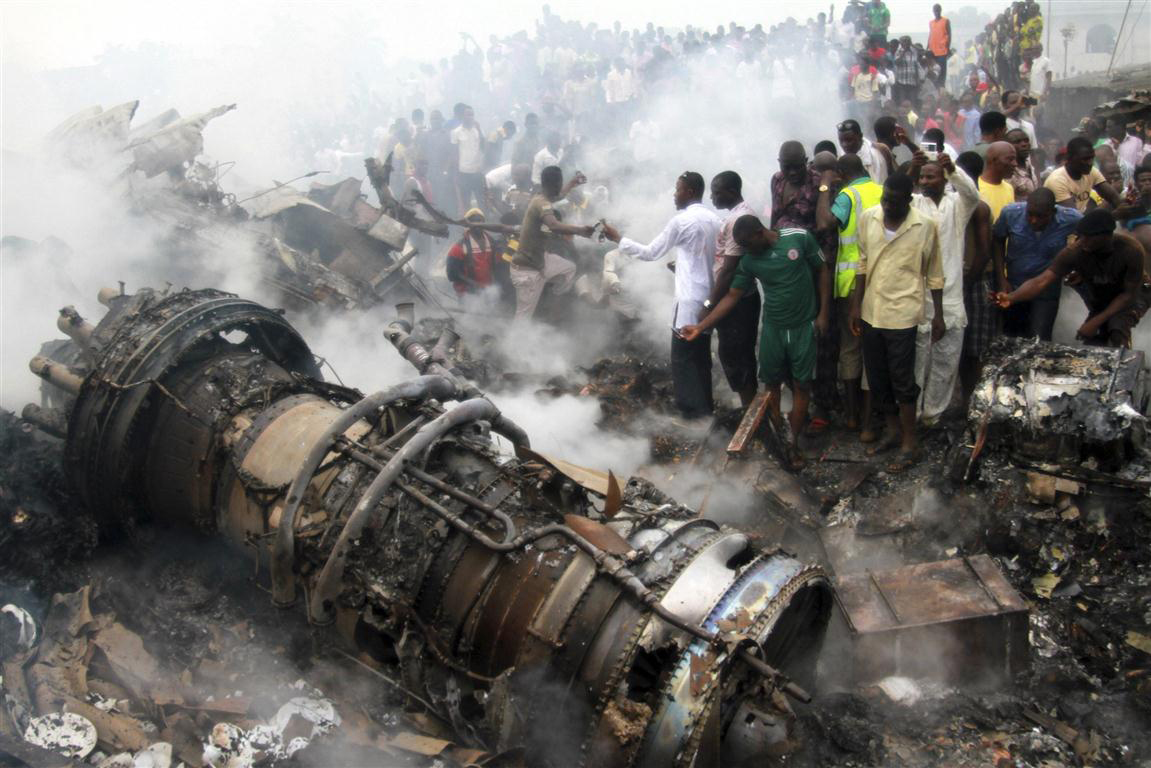
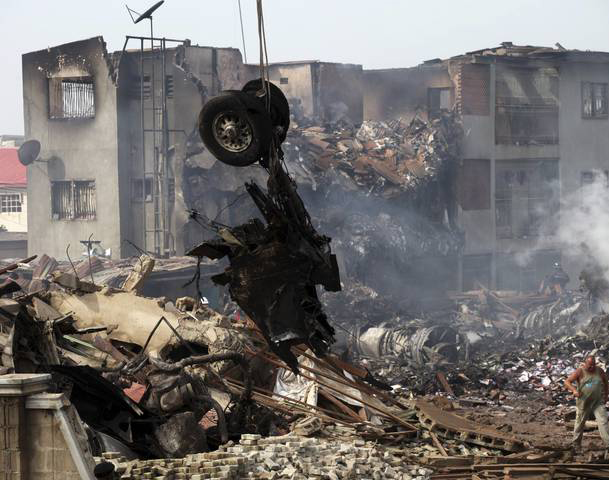
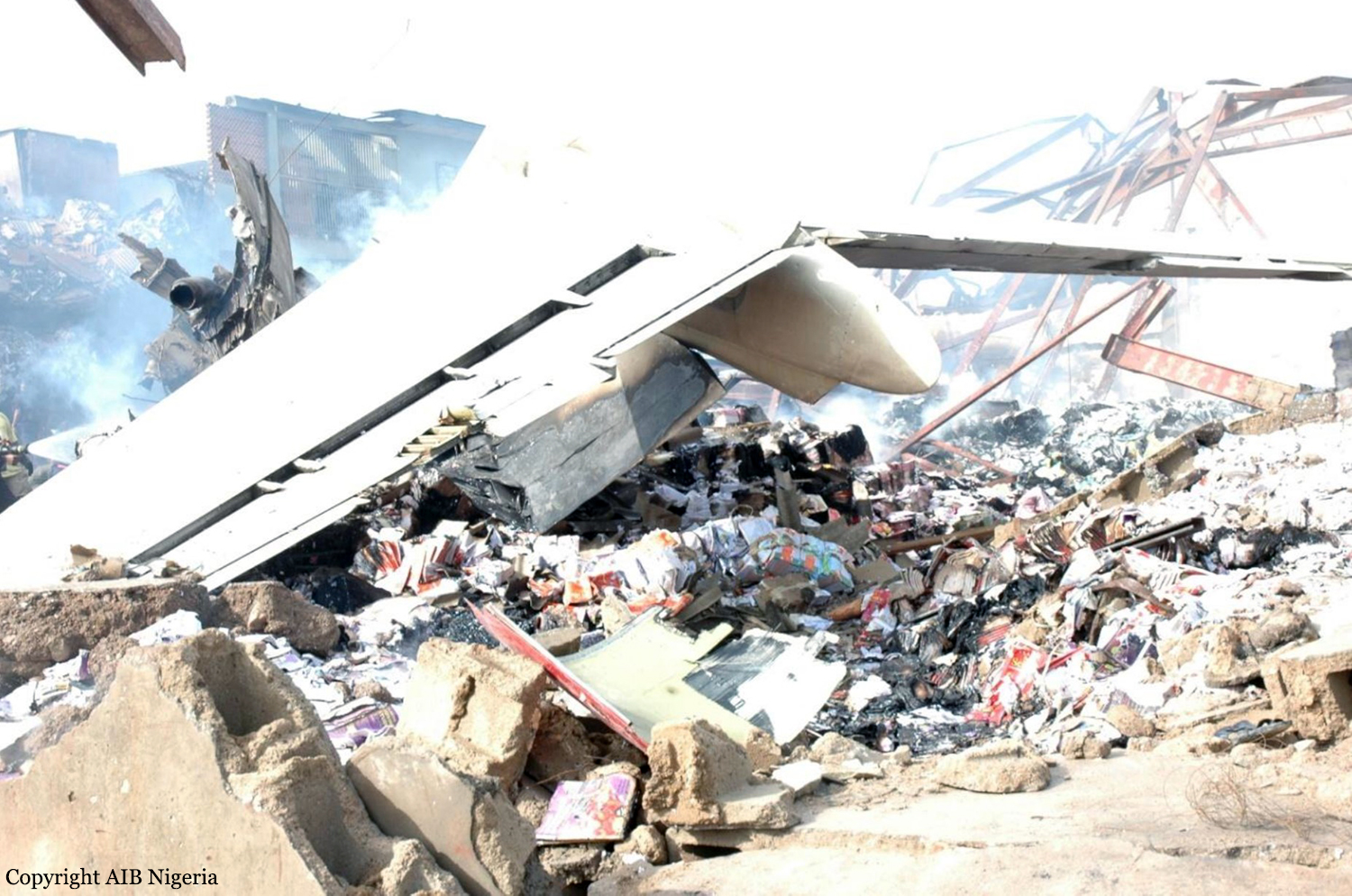
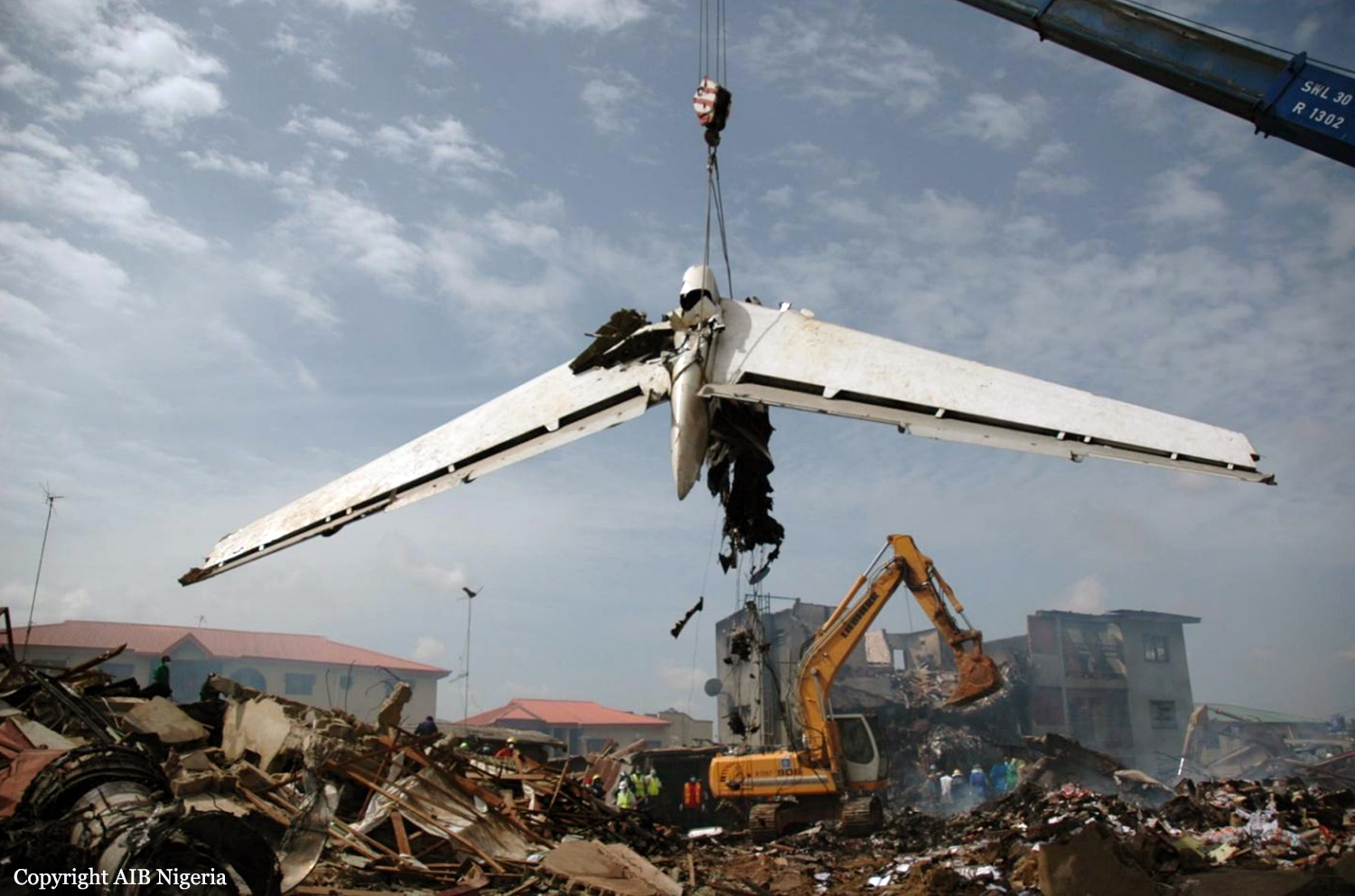
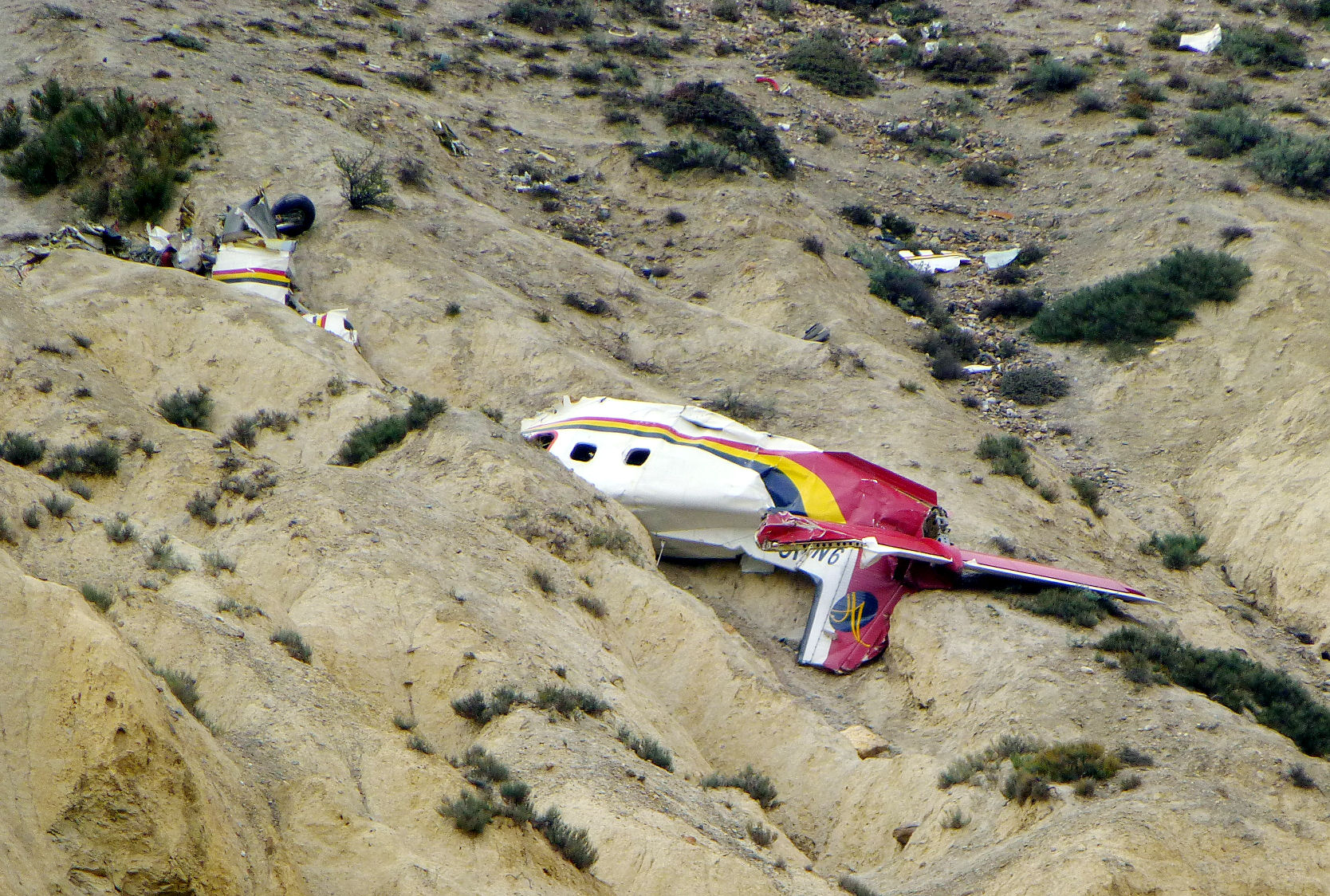
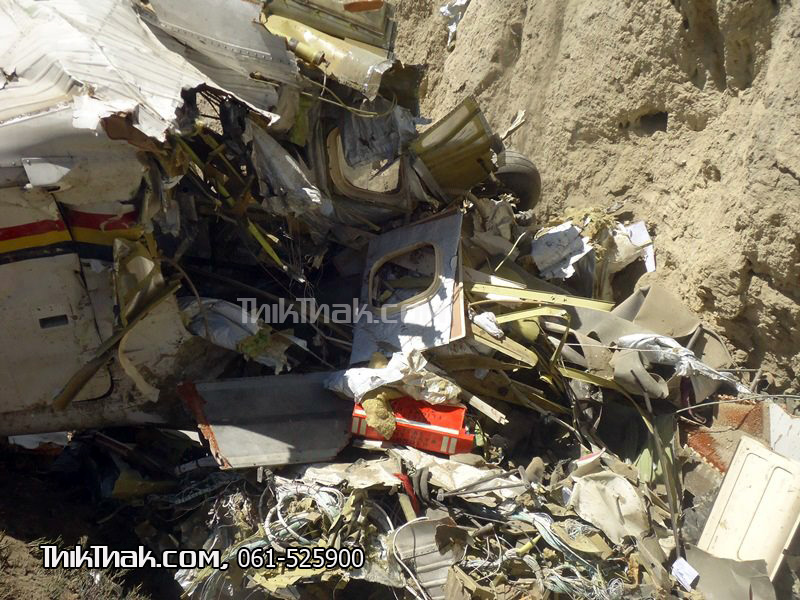
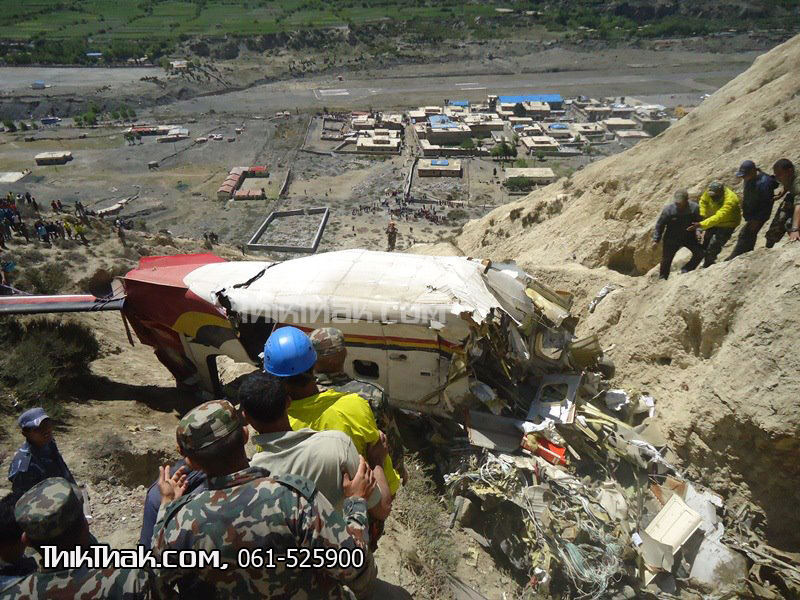
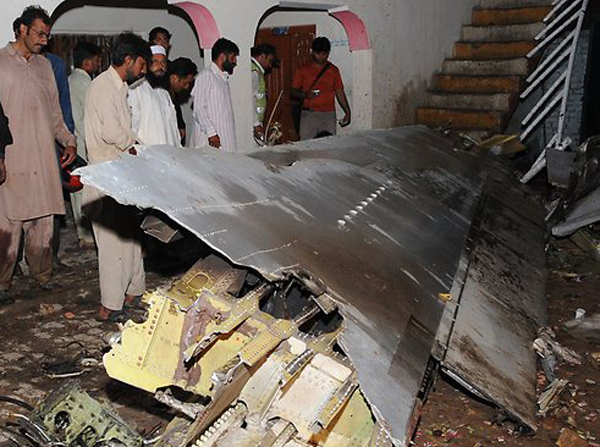
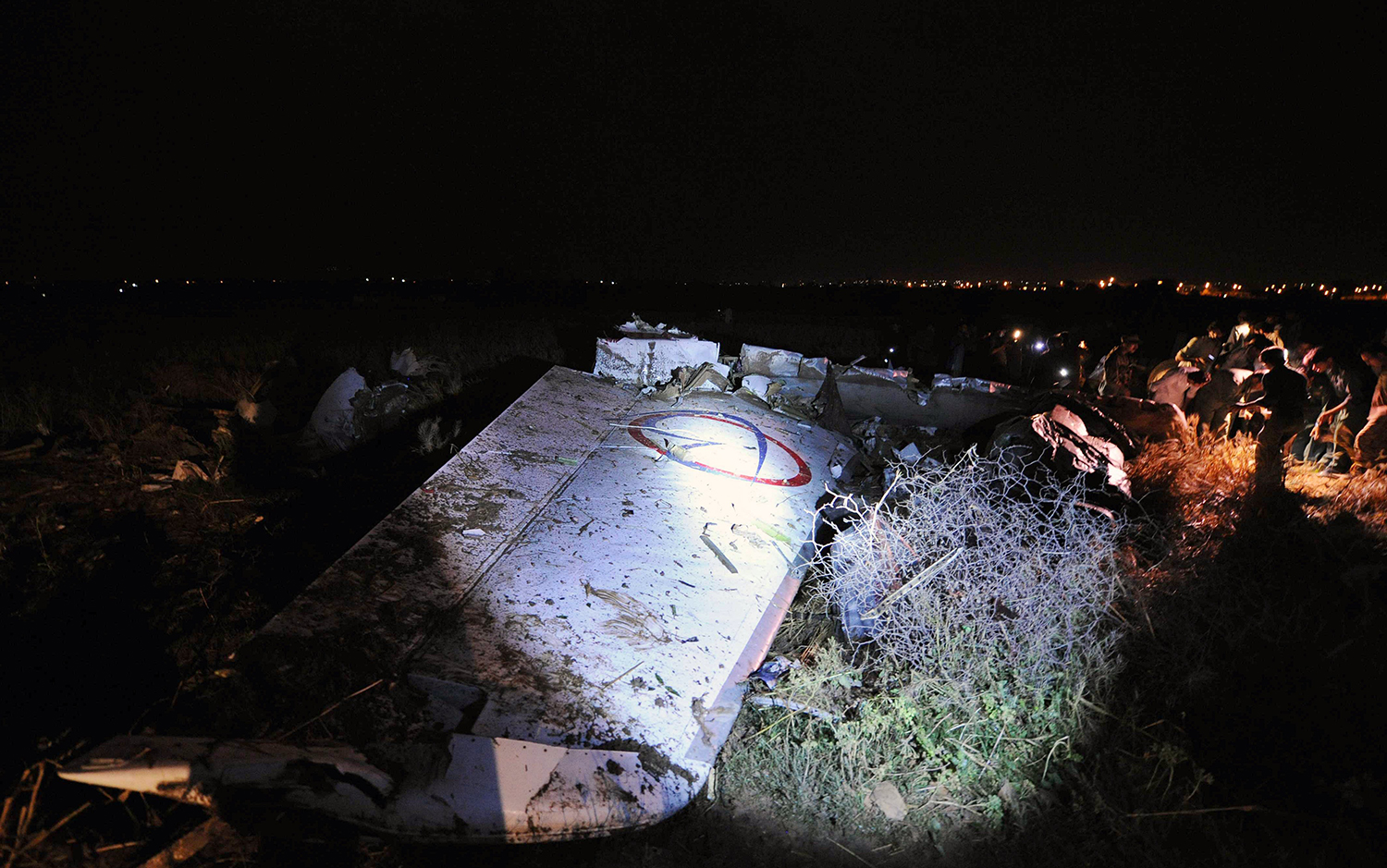
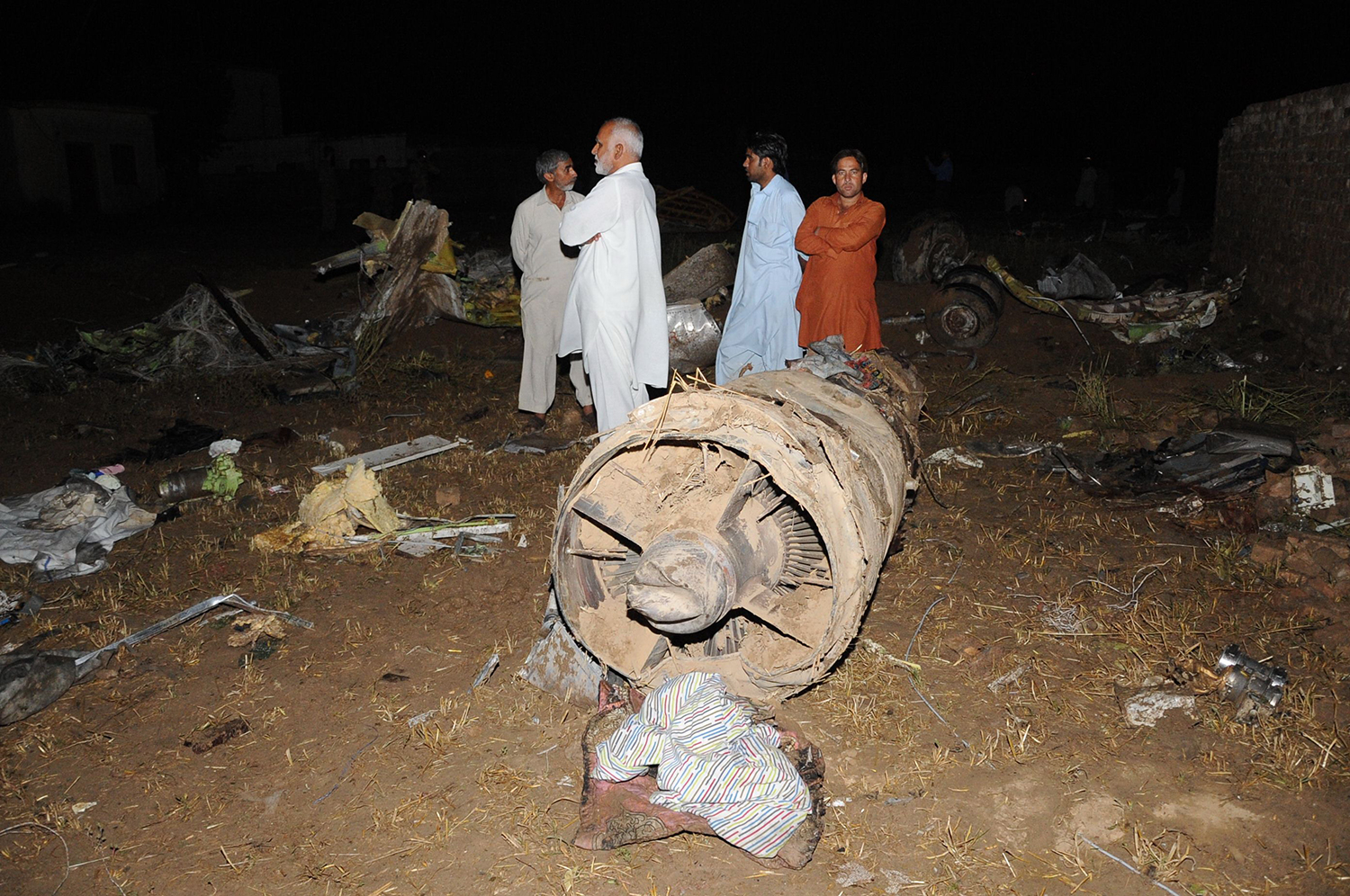
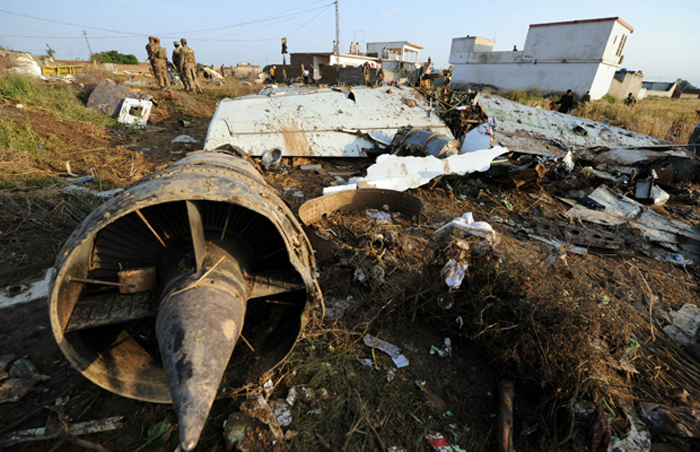
A Dornier 228 aircraft, registration 9N-AHA, was planned to operate a flight from Tribhuvan International Airport (TIA), Kathmandu, to Tensing/Hillary Airport, Lukla with 16 passengers and 3 crews. The Commander was the Pilot Flying (PF) which was in accordance with common practice for flight crews operating this route. The 0020Z METAR for TIA reported calm wind, 3,000 m visibility in mist, scattered cloud at 2,000 ft AAL, broken cloud at 10,000 ft AAL, a temperature of 19° C and a QNH of 1017 HPa. ATC broadcast a change in the QNH to 1018 HPa at 0029 hrs. At 0028 hrs (0613 am), the Co-pilot asked ATC for taxi clearance and 9N-AHA taxied towards Intersection 2 for Runway 20. While taxiing towards the runway the flight crew carried out the before takeoff checklist during which the Commander confirmed that Flaps 1 was set and all four booster pumps were ON. There was no emergency brief or discussion about the reference speeds to be used during the takeoff. The flight crew changed frequency and contacted the tower controller who gave them clearance to enter Runway 20 from the intersection and wait for clearance to takeoff. The Commander asked for the line-up checks to be completed during which the Speed Lever was selected to HIGH. After lining up, the Commander said "THERE IS A BIRD" and, three seconds later "I WILL TAKE FLAPS TWO" which was acknowledged by the co-pilot. The aircraft was cleared for departure and began its takeoff run at 0032 hrs. Two seconds after beginning the takeoff roll, the Commander said "WATCH OUT THE BIRD". The Co-pilot called "50 KNOTS " as the aircraft approached 50 kt and the Commander replied "CHECK". Two seconds later, the co-pilot called "BIRD CLEAR SIR" as the aircraft accelerated through 58 kt. Approaching 70 kt, approximately 13 kt below V1 and Vr , the first officer called "VEE ONE ROTATE". The aircraft began to rotate but did not lift off the ground and the nose was briefly lowered again. As the aircraft reached 86 kt, it lifted off the ground and the landing gear was raised immediately. As the aircraft began to climb, it accelerated to 89 kt over approximately 2 seconds. It continued to climb to 100 ft above the runway over the next 11 seconds but, during this time, the speed decreased to 77 kt. The aircraft then flew level for 14 seconds during which time the following occurred: the speed decreased to 69 kt; the air traffic controller asked "ANY TECHNICAL?" to which the pilot replied "[uncertain]….DUE BIRD HIT"; it's heading changed slowly from 200 °M to approximately 173 °M; and the stall warning was triggered for three seconds as the aircraft decelerated through 71 kt. Two seconds after the stall warning ended, it was triggered again for approximately six seconds with the airspeed at 69 kt. The aircraft began a gentle descent at 69 kt with the stall warning sounding and the rate of turn to the left increased rapidly. It departed controlled flight, most probably left wing low, and crashed into a small open area 420 m south-east of the end of Runway 20. A runway inspection found the remains of a bird, identified as a "Black Kite", at a position 408 m from Intersection 2. No bird strike was reported in relation to any other departure.
Probable cause:
Causal Factors:
The investigation identified the following causal factors:
1. During level flight phase of the aircraft, the drag on the aircraft was greater than the power available and the aircraft decelerated. That resulted in excessive drag in such critical phase of ascent lowering the required thrust. The investigation was unable to determine the reason for the reduced thrust.
2. The flight crew did not maintain the airspeed above the stall speed and there was insufficient height available to recover when the aircraft departed controlled flight.
Contributory Factors:
The investigation identified the following contributory factors:
1. The flight crew did not maintain V2 during the climb and so the power required to maintain the level flight was greater than it would otherwise have been.
2. The flight crew did not maintain the runway centreline which removed the option of landing the aircraft on the runway remaining.
The investigation identified the following causal factors:
1. During level flight phase of the aircraft, the drag on the aircraft was greater than the power available and the aircraft decelerated. That resulted in excessive drag in such critical phase of ascent lowering the required thrust. The investigation was unable to determine the reason for the reduced thrust.
2. The flight crew did not maintain the airspeed above the stall speed and there was insufficient height available to recover when the aircraft departed controlled flight.
Contributory Factors:
The investigation identified the following contributory factors:
1. The flight crew did not maintain V2 during the climb and so the power required to maintain the level flight was greater than it would otherwise have been.
2. The flight crew did not maintain the runway centreline which removed the option of landing the aircraft on the runway remaining.
Final Report: