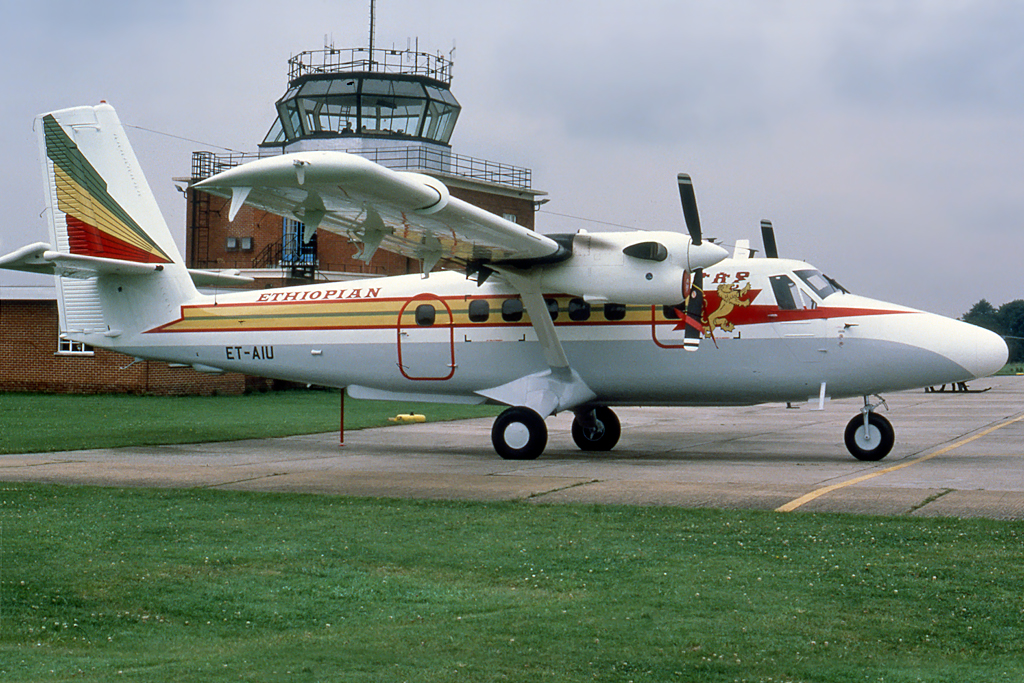
Crash of a Learjet 35A in Buenos Aires
Date & Time:
Mar 7, 2019 at 1930 LT
Registration:
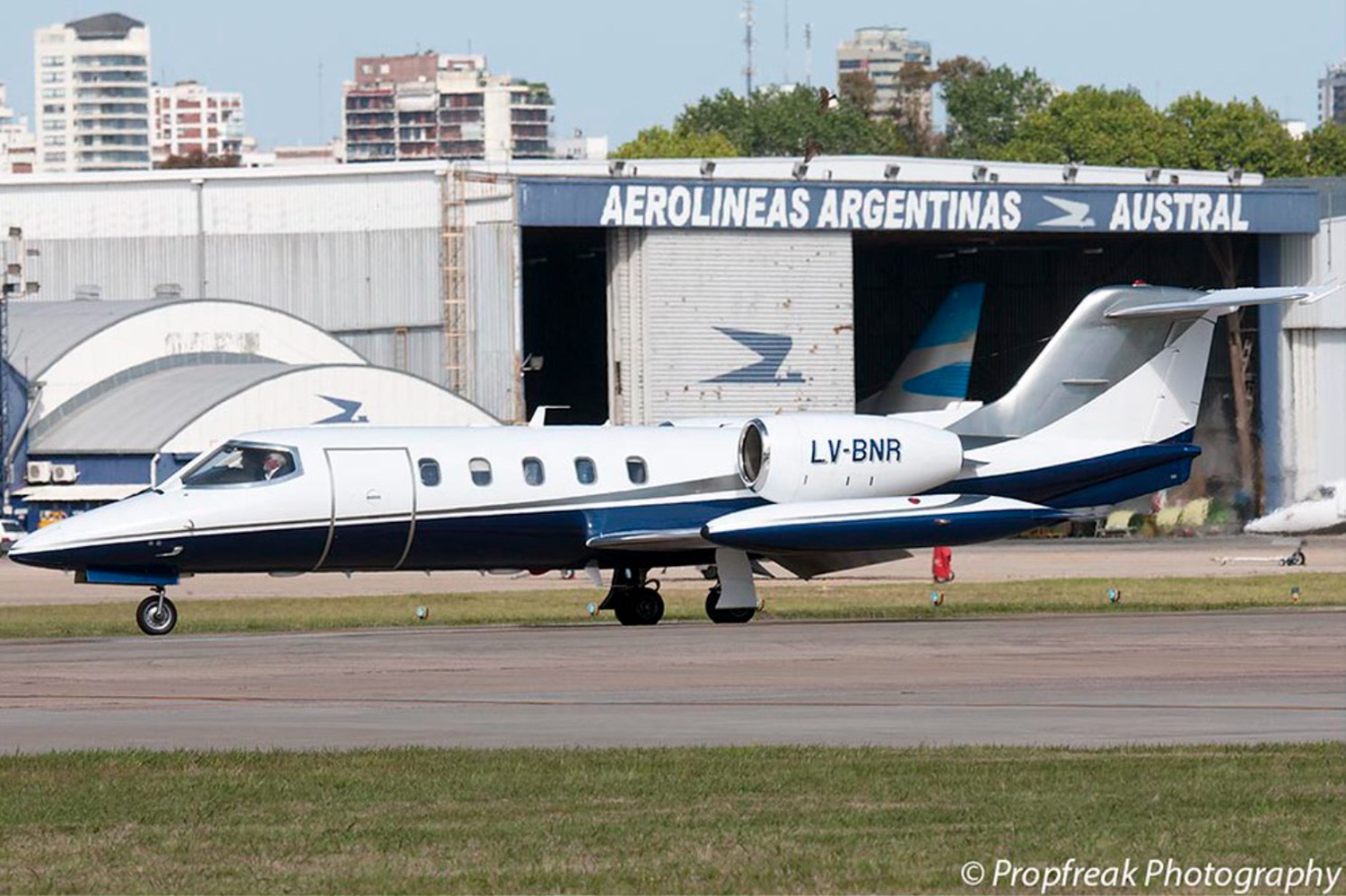
LV-BNR
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Rosario – Buenos Aires
MSN:
35-373
YOM:
1981
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
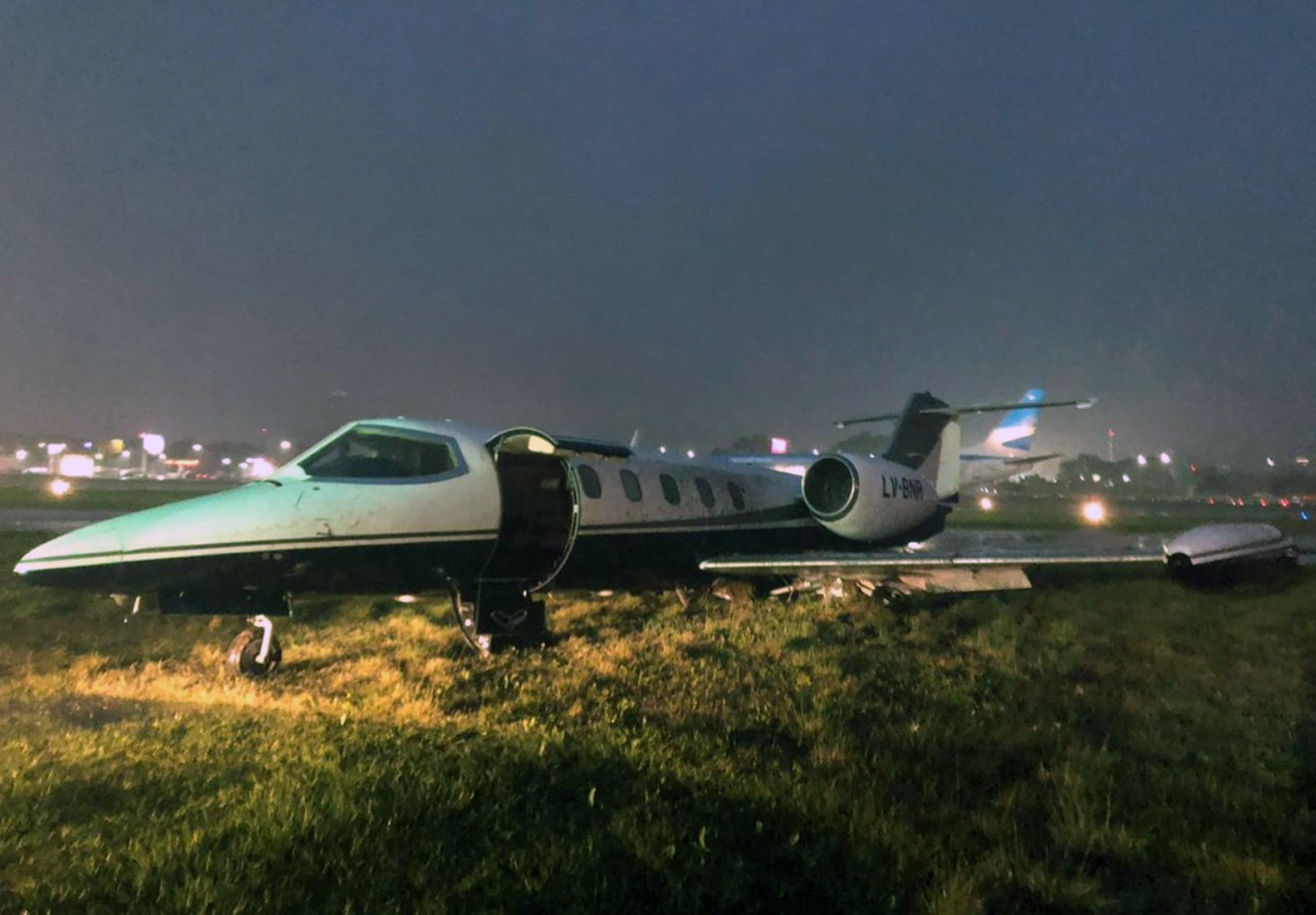
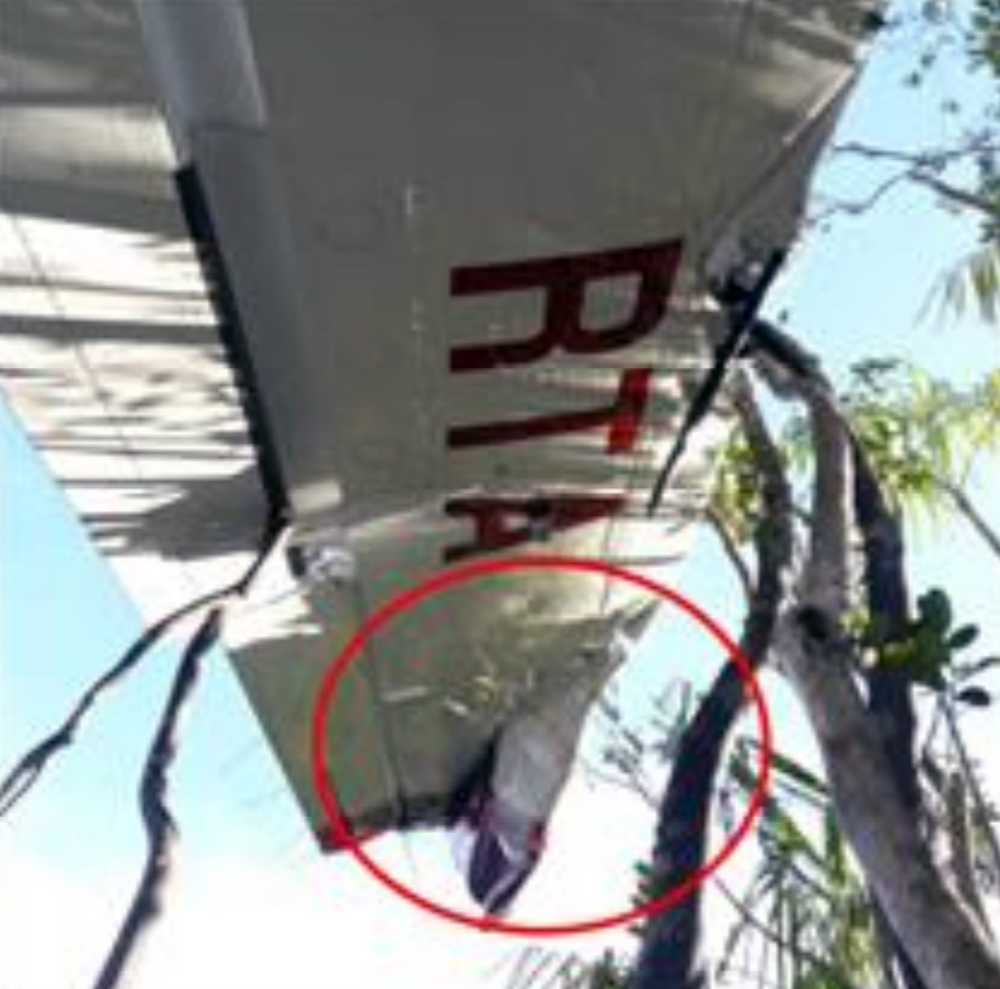
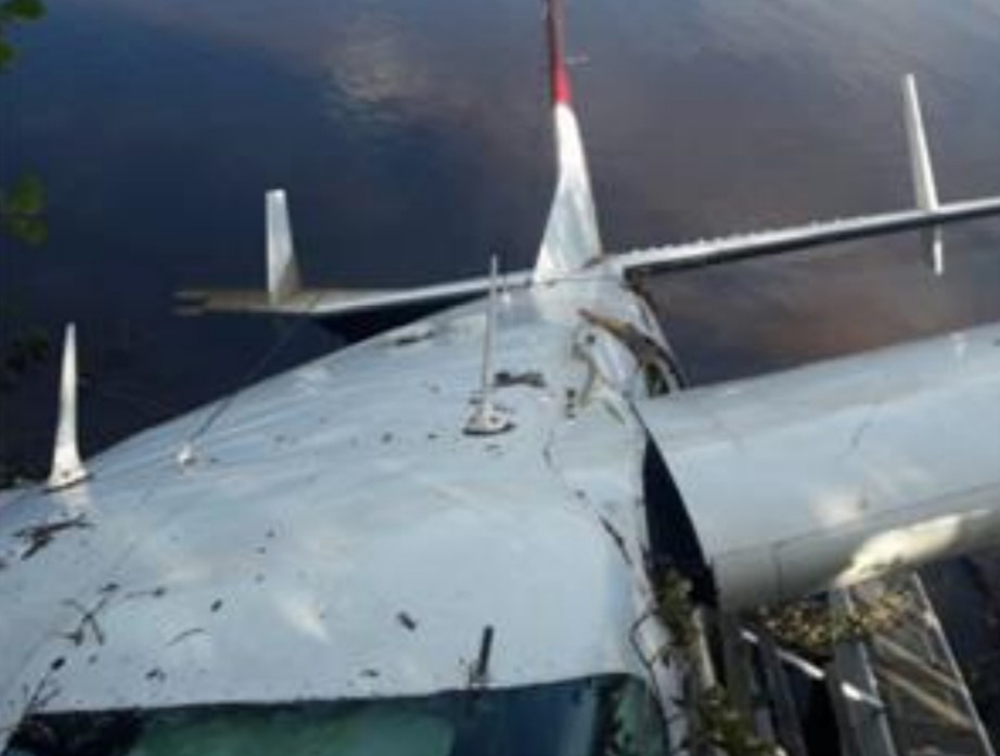
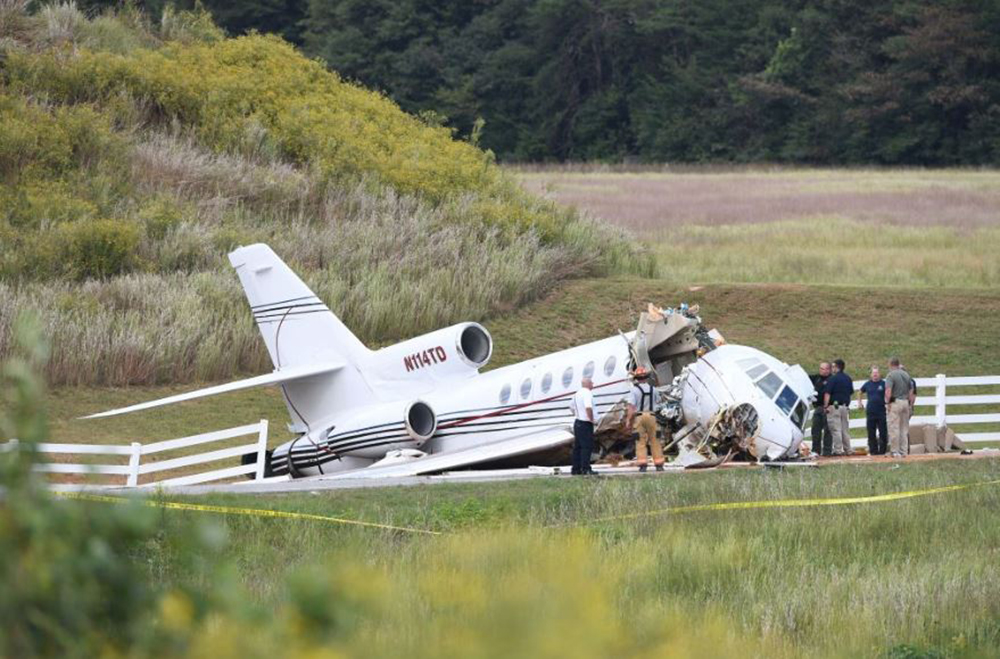
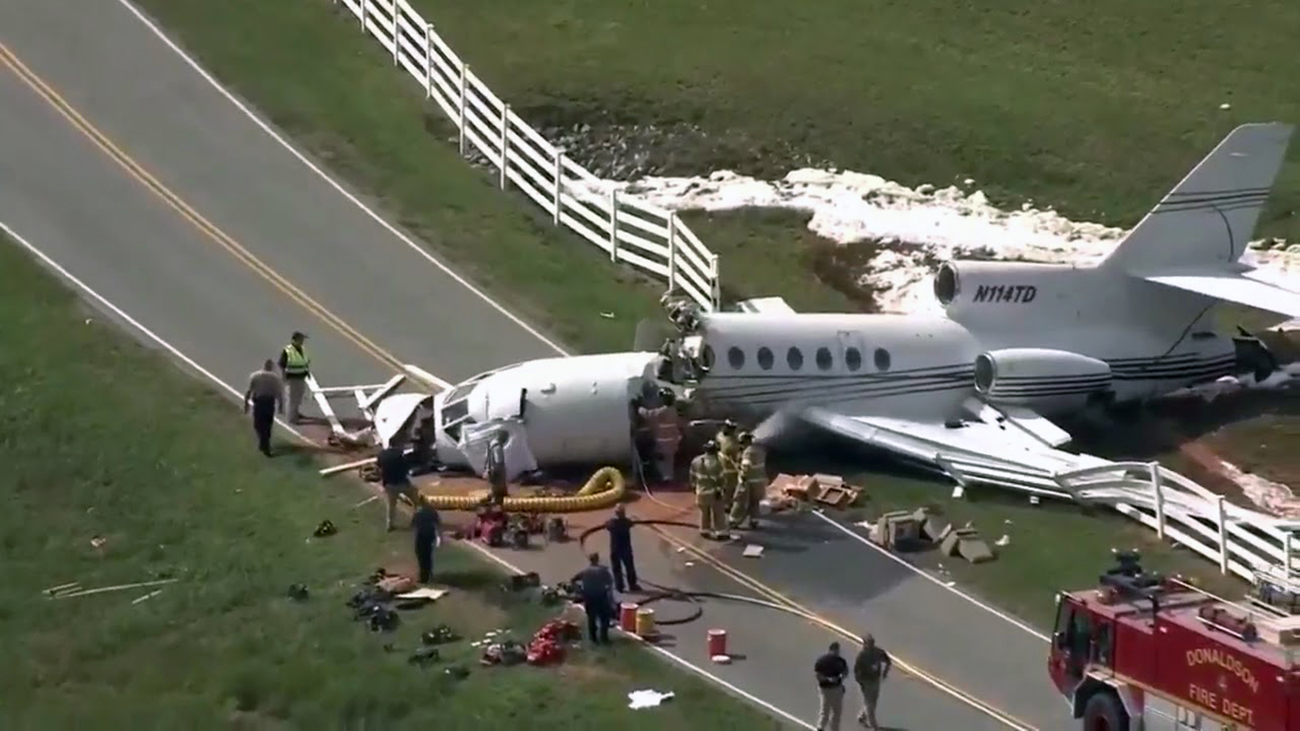
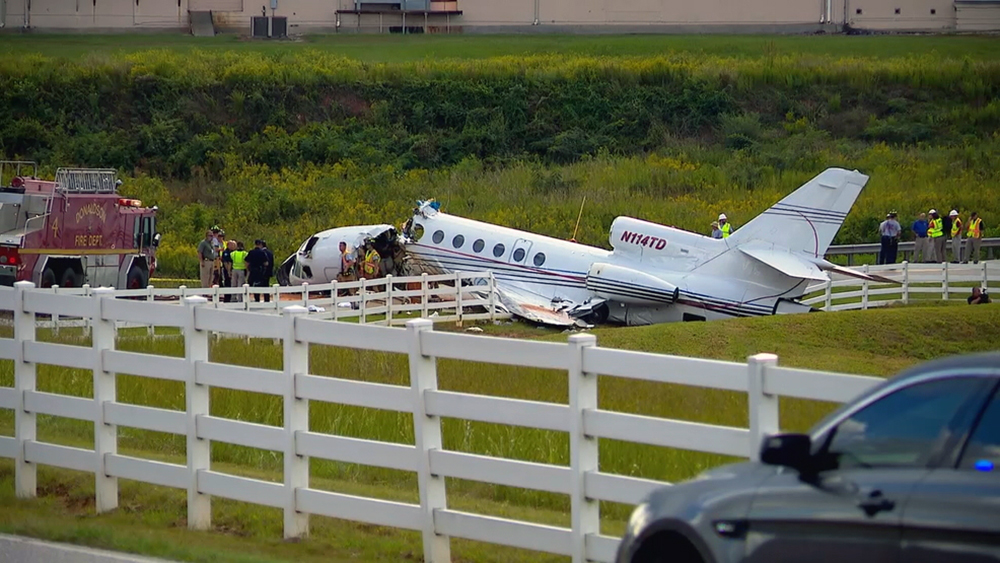
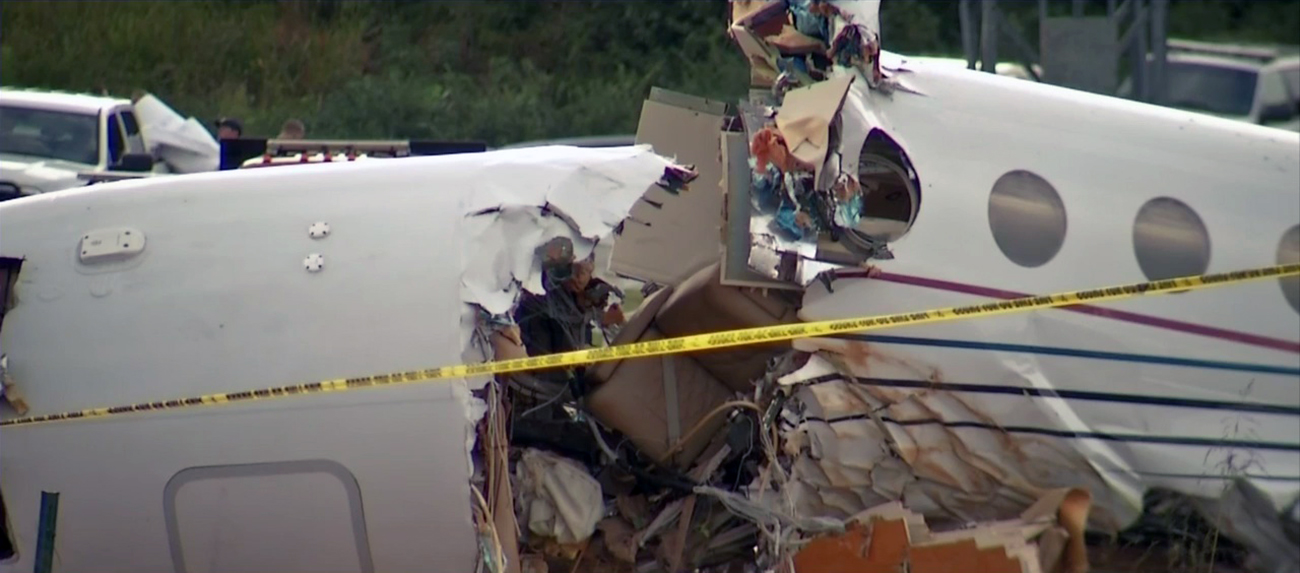
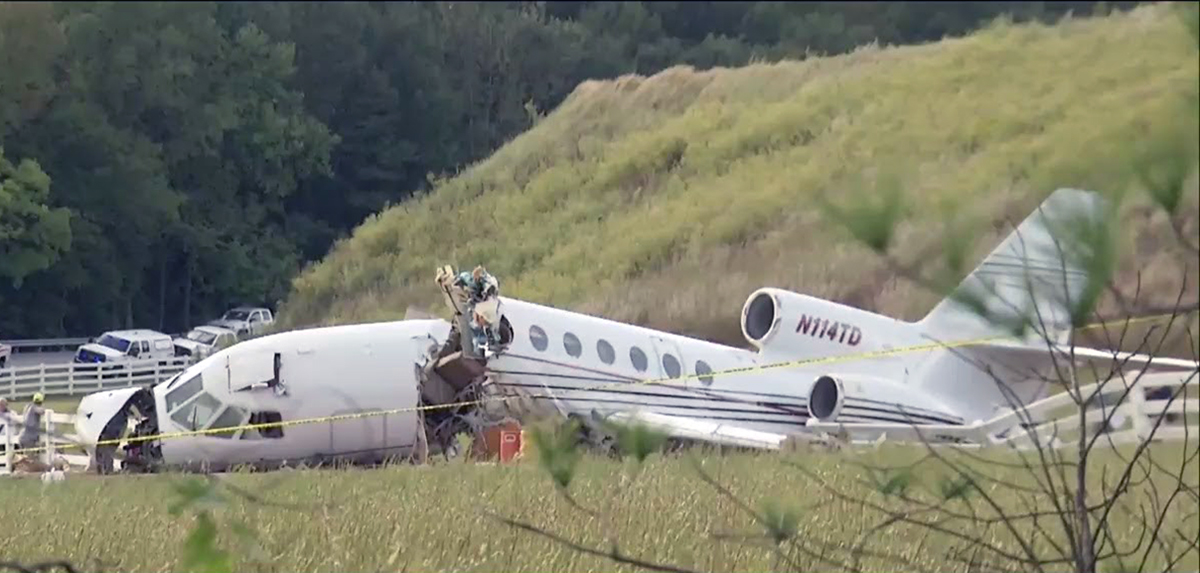
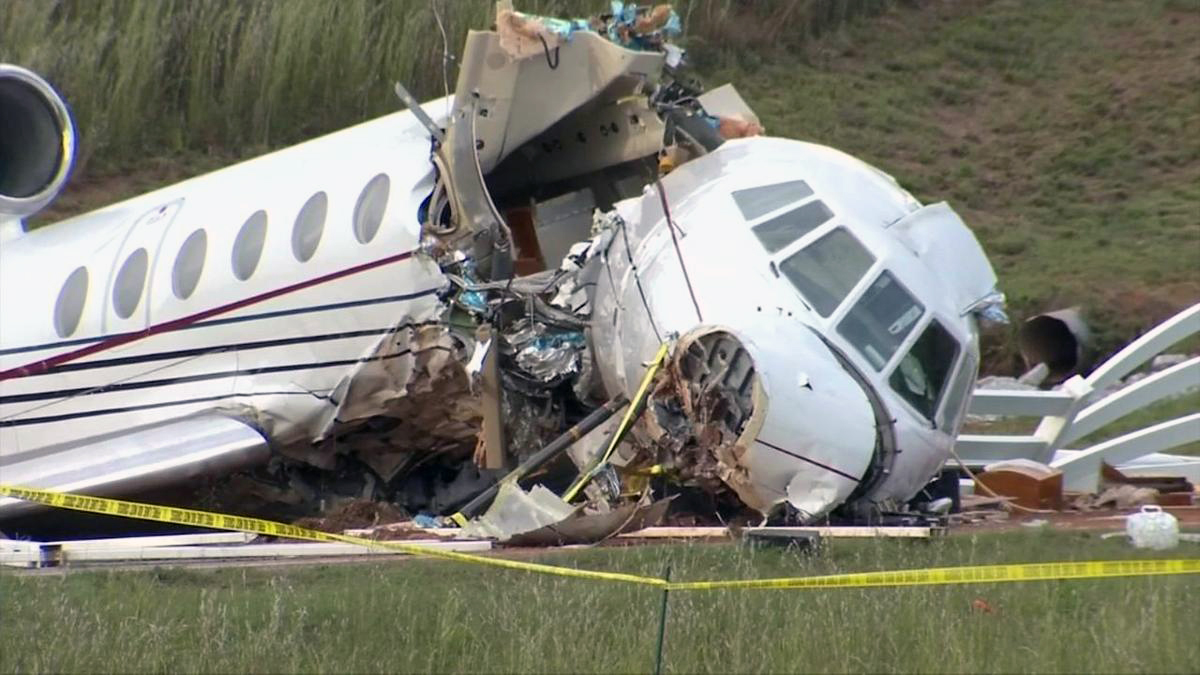
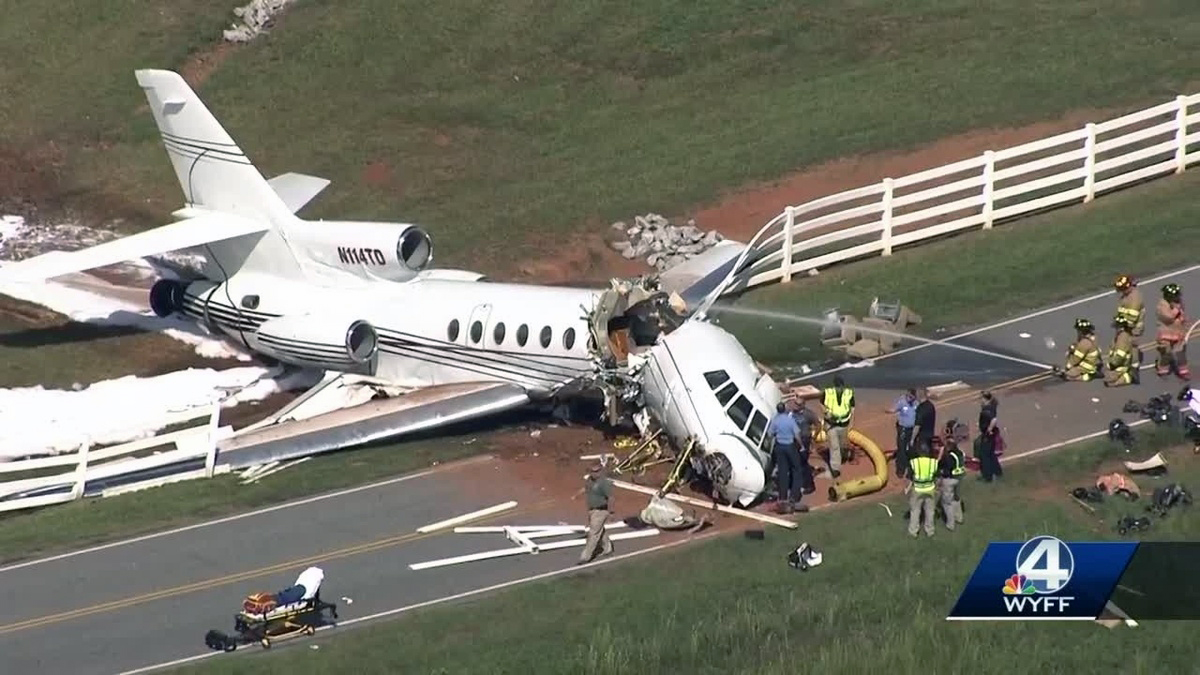
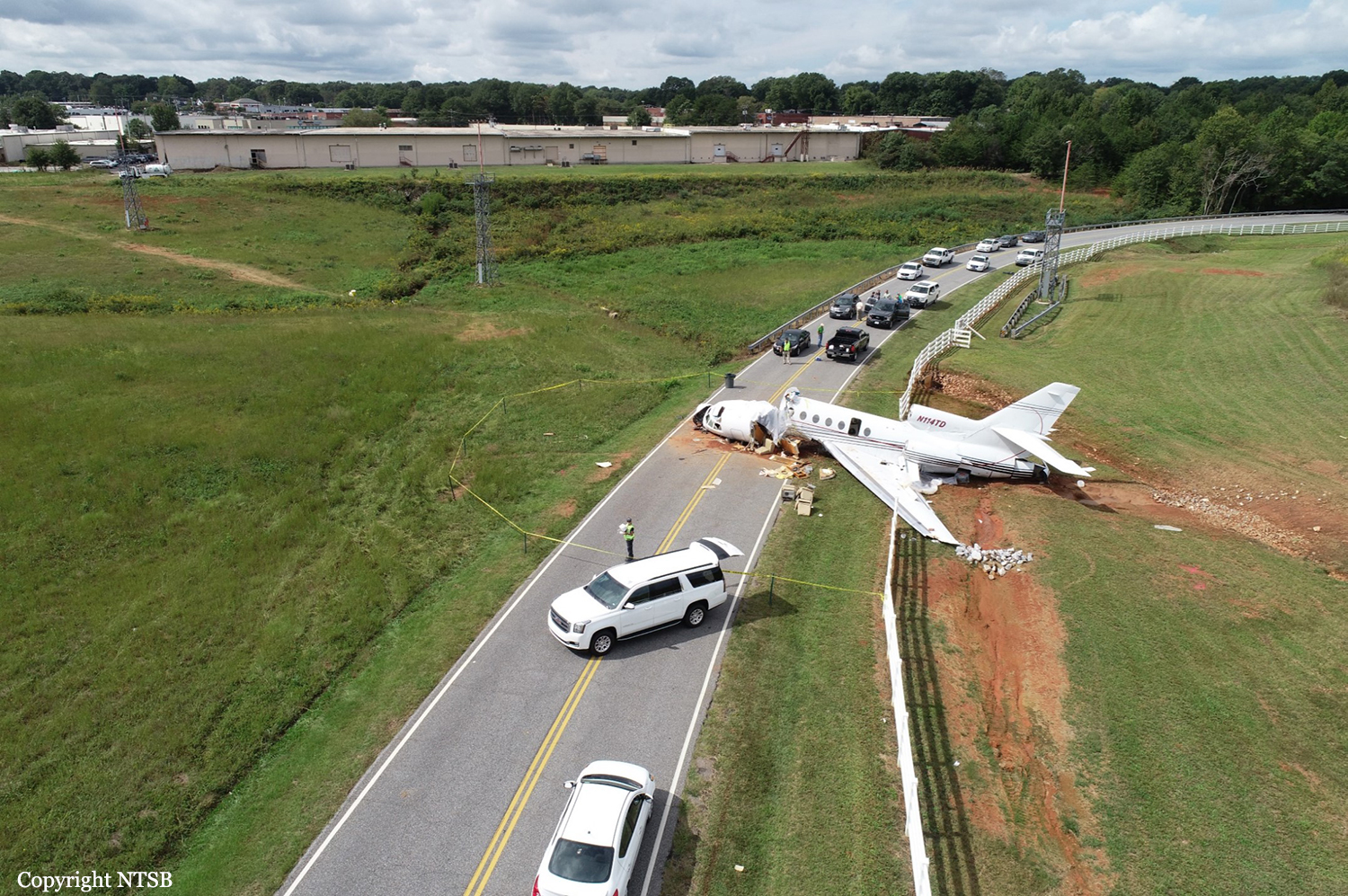
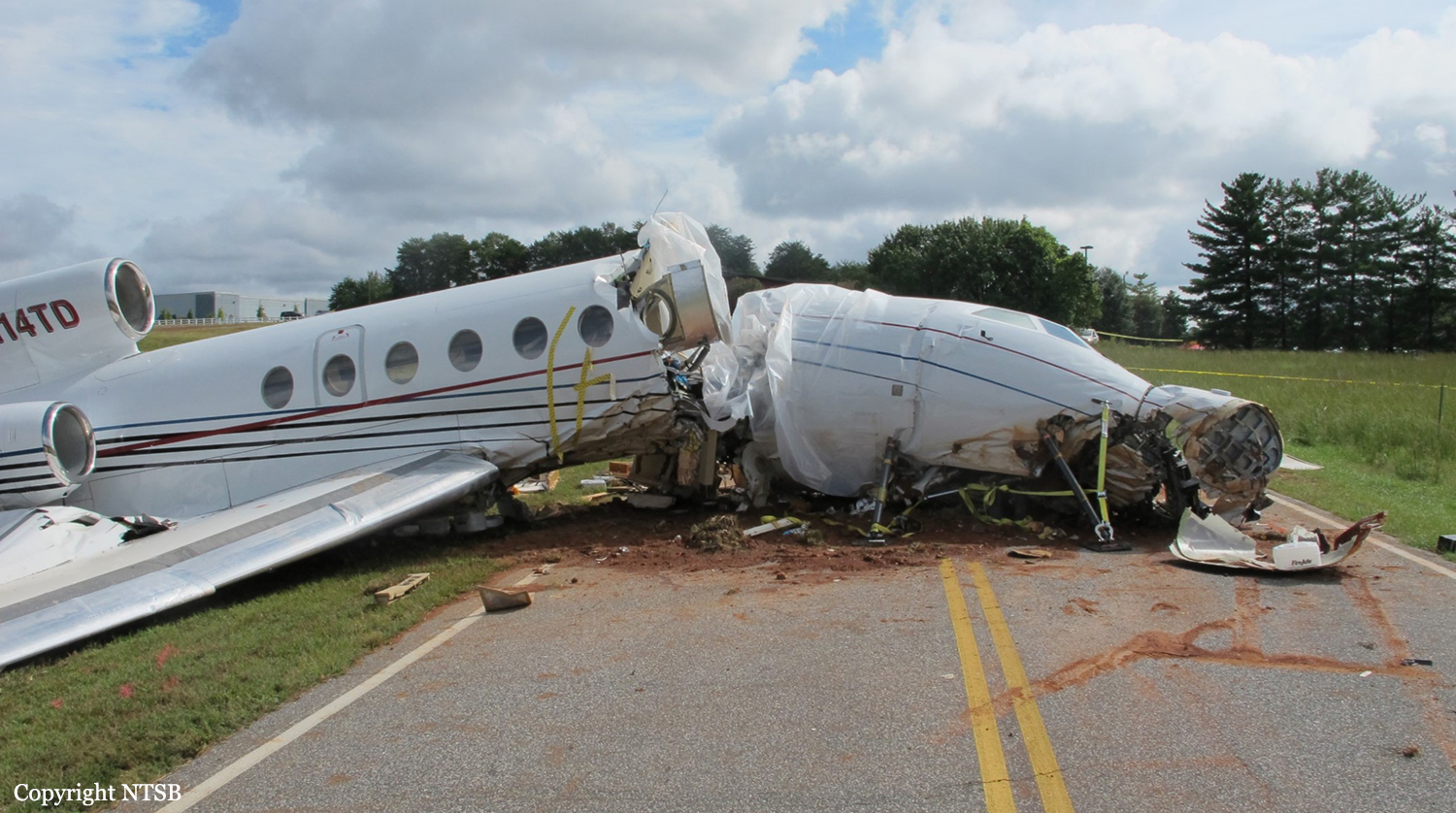
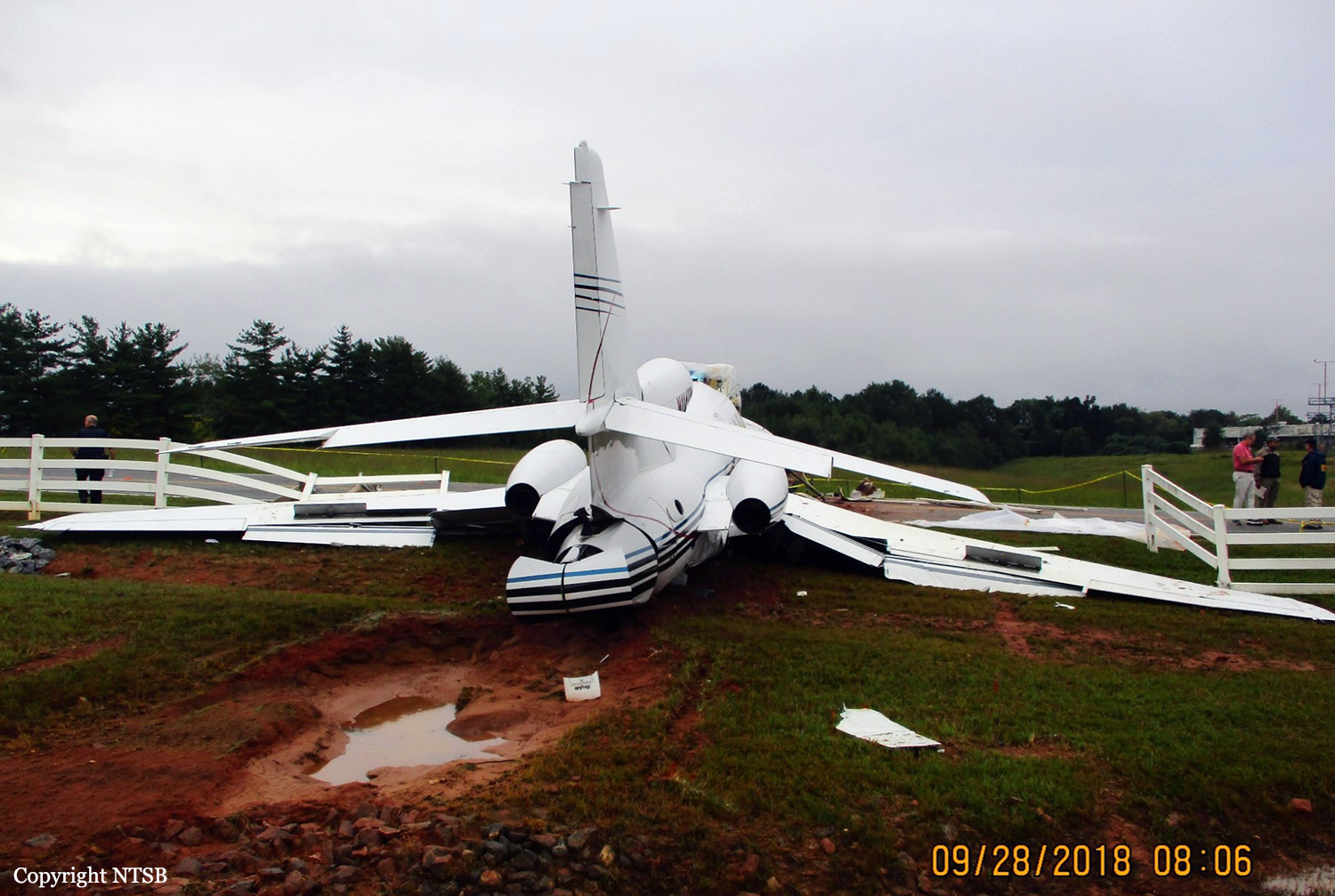
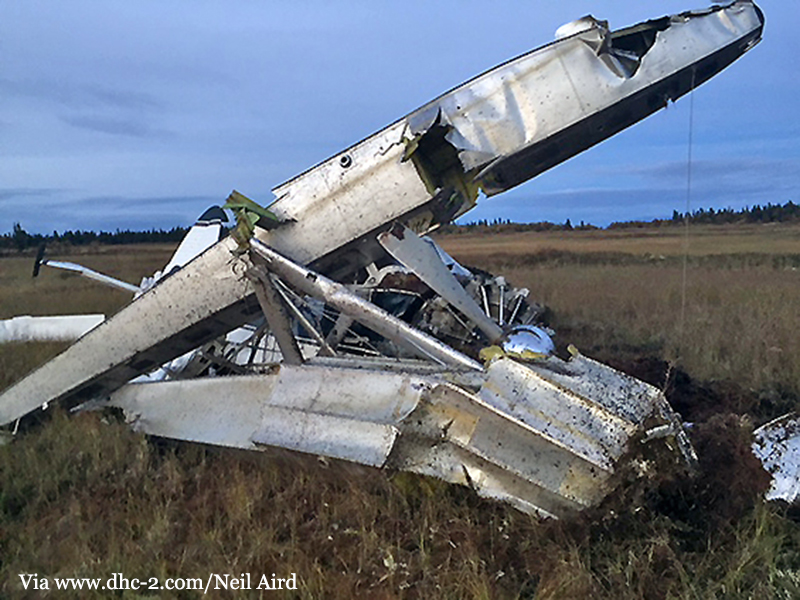
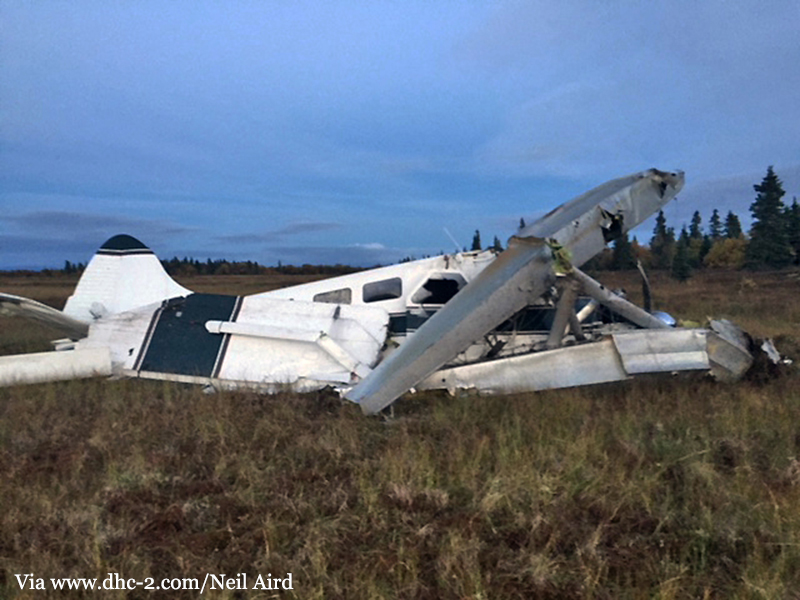
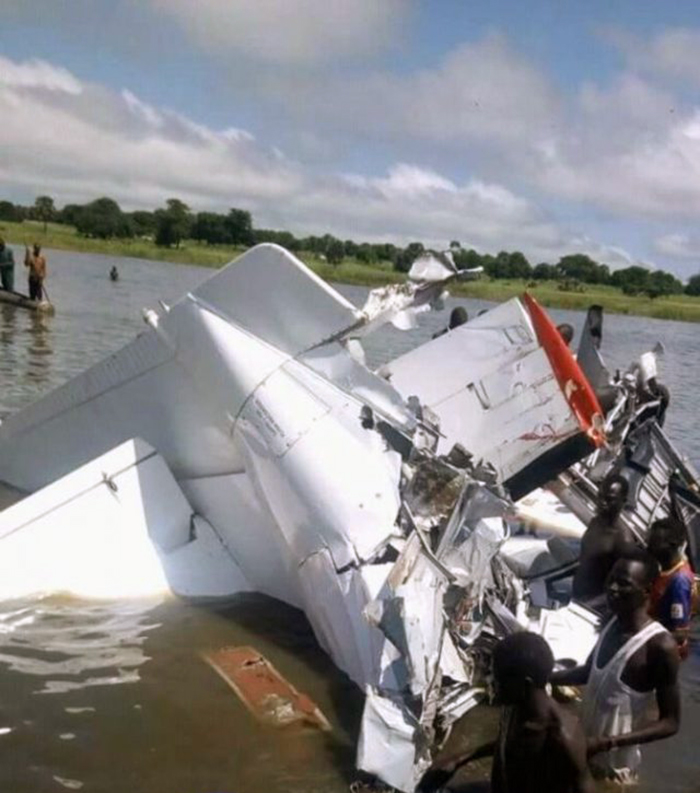
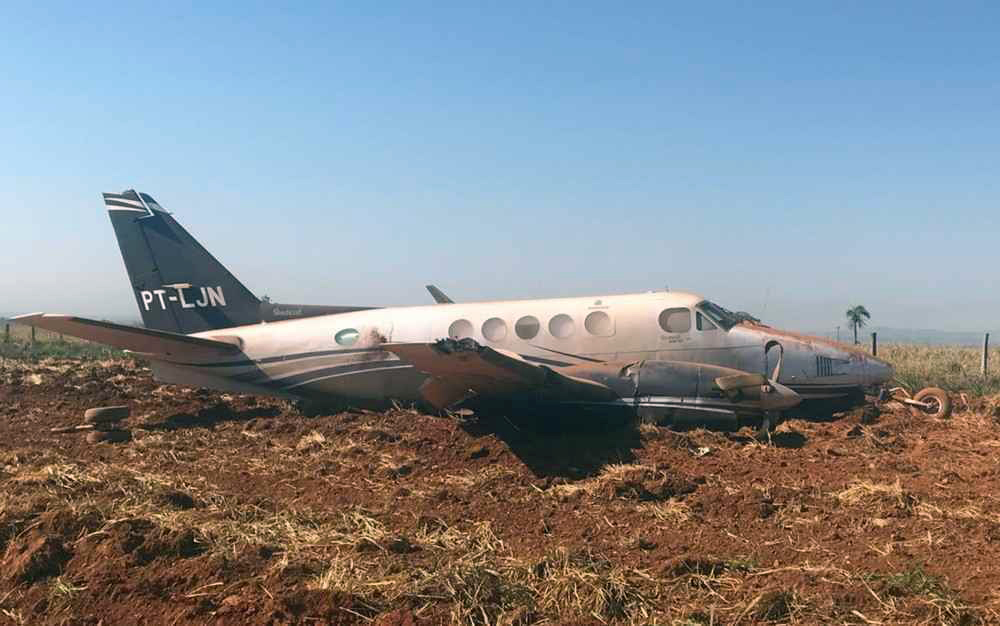
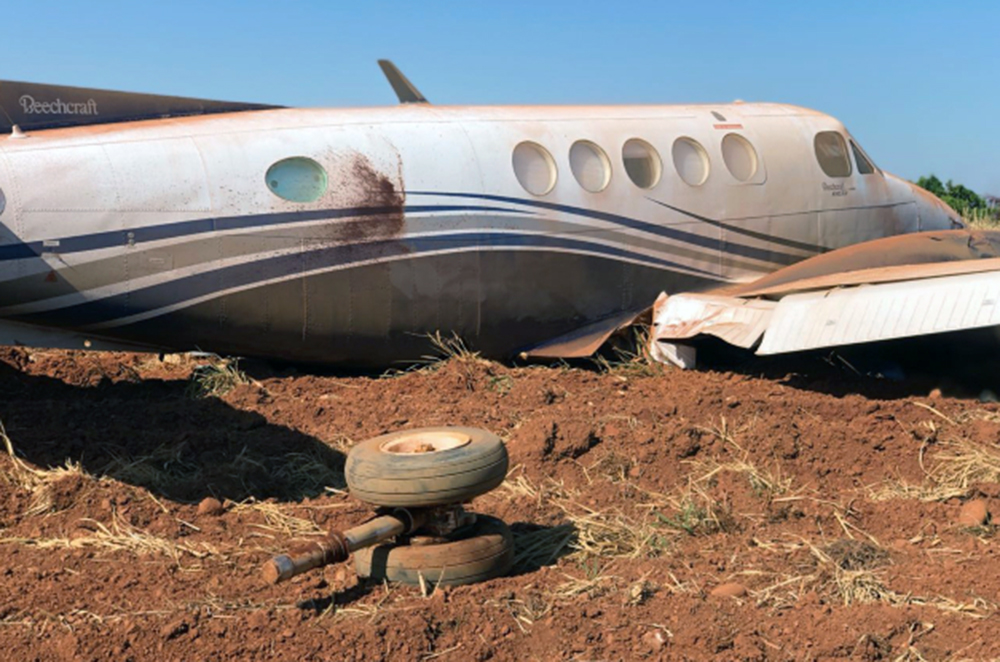
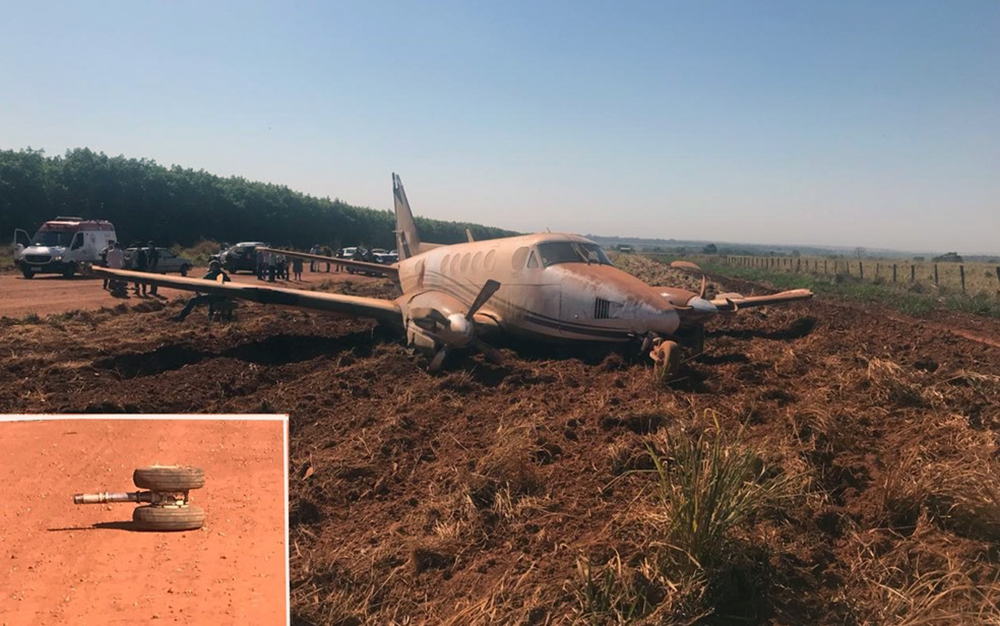
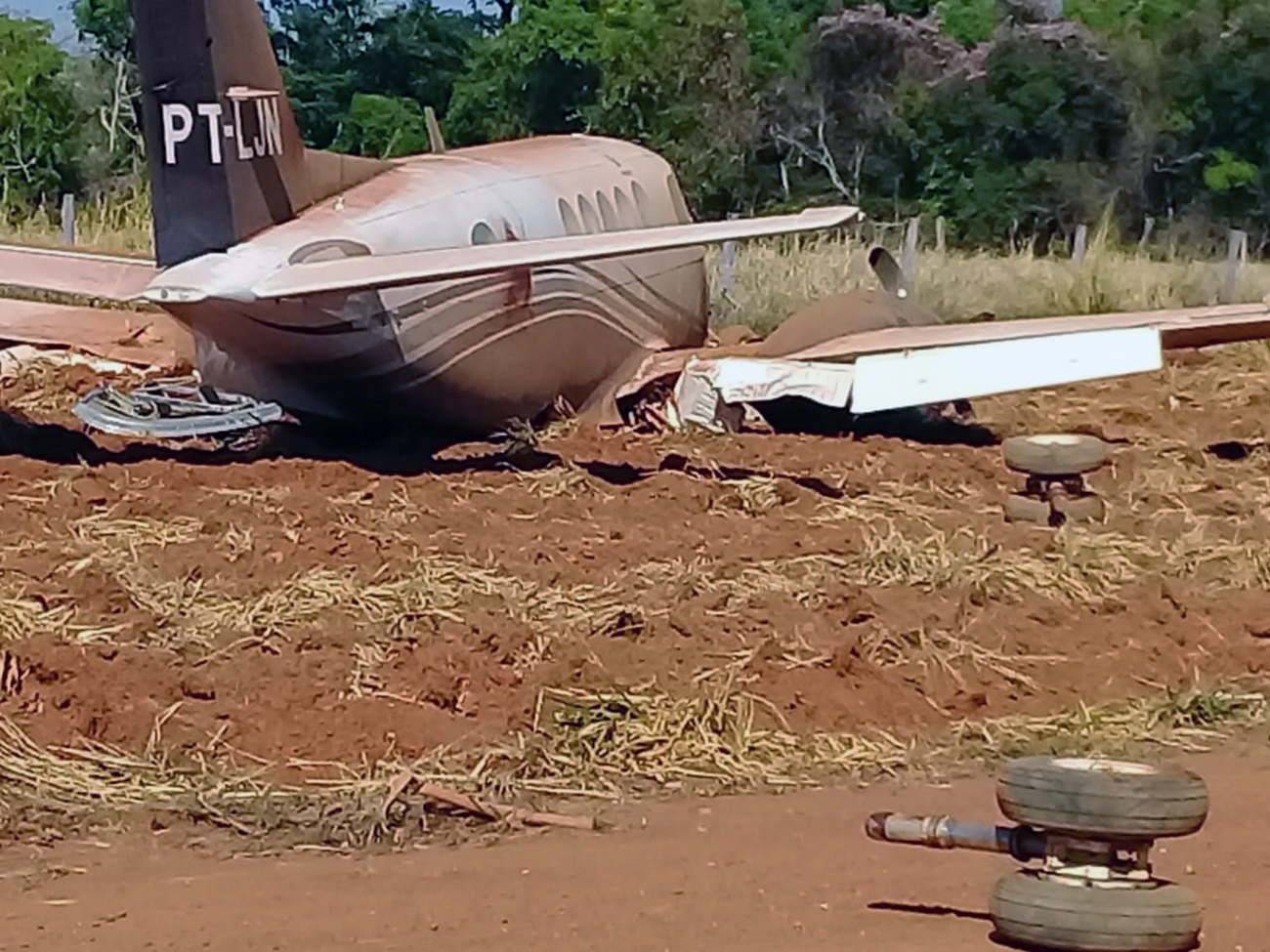
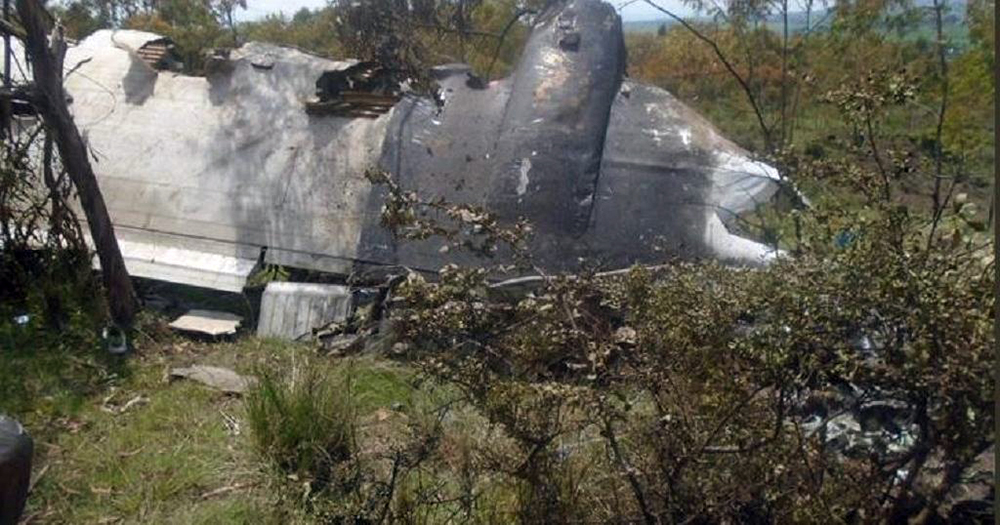
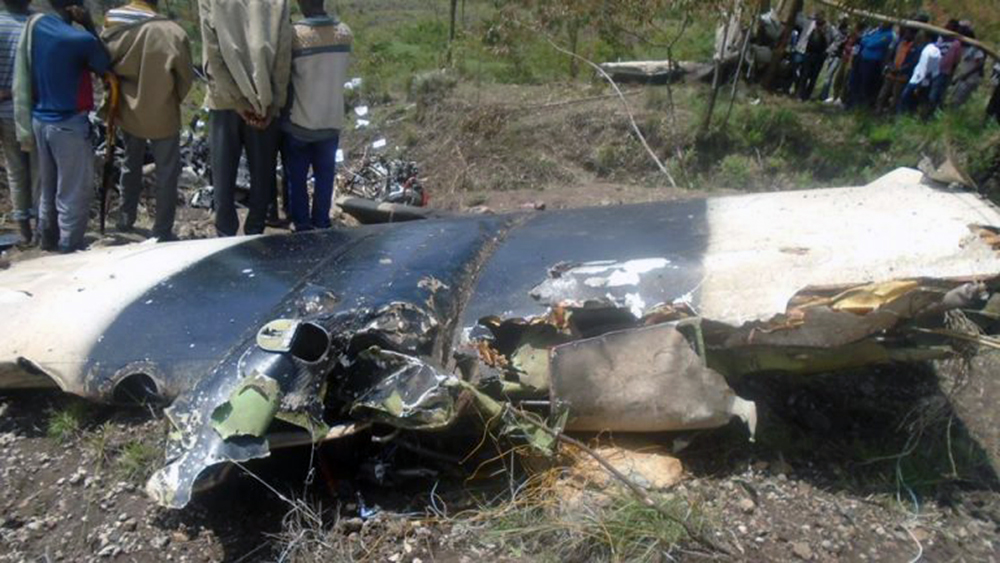
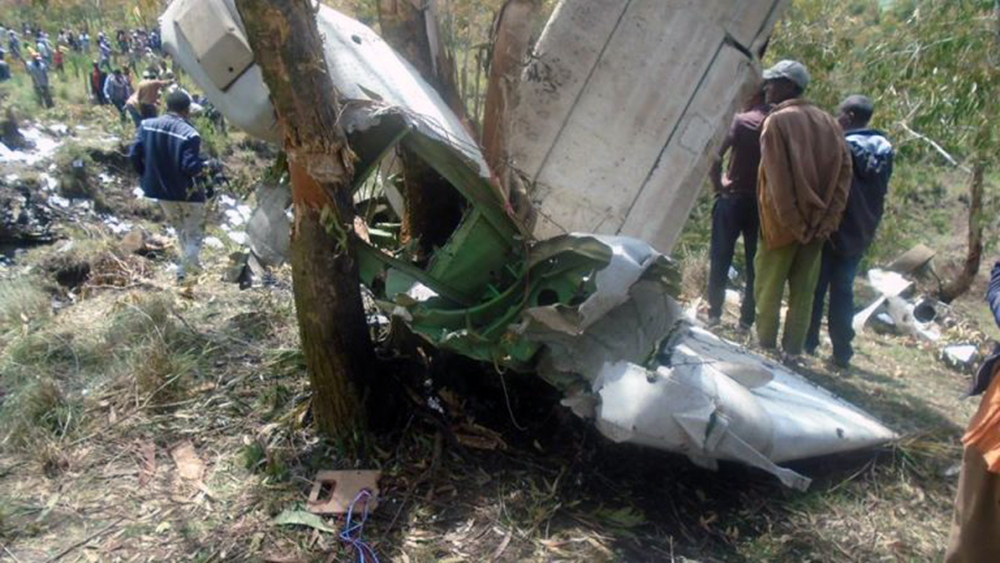
The aircraft departed Rosario-Islas Malvinas Airport at 1900LT on a charter flight to Buenos Aires, carrying two passengers and two pilots. On approach to Buenos Aires-Aeroparque-Jorge Newbury Airport by night, the crew encountered poor weather conditions with thunderstorm activity, heavy rain falls and strong winds. The aircraft landed 200 metres past the runway 13 threshold and the crew stated the braking procedure. After a course of about 500 metres, the aircraft deviated to the left and veered off runway. It rolled on a grassy area then contacted the concrete taxiway, causing both main landing gear to be torn off. The aircraft came to rest 860 metres from the runway threshold and was damaged beyond repair. All four occupants evacuated safely.
Probable cause:
Conclusions regarding factors related to the accident:
- At the time of the event, meteorological conditions were poor with a strong storm, rain and gusts of wind.
- Visual cues may have been reduced due to heavy rain falls.
- The aircraft was displaced from the runway center line when it made contact with the ground.
- The aircraft made contact with the left landing gear off the runway due to strong gusts of wind.
- The lateral excursion to the grassy area occurred due to the impossibility of recovering the trajectory of the aircraft, once it was displaced by the action of the wind.
- At the time of the event, meteorological conditions were poor with a strong storm, rain and gusts of wind.
- Visual cues may have been reduced due to heavy rain falls.
- The aircraft was displaced from the runway center line when it made contact with the ground.
- The aircraft made contact with the left landing gear off the runway due to strong gusts of wind.
- The lateral excursion to the grassy area occurred due to the impossibility of recovering the trajectory of the aircraft, once it was displaced by the action of the wind.
Final Report: